The Effect of Virus-Specific Vaccination on Laboratory Infection Markers of Children with Acute Rotavirus-Associated Acute Gastroenteritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Rotavirus Vaccination
2.5. Laboratory Assessments
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dey, S.K.; Sharif, N.; Sarkar, O.S.; Sarkar, M.K.; Talukder, A.A.; Phan, T.; Ushijima, H. Molecular epidemiology and surveillance of circulating rotavirus among children with gastroenteritis in Bangladesh during 2014–2019. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johne, R.; Schilling-Loeffler, K.; Ulrich, R.G.; Tausch, S.H. Whole Genome Sequence Analysis of a Prototype Strain of the Novel Putative Rotavirus Species L. Viruses 2022, 14, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johne, R.; Tausch, S.H.; Grützke, J.; Falkenhagen, A.; Patzina-Mehling, C.; Beer, M.; Höper, D.; Ulrich, R.G. Distantly Related Rotaviruses in Common Shrews, Germany, 2004–2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 2310–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RCWG Rotavirus Classification Working Group. List of Accepted Genotypes. Laboratory of Viral Metagenomics. Available online: https://rega.kuleuven.be/cev/viralmetagenomics/virus-classification/rcwg (accessed on 2 July 2021).
- Zhao, L.; Shi, X.; Meng, D.; Guo, J.; Li, Y.; Liang, L.; Wang, J. Prevalence and genotype distribution of group A rotavirus circulating in Shanxi Province, China during 2015–2019. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.H.; Pang, B.B.; Chen, N.; Kobayashi, N. Surveillance of Human Rotavirus in Wuhan, China (2011–2019): Predominance of G9P and Emergence of G12. Pathogens 2020, 9, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, H.; Henschke, N.; Hungerford, D.; Pitan, F.; Ndwandwe, D.; Cunliffe, N.; Soares-Weiser, K. Vaccines for preventing rotavirus diarrhoea: Vaccines in use. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 11, CD008521. [Google Scholar]
- Soares-Weiser, K.; Bergman, H.; Henschke, N.; Pitan, F.; Cunliffe, N. Vaccines for preventing rotavirus diarrhoea: Vaccines in use. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 2019, CD008521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuzhakov, A.; Yuzhakova, K.; Kulikova, N.; Kisteneva, L.; Cherepushkin, S.; Smetanina, S.; Grebennikova, T. Prevalence and Genetic Diversity of Group A Rotavirus Genotypes in Moscow (2019–2020). Pathogens 2021, 10, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestari, F.B.; Vongpunsawad, S.; Wanlapakorn, N.; Poovorawan, Y. Rotavirus infection in children in Southeast Asia 2008–2018: Disease burden, genotype distribution, seasonality, and vaccination. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desselberger, U. Differences of Rotavirus Vaccine Effectiveness by Country: Likely Causes and Contributing Factors. Pathogens 2017, 6, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, E.P.; Ramani, S.; Lopman, B.A.; Church, J.A.; Iturriza, M.; Prendergast, A.J.; Grassly, N. Causes of impaired oral vaccine efficacy in developing countries. Future Microbiol. 2018, 13, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Li, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Fei, Y. Decreased Lymphocyte to Monocyte Ratio and Increased Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio Observed in Rotavirus-Positive Acute Gastroenteritis in Children: A Retrospective Study. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2020, 50, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Yang, X.R.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.F.; Sun, C.; Guo, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.M.; Qiu, S.J.; Zhou, J.; et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts prognosis of patients after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 6212–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceyhan, M.; Alhan, E.; Salman, N.; Kurugol, Z.; Yildirim, I.; Celik, U.; Keser, M.; Koturoglu, G.; Tezer, H.; Bulbul, E.K.; et al. Multicenter prospective study on the burden of rotavirus gastroenteritis in Turkey, 2005–2006: A hospital-based study. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 200 (Suppl. 1), S234–S238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, M.M.; Parashar, U.D.; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Prevention of rotavirus gastroenteritis among infants and children: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2009, 58, 1–25, Erratum in: MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2010, 59, 1074.. [Google Scholar]
- Tate, J.E.; Burton, A.H.; Boschi-Pinto, C.; Parashar, U.D.; World Health Organization–Coordinated Global Rotavirus Surveillance Network. Global, Regional, and National Estimates of Rotavirus Mortality in Children <5 Years of Age, 2000–2013. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 62 (Suppl. 2), S96–S105. [Google Scholar]
- Troeger, C.; Khalil, I.A.; Rao, P.C.; Cao, S.; Blacker, B.F.; Ahmed, T.; Armah, G.; Bines, J.E.; Brewer, T.G.; Colombara, D.V.; et al. Rotavirus Vaccination and the Global Burden of Rotavirus Diarrhea Among Children Younger Than 5. JAMA Pediatr. 2018, 172, 958–965, Erratum in: JAMA Pediatr. 2022, 176, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Meeting of the strategic advisory group of experts on immunization, October 2009—Conclusions and recommendations. Relev. Epidemiol. Hebd. 2009, 84, 517–532. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Rotavirus vaccines WHO position paper: January 2013—Recomendations. Vaccine 2013, 31, 6170–6171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennehy, P.H.; Cortese, M.M.; Begue, R.E. A case-control study to determine risk factors for hospitalization for rotavirüs gastroenteritis in US Children. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2006, 25, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.S.; Wang, Y.; Shane, A.L.; Nguyen, T.; Ray, P.; Dennehy, P.; Baek, L.J.; Parashar, U.; Glass, R.I.; Jiang, B. Inhibitory effect of breast milk on infectivity of live oral rotavirus vaccines. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2010, 29, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vesikari, T.; Prymula, R.; Schuster, V.; Tejedor, J.-C.; Cohen, R.; Bouckenooghe, A.; Damaso, S.; Han, H.H. Efficacy and immunogenicity of live-attenuated human rotavirus vaccine in breast-fed and formula-fed European infants. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2012, 31, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinón-Torres, F.; Greenberg, D.; Varman, M.; Killar, J.A.; Hille, D.; Strable, E.L.; Stek, J.E.; Kaplan, S.S. Safety, Tolerability and Immunogenicity of Pentavalent Rotavirus Vaccine Manufactured by a Modified Process. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2017, 36, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adlhoch, C.; Hoehne, M.; Littmann, M.; Marques, A.M.; Lerche, A.; Dehnert, M.; Eckmanns, T.; Wichmann, O.; Koch, J. Rotavirus vaccine effectiveness and case-control study on risk factors for breakthrough infections in Germany, 2010–2011. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2013, 32, e82–e89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plenge-Bönig, A.; Soto-Ramírez, N.; Karmaus, W.; Petersen, G.; Davis, S.; Forster, J. Breastfeeding protects against acute gastroenteritis due to rotavirus in infants. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2010, 169, 1471–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.; Sabui, T.K.; Basu, S.; Pal, N. A prospective study of rotavirus diarrhea in children under 1 year of age. Clin. Pediatr. 2007, 46, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giwa, F.J.; Garba, M.; Mukhtar, A.; Idris, M.; Lartey, B.; Damanka, S.; Samaila, M.; Muktar, H.; Olayinka, A.; Armah, G. Circulating Rotavirus Genotypes among Children Younger than 5 Years with Acute Gastroenteritis in Zaria, Northwestern Nigeria. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. 2021, 16, 223–229. [Google Scholar]
- Wobudeya, E.; Bachou, H.; Karamagi, C.K.; Kalyango, J.N.; Mutebi, E.; Wamani, H. Breastfeeding and the risk of rotavirus diarrhea in hospitalized infants in Uganda: A matched case control study. BMC Pediatr. 2011, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, J.; Steele, A.D.; Franco, M.A. Correlates of protection for rotavirus vaccines: Possible alternative trial endpoints, opportunities, and challenges. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2014, 10, 3659–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suastika, N.K.W.; Suega, K. Diagnosticvalue of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio for assessing the disease severity in COVİD-19 patients. East. J. Med. 2021, 26, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, A.P.; Estes, M.K. Microbes and microbial toxins: Paradigms for microbial-mucosal interactions. VIII. Pathological consequences of rotavirus infection and its enterotoxin. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2001, 281, G303–G310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, R.F.; Barnes, G.L.; Cipriani, E.; Lund, J.S. Clinical immunity after neonatal rotavirus infection: A prospective longitudinal study in young children. N. Engl. J. Med. 1983, 309, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velázquez, F.R.; Matson, D.O.; Calva, J.J.; Guerrero, M.L.; Morrow, A.L.; Carter-Campbell, S.; Glass, R.I.; Estes, M.K.; Pickering, L.K.; Ruiz-Palacios, G.M. Rotavirus infections in infants as protection against subsequent infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 335, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vesikari, T.; Matson, D.O.; Dennehy, P.; Van Damme, P.; Santosham, M.; Rodriguez, Z.; Dallas, M.J.; Heyse, J.F.; Goveia, M.G.; Black, S.B.; et al. Safety and efficacy of a pentavalent human-bovine (WC3) reassortant rotavirus vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, A.; Lewis, M.G.; Venkatesh, B.T.; Nair, S.N. Effect of Exclusive Breastfeeding on Rotavirus Infection among Children. Indian J. Pediatr. 2016, 83, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, T.K.; Bresee, J.S.; Glass, R.I. Rotavirus vaccines and the prevention of hospital-acquired diarrhea in children. Vaccine 2004, 22 (Suppl. 1), S49–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, V.S.; Marques, D.P.; Martins-Filho, P.R.; Cuevas, L.E.; Gurgel, R.Q. Effectiveness of rotavirus vaccines against rotavirus infection and hospitalization in Latin America: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2016, 5, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.P.; Dahl, R.M.; Parashar, U.D.; Lopman, B.A. Annual changes in rotavirus hospitalization rates before and after rotavirus vaccine implementation in the United States. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | All Group | Rotavirus Vaccinated | Rotavirus Unvaccinated | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n: 630; %) | (n: 310; 49.2%) | (n: 320; 50.8%) | ||
| Age (month) | 27.5 (15–46) | 29 (15–52) | 27 (15–43) | 0.114 ‡ |
| Gender | 0.266 * | |||
| Male | 364 (57.8) | 186 (60) | 178 (55.6) | |
| Female | 266 (42.2) | 124 (40) | 142 (44.4) | |
| Fever | 0.022 * | |||
| No | 464 (73.7) | 241 (77.7) | 223 (69.7) | |
| Yes | 166 (26.3) | 69 (22.3) | 97 (30.3) | |
| Hospitalized | <0.001 * | |||
| No | 444 (70.5) | 249 (80.3) | 195 (60.9) | |
| Yes | 186 (29.5) | 61 (19.7) | 125 (39.1) | |
| Breastfed | <0.001 * | |||
| No | 479 (76) | 212 (68.4) | 267 (83.4) | |
| Yes | 151 (24) | 98 (31.6) | 53 (16.6) |
| All Group (n = 630) | Rotavirus Vaccinated (n = 310) | Rotavirus Unvaccinated (n = 320) | p Value ‡ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBC (103/µL) | 10,030 (8048–12,533) | 9885 (7598–12,133) | 10,175 (8193–13,160) | 0.045 |
| HGB (g/dL) | 11.8 (11.1–12.4) | 11.5 (11–12.13) | 12.1 (11.3–12.7) | <0.001 |
| HCT (%) | 35.3 (33.1–37.5) | 34.1 (32.38–36.2) | 36.5 (34.1–37.8) | <0.001 |
| PLT (103/mL) | 321 (261–378) | 320 (265–387) | 322 (258–371) | 0.542 |
| LYM (103/µL) | 3.34 (1.56–5.62) | 4.97 (2.45–6.61) | 2 (1.25–3.9) | <0.001 |
| LYM % | 34.55 (17.15–60.75) | 54.9 (32.55–67.73) | 21.4 (12.1–36.88) | <0.001 |
| Neutrophil (103/µL) | 6.57 (4.28–8.93) | 7.13 (4.11–8.73) | 6.49 (4.49–9.32) | 0.261 |
| Neutrophil % | 52.25 (25.75–71.8) | 31.3 (19.7–54.4) | 65.6 (45.925–77.75) | <0.001 |
| Monocyte (103/µL) | 0.9 (0.68–1.18) | 0.82 (0.64–1.09) | 0.98 (0.7–1.3) | <0.001 |
| Monocyte (%) | 9 (6.9–12.4) | 8.5 (6.55–11.9) | 9.4 (7.425–12.8) | 0.001 |
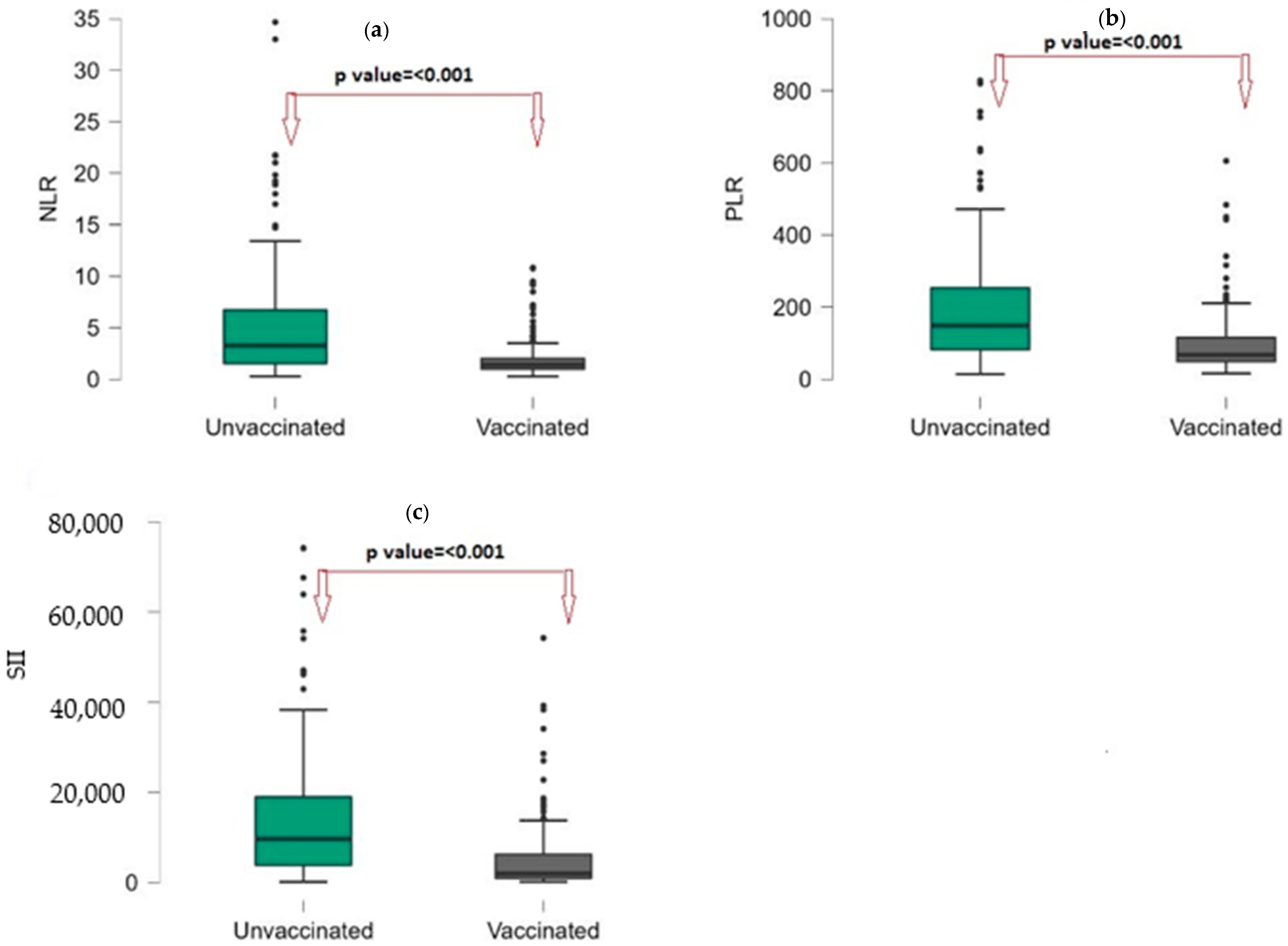
| NLR | 1.84 (1.1–4.2) | 1.4 (0.98–2.03) | 3.27 (1.53–6.73) | <0.001 |
| PLR | 98.89 (59.4–196.48) | 67.73 (48.9–115.93) | 148.99 (81.83–254.09) | <0.001 |
| SII | 4430 (1817–9114) | 1952 (968–6314) | 9678 (3822–19,244) | <0.001 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 4.31 (0.8–12.3) | 2.08 (0.64–9.51) | 6.29 (1.36–21) | <0.001 |
| ALT (U/L) | 20.3 (15.4–25) | 19 (15.4–26) | 21 (16.08–24) | 0.469 |
| AST (U/L) | 37 (29.78–42.93) | 36 (29–40.3) | 38.2 (32–43) | 0.028 |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 10.7 (7.08–15.7) | 9.5 (6.54–16.6) | 11.21 (7.85–14.9) | 0.155 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.47 (0.4–0.63) | 0.46 (0.37–0.55) | 0.52 (0.43–0.75) | <0.001 |
| Sodium (mEq/L) | 137 (135–139) | 137 (136–139) | 137 (134–139) | 0.286 |
| Potassium (mEq/L) | 4.2 (3.87–4.6) | 4.2 (3.62–4.64) | 4.235 (3.91–4.59) | 0.06 |
| All Group (n = 630) | Breastfed (n = 151) | Non-Breastfed (n = 479) | p Value ‡ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBC (103/µL) | 10,030 (8048–12,533) | 9880 (7460–12,010) | 10,120 (8100–12,710) | 0.309 |
| HGB (g/dL) | 11.8 (11.1–12.4) | 11.5 (10.9–12.2) | 11.8 (11.1–12.5) | 0.012 |
| HCT (%) | 35.3 (33.1–37.5) | 34.6 (32.6–36.9) | 35.5 (33.3–37.6) | 0.003 |
| PLT (103/mL) | 321 (261–378) | 319 (255–384) | 322 (263–376) | 0.537 |
| LYM (103/µL) | 3.34 (1.56–5.62) | 3.76 (2.15–5.82) | 3 (1.44–5.61) | 0.006 |
| LYM (%) | 34.55 (17.15–60.75) | 38.6 (21.7–61.9) | 34 (14.1–59.6) | 0.007 |
| Neutrophil (103/µL) | 6.57 (4.28–8.93) | 6.66 (4.14–8.87) | 6.52 (4.3–8.97) | 0.734 |
| Neutrophil (%) | 52.25 (25.75–71.8) | 45.9 (24–64.4) | 53.3 (26.9–74.2) | 0.003 |
| Monocyte (103/µL) | 0.9 (0.68–1.18) | 0.88 (0.69–1.19) | 0.9 (0.67–1.16) | 0.798 |
| Monocyte (%) | 9 (6.9–12.4) | 9.3 (7.7–12.6) | 8.9 (6.8–12.3) | 0.106 |
| NLR | 1.84 (1.1–4.2) | 1.77 (1.18–2.6) | 1.91 (1.09–4.86) | 0.029 |
| PLR | 98.89 (59.4–196.48) | 80.93 (54.47–148.91) | 110.49 (61.2–212.8) | 0.001 |
| SII | 4430 (1817–9114) | 3581 (1299–9282) | 5826 (1530–14,842) | 0.001 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 4.31 (0.8–12.3) | 5.54 (0.86–12.66) | 4.06 (0.79–12.3) | 0.194 |
| ALT (U/L) | 20.3 (15.4–25) | 20 (15.4–25) | 20.4 (15.4–25) | 0.643 |
| AST (U/L) | 37 (29.78–42.93) | 36 (29.1–40.3) | 37 (30–43) | 0.588 |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 10.7 (7.08–15.7) | 10.7 (6.9–16.7) | 10.79 (7.24–15.6) | 0.888 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.47 (0.4–0.63) | 0.47 (0.4–0.62) | 0.47 (0.4–0.63) | 0.73 |
| Sodium (mEq/L) | 137 (135–139) | 137 (136–139) | 137 (135–139) | 0.13 |
| Potassium (mEq/L) | 4.2 (3.87–4.6) | 4.2 (3.87–4.64) | 4.2 (3.86–4.6) | 0.527 |
| Breastfed | Non-Breastfed | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rotavirus Vaccinated | Rotavirus Unvaccinated | p Value | Rotavirus Vaccinated | Rotavirus Unvaccinated | p Value ‡ | |
| WBC (103/µL) | 8520 (6800–10,373) | 8900 (7460–11,553) | 0.135 | 9840 (7670–12,140) | 10,250 (8200–13,270) | 0.054 |
| HGB (g/dL) | 11.8 (11.1–12.3) | 11.8 (11–12.6) | 0.966 | 11.5 (11–12.2) | 12.1 (11.4–12.8) | <0.001 |
| HCT (%) | 35.2 (32.8–37.8) | 35.4 (33.1–37.5) | 0.856 | 34.4 (32.4–37) | 36.8 (34.2–38) | <0.001 |
| PLT (103/mL) | 317 (273–362) | 301 (251–359) | 0.104 | 326 (265–388) | 322 (260–368) | 0.415 |
| LYM (103/µL) | 4.37 (3–5.74) | 3.8 (2.7–5.19) | 0.005 | 4.98 (2.46–6.73) | 1.93 (1.17–3.66) | <0.001 |
| LYM (%) | 33 (20–57) | 28 (15–47) | 0.011 | 56 (31.6–69.15) | 20.3 (10.9–35) | <0.001 |
| Neutrophil (103/µL) | 5.28 (3.58–7.97) | 4.71 (3.62–7.02) | 0.256 | 6.69 (4.11–8.68) | 6.68 (4.5–9.8) | 0.077 |
| Neutrophil (%) | 51 (31–64) | 55 (38–66) | 0.025 | 30 (20–54) | 68 (49.3–80.3) | <0.001 |
| Monocyte (103/µL) | 0.89 (0.7–1.19) | 1 (0.68–1.23) | 0.270 | 0.82 (0.6–1.11) | 0.96 (0.71–1.22) | 0.001 |
| Monocyte (%) | 9.05 (7.37–12.5) | 10.45 (8.08–13.8) | 0.005 | 8.3 (6.2–11.95) | 9.1 (7.1–12.5) | 0.005 |
| NLR | 1.36 (0.79–1.91) | 1.35 (0.77–2.1) | 0.479 | 1.38 (0.93–2.11) | 3.49 (1.6–6.95) | <0.001 |
| PLR | 74 (53–98) | 80 (61–116) | 0.047 | 66 (50–117) | 158 (88–261.67) | <0.001 |
| SII | 3438 (1731–6062) | 4308 (2504–6407) | 0.020 | 1898 (972–6371) | 10,280 (4384–20,460) | <0.001 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 1.45 (0.69–3.02) | 1.49 (0.76–2.86) | 0.573 | 1.64 (0.64–6.67) | 6 (1.27–18.1) | <0.001 |
| ALT (U/L) | 20 (15.4–25) | 21 (15.4–25) | 0.492 | 19 (15.4–28) | 20.9 (16–24) | 0.959 |
| AST (U/L) | 36 (29.1–41.63) | 37 (32–47) | 0.148 | 36 (29–43.2) | 38.2 (32–43) | 0.152 |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 9.5 (6.6–16.6) | 10.55 (7.3–15.15) | 0.569 | 9.5 (6.54–16.6) | 11.21 (7.85–15) | 0.062 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.47 (0.37–0.56) | 0.51 (0.44–0.7) | 0.001 | 0.46 (0.37–0.55) | 0.49 (0.42–0.74) | <0.001 |
| Sodium (mEq/L) | 137 (136–139) | 137 (136–139) | 0.916 | 137 (136–139) | 137 (134–139) | 0.652 |
| Potassium (mEq/L) | 4.2 (3.7–4.6) | 4.3 (3.9–4.7) | 0.023 | 4.2 (3.6–4.6) | 4.2 (3.9–4.6) | 0.111 |
| All Group (n = 630) | Not Hospitalized (n: 444; 70.5%) | Hospitalized (n: 186; 29.5%) | p Value ‡ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBC (103/µL) | 10,030 (8048–12,533) | 9880 (7855–12,030) | 10,545 (8170–14,000) | 0.013 |
| HGB (g/dL) | 11.8 (11.1–12.4) | 11.7 (11.1–12.3) | 12 (11.2–12.7) | 0.005 |
| HCT (%) | 35.3 (33.1–37.5) | 35.1 (32.9–37.2) | 35.95 (33.5–37.8) | 0.013 |
| PLT (103/mL) | 321 (261–378) | 328 (265–385) | 307 (247–357) | 0.005 |
| LYM (103/µL) | 3.34 (1.56–5.62) | 3.53 (1.89–5.92) | 2.29 (1.17–5.12) | <0.001 |
| LYM % | 34.55 (17.15–60.75) | 37.25 (19.6–61.4) | 25.3 (11.2–52.1) | <0.001 |
| Neutrophil (103/µL) | 6.57 (4.28–8.93) | 6.26 (4.14–8.725) | 7.695 (4.53–9.8) | 0.016 |
| Neutrophil % | 52.25 (25.75–71.8) | 47.6 (24.9–68.85) | 61.7 (34.4–80.4) | <0.001 |
| Monocyte (103/µL) | 0.9 (0.68–1.18) | 0.9 (0.68–1.195) | 0.855 (0.67–1.15) | 0.565 |
| Monocyte (%) | 9 (6.9–12.4) | 9.2 (7.1–12.5) | 8.6 (6.7–11.9) | 0.07 |
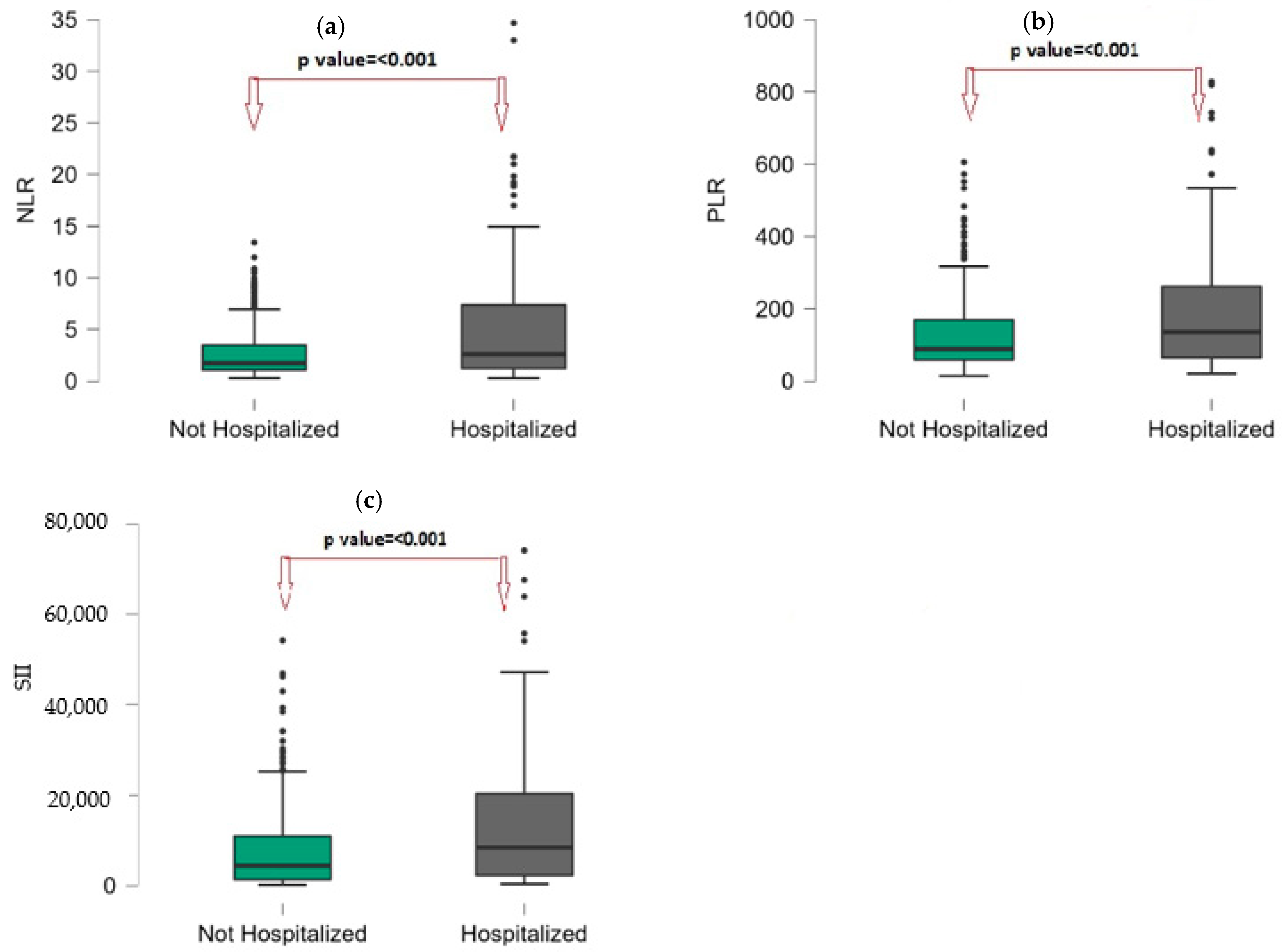
| NLR | 1.84 (1.1–4.2) | 1.73 (1.07–3.49) | 2.61 (1.19–7.41) | <0.001 |
| PLR | 98.89 (59.4–196.48) | 88.79 (58.65–169.3) | 135.59 (64.7–261.87) | <0.001 |
| SII | 4430 (1817–9114) | 4384 (1321–10,959) | 8375 (2215–20,460) | <0.001 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 4.31 (0.8–12.3) | 4.21 (0.8–11.45) | 4.65 (0.78–15) | 0.418 |
| ALT (U/L) | 20.3 (15.4–25) | 20.4 (15.4–25.5) | 20 (15.4–23) | 0.244 |
| AST (U/L) | 37 (29.78–42.93) | 36.1 (29.1–42) | 38.2 (32–43.2) | 0.118 |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 10.7 (7.08–15.7) | 10.89 (6.9–16.6) | 10.2 (7.5–14.77) | 0.348 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.47 (0.4–0.63) | 0.47 (0.4–0.59) | 0.49 (0.42–0.71) | 0.256 |
| Sodium (mEq/L) | 137 (135–139) | 137 (136–139) | 136 (134–138) | 0.001 |
| Potassium (mEq/L) | 4.2 (3.87–4.6) | 4.3 (3.9–4.64) | 4.12 (3.76–4.5) | 0.021 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Okuyan, O.; Elgormus, Y.; Sayili, U.; Dumur, S.; Isık, O.E.; Uzun, H. The Effect of Virus-Specific Vaccination on Laboratory Infection Markers of Children with Acute Rotavirus-Associated Acute Gastroenteritis. Vaccines 2023, 11, 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030580
Okuyan O, Elgormus Y, Sayili U, Dumur S, Isık OE, Uzun H. The Effect of Virus-Specific Vaccination on Laboratory Infection Markers of Children with Acute Rotavirus-Associated Acute Gastroenteritis. Vaccines. 2023; 11(3):580. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030580
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkuyan, Omer, Yusuf Elgormus, Ugurcan Sayili, Seyma Dumur, Ozlem Erkan Isık, and Hafize Uzun. 2023. "The Effect of Virus-Specific Vaccination on Laboratory Infection Markers of Children with Acute Rotavirus-Associated Acute Gastroenteritis" Vaccines 11, no. 3: 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030580
APA StyleOkuyan, O., Elgormus, Y., Sayili, U., Dumur, S., Isık, O. E., & Uzun, H. (2023). The Effect of Virus-Specific Vaccination on Laboratory Infection Markers of Children with Acute Rotavirus-Associated Acute Gastroenteritis. Vaccines, 11(3), 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030580






