Exosomes as Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnostic Biomarkers and Therapeutic Agents
Abstract
1. Introduction
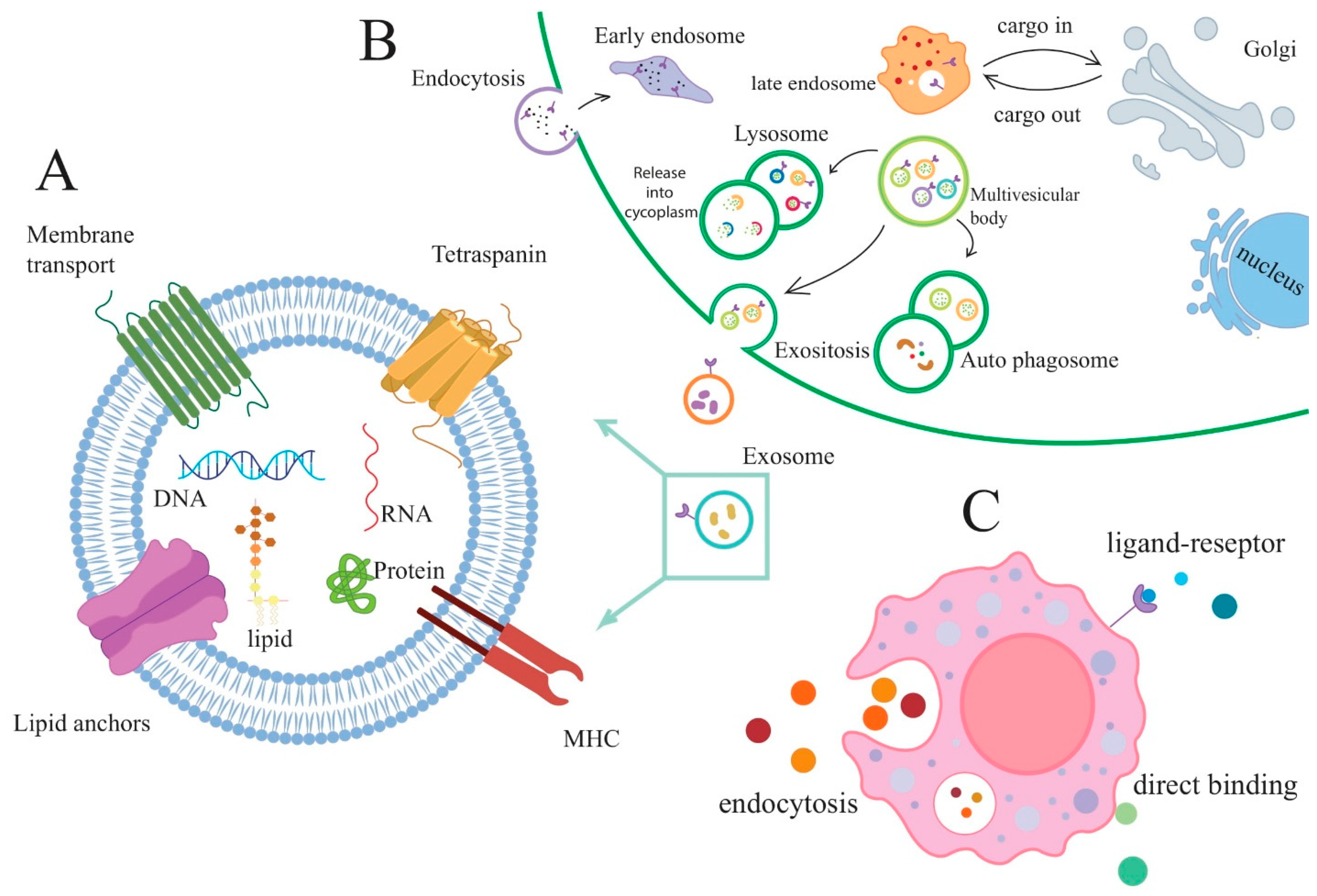
2. Exosomes
3. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes
4. Exosomes as a Biomarker for RA Diagnostic
5. The Therapeutic Ability of Exosomes in RA Treatment
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, L.; Kan, L. Mesenchymal Stem Cell–Originated Exosomal Circular RNA circFBXW7 Attenuates Cell Proliferation, Migration and Inflammation of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes by Targeting miR-216a-3p/HDAC4 in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Fang, Y.; Rao, Y.; Tan, W.; Zhou, W.; Wu, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sunagawa, M.; et al. Synovial fibroblast-derived exosomal microRNA-106b suppresses chondrocyte proliferation and migration in rheumatoid arthritis via down-regulation of PDK4. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 98, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, Y.; Fang, Y.; Tan, W.; Liu, D.; Pang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, G. Delivery of long non-coding RNA NEAT1 by peripheral blood monouclear cells-derived exosomes promotes the occurrence of rheumatoid arthritis via the MicroRNA-23a/MDM2/SIRT6 axis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 551681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, D.G.; Lim, G.T.; Kwon, S.; Um, W.; Oh, B.H.; Song, S.H.; Lee, J.; Jo, D.G.; Cho, Y.W.; Park, J.H. Metabolically engineered stem cell–derived exosomes to regulate macrophage heterogeneity in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe0083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavasolian, F.; Moghaddam, A.S.; Rohani, F.; Abdollahi, E.; Janzamin, E.; Momtazi-Borojeni, A.A.; Moallem, S.A.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Sahebkar, A. Exosomes: Effectual players in rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, A.; Kato, Y.; Higa, S.; Yoshizaki, K. IL-6 inhibitor for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive review. Mod. Rheumatol. 2019, 29, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.-H.; Wu, C.-S.; Chiou, S.-H.; Chang, C.-H.; Liao, H.-J. Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Exosomes as a Novel Anti-Inflammatory Agent and the Current Therapeutic Targets for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamani, P.; Fereydouni, N.; Butler, A.E.; Navashenaq, J.G.; Sahebkar, A. The therapeutic and diagnostic role of exosomes in cardiovascular diseases. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 29, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanjani, N.A.; Esmaelizad, N.; Zanganeh, S.; Gharavi, A.T.; Heidarizadeh, P.; Radfar, M.; Omidi, F.; MacLoughlin, R.; Doroudian, M. Emerging role of exosomes as biomarkers in cancer treatment and diagnosis. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2022, 169, 103565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahand, J.S.; Vandchali, N.R.; Darabi, H.; Doroudian, M.; Banafshe, H.R.; Moghoofei, M.; Babaei, F.; Salmaninejad, A.; Mirzaei, H. Exosomal microRNAs: Novel players in cervical cancer. Epigenomics 2020, 12, 1651–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Jang, H.; Cho, H.; Choi, J.; Hwang, K.Y.; Choi, Y.; Kim, S.H.; Yang, Y. Recent Advances in Exosome-Based Drug Delivery for Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.G.N.; Kang, J.H.; You, J.Y.; Kang, H.C.; Rhee, W.J.; Ko, Y.T.; Shim, M.S. Safe and Targeted Sonodynamic Cancer Therapy Using Biocompatible Exosome-Based Nanosonosensitizers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 25575–25588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharavi, A.T.; Hanjani, N.A.; Movahed, E.; Doroudian, M. The role of macrophage subtypes and exosomes in immunomodulation. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2022, 27, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, M. Role of exosomes in the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of central nervous system diseases. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, K.; Xiang, S.; Li, Z.; Weng, X. Emerging Role of Exosomes in the Joint Diseases. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 2008–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejrati, A.; Hasani, B.; Esmaili, M.; Bashash, D.; Tavakolinia, N.; Zafari, P. Role of exosome in autoimmunity, with a particular emphasis on rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 24, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, X.-Y.; Zhou, P.-J.; He, Z.; Yan, H.-Z.; Xu, D.-D.; Wang, Y.; Fu, W.-Y.; Ruan, B.-B.; Wang, S.; et al. Use of immune modulation by human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells to treat experimental arthritis in mice. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 2595. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Zhu, L.; In, I.I.; Chen, Y.; Jia, N.; Zhu, W. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells-secreted exosomal microRNA-192-5p delays inflammatory response in rheumatoid arthritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 78, 105985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehbidi, M.Y.; Goodarzi, N.; Azhdari, M.H.; Doroudian, M. Mesenchymal stem cells and their derived exosomes to combat Covid–19. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, 32, e2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasempour, E.; Hesami, S.; Movahed, E.; Keshel, S.H.; Doroudian, M. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a new therapeutic strategy in the brain tumors. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaseelan, V.P.; Arumugam, P. Dissecting the theranostic potential of exosomes in autoimmune disorders. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 16, 935–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Zhang, W.; Jia, J.; Lu, Q.; Eric Gershwin, M. Exosomal microRNA in autoimmunity. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 16, 932–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakeri, Z.; Salmaninejad, A.; Hosseini, N.; Shahbakhsh, Y.; Fadaee, E.; Shahrzad, M.K.; Fadaei, S. MicroRNA and exosome: Key players in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 10930–10944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raju, D.; Bathini, S.; Badilescu, S.; Ghosh, A.; Packirisamy, M. Microfluidic Platforms for the Isolation and Detection of Exosomes: A Brief Review. Micromachines 2022, 13, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Anderson, J.D.; Rahnama, L.M.; Gu, S.V.; Knowlton, A.A. Exosomes in disease and regeneration: Biological functions, diagnostics, and beneficial effects. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2020, 319, H1162–H1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhdari, M.H.; Goodarzi, N.; Doroudian, M.; MacLoughlin, R. Molecular Insight into the Therapeutic Effects of Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in Respiratory Diseases and the Potential for Pulmonary Delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikfarjam, S.; Rezaie, J.; Zolbanin, N.M.; Jafari, R. Mesenchymal stem cell derived-exosomes: A modern approach in translational medicine. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrazzo, P.; Crupi, A.N.; Alviano, F.; Teodori, L.; Bonsi, L. Exploring the roles of MSCs in infections: Focus on bacterial diseases. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 97, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Jin, S.; Ding, C.; Wang, Y.; He, D.; Liu, Y. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosome Therapy of Microbial Diseases: From Bench to Bed. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrazzo, P.; Pizzuti, V.; Zia, S.; Sargenti, A.; Gazzola, D.; Roda, B.; Bonsi, L.; Alviano, F. Microfluidic Tools for Enhanced Characterization of Therapeutic Stem Cells and Prediction of Their Potential Antimicrobial Secretome. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Yang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Denslin, V.; Yu, C.C.; Tee, C.A.; Lim, C.T.; Han, J.; Lee, E.H. Label-free separation of mesenchymal stem cell subpopulations with distinct differentiation potencies and paracrine effects. Biomaterials 2020, 240, 119881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolini, A.; Ferrari, P.; Biava, P. Exosomes and Cell Communication: From Tumour-Derived Exosomes and Their Role in Tumour Progression to the Use of Exosomal Cargo for Cancer Treatment. Cancers 2021, 13, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, M.; Martin-Jaular, L.; Lavieu, G.; Théry, C. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluchino, S.; Smith, J.A. Explicating Exosomes: Reclassifying the Rising Stars of Intercellular Communication. Cell 2019, 177, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsherbini, A.; Bieberich, E. Ceramide and Exosomes: A Novel Target in Cancer Biology and Therapy. Adv. Cancer Res. 2018, 140, 121–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashouri, L.; Yousefi, H.; Aref, A.R.; Ahadi, A.M.; Molaei, F.; Alahari, S.K. Exosomes: Composition, biogenesis, and mechanisms in cancer metastasis and drug resistance. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wei, W.; Liu, M.-L. Extracellular vesicles in autoimmune vasculitis—Little dirts light the fire in blood vessels. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Console, L.; Scalise, M.; Indiveri, C. Exosomes in inflammation and role as biomarkers. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 488, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Z.; Zhou, S.; Li, S.; Kuang, L.; Chen, H.; Luo, X.; Ouyang, J.; He, M.; Du, X.; Chen, L. Exosomes: Roles and therapeutic potential in osteoarthritis. Bone Res. 2020, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, A.G.; Shah, K.; Cromer, B.; Sumer, H. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Their Therapeutic Potential. Stem Cells Int. 2020, 2020, 8825771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosenza, S.; Ruiz, M.; Maumus, M.; Jorgensen, C.; Noël, D. Pathogenic or Therapeutic Extracellular Vesicles in Rheumatic Diseases: Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Vesicles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshtkar, S.; Azarpira, N.; Ghahremani, M.H. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: Novel frontiers in regenerative medicine. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tu, H.; Yang, Y.; Fang, L.; Wu, Q.; Li, J. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Roles in Tumor Growth, Progression, and Drug Resistance. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 175839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Z.; Qian, Y.; Wang, G.; Duan, M.; Zhao, H.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, X. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome: A tumor regulator and carrier for targeted tumor therapy. Cancer Lett. 2022, 526, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Fang, J.; Chen, M.; Xu, Y.; Chen, X. Mesenchymal stem cells as a double-edged sword in tumor growth: Focusing on MSC-derived cytokines. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2021, 26, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado-Díaz, A.; Quesada-Gómez, J.M.; Dorado, G. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSC) in Regenerative Medicine: Applications in Skin Wound Healing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varderidou-Minasian, S.; Lorenowicz, M.J. Mesenchymal stromal/stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in tissue repair: Challenges and opportunities. Theranostics 2020, 10, 5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, H.; Canciani, E.; Raineri, D.; Cappellano, G.; Rimondini, L.; Chiocchetti, A. Extracellular Vesicles in Musculoskeletal Regeneration: Modulating the Therapy of the Future. Cells 2021, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez-Mó, M.; Siljander, P.R.-M.; Andreu, Z.; Bedina Zavec, A.; Borràs, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J.; et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Choi, D.-Y.; Yun, S.J.; Choi, S.-M.; Kang, J.W.; Jung, J.W.; Hwang, D.; Kim, K.P.; Kim, D.-W. Proteomic Analysis of Microvesicles Derived from Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, T.; Sánchez-Abarca, L.I.; Muntión, S.; Preciado, S.; Puig, N.; López-Ruano, G.; Hernández-Hernández, Á.; Redondo, A.; Ortega, R.; Rodríguez, C. MSC surface markers (CD44, CD73, and CD90) can identify human MSC-derived extracellular vesicles by conventional flow cytometry. Cell Commun. Signal. 2016, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopatina, T.; Gai, C.; Deregibus, M.C.; Kholia, S.; Camussi, G. Cross talk between cancer and mesenchymal stem cells through extracellular vesicles carrying nucleic acids. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, S.; Grange, C.; Deregibus, M.C.; Calogero, R.A.; Saviozzi, S.; Collino, F.; Morando, L.; Busca, A.; Falda, M.; Bussolati, B.; et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Microvesicles Protect against Acute Tubular Injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 1053–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, R.C.; Tan, S.S.; Teh, B.J.; Sze, S.K.; Arslan, F.; De Kleijn, D.P.; Choo, A.; Lim, S.K. Proteolytic Potential of the MSC Exosome Proteome: Implications for an Exosome-Mediated Delivery of Therapeutic Proteasome. Int. J. Proteom. 2012, 2012, 971907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, H.; Sahebkar, A.; Jaafari, M.R.; Goodarzi, M.; Mirzaei, H.R. Diagnostic and therapeutic potential of exosomes in cancer: The beginning of a new tale? J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 3251–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barile, L.; Vassalli, G. Exosomes: Therapy delivery tools and biomarkers of diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 174, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xia, W.; Lv, Z.; Xin, Y.; Ni, C.; Yang, L. Liquid biopsy for cancer: Circulating tumor cells, circulating free DNA or exosomes? Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 41, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, S.; Hilton, H.; Burczynski, M.E. The multifaceted exosome: Biogenesis, role in normal and aberrant cellular function, and frontiers for pharmacological and biomarker opportunities. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 1484–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, M.; Raposo, G. Exosomes—Vesicular carriers for intercellular communication. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009, 21, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Wu, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Li, D.; Lu, Q. Recent advances of exosomes in immune modulation and autoimmune diseases. Autoimmunity 2016, 49, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, B.; Merriman, M.E.; Harrison, A.; Nissen, M.J.; Smith, M.; Stamp, L.; Steer, S.; Merriman, T.; Vyse, T.J. A Genetic Association Study of Serum Acute-Phase C-Reactive Protein Levels in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Implications for Clinical Interpretation. PLoS Med. 2010, 7, e1000341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.; Lee, S.K.; Lim, M.; Sheen, D.; Choi, E.-H.; Kim, S.A. Exosomal amyloid A and lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronic acid receptor-1 proteins are associated with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 19, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Kim, D.; Han, J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, M.; Jin, E.-J. PBMC and exosome-derived Hotair is a critical regulator and potent marker for rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 15, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buch, M.H.; Seto, Y.; Bingham, S.J.; Bejarano, V.; Bryer, D.; White, J.; Emery, P. C-reactive protein as a predictor of infliximab treatment outcome in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Defining subtypes of nonresponse and subsequent response to etanercept. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun-Moscovici, Y.; Markovits, D.; Zinder, O.; Schapira, D.; Rozin, A.; Ehrenburg, M.; Sagi-Dain, L.; Hoffer, E.; Nahir, A.M.; Balbir-Gurman, A. Anti-cyclic citrullinated protein antibodies as a predictor of response to anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2006, 33, 497–500. [Google Scholar]
- Meissner, B.; Trivedi, D.; You, M.; Rosenblatt, L. Switching of biologic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in a real world setting. J. Med. Econ. 2014, 17, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hood, J.L. Post isolation modification of exosomes for nanomedicine applications. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 1745–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancho-Albero, M.; Navascués, N.; Mendoza, G.; Sebastián, V.; Arruebo, M.; Martín-Duque, P.; Santamaría, J. Exosome origin determines cell targeting and the transfer of therapeutic nanoparticles towards target cells. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 17, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Tong, Z.; Sun, S.; Mao, Z. Enhancement of tumour penetration by nanomedicines through strategies based on transport processes and barriers. J. Control. Release 2020, 328, 28–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meldolesi, J. Exosomes and Ectosomes in Intercellular Communication. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R435–R444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liang, Y.; Li, X.; Ouyang, K.; Wang, M.; Cao, T.; Li, W.; Liu, J.; Xiong, J.; Li, B.; et al. Exosome-mediated delivery of kartogenin for chondrogenesis of synovial fluid-derived mesenchymal stem cells and cartilage regeneration. Biomaterials 2021, 269, 120539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nooshabadi, V.T.; Mardpour, S.; Yousefi-Ahmadipour, A.; Allahverdi, A.; Izadpanah, M.; Daneshimehr, F.; Ai, J.; Banafshe, H.R.; Ebrahimi-Barough, S. The extracellular vesicles-derived from mesenchymal stromal cells: A new therapeutic option in regenerative medicine. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 8048–8073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Teo, K.Y.W.; Chuah, S.J.; Lai, R.C.; Lim, S.K.; Toh, W.S. MSC exosomes alleviate temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis by attenuating inflammation and restoring matrix homeostasis. Biomaterials 2019, 200, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Ma, D.; Zhang, G.; Gao, J.; Su, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Han, J.; Tian, M.; Wei, C.; et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles ameliorate collagen-induced arthritis via immunomodulatory T lymphocytes. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 135, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujimaru, K.; Takanashi, M.; Sudo, K.; Ishikawa, A.; Mineo, S.; Ueda, S.; Kumagai, K.; Kuroda, M. Extracellular microvesicles that originated adipose tissue derived mesenchymal stem cells have the potential ability to improve rheumatoid arthritis on mice. Regen. Ther. 2020, 15, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Xu, K.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Y.; Gao, J.; Tian, M.; Wei, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, L. Immunomodulatory effect of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on T lymphocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 74, 105687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.-Q.; Fang, Y.-X.; Liu, Y.; Meng, F.-R.; Wu, X.; Zhang, C.-W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Liu, D. MicroRNA-21 from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles targets TET1 to suppress KLF4 and alleviate rheumatoid arthritis. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2021, 12, 20406223211007369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Xia, Y.; Yan, F.; Lu, Y. Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Cell–Derived miRNA-150-5p–Expressing Exosomes in Rheumatoid Arthritis Mediated by the Modulation of MMP14 and VEGF. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 2472–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Qiu, B. Exosomal MicroRNA-320a Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Regulates Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-Like Synoviocyte Activation by Suppressing CXCL9 Expression. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.-Y.; Chen, L.-Q. The inhibition by human MSCs-derived miRNA-124a overexpression exosomes in the proliferation and migration of rheumatoid arthritis-related fibroblast-like synoviocyte cell. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2020, 21, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosenza, S.; Toupet, K.; Maumus, M.; Luz-Crawford, P.; Blanc-Brude, O.; Jorgensen, C.; Noël, D. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes are more immunosuppressive than microparticles in inflammatory arthritis. Theranostics 2018, 8, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Cheng, W.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Luo, B.; Huang, W.; Gu, J. miR-34a in extracellular vesicles from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells reduces rheumatoid arthritis inflammation via the cyclin I/ATM/ATR/p53 axis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 1896–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Headland, S.E.; Jones, H.R.; Norling, L.V.; Kim, A.; Souza, P.R.; Corsiero, E.; Gil, C.D.; Nerviani, A.; Dell’Accio, F.; Pitzalis, C.; et al. Neutrophil-derived microvesicles enter cartilage and protect the joint in inflammatory arthritis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 315ra190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Zhu, D.; Tian, J.; Tang, X.; Guo, H.; Ma, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, S. Granulocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cell Exosomal Prostaglandin E2 Ameliorates Collagen-Induced Arthritis by Enhancing IL-10+ B Cells. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 588500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Xu, K.; Zhang, G.; Han, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L. FRI0510 the effect and mechanism of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on bone destruction of collagen induced arthritis rats. BMJ 2019, 78, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, R.; Liu, T.; Yang, L.; Yin, G.; Xie, Q. Immunomodulatory Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, C.; Guan, C.; Ma, X.; Meng, S. Mesenchymal stem cell-originated exosomal lncRNA HAND2-AS1 impairs rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocyte activation through miR-143-3p/TNFAIP3/NF-κB pathway. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2021, 16, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharlooi, H.; Azimi, M.; Salehi, Z.; Izad, M. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: A Promising Therapeutic Ace Card to Address Autoimmune Diseases. Int. J. Stem Cells 2020, 13, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, M.; Lu, Q. Dysregulation of microRNAs in autoimmune diseases: Pathogenesis, biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets. Cancer Lett. 2018, 428, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Source | Sub-Type Factor | Study Model | Biological Effects | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hUCMSCs | sEVs | CIA rats | Decreasing: immunomodulatory effect of T lymphocytes Synovial hyperplasia, synovial inflammatory cell infiltration, paw oedema and arthritis index | [75] |
| AMSCs | MVs | IL-1Ra−/− mouse BALB/c mouse | Decreasing: IL-1Ra contained in EVs transferred IL-1β, IFN-γ, and TNF-α in serum, synovial hyperplasia and pannus formation, thickness of joints of paws | [76] |
| hUCMSCs | EVs | normal group rats CIA rat model group | Restoring the balance of Treg/Th17 inside the spleen, regulating the expression of RORγt and Foxp3 inside joints, inhibiting IL-17, and enhancing the expression of TGF-β in the serum, consequently improves arthritis | [77] |
| BMSCs | miR-21 | BALB/c mice CIA mice | Promoting mFLS cell proliferation and suppressing inflammatory cytokine secretion by targeting the TET1/KLF4 regulatory axis, thereby miR-21 reduces RA progression | [78] |
| BMSC Wistar rats, bone marrow Mouse bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells | miR-192-5p | CIA rat | Reduction of RAC2 expression in synovial tissues. Blocking the inflammatory response by reducing levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokines PGE2, IL-1, TNF-, NO, and iNOS | [18] |
| BMSC DBA/1J mice, bone marrow | miR150-5p | CIA rat | Inhibition of Pro-inflammatory Cytokine-Induced Invasion, Migration, and Tube formation by Targeting and downregulating MMP14, VEGF in FLS. modulate angiogenesis | [79] |
| BMSC RA patients, bone marrow | miR-320a | CIA mouse | Inhibition of FLS activation, migration, and invasion in RA by targeting CXCL9 expression suppression results in attenuation of arthritis and bone damage. | [80] |
| Human MSCs | miRNA-124a | NR | After co-culture of MSC exosome miR-124a with RA-FLS, it arrested the MH7A cell cycle in G0/G1 phase, reducing wound closure percentage and wound healing rate; Proliferation, invasion, migration, and promoted apoptosis RA-FLS inhibited | [81] |
| BMSCs | EVs MPs Exosomes | DTH Mouse CIA Mouse | The immune-modulating effect in the inflammatory arthritis model by reducing the proliferation of T and B lymphocytes and inducing the Treg cell population, increasing Treg cells, and reducing plasmablast differentiation, thus reducing bone destruction and erosion | [82] |
| BMSCs | SEVs miR-34a | RA rat | Reducing RA inflammation by inhibiting the cyclin I/ATM/ATR/p53 signaling pathway; inhibition of RA-FLS proliferation and resistance to apoptosis in vitro | [83] |
| Human neutrophils | MVs | K/BxN arthritis mouse model | neutrophil-derived AnxA1+ MVs reduced cartilage destruction decreasing | [84] |
| G-MDSCs | sEVs | CIA mouse | The proportion of IL-10 producing B cells by prostaglandinE2 exosomal stimulation c, plasma cells, and follicular helper T cells as well as CIA development in mice decreasing | [85] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heydari, R.; Koohi, F.; Rasouli, M.; Rezaei, K.; Abbasgholinejad, E.; Bekeschus, S.; Doroudian, M. Exosomes as Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnostic Biomarkers and Therapeutic Agents. Vaccines 2023, 11, 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030687
Heydari R, Koohi F, Rasouli M, Rezaei K, Abbasgholinejad E, Bekeschus S, Doroudian M. Exosomes as Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnostic Biomarkers and Therapeutic Agents. Vaccines. 2023; 11(3):687. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030687
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeydari, Romina, Fatemeh Koohi, Milad Rasouli, Kimia Rezaei, Elham Abbasgholinejad, Sander Bekeschus, and Mohammad Doroudian. 2023. "Exosomes as Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnostic Biomarkers and Therapeutic Agents" Vaccines 11, no. 3: 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030687
APA StyleHeydari, R., Koohi, F., Rasouli, M., Rezaei, K., Abbasgholinejad, E., Bekeschus, S., & Doroudian, M. (2023). Exosomes as Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnostic Biomarkers and Therapeutic Agents. Vaccines, 11(3), 687. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030687







