An Open-Label, Randomized Field Trial Demonstrates Safety and Immunogenicity of Inactivated gE-Deleted Marker Vaccine Against Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis in Cattle
Abstract
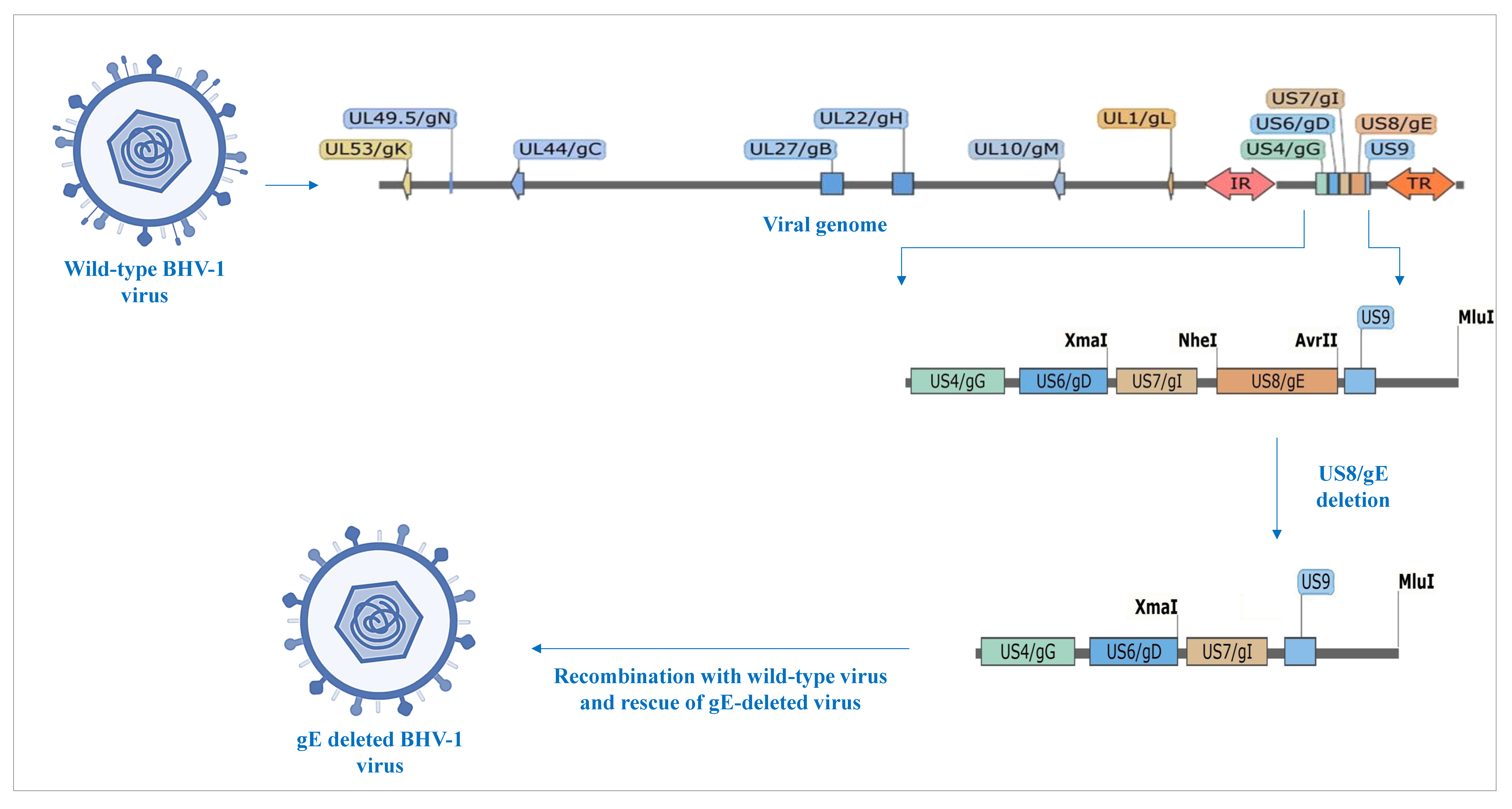
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Trial Design
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Sample Size Calculation
2.4. Test Substances and Vaccination Schedule
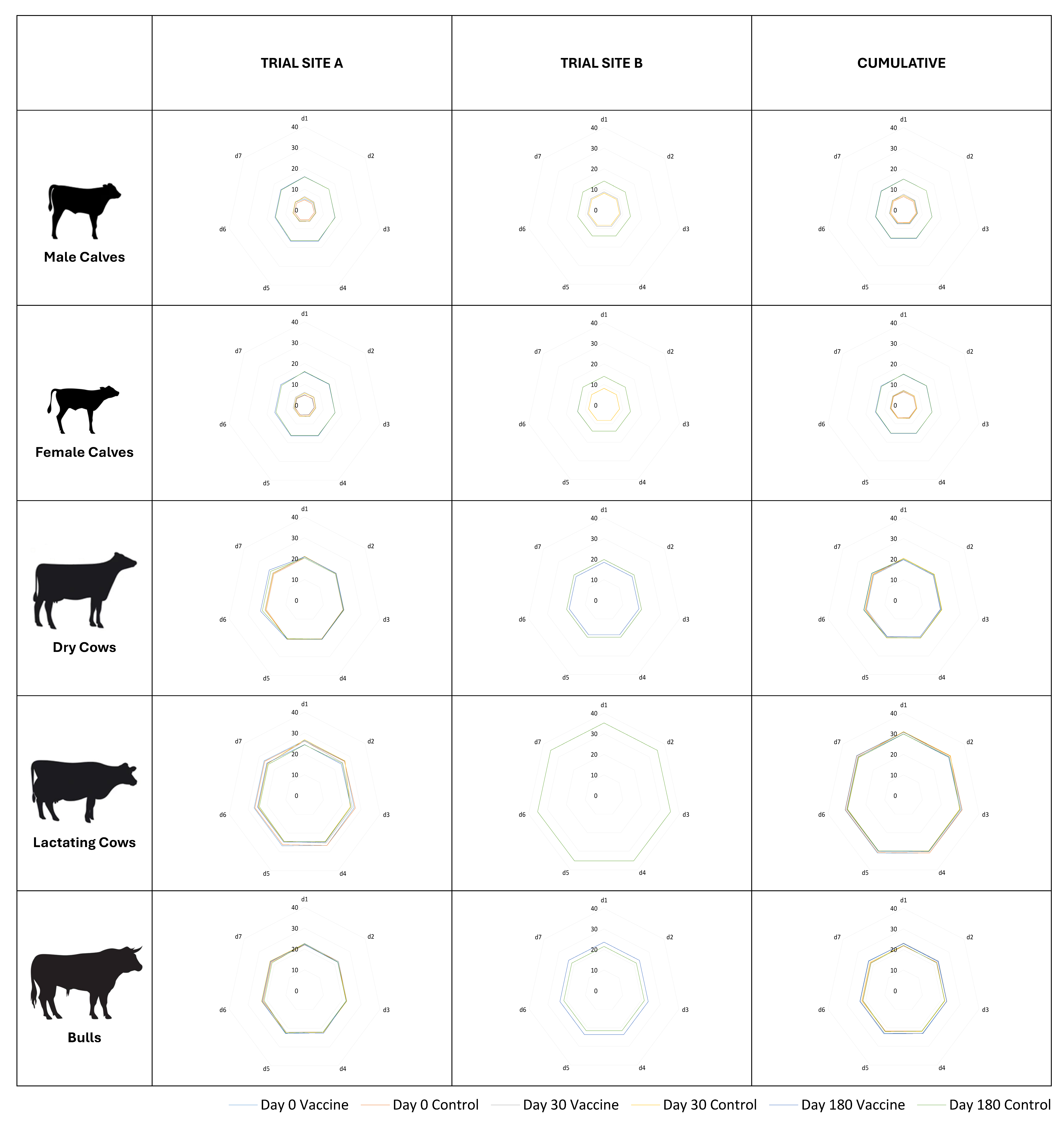
2.5. Safety
2.6. Immunogenicity
2.7. Statistical Analyses
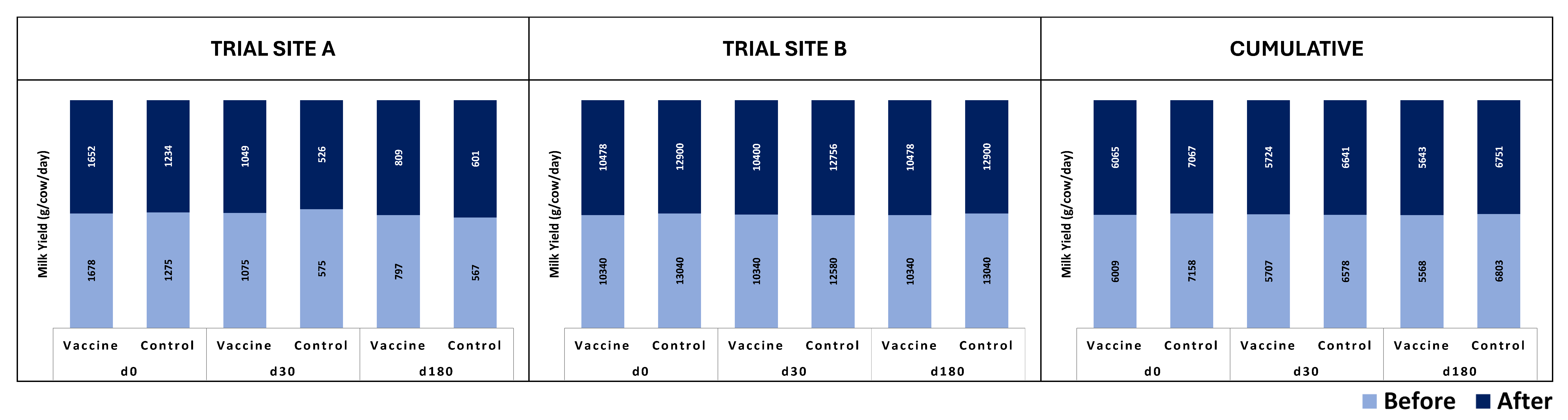
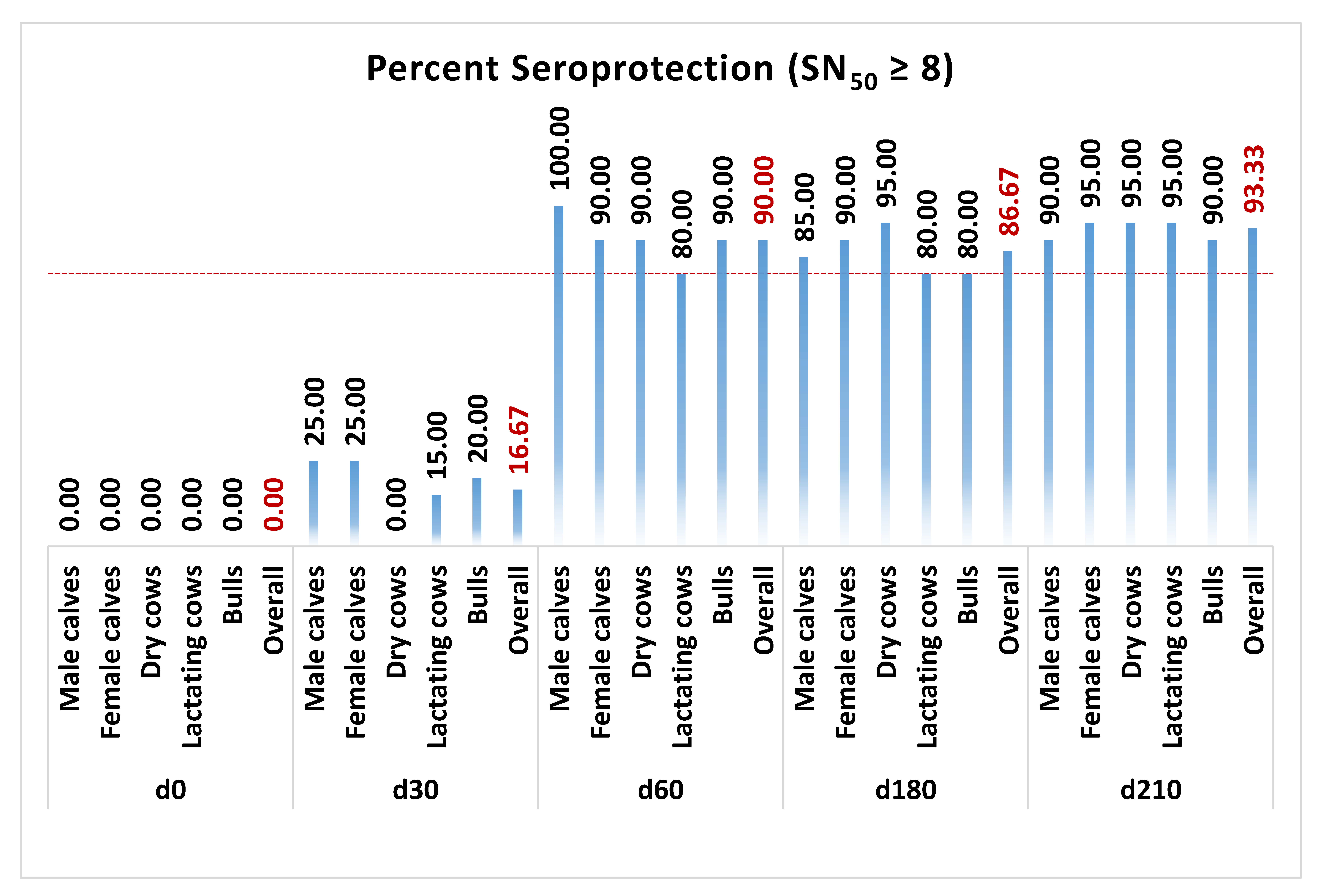
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| AB-ELISA | Avidin Biotin Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| BoHV-1 | Bovine Herpesvirus-1 |
| DIVA | Differentiating infected from vaccinated animals |
| gE | Glycoprotein-E |
| HF | Holstein Friesian |
| IBR | Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis |
| IPB | Infectious Pustular Balanoposthitis |
| IPV | Infectious Pustular Vulvovaginitis |
| MDA | Maternally derived antibody |
| msl | Meters above sea level |
| SNT50 | Median serum neutralization titer |
| TCID50 | Median tissue culture infective dose |
| WOAH | World Organization for Animal Health |
References
- Madin, S.H.; York, C.J.; McKercher, D.G. Isolation of the infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus. Science 1956, 124, 721–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rychner, J.J. Bujatrik oder Systematisches Handbuch der Äusserlichen und Innerlichen Krankheiten des Rindviehes; Bern, Chr. Fischer: Basel, Switzerland, 1841. [Google Scholar]
- Reisinger, L.; Reimann, H. Beitrag Zur Atiologic des lachenausschlages des Rindes. Wine Tirrarztl. Mch. 1928, 15, 249–261. [Google Scholar]
- Furuoka, H.; Izumida, N.; Horiuchi, M.; Osame, S.; Matsui, T. Bovine herpesvirus meningoencephalitis association with infectious bovine rhinotracheitis (IBR) vaccine. Acta Neuropathol. 1995, 90, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iscaro, C.; Cambiotti, V.; Petrini, S.; Feliziani, F. Control programs for infectious bovine rhinotracheitis (IBR) in European countries: An overview. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2021, 22, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, P.; Patil, S.S.; Shome, R.; Rahman, H. Sero-epidemiology of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis and brucellosis in organised dairy farms in Southern India. Indian J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 85, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.S.; Prajapati, A.; Krishnamoorthy, P.; Desai, G.S.; Reddy, G.B.M.; Suresh, K.P.; Rahman, H. Seroprevalence of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis in organized dairy farms of India. Indian J. Anim. Res. 2017, 51, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, A.; McAloon, C.; Sugrue, K.; Fitzgerald, R.; Sheridan, C.; Cowley, B.; McAloon, C.; Kennedy, E. Investigation into the safety, and serological responses elicited by delivery of live intranasal vaccines for bovine herpes virus type 1, bovine respiratory syncytial virus, and parainfluenza type 3 in pre-weaned calves. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1283013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrucci, G.; Osburn, B.I.; Frigeri, F.; Ferrari, M.; Salvatori, D.; Dico, M.L.; Barreca, F. The use of immunomodulators in the control of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2000, 23, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Abraham, A.; Rodríguez-Mallon, A.; Unajak, S.; Bannantine, J.P. Challenges in veterinary vaccine development. In Vaccine Design: Methods and Protocols, Volume 2. Vaccines for Veterinary Diseases; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 3–34. [Google Scholar]
- Makoschey, B.; Keil, G.M. Early immunity induced by a glycoprotein E-negative vaccine for infectious bovine rhinotracheitis. Vet. Rec. 2000, 147, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampe, B.; Duchateau, L.; Speybroeck, N.; Berkvens, D.; Dupont, A.; Kerkhofs, P.; Thiry, E.; Dispas, M. Assessment of the long-term effect of vaccination on transmission of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus in cattle herds hyperimmunized with glycoprotein E–deleted marker vaccine. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2012, 73, 1787–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NAAS. Veterinary Vaccines and Diagnostics; Policy Paper No. 46; National Academy of Agricultural Sciences: New Delhi, India, 2010; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, S.S.; Suresh, K.P.; Velankar, A.; Shivaranjini, C.; Hemadri, D.; Hiremath, J.; Jacob, S.S. Seroprevalence of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis (IBR) in India: A 5-year study. Vet. Ital. 2022, 58, 339–345. [Google Scholar]
- Somasundaram, R.; Gontu, A.; Ponsekaran, S.; Arumugam, U.; Yerragunta, V.; Swapna, E.; Kommoju, N.S.; Rachapudi, K.; Lingala, R. Development of glycoprotein-E deleted BHV-1 marker vaccine. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Virus Evolution, Infection and Disease Control, Hyderabad, India, 15–17 December 2022; p. P2. [Google Scholar]
- Penta, N.; Ponsekaran, S.; Yerragunta, V.; Kommoju, N.; Rachapudi, K.; Sarangi, L.N.; Muthappa, P.N.; Pamidikondala, K.; Karnati, S.; Pattnaik, P.; et al. Indigenously developed DIVA-Compliant Inactivated BHV-1 Vaccine. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Emerging Viruses: Pandemic & Biosecurity Perspectives, Gwalior, India, 11–13 November 2024; p. 195. [Google Scholar]
- GCP, VICH GL. Good Clinical Practice. 2000. Available online: https://vichsec.org/guidelines/ (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- WOAH. WOAH Terrestrial Manual, Chapter 3.4.11. Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis/Infectious Pustular Vulvovaginitis. 2024. Available online: https://www.woah.org/fileadmin/Home/eng/Health_standards/tahm/3.04.11_IBR_IPV.pdf (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- De Brun, L.; Leites, M.; Furtado, A.; Campos, F.; Roehe, P.; Puentes, R. Field Evaluation of commercial vaccines against infectious bovine rhinotracheitis (IBR) virus using different immunization protocols. Vaccines 2021, 9, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Code of Federal Regulations. Section 113.310 Bovine Rhinotracheitis Vaccine. 2023. Available online: https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/CFR-2024-title9-vol1/pdf/CFR-2024-title9-vol1-sec113-310.pdf (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Kraus, D. Consolidated data analysis and presentation using an open-source add-in for the Microsoft Excel® spreadsheet software. Med. Writ. 2014, 23, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.; Singh, S.P.; Kumar, R.; Diwakar, R.P.; Kumar, P. A Review on Current Status of Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis in India. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2018, 7, 411–426. [Google Scholar]
- Laveso, G.; Alessi, A.C.; Fanton, E.B.; Valente, C.H. Bovine IPV in Bauru region, Sao PauloState, Brazil, Econtro de pesquisas Veterinarias, 8 and 9 de Novernbro. Vet. Bull 1984, 55, 6193. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, I.C.D.; Almeida, Y.V.; Donatele, D.M.; Clipes, R.C.; Barioni, G.; Zanini, M.S.; Filippo, P.A.D. Seroprevalence and associated factors of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis and bovine viral diarrhea in dairy cows in the Caparaó region, Espírito Santo, Brazil. Ciência Rural 2021, 51, e20200220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engdawork, A.; Aklilu, H. Infectious bovine rhinotracheitis: Epidemiology, control, and impacts on livestock production and genetic resources. Vet. Res. Notes 2024, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrotra, M.L.; Rajya, B.S.; Kumar, S. Infectious bovine rhinotracheitis (IBR)-keratoconjunctivitis in calves. Indian J. Vet. Path 1976, 1, 70–73. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Qi, Y.; Wen, X.; Li, C.; Liu, X.; Ni, H. Meta-analysis of prevalence of bovine herpes virus 1 in cattle in Mainland China. Acta Trop. 2018, 187, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, H.U.; Rabbani, M.; Ghafoor, A.; Riaz, A.; Awan, F.N.; Raza, S. First isolation and genetic characterization of bovine herpesvirus 1 from cattle in Pakistan. Pak. Vet. J. 2020, 41, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, Y.H.; Myint, H.H.; Tin, Y.K.; Myint, M.Z. Occurrence of Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis and its associated risk factors in local cattle in Myanmar. In Sustainable Animal Production and Health; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021; p. 120. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, H.; Bhattacharya, M.; Rajkhowa, J.; Soud, N.; Nandankar, U.; Mukherjee, S. Seroprevalence of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis in yaks (Poephagus grunniens) in India. Indian J. Anim. Sci. 2007, 77, 793–795. [Google Scholar]
- Nandi, S.; Kumar, M.; Yadav, V.; Chander, V. Serological evidences of bovine herpesvirus-1 infection in bovines of organized farms in India. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2011, 58, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straub, O.C. Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis virus. Virus Infect. Rumin. 1990, 3, 71–108. [Google Scholar]
- Nettleton, P.; Russell, G. Update on infectious bovine rhinotracheitis. Practice 2017, 39, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martucciello, A.; Balestrieri, A.; Righi, C.; Cappelli, G.; Scoccia, E.; Grassi, C.; Brandi, S.; Rossi, E.; Galiero, G.; Gioia, D.; et al. Evaluation of an immunization protocol using bovine alphaherpesvirus 1 gE-deleted marker vaccines against Bubaline alphaherpesvirus 1 in water buffaloes. Vaccines 2023, 11, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, C.C.; Fulton, R.W.; O’Toole, D.; Gillette, B.; Daly, R.F.; Perry, G.; Clement, T. Bovine herpesvirus 1 modified live virus vaccines for cattle reproduction: Balancing protection with undesired effects. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 206, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, B.C.; Smith, P.C.; Nusbaum, K.E.; Stringfellow, D.A. The effect of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis vaccine on reproductive efficiency in cattle vaccinated during estrus. Theriogenology 1990, 33, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.C.; Nusbaum, K.E.; Kwapien, R.P.; Stringfellow, D.A.; Driggers, K. Necrotic oophoritis in heifers vaccinated intravenously with infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus vaccine during estrus. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1990, 51, 969–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.M.; Van der Maaten, M.J.; Whetstone, C.A. Infertility in heifers inoculated with modified-live bovine herpesvirus-1 vaccinal strains against infectious bovine rhinotracheitis on postbreeding day 14. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1989, 50, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKercher, D.G.; Crenshaw, G.L. Comparative efficacy of intranasally and parenterally administered infectious bovine rhinotracheitis vaccines. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1971, 159, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.W.; Carter, G.R.; Carter, F.A. Infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus recovered from the milk of a cow with mastitis. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1974, 164, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, V.B.; Newberne, J.W.; Mitchell, F.E. Vaccination of pregnant cattle with infectious bovine rhinotracheitis vaccine. Vet. Med. 1961, 56, 437–440. [Google Scholar]
- Deka, D.; Maiti, N.K.; Oberoi, M.S. Detection of bovine herpesvirus-1 infection in breeding bull semen by virus isolation and polymerase chain reaction. Rev. Sci. Tech.-Off. Int. Des. Épizooties 2005, 24, 1085. [Google Scholar]
- Petrini, S.; Martucciello, A.; Righi, C.; Cappelli, G.; Torresi, C.; Grassi, C.; Scoccia, E.; Costantino, G.; Casciari, C.; Sabato, R.; et al. Assessment of different infectious bovine rhinotracheitis marker vaccines in calves. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahrs, R.F. Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis: A review and update. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1977, 171, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastoret, P.P.; Babiuk, L.A.; Misra, V.; Griebel, P. Reactivation of temperature-sensitive and non-temperature-sensitive infectious bovine rhinotracheitis vaccine virus with dexamethasone. Infect. Immun. 1980, 29, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolar, J.R., Jr.; Shechmeister, I.L.; Strack, L.E. Field experiments with formalin-killed-virus vaccine against infectious bovine rhinotracheitis, bovine viral diarrhea and parainfluenza-3. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1973, 34, 1469–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipper, I.A.; Kelling, C.L. Evaluation of inactivated infectious bovine rhinotracheitis vaccines. Can. J. Comp. Med. 1975, 39, 402. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Y.K.; Lu, Y.S.; Chiu, S.Y.; Lee, Y.L.; Lin, D.T.; Lin, D.F.; Kwang, M.J.; Tsai, H.J. The development of multivalent inactivated vaccines composed of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis, bovine viral diarrhoea, and parainfluenza-3 viral antigens. J. Chin. Soc. Vet. Sci. 1992, 18, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Strube, W.; Auer, S.; Abar, B.; Bergle, R.D.; Block, W.; Heinen, E.; Kretzdorn, D.; Rodenbach, C.; Schmeer, N. Infectious bovine rhinotracheitis marker vaccines-chemically inactivated and live attenuated-for the improvement of BHV1 control programs: I. Safety aspects in the vaccine development. In Proceedings of the 18th World Buiatrics Congress: 26th Congress of the Italian Association of Buiatrics, Bologna, Italy, 29 August–2 September 1994; Volume 1, pp. 761–764. [Google Scholar]
- Petzhold, S.A.; Reckziegel, P.E.; Prado, J.A.P.; Teixeira, J.C.; Wald, V.B.; Esteves, P.A.; Spilki, F.R.; Roehe, P.M. Neutralizing antibodies to bovine herpesviruses types 1 (BHV-1) and 5 (BHV-5) induced by an experimental, oil-adjuvanted, BHV-1 vaccine. Braz. J. Vet. Res. Anim. Sci. 2001, 38, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oirschot, J.T. Bovine viral vaccines, diagnostics, and eradication: Past, present, and future. Adv. Vet. Med. 1999, 41, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Misra, V.; Babiuk, L.A.; Darcel, C.L.Q. Analysis of bovine herpes virus-type 1 isolates by restriction endonuclease fingerprinting. Arch. Virol. 1983, 76, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, J.; McEntee, K.; Kendrick, J.; Wagner, W. Comparison of infectious pustular vulvovaginitis virus with infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus. Cornell Vet. 1959, 49, 288–297. [Google Scholar]
- McKercher, D.G.; Straub, O.C.; Saito, J.K.; Wada, E.M. Comparative studies of the etiological agents of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis and infectious pustular vulvovaginitis. Can. J. Comp. Med. Vet. Sci. 1959, 23, 320. [Google Scholar]
- Dongre, V.B.; Gandhi, R.S.; Salunke, V.M.; Kokate, L.S.; Durge, S.M.; Khandait, V.N.; Patil, P.V. Present status and future prospects of Deoni Cattle. Indian J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 87, 800–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iype, S. Vechur cattle–from extinction to sustainability. Anim. Genet. Resour. 2013, 52, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, S.; Kumar, A.; Chaudhary, S.; Maan, S. Bovine herpesvirus 1 (BoHV-1) in cattle and buffalo: A review with emphasis on seroprevalence in India. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2019, 8, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parreño, V.; Marcoppido, G.; Vega, C.; Garaicoechea, L.; Rodriguez, D.; Saif, L.; Fernández, F. Milk supplemented with immune colostrum: Protection against rotavirus diarrhea and modulatory effect on the systemic and mucosal antibody responses in calves experimentally challenged with bovine rotavirus. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2010, 136, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, J.B.; Tresamol, P.V.; Saseendranath, M.R. Seroprevalence of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis in cattle population of Kerala. Indian Vet. J. 2003, 80, 393–396. [Google Scholar]
- Tresamol, P.V.; Rincy, K.M.; Dev, P.A. Seroprevalence of Bovine Herpes Virus-1 among Cattle and Buffaloes in Central Kerala, India. Int. J. Livest. Res. 2019, 1, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, J.C.; van Lieshout, J.A.H.; De Wit, J.J.; Graat, E.A.M.; Somers, M.J.M. The serological BHV1 status of dams determines the precolostral status of their calves. Vet. Q. 2000, 22, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menanteau-Horta, A.M.; Ames, T.R.; Johnson, D.W.; Meiske, J.C. Effect of maternal antibody upon vaccination with infectious bovine rhinotracheitis and bovine virus diarrhea vaccines. Can. J. Comp. Med. 1985, 49, 10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brar, J.S.; Johnson, D.W.; Muscoplat, C.C.; Shope, R.E., Jr.; Meiske, J.C. Maternal immunity to infectious bovine rhinotracheitis and bovine viral diarrhea viruses: Duration and effect on vaccination in young calves. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1978, 39, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peek, S.F.; Divers, T.J. Rebhun’s Diseases of Dairy Cattle-E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. 2018. Available online: https://books.google.co.in/books?id=ByjRDwAAQBAJ (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Blaske, S.; Epperson, K.M.; Quail, L.K.; Ketchum, J.N.; Guy, C.P.; Long, C.R.; Perry, G.A. 155 Impact of Ambient Temperature on Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus and Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis Vaccination Response. J. Anim. Sci. 2023, 101 (Suppl. 3), 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, A.S.; Rajawat, D.; Jisna, K.S.; Panwar, A.; Patra, M.K. Transient impacts of vaccination on livestock production: A holistic review. Indian J. Anim. Health 2024, 63, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, J.C.; Frankena, K.; Van Oirschot, J.T. Effect on milk production of vaccination with a bovine herpesvirus 1 gene-deleted vaccine. Vet. Rec. 1997, 140, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retamal, P.; Ábalos, P.; Alegría-Morán, R.; Valdivieso, N.; Vordermeier, M.; Jones, G.; Saadi, K.; Perez Watt, C.; Salinas, C.; Ávila, C.; et al. Vaccination of Holstein heifers with Mycobacterium bovis BCG strain induces protection against bovine tuberculosis and higher milk production yields in a natural transmission setting. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarangi, L.N.; Rana, S.K.; Dash, S.K.; Bhattacharya, K.; Surendra, V.S.; Ponnanna, N.M.; Sharma, G.K.; SDGs, U.N. Control of Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis Through Inactivated Marker Vaccine: A Field Study in India. Available online: https://www.nddb.org/sites/default/files/pdfs/research-publications/2020_IDF_Laxmi_IBR_vaccination.pdf (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Babiuk, L.A.; Tikoo, S.K. Immunology of bovine herpesvirus 1 infection. Vet. Microbiol. 1996, 53, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Group | Vaccine Arm | Control Arm |
|---|---|---|
| Male calves | 10 | 5 |
| Female calves | 10 | 5 |
| Dry cows | 10 | 5 |
| Lactating cows | 10 | 5 |
| Breeding bulls | 5 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ganguly, B.; Tayshete, S.; Melepat, D.P.; Awandkar, S.; Karnati, S.; Pattnaik, P.; Kanakasapapathy, A.K. An Open-Label, Randomized Field Trial Demonstrates Safety and Immunogenicity of Inactivated gE-Deleted Marker Vaccine Against Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis in Cattle. Vaccines 2025, 13, 579. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13060579
Ganguly B, Tayshete S, Melepat DP, Awandkar S, Karnati S, Pattnaik P, Kanakasapapathy AK. An Open-Label, Randomized Field Trial Demonstrates Safety and Immunogenicity of Inactivated gE-Deleted Marker Vaccine Against Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis in Cattle. Vaccines. 2025; 13(6):579. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13060579
Chicago/Turabian StyleGanguly, Bhaskar, Sarvesh Tayshete, Deepa Padinjare Melepat, Sudhakar Awandkar, Srinivas Karnati, Priyabrata Pattnaik, and Anand Kumar Kanakasapapathy. 2025. "An Open-Label, Randomized Field Trial Demonstrates Safety and Immunogenicity of Inactivated gE-Deleted Marker Vaccine Against Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis in Cattle" Vaccines 13, no. 6: 579. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13060579
APA StyleGanguly, B., Tayshete, S., Melepat, D. P., Awandkar, S., Karnati, S., Pattnaik, P., & Kanakasapapathy, A. K. (2025). An Open-Label, Randomized Field Trial Demonstrates Safety and Immunogenicity of Inactivated gE-Deleted Marker Vaccine Against Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis in Cattle. Vaccines, 13(6), 579. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13060579







