Co-Immunization with DNA Vaccines Expressing SABP1 and SAG1 Proteins Effectively Enhanced Mice Resistance to Toxoplasma gondii Acute Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice and Parasites
2.2. Polyclonal Antibody Preparation against Recombinant SABP1 and SAG1 Proteins Expressed by E. coil
2.3. Eukaryotic Expression Plasmid Construction
- pVAX1-SABP1-5: 5′ AACTTAAGCTTGCCACCATGGGATCTGGCAACAAC 3′,
- pVAX1-SABP1-3: 5′ TCCGTCTAGATCAATGGTGATGGTGATGATGCTTC 3′,
- pVAX1-SAG1-5: 5′ ACCCAAGCTTATGGGCAGCAGCCAT 3′,
- pVAX1-SAG1-3: 5′ CTAGTCTAGATCAGTGGTGGTGGGTGGGTGGGT 3′.
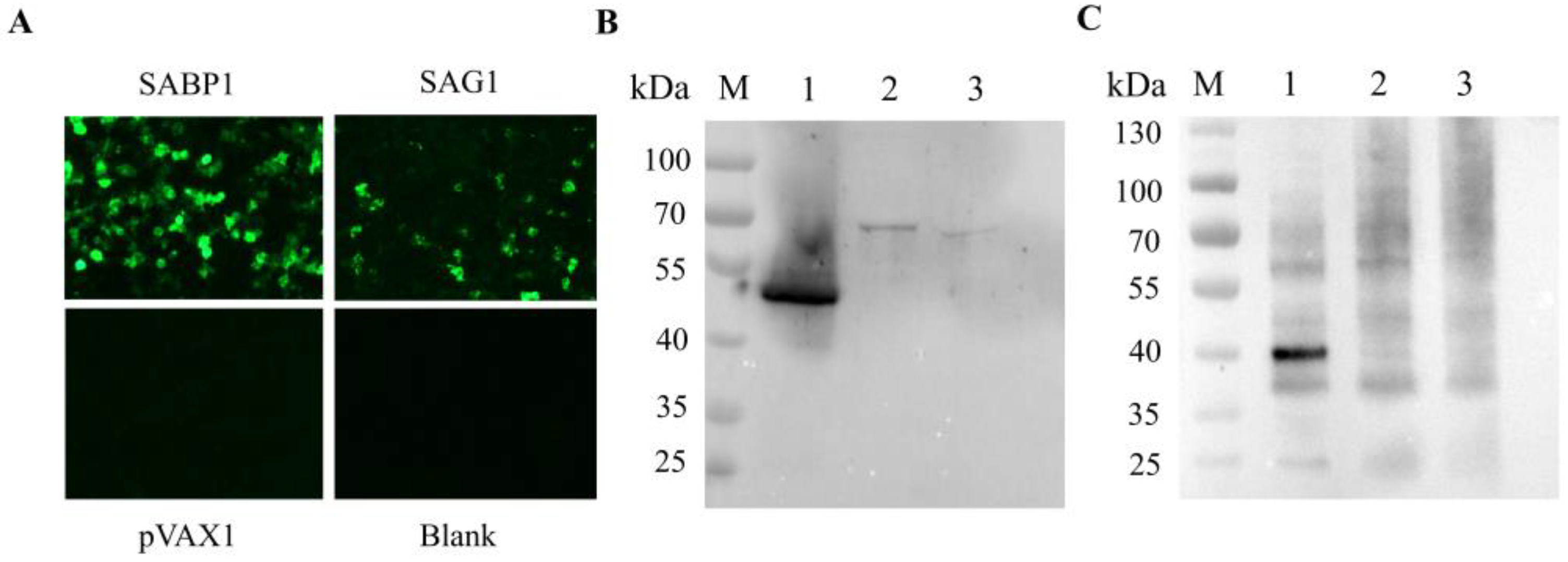
2.4. IFA and Western Blot Detection of pVAX1-SABP1 and pVAX1-SAG1 In Vitro
2.5. Mouse Immunization and T. gondii Challenge
2.6. Antibody Response Measurement
2.7. Spleen Lymphocyte Proliferation Test (CCK-8)
2.8. Cytokine Assays
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bioinformatic Analysis Identified B and T Cell Epitopes of the SABP1 and SAG1 Proteins
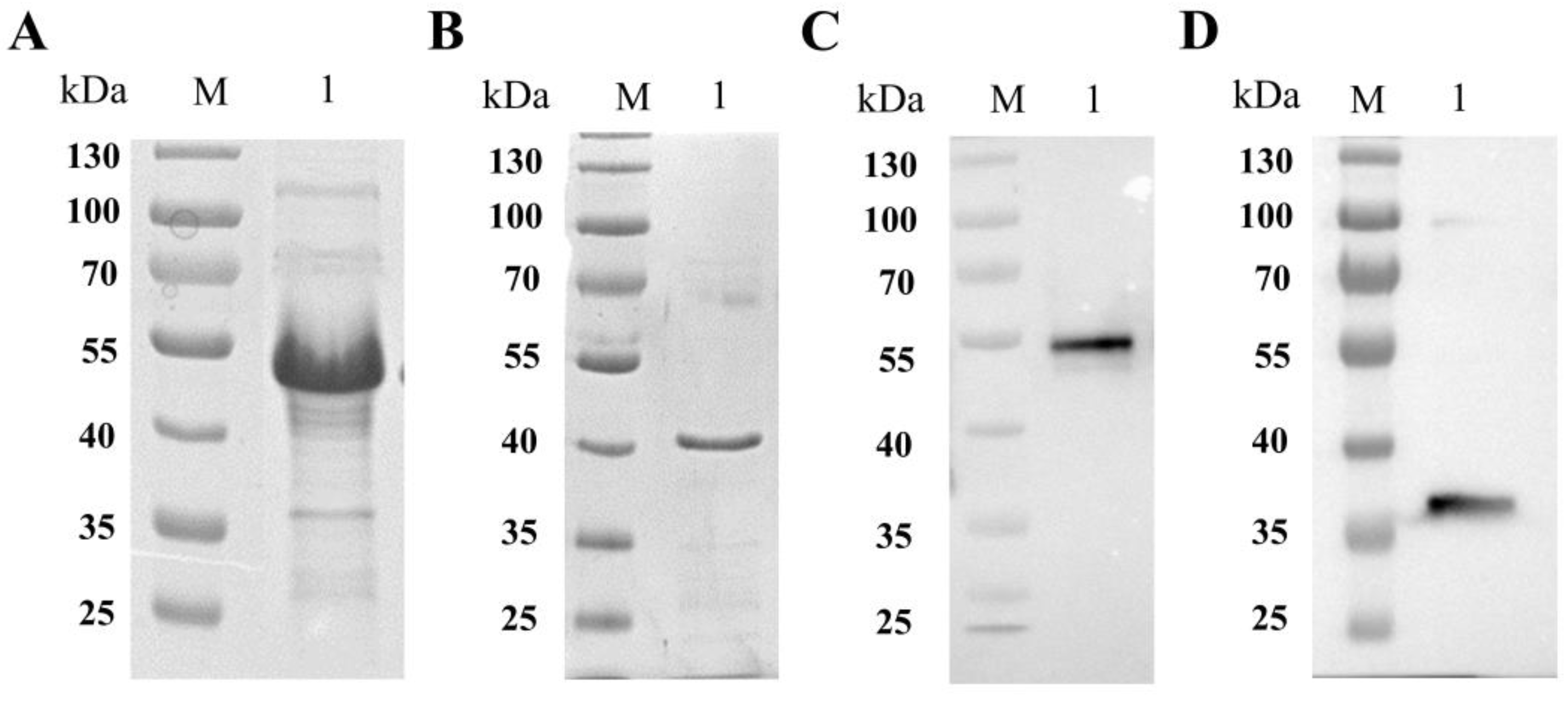
3.2. Preparation of Polyclonal Antibody of Recombinant SABP1 and SAG1 Proteins Expressed by E. coli
3.3. Expression of pVAX1-SABP1 and pVAX1–SAG1 in HEK293T Cells
3.4. Combined DNA Vaccines Induced Mice to Produce Higher Levels of IgG and Subtype IgG1, IgG2a Abs
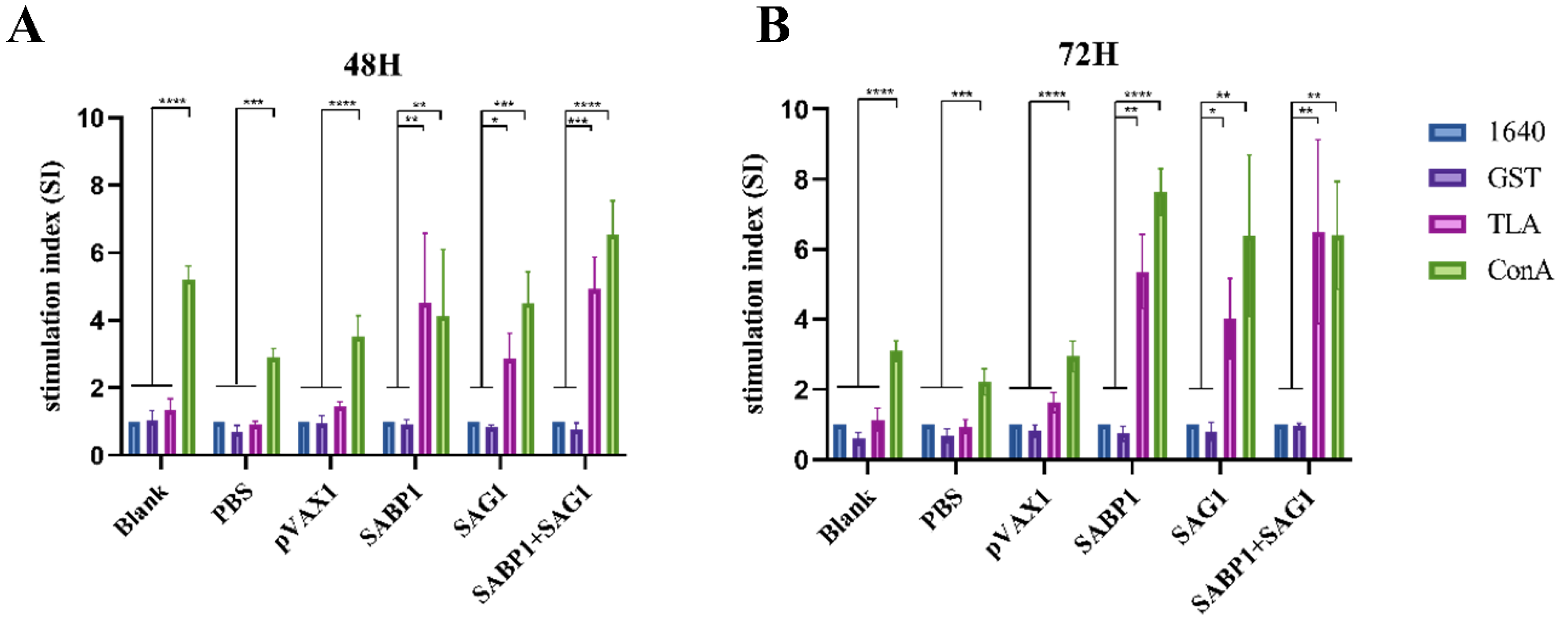
3.5. Splenocyte Proliferation
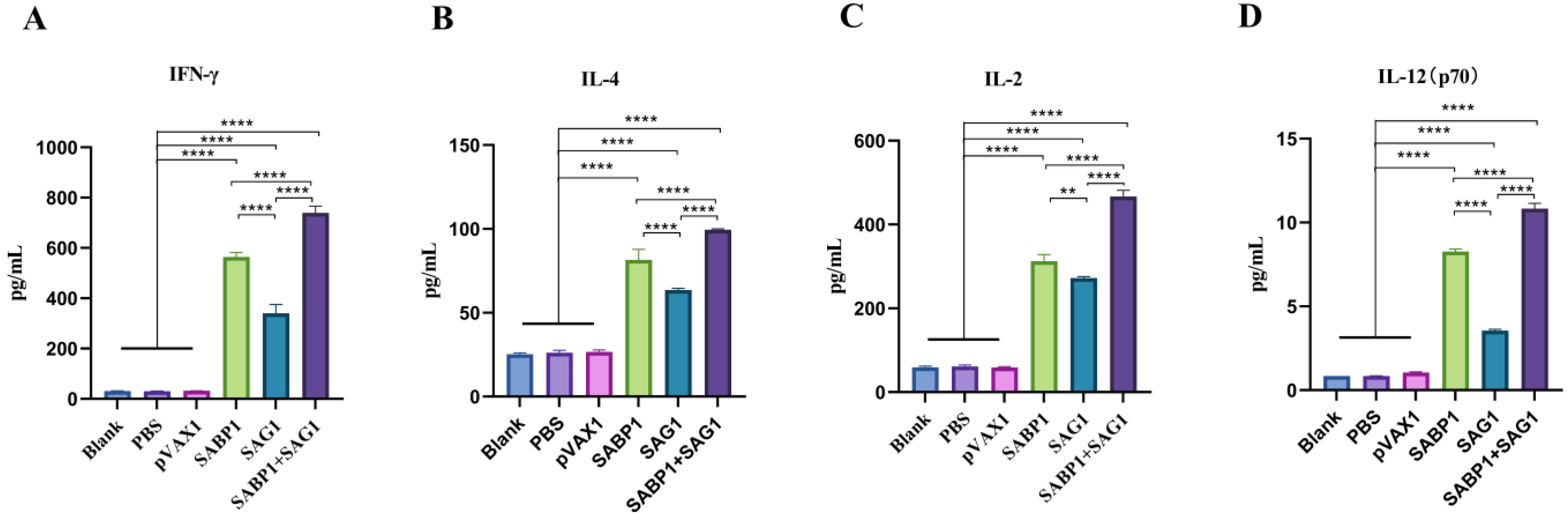
3.6. Th1 Cytokines (IFN-γ, IL-12p70, IL-2) and Th2 Cytokines (IL-4) Significantly Increased Levels in Combined Immunized Mice
3.7. Combined DNA Vaccines Immunization Effectively Prolonged the Survival Time of T. gondii-Infected Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hakimi, M.A.; Olias, P.; Sibley, L.D. Toxoplasma Effectors Targeting Host Signaling and Transcription. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 615–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molan, A.; Nosaka, K.; Hunter, M.; Wang, W. Global status of Toxoplasma gondii infection: Systematic review and prevalence snapshots. Trop. Biomed. 2019, 36, 898–925. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Cheng, H.W.; Huang, K.Q.; Xu, Y.H.; Li, Y.N.; Du, J.; Yu, L.; Luo, Q.L.; Wei, W.; Jiang, L.; et al. Toxoplasma gondii prevalence in food animals and rodents in different regions of China: Isolation, genotyping and mouse pathogenicity. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Elsheikha, H.M.; Marra, C.M.; Zhu, X.Q. Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management of Cerebral Toxoplasmosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 34, e00115-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flegr, J.; Prandota, J.; Sovickova, M.; Israili, Z.H. Toxoplasmosis—A global threat. Correlation of latent toxoplasmosis with specific disease burden in a set of 88 countries. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, M.; Petersen, E.; Zhu, X.Q. Vaccines against Toxoplasma gondii: New developments and perspectives. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2013, 12, 1287–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Zhang, N.Z.; Li, T.T.; He, J.J.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Zhu, X.Q. Advances in the Development of Anti-Toxoplasma gondii Vaccines: Challenges, Opportunities, and Perspectives. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jongert, E.; Roberts, C.W.; Gargano, N.; Forster-Waldl, E.; Petersen, E. Vaccines against Toxoplasma gondii: Challenges and opportunities. Memórias Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2009, 104, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrells, A.; Benavides, J.; Canton, G.; Garcia, J.L.; Bartley, P.M.; Nath, M.; Thomson, J.; Chianini, F.; Innes, E.A.; Katzer, F. Vaccination of pigs with the S48 strain of Toxoplasma gondii—Safer meat for human consumption. Vet. Res. 2015, 46, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Z.Y.; Petersen, E.; Huang, S.Y.; Zhou, D.H.; Zhu, X.Q. DNA vaccination with genes encoding Toxoplasma gondii antigens ROP5 and GRA15 induces protective immunity against toxoplasmosis in Kunming mice. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2015, 14, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, D.H.; Li, Z.Y.; Petersen, E.; Huang, S.Y.; Song, H.Q.; Zhu, X.Q. Toxoplasma gondii: Protective immunity induced by rhoptry protein 9 (TgROP9) against acute toxoplasmosis. Exp. Parasitol. 2014, 139, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, J.Q.; Huang, S.; Ye, W.; Fan, X.Y.; Huang, R.; Ye, S.C.; Yu, C.Y.; Wu, W.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, W.; et al. Evaluation of Protective Immune Response Induced by a DNA Vaccine Encoding GRA8 against Acute Toxoplasmosis in a Murine Model. Korean J. Parasitol. 2018, 56, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Q.; Fang, R.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Li, Y.; Fang, K.; Khan, M.K.; Hu, M.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Protective immunity induced by a DNA vaccine-encoding Toxoplasma gondii microneme protein 11 against acute toxoplasmosis in BALB/c mice. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 2871–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, N.Z.; Tan, Q.D.; Chen, J.; Lu, J.; Xu, Q.M.; Zhu, X.Q. Evaluation of immuno-efficacy of a novel DNA vaccine encoding Toxoplasma gondii rhoptry protein 38 (TgROP38) against chronic toxoplasmosis in a murine model. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Lou, D.; Ding, J.; Zhuo, X.; Ding, H.; Kong, Q.; Lu, S. GRA24-Based DNA Vaccine Prolongs Survival in Mice Challenged with a Virulent Toxoplasma gondii Strain. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.N.; Wang, J.L.; Chen, K.; Yue, D.M.; Zhang, X.X.; Huang, S.Y.; Zhu, X.Q. Evaluation of protective immunity induced by DNA vaccination with genes encoding Toxoplasma gondii GRA17 and GRA23 against acute toxoplasmosis in mice. Exp. Parasitol. 2017, 179, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Hong, L.; Zhou, C.; Chen, J. Immunization with a DNA Vaccine Encoding the Toxoplasma gondii’s GRA39 Prolongs Survival and Reduce Brain Cyst Formation in a Murine Model. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 630682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.C.; Ma, L.J.; Zhang, J.L.; Liu, J.F.; He, Y.; Feng, J.Y.; Chen, J. Protective Immunity Induced by TgMIC5 and TgMIC16 DNA Vaccines Against Toxoplasmosis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 686004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.A. DNA vaccines: An historical perspective and view to the future. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 239, 62–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulveda, P.; Hontebeyrie, M.; Liegeard, P.; Mascilli, A.; Norris, K.A. DNA-Based immunization with Trypanosoma cruzi complement regulatory protein elicits complement lytic antibodies and confers protection against Trypanosoma cruzi infection. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 4986–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, R.; Feng, H.; Hu, M.; Khan, M.K.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, J. Evaluation of immune responses induced by SAG1 and MIC3 vaccine cocktails against Toxoplasma gondii. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 187, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoseinian Khosroshahi, K.; Ghaffarifar, F.; D’Souza, S.; Sharifi, Z.; Dalimi, A. Evaluation of the immune response induced by DNA vaccine cocktail expressing complete SAG1 and ROP2 genes against toxoplasmosis. Vaccine 2011, 29, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Oledzka, G.; McFarlane, R.G.; Spellerberg, M.B.; Smith, S.M.; Gelder, F.B.; Kur, J.; Stankiewicz, M. Immunological response of sheep to injections of plasmids encoding Toxoplasma gondii SAG1 and ROP1 genes. Parasite Immunol. 2010, 32, 671–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobati, H.; Dalimi, A.; Kazemi, B.; Ghaffarifar, F. Evaluation of Anti-Toxoplasma gondii Immune Responses in BALB/c Mice Induced by DNA Vaccines Encoding Surface Antigen 1 (SAG1) and 3 (SAG3). Mol. Genet. Microbiol. Virol. 2019, 34, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, J.; Xiao, T.; Huang, X.D.; Wang, L.J.; Huang, B.C.; Yin, K.; Liu, G.Z.; Xu, C.; Wei, Q.K. Protective immunity induced by a DNA vaccine cocktail expressing TgSAG1, TgROP2, and the genetic adjuvant HBsAg against Toxoplasma gondii infection. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 147, 104441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Yu, X.; He, Y.; Chen, S. A Novel Combined DNA Vaccine Encoding Toxoplasma gondii SAG1 and ROP18 Provokes Protective Immunity Against a Lethal Challenge in Mice. Acta Parasitol. 2021, 66, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; Yang, N.; Jiang, N.; Wang, D.; Chen, Q. A sialic acid-binding protein SABP1 facilitated host cell attachment and invasion by Toxoplasma gondii. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Li, G.; Chen, W.; Jia, Z.; Yang, X.; Pan, X.; Ma, D. Eimeria tenella: IMP1 protein delivered by Lactococcus lactis induces immune responses against homologous challenge in chickens. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 289, 109320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Lei, T.; Yang, D.; Hao, P.; Li, B.; Liu, Q. Toxoplasma gondii immune mapped protein-1 (TgIMP1) is a novel vaccine candidate against toxoplasmosis. Vaccine 2012, 30, 2282–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iván, P.-F.; Sungwon, K.; Virginia, M.-H.; Francesca, S.; Tomley, F.M.; Blake, D.P. Vaccination with transgenic Eimeria tenella expressing Eimeria maxima AMA1 and IMP1 confers partial protection against high-level E. maxima challenge in a broiler model of coccidiosis. Parasites Vectors 2021, 13, 343. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; Benjamin, S.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Y.; Soldati-Favre, D. Toxoplasma gondii immune mapped protein 1 is anchored to the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane and adopts a novel protein fold. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1865, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, H. Moving towards improved vaccines for Toxoplasma gondii. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2018, 18, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, G.; Lin, Q.; Qiu, J.; Qin, M.; Tang, X.; Suo, X.; Huang, Z.; Liu, X. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of an Eimeria vaccine candidate based on Eimeria tenella immune mapped protein 1 and chicken CD40 ligand. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 210, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, G.; Lin, Q.; Wei, W.; Qin, M.; Huang, Z. Protective immunity against Eimeria tenella infection in chickens induced by immunization with a recombinant C-terminal derivative of EtIMP1. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2014, 162, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Qin, M.; Liu, X.; Suo, J.; Wu, W. An Eimeria vaccine candidate based on Eimeria tenella immune mapped protein 1 and the TLR-5 agonist Salmonella typhimurium FliC flagellin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 440, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Mei, M.; Zhang, X.; Han, F.; Jia, B.; Wei, X.; Chang, Z.; Lu, H.; Yin, J.; Chen, Q.; et al. The extracellular matrix protein mindin as a novel adjuvant elicits stronger immune responses for rBAG1, rSRS4 and rSRS9 antigens of Toxoplasma gondii in BALB/c mice. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert-Gangneux, F.; Darde, M.L. Epidemiology of and diagnostic strategies for toxoplasmosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 264–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayles, P.C.; Gibson, G.W.; Johnson, L.L. B cells are essential for vaccination-induced resistance to virulent Toxoplasma gondii. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, C.A.; Sibley, L.D. Modulation of innate immunity by Toxoplasma gondii virulence effectors. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 766–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pifer, R.; Yarovinsky, F. Innate responses to Toxoplasma gondii in mice and humans. Trends Parasitol. 2011, 27, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigley, J.P.; Fox, B.A.; Bzik, D.J. Cell-mediated immunity to Toxoplasma gondii develops primarily by local Th1 host immune responses in the absence of parasite replication. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 1069–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Ding, J.; Chen, X.; Yu, H.; Lou, D.; Tong, Q.; Kong, Q.; Lu, S. Immuno-Efficacy of a T. gondii Secreted Protein with an Altered Thrombospondin Repeat (TgSPATR) As a Novel DNA Vaccine Candidate against Acute Toxoplasmosis in BALB/c Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, L. SAG4 DNA and Peptide Vaccination Provides Partial Protection against T. gondii Infection in BALB/c Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, N.M.; Vieira, J.C.; Carneiro, C.M.; Tafuri, W.L. Toxoplasma gondii: The role of IFN-gamma, TNFRp55 and iNOS in inflammatory changes during infection. Exp. Parasitol. 2009, 123, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont, C.D.; Christian, D.A.; Hunter, C.A. Immune response and immunopathology during toxoplasmosis. Semin. Immunopathol. 2012, 34, 793–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, U.; Klamp, T.; Groot, M.; Howard, J.C. Cellular responses to interferon-gamma. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1997, 15, 749–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, C.M.; Boulter, N.R.; Ikin, R.J.; Smith, N.C. The immunobiology of the innate response to Toxoplasma gondii. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeij, J.P.; Frickel, E.M. Exposing Toxoplasma gondii hiding inside the vacuole: A role for GBPs, autophagy and host cell death. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2017, 40, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, G.R.; Stanford, M.R. Immunity and Toxoplasma retinochoroiditis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 153, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matowicka-Karna, J.; Dymicka-Piekarska, V.; Kemona, H. Does Toxoplasma gondii infection affect the levels of IgE and cytokines (IL-5, IL-6, IL-10, IL-12, and TNF-alpha)? Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2009, 2009, 374696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRosa, D.F.; Stumhofer, J.S.; Gelman, A.E.; Rahman, A.H.; Taylor, D.K.; Hunter, C.A.; Turka, L.A. T cell expression of MyD88 is required for resistance to Toxoplasma gondii. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3855–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
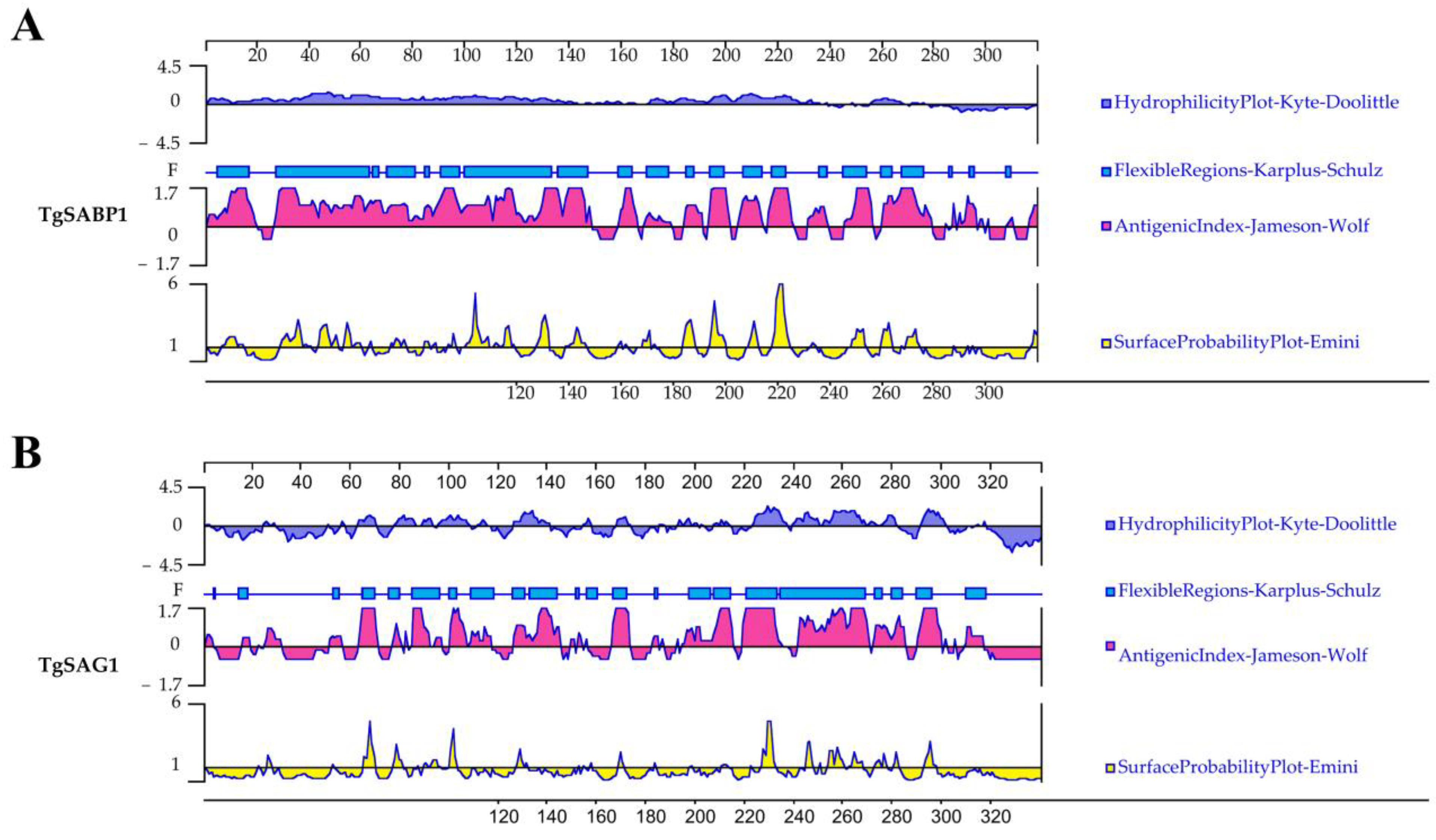


| MHC II Allele 1 | Start-Stop 2 | Percentile Rank 3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAG1 | SABP1 | SAG1 | SABP1 | |
| H2-IAb | 26–40 | 33–47 | 0.95 | 1.7 |
| H2-IAd | 20–34 | 20–34 | 2.75 | 9.55 |
| H2-IEd | 14–28 | 10–24 | 3.35 | 0.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sang, X.; Li, X.; Chen, R.; Feng, Y.; He, T.; Zhang, X.; El-Ashram, S.; Al-Olayan, E.; Yang, N. Co-Immunization with DNA Vaccines Expressing SABP1 and SAG1 Proteins Effectively Enhanced Mice Resistance to Toxoplasma gondii Acute Infection. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11071190
Sang X, Li X, Chen R, Feng Y, He T, Zhang X, El-Ashram S, Al-Olayan E, Yang N. Co-Immunization with DNA Vaccines Expressing SABP1 and SAG1 Proteins Effectively Enhanced Mice Resistance to Toxoplasma gondii Acute Infection. Vaccines. 2023; 11(7):1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11071190
Chicago/Turabian StyleSang, Xiaoyu, Xiang Li, Ran Chen, Ying Feng, Ting He, Xiaohan Zhang, Saeed El-Ashram, Ebtsam Al-Olayan, and Na Yang. 2023. "Co-Immunization with DNA Vaccines Expressing SABP1 and SAG1 Proteins Effectively Enhanced Mice Resistance to Toxoplasma gondii Acute Infection" Vaccines 11, no. 7: 1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11071190
APA StyleSang, X., Li, X., Chen, R., Feng, Y., He, T., Zhang, X., El-Ashram, S., Al-Olayan, E., & Yang, N. (2023). Co-Immunization with DNA Vaccines Expressing SABP1 and SAG1 Proteins Effectively Enhanced Mice Resistance to Toxoplasma gondii Acute Infection. Vaccines, 11(7), 1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11071190







