Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection: From Silent Threat to Vaccine Horizon
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology of cCMV Infection
3. Diagnostic Evaluation
3.1. Diagnosis of cCMV in Pregnancy
3.1.1. Maternal Primary Infection—MPI
3.1.2. Maternal Non-Primary Infection—MNPI
3.2. Diagnosis of Fetal Infection
3.3. Antenatal Ultrasound Findings
3.4. Prenatal Predictors of cCMV Outcomes
3.5. Diagnosis in the Neonate
4. Pathogenesis
4.1. CMV Infection During Pregnancy
4.2. Immune Response
5. Clinical Status
5.1. Clinical Manifestation Depending on the Timing of Maternal Infection
5.1.1. First Trimester Maternal CMV Infection
5.1.2. Second and Third Trimester Maternal Infection
5.2. Signs That Can Appear Soon After Delivery
5.2.1. Associated Laboratory Abnormalities
5.2.2. Neuroimaging Abnormalities
5.3. Long-Term Complications
5.4. Asymptomatic Infection
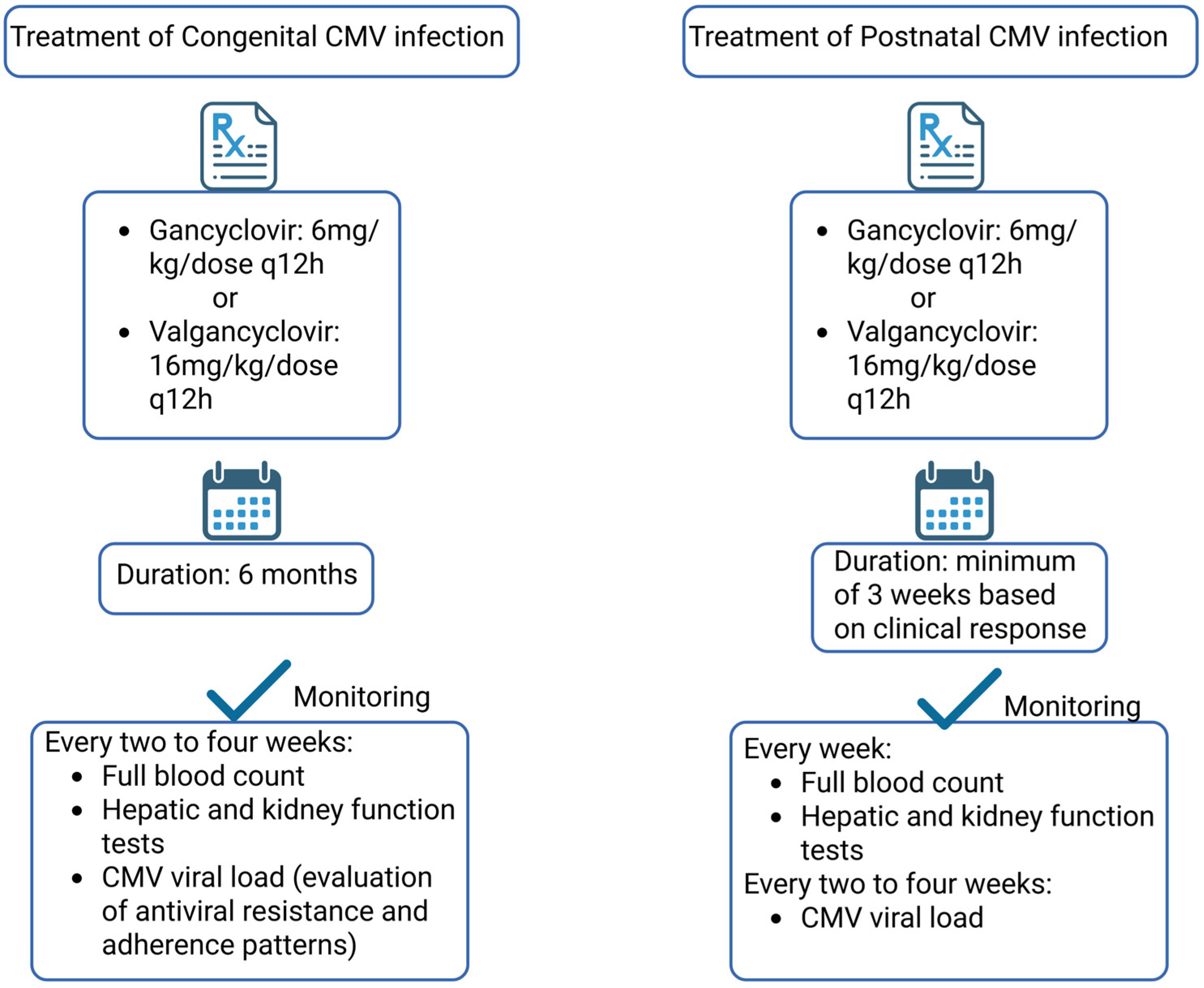
6. Therapeutic Approaches and Clinical Management of Fetuses and Neonates Diagnosed with cCMV
7. Prevention of cCMV Infection According to the Latest Guidelines
7.1. Promotion of Hygiene and Education
7.2. Prenatal Screening and CMV Testing
7.3. CMV-Specific Hyperimmune Globulin (CMV-HIG)
7.4. Antiviral Therapy for Managing cCMV
7.5. Vaccines Against Human CMV Under Development
7.5.1. Categories of Candidate Vaccines
7.5.2. Clinical Efficacy and Safety
7.5.3. Barriers in Development
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baker, M.R.; Wang, X.; Melvin, A.J. Timing of congenital cytomegalovirus diagnosis and missed opportunities. Front. Pediatr. 2025, 13, 1475121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpan, U.S.; Pillarisetty, L.S. Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Salomè, S.; Corrado, F.R.; Mazzarelli, L.L.; Maruotti, G.M.; Capasso, L.; Blazquez-Gamero, D.; Raimondi, F. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection: The state of the art and future perspectives. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1276912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, N.L.; King, C.C.; Kourtis, A.P. Cytomegalovirus infection in pregnancy. Birth Defects Res. 2017, 109, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boppana, S.B.; Hui, L. Cytomegalovirus Infection in Pregnancy. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/cytomegalovirus-infection-in-pregnancy (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Kenneson, A.; Cannon, M.J. Review and meta-analysis of the epidemiology of congenital cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection. Rev. Med. Virol. 2007, 17, 253–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, S.M.; Goshia, T.; Sinha, M.; Fraley, S.I.; Williams, M. Decoding human cytomegalovirus for the development of innovative diagnostics to detect congenital infection. Pediatr. Res. 2024, 95, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leruez-Ville, M.; Foulon, I.; Pass, R.; Ville, Y. Cytomegalovirus infection during pregnancy: State of the science. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 223, 330–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trisko, E.; Gosnell, K.; Douglas, T.; Wu, K. Provider-Led Interventions to Reduce Congenital Cytomegalovirus. J. Midwifery Women’s Health 2025, 70, 576–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Antonio, F.; Marinceu, D.; Prasad, S.; Khalil, A. Effectiveness and safety of prenatal valacyclovir for congenital cytomegalovirus infection: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2023, 61, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokou, R.; Lianou, A.; Lampridou, M.; Panagiotounakou, P.; Kafalidis, G.; Paliatsiou, S.; Volaki, P.; Tsantes, A.G.; Boutsikou, T.; Iliodromiti, Z.; et al. Neonates at Risk: Understanding the Impact of High-Risk Pregnancies on Neonatal Health. Medicina 2025, 61, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ssentongo, P.; Hehnly, C.; Birungi, P.; Roach, M.A.; Spady, J.; Fronterre, C.; Wang, M.; Murray-Kolb, L.E.; Al-Shaar, L.; Chinchilli, V.M.; et al. Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection Burden and Epidemiologic Risk Factors in Countries With Universal Screening: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2120736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, H.; Barnabas, S. Congenital cytomegalovirus in Sub-Saharan Africa-A narrative review with practice recommendations. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1359663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsico, C.; Kimberlin, D.W. Congenital Cytomegalovirus infection: Advances and challenges in diagnosis, prevention and treatment. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2017, 43, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelini, P.; d’Angelo, P.; De Cicco, M.; Achille, C.; Sarasini, A.; Fiorina, L.; Cirasola, D.; Marazzi, V.; Piccini, S.; Furione, M.; et al. Human cytomegalovirus non-primary infection during pregnancy: Antibody response, risk factors and newborn outcome. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 1375–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choodinatha, H.K.; Jeon, M.R.; Choi, B.Y.; Lee, K.N.; Kim, H.J.; Park, J.Y. Cytomegalovirus infection during pregnancy. Obstet. Gynecol. Sci. 2023, 66, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. CMV in Newborns. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/cytomegalovirus/congenital-infection/index.html (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- ACOG. Cytomegalovirus, Parvovirus B19, Varicella Zoster, and Toxoplasmosis in Pregnancy; Reaffirmed 2024; ACOG: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, A.; Heath, P.T.; Jones, C.E.; Soe, A.; Ville, Y.G. Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection: Update on Screening, Diagnosis and Treatment: Scientific Impact Paper No. 56. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2025, 132, e42–e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leruez-Ville, M.; Chatzakis, C.; Lilleri, D.; Blazquez-Gamero, D.; Alarcon, A.; Bourgon, N.; Foulon, I.; Fourgeaud, J.; Gonce, A.; Jones, C.E.; et al. Consensus recommendation for prenatal, neonatal and postnatal management of congenital cytomegalovirus infection from the European congenital infection initiative (ECCI). Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2024, 40, 100892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Świątkowska-Freund, M.; Bednarek, S.; Sasak-Cieślar, N.; Kocięcka, N.; Powroźnik, P.; Waldman, A. Cytomegalovirus Seroprevalence in Northern Poland in the Population Planning Pregnancy and Pregnant Women. Viruses 2025, 17, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, K.P.; Guirado, L.; Cahuana, A.; Marcos, M.A.; Mercadé, I.; Casals Font, E.; Liu, Q.; Medina, C.; López, M.; Gómez-Roig, M.D.; et al. First-Trimester Universal One-Time Serology Screening for Cytomegalovirus: A Pilot Study at Two Tertiary Referral Centers in Barcelona (Catalunya, Spain). Fetal Diagn. Ther. 2025, 52, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, H.E.; Lapé-Nixon, M. Role of cytomegalovirus (CMV) IgG avidity testing in diagnosing primary CMV infection during pregnancy. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2014, 21, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, E.; Zhang, Z.; Thorp, E.B.; Hummel, M. Cytomegalovirus Latency and Reactivation: An Intricate Interplay With the Host Immune Response. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vauloup-Fellous, C.; Berth, M.; Heskia, F.; Dugua, J.M.; Grangeot-Keros, L. Re-evaluation of the VIDAS® cytomegalovirus (CMV) IgG avidity assay: Determination of new cut-off values based on the study of kinetics of CMV-IgG maturation. J. Clin. Virol. 2013, 56, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vauloup-Fellous, C.; Lazzarotto, T.; Revello, M.G.; Grangeot-Keros, L. Clinical evaluation of the Roche Elecsys CMV IgG Avidity assay. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 1365–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasini, A.; Arossa, A.; Zavattoni, M.; Fornara, C.; Lilleri, D.; Spinillo, A.; Baldanti, F.; Furione, M. Pitfalls in the Serological Diagnosis of Primary Human Cytomegalovirus Infection in Pregnancy Due to Different Kinetics of IgM Clearance and IgG Avidity Index Maturation. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorrenti, S.; Elbarbary, N.; D’Antonio, F.; Mascio, D.D.; Khalil, A. Diagnosis and management of congenital Cytomegalovirus: Critical Appraisal of Clinical Practice Guidelines. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2025, 306, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzakis, C.; Sotiriadis, A.; Dinas, K.; Ville, Y. Neonatal and long-term outcomes of infants with congenital cytomegalovirus infection and negative amniocentesis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2023, 61, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontes, K.F.M.; Nardozza, L.M.M.; Peixoto, A.B.; Werner, H.; Tonni, G.; Granese, R.; Araujo Júnior, E. Cytomegalovirus and Pregnancy: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, M.; Daiminger, A.; Exler, S.; Enders, G. Amniocentesis for prenatal diagnosis of cytomegalovirus infection: Challenging the 21 weeks’ threshold. Prenat. Diagn. 2017, 37, 940–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure-Bardon, V.; Fourgeaud, J.; Guilleminot, T.; Magny, J.F.; Salomon, L.J.; Bernard, J.P.; Leruez-Ville, M.; Ville, Y. First-trimester diagnosis of congenital cytomegalovirus infection after maternal primary infection in early pregnancy: Feasibility study of viral genome amplification by PCR on chorionic villi obtained by CVS. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 57, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alberti, E.; Rizzo, G.; Khalil, A.; Mappa, I.; Pietrolucci, M.E.; Capannolo, G.; Alameddine, S.; Sorrenti, S.; Zullo, F.; Giancotti, A.; et al. Counseling in fetal medicine: Congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2024, 295, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajden Haratz, K.; Malinger, G.; Miremberg, H.; Hartoov, J.; Wolman, I.; Jaffa, A.; Busilov, M.; Birnbaum, R. Callosal Injuries in Cytomegalovirus Fetopathy: A Neurosonographic Study. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 2025, 52, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ancora, G.; Lanari, M.; Lazzarotto, T.; Venturi, V.; Tridapalli, E.; Sandri, F.; Menarini, M.; Ferretti, E.; Faldella, G. Cranial ultrasound scanning and prediction of outcome in newborns with congenital cytomegalovirus infection. J. Pediatr. 2007, 150, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Burgos, E.M.; Regojo-Zapata, R.M.; Caballero-Ferrero, Á.; Martínez-Payo, C.; Viñuela-Benéitez, M.D.C.; Montero, D.; De La Calle, M. The Spectrum of Placental Findings of First-Trimester Cytomegalovirus Infection Related to the Presence of Symptoms in the Newborns and Stillbirths. Mod. Pathol. 2025, 38, 100808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, S.T.; Scott, G.; Naing, Z.; Iwasenko, J.; Hall, B.; Graf, N.; Arbuckle, S.; Craig, M.E.; Rawlinson, W.D. Human cytomegalovirus-induces cytokine changes in the placenta with implications for adverse pregnancy outcomes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picone, O.; Teissier, N.; Cordier, A.G.; Vauloup-Fellous, C.; Adle-Biassette, H.; Martinovic, J.; Senat, M.V.; Ayoubi, J.M.; Benachi, A. Detailed in utero ultrasound description of 30 cases of congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Prenat. Diagn. 2014, 34, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Eede, E.; De Keersmaecker, B.; Lagrou, K.; Van der Veeken, L.; Vanwinkel, S.; Vangoitsenhoven, M.; Aertsen, M.; De Catte, L. Prevalence and timing of prenatal ultrasound findings in cytomegalovirus-infected pregnancies. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2025, 104, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartek, V.; Beke, A. Investigation of Pre- and Postnatal Abnormalities Caused by Prenatal CMV Infection—Systematic Review. Children 2025, 12, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faure-Bardon, V.; Millischer, A.E.; Deloison, B.; Sonigo, P.; Grévent, D.; Salomon, L.; Stirnemann, J.; Nicloux, M.; Magny, J.F.; Leruez-Ville, M.; et al. Refining the prognosis of fetuses infected with Cytomegalovirus in the first trimester of pregnancy by serial prenatal assessment: A single-centre retrospective study. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2020, 127, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidenari, A.; Dionisi, C.; Nati, M.; Marsico, C.; Gabrielli, L.; Capretti, M.G.; Toni, F.; Lazzarotto, T.; Simonazzi, G. Follow-Up of Infants With Congenital Cytomegalovirus Following Maternal Primary Infection in the First Trimester and Normal Fetal Brain Imaging at Midgestation. Prenat. Diagn. 2025, 45, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leruez-Ville, M.; Stirnemann, J.; Sellier, Y.; Guilleminot, T.; Dejean, A.; Magny, J.F.; Couderc, S.; Jacquemard, F.; Ville, Y. Feasibility of predicting the outcome of fetal infection with cytomegalovirus at the time of prenatal diagnosis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 215, e341–e349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipitz, S.; Yinon, Y.; Malinger, G.; Yagel, S.; Levit, L.; Hoffman, C.; Rantzer, R.; Weisz, B. Risk of cytomegalovirus-associated sequelae in relation to time of infection and findings on prenatal imaging. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2013, 41, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, B.; Simonazzi, G.; Puccetti, C.; Lanari, M.; Farina, A.; Lazzarotto, T.; Rizzo, N. Ultrasound prediction of symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2008, 198, e381–e387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picone, O.; Vauloup-Fellous, C.; Cordier, A.G.; Guitton, S.; Senat, M.V.; Fuchs, F.; Ayoubi, J.M.; Grangeot Keros, L.; Benachi, A. A series of 238 cytomegalovirus primary infections during pregnancy: Description and outcome. Prenat. Diagn. 2013, 33, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoist, G.; Salomon, L.J.; Jacquemard, F.; Daffos, F.; Ville, Y. The prognostic value of ultrasound abnormalities and biological parameters in blood of fetuses infected with cytomegalovirus. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2008, 115, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanelli, R.M.; Magny, J.F.; Jacquemard, F. Prognostic markers of symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 12, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, E.; Revello, M.G.; Furione, M.; Zavattoni, M.; Lilleri, D.; Tassis, B.; Quarenghi, A.; Rustico, M.; Nicolini, U.; Ferrazzi, E.; et al. Prognostic markers of symptomatic congenital human cytomegalovirus infection in fetal blood. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2011, 118, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buca, D.; Di Mascio, D.; Rizzo, G.; Giancotti, A.; D’Amico, A.; Leombroni, M.; Makatsarya, A.; Familiari, A.; Liberati, M.; Nappi, L.; et al. Outcome of fetuses with congenital cytomegalovirus infection and normal ultrasound at diagnosis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 57, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cradeur, A.; Jackson, A.; Ware, E.; Fourrier, T.L.; Mankekar, G. Congenital Cytomegalovirus (cCMV) Infection as a Leading Cause of Pediatric Hearing Loss: Review. Children 2025, 12, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldon, M.L.; Raveentheran, G.; Amin, Z.; Chan, S.M.; Aoyama, R.; Tee, N.; Ng, S.Y.; Lee, C.K.; Ng, P.G.; Low, J.M. Congenital cytomegalovirus screening in neonates born after 35 weeks gestation—Is targeted screening beneficial? Front. Pediatr. 2025, 13, 1510612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Qian, J.; Zhu, J. Dried blood spots PCR assays to screen congenital cytomegalovirus infection: A meta-analysis. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleiss, M.R.; Blázquez-Gamero, D. Universal newborn screening for congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2025, 9, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, S.A.; Ahmed, A.; Palmer, A.L.; Michaels, M.G.; Sánchez, P.J.; Stewart, A.; Bernstein, D.I.; Feja, K.; Fowler, K.B.; Boppana, S.B. Newborn Dried Blood Spot Polymerase Chain Reaction to Identify Infants with Congenital Cytomegalovirus-Associated Sensorineural Hearing Loss. J. Pediatr. 2017, 184, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Robles, V.; Weimer, K.E.D.; Gehtland, L.M.; Kucera, K.S. Improved Dried Blood Spot PCR Assay for Universal Congenital Cytomegalovirus Screening in Newborns. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0404122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landers, D.; Osterholm, E.; Herd, H.; Huang, T.; Hernandez-Alvarado, N.; Kruc, R.; Graupmann, E.; Schleiss, M. Analysis of Dried Blood Spot and Saliva PCR Screening for Detection of Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection Informs Implementation of a Novel Universal Newborn Screening Program. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2024, 230, S630–S631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilavsky, E.; Watad, S.; Levy, I.; Linder, N.; Pardo, J.; Ben-Zvi, H.; Attias, J.; Amir, J. Positive IgM in Congenital CMV Infection. Clin. Pediatr. 2017, 56, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revello, M.G.; Zavattoni, M.; Baldanti, F.; Sarasini, A.; Paolucci, S.; Gerna, G. Diagnostic and prognostic value of human cytomegalovirus load and IgM antibody in blood of congenitally infected newborns. J. Clin. Virol. 1999, 14, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Qian, Y.; Yu, W.; Guo, G.; Wang, H.; Xue, X. Functional Profile of Human Cytomegalovirus Genes and Their Associated Diseases: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins-McMillen, D.; Buehler, J.; Peppenelli, M.; Goodrum, F. Molecular Determinants and the Regulation of Human Cytomegalovirus Latency and Reactivation. Viruses 2018, 10, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, P.; Baraniak, I.; Reeves, M. The pathogenesis of human cytomegalovirus. J. Pathol. 2015, 235, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emery, V.C.; Hassan-Walker, A.F.; Burroughs, A.K.; Griffiths, P.D. Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) replication dynamics in HCMV-naive and -experienced immunocompromised hosts. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 185, 1723–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, P.; Reeves, M. Pathogenesis of human cytomegalovirus in the immunocompromised host. Nat. Reviews. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 1723–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.; Li, X. Human cytomegalovirus: Pathogenesis, prevention, and treatment. Mol. Biomed. 2024, 5, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, B.L.; Clifton, R.G.; Rouse, D.J.; Saade, G.R.; Dinsmoor, M.J.; Reddy, U.M.; Pass, R.; Allard, D.; Mallett, G.; Fette, L.M.; et al. A Trial of Hyperimmune Globulin to Prevent Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagno, S.; Pass, R.F.; Dworsky, M.E.; Henderson, R.E.; Moore, E.G.; Walton, P.D.; Alford, C.A. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection: The relative importance of primary and recurrent maternal infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 1982, 306, 945–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. Cytomegalovirus (CMV) and Congenital CMV Infection. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/cytomegalovirus/about/index.html (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Kurath, S.; Halwachs-Baumann, G.; Müller, W.; Resch, B. Transmission of cytomegalovirus via breast milk to the prematurely born infant: A systematic review. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2010, 16, 1172–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Hu, W.; Sun, X.; Chen, L.; Luo, X. Transmission of cytomegalovirus via breast milk in low birth weight and premature infants: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pediatr. 2021, 21, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamprecht, K.; Maschmann, J.; Jahn, G.; Poets, C.F.; Goelz, R. Cytomegalovirus transmission to preterm infants during lactation. J. Clin. Virol. 2008, 41, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsgren, M. Cytomegalovirus in Breast Milk: Reassessment of Pasteurization and Freeze-Thawing. Pediatr. Res. 2004, 56, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Winston, D.J.; Razonable, R.R.; Lyon, G.M.; Silveira, F.P.; Wagener, M.M.; Stevens-Ayers, T.; Edmison, B.; Boeckh, M.; Limaye, A.P. Effect of Preemptive Therapy vs Antiviral Prophylaxis on Cytomegalovirus Disease in Seronegative Liver Transplant Recipients With Seropositive Donors: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 323, 1378–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigemura, T.; Yanagisawa, R.; Komori, K.; Morita, D.; Kurata, T.; Tanaka, M.; Sakashita, K.; Nakazawa, Y. Prevention of transfusion-transmitted cytomegalovirus infection using leukoreduced blood components in patients receiving seronegative umbilical cord blood transplantation. Transfusion 2019, 59, 3065–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokou, R.; Gounari, E.A.; Tsantes, A.G.; Piovani, D.; Bonovas, S.; Tsantes, A.E.; Iacovidou, N. Bridging the evidence-to-practice gap: Advancing neonatal blood transfusion. A narrative review of recent guidelines. Blood Rev. 2025, 71, 101282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokou, R.; Gounari, E.A.; Lianou, A.; Tsantes, A.G.; Piovani, D.; Bonovas, S.; Iacovidou, N.; Tsantes, A.E. Rethinking Platelet and Plasma Transfusion Strategies for Neonates: Evidence, Guidelines, and Unanswered Questions. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, M.M.; Dağ, F.; Hengel, H.; Messerle, M.; Kalinke, U.; Čičin-Šain, L. Cytomegalovirus immune evasion of myeloid lineage cells. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 204, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalod, M.; Hamilton, T.; Salomon, R.; Salazar-Mather, T.P.; Henry, S.C.; Hamilton, J.D.; Biron, C.A. Dendritic cell responses to early murine cytomegalovirus infection: Subset functional specialization and differential regulation by interferon alpha/beta. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 885–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prendergast, A.J.; Klenerman, P.; Goulder, P.J.R. The impact of differential antiviral immunity in children and adults. Nat. reviews. Immunol. 2012, 12, 636–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGovern, N.; Shin, A.; Low, G.; Low, D.; Duan, K.; Yao, L.J.; Msallam, R.; Low, I.; Shadan, N.B.; Sumatoh, H.R.; et al. Human fetal dendritic cells promote prenatal T-cell immune suppression through arginase-2. Nature 2017, 546, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mold, J.E.; Michaëlsson, J.; Burt, T.D.; Muench, M.O.; Beckerman, K.P.; Busch, M.P.; Lee, T.-H.; Nixon, D.F.; McCune, J.M. Maternal alloantigens promote the development of tolerogenic fetal regulatory T cells in Utero. Science 2008, 322, 1562–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivarsson, M.A.; Loh, L.; Marquardt, N.; Kekäläinen, E.; Berglin, L.; Björkström, N.K.; Westgren, M.; Nixon, D.F.; Michaëlsson, J. Differentiation and functional regulation of human fetal NK cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3889–3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcoe, J.P.; Lim, J.R.; Schaubert, K.L.; Fodil-Cornu, N.; Matka, M.; McCubbrey, A.L.; Farr, A.R.; Vidal, S.M.; Laouar, Y. TGF-β is responsible for NK cell immaturity during ontogeny and increased susceptibility to infection during mouse infancy. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, Q.; Romagnani, C. About Training and Memory: NK-Cell Adaptation to Viral Infections. Adv. Immunol. 2017, 133, 171–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyola, D.E.; Fortuny, C.; Muntasell, A.; Noguera-Julian, A.; Muñoz-Almagro, C.; Alarcón, A.; Juncosa, T.; Moraru, M.; Vilches, C.; López-Botet, M. Influence of congenital human cytomegalovirus infection and the NKG2C genotype on NK-cell subset distribution in children. Eur. J. Immunol. 2012, 42, 3256–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaynor, L.M.; Colucci, F. Uterine Natural Killer Cells: Functional Distinctions and Influence on Pregnancy in Humans and Mice. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siewiera, J.; El Costa, H.; Tabiasco, J.; Berrebi, A.; Cartron, G.; Bouteiller, P.; Jabrane-Ferrat, N.; Jonjic, S. Human cytomegalovirus infection elicits new decidual natural killer cell effector functions. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harty, J.T.; Badovinac, V.P. Shaping and reshaping CD8+ T-cell memory. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudd, B.D.; Venturi, V.; Smith, N.L.; Nzingha, K.; Goldberg, E.L.; Li, G.; Nikolich-Zugich, J.; Davenport, M.P.; Jameson, S.C. Acute neonatal infections ‘lock-in’ a suboptimal CD8+ T cell repertoire with impaired recall responses. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.L.; Wissink, E.; Wang, J.; Pinello, J.F.; Davenport, M.P.; Grimson, A.; Rudd, B.D. Rapid proliferation and differentiation impairs the development of memory CD8+ T cells in early life. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Lee, H.-H.; Bell, J.; Gregg, R.K.; Ellis, J.S.; Gessner, A.; Zaghouani, H. IL-4 utilizes an alternative receptor to drive apoptosis of Th1 cells and skews neonatal immunity toward Th2. Immunity 2004, 20, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ould, M.A.E.; Luton, D.; Yadini, M.; Pedron, B.; Aujard, Y.; Jacqz-Aigrain, E.; Jacquemard, F.; Sterkers, G. Cellular immune response of fetuses to cytomegalovirus. Pediatr. Res. 2004, 55, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchant, A.; Appay, V.; van der Sande, M.; Dulphy, N.; Liesnard, C.; Kidd, M.; Kaye, S.; Ojuola, O.; Gillespie, G.M.; Cuero, A.L.V.; et al. Mature CD8+ T lymphocyte response to viral infection during fetal life. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermijlen, D.; Brouwer, M.; Donner, C.; Liesnard, C.; Tackoen, M.; Van Rysselberge, M.; Twité, N.; Goldman, M.; Marchant, A.; Willems, F. Human cytomegalovirus elicits fetal gammadelta T cell responses in utero. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 807–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avanzini, M.; Maccario, R.; Belloni, C.; Carrera, G.; Bertaina, A.; Cagliuso, M.; La Rocca, M.; Valsecchi, C.; Mantelli, M.; Castellazzi, A.; et al. B lymphocyte subsets and their functional activity in the early months of life. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2010, 23, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brizić, I.; Hiršl, L.; Britt, W.J.; Krmpotić, A.; Jonjić, S. Immune responses to congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Microbes Infect. 2017, 20, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oczkowski, S.J.; Mazzetti, I.; Cupido, C.; Fox-Robichaud, A.E.; Oczkowski, S.J.; Mazzetti, I.; Cupido, C.; Fox-Robichaud, A.E. The offering of family presence during resuscitation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Intensive Care 2015, 3, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigro, G.; Adler, S.P.; La Torre, R.; Best, A.M. Passive immunization during pregnancy for congenital cytomegalovirus infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1350–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigro, G.; Muselli, M.; on behalf of the Congenital Cytomegalic Disease Collaborating, G. Prevention of Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection: Review and Case Series of Valaciclovir versus Hyperimmune Globulin Therapy. Viruses 2023, 15, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, A.Y.; Mussi-Pinhata, M.M.; Boppana, S.B.; Novak, Z.; Wagatsuma, V.M.; de Frizzo Oliveira, P.; Duarte, G.; Britt, W.J. Human cytomegalovirus reinfection is associated with intrauterine transmission in a highly cytomegalovirus-immune maternal population. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 202, 297-e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Fu, T.M. Progress on human cytomegalovirus vaccines for prevention of congenital infection and disease. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2014, 6, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilleri, D.; Kabanova, A.; Revello, M.G.; Percivalle, E.; Sarasini, A.; Genini, E.; Sallusto, F.; Lanzavecchia, A.; Corti, D.; Gerna, G. Fetal human cytomegalovirus transmission correlates with delayed maternal antibodies to gH/gL/pUL128-130-131 complex during primary infection. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jückstock, J.; Rothenburger, M.; Friese, K.; Traunmüller, F. Passive Immunization against Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection: Current State of Knowledge. Pharmacology 2015, 95, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Morioka, I.; Koda, T.; Nakamachi, Y.; Okazaki, Y.; Noguchi, Y.; Ogi, M.; Chikahira, M.; Tanimura, K.; Ebina, Y.; et al. Low total IgM values and high cytomegalovirus loads in the blood of newborns with symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection. J. Perinat. Med. 2015, 43, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlinson, W.D.; Boppana, S.B.; Fowler, K.B.; Kimberlin, D.W.; Lazzarotto, T.; Alain, S.; Daly, K.; Doutré, S.; Gibson, L.; Giles, M.L.; et al. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection in pregnancy and the neonate: Consensus recommendations for prevention, diagnosis, and therapy. Lancet. Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, e177–e188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaramuzzino, F.; Di Pastena, M.; Chiurchiu, S.; Romani, L.; De Luca, M.; Lucignani, G.; Amodio, D.; Seccia, A.; Marsella, P.; Grimaldi Capitello, T.; et al. Secondary cytomegalovirus infections: How much do we still not know? Comparison of children with symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus born to mothers with primary and secondary infection. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 885926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannattasio, A.; Di Costanzo, P.; De Matteis, A.; Milite, P.; De Martino, D.; Bucci, L.; Augurio, M.R.; Bravaccio, C.; Ferrara, T.; Capasso, L.; et al. Outcomes of congenital cytomegalovirus disease following maternal primary and non-primary infection. J. Clin. Virol. 2017, 96, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, G.; Daiminger, A.; Bäder, U.; Exler, S.; Enders, M. Intrauterine transmission and clinical outcome of 248 pregnancies with primary cytomegalovirus infection in relation to gestational age. J. Clin. Virol. 2011, 52, 244–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatzakis, C.; Ville, Y.; Makrydimas, G.; Dinas, K.; Zavlanos, A.; Sotiriadis, A. Timing of primary maternal cytomegalovirus infection and rates of vertical transmission and fetal consequences. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 223, 870–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipitz, S.; Hoffmann, C.; Feldman, B.; Tepperberg-Dikawa, M.; Schiff, E.; Weisz, B. Value of prenatal ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in assessment of congenital primary cytomegalovirus infection. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 36, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foulon, I.; De Brucker, Y.; Buyl, R.; Lichtert, E.; Verbruggen, K.; Piérard, D.; Camfferman, F.A.; Gucciardo, L.; Gordts, F. Hearing Loss With Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection. Pediatrics 2019, 144, e20183095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njue, A.; Coyne, C.; Margulis, A.V.; Wang, D.; Marks, M.A.; Russell, K.; Das, R.; Sinha, A. The Role of Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection in Adverse Birth Outcomes: A Review of the Potential Mechanisms. Viruses 2020, 13, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demmler-Harrison, G.J. Congenital Cytomegalovirus (cCMV) Infection: Clinical Features and Diagnosis. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/congenital-cytomegalovirus-ccmv-infection-clinical-features-and-diagnosis (accessed on 3 May 2025).
- Al Abdali, K.; Al Wardi, T.; Elfatih, R.; Al Bulushi, Y.; Al Jabri, M. Congenital Cytomegalovirus Pneumonitis Mimicking Childhood Interstitial Lung Disease: A Case Report and Review of Diagnostic Challenges. Cureus 2025, 17, e87869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, M.R.; Haisley, L.D.; Dobyns, W.B.; Schleiss, M.R. Beyond hearing loss: Exploring neurological and neurodevelopmental sequelae in asymptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Pediatr. Res. 2025, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkan Miller, T.; Weisz, B.; Yinon, Y.; Weissbach, T.; De Castro, H.; Avnet, H.; Hoffman, C.; Katorza, E.; Lipitz, S. Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection Following Second and Third Trimester Maternal Infection Is Associated With Mild Childhood Adverse Outcome Not Predicted by Prenatal Imaging. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2021, 10, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boppana, S.B.; Ross, S.A.; Fowler, K.B. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection: Clinical outcome. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57 (Suppl. S4), S178–S181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boppana, S.B.; Pass, R.F.; Britt, W.J.; Stagno, S.; Alford, C.A. Symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection: Neonatal morbidity and mortality. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1992, 11, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreher, A.M.; Arora, N.; Fowler, K.B.; Novak, Z.; Britt, W.J.; Boppana, S.B.; Ross, S.A. Spectrum of disease and outcome in children with symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection. J. Pediatr. 2014, 164, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallach, A.; Albert, M.; Marco-Hernández, A.V.; Boronat, N.; Cernada, M.; Vila, M. Neurological sequelae in patients with congenital cytomegalovirus. An. De Pediatría 2020, 93, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alifieraki, S.; Payne, H.; Hathaway, C.; Tan, R.W.Y.; Lyall, H. Delays in diagnosis and treatment initiation for congenital cytomegalovirus infection–Why we need universal screening. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 988039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moresco, B.L.; Svoboda, M.D.; Ng, Y.T. A Quiet Disease With Loud Manifestations. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2018, 26, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghekiere, S.; Allegaert, K.; Cossey, V.; Van Ranst, M.; Cassiman, C.; Casteels, I. Ophthalmological findings in congenital cytomegalovirus infection: When to screen, when to treat? J. Pediatr. Ophthalmol. Strabismus 2012, 49, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.D.; Demmler-Harrison, G.J.; Coats, D.K.; Paysse, E.A.; Bhatt, A.; Edmond, J.C.; Yen, K.G.; Steinkuller, P.; Miller, J. Long-term Visual and Ocular Sequelae in Patients With Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2017, 36, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besbas, N.; Bayrakci, U.S.; Kale, G.; Cengiz, A.B.; Akcoren, Z.; Akinci, D.; Kilic, I.; Bakkaloglu, A. Cytomegalovirus-related congenital nephrotic syndrome with diffuse mesangial sclerosis. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2006, 21, 740–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mena, W.; Royal, S.; Pass, R.F.; Whitley, R.J.; Philips, J.B., 3rd. Diabetes insipidus associated with symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection. J. Pediatr. 1993, 122, 911–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salisbury, S.; Embil, J.A. Graves disease following congenital cytomegalovirus infection. J. Pediatr. 1978, 92, 954–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luck, S.E.; Wieringa, J.W.; Blázquez-Gamero, D.; Henneke, P.; Schuster, K.; Butler, K.; Capretti, M.G.; Cilleruelo, M.J.; Curtis, N.; Garofoli, F.; et al. Congenital Cytomegalovirus: A European Expert Consensus Statement on Diagnosis and Management. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2017, 36, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vande Walle, C.; Keymeulen, A.; Schiettecatte, E.; Acke, F.; Dhooge, I.; Smets, K.; Herregods, N. Brain MRI findings in newborns with congenital cytomegalovirus infection: Results from a large cohort study. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 8001–8010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capretti, M.G.; Lanari, M.; Tani, G.; Ancora, G.; Sciutti, R.; Marsico, C.; Lazzarotto, T.; Gabrielli, L.; Guerra, B.; Corvaglia, L.; et al. Role of cerebral ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in newborns with congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Brain Dev. 2014, 36, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcon, A.; Martinez-Biarge, M.; Cabañas, F.; Hernanz, A.; Quero, J.; Garcia-Alix, A. Clinical, biochemical, and neuroimaging findings predict long-term neurodevelopmental outcome in symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection. J. Pediatr. 2013, 163, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diogo, M.C.; Glatter, S.; Binder, J.; Kiss, H.; Prayer, D. The MRI spectrum of congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Prenat. Diagn. 2020, 40, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannattasio, A.; Bruzzese, D.; Di Costanzo, P.; Capone, E.; Romano, A.; D’Amico, A.; Bravaccio, C.; Grande, C.; Capasso, L.; Raimondi, F. Neuroimaging Profiles and Neurodevelopmental Outcome in Infants With Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2018, 37, 1028–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Toribe, Y.; Mogami, Y.; Yanagihara, K.; Nishikawa, M. Epilepsy in patients with congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Brain Dev. 2008, 30, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shears, A.; Yan, G.; Mortimer, H.; Cross, E.; Sapuan, S.; Kadambari, S.; Luck, S.; Heath, P.T.; Walter, S.; Fidler, K.J. Vestibular and balance dysfunction in children with congenital CMV: A systematic review. Arch. Dis. Childhood. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2022, 107, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarini, F.; Levivien, S.; Madec, Y.; Taieb, F.; Mottez, E.; Buivan, T.P.; Maudoux, A.; Wiener-Vacher, S.; Nevoux, J.; Van Den Abbeele, T.; et al. Olfactory function in congenital cytomegalovirus infection: A prospective study. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2022, 181, 1859–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goderis, J.; De Leenheer, E.; Smets, K.; Van Hoecke, H.; Keymeulen, A.; Dhooge, I. Hearing loss and congenital CMV infection: A systematic review. Pediatrics 2014, 134, 972–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinninti, S.; Christy, J.; Almutairi, A.; Cochrane, G.; Fowler, K.B.; Boppana, S. Vestibular, Gaze, and Balance Disorders in Asymptomatic Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection. Pediatrics 2021, 147, e20193945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, A.W.; McMullan, B.; Rawlinson, W.D.; Palasanthiran, P. Hearing and neurodevelopmental outcomes for children with asymptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection: A systematic review. Rev. Med. Virol. 2017, 25, e1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee on Infectious Diseases, A.A.P. Cytomegalovirus Infection. In Red Book: 2024–2027 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases; Kimberlin, D.W., Banerjee, R., Barnett, E.D., Lynfield, R., Sawyer, M.H., Eds.; American Academy of Pediatrics: Itasca, IL, USA, 2024; pp. 344–352. [Google Scholar]
- Pesch, M.H.; Kuboushek, K.; McKee, M.M.; Thorne, M.C.; Weinberg, J.B. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection. BMJ 2021, 373, n1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, G.H. Treatment of congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2022, 66, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimberlin, D.W.; Lin, C.-Y.; Sánchez, P.J.; Demmler, G.J.; Dankner, W.; Shelton, M.; Jacobs, R.F.; Vaudry, W.; Pass, R.F.; Kiell, J.M. Effect of ganciclovir therapy on hearing in symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus disease involving the central nervous system: A randomized, controlled trial. J. Pediatr. 2003, 143, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimberlin, D.W.; Jester, P.M.; Sánchez, P.J.; Ahmed, A.; Arav-Boger, R.; Michaels, M.G.; Ashouri, N.; Englund, J.A.; Estrada, B.; Jacobs, R.F. Valganciclovir for symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, E.; Kakkar, F.; Riley, L.E.; Ciaranello, A.L.; Prabhu, M. Evaluation and Management of Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection. Obstet. Gynecol. 2025, 145, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohmer, J.; Lobaina, D.; Faliv, M.; Lotharius, K.; Jhumkhawala, V.; Fridman, S.; Follin, T.; Sacca, L. Assessing the Scope of Evidence-Based Interventions and Policy Mobilization Efforts on CMV Infection Prevention in U.S. Pregnant Women: A Scoping Review. Women 2025, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak-Krzyszkowska, M.; Górecka, J.; Huras, H.; Massalska-Wolska, M.; Staśkiewicz, M.; Gach, A.; Kondracka, A.; Staniczek, J.; Górczewski, W.; Borowski, D.; et al. Cytomegalovirus Infection in Pregnancy Prevention and Treatment Options: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Viruses 2023, 15, 2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Muñoz, M.F.; Martín-Martín, C.; Kovacheva, K.; Olivares, M.E.; Izquierdo, N.; Pérez-Romero, P.; García-Ríos, E. Hygiene-based measures for the prevention of cytomegalovirus infection in pregnant women: A systematic review. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2024, 24, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, S.P.; Finney, J.W.; Manganello, A.M.; Best, A.M. Prevention of child-to-mother transmission of cytomegalovirus among pregnant women. J. Pediatr. 2004, 145, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, M.J.; Davis, K.F. Washing our hands of the congenital cytomegalovirus disease epidemic. BMC Public Health 2005, 5, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, M.J.; Schmid, D.S.; Hyde, T.B. Review of cytomegalovirus seroprevalence and demographic characteristics associated with infection. Rev. Med. Virol. 2010, 20, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanzieri, T.M.; Pesch, M.H.; Grosse, S.D. Considering Antiviral Treatment to Preserve Hearing in Congenital CMV. Pediatrics 2023, 151, e2022059895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vauloup-Fellous, C.; Picone, O.; Cordier, A.G.; Parent-du-Châtelet, I.; Senat, M.V.; Frydman, R.; Grangeot-Keros, L. Does hygiene counseling have an impact on the rate of CMV primary infection during pregnancy? Results of a 3-year prospective study in a French hospital. J. Clin. Virol. 2009, 46 (Suppl. S4), S49–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordier, A.G.; Guitton, S.; Vauloup-Fellous, C.; Grangeot-Keros, L.; Benachi, A.; Picone, O. Awareness and knowledge of congenital cytomegalovirus infection among health care providers in France. J. Clin. Virol. 2012, 55, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revello, M.G.; Tibaldi, C.; Masuelli, G.; Frisina, V.; Sacchi, A.; Furione, M.; Arossa, A.; Spinillo, A.; Klersy, C.; Ceccarelli, M.; et al. Prevention of Primary Cytomegalovirus Infection in Pregnancy. EBioMedicine 2015, 2, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvert, A.; Vandrevala, T.; Parsons, R.; Barber, V.; Book, A.; Book, G.; Carrington, D.; Greening, V.; Griffiths, P.; Hake, D.; et al. Changing knowledge, attitudes and behaviours towards cytomegalovirus in pregnancy through film-based antenatal education: A feasibility randomised controlled trial of a digital educational intervention. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2021, 21, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartnik, P.; Bender, A.; Kacperczyk-Bartnik, J.; Ciebiera, M.; Urban, A.; Sienko, A.; Bilir, E.; Romejko-Wolniewicz, E.; Sieńko, J. Awareness of Pregnant Patients about Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection-A Semi-Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussami, D.; Sartori, P.; Martinez de Tejada, B.; Farin, A.; Rieder, W.; Rouiller, S.; Robyr, R.; Muller Brochut, A.-C.; Grant, G.; Ben Ali, N.; et al. Awareness and knowledge of cytomegalovirus infection among pregnant women in French-speaking Switzerland. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2025, 25, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucoiran, I.; Yudin, M.; Poliquin, V.; Caddy, S.; Gantt, S.; Castillo, E. Guideline No. 420: Cytomegalovirus Infection in Pregnancy. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Can. 2021, 43, 893–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billette de Villemeur, A.; Tattevin, P.; Salmi, L.R. Hygiene promotion might be better than serological screening to deal with Cytomegalovirus infection during pregnancy: A methodological appraisal and decision analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revello, M.G.; Furione, M.; Rognoni, V.; Arossa, A.; Gerna, G. Cytomegalovirus DNAemia in pregnant women. J. Clin. Virol. 2014, 61, 590–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revello, M.G.; Lazzarotto, T.; Guerra, B.; Spinillo, A.; Ferrazzi, E.; Kustermann, A.; Guaschino, S.; Vergani, P.; Todros, T.; Frusca, T.; et al. A randomized trial of hyperimmune globulin to prevent congenital cytomegalovirus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1316–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Qushayri, A.E.; Ghozy, S.; Abbas, A.S.; Dibas, M.; Dahy, A.; Mahmoud, A.R.; Afifi, A.M.; El-Khazragy, N. Hyperimmunoglobulin therapy for the prevention and treatment of congenital cytomegalovirus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2021, 19, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karofylakis, E.; Thomas, K.; Kavatha, D.; Galani, L.; Tsiodras, S.; Giamarellou, H.; Papaevangelou, V.; Antoniadou, A. Cytomegalovirus-Specific Hyperimmune Immunoglobulin Administration for Secondary Prevention after First-Trimester Maternal Primary Infection: A 13-Year Single-Center Cohort Study. Viruses 2024, 16, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirwani-Hartl, N.; Palmrich, P.; Haberl, C.; Perkmann-Nagele, N.; Kiss, H.; Berger, A.; Rittenschober-Böhm, J.; Kasprian, G.; Kienast, P.; Khalil, A.; et al. Biweekly Versus Monthly Hyperimmune Globulin Therapy for Primary Cytomegalovirus Infection in Pregnancy. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagan, K.O.; Enders, M.; Schampera, M.S.; Baeumel, E.; Hoopmann, M.; Geipel, A.; Berg, C.; Goelz, R.; De Catte, L.; Wallwiener, D.; et al. Prevention of maternal-fetal transmission of cytomegalovirus after primary maternal infection in the first trimester by biweekly hyperimmunoglobulin administration. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 53, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, E.; Bowlin, T.; Brooks, J.; Chiang, L.; Hussein, I.; Kimberlin, D.; Kauvar, L.M.; Leavitt, R.; Prichard, M.; Whitley, R. Advances in the Development of Therapeutics for Cytomegalovirus Infections. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221 (Suppl. S1), S32–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahar-Nissan, K.; Pardo, J.; Peled, O.; Krause, I.; Bilavsky, E.; Wiznitzer, A.; Hadar, E.; Amir, J. Valaciclovir to prevent vertical transmission of cytomegalovirus after maternal primary infection during pregnancy: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzakis, C.; Shahar-Nissan, K.; Faure-Bardon, V.; Picone, O.; Hadar, E.; Amir, J.; Egloff, C.; Vivanti, A.; Sotiriadis, A.; Leruez-Ville, M.; et al. The effect of valacyclovir on secondary prevention of congenital cytomegalovirus infection, following primary maternal infection acquired periconceptionally or in the first trimester of pregnancy. An individual patient data meta-analysis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2024, 230, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Périllaud-Dubois, C.; Hachicha-Maalej, N.; Lepers, C.; Letamendia, E.; Teissier, N.; Cousien, A.; Sibiude, J.; Deuffic-Burban, S.; Vauloup-Fellous, C.; Picone, O. Cost-effectiveness of screening and valacyclovir-based treatment strategies for first-trimester cytomegalovirus primary infection in pregnant women in France. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2023, 62, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leruez-Ville, M.; Ghout, I.; Bussières, L.; Stirnemann, J.; Magny, J.F.; Couderc, S.; Salomon, L.J.; Guilleminot, T.; Aegerter, P.; Benoist, G.; et al. In utero treatment of congenital cytomegalovirus infection with valacyclovir in a multicenter, open-label, phase II study. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 215, 462-e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzubay, S.K.; Gagliuso, A.H.; Arora, M.; Doshi, U.; Caughey, A.B. Universal screening and valacyclovir for first trimester primary cytomegalovirus: A cost-effectiveness analysis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2025, 233, e1–e191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotkin, S.A.; Boppana, S.B. Vaccination against the human cytomegalovirus. Vaccine 2019, 37, 7437–7442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, D.I.; Munoz, F.M.; Callahan, S.T.; Rupp, R.; Wootton, S.H.; Edwards, K.M.; Turley, C.B.; Stanberry, L.R.; Patel, S.M.; McNeal, M.M.; et al. Safety and efficacy of a cytomegalovirus glycoprotein B (gB) vaccine in adolescent girls: A randomized clinical trial. Vaccine 2016, 34, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, P.D.; McLean, A.; Emery, V.C. Encouraging prospects for immunisation against primary cytomegalovirus infection. Vaccine 2001, 19, 1356–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lankina, A.; Raposo, M.; Hargreaves, A.; Atkinson, C.; Griffiths, P.; Reeves, M.B. Developing a Vaccine Against Human Cytomegalovirus: Identifying and Targeting HCMV’s Immunological Achilles’ Heel. Vaccines 2025, 13, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britt, W.J. Human Cytomegalovirus Infection in Women With Preexisting Immunity: Sources of Infection and Mechanisms of Infection in the Presence of Antiviral Immunity. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221 (Suppl. S1), S1–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, P.D. CMV vaccine trial endpoints. J. Clin. Virol. 2009, 46 (Suppl. S4), S64–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Cao, Z.; Wang, S.; Lee, R.B.; Wang, X.; Murata, H.; Adler, S.P.; McVoy, M.A.; Snapper, C.M. Novel trimeric human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein B elicits a high-titer neutralizing antibody response. Vaccine 2018, 36, 5580–5590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, C.S.; Baraniak, I.; Lilleri, D.; Reeves, M.B.; Griffiths, P.D.; Permar, S.R. Immune Correlates of Protection Against Human Cytomegalovirus Acquisition, Replication, and Disease. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221 (Suppl. S1), S45–S59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Permar, S.R.; Schleiss, M.R.; Plotkin, S.A. A vaccine against cytomegalovirus: How close are we? J. Clin. Investig. 2025, 135, e182317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.Y.; McGregor, A. A Fully Protective Congenital CMV Vaccine Requires Neutralizing Antibodies to Viral Pentamer and gB Glycoprotein Complexes but a pp65 T-Cell Response Is Not Necessary. Viruses 2021, 13, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bialas, K.M.; Permar, S.R. The March towards a Vaccine for Congenital CMV: Rationale and Models. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rieder, F.; Steininger, C. Cytomegalovirus vaccine: Phase II clinical trial results. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20 (Suppl. S5), S95–S102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pass, R.F.; Zhang, C.; Evans, A.; Simpson, T.; Andrews, W.; Huang, M.-L.; Corey, L.; Hill, J.; Davis, E.; Flanigan, C.; et al. Vaccine Prevention of Maternal Cytomegalovirus Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, A.C.; Baraniak, I.A.; Lankina, A.; Moulder, Z.; Holenya, P.; Atkinson, C.; Tang, G.; Mahungu, T.; Kern, F.; Griffiths, P.D.; et al. The cytomegalovirus gB/MF59 vaccine candidate induces antibodies against an antigenic domain controlling cell-to-cell spread. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenks, J.A.; Nelson, C.S.; Roark, H.K.; Goodwin, M.L.; Pass, R.F.; Bernstein, D.I.; Walter, E.B.; Edwards, K.M.; Wang, D.; Fu, T.M.; et al. Antibody binding to native cytomegalovirus glycoprotein B predicts efficacy of the gB/MF59 vaccine in humans. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eabb3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baraniak, I.; Gomes, A.C.; Sodi, I.; Langstone, T.; Rothwell, E.; Atkinson, C.; Pichon, S.; Piras-Douce, F.; Griffiths, P.D.; Reeves, M.B. Seronegative patients vaccinated with cytomegalovirus gB-MF59 vaccine have evidence of neutralising antibody responses against gB early post-transplantation. EBioMedicine 2019, 50, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akingbola, A.; Adegbesan, A.; Adewole, O.; Adegoke, K.; Benson, A.E.; Jombo, P.A.; Uchechukwu Eboson, S.; Oluwasola, V.; Aiyenuro, A. The mRNA-1647 vaccine: A promising step toward the prevention of cytomegalovirus infection (CMV). Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2025, 21, 2450045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierro, C.; Brune, D.; Shaw, M.; Schwartz, H.; Knightly, C.; Lin, J.; Carfi, A.; Natenshon, A.; Kalidindi, S.; Reuter, C.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of a Messenger RNA-Based Cytomegalovirus Vaccine in Healthy Adults: Results From a Phase 1 Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Infect. Dis. 2024, 230, e668–e678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiavarini, M.; Genga, A.; Ricciotti, G.M.; D’Errico, M.M.; Barbadoro, P. Safety, Immunogenicity, and Efficacy of Cytomegalovirus Vaccines: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Vaccines 2025, 13, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, A.; La Rosa, C.; Curtsinger, J.; Cao, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Lingaraju, C.R.; Weisdorf, D.J.; Cichocki, F.; Miller, J.S.; Diamond, D.J. CMV Triplex Vaccine to Enhance Adaptive NK and T-cell Reconstitution After Autologous Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2022, 28, 343.e1–343.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldoss, I.; La Rosa, C.; Baden, L.R.; Longmate, J.; Ariza-Heredia, E.J.; Rida, W.N.; Lingaraju, C.R.; Zhou, Q.; Martinez, J.; Kaltcheva, T. Poxvirus vectored cytomegalovirus vaccine to prevent cytomegalovirus viremia in transplant recipients: A phase 2, randomized clinical trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 172, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- City of Hope Medical Center. Triplex Vaccine in Preventing CMV Infection in Patients Undergoing Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04060277 (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Das, R.; Blázquez-Gamero, D.; Bernstein, D.I.; Gantt, S.; Bautista, O.; Beck, K.; Conlon, A.; Rosenbloom, D.I.S.; Wang, D.; Ritter, M.; et al. Safety, efficacy, and immunogenicity of a replication-defective human cytomegalovirus vaccine, V160, in cytomegalovirus-seronegative women: A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2b trial. Lancet. Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 1383–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, S.P.; Lewis, N.; Conlon, A.; Christiansen, M.P.; Al-Ibrahim, M.; Rupp, R.; Fu, T.M.; Bautista, O.; Tang, H.; Wang, D.; et al. Phase 1 Clinical Trial of a Conditionally Replication-Defective Human Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Vaccine in CMV-Seronegative Subjects. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 220, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, S.; Oshima, N.; Iwasa, T.; Fukao, Y.; Sawata, M. Safety, Tolerability, and Immunogenicity of V160, a Conditionally Replication-Defective Cytomegalovirus Vaccine, in Healthy Japanese Men in a Randomized, Controlled Phase 1 Study. Antibodies 2023, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwendinger, M.; Thiry, G.; De Vos, B.; Leroux-Roels, G.; Bruhwyler, J.; Huygens, A.; Ganeff, C.; Buchinger, H.; Orlinger, K.K.; Pinschewer, D.D.; et al. A Randomized Dose-Escalating Phase I Trial of a Replication-Deficient Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus Vector-Based Vaccine Against Human Cytomegalovirus. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 225, 1399–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hookipa Biotech GmbH. A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2 Study of HB-101, a Bivalent Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Vaccine, in CMV-Seronegative Recipient (R−) Patients Awaiting Kidney Transplantation From Living CMV-Seropositive Donors (D+); Hookipa Biotech GmbH: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, L.; Dunham, K.; Stamer, M.; Mulieri, K.M.; Lucas, K.G. Expansion of cytomegalovirus pp65 and IE-1 specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes for cytomegalovirus-specific immunotherapy following allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2008, 14, 1156–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perotti, M.; Marcandalli, J.; Demurtas, D.; Sallusto, F.; Perez, L. Rationally designed Human Cytomegalovirus gB nanoparticle vaccine with improved immunogenicity. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1009169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abusalah, M.A.H.; Chopra, H.; Sharma, A.; Mustafa, S.A.; Choudhary, O.P.; Sharma, M.; Dhawan, M.; Khosla, R.; Loshali, A.; Sundriyal, A.; et al. Nanovaccines: A game changing approach in the fight against infectious diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 167, 115597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxmi, B.; Devi, P.U.M.; Naveen, T.; Buddolla, V. Virus-like particles: Innovative strategies for combatting emerging and re-emerging viral threats. Microbe 2025, 7, 100351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langley, J.M.; Gantt, S.; Halperin, S.A.; Ward, B.; McNeil, S.; Ye, L.; Cai, Y.; Smith, B.; Anderson, D.E.; Mitoma, F.D. An enveloped virus-like particle alum-adjuvanted cytomegalovirus vaccine is safe and immunogenic: A first-in-humans Canadian Immunization Research Network (CIRN) study. Vaccine 2024, 42, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gantt, S.; Quach, C.; Anderson, D.E.; Diaz-Mitoma, F.; Langley, J. LB18. An Enveloped Virus-like Particle (eVLP) Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Vaccine Is Immunogenic and Safe: Results of a First-in-Humans Study. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2018, 5 (Suppl. S1), S765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, M.; Fadaee Dowlat, B.; Yaghmayee, S.; Habibian, A.; Keshavarzi, S.; Oksenych, V.; Naderian, R. Next-Generation Vaccine Platforms: Integrating Synthetic Biology, Nanotechnology, and Systems Immunology for Improved Immunogenicity. Vaccines 2025, 13, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, P.R.; Roberts, J. Scientific and Regulatory Considerations for Efficacy Studies of Cytomegalovirus Vaccines. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221, S103–S108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotkin, S.A. Can We Prevent Congenital Infection by Cytomegalovirus? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 76, 1705–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotkin, S.A. Preventing Infection by Human Cytomegalovirus. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221 (Suppl. S1), S123–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schleiss, M.R.; Permar, S.R.; Plotkin, S.A. Progress toward Development of a Vaccine against Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2017, 24, e00268-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maidji, E.; McDonagh, S.; Genbacev, O.; Tabata, T.; Pereira, L. Maternal Antibodies Enhance or Prevent Cytomegalovirus Infection in the Placenta by Neonatal Fc Receptor-Mediated Transcytosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 168, 1210–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Permar, S.R.; Kaur, A.; Fruh, K. Derisking Human Cytomegalovirus Vaccine Clinical Development in Relevant Preclinical Models. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 226, 563–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schleiss, M.R.; Fernández-Alarcón, C.; Bierle, C.J.; Geballe, A.P.; Badillo-Guzman, A.; Tanna, C.E.; Tsriwong, K.; Blackstad, M.; Wang, J.B.; McVoy, M.A. Replication-deficient whole-virus vaccines against cytomegalovirus induce protective immunity in a guinea pig congenital infection model. J. Virol. 2025, 99, e00207-25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, C.; Früh, K. Rhesus CMV: An emerging animal model for human CMV. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2008, 197, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.; Otero, C.E.; Li, K.; Valencia, S.M.; Nelson, A.N.; Permar, S.R. Vaccines for Perinatal and Congenital Infections—How Close Are We? Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bialas, K.M.; Tanaka, T.; Tran, D.; Varner, V.; Rosa, E.C.D.L.; Chiuppesi, F.; Wussow, F.; Kattenhorn, L.; Macri, S.; Kunz, E.L.; et al. Maternal CD4+ T cells protect against severe congenital cytomegalovirus disease in a novel nonhuman primate model of placental cytomegalovirus transmission. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 13645–13650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, D.S.; Chong, G.L.M.; Chemaly, R.F.; Cremer, O.L. Comparative clinical manifestations and immune effects of cytomegalovirus infections following distinct types of immunosuppression. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpini, S.; Morigi, F.; Betti, L.; Dondi, A.; Biagi, C.; Lanari, M.; Scarpini, S.; Morigi, F.; Betti, L.; Dondi, A.; et al. Development of a Vaccine against Human Cytomegalovirus: Advances, Barriers, and Implications for the Clinical Practice. Vaccines 2021, 9, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, S.; Chiopris, G.; Messina, G.; D’Alvano, T.; Perrone, S.; Principi, N. Prevention of Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection with Vaccines: State of the Art. Vaccines 2021, 9, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. Vaccines and Preventable Diseases. Administering HPV Vaccine. Dosage and Schedule. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/vpd/hpv/hcp/administration.html#:~:text=HPV%20vaccines%20are%20administered%20as,years%2C%20and%20for%20immunocompromised%20persons (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Ge, Y.W.; Yin, M.Z.; Shu, J.T.; Wu, Y.J.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, Y.H.; Qin, G. Health and economic evaluation of cytomegalovirus vaccination strategy among young women in China: A modelling study. BMJ Public Health 2025, 3, e002522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Vaccine Platform | Key Candidates | Trial Phase | Key Findings | Pregnancy-Specific Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| gB-Based Subunit Vaccines | gB/MF59 [184] | Phase II (completed) | ~50% efficacy in seronegative women; antibody responses to native gB important; limited cell-to-cell spread neutralization | No approval for use in pregnancy; limited safety data available |
| mRNA Vaccines | mRNA-1647 [167] | Phase III (ongoing) | Encodes full-length gB + pentamer complex; strong neutralizing Ab qne T-cell responses; long-lasting immunity | Phase III includes women of childbearing age; results expected by 2026. Not currently approved for pregnant women |
| Viral Vectored Vaccines | Triplex (MVA) [197], V160 [195], HB-101 [198,199] | Phase I–II | Strong T-cell responses (esp. pp65, IE1); V160 showed ~42% efficacy; well tolerated | Mostly studied in transplant recipients; not yet approved or sufficiently tested in pregnant populations |
| Virus-Like Particle (VLP) Vaccines | eVLP-gB + alum [204] | Phase I (first-in-human) | Well tolerated, potent antibody titers including AD-2 response; 100% neutralization in fibroblasts at high dose | Suggested for maternal immunization, but no current pregnancy-specific trials or approval |
| Next-Gen/Computational Platforms | Multivalent VLPs, epitope-optimized constructs [206] | Preclinical | Designed to enhance breadth/durability; TLR ligand integration; scalable and stable | Preclinical only; not yet tested in humans, including pregnant women |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moutsopoulou, R.A.; Markou, A.; Lianou, A.; Leontari, K.; Iliodromiti, Z.; Boutsikou, T.; Kafalidis, G.; Paliatsiou, S.; Volaki, P.; Iacovidou, N.; et al. Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection: From Silent Threat to Vaccine Horizon. Vaccines 2025, 13, 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13090929
Moutsopoulou RA, Markou A, Lianou A, Leontari K, Iliodromiti Z, Boutsikou T, Kafalidis G, Paliatsiou S, Volaki P, Iacovidou N, et al. Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection: From Silent Threat to Vaccine Horizon. Vaccines. 2025; 13(9):929. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13090929
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoutsopoulou, Rafaela Anna, Aikaterini Markou, Alexandra Lianou, Konstantina Leontari, Zoi Iliodromiti, Theodora Boutsikou, Georgios Kafalidis, Styliani Paliatsiou, Paraskevi Volaki, Nicoletta Iacovidou, and et al. 2025. "Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection: From Silent Threat to Vaccine Horizon" Vaccines 13, no. 9: 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13090929
APA StyleMoutsopoulou, R. A., Markou, A., Lianou, A., Leontari, K., Iliodromiti, Z., Boutsikou, T., Kafalidis, G., Paliatsiou, S., Volaki, P., Iacovidou, N., Tsantes, A. G., & Sokou, R. (2025). Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection: From Silent Threat to Vaccine Horizon. Vaccines, 13(9), 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13090929










