Broadly Neutralizing Antibody Characteristics in Hepatitis C Virus Infection and Implications for Vaccine Design
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Evidence for HCV Vaccine Feasibility
3. Immune Correlates of Protection
4. Targets of bNAb in HCV
4.1. The Variable Regions of E2
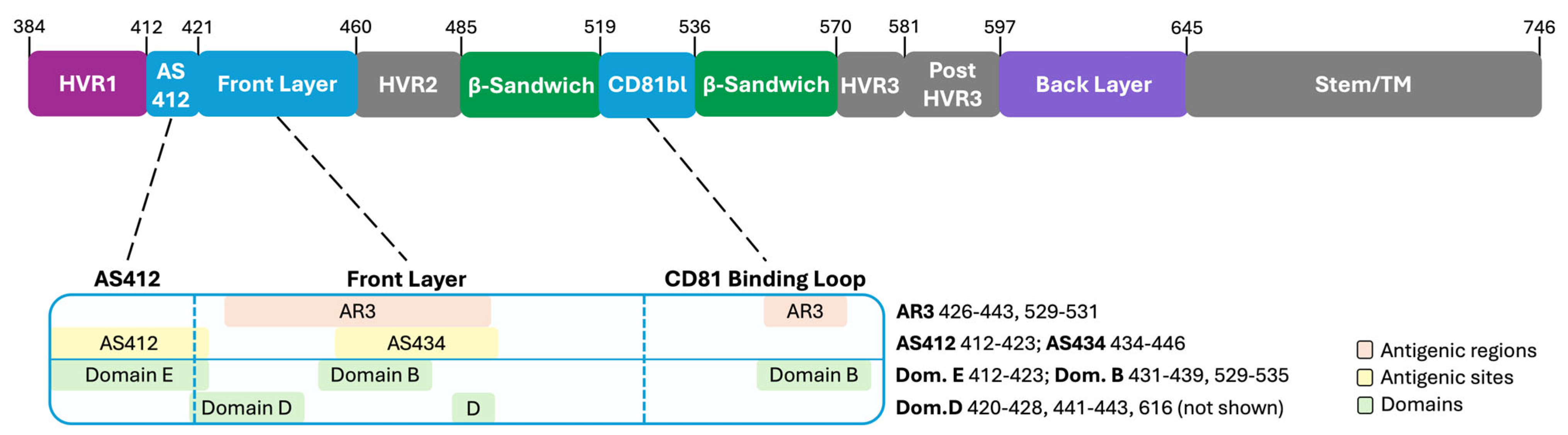
4.2. The Neutralizing Face of E2
4.3. The β-Sandwich and the Back Layer of E2
4.4. E1 and the E1E2 Complex
5. Common Features of HCV-Specific bNAb
6. Immune Escape
7. HCV Vaccine Efforts
8. Challenges and Future Directions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Purcell, R. The hepatitis C virus: Overview. Hepatology 1997, 26, 11S–14S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lingala, S.; Ghany, M.G. Natural history of hepatitis C. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 44, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manns, M.P.; Buti, M.; Gane, E.; Pawlotsky, J.-M.; Razavi, H.; Terrault, N.; Younossi, Z. Hepatitis C virus infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aisyah, D.N.; Shallcross, L.; Hully, A.J.; O’Brien, A.; Hayward, A. Assessing hepatitis C spontaneous clearance and understanding associated factors—A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Viral Hepat. 2018, 25, 680–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebely, J.; Page, K.; Sacks-Davis, R.; van der Loeff, M.S.; Rice, T.M.; Bruneau, J.; Morris, M.D.; Hajarizadeh, B.; Amin, J.; Cox, A.L. The effects of female sex, viral genotype, and IL28B genotype on spontaneous clearance of acute hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 2014, 59, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modaresi Esfeh, J.; Ansari-Gilani, K. Steatosis and hepatitis C. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2016, 4, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stroffolini, T.; Stroffolini, G. Prevalence and modes of transmission of hepatitis C virus infection: A historical worldwide review. Viruses 2024, 16, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degenhardt, L.; Peacock, A.; Colledge, S.; Leung, J.; Grebely, J.; Vickerman, P.; Stone, J.; Cunningham, E.B.; Trickey, A.; Dumchev, K. Global prevalence of injecting drug use and sociodemographic characteristics and prevalence of HIV, HBV, and HCV in people who inject drugs: A multistage systematic review. Lancet Glob. Health 2017, 5, e1192–e1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibbell, J.E.; Asher, A.K.; Patel, R.C.; Kupronis, B.; Iqbal, K.; Ward, J.W.; Holtzman, D. Increases in acute hepatitis C virus infection related to a growing opioid epidemic and associated injection drug use, United States, 2004 to 2014. Am. J. Public Health 2018, 108, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-H.; Johnson, L.; Limketkai, B.N.; Jusuf, E.; Sun, J.; Kim, B.; Price, J.C.; Woreta, T.A. Trends in the prevalence of hepatitis C infection during pregnancy and maternal-infant outcomes in the US, 1998 to 2018. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2324770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mast, E.E.; Hwang, L.-Y.; Seto, D.S.; Nolte, F.S.; Nainan, O.V.; Wurtzel, H.; Alter, M.J. Risk factors for perinatal transmission of hepatitis C virus (HCV) and the natural history of HCV infection acquired in infancy. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 192, 1880–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resti, M.; Azzari, C.; Mannelli, F.; Moriondo, M.; Novembre, E.; de Martino, M.; Vierucci, A. Mother to child transmission of hepatitis C virus: Prospective study of risk factors and timing of infection in children born to women seronegative for HIV-1. BMJ 1998, 317, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, S.A.; Sulkowski, M.S. Chronic hepatitis C: Advances in Therapy and the remaining challenges. Med. Clin. 2023, 107, 423–433. [Google Scholar]
- Martinello, M.; Solomon, S.S.; Terrault, N.A.; Dore, G.J. Hepatitis C. Lancet 2023, 402, 1085–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, M.J.; Gotham, D.; Khwairakpam, G.; Hill, A. Price of a hepatitis C cure: Cost of production and current prices for direct-acting antivirals in 50 countries. J. Virus Erad. 2020, 6, 100001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.s.; Yang, J.D.; El-Serag, H.B.; Kanwal, F. Awareness of chronic viral hepatitis in the United States: An update from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J. Viral Hepat. 2019, 26, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrault, N.A. Hepatitis C elimination: Challenges with under-diagnosis and under-treatment. F1000Research 2019, 8, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blach, S.; Terrault, N.A.; Tacke, F.; Gamkrelidze, I.; Craxi, A.; Tanaka, J.; Waked, I.; Dore, G.J.; Abbas, Z.; Abdallah, A.R. Global change in hepatitis C virus prevalence and cascade of care between 2015 and 2020: A modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 396–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, E.W.; Bradley, H.; Barker, L.K.; Lewis, K.; Shealey, J.; Valverde, E.; Sullivan, P.; Gupta, N.; Hofmeister, M.G. Estimating hepatitis C prevalence in the United States, 2017–2020. Hepatology 2024, 81, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Progress Report on HIV, Viral Hepatitis, and Sexually Transmitted Infections; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Razavi, H.; Sanchez Gonzalez, Y.; Yuen, C.; Cornberg, M. Global timing of hepatitis C virus elimination in high-income countries. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinello, M.; Grebely, J.; Petoumenos, K.; Gane, E.; Hellard, M.; Shaw, D.; Sasadeusz, J.; Applegate, T.L.; Dore, G.J.; Matthews, G.V. HCV reinfection incidence among individuals treated for recent infection. J. Viral Hepat. 2017, 24, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midgard, H.; Bjøro, B.; Mæland, A.; Konopski, Z.; Kileng, H.; Damås, J.K.; Paulsen, J.; Heggelund, L.; Sandvei, P.K.; Ringstad, J.O. Hepatitis C reinfection after sustained virological response. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valencia, J.; Alvaro-Meca, A.; Troya, J.; Cuevas, G.; Gutiérrez, J.; Morro, A.; Alvarez, J.; Pulido, L.; Cañamares, I.; Escobar, I. High rates of early HCV reinfection after DAA treatment in people with recent drug use attended at mobile harm reduction units. Int. J. Drug Policy 2019, 72, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, A.M.; Nath, S.; Simmons, B. The road to elimination of hepatitis C: Analysis of cures versus new infections in 91 countries. J. Virus Erad. 2017, 3, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesudian, A.B.; Gambarin-Gelwan, M.; Jacobson, I.M. Advances in the treatment of hepatitis C virus infection. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 8, 91. [Google Scholar]
- Osburn, W.O.; Fisher, B.E.; Dowd, K.A.; Urban, G.; Liu, L.; Ray, S.C.; Thomas, D.L.; Cox, A.L. Spontaneous control of primary hepatitis C virus infection and immunity against persistent reinfection. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frumento, N.; Figueroa, A.; Wang, T.; Zahid, M.N.; Wang, S.; Massaccesi, G.; Stavrakis, G.; Crowe, J.E., Jr.; Flyak, A.I.; Ji, H.; et al. Repeated exposure to heterologous hepatitis C viruses associates with enhanced neutralizing antibody breadth and potency. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e160058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinchen, V.J.; Cox, A.L.; Bailey, J.R. Can broadly neutralizing monoclonal antibodies lead to a hepatitis C virus vaccine? Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.; Honegger, J.R.; Walker, C. T-cell immunity against the hepatitis C virus: A persistent research priority in an era of highly effective therapy. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2021, 11, a036954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimme, R. T cell immunity to hepatitis C virus: Lessons for a prophylactic vaccine. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hakeem, M.S.; Bédard, N.; Murphy, D.; Bruneau, J.; Shoukry, N.H. Signatures of protective memory immune responses during hepatitis C virus reinfection. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 870–881.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimbeni, M.; Mizukoshi, E.; Bosmann, M.; Major, M.E.; Mihalik, K.; Rice, C.M.; Feinstone, S.M.; Rehermann, B. Kinetics of CD4+ and CD8+ memory T-cell responses during hepatitis C virus rechallenge of previously recovered chimpanzees. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 4781–4793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaki, A.; Wiese, M.; Maertens, G.; Depla, E.; Seifert, U.; Liebetrau, A.; Miller, J.L.; Manns, M.P.; Rehermann, B. Cellular immune responses persist and humoral responses decrease two decades after recovery from a single-source outbreak of hepatitis C. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoletti, A.; Ferrari, C. Kinetics of the immune response during HBV and HCV infection. Hepatology 2003, 38, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Sällberg, M.; Sönnerborg, A.; Weiland, O.; Mattsson, L.; Jin, L.; Birkett, A.; Peterson, D.; Milich, D.R. Limited humoral immunity in hepatitis C virus infection. Gastroenterology 1999, 116, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, J.; Healey, C.; Watson, J.; Wong, V.; Duddridge, M.; Snowden, N.; Rosenberg, W.; Fleming, K.; Chapel, H.; Chapman, R. Clinical outcome of hypogammaglobulinaemic patients following outbreak of acute hepatitis C: 2 year follow up. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1997, 110, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razvi, S.; Schneider, L.; Jonas, M.M.; Cunningham-Rundles, C. Outcome of intravenous immunoglobulin-transmitted hepatitis C virus infection in primary immunodeficiency. Clin. Immunol. 2001, 101, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavillette, D.; Morice, Y.; Germanidis, G.; Donot, P.; Soulier, A.; Pagkalos, E.; Sakellariou, G.; Intrator, L.; Bartosch, B.; Pawlotsky, J.-M. Human serum facilitates hepatitis C virus infection, and neutralizing responses inversely correlate with viral replication kinetics at the acute phase of hepatitis C virus infection. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 6023–6034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestka, J.M.; Zeisel, M.B.; Bläser, E.; Schürmann, P.; Bartosch, B.; Cosset, F.-L.; Patel, A.H.; Meisel, H.; Baumert, J.; Viazov, S. Rapid induction of virus-neutralizing antibodies and viral clearance in a single-source outbreak of hepatitis C. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 6025–6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feray, C.; Gigou, M.; Samuel, D.; Ducot, B.; Maisonneuve, P.; Reynes, M.; Bismuth, A.; Bismuth, H. Incidence of hepatitis C in patients receiving different preparations of hepatitis B immunoglobulins after liver transplantation. Ann. Intern. Med. 1998, 128, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knodell, R.; Ginsberg, A.; Conrad, M.; Bell, C.; Flannery, E.P. Efficacy of prophylactic gamma-globulin in preventing non-A, non-B post-transfusion hepatitis. Lancet 1976, 307, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazza, M.; Sagliocca, L.; Tosone, G.; Guadagnino, V.; Stazi, M.A.; Orlando, R.; Borgia, G.; Rosa, D.; Abrignani, S.; Palumbo, F. Sexual transmission of the hepatitis C virus and efficacy of prophylaxis with intramuscular immune serum globulin: A randomized controlled trial. Arch. Intern. Med. 1997, 157, 1537–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, Y.P.; Dorner, M.; Mommersteeg, M.C.; Xiao, J.W.; Balazs, A.B.; Robbins, J.B.; Winer, B.Y.; Gerges, S.; Vega, K.; Labitt, R.N. Broadly neutralizing antibodies abrogate established hepatitis C virus infection. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 254ra129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giang, E.; Dorner, M.; Prentoe, J.C.; Dreux, M.; Evans, M.J.; Bukh, J.; Rice, C.M.; Ploss, A.; Burton, D.R.; Law, M. Human broadly neutralizing antibodies to the envelope glycoprotein complex of hepatitis C virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 6205–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keck, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.; Lau, P.; Lund, G.; Rangarajan, S.; Fauvelle, C.; Liao, G.C.; Holtsberg, F.W.; Warfield, K.L.; Aman, M.J. Affinity maturation of a broadly neutralizing human monoclonal antibody that prevents acute hepatitis C virus infection in mice. Hepatology 2016, 64, 1922–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, M.; Maruyama, T.; Lewis, J.; Giang, E.; Tarr, A.W.; Stamataki, Z.; Gastaminza, P.; Chisari, F.V.; Jones, I.M.; Fox, R.I. Broadly neutralizing antibodies protect against hepatitis C virus quasispecies challenge. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, T.J.; Broering, T.J.; Leav, B.A.; Blair, B.M.; Rowley, K.J.; Boucher, E.N.; Wang, Y.; Cheslock, P.S.; Knauber, M.; Olsen, D.B. Human monoclonal antibody HCV1 effectively prevents and treats HCV infection in chimpanzees. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowd, K.A.; Netski, D.M.; Wang, X.H.; Cox, A.L.; Ray, S.C. Selection pressure from neutralizing antibodies drives sequence evolution during acute infection with hepatitis C virus. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 2377–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban-Riesco, L.; Depaulis, F.; Moreau, A.; Bacq, Y.; Dubois, F.; Goudeau, A.; Gaudy-Graffin, C. Rapid and sustained autologous neutralizing response leading to early spontaneous recovery after HCV infection. Virology 2013, 444, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logvinoff, C.; Major, M.; Oldach, D.; Heyward, S.; Talal, A.; Balfe, P.; Feinstone, S.; Alter, H.; Rice, C.; McKeating, J.A. Neutralizing antibody response during acute and chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10149–10154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osburn, W.O.; Snider, A.E.; Wells, B.L.; Latanich, R.; Bailey, J.R.; Thomas, D.L.; Cox, A.L.; Ray, S.C. Clearance of hepatitis C infection is associated with the early appearance of broad neutralizing antibody responses. Hepatology 2014, 59, 2140–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.-C.; Yang, C.-H.; Lo, S.-Y. Hepatitis C viral replication complex. Viruses 2021, 13, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, M.C.; Janus, B.M.; Yin, R.; Wang, R.; Guest, J.D.; Pozharski, E.; Law, M.; Mariuzza, R.A.; Toth, E.A.; Pierce, B.G. Structure of engineered hepatitis C virus E1E2 ectodomain in complex with neutralizing antibodies. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrents de la Peña, A.; Sliepen, K.; Eshun-Wilson, L.; Newby, M.L.; Allen, J.D.; Zon, I.; Koekkoek, S.; Chumbe, A.; Crispin, M.; Schinkel, J. Structure of the hepatitis C virus E1E2 glycoprotein complex. Science 2022, 378, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augestad, E.H.; Holmboe Olesen, C.; Grønberg, C.; Soerensen, A.; Velázquez-Moctezuma, R.; Fanalista, M.; Bukh, J.; Wang, K.; Gourdon, P.; Prentoe, J. The hepatitis C virus envelope protein complex is a dimer of heterodimers. Nature 2024, 633, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colpitts, C.C.; Tsai, P.-L.; Zeisel, M.B. Hepatitis C virus entry: An intriguingly complex and highly regulated process. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Hossain, R.A.; Yost, S.A.; Bu, W.; Wang, Y.; Dearborn, A.D.; Grakoui, A.; Cohen, J.I.; Marcotrigiano, J. Structural insights into hepatitis C virus receptor binding and entry. Nature 2021, 598, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevvana, M.; Keck, Z.; Foung, S.K.; Kuhn, R.J. Structural perspectives on HCV humoral immune evasion mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2021, 49, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzarum, N.; Wilson, I.A.; Law, M. The neutralizing face of hepatitis C virus E2 envelope glycoprotein. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez-Moctezuma, R.; Augestad, E.H.; Castelli, M.; Holmboe Olesen, C.; Clementi, N.; Clementi, M.; Mancini, N.; Prentoe, J. Mechanisms of hepatitis C virus escape from vaccine-relevant neutralizing antibodies. Vaccines 2021, 9, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farci, P.; Bukh, J.; Purcell, R.H. (Eds.) The quasispecies of hepatitis C virus and the host immune response. In Springer Seminars in Immunopathology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, Y.K.; Hijikata, M.; Iwamoto, A.; Alter, H.J.; Purcell, R.H.; Yoshikura, H. Neutralizing antibodies against hepatitis C virus and the emergence of neutralization escape mutant viruses. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 1494–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavie, M.; Hanoulle, X.; Dubuisson, J. Glycan shielding and modulation of hepatitis C virus neutralizing antibodies. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, N.; Sekiya, H.; Ootsuyama, Y.; Nakazawa, T.; Hijikata, M.; Ohkoshi, S.; Shimotohno, K. Humoral immune response to hypervariable region 1 of the putative envelope glycoprotein (gp70) of hepatitis C virus. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 3923–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, Z.-Y.; Fuerst, T.R.; Mariuzza, R.A.; Foung, S.K. B Cell Responses and Control of HCV Infection. In Hepatitis C Virus I: Cellular and Molecular Virology; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2016; pp. 331–357. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, R.; Meyer, K.; Banerjee, A.; Basu, A.; Coates, S.; Abrignani, S.; Houghton, M.; Frey, S.E.; Belshe, R.B. Characterization of antibodies induced by vaccination with hepatitis C virus envelope glycoproteins. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 862–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, S.C.; Wang, Y.-M.; Laeyendecker, O.; Ticehurst, J.R.; Villano, S.A.; Thomas, D.L. Acute hepatitis C virus structural gene sequences as predictors of persistent viremia: Hypervariable region 1 as a decoy. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 2938–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keck, Z.-y.; Girard-Blanc, C.; Wang, W.; Lau, P.; Zuiani, A.; Rey, F.A.; Krey, T.; Diamond, M.S.; Foung, S.K. Antibody response to hypervariable region 1 interferes with broadly neutralizing antibodies to hepatitis C virus. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 3112–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentoe, J.; Jensen, T.B.; Meuleman, P.; Serre, S.B.; Scheel, T.K.; Leroux-Roels, G.; Gottwein, J.M.; Bukh, J. Hypervariable region 1 differentially impacts viability of hepatitis C virus strains of genotypes 1 to 6 and impairs virus neutralization. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 2224–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhammad, Y.; Gu, J.; Boo, I.; Harrison, D.; McCaffrey, K.; Vietheer, P.T.; Edwards, S.; Quinn, C.; Coulibaly, F.; Poumbourios, P. Monoclonal antibodies directed toward the hepatitis C virus glycoprotein E2 detect antigenic differences modulated by the N-terminal hypervariable region 1 (HVR1), HVR2, and intergenotypic variable region. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 12245–12261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummer, H.E. Challenges to the development of vaccines to hepatitis C virus that elicit neutralizing antibodies. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinchen, V.J.; Zahid, M.N.; Flyak, A.I.; Soliman, M.G.; Learn, G.H.; Wang, S.; Davidson, E.; Doranz, B.J.; Ray, S.C.; Cox, A.L. Broadly neutralizing antibody mediated clearance of human hepatitis C virus infection. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 24, 717–730.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, M. Antibody responses in hepatitis C infection. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2021, 11, a036962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owsianka, A.M.; Timms, J.M.; Tarr, A.W.; Brown, R.J.; Hickling, T.P.; Szwejk, A.; Bienkowska-Szewczyk, K.; Thomson, B.J.; Patel, A.H.; Ball, J.K. Identification of conserved residues in the E2 envelope glycoprotein of the hepatitis C virus that are critical for CD81 binding. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 8695–8704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broering, T.J.; Garrity, K.A.; Boatright, N.K.; Sloan, S.E.; Sandor, F.; Thomas, W.D., Jr.; Szabo, G.; Finberg, R.W.; Ambrosino, D.M.; Babcock, G.J. Identification and characterization of broadly neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies directed against the E2 envelope glycoprotein of hepatitis C virus. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 12473–12482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, B.G.; Keck, Z.-Y.; Lau, P.; Fauvelle, C.; Gowthaman, R.; Baumert, T.F.; Fuerst, T.R.; Mariuzza, R.A.; Foung, S.K. Global mapping of antibody recognition of the hepatitis C virus E2 glycoprotein: Implications for vaccine design. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E6946–E6954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owsianka, A.; Tarr, A.W.; Juttla, V.S.; Lavillette, D.; Bartosch, B.; Cosset, F.-L.; Ball, J.K.; Patel, A.H. Monoclonal antibody AP33 defines a broadly neutralizing epitope on the hepatitis C virus E2 envelope glycoprotein. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 11095–11104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, J.R.; Flyak, A.I.; Cohen, V.J.; Li, H.; Wasilewski, L.N.; Snider, A.E.; Wang, S.; Learn, G.H.; Kose, N.; Loerinc, L. Broadly neutralizing antibodies with few somatic mutations and hepatitis C virus clearance. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e92872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owsianka, A.M.; Tarr, A.W.; Keck, Z.-Y.; Li, T.-K.; Witteveldt, J.; Adair, R.; Foung, S.K.; Ball, J.K.; Patel, A.H. Broadly neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies to the hepatitis C virus E2 glycoprotein. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, Z.-y.; Xia, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Krey, T.; Prentoe, J.; Carlsen, T.; Li, A.Y.-J.; Patel, A.H.; Lemon, S.M. Human monoclonal antibodies to a novel cluster of conformational epitopes on HCV E2 with resistance to neutralization escape in a genotype 2a isolate. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasher, N.A.; Eltahla, A.A.; Underwood, A.; Boo, I.; Rizzetto, S.; Walker, M.R.; Rodrigo, C.; Luciani, F.; Maher, L.; Drummer, H.E. B cell immunodominance in primary hepatitis C virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogega, C.O.; Skinner, N.E.; Schoenle, M.V.; Wilcox, X.E.; Frumento, N.; Wright, D.A.; Paul, H.T.; Sinnis-Bourozikas, A.; Clark, K.E.; Figueroa, A. Convergent evolution and targeting of diverse E2 epitopes by human broadly neutralizing antibodies are associated with HCV clearance. Immunity 2024, 57, 890–903.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, J.-C.; Russell, R.S.; Goossens, V.; Priem, S.; Walter, H.; Depla, E.; Union, A.; Faulk, K.N.; Bukh, J.; Emerson, S.U. Isolation and characterization of broadly neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies to the e1 glycoprotein of hepatitis C virus. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Kadam, R.U.; Giang, E.; Ruwona, T.B.; Nieusma, T.; Culhane, J.C.; Stanfield, R.L.; Dawson, P.E.; Wilson, I.A.; Law, M. Structure of hepatitis C virus envelope glycoprotein E1 antigenic site 314–324 in complex with antibody IGH526. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 2617–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, Z.-Y.; Sung, V.M.; Perkins, S.; Rowe, J.; Paul, S.; Liang, T.J.; Lai, M.M.; Foung, S.K. Human monoclonal antibody to hepatitis C virus E1 glycoprotein that blocks virus attachment and viral infectivity. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 7257–7263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colbert, M.D.; Flyak, A.I.; Ogega, C.O.; Kinchen, V.J.; Massaccesi, G.; Hernandez, M.; Davidson, E.; Doranz, B.J.; Cox, A.L.; Crowe, J.E., Jr.; et al. Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies Targeting New Sites of Vulnerability in Hepatitis C Virus E1E2. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesalam, A.A.; Desombere, I.; Farhoudi, A.; Van Houtte, F.; Verhoye, L.; Ball, J.; Dubuisson, J.; Foung, S.K.; Patel, A.H.; Persson, M.A. Development and characterization of a human monoclonal antibody targeting the N-terminal region of hepatitis C virus envelope glycoprotein E1. Virology 2018, 514, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, A.R. Understanding the human antibody repertoire. mAbs 2020, 12, 1729683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sender, R.; Weiss, Y.; Navon, Y.; Milo, I.; Azulay, N.; Keren, L.; Fuchs, S.; Ben-Zvi, D.; Noor, E.; Milo, R. The total mass, number, and distribution of immune cells in the human body. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2308511120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasca, D.; Diaz, A.; Romero, M.; Landin, A.M.; Blomberg, B.B. Age effects on B cells and humoral immunity in humans. Ageing Res. Rev. 2011, 10, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Tzarum, N.; Wilson, I.A.; Law, M. VH1-69 antiviral broadly neutralizing antibodies: Genetics, structures, and relevance to rational vaccine design. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 34, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briney, B.; Inderbitzin, A.; Joyce, C.; Burton, D.R. Commonality despite exceptional diversity in the baseline human antibody repertoire. Nature 2019, 566, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capella-Pujol, J.; de Gast, M.; Radić, L.; Zon, I.; Chumbe, A.; Koekkoek, S.; Olijhoek, W.; Schinkel, J.; van Gils, M.J.; Sanders, R.W. Signatures of VH 1-69-derived hepatitis C virus neutralizing antibody precursors defined by binding to envelope glycoproteins. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, S.C. Mechanism of membrane fusion by viral envelope proteins. Adv. Virus Res. 2005, 64, 231–261. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Flyak, A.I.; Ruiz, S.; Colbert, M.D.; Luong, T.; Crowe, J.E., Jr.; Bailey, J.R.; Bjorkman, P.J. HCV broadly neutralizing antibodies use a CDRH3 disulfide motif to recognize an E2 glycoprotein site that can be targeted for vaccine design. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 24, 703–716.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frumento, N.; Flyak, A.I.; Bailey, J.R. Mechanisms of HCV resistance to broadly neutralizing antibodies. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2021, 50, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzarum, N.; Giang, E.; Kong, L.; He, L.A.-O.; Prentoe, J.A.-O.; Augestad, E.A.-O.; Hua, Y.; Castillo, S.A.-O.; Lauer, G.A.-O.; Bukh, J.A.-O.; et al. Genetic and structural insights into broad neutralization of hepatitis C virus by human V(H)1-69 antibodies. Sci. Adv. 2012, 5, eaav1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliyahu, S.; Sharabi, O.; Elmedvi, S.; Timor, R.; Davidovich, A.; Vigneault, F.; Clouser, C.; Hope, R.; Nimer, A.; Braun, M. Antibody repertoire analysis of hepatitis C virus infections identifies immune signatures associated with spontaneous clearance. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, N.E.; Ogega, C.O.; Frumento, N.; Clark, K.E.; Yegnasubramanian, S.; Schuebel, K.; Meyers, J.; Gupta, A.; Wheelan, S.; Cox, A.L.; et al. Convergent antibody responses are associated with broad neutralization of hepatitis C virus. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1135841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perales, C. Quasispecies dynamics and clinical significance of hepatitis C virus (HCV) antiviral resistance. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 56, 105562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgia, S.M.; Hedskog, C.; Parhy, B.; Hyland, R.H.; Stamm, L.M.; Brainard, D.M.; Subramanian, M.G.; McHutchison, J.G.; Mo, H.; Svarovskaia, E. Identification of a novel hepatitis C virus genotype from Punjab, India: Expanding classification of hepatitis C virus into 8 genotypes. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 1722–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, Z.-Y.; Olson, O.; Gal-Tanamy, M.; Xia, J.; Patel, A.H.; Dreux, M.; Cosset, F.-L.c.; Lemon, S.M.; Foung, S.K. A point mutation leading to hepatitis C virus escape from neutralization by a monoclonal antibody to a conserved conformational epitope. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 6067–6072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, Z.-Y.; Saha, A.; Xia, J.; Wang, Y.; Lau, P.; Krey, T.; Rey, F.A.; Foung, S.K. Mapping a region of hepatitis C virus E2 that is responsible for escape from neutralizing antibodies and a core CD81-binding region that does not tolerate neutralization escape mutations. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 10451–10463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velázquez-Moctezuma, R.; Galli, A.; Law, M.; Bukh, J.; Prentoe, J. Hepatitis C virus escape studies of human antibody AR3A reveal a high barrier to resistance and novel insights on viral antibody evasion mechanisms. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, J.R.; Wasilewski, L.N.; Snider, A.E.; El-Diwany, R.; Osburn, W.O.; Keck, Z.; Foung, S.K.; Ray, S.C. Naturally selected hepatitis C virus polymorphisms confer broad neutralizing antibody resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, Z.-y.; Li, S.H.; Xia, J.; von Hahn, T.; Balfe, P.; McKeating, J.A.; Witteveldt, J.; Patel, A.H.; Alter, H.; Rice, C.M. Mutations in hepatitis C virus E2 located outside the CD81 binding sites lead to escape from broadly neutralizing antibodies but compromise virus infectivity. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 6149–6160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantua, H.; Diao, J.; Ultsch, M.; Hazen, M.; Mathieu, M.; McCutcheon, K.; Takeda, K.; Date, S.; Cheung, T.K.; Phung, Q. Glycan shifting on hepatitis C virus (HCV) E2 glycoprotein is a mechanism for escape from broadly neutralizing antibodies. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 1899–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentoe, J.; Velázquez-Moctezuma, R.; Augestad, E.H.; Galli, A.; Wang, R.; Law, M.; Alter, H.; Bukh, J. Hypervariable region 1 and N-linked glycans of hepatitis C regulate virion neutralization by modulating envelope conformations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 10039–10047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidorkiewicz, M. Hepatitis C virus uses host lipids to its own advantage. Metabolites 2021, 11, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauvelle, C.; Felmlee, D.J.; Crouchet, E.; Lee, J.; Heydmann, L.; Lefèvre, M.; Magri, A.; Hiet, M.-S.; Fofana, I.; Habersetzer, F. Apolipoprotein E mediates evasion from hepatitis C virus neutralizing antibodies. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 206–217.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimacombe, C.L.; Grove, J.; Meredith, L.W.; Hu, K.; Syder, A.J.; Flores, M.V.; Timpe, J.M.; Krieger, S.E.; Baumert, T.F.; Tellinghuisen, T.L. Neutralizing antibody-resistant hepatitis C virus cell-to-cell transmission. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 596–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timpe, J.M.; Stamataki, Z.; Jennings, A.; Hu, K.; Farquhar, M.J.; Harris, H.J.; Schwarz, A.; Desombere, I.; Roels, G.L.; Balfe, P. Hepatitis C virus cell-cell transmission in hepatoma cells in the presence of neutralizing antibodies. Hepatology 2008, 47, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, E.; Cooke, G.S.; Lauer, G.M.; Chung, R.T. Implementation of a controlled human infection model for evaluation of HCV vaccine candidates. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1757–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, C.M. Designing an HCV vaccine: A unique convergence of prevention and therapy? Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 23, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, A.L.; Netski, D.M.; Mosbruger, T.; Sherman, S.G.; Strathdee, S.; Ompad, D.; Vlahov, D.; Chien, D.; Shyamala, V.; Ray, S.C. Prospective evaluation of community-acquired acute-phase hepatitis C virus infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westbrook, R.H.; Dusheiko, G. Natural history of hepatitis C. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, S58–S68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamal, S.M. Acute hepatitis C: A systematic review. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 1283–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, K.; Melia, M.T.; Veenhuis, R.T.; Winter, M.; Rousseau, K.E.; Massaccesi, G.; Osburn, W.O.; Forman, M.; Thomas, E.; Thornton, K. Randomized trial of a vaccine regimen to prevent chronic HCV infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Escobar, E.; Roingeard, P.; Beaumont, E. Current hepatitis C vaccine candidates based on the induction of neutralizing antibodies. Viruses 2023, 15, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzymski, P.; Jibril, A.T.; Rahmah, L.; Abarikwu, S.O.; Hashem, F.; Lawati, A.A.; Morrison, F.M.M.; Marquez, L.P.; Mohamed, K.; Khan, A. Is there still hope for the prophylactic hepatitis C vaccine? A review of different approaches. J. Med. Virol. 2024, 96, e29900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemlin, M.; Klinger, M.; Link, J.; Zemlin, C.; Bauer, K.; Engler, J.A.; Schroeder, H.W., Jr.; Kirkham, P.M. Expressed murine and human CDR-H3 intervals of equal length exhibit distinct repertoires that differ in their amino acid composition and predicted range of structures. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 334, 733–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Bao, Y.; Meng, Q.; Hu, X.; Meng, Q.; Ren, L.; Li, N.; Zhao, Y. Immunoglobulin genomics in the guinea pig (Cavia porcellus). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, K.; Inchauspe, G.; Shikata, T.; Prince, A.M. Three different patterns of hepatitis C virus infection in chimpanzees. Hepatology 1992, 15, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berggren, K.A.; Suzuki, S.; Ploss, A. Animal models used in hepatitis C virus research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartosch, B.; Bukh, J.; Meunier, J.-C.; Granier, C.; Engle, R.E.; Blackwelder, W.C.; Emerson, S.U.; Cosset, F.-L.; Purcell, R.H. In vitro assay for neutralizing antibody to hepatitis C virus: Evidence for broadly conserved neutralization epitopes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 14199–14204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, M.E.; Mihalik, K.; Puig, M.; Rehermann, B.; Nascimbeni, M.; Rice, C.M.; Feinstone, S.M. Previously infected and recovered chimpanzees exhibit rapid responses that control hepatitis C virus replication upon rechallenge. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 6586–6595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.J.; Feld, J.J.; Cox, A.L.; Rice, C.M. Controlled human infection model—Fast track to HCV vaccine? N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alter, H.J.; Barnes, E.; Biondi, M.J.; Cox, A.L.; Eberts, J.D.; Feld, J.J.; Liang, T.J.; Morrison, J.; Rice, C.M.; Shoukry, N.H. Joint statement in support of hepatitis C human challenge studies. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 967–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darton, T.C.; Blohmke, C.J.; Moorthy, V.S.; Altmann, D.M.; Hayden, F.G.; Clutterbuck, E.A.; Levine, M.M.; Hill, A.V.; Pollard, A.J. Design, recruitment, and microbiological considerations in human challenge studies. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, A.J.; Geysen, H.M.; Christopherson, C.; Hall, J.E.; Mason, T.J.; Saracco, G.; Bonino, F.; Crawford, K.; Marion, C.D.; Crawford, K.A. Evidence for immune selection of hepatitis C virus (HCV) putative envelope glycoprotein variants: Potential role in chronic HCV infections. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 3468–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibert, A.; Meisel, H.; Kraas, W.; Schulz, A.; Jung, G.; Roggendorf, M. Early antibody response against hypervariable region 1 is associated with acute self-limiting infections of hepatitis C virus. Hepatology 1997, 25, 1245–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, A.; Eltahla, A.; Lloyd, A.R.; Rodrigo, C.; Agapiou, D.; Bull, R.A.; Tedla, N. Optimisation and validation of a new method for antibody dependent cellular phagocytosis in hepatitis C virus infection. J. Immunol. Methods 2021, 495, 113087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nattermann, J.; Schneiders, A.M.; Leifeld, L.; Langhans, B.; Schulz, M.; Inchauspé, G.; Matz, B.; Brackmann, H.H.; Houghton, M.; Sauerbruch, T. Serum antibodies against the hepatitis C virus E2 protein mediate antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). J. Hepatol. 2005, 42, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pihl, A.F.; Feng, S.; Offersgaard, A.; Alzua, G.P.; Augestad, E.H.; Mathiesen, C.K.; Jensen, T.B.; Krarup, H.; Law, M.; Prentoe, J. Inactivated whole hepatitis C virus vaccine employing a licensed adjuvant elicits cross-genotype neutralizing antibodies in mice. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gridley, J.; Holland, B.; Salinas, E.; Trivedi, S.; Dravid, P.; Elrod, E.; Jin, F.; Kumari, A.; Batista, M.N.; Thapa, M. Concerted synergy between viral-specific IgG and CD8+ T cells is critical for clearance of an HCV-related rodent hepacivirus. Hepatology 2024, 80, 937–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skinner, N.E. Broadly Neutralizing Antibody Characteristics in Hepatitis C Virus Infection and Implications for Vaccine Design. Vaccines 2025, 13, 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13060612
Skinner NE. Broadly Neutralizing Antibody Characteristics in Hepatitis C Virus Infection and Implications for Vaccine Design. Vaccines. 2025; 13(6):612. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13060612
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkinner, Nicole E. 2025. "Broadly Neutralizing Antibody Characteristics in Hepatitis C Virus Infection and Implications for Vaccine Design" Vaccines 13, no. 6: 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13060612
APA StyleSkinner, N. E. (2025). Broadly Neutralizing Antibody Characteristics in Hepatitis C Virus Infection and Implications for Vaccine Design. Vaccines, 13(6), 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13060612





