A Pentavalent Epstein-Barr Virus-Like Particle Vaccine Elicits High Titers of Neutralizing Antibodies against Epstein-Barr Virus Infection in Immunized Rabbits
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Animals and Ethics Statement
2.2. Cell Lines
2.3. Antibodies
2.4. Virus Production and Purification
2.5. Plasmids
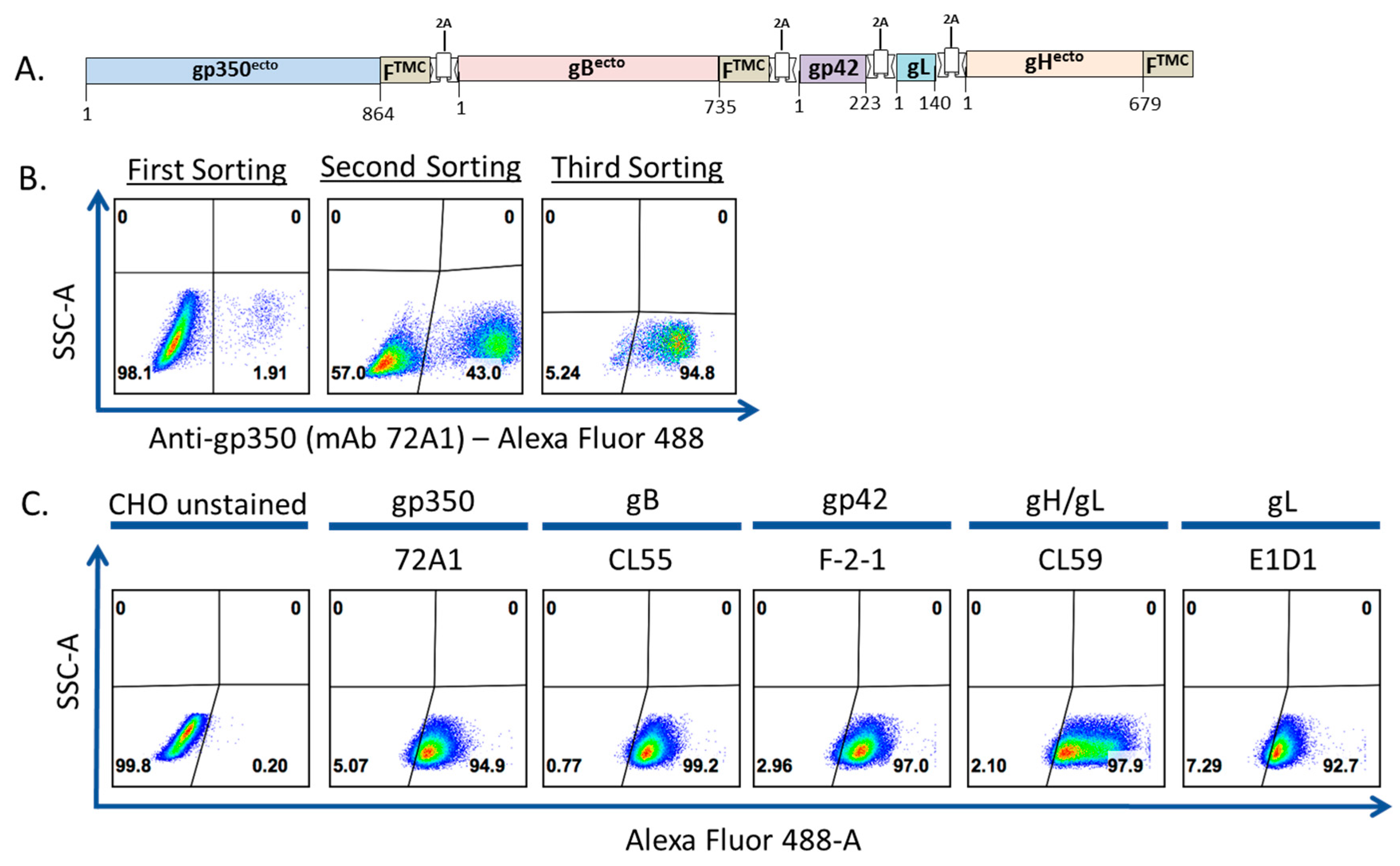
2.6. Transfection of gp350-F-gB-F-gp42-gL-gH-F and Generation of Stable CHO Cell Line
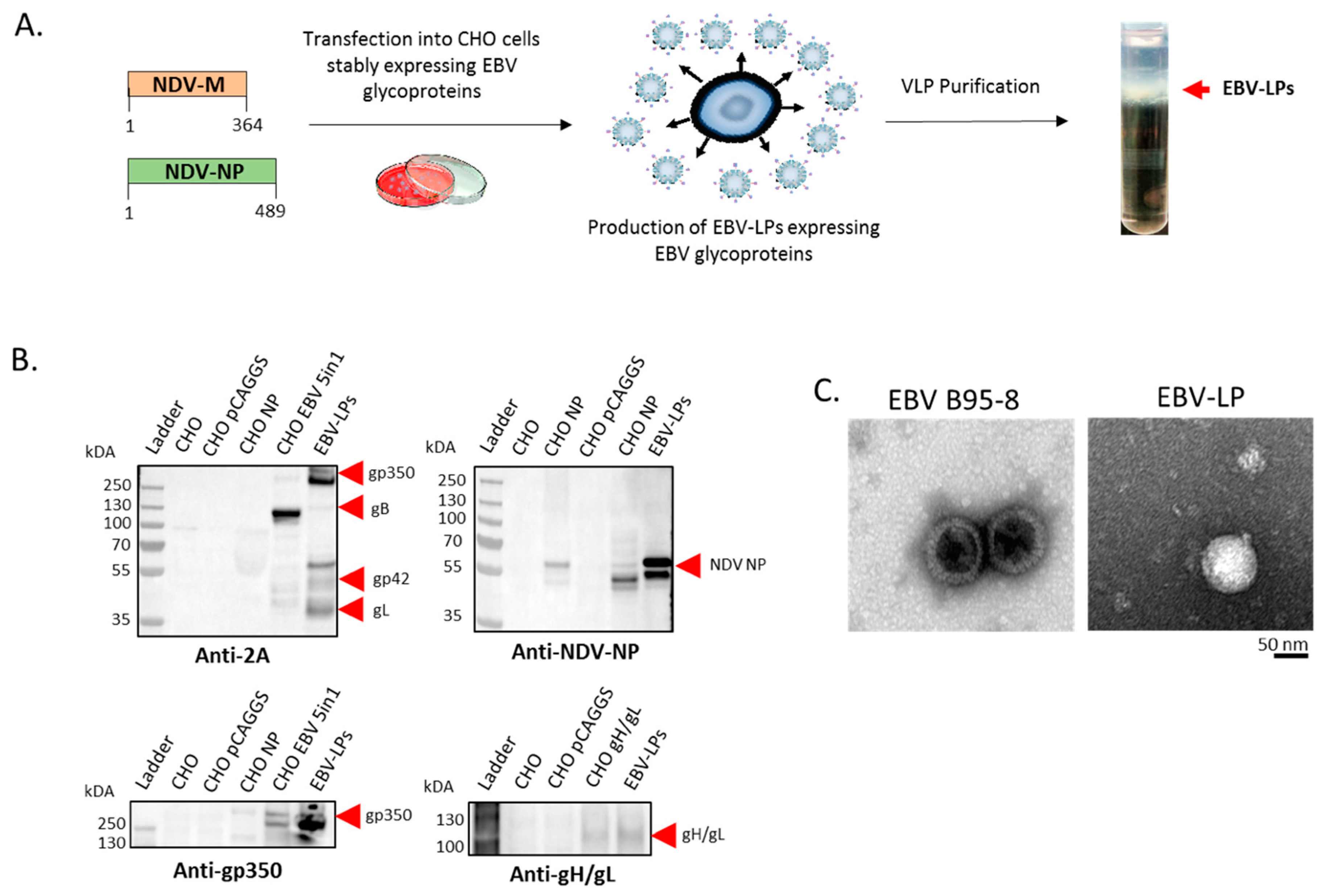
2.7. Transfection, Generation, and Purification of EBV-LPs
2.8. SDS-PAGE, Coomassie Staining, and Immunoblotting
2.9. Transmission Electron Microcopy (TEM)
2.10. Recombinant EBV Proteins
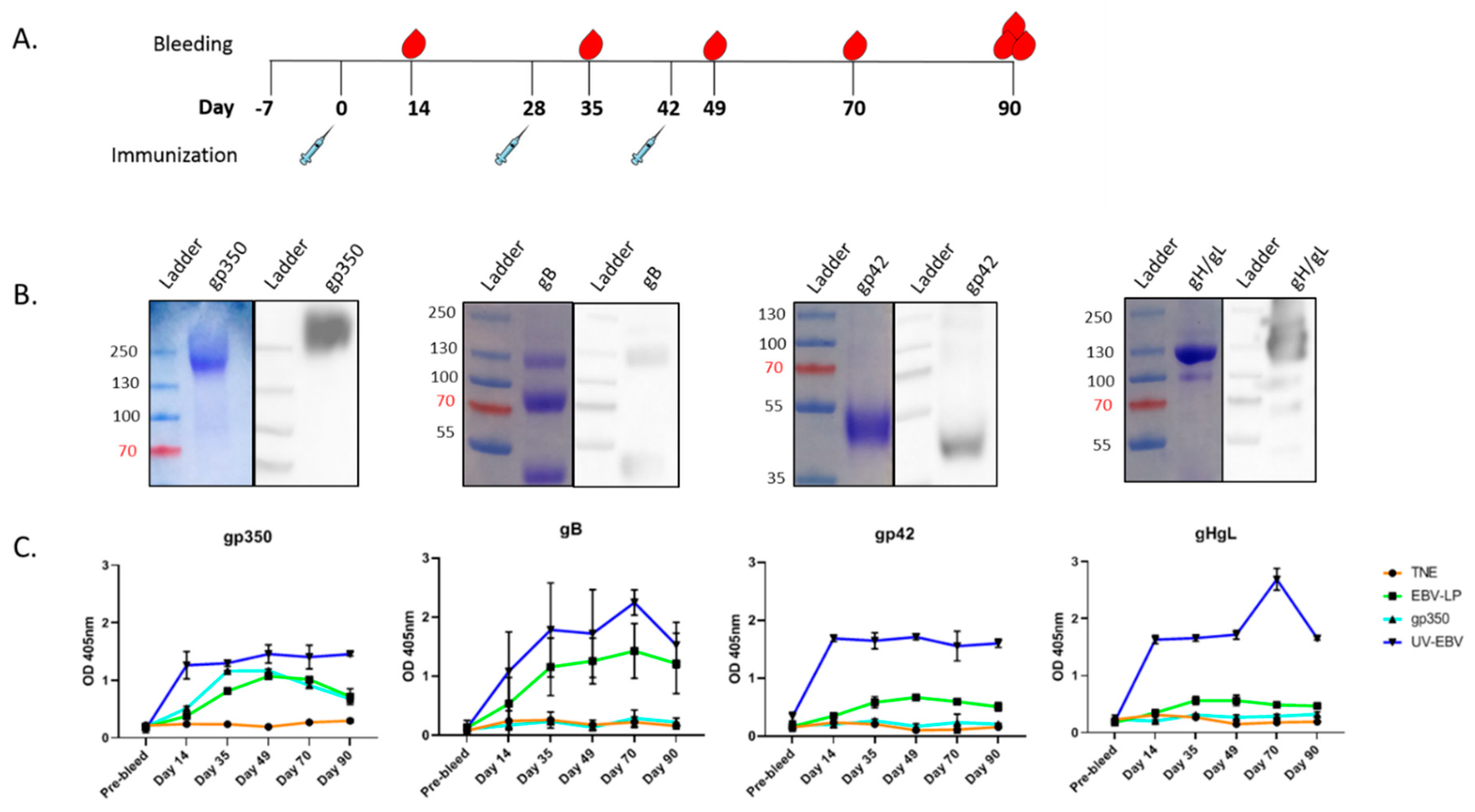
2.11. Immunization of Rabbits
2.12. Determination of Glycoprotein-Specific Antibody Titers in Serum of Immunized Rabbits
2.13. Purification of IgG Antibodies from Rabbit Sera, and Determination of Glycoprotein-Specific Antibody Titers
2.14. EBV-eGFP Neutralization Assay in B cells and Epithelial Cells
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Construction, Purification, and Characterization of EBV-LP Vaccine Candidate That Incorporates Five EBV Glycoproteins
3.2. Pentavalent EBV-LPs Are Immunogenic and Elicit EBV-Glycoprotein-Specific Antibodies in Rabbits
3.3. EBV-LPs Produce Robust nAb Responses in Immunized Rabbits That Prevent EBV Infection of Both B Cell and Epithelial Cell Lines
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cohen, J.I.; Mocarski, E.S.; Raab-Traub, N.; Corey, L.; Nabel, G.J. The need and challenges for development of an Epstein-Barr virus vaccine. Vaccine 2013, 31, B194–B196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Qu, J.; Peng, Q.; Gan, R. Molecular mechanisms of EBV-driven cell cycle progression and oncogenesis. Med Microbiol. Immunol. 2018, 208, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harley, J.B.; Chen, X.; Pujato, M.; Miller, D.; Maddox, A.; Forney, C.; Magnusen, A.F.; De La Cruz-Lynch, A.; Chetal, K.; Yukawa, M.; et al. Transcription factors operate across disease loci, with EBNA2 implicated in autoimmunity. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.I.; Fauci, A.S.; Varmus, H.; Nabel, G.J. Epstein-Barr Virus: An Important Vaccine Target for Cancer Prevention. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 107fs7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munger, K.; Levin, L.I.; O’Reilly, E.J.; Falk, K.I.; Ascherio, A. Anti-Epstein–Barr virus antibodies as serological markers of multiple sclerosis: A prospective study among United States military personnel. Mult. Scler. J. 2011, 17, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handel, A.E.; Williamson, A.J.; Disanto, G.; Handunnetthi, L.; Giovannoni, G.; Ramagopalan, S.V. An Updated Meta-Analysis of Risk of Multiple Sclerosis following Infectious Mononucleosis. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.I. Vaccine Development for Epstein-Barr Virus. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1045, 477–493. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J.I. Epstein-barr virus vaccines. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2015, 4, e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, S.L.; Suhrbier, A.; Miles, J.J.; Lawrence, G.; Pye, S.J.; Le, T.T.; Rosenstengel, A.; Nguyen, T.; Allworth, A.; Burrows, S.; et al. Phase I Trial of a CD8+ T-Cell Peptide Epitope-Based Vaccine for Infectious Mononucleosis. J. Virol. 2007, 82, 1448–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.Y.; Huang, T.M.; Ruan, L.; Miao, Y.H.; Lu, H.; Chu, C.M.; Motz, M.; Wolf, H. First EBV vaccine trial in humans using recombinant vaccinia virus expressing the major membrane antigen. Dev. Boil. Stand. 1995, 84, 171–177. [Google Scholar]
- Moutschen, M.; Leonard, P.; Sokal, E.M.; Smets, F.; Haumont, M.; Mazzu, P.; Bollen, A.; Denamur, F.; Peeters, P.; Dubin, G.; et al. Phase I/II studies to evaluate safety and immunogenicity of a recombinant gp350 Epstein–Barr virus vaccine in healthy adults. Vaccine 2007, 25, 4697–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokal, E.M.; Hoppenbrouwers, K.; Vandermeulen, C.; Moutschen, M.; Léonard, P.; Moreels, A.; Haumont, M.; Bollen, A.; Smets, F.; Denis, M. Recombinant gp350 Vaccine for Infectious Mononucleosis: A Phase 2, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial to Evaluate the Safety, Immunogenicity, and Efficacy of an Epstein-Barr Virus Vaccine in Healthy Young Adults. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 196, 1749–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rees, L.; Tizard, E.J.; Morgan, A.J.; Cubitt, W.D.; Finerty, S.; Oyewole-Eletu, T.A.; Owen, K.; Royed, C.; Stevens, S.J.C.; Shroff, R.; et al. A Phase I Trial of Epstein-Barr Virus Gp350 Vaccine for Children With Chronic Kidney Disease Awaiting Transplantation. Transplant 2009, 88, 1025–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, H.; Meckiff, B.J.; Taylor, G. The T-cell Response to Epstein-Barr Virus-New Tricks from an Old Dog. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaeuferle, T.; Krauss, R.; Blaeschke, F.; Willier, S.; Feuchtinger, T. Strategies of adoptive T -cell transfer to treat refractory viral infections post allogeneic stem cell transplantation. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, L.P.; Bollard, C.M.; Keller, M.D. Adoptive T Cell Therapy for Epstein–Barr Virus Complications in Patients With Primary Immunodeficiency Disorders. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Zyl, D.G.; Mautner, J.; Delecluse, H.-J. Progress in EBV Vaccines. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, A. Exploiting Mucosal Immunity for Antiviral Vaccines. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 34, 575–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, S.; Friedman, H.M. A paradigm shift: Vaccine-induced antibodies as an immune correlate of protection against herpes simplex virus type 1 genital herpes. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 209, 813–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, P.B.; Gabriel, E.; Miao, X.; Li, X.; Su, S.-C.; Parrino, J.; Chan, I.S.F. Fold rise in antibody titers by measured by glycoprotein-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay is an excellent correlate of protection for a herpes zoster vaccine, demonstrated via the vaccine efficacy curve. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belshe, R.B.; Leone, P.A.; Bernstein, D.I.; Wald, A.; Levin, M.J.; Stapleton, J.T.; Gorfinkel, I.; Morrow, R.L.A.; Ewell, M.G.; Stokes-Riner, A.; et al. Efficacy results of a trial of a herpes simplex vaccine. New Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Thorley-Lawson, D.; A Poodry, C. Identification and isolation of the main component (gp350-gp220) of Epstein-Barr virus responsible for generating neutralizing antibodies in vivo. J. Virol. 1982, 43, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janz, A.; Oezel, M.; Kurzeder, C.; Mautner, J.; Pich, D.; Kost, M.; Hammerschmidt, W.; Delecluse, H.-J. Infectious Epstein-Barr virus lacking major glycoprotein BLLF1 (gp350/220) demonstrates the existence of additional viral ligands. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 10142–10152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathiyamoorthy, K.; Jiang, J.; Hu, Y.X.; Rowe, C.L.; Möhl, B.S.; Chen, J.; Jiang, W.; Mellins, E.D.; Longnecker, R.; Zhou, Z.H.; et al. Assembly and Architecture of the EBV B Cell Entry Triggering Complex. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiyamoorthy, K.; Hu, Y.X.; Möhl, B.S.; Chen, J.; Longnecker, R.; Jardetzky, T.S. Structural basis for Epstein–Barr virus host cell tropism mediated by gp42 and gHgL entry glycoproteins. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingeroth, J.D.; Weis, J.J.; Tedder, T.F.; Strominger, J.L.; Biro, P.A.; Fearon, D.T. Epstein-Barr virus receptor of human B lymphocytes is the C3d receptor CR2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 4510–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogembo, J.G.; Kannan, L.; Ghiran, I.; Nicholson-Weller, A.; Finberg, R.W.; Tsokos, G.C.; Fingeroth, J.D. Human complement receptor type 1/CD35 is an Epstein-Barr Virus receptor. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, J.; Weis, J.; Fearon, D.; Whang, Y.; Kieff, E. Epstein-Barr virus gp350/220 binding to the B lymphocyte C3d receptor mediates adsorption, capping, and endocytosis. Cell 1987, 50, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Spriggs, M.K.; Kovats, S.; Turk, S.M.; Comeau, M.R.; Nepom, B.; Hutt-Fletcher, L.M. Epstein-Barr virus uses HLA class II as a cofactor for infection of B lymphocytes. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 4657–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, S.A.; Jackson, J.O.; Jardetzky, T.S.; Longnecker, R. Fusing structure and function: A structural view of the herpesvirus entry machinery. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 9, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Sathiyamoorthy, K.; Zhang, X.; Schaller, S.; Perez-White, B.; Jardetzky, T.S.; Longnecker, R. Ephrin receptor A2 is a functional entry receptor for Epstein-Barr virus. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.-B.; Zhang, A.; Chen, M.-L.; Fang, Z.-X.; Dong, X.-D.; Li, S.-B.; Du, Y.; Xiong, D.; et al. Ephrin receptor A2 is an epithelial cell receptor for Epstein–Barr virus entry. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesnokova, L.S.; Nishimura, S.L.; Hutt-Fletcher, L.M. Fusion of epithelial cells by Epstein-Barr virus proteins is triggered by binding of viral glycoproteins gHgL to integrins alphavbeta6 or alphavbeta8. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20464–20469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesnokova, L.S.; Hutt-Fletcher, L.M. Fusion of Epstein-Barr virus with epithelial cells can be triggered by alphavbeta5 in addition to alphavbeta6 and alphavbeta8, and integrin binding triggers a conformational change in glycoproteins gHgL. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 13214–13223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutt-Fletcher, L.M. EBV glycoproteins: Where are we now? Futur. Virol. 2015, 10, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-H.; Yang, Y.-J.; Cheng, W.-C.; Wang, W.-M.; Lin, S.-H.; Shieh, C.-C. Higher Risk for Hematological Malignancies in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Nationwide Population-based Study in Taiwan. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 111, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molesworth, S.J.; Lake, C.M.; Borza, C.M.; Turk, S.M.; Hutt-Fletcher, L.M. Epstein-Barr Virus gH Is Essential for Penetration of B Cells but Also Plays a Role in Attachment of Virus to Epithelial Cells. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 6324–6332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sashihara, J.; Burbelo, P.D.; Savoldo, B.; Pierson, T.C.; Cohen, J.I. Human antibody titers to Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) gp350 correlate with neutralization of infectivity better than antibody titers to EBV gp42 using a rapid flow cytometry-based EBV neutralization assay. Virology 2009, 391, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, W.; Joyce, M.G.; Nguyen, H.; Banh, D.V.; Aguilar, F.; Tariq, Z. Immunization with Components of the Viral Fusion Apparatus Elicits Antibodies That Neutralize Epstein-Barr Virus in B Cells and Epithelial Cells. Immunity 2019, 50, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strnad, B.C.; Schuster, T.; Klein, R.; Hopkins, R.F.; Witmer, T.; Neubauer, R.H.; Rabin, H. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against the Epstein-Barr virus membrane antigen. J. Virol. 1982, 41, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balachandran, N.; Oba, D.E.; Hutt-Fletcher, L.M. Antigenic cross-reactions among herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2, Epstein-Barr virus, and cytomegalovirus. J. Virol. 1987, 61, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Cao, Z.; Chen, Q.; Arjunaraja, S.; Snow, A.; Snapper, C.M. Rabbits immunized with Epstein-Barr virus gH/gL or gB recombinant proteins elicit higher serum virus neutralizing activity than gp350. Vaccine 2016, 34, 4050–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Turk, S.M.; Hutt-Fletcher, L.M. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) BZLF2 gene product associates with the gH and gL homologs of EBV and carries an epitope critical to infection of B cells but not of epithelial cells. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 3987–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, E.; Foley, J.; Tison, T.; Silva, R.; Ogembo, J.G. Novel Epstein-Barr virus-like particles incorporating gH/gL-EBNA1 or gB-LMP2 induce high neutralizing antibody titers and EBV-specific T-cell responses in immunized mice. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 19255–19273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanekiyo, M.; Bu, W.; Joyce, M.G.; Meng, G.; Whittle, J.R.; Baxa, U.; Yamamoto, T.; Narpala, S.; Todd, J.-P.; Rao, S.S.; et al. Rational Design of an Epstein-Barr Virus Vaccine Targeting the Receptor-Binding Site. Cell 2015, 162, 1090–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snijder, J.; Ortego, M.S.; Weidle, C.; Stuart, A.B.; Gray, M.D.; McElrath, M.J.; Pancera, M.; Veesler, D.; McGuire, A.T. An Antibody Targeting the Fusion Machinery Neutralizes Dual-Tropic Infection and Defines a Site of Vulnerability on Epstein-Barr Virus. Immunity 2018, 48, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bootz, A.; Karbach, A.; Spindler, J.; Kropff, B.; Reuter, N.; Sticht, H.; Winkler, T.H.; Britt, W.J.; Mach, M. Protective capacity of neutralizing and non-neutralizing antibodies against glycoprotein B of cytomegalovirus. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouts, A.E.; Comps-Agrar, L.; Stengel, K.F.; Ellerman, D.; Schoeffler, A.J.; Warming, S.; Eaton, D.L.; Feierbach, B. Mechanism for neutralizing activity by the anti-CMV gH/gL monoclonal antibody MSL-109. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 8209–8214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, T.M.; Huang, Z.-Y.; Gallagher, J.R.; Lin, Y.; Lou, H.; Whitbeck, J.C.; Wald, A.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J. Patient-Specific Neutralizing Antibody Responses to Herpes Simplex Virus Are Attributed to Epitopes on gD, gB, or Both and Can Be Type Specific. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 9213–9231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Ponce-De-Leon, M.; Jiang, H.; Dubin, G.; Lubinski, J.M.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Cohen, G.H. The gH-gL Complex of Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) Stimulates Neutralizing Antibody and Protects Mice against HSV Type 1 Challenge. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogembo, J.G.; Muraswki, M.R.; McGinnes, L.W.; Parcharidou, A.; Sutiwisesak, R.; Tison, T.; Avendano, J.; Agnani, D.; Finberg, R.W.; Morrison, T.G.; et al. A chimeric EBV gp350/220-based VLP replicates the virion B-cell attachment mechanism and elicits long-lasting neutralizing antibodies in mice. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorley-Lawson, D.A.; Geilinger, K. Monoclonal antibodies against the major glycoprotein (gp350/220) of Epstein-Barr virus neutralize infectivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 5307–5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutsvunguma, L.Z.; Rodriguez, E.; Escalante, G.M.; Muniraju, M.; Williams, J.C.; Warden, C.; Qin, H.; Wang, J.; Wu, X.; Barasa, A.; et al. Identification of multiple potent neutralizing and non-neutralizing antibodies against Epstein-Barr virus gp350 protein with potential for clinical application and as reagents for mapping immunodominant epitopes. Virology 2019, 536, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun-Ichi, M.; Satoshi, T.; Kimi, A.; Fumi, T.; Akira, T.; Kiyoshi, T.; Ken-Ichi, Y. Expression vector system based on the chicken β-actin promoter directs efficient production of interleukin-5. Gene 1989, 79, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.-R.; Li, L.-H.; Park, H.-J.; Park, J.-H.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, M.-K.; Shin, B.A.; Choi, S.-Y. High Cleavage Efficiency of a 2A Peptide Derived from Porcine Teschovirus-1 in Human Cell Lines, Zebrafish and Mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiuppesi, F.; Nguyen, J.; Park, S.; Contreras, H.; Kha, M.; Meng, Z.; Kaltcheva, T.; Iniguez, A.; Martinez, J.; La Rosa, C.; et al. Multiantigenic Modified Vaccinia Virus Ankara Vaccine Vectors To Elicit Potent Humoral and Cellular Immune Reponses against Human Cytomegalovirus in Mice. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01012-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantua, H.D.; McGinnes, L.W.; Peeples, M.E.; Morrison, T. Requirements for the Assembly and Release of Newcastle Disease Virus-Like Particles. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 11062–11073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulama, D.H.; Mutsvunguma, L.Z.; Totonchy, J.; Ye, P.; Foley, J.; Escalante, G.M.; Rodriguez, E.; Nabiee, R.; Muniraju, M.; Wussow, F.; et al. A multivalent Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like particle vaccine capable of eliciting high titers of neutralizing antibodies in immunized rabbits. Vaccine 2019, 37, 4184–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barasa, A.; Ye, P.; Phelps, M.; Ganapathiram, A.; Tison, T.; Ogembo, J.G. BALB/c mice immunized with a combination of virus-like particles incorporating Kaposi sarcomaassociated herpesvirus (KSHV) envelope glycoproteins gpK8.1, gB, and gH/gL induced comparable serum neutralizing antibody activity to UV-inactivated KSHV. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 34481–34497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, O.M.; Wall, J.B.J.; Zheng, M.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Vaseghi, H.R.; Qian, L.; Liu, J. Systematic comparison of 2A peptides for cloning multi-genes in a polycistronic vector. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbiani, D.F.; Bozzacco, L.; Keeffe, J.R.; Khouri, R.; Olsen, P.C.; Gazumyan, A.; Schaefer-Babajew, D.; Ávila-Ríos, S.; Nogueira, L.; Patel, R.; et al. Recurrent Potent Human Neutralizing Antibodies to Zika Virus in Brazil and Mexico. Cell 2017, 169, 597–609.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheru, L.; Wu, Y.; Diouf, A.; Moretz, S.E.; Muratova, O.V.; Song, G.; Fay, M.P.; Miller, L.H.; Long, C.A.; Miura, K. The IC50 of anti-Pfs25 antibody in membrane-feeding assay varies among species. Vaccine 2010, 28, 4423–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiss, R.; Jochum, S.; Wanner, G.; Reisbach, G.; Hammerschmidt, W.; Zeidler, R. A Virus-Like Particle-Based Epstein-Barr Virus Vaccine. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 13105–13113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zyl, D.; Tsai, M.-H.; Shumilov, A.; Schneidt, V.; Poirey, R.; Schlehe, B.; Fluhr, H.; Mautner, J.; Delecluse, H.-J. Immunogenic particles with a broad antigenic spectrum stimulate cytolytic T cells and offer increased protection against EBV infection ex vivo and in mice. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuenmayor, J.; Gòdia, F.; Cervera, L. Production of virus-like particles for vaccines. New Biotechnol. 2017, 39, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domi, A.; Feldmann, F.; Basu, R.; McCurley, N.; Shifflett, K.; Emanuel, J.; Hellerstein, M.S.; Guirakhoo, F.; Orlandi, C.; Flinko, R.; et al. A Single Dose of Modified Vaccinia Ankara expressing Ebola Virus Like Particles Protects Nonhuman Primates from Lethal Ebola Virus Challenge. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázaro-Frías, A.; Gómez-Medina, S.; Sánchez-Sampedro, L.; Ljungberg, K.; Ustav, M.; Liljestrom, P.; Munoz-Fontela, C.; Esteban, M.; García-Arriaza, J. Distinct Immunogenicity and Efficacy of Poxvirus-Based Vaccine Candidates against Ebola Virus Expressing GP and VP40 Proteins. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00363-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweneker, M.; Laimbacher, A.S.; Zimmer, G.; Wagner, S.; Schraner, E.M.; Wolferstätter, M.; Klingenberg, M.; Dirmeier, U.; Steigerwald, R.; Lauterbach, H.; et al. Recombinant Modified Vaccinia Virus Ankara Generating Ebola Virus-Like Particles. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00343-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia, M.D.; O Sow, S.; E Lyke, K.; Haidara, F.C.; Diallo, F.; Doumbia, M.; Traore, A.; Coulibaly, F.; Kodio, M.; Onwuchekwa, U.; et al. Use of ChAd3-EBO-Z Ebola virus vaccine in Malian and US adults, and boosting of Malian adults with MVA-BN-Filo: A phase 1, single-blind, randomised trial, a phase 1b, open-label and double-blind, dose-escalation trial, and a nested, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 16, 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, M.M.; Tapia, M.; Hill, A.V.; Sow, S.O. How the current West African Ebola virus disease epidemic is altering views on the need for vaccines and is galvanizing a global effort to field-test leading candidate vaccines. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 211, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Anywaine, Z.; Whitworth, H.; Kaleebu, P.; PrayGod, G.; Shukarev, G.; Manno, D.; Kapiga, S.; Grosskurth, H.; Kalluvya, S.; Bockstal, V.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of a 2-Dose Heterologous Vaccination Regimen With Ad26.ZEBOV and MVA-BN-Filo Ebola Vaccines: 12-Month Data From a Phase 1 Randomized Clinical Trial in Uganda and Tanzania. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 220, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milligan, I.D.; Gibani, M.M.; Sewell, R.; Clutterbuck, E.A.; Campbell, D.; Plested, E.; Nuthall, E.; Voysey, M.; Silva-Reyes, L.; McElrath, M.J.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of Novel Adenovirus Type 26– and Modified Vaccinia Ankara–Vectored Ebola Vaccines. JAMA 2016, 315, 1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monath, T.P.; Fast, P.E.; Modjarrad, K.; Clarke, D.K.; Martin, B.K.; Fusco, J.; Nichols, R.; Heppner, D.G.; Simon, J.K.; Dubey, S.; et al. rVSVDeltaG-ZEBOV-GP (also designated V920) recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus pseudotyped with Ebola Zaire Glycoprotein: Standardized template with key considerations for a risk/benefit assessment. Vaccine X 2019, 1, 100009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duraiswamy, J.; Bharadwaj, M.; Tellam, J.; Connolly, G.; Cooper, L.; Moss, D.; Thomson, S.; Yotnda, P.; Khanna, R. Induction of therapeutic T-cell responses to subdominant tumor-associated viral oncogene after immunization with replication-incompetent polyepitope adenovirus vaccine. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 1483–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, E.P.; Taylor, G.S.; Jia, H.; Ma, B.; Chan, S.; Ho, R.; Wong, W.-L.; Wilson, S.; Johnson, B.; Edwards, C.; et al. Phase I trial of recombinant modified vaccinia ankara encoding Epstein-Barr viral tumor antigens in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 1676–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.S.; Jia, H.; Harrington, K.; Lee, L.W.; Turner, J.E.; Ladell, K.; Price, D.A.; Tanday, M.; Matthews, J.; Roberts, C.; et al. A recombinant modified vaccinia ankara vaccine encoding Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) target antigens: A phase I trial in UK patients with EBV-positive cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 5009–5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rühl, J.; Citterio, C.; Engelmann, C.; Haigh, T.A.; Dzionek, A.; Dreyer, J.H.; Khanna, R.; Taylor, G.S.; Wilson, J.B.; Leung, C.S.; et al. Heterologous prime-boost vaccination protects against EBV antigen–expressing lymphomas. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 2071–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| 2A Position | Nucleotide Sequence | Amino Acid Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| gp350-gB | GCTACTAACTTCAGCCTGCTGAAGCAGGCTGGAGACGTGGAGGAGAACCCTGGACC | A T N F S L L K Q A G D V E E N P G P |
| gB-g42 | GCCACCAATTTCTCGTTACTTAAACAAGCGGGTGACGTTGAAGAGAATCCGGGACCT | A T N F S L L K Q A G D V E E N P G P |
| g42-gL | GCGACTAACTTCTCATTGTTGAAACAGGCAGGAGATGTCGAAGAGAACCCTGGTCCA | A T N F S L L K Q A G D V E E N P G P |
| gL-gH | GCAACGAATTTCTCCCTTCTAAAGCAAGCCGGTGACGTGGAGGAGAATCCCGGACCC | A T N F S L L K Q A G D V E E N P G P |
| Primer Name | Primer Sequence (5’-3’) |
|---|---|
| Cloning Primers | |
| EBV gH-gL-Fc-His FWD | AAAAAGCGGCCGCGCCACCATGCGTGCTGTTGGTGTATTTC |
| EBV gH-gL-Fc-His REV | AAAAAACTAGTGTGTGCTCTTTCTTCATACAGG |
| Sequencing primers | |
| FC-Hisseqprimer4 | GCTTTAATAAGATCTCTAG |
| FC-Hisseqprimer5 | TGCTGGGCACGGTGGGCATG |
| FC-Hisseqprimer6 | GGGTCTTTTCTGCAGAAGCTTG |
| IC50 *(µg/mL) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-Line | gp350 | UV-EBV | EBV-LPs | mAb 72A1 | mAb 2L10 |
| HEK-293 | 5.67 | 3.11 | 2.85 | 6.25 | nd |
| Raji | 8.97 | 3.42 | 3.71 | 4.81 | nd |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Escalante, G.M.; Foley, J.; Mutsvunguma, L.Z.; Rodriguez, E.; Mulama, D.H.; Muniraju, M.; Ye, P.; Barasa, A.K.; Ogembo, J.G. A Pentavalent Epstein-Barr Virus-Like Particle Vaccine Elicits High Titers of Neutralizing Antibodies against Epstein-Barr Virus Infection in Immunized Rabbits. Vaccines 2020, 8, 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8020169
Escalante GM, Foley J, Mutsvunguma LZ, Rodriguez E, Mulama DH, Muniraju M, Ye P, Barasa AK, Ogembo JG. A Pentavalent Epstein-Barr Virus-Like Particle Vaccine Elicits High Titers of Neutralizing Antibodies against Epstein-Barr Virus Infection in Immunized Rabbits. Vaccines. 2020; 8(2):169. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8020169
Chicago/Turabian StyleEscalante, Gabriela M., Joslyn Foley, Lorraine Z. Mutsvunguma, Esther Rodriguez, David H. Mulama, Murali Muniraju, Peng Ye, Anne K. Barasa, and Javier Gordon Ogembo. 2020. "A Pentavalent Epstein-Barr Virus-Like Particle Vaccine Elicits High Titers of Neutralizing Antibodies against Epstein-Barr Virus Infection in Immunized Rabbits" Vaccines 8, no. 2: 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8020169
APA StyleEscalante, G. M., Foley, J., Mutsvunguma, L. Z., Rodriguez, E., Mulama, D. H., Muniraju, M., Ye, P., Barasa, A. K., & Ogembo, J. G. (2020). A Pentavalent Epstein-Barr Virus-Like Particle Vaccine Elicits High Titers of Neutralizing Antibodies against Epstein-Barr Virus Infection in Immunized Rabbits. Vaccines, 8(2), 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8020169






