Safety, Immunogenicity, and Efficacy of COVID-19 Vaccines in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Background
2. Methods
2.1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Literature Screening
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
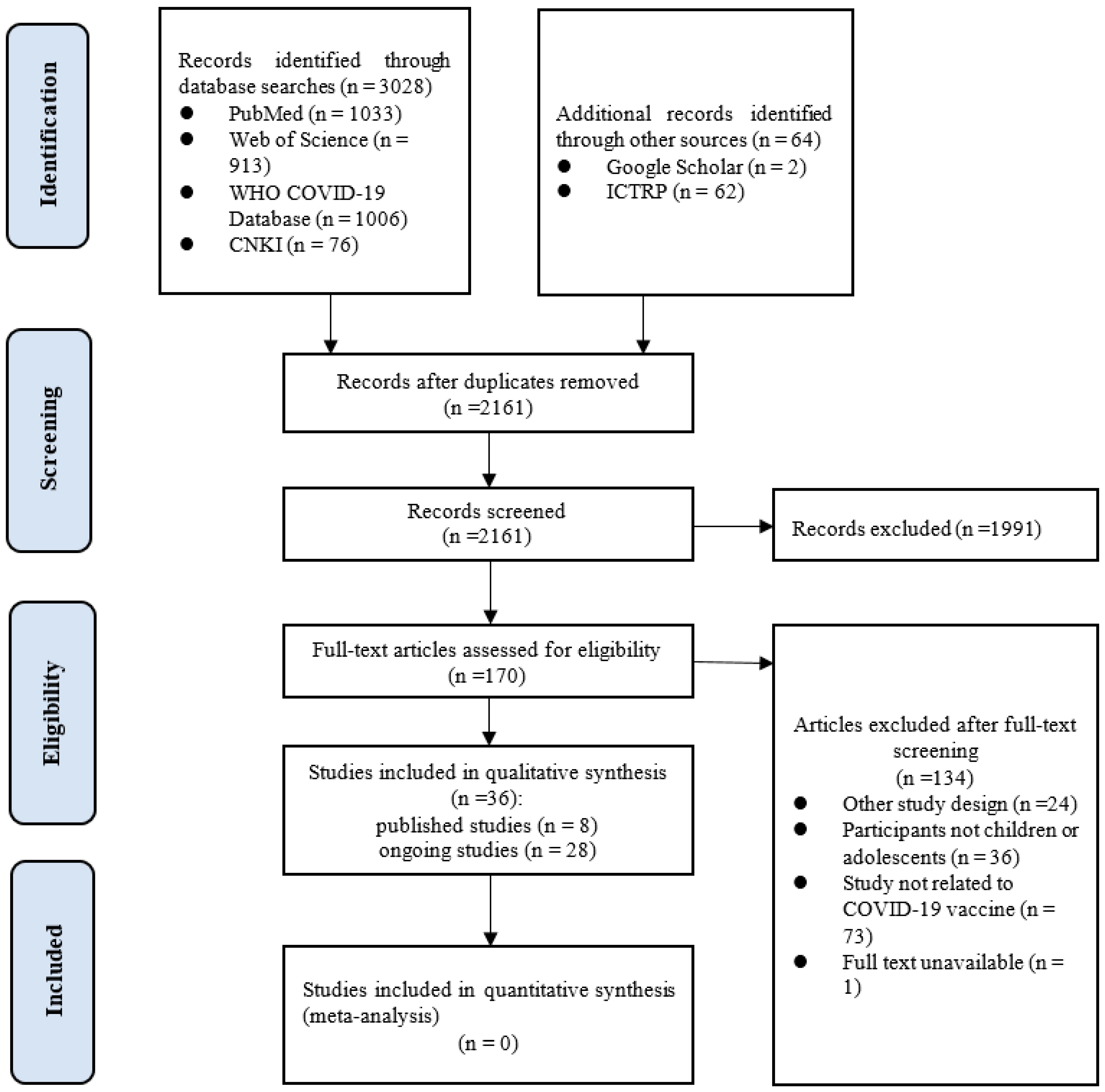
3.1. Literature Search
3.2. Characteristics of the Included Clinical Studies
3.3. Quality of Included Studies
3.4. Safety of COVID-19 Vaccines
3.5. Immunogenicity of the COVID-19 Vaccines
3.6. Efficacy of the COVID-19 Vaccines
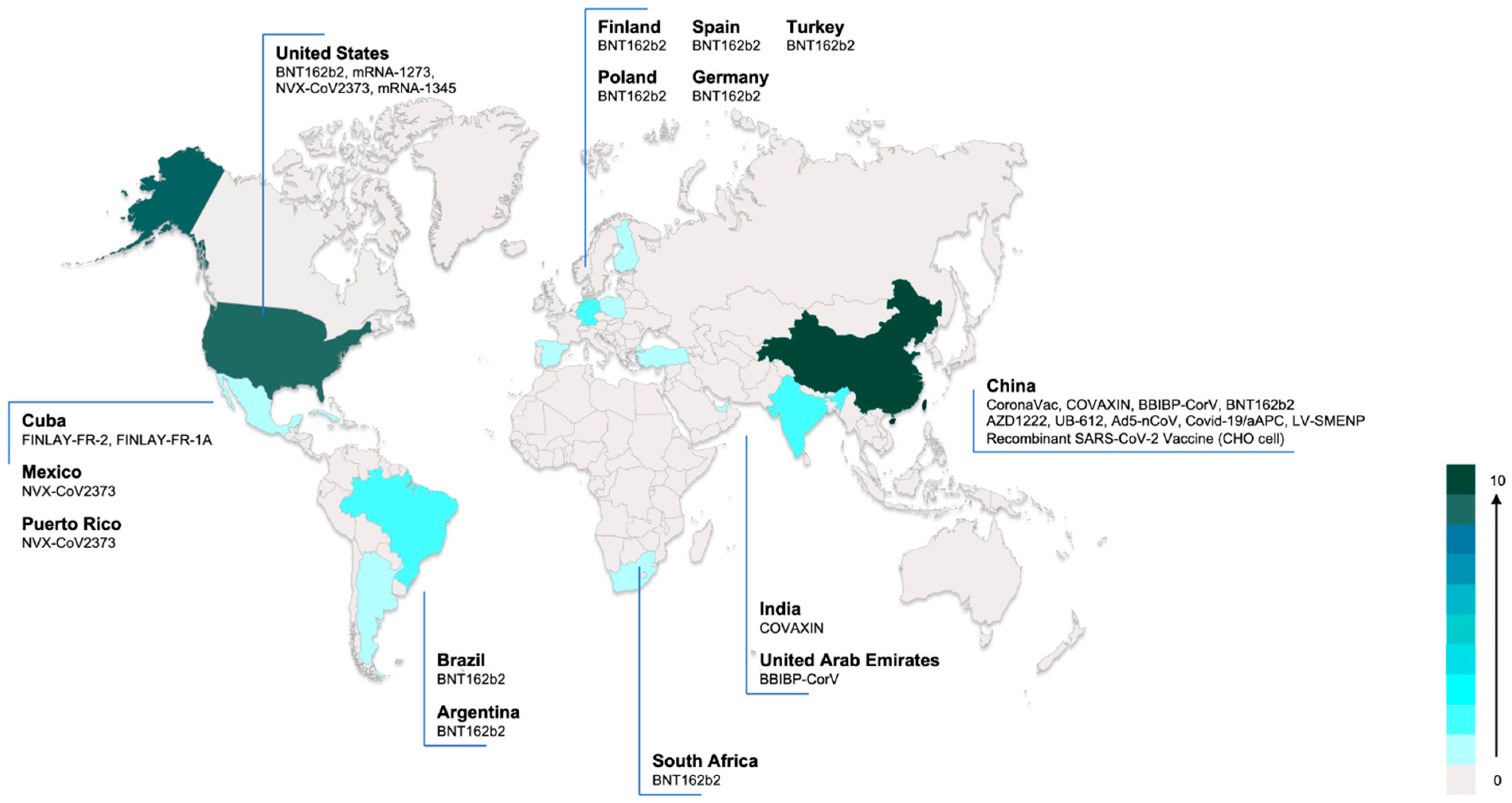
3.7. Ongoing Clinical Studies
4. Discussion
4.1. Principal Findings
4.2. Potential Impact for Future Research and Practice
4.3. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- CDC. Vaccines: The Basics. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/vpd/vpd-vac-basics.html (accessed on 8 August 2021).
- The World Bank. Population Ages 0–14 (% of Total Population). Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.POP.0014.TO.ZS (accessed on 8 August 2021).
- Xing, K.; Tu, X.Y.; Liu, M.; Liang, Z.W.; Chen, J.N.; Li, J.J.; Jiang, L.G.; Xing, F.Q.; Jiang, Y. Efficacy and safety of COVID-19 vaccines: A systematic review. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi 2021, 23, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pormohammad, A.; Zarei, M.; Ghorbani, S.; Mohammadi, M.; Razizadeh, M.H.; Turner, D.L.; Turner, R.J. Efficacy and Safety of COVID-19 Vaccines: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Vaccines 2021, 9, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, I.; Murray, S.M.; Reynolds, C.J.; Altmann, D.M.; Boyton, R.J. Comparative systematic review and meta-analysis of reactogenicity, immunogenicity and efficacy of vaccines against SARS-CoV-2. NPJ Vaccines 2021, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, L.; Jin, H.; Lin, L. Vaccination against COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of acceptability and its predictors [published online ahead of print, 22 June 2021]. Prev. Med. 2021, 150, 106694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaar, O.; Klimek, L.; Hamelmann, E.; Kleine-Tebbe, J.; Taube, C.; Wagenmann, M.; Werfel, T.; Brehler, R.; Novak, N.; Mülleneisen, N.; et al. COVID-19 vaccination of patients with allergies and type-2 inflammation with concurrent antibody therapy (biologicals)–A Position Paper of the German Society of Allergology and Clinical Immunology (DGAKI) and the German Society for Applied Allergology (AeDA). Allergol. Select. 2021, 5, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazlewood, G.S.; Pardo, J.P.; Barnabe, C.; Schieir, O.; Barber, C.; Bernatsky, S.; Colmegna, I.; Hitchon, C.; Loeb, M.; Mertz, D.; et al. Canadian Rheumatology Association Recommendation for the Use of COVID-19 Vaccination for Patients with Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. J. Rheumatol. 2021, 48, 1330–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Interim Recommendations for Use of the Inactivated COVID-19 Vaccine, CoronaVac, Developed by Sinovac. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-vaccines-SAGE_recommendation-Sinovac-CoronaVac-2021.1 (accessed on 8 August 2021).
- Zimmermann, P.; Curtis, N. Why is COVID-19 less severe in children? A review of the proposed mechanisms underlying the age-related difference in severity of SARS-CoV-2 infections. Arch. Dis. Child. 2021, 106, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opel, D.J.; Diekema, D.S.; Ross, L.F. Should We Mandate a COVID-19 Vaccine for Children? JAMA Pediatrics 2021, 175, 125–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Li, W.; Zhao, S.; Li, Q.; Shi, Q.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Estill, J.; Luo, Z.; et al. Guidelines for the Management of Children and Adolescent with COVID-19: Protocol for an update. Transl. Pediatrics 2021, 10, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. BMJ 2009, 339, b2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higgins, J.; Thomas, J. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. 2021. Available online: https://training.cochrane.org/handbook/current (accessed on 8 August 2021).
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Jüni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savovic, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.; et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wells, G.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Robertson, J.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies in Meta-Analyses; Ottawa Hospital Research Institute: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2011; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Murad, M.H.; Sultan, S.; Haffar, S.; Bazerbachi, F. Methodological quality and synthesis of case series and case reports. BMJ Evid.-Based Med. 2018, 23, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joanna Briggs Institute. Checklist for Analytical Cross Sectional Studies; The Joanna Briggs Institute: Adelaide, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B.; Song, Y.; Li, C.; Yang, W.; Ma, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Li, M.; Lian, X.; Jiao, W.; Wang, L.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (CoronaVac) in healthy children and adolescents: A double-blind, randomised, controlled, phase 1/2 clinical trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenck, R.W., Jr.; Klein, N.P.; Kitchin, N.; Gurtman, A.; Absalon, J.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Walter, E.B.; Senders, S.; Bailey, R.; et al. Safety, immunogenicity, and efficacy of the BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine in adolescents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revon-Riviere, G.; Ninove, L.; Min, V.; Rome, A.; Coze, C.; Verschuur, A.; de Lamballerie, X.; André, N. BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine in AYA with cancer: A monocentric experience. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 154, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snapiri, O.; Shirman, N.; Weissbach, A.; Weissbach, A.; Lowenthal, A.; Ayalon, I.; Adam, D.; Yarden-Bilavsky, H.; Bilavsky, E. Transient Cardiac Injury in Adolescents Receiving the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine. Pediatric Infect. Dis. J. 2021, 40, e360–e363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minocha, P.K.; Better, D.; Singh, R.K.; Hoque, T. Recurrence of Acute Myocarditis Temporally Associated With Receipt of the mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine in an Adolescent Male. J. Pediatrics 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, K.; Johnson, T.J. Myopericarditis in a Previously Healthy Adolescent Male Following COVID-19 Vaccination: A Case Report. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, M.; Ferguson, I.D.; Lewis, P.; Jaggi, P.; Gagliardo, C.; Collins, J.S.; Shaughnessy, R.; Caron, R.; Fuss, C.; Corbin, K.; et al. Symptomatic acute myocarditis in seven adolescents following Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccination. Pediatrics 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schauer, J.; Buddhe, S.; Colyer, J.; Sagiv, E.; Law, Y.; Chikkabyrappa, S.M.; Portman, M.A. Myopericarditis after the Pfizer mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine in Adolescents. J. Pediatrics 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.E.; Amlôt, R.; Weinman, J.; Yiend, J.; Rubin, G.J. A systematic review of factors affecting vaccine uptake in young children. Vaccine 2017, 35, 6059–6069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruf, B.R.; Knuf, M. The burden of seasonal and pandemic influenza in infants and children. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2014, 173, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wijnans, L.; de Bie, S.; Dieleman, J.; Bonhoeffer, J.; Sturkenboom, M. Safety of pandemic H1N1 vaccines in children and adolescents. Vaccine 2011, 29, 7559–7571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.Y.; Shao, P.L.; Chang, L.Y.; Huang, Y.C.; Chiu, C.H.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Lin, T.Y.; Huang, L.M. Immunogenicity and safety of a monovalent vaccine for the 2009 pandemic influenza virus A (H1N1) in children and adolescents. Vaccine 2010, 28, 5864–5870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riphagen, S.; Gomez, X.; Gonzalez-Martinez, C.; Wilkinson, N.; Theocharis, P. Hyperinflammatory shock in children during COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet 2020, 395, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licciardi, F.; Pruccoli, G.; Denina, M.; Parodi, E.; Taglietto, M.; Rosati, S.; Montin, D. SARS-CoV-2-Induced Kawasaki-Like Hyperinflammatory Syndrome: A Novel COVID Phenotype in Children. Pediatrics 2020, 146, e20201711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdoni, L.; Mazza, A.; Gervasoni, A.; Martelli, L.; Ruggeri, M.; Ciuffreda, M.; Bonanomi, E.; D’Antiga, L. An outbreak of severe Kawasaki-like disease at the Italian epicentre of the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic: An observational cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, E.; Bamford, A.; Kenny, J.; Kaforou, M.; Jones, C.E.; Shah, P.; Ramnarayan, P.; Fraisse, A.; Miller, O.; Davies, P.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of 58 Children with a Pediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome Temporally Associated With SARS-CoV-2. JAMA 2020, 324, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, A.; Gupta, S.; Sood, M.; Sharma, S.; Verma, S. A Systematic Review of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children Associated With SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2020, 39, e340–e346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, L.K. Kawasaki disease and immunisation: A systematic review. Vaccine 2017, 35, 1770–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccines Candidates by Trial Phase. Available online: https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines (accessed on 8 August 2021).
- COVID-19 NMA. Available online: https://covid-nma.com/vaccines/mapping/ (accessed on 8 August 2021).
- Kaur, R.J.; Dutta, S.; Bhardwaj, P.; Charan, J.; Dhingra, S.; Mitra, P.; Singh, K.; Yadav, D.; Sharma, P.; Misra, S. Adverse Events Reported From COVID-19 Vaccine Trials: A Systematic Review [published online ahead of print, 2021 Mar 27]. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Interim Recommendations for Use of the Pfizer–BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine, BNT162b2, under Emergency Use Listing: Interim Guidance, First Issued 8 January 2021, Updated 15 June 2021[R]; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 Vaccines for Children and Teens. Updated 23 July 2021. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/recommendations/adolescents.html (accessed on 8 August 2021).
- Food and Drug Administration. Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine Emergency Use Authorization; US Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2021. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/emergency-preparedness-and-response/coronavirus-disease-2019-covid-19/pfizer-biontech-covid-19-vaccine (accessed on 8 August 2021).
- The Canadian Paediatric Society. COVID-19 Vaccine for Children. Updated 12 July 2021. Available online: https://www.cps.ca/en/documents/position/covid-19-vaccine-for-children (accessed on 8 August 2021).
- European Medicines Agency. COVID-19 Vaccine Spikevax Approved for Children Aged 12 to 17 in EU. 23 July 2021. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/covid-19-vaccine-spikevax-approved-children-aged-12-17-eu (accessed on 8 August 2021).
- European Center for Disease Prevention and Control. Interim Public Health Considerations for COVID-19 Vaccination of Adolescents in the EU/EEA; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 1 June 2021; Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/interim-public-health-considerations-covid-19-vaccination-adolescents-eueea#no-link (accessed on 8 August 2021).
- Goldman, R.D.; Staubli, G.; Cotanda, C.P.; Brown, J.C.; Hoeffe, J.; Seiler, M.; Gelernter, R.; Hall, J.E.; Griffiths, M.A.; Davis, A.L.; et al. Factors Associated with Parents’ Willingness to Enroll Their Children in Trials for COVID-19 Vaccination. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2021, 17, 1607–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Xiu, S.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Han, Y.; Dong, S.; Huang, J.; Cui, T.; Yang, L.; Shi, N.; et al. Vaccine Hesitancy: COVID-19 and Influenza Vaccine Willingness among Parents in Wuxi, China-A Cross-Sectional Study. Vaccines 2021, 9, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nour, R. A Systematic Review of Methods to Improve Attitudes towards Childhood Vaccinations. Cureus 2019, 11, e5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Name of Vaccine | Participants | Sample Size | Follow-Up Duration | Study Design | Country | Funding | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoronaVac | Healthy children and adolescents aged 3–17 years | 552 | 4.1 months | RCT Phase 1–2 | China | Public/nonprofit (Chinese National Key Research and Development Program and Beijing Science and Technology Program) | Han et al., 2021 [19] |
| BNT162b2 | Adolescents aged 12–15 years with no previous COVID-19 diagnosis or SARS-CoV-2 infection | 2264 | 4.7 months | RCT Phase 3 | USA | Private (BioNTech and Pfizer) | Frenck et al., 2021 [20] |
| BNT162b2 | Adolescents and young adults aged 16 years with solid tumor older than | 9 | NR * | Case series | France | NR * | Riviere et al., 2021 [21] |
| BNT162b2 | Adolescents aged 16–18 years | 7 | NR * | Case series | Israel | None | Snapiri et al., 2021 [22] |
| BNT162b2 | An adolescent aged 17 years | 1 | 2 weeks | Case report | USA | NR * | Minocha et al., 2021 [23] |
| BNT162b2 | A previously healthy adolescent aged 16 years | 1 | 2 weeks | Case report | USA | NR * | McLean et al., 2021 [24] |
| BNT162b2 | Healthy adolescents 14–18 years | 5 | unclear | Case report | USA | None | Marshall et al., 2021 [25] |
| BNT162b2 | Children and adolescents aged 12–17 years | 13 | 3 months | Case report | USA | NR * | Schauer et al., 2021 [26] |
| Risk of Bias in the Included Rcts Assessed by the Risk of Bias Tool | ||||||||
| Selection bias | Performance bias | Detection bias | Attrition bias | Reporting bias | Other bias | Study | ||
| Random sequence generation | Allocation concealment | Blinding of participants and personnel | Blinding of outcome assessment | Incomplete outcome data | Selective reporting | Anything else, ideally prespecified | ||
| low | low | low | low | low | low | low | Han et al., 2021 [19] | |
| low | low | low | low | unclear | low | low | Frenck et al., 2021 [20] | |
| Methdological quality in the case series and case reports assessed by Murad et al. checklist | ||||||||
| Selection | Ascertainment | Causality | Reporting | Study | ||||
| Does the patient(s) represent(s) the whole experience of the investigator (centre) or is the selection method unclear to the extent that other patients with similar presentation may not have been reported? | Was the exposure adequately ascertained? | Was the outcome adequately ascertained? | Were other alternative causes that may explain the observation ruled out? | Was there a challenge/rechallenge phenomenon? | Was there a dose-response effect? | Was follow-up long enough for outcomes to occur? | Is the case(s) described with sufficient details to allow other investigators to replicate the research or to allow practitioners make inferences related to their own practice? | |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | N/A | N/A | 0 | 0 | Revon-Riviere et al., 2021 [21] |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | N/A | N/A | 0 | 1 | Snapiri et al., 2021 [22] |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | N/A | N/A | 1 | 1 | Minocha et al., 2021 [23] |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | N/A | N/A | 1 | 1 | McLean et al., 2021 [24] |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | N/A | N/A | 0 | 1 | Marshall et al., 2021 [25] |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | N/A | N/A | 1 | 1 | Schauer et al., 2021 [26] |
| Vaccination | Age | Sex | Symptoms | Diagnosis | Time of Onset (Days Since Vaccination) | Length of Hospitalization (Days) | Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BNT162b2, second dose | 17 | M | Chest pain | Perimyocarditis | 3 | 4 | Snapiri et al., 2021 [22] |
| BNT162b2, second dose | 16 | M | Chest pain | Perimyocarditis | 1 | 6 | Snapiri et al., 2021 [22] |
| BNT162b2, second dose | 16 | M | Chest pain, cough | Perimyocarditis | 2 | 6 | Snapiri et al., 2021 [22] |
| BNT162b2, second dose | 16 | M | Chest pain, nausea | Perimyocarditis | 3 | 4 | Snapiri et al., 2021 [22] |
| BNT162b2, second dose | 17 | M | Chest pain, headache | Perimyocarditis | 1 | 5 | Snapiri et al., 2021 [22] |
| BNT162b2, second dose | 16 | M | Chest pain, dyspnea, diarrhea, fever | Perimyocarditis | 2 | 5 | Snapiri et al., 2021 [22] |
| BNT162b2, second dose | 17 | M | Chest pain, dyspnea | Perimyocarditis | 3 | 3 | Snapiri et al., 2021 [22] |
| BNT162b2, second dose | 17 | M | Chest pain, fever, body aches, | Myocarditis | 1 | 6 | Minocha et al., 2021 [23] |
| BNT162b2, second dose | 16 | M | Chest pain | Myopericarditis | 2.5 | 6 | McLean et al., 2021 [24] |
| BNT162b2, second dose | 16 | M | Chest pain, bilateral arm pain, fever, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, headache | Myocarditis | 2 | 6 | Marshall et al., 2021 [25] |
| BNT162b2, second dose | 17 | M | Chest pain, bilateral arm pain, numbness, paresthesia | Myopericarditis | 2 | 2 | Marshall et al., 2021 [25] |
| BNT162b2, second dose | 17 | M | Chest pain, bilateral arm pain, abdominal pain, fever, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, SOB, palpitations | Myocarditis | 4 | 5 | Marshall et al., 2021 [25] |
| BNT162b2, second dose | 16 | M | Chest pain, SOB | Myocarditis | 3 | 3 | Marshall et al., 2021 [25] |
| BNT162b2, second dose | 14 | M | Chest pain, fever, SOB | Myopericarditis | 2 | 4 | Marshall et al., 2021 [25] |
| BNT162b2, second dose | 16 | M | Chest pain, fever, chills, myalgias, headache, SOB | Myopericarditis | 2 | 1 | Schauer et al., 2021 [26] |
| BNT162b2, second dose | 16 | M | Chest pain, fever, myalgias | Myopericarditis | 2 | 1 | Schauer et al., 2021 [26] |
| BNT162b2, second dose | 16 | M | Chest pain, myalgias, headache | Myopericarditis | 3 | 3 | Schauer et al., 2021 [26] |
| BNT162b2, second dose | 17 | M | Chest pain, fever, malaise | Myopericarditis | 3 | 1 | Schauer et al., 2021 [26] |
| BNT162b2, second dose | 15 | M | Chest pain, myalgias, SOB | Myopericarditis | 2 | 2 | Schauer et al., 2021 [26] |
| BNT162b2, second dose | 15 | F | Chest pain, vomiting | Myopericarditis | 3 | 1 | Schauer et al., 2021 [26] |
| BNT162b2, second dose | 15 | M | Chest pain, fevers, SOB | Myopericarditis | 3 | 3 | Schauer et al., 2021 [26] |
| BNT162b2, second dose | 15 | M | Chest pain, chills | Myopericarditis | 3 | 3 | Schauer et al., 2021 [26] |
| BNT162b2, second dose | 12 | M | Chest pain | Myopericarditis | 3 | 2 | Schauer et al., 2021 [26] |
| BNT162b2, second dose | 14 | M | Chest pain, fever, headache | Myopericarditis | 3 | 3 | Schauer et al., 2021 [26] |
| BNT162b2, second dose | 14 | M | Chest pain, malaise, SOB | Myopericarditis | 4 | 2 | Schauer et al., 2021 [26] |
| BNT162b2, second dose | 16 | M | Chest pain, SOB | Myopericarditis | 2 | 2 | Schauer et al., 2021 [26] |
| BNT162b2, second dose | 15 | M | Chest pain | Myopericarditis | 3 | 2 | Schauer et al., 2021 [26] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, M.; Luo, X.; Shen, Q.; Lei, R.; Liu, X.; Liu, E.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y. Safety, Immunogenicity, and Efficacy of COVID-19 Vaccines in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9101102
Lv M, Luo X, Shen Q, Lei R, Liu X, Liu E, Li Q, Chen Y. Safety, Immunogenicity, and Efficacy of COVID-19 Vaccines in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Vaccines. 2021; 9(10):1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9101102
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Meng, Xufei Luo, Quan Shen, Ruobing Lei, Xiao Liu, Enmei Liu, Qiu Li, and Yaolong Chen. 2021. "Safety, Immunogenicity, and Efficacy of COVID-19 Vaccines in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review" Vaccines 9, no. 10: 1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9101102
APA StyleLv, M., Luo, X., Shen, Q., Lei, R., Liu, X., Liu, E., Li, Q., & Chen, Y. (2021). Safety, Immunogenicity, and Efficacy of COVID-19 Vaccines in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Vaccines, 9(10), 1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9101102






