In the early days of Catholic campus ministry in the United States, ministry within higher education was typically provided by ordained and religious staff of Catholic campuses. After 1883, students attending public universities gained access to ministry through Newman Centers (
Starks 2018;
Day and Kawentel 2020b). Newman Centers were initially also staffed by ordained and religious Catholics, but as lay ministry grew more common, so too were both Newman Centers and Catholic university ministries led by lay faithful. It was in this milieu of Catholic campus ministry that the United States Conference of Catholic Bishops (USCCB) wrote
Empowered by the Spirit in 1985. This document reflects the campus ministers of its day, correctly assuming that Catholic campus ministers were typically available for students as well as staff and faculty, that ministers had a robust education in or seasoned experience with ministry and that campus ministry would be holistic while incorporating important aspects of the Catholic intellectual tradition, such as conscience formation and educating for peace and justice.
Shortly after the publication of
Empowered by the Spirit, Catholic campus ministry underwent significant changes. Campus ministers who identified as “missionaries” began to serve Catholic undergraduates on a handful of campuses. These missionaries are recent college graduates who participate in a brief (5–6 weeks) training with periodic regional training and commit to serving for two years. These missionaries continued to grow in number, and now comprise roughly one-fourth of Catholic campus ministers (
Starks and Day 2018). To better understand these changes in the Catholic campus ministry landscape, the USCCB Secretariat of Education commissioned two studies. The first was a national survey of the identified 1911 campus ministers, including more than 500 missionaries, with 1117 responding to the survey (
Starks and Day 2018). The second was a national in-depth interview study with 45 campus ministers (
Day and Kawentel 2020a). This article will draw upon the data from these studies to show the similarities among and differences between long-term campus ministers with degrees in ministry (hereafter “professional ministers”) and missionaries in their ministerial priorities. Ministry teams that combine both professional and missionary ministers are becoming increasingly common. Further, the data show that ministerial differences have led to challenging working environments on some, but certainly not all, campuses. In desiring to more intentionally foster shared vision and greater collaboration within blended ministry teams, a USCCB commissioned task force articulated insights for campuses seeking to integrate professional and missionary ministers. The article concludes by highlighting broader insights for creating goodwill and efficacy among ministerial teams.
1. Background
Before exploring the data from the two studies and determining effective pastoral approaches, it is important to outline the social context of young adults, with particular attention to young adult Catholics. Beginning with young adults broadly, there is a new phase of life that psychologist
Arnett (
2004) coined “emerging adulthood.” This phase did not exist in prior generations and falls between adolescence and full adulthood; life course milestones such as getting married or having a child can affect the beginning and end of this age, but typically this is understood to begin at 18 and end at 29. Emerging adults—regardless of race, economic background or other factors—are characterized by an intentional exploration and formation of identity (something once exclusive to adolescence), a sense of being in-between adolescence and adulthood (growing in responsibility while still dependent emotionally and financially on family of origin), and a time of instability (especially geographic moves, career changes, and a number of romantic relationships). Undergraduates, even while they may have a fairly predictable four-year plan, are no less caught up in discovering who they are and what their future might hold. It is a time of transition and fluidity, and is accompanied by both hopes and anxieties. It is shaped much by digital communication, which has profoundly affected the lives of Millennials and iGen Americans (
Ansari 2015;
Freitas 2017). The Catholic Church—at the highest levels—has acknowledged the gifts and struggles of the world’s young adults (
Pope Francis 2019).
The latest research on the spiritual lives of young adult Catholics captures a variety of experiences. Perhaps attracting the most attention are the studies of waning Catholic identity and disaffiliation. First, disaffiliation is not unique to young adults. Although nearly one-third of Americans were raised Catholic, only 59% of these identify as Catholics as adults.
1 Those who leave are not “replaced” by adult converts; for every adult who enters Catholicism, 6.5 Catholics leave. The reasons for this disaffiliation are complex and many (
Bullivant 2019). Interviews with teens and young adults themselves provide two main pathways of exit. The first is one of gradual disengagement over time; it is not so much about young people leaving as it is simply drifting (
Smith et al. 2014). These young adults were not particularly engaged as teens and when they left home, college and careers filled their schedule. Religion is more crowded out of one’s life than it is rejected. The second pathway is that leaving Catholicism is a discerned choice (
Clydesdale and Garces-Foley 2019). Sometimes this departure stems from injury (either a difficult event in life that they are unable to reconcile with an image of a loving God or perceived hypocrisy among believers) and for others it is precipitated by a disagreement with a Church teaching (
McCarty and Vitek 2017). Even among those who leave there are differences among experiences, with some feeling relieved to leave Catholicism (
McCarty and Vitek 2017) and others feeling deep loss (
Oakes 2015).
There is no cookie-cutter model that promises to attract young adults, but there are some patterns that campus ministries and parishes with large numbers of active young adults hold in common (
Clydesdale and Garces-Foley 2019). First, an inclusive and welcoming community is important. They like having large numbers of young adults in the congregation, but—as the study only examined organizations with large numbers of young adults—there may also be young adults who prefer more intimate settings. Second, they appreciate having distinctly spiritual experiences available to them, but having other young adults present remains important. Finally, the leadership is important, especially that of the pastor. Twenty-something Catholics are attracted to campus ministries and parishes with priests that embody their own sense of Catholicity, whether that be a priest who prioritizes magisterial authority or a priest who emphasizes inclusivity and is nonjudgmental. Contemporary young adult Catholics have diverse needs from and hopes for the Church (
Day 2018). For ministers, this means that there is no single model that works for today’s Catholic undergraduates, and campus ministries that employ mixed approaches—engaging the full range of Catholic ecclesiologies, christologies, liturgical experiences, senses of mission and others—are more likely to ensure that a Catholic student feels “fed” after a pastoral encounter. However, as will be discussed below, ministers often tend toward particular practices, which might include some students while alienating others.
2. Materials and Methods
This report will distill the most central findings on professionals and missionaries from the two USCCB campus ministry studies. The 2018 survey garnered a response rate of 56% (1117 responded of the 1911 identified). The 2020 interview study included responses from 45 campus ministers from Southern California, the Indiana/Ohio region, and Atlanta, Georgia. A more in-depth description of the methods can be found within the respective reports.
Table 1 summarizes the demographics of the participants from each study.
3. Results
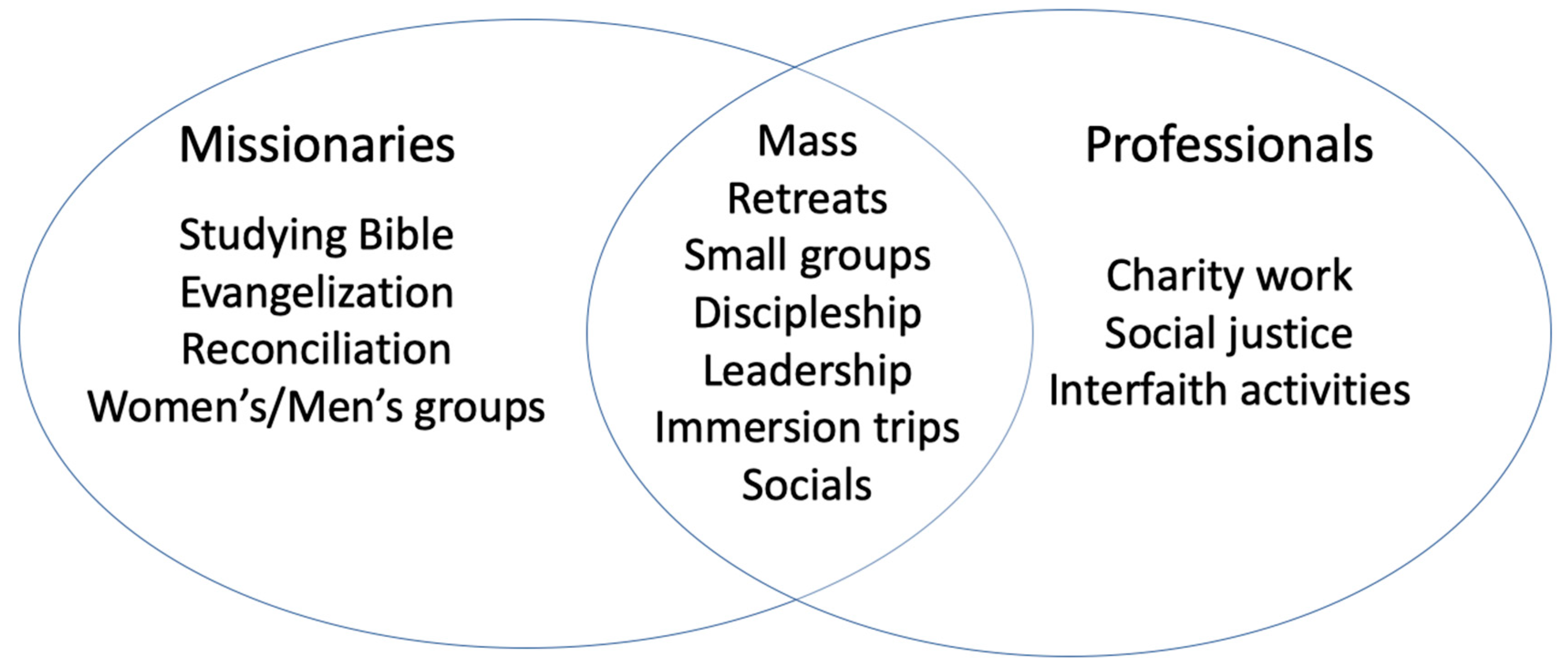
Ministers were asked what activities, in their estimation, were significant for students’ growth in faith (
Figure 1). At least three-fourths of both missionaries and professional campus ministers identified the following activities as significant (very or moderately) for students: mass (94% of missionaries and 92% of professional ministers), retreats (87% and 91%), small group Bible and faith-sharing groups (95% of missionaries and 83% of professional ministers), discipleship/one-on-one mentoring (95% vs. 80%), leadership development (78% and 80%), immersion trips (75% and 81%), and social events (78% and 77%). This demonstrates a clear basis for common action in engaging students. Looking at the contrasting or distinctive elements, missionaries elevate particular activities such as studying the Bible (91% of missionaries vs. 73% of professionals), evangelization (90% vs. 62%), the Sacrament of Reconciliation (86% vs. 66%), and men’s/women’s groups (85% vs. 65%); these activities promote personal holiness and a personal, “vertical” relationship with God, but have less emphasis on the relationship with one’s neighbor. Professional campus ministers elevate the importance of service/charitable work (79% of professionals vs. 56% of missionaries), social justice/advocacy (68% vs. 36%), and ecumenical/interfaith activities (40% of professionals vs. 25% of missionaries) for growth in faith; these encourage a “horizontal” orientation towards God through neighbors, but have less emphasis on the vertical dimension of one’s individual relationship with God.
Initially these areas of similarity and difference were understood as opportunities in which these two types of ministers could provide a more holistic ministry through collaboration. However, the interviews revealed that these two distinct sets of ministerial priorities emerge from different visions of how Catholic campus ministry should operate. To be clear, there are some professional and missionary blended ministry teams that flourish and collaborate well in their ministry with students. Yet, there are times when these disparities in vision can lead to parallel ministries that may compete for students. The qualitative study identified four principles that professional/missionary blended ministries need to be fruitful: (1) a shared vision, (2) regular communication that cultivates a sense of team, (3) fully understanding the various ministers’ roles and competencies, and (4) utilizing professional ministers’ leadership effectively. As these three latter features may be more particular manifestations of the first feature, shared vision will be addressed first. These four principles constitute the needs for successful mixed ministries. When these are attended to, ministry teams experience gratitude and integration. When not addressed, teams experience more difficulties. To be clear, the findings do not indicate that any particular model is better than the others. However, in the case of ministries that utilize both professional ministers and missionaries, having them operate independently on the same campus risks creating a sense of suspicion or competition between them. Campuses that fostered integration of these models had more fruitful ministries; the task force (their efforts are described below) has created a process for effective integration of professional ministers and missionaries.
In promoting a shared vision, two considerations are beneficial. First, whether the charisms of the missionary organization complement the ministry of the host campus. Second, if so, discerning the steps, gifts or fit that would facilitate the successful pairing of individual missionaries to a campus team. Some of the interviewees said they were told—and not consulted—by their diocese that missionaries would be added to their existing ministerial team. This can be very difficult for professional ministers—first, because they provide the primary pastoral care for the campus and appreciate consultation. Second, because some professionals believe that missionaries will undermine their pastoral work due to differences in theological orientations and pastoral practices. Likewise, missionaries sense when they are not wanted by the professional ministry team and may simply default to the activities learned in their training, forming two parallel—rather than integrated—ministries. Listening well to the experiences of the existing campus ministry team affords prayerful discernment regarding ministerial direction. If mixing these models is deemed appropriate, the diocese can actively facilitate the integration of these two models. Integration calls for diocesan leaders to exercise pastoral sensitivity, humility, and reflection. Poorly integrated teams bring down the morale of everyone involved as well as the vitality of the ministry. Both professionals and missionaries need the support, respect, and accompaniment of their leadership as they strive to live their call.
The second principle that characterized well-functioning teams was regular communication that promoted a sense of team. Some teams had excellent communication from the beginning. Others did not. Although these types of candid conversations can be difficult, they are critical to the health of any ministry organization. They require intentionality, regularity, goodwill, and commitment, as one minister said, “I firmly believe that tough conversations are things that are a little harder to talk about. You don’t know how the other people are going to take it. [Tough conversations] are very, very good if they’re done well.” Christian charity and a commitment to stay in the conversation is key as they gradually build trust, reflected in the vulnerability and humility of this missionary, “I told [my chaplain] in our first meeting, over the summer, I was like, ‘[Chaplain], I’ve learned a lot of what I didn’t do well last year and I want to do better for you this year.’ And so it’s really on [the chaplain] and myself to be in good communication so that [the chaplain] can help [their university Catholic organization] be a home for the Catholics on this campus and we, as [missionary organization], can help it grow and help it be fed into shape.” Despite the rough start, the staff interviewed here are very proud of the collaboration that has come to fruition.
The third principle for successful blended ministry teams is to clarify the role of degree-trained ministers and missionaries. Each of these ministers has enjoyed very different types of training that bring with them distinct skill sets. Recognizing these differences should make room for complementarity and collaboration. It should also create a space for self-aware ministers to reflect upon their pastoral competencies and limits. When different roles and skills and corresponding tasks are coordinated and appreciated by both, the two types of ministers act as “many parts, one body” rather than misunderstanding or competing with one another.
The fourth principle is to make good use of the leadership skills of the professional minister. Given the very different training these two groups of campus ministers have, it would be very helpful for a professional minister to put time into the ongoing formation and support of the missionaries, as well as helping them translate their missionary formation in a way that is sensitive to the needs of a specific campus. The challenges of missionaries with limited ministerial formation and experience could be mitigated by having someone from the professional ministry team who helps form them in a way that makes sense of their missionary training for a specific campus culture. This formation could include emotional and spiritual support, professional development, and theological reflection, much as a mentor in a field education placement would do. Perhaps utilizing a mentor—such as a diocesan employee or faculty member—for some aspects of this formation could support the professional team with this effort. This would also help to bridge these two models. Thinking about ways the diocese, the Catholic community on campus, and the professional team could support one another in a more contextualized formation would be enormously beneficial for collaboration.
In sum, there are two main types of campus ministers in the United States today. While they share important practices in common, each also emphasizes distinct aspects of the Catholic tradition, aspects that resonate with different populations of young adults. In bringing these two models into collaboration, or at least learning what is best about them and incorporating them into an existing ministry, students would gain access to a wider variety of formative opportunities. Ensuring good practices through a shared vision, regular communication, role clarification, and making good use of the leadership of degree-formed ministers will help blended ministries to flourish.
4. Discussion
The data from the two studies were illuminating for the USCCB Secretariat of Education and campus ministry leaders. The Secretariat recognized the potential for challenges among blended ministry teams and wanted to better support these. This discussion section will outline the practical ways the USCCB is responding to these data, especially the work of a task force that hopes to pave a way forward. The task force includes campus ministry practitioners—professionals and missionaries—as well as missionary organization leaders and a curriculum specialist. The members designed a process and created resources to facilitate the integration of blended ministry teams. Further, significant insights on alignment and decision making emerged through the work of the task force.
Although there was agreement on the value of the four principles, the task force members voiced concern about a necessary precursor to a shared vision, namely the initial decision to pair a missionary organization with an existing ministry. The language of alignment between the professional team and the missionary organization—or even with the diocese and the missionary organization—surfaced in considering the initial decision. The discussions of alignment centered on two aspects: coming to know the various ministries and organizations as well as how decisions are made.
Coming to know each other requires a mutual understanding of core values and the central missions of the missionary organization, the campus ministry site, and the diocese. This knowledge comes over time through the cultivation of a relationship and requires many conversations. Elements that contribute to discerning alignment include attending missionary conferences, visiting campus, observing missionary training, articulating the reality of the campus culture and its Catholic community, and prayer. Each element contributes to a greater understanding among the involved parties. Discerning campuses benefit from a clarity regarding the constitutive dimensions of their ministry and that of the missionary organization. The party that initiates this inquiry varies. Sometimes a campus team inquires about the missionary organization, often in consultation with the diocese; in other situations, the diocese begins the conversation; in some cases, the missionary organization approaches the diocese.
The second aspect of determining alignment is the decision to invite missionaries to a campus. In the best of circumstances, the local bishop, in consultation with his professional campus ministers, through ministry assessment, identifies the benefits of collaborating with one or more missionary organizations. The bishop and the professional ministers may discern a desire for more peer ministry or the complementarity of the professional campus team with a missionary organization as a way of expanding the reach of campus ministry. The qualitative study found that some professional ministers who were not consulted about the arriving missionaries were frustrated by the lack of communication. Similarly, missionaries reported challenges in not always feeling welcomed to a campus when professional ministers were not part of the decision. When the decision is made collaboratively between the bishop and the professional ministers, the result is greater ownership by all involved. Dialogue with diocesan leadership about assessments, goals, and expectations would be welcomed by the professional ministers and would lay a solid foundation for greater collaboration among professionals, missionaries, and the diocese.
Ultimately, the task force formulated a layered approach to integrating missionary and professional teams; this process currently involves three sessions. The first session, “Creating a Vision Statement,” has the professional team or the host team revisit their vision statement before the missionaries arrive. The better prepared the host team is to receive missionaries, the more likely they will achieve a unified vision. The second session, “Conversation Starters,” offers suggestions for dialogue that will begin to foster a productive working relationship. The third session, “Creating a Shared Mission,” builds on the first session and affords the host team and missionaries a chance to share their vision for campus ministry. Together they create a common mission statement for the ministry as a blended team. The vision statement is an articulation of things hoped for and the mission statement expresses the work to be completed during the academic year. The mission statement, in service to the vision, guides the strategic plan and activities of the blended team. A resource document highlights themes of campus ministry such as evangelization, community and sacramental life, formation, justice and care for the poor, and the Catholic intellectual tradition; these are rooted in
Empowered by the Spirit (
USCCB 1985),
Ex Corde Ecclesiae (
Pope John Paul II 1990), and
Evangelii Gaudium (
Pope Francis 2013).
With the missionaries and professional ministers in place, the process returns to the principle of shared vision. The professional ministers, as a host team, receive and welcome the missionaries into the particular context of their unique campus setting. As missionaries arrive with a clear sense of purpose, the host team must be ready to articulate who they are, how students are served, and the team’s overall purpose. This becomes an opportune time to define terms for greater clarity and appreciation between professional ministers and the missionaries. Cultivating a common language and understanding helps the professional ministers and missionaries create a shared mission statement for the coming year. The process affords greater awareness of the full scope of the ministry, including the breadth of the campus community—especially its culture and institutional relationships—and the particular gifts each minister contributes to the mission of campus ministry.
The second principle of communication expands the concept to include building trust among the team members. Recognizing the important role relational ministry plays, the task force emphasized communication and trust-building in the second session. This skill of trustworthy communication is not only valuable for interaction with students, but for the interaction of the pastoral team, as well. As in any group dynamic, adding new members creates a new group. The “Conversation Starters” session recognizes this new group and encourages communication that is intentional, personal, pastoral, and ongoing. The idea of conversation starters invites professional ministers and missionaries to share their faith journey, their call stories, and what they love about the Catholic faith and the Roman Catholic Church, affirming their common ground. The session materials provide a range of suggestions for small and large teams, for initial efforts and ongoing dialogue. Often the missionaries arrive close to the launch of the academic year when time is short and intense. The session serves as a gentle reminder to begin the conversation and even more importantly to make a commitment to regular communication that leads to greater trust among the team. Sharing among the team deepens the understanding and appreciation of each person, their gifts, and their challenges. Communication rooted in humility, charity, and compassion builds a cohesive team, which in turn strengthens the team’s capacity to pursue their mission and serve the campus community more holistically.
The building blocks of alignment, shared vision, and trustworthy communication equip the team with an awareness of their common mission and pastoral team’s gifts. The articulation of a common mission provides an excellent framework to then clarify roles and responsibilities of the professional ministers and missionaries. Understanding the mission and recognizing the gifts and responsibilities of the pastoral team helps each campus minister—professional and missionary—to understand their contribution. Ongoing communication allows members of the team to see the connectedness of their efforts and better coordinate pastoral responses.
The fourth principle calls for making good use of the leadership of the professional minister. This principle recognizes several vital dimensions necessary for the sustainability and flourishing of the ministry in the long term. Missionaries make a two-year commitment and some generously serve beyond that time. They bring a fresh enthusiasm and a peer dimension to campus ministry. The missionary’s engagement of undergraduate students brings a valuable contribution to campus ministry, but it is one dimension of the ministry.
The professional minister is responsible for the full scope of the ministry. Equipped with more education and formation, the professional minister engages the campus community (i.e., faculty, staff, administration and students), cultivates ongoing relationships with the institution, and maintains the connection with the diocese. Dialogue with the local bishop and diocesan staff are essential to implementing the diocesan vision and mission for campus ministry. Sustaining campus ministry into the future relies upon the continuity of professional ministers, who typically serve between six and ten years. The professional minister builds up the ministry with attention to development, facilities, and staffing. Further, in recognizing the greater education and ministerial experience of the professional minister, missionaries can increase their own formation by directly requesting mentorship from the professional staff. The professional team can facilitate this formation by hosting an on-boarding orientation for the arriving missionaries, as well as providing each of the missionaries a campus-affiliated mentor, such as a Catholic faculty member.
5. Implications for Ministry
This exploration of blended ministry provides valuable insights for a pastoral team that readily applies to pastoral teams more broadly. It is always good to begin with appreciation. Appreciation engenders mutual respect, humility, and hope, which are necessary virtues for a productive, collaborative ministry. These qualities also recognize that each person has something to contribute and something to learn. Beyond the pastoral team, these attitudes serve to recognize the uniqueness and giftedness of each person, a theme that resonates well with young adults. The truth is that campus ministry presently serves 25% of four-year colleges and universities. For the Church to reach more young adults on campus or through Catholic parishes, the Church needs everyone’s gifts working in concert to share the good news.
Consultation is a valuable dimension as it models appreciation, mutual respect, humility, and hope. Having diocesan leaders consult with the host campus can make a huge difference in the efficacy and morale of a blended team. First, articulating a vision and mission for the ministry that is shared among professional ministers, missionaries, and diocesan leaders creates ministerial alignment, which leads to effective collaboration. Second, consultation affirms important relationships with university staff, diocesan personnel, and alums, which provides consistency and longevity within the campus’ ministry. Consultation fosters the growth and sustainability of the ministry that draws upon the stability of the professional ministers.
As part of the Church’s evangelizing mission, campus ministry provides unique opportunities to encounter women and men—those of the Catholic faith, other faiths and no faith. To make the most of this opportunity, campus ministry has a responsibility to present the fullness of the Catholic tradition. This allows the richness of the Catholic faith to become more accessible to seekers and more resonant with believers. Campus ministry encourages growth through experiences of sacramental life, faith formation, intellectual discourse, work for justice, care for the poor, and encounters with Jesus. The local expression of the Church on campus is rooted in the self-awareness of campus ministers and missionaries, especially through their sense of purpose and shared mission. Respect and appreciation for the varied ministerial approaches and different spiritual opportunities makes the faith more accessible for students and the entire campus community.
The task force’s consideration of alignment recognizes that ministry places the mission of the Church first, reminding us that the Church’s mission is larger than any one organization, congregation, ministry site or individual. Participating in the ministry of the Church can be a point of cohesion for professional campus ministers and missionaries alike. This foundation understands that blended ministries are not about bringing extra hands to campus ministry, but rather working to build something new together. Here, campus ministry moves beyond a simple division of labor to a notion of beloved sons and daughters, bringing the exciting distinctions of their gifts in service to renewing the Church’s mission.