Intranasal Liposomal Formulation of Spike Protein Adjuvanted with CpG Protects and Boosts Heterologous Immunity of hACE2 Transgenic Mice to SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Vaccine Formulation
2.2. Physicochemical Characterization
2.3. Toxicity of Vaccine Formulation
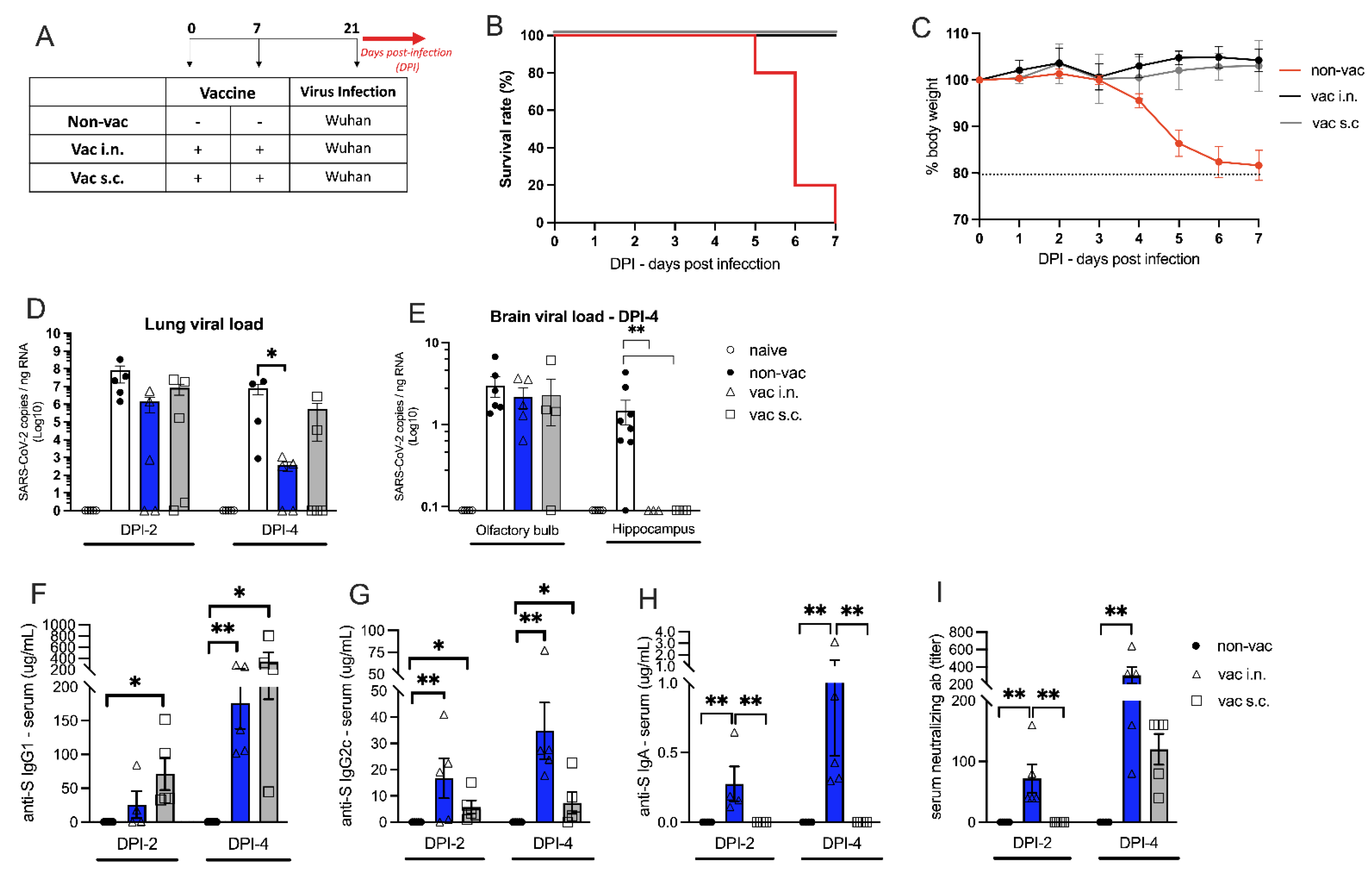
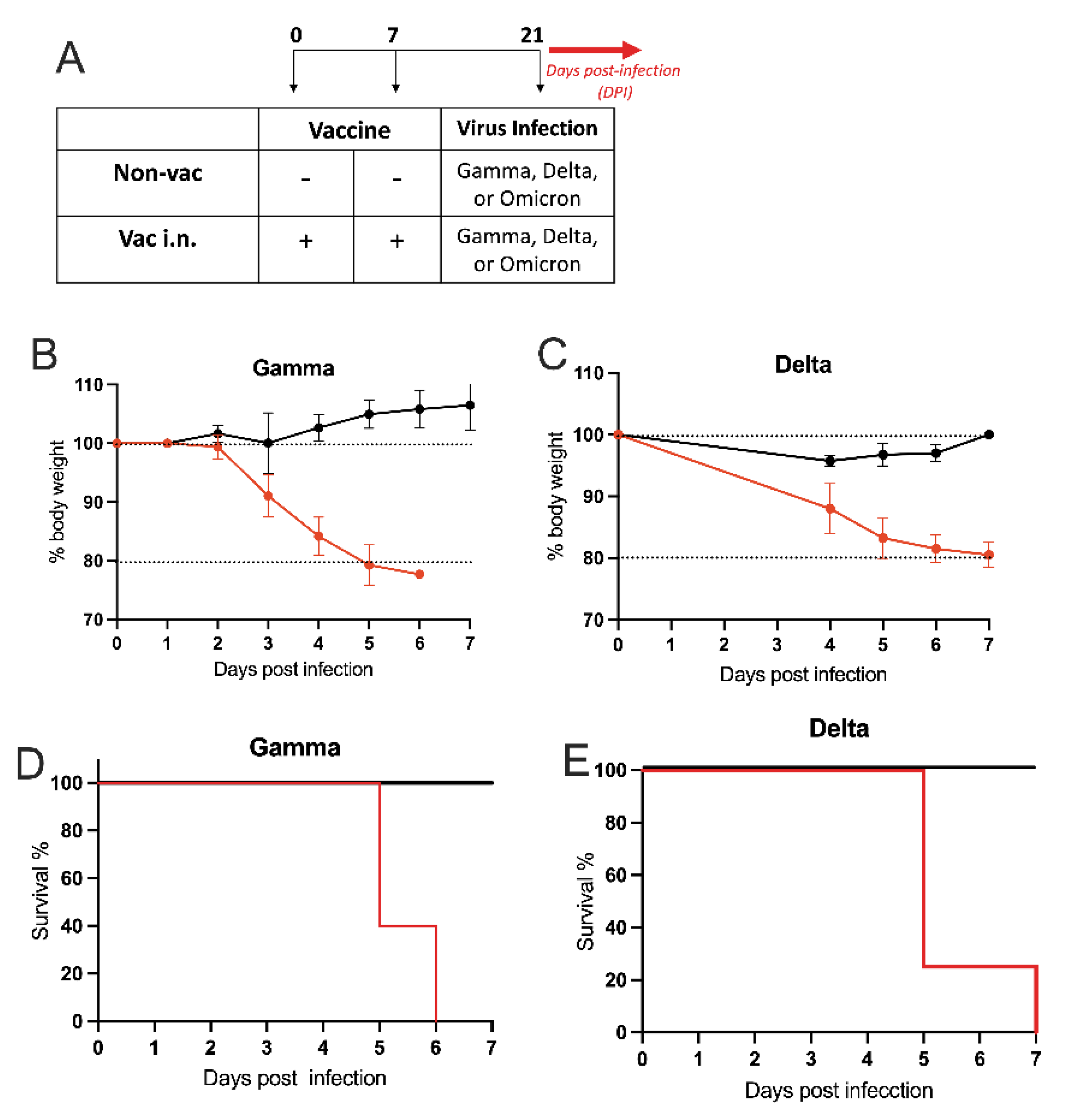
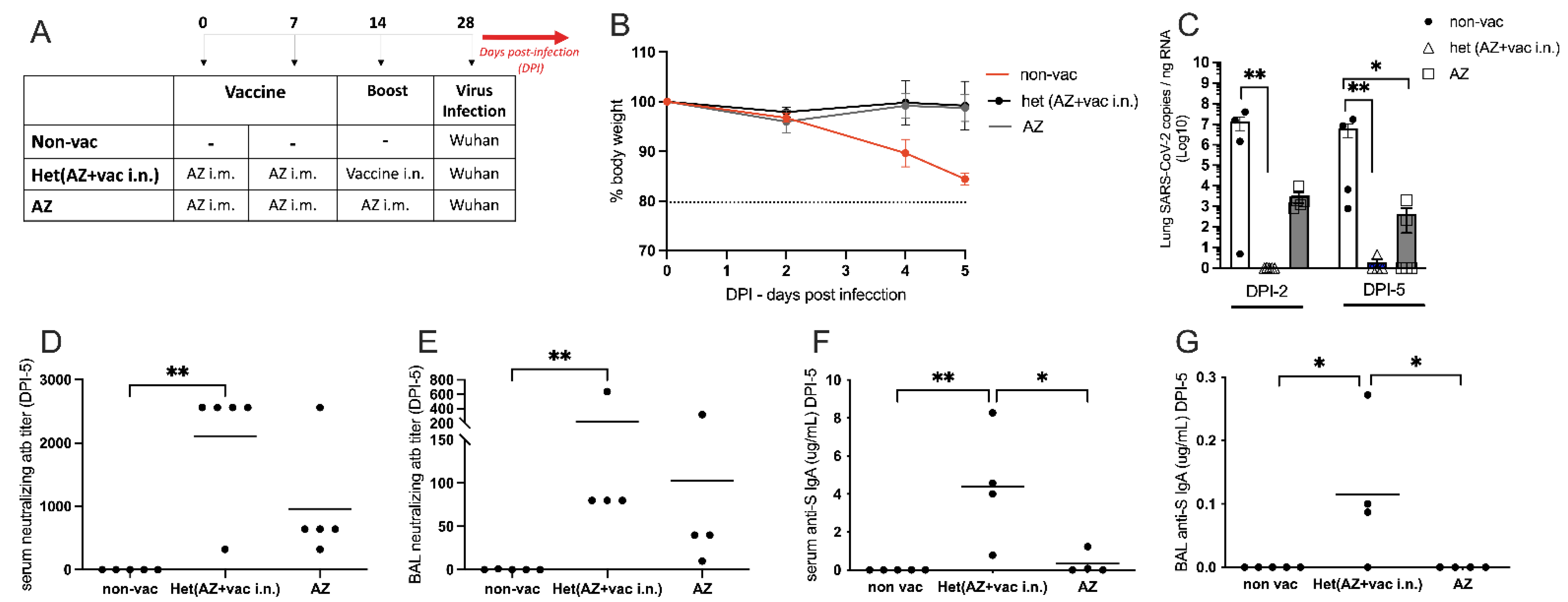
2.4. COVID-19 Animal Model
2.5. Nucleic Acid Extraction and RT-qPCR (Quantitative Real-Time PCR Based on Reverse Transcriptase) Assay for SARS-CoV-2
2.6. RNA Isolation, cDNA Synthesis, and RT-qPCR for Cytokines
2.7. Virus Neutralization Test (VNT)
2.8. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) for Antibodies
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Toxicity of Nasal Vaccine Formulation
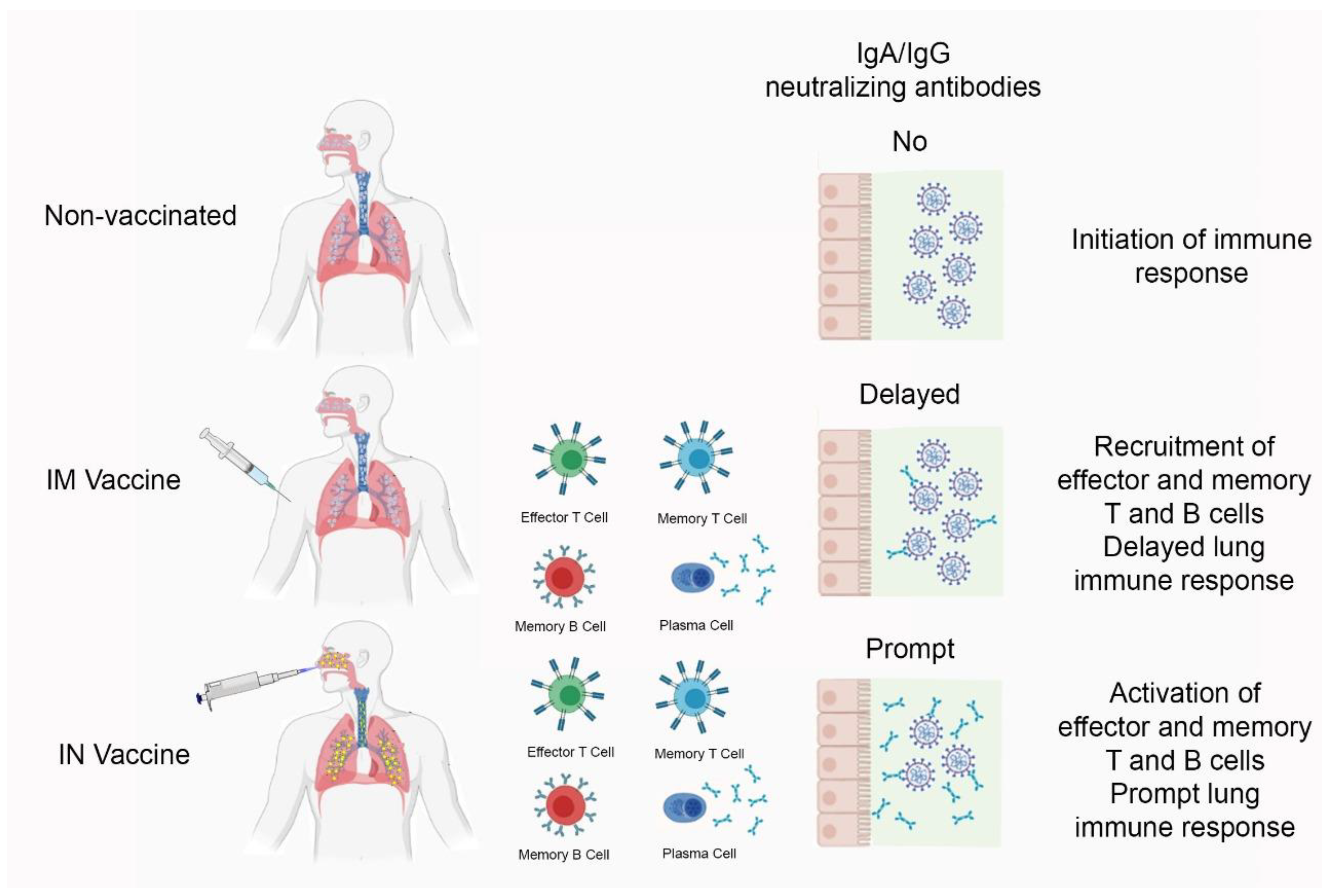
3.2. The Effect of Intranasal Versus Subcutaneous Vaccine Administration
3.3. Intranasal Vaccine Protects against SARS-CoV-2 Variants
3.4. Comparison of Intranasal Liposomal Vaccine with the Intramuscular Adenoviral-Vectored SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine from Oxford/AstraZeneca (AZ)
3.5. Intranasal Vaccine Boosts Heterologous Immunity and Is More Effective Than Homologous Oxford/AstraZeneca (AZ) Vaccine Boost
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seyed Hosseini, E.; Riahi Kashani, N.; Nikzad, H.; Azadbakht, J.; Hassani Bafrani, H.; Haddad Kashani, H. The Novel Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19): Mechanism of Action, Detection and Recent Therapeutic Strategies. Virology 2020, 551, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, F.S.; Schwetz, T.A.; Tabak, L.A.; Lander, E.S. ARPA-H: Accelerating Biomedical Breakthroughs. Science 2021, 373, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harder, T.; Külper-Schiek, W.; Reda, S.; Treskova-Schwarzbach, M.; Koch, J.; Vygen-Bonnet, S.; Wichmann, O. Effectiveness of COVID-19 Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 Infection with the Delta (B.1.617.2) Variant: Second Interim Results of a Living Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, 1 January to 25 August 2021. Eurosurveillance 2021, 26, 2100920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slavov, S.N.; de La-Roque, D.G.L.; da Costa, P.N.M.; Rodrigues, E.S.; Santos, E.V.; Borges, J.S.; Evaristo, M.; de Matos Maçonetto, J.; Marques, A.A.; Milhomens, J.; et al. Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern in Vaccination Model City in the State of Sao Paulo, Brazil. Viruses 2022, 14, 2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, E.G.; Lustig, Y.; Cohen, C.; Fluss, R.; Indenbaum, V.; Amit, S.; Doolman, R.; Asraf, K.; Mendelson, E.; Ziv, A.; et al. Waning Immune Humoral Response to BNT162b2 COVID-19 Vaccine over 6 Months. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Muecksch, F.; Muenn, F.; Cho, A.; Zong, S.; Raspe, R.; Ramos, V.; Johnson, B.; Tanfous, T.B.; Dasilva, J.; et al. Humoral Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 Elicited by Combination COVID-19 Vaccination Regimens. J. Exp. Med. 2022, 219, e20220826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogra, P.L. Mucosal Immune Response to Poliovirus Vaccines in Childhood. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1984, 6 (Suppl. S2), S361–S368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterlin, D.; Mathian, A.; Miyara, M.; Mohr, A.; Anna, F.; Claër, L.; Quentric, P.; Fadlallah, J.; Devilliers, H.; Ghillani, P.; et al. IgA Dominates the Early Neutralizing Antibody Response to SARS-CoV-2. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabd2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.O.; Shrihari, S.; Gorman, M.J.; Ying, B.; Yaun, D.; Raju, S.; Chen, R.E.; Dmitriev, I.P.; Kashentseva, E.; Adams, L.J.; et al. An Intranasal Vaccine Durably Protects against SARS-CoV-2 Variants in Mice. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afkhami, S.; D’Agostino, M.R.; Zhang, A.; Stacey, H.D.; Marzok, A.; Kang, A.; Singh, R.; Bavananthasivam, J.; Ye, G.; Luo, X.; et al. Respiratory Mucosal Delivery of Next-Generation COVID-19 Vaccine Provides Robust Protection against Both Ancestral and Variant Strains of SARS-CoV-2. Cell 2022, 185, 896–915.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See, R.H.; Zakhartchouk, A.N.; Petric, M.; Lawrence, D.J.; Mok, C.P.Y.; Hogan, R.J.; Rowe, T.; Zitzow, L.A.; Karunakaran, K.P.; Hitt, M.M.; et al. Comparative Evaluation of Two Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) Vaccine Candidates in Mice Challenged with SARS Coronavirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, J.T.; Azevedo, P.; Fumagalli, M.J.; Hojo-Souza, N.S.; Salazar, N.; Almeida, G.G.; Oliveira, L.I.; Faustino, L.; Antonelli, L.R.; Marçal, T.G.; et al. Promotion of Neutralizing Antibody-Independent Immunity to Wild-Type and SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern Using an RBD-Nucleocapsid Fusion Protein. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israelow, B.; Mao, T.; Klein, J.; Song, E.; Menasche, B.; Omer, S.B.; Iwasaki, A. Adaptive Immune Determinants of Viral Clearance and Protection in Mouse Models of SARS-CoV-2. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabl4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alameh, M.G.; Tombácz, I.; Bettini, E.; Lederer, K.; Sittplangkoon, C.; Wilmore, J.R.; Gaudette, B.T.; Soliman, O.Y.; Pine, M.; Hicks, P.; et al. Lipid Nanoparticles Enhance the Efficacy of MRNA and Protein Subunit Vaccines by Inducing Robust T Follicular Helper Cell and Humoral Responses. Immunity 2021, 54, 2877–2892.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Maruya, M.; Kawamoto, S.; Sitnik, K.; Kitamura, H.; Agace, W.W.; Fagarasan, S. The Sensing of Environmental Stimuli by Follicular Dendritic Cells Promotes Immunoglobulin A Generation in the Gut. Immunity 2010, 33, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, L.; Deng, W.; Huang, B.; Gao, H.; Liu, J.; Ren, L.; Wei, Q.; Yu, P.; Xu, Y.; Qi, F.; et al. The Pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 in HACE2 Transgenic Mice. Nature 2020, 583, 830–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvim, R.G.F.; Lima, T.M.; Rodrigues, D.A.S.; Marsili, F.F.; Bozza, V.B.T.; Higa, L.M.; Monteiro, F.L.; Abreu, D.P.B.; Leitão, I.C.; Carvalho, R.S.; et al. From a Recombinant Key Antigen to an Accurate, Affordable Serological Test: Lessons Learnt from COVID-19 for Future Pandemics. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 186, 108537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrapp, D.; Wang, N.; Corbett, K.S.; Goldsmith, J.A.; Hsieh, C.-L.; Abiona, O.; Graham, B.S.; Mclellan, J.S. Cryo-EM Structure of the 2019-NCoV Spike in the Prefusion Conformation. Science 2020, 367, 1260–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reigado, G.R.; Adriani, P.P.; dos Santos, J.F.; Freitas, B.L.; Fernandes, M.T.P.; Chambergo Alcalde, F.S.; Leo, P.; Nunes, V.A. Delivery of Superoxide Dismutase by TAT and Abalone Peptides for the Protection of Skin Cells against Oxidative Stress. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2022, 69, 2673–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Präbst, K.; Engelhardt, H.; Ringgeler, S.; Hübner, H. Basic Colorimetric Proliferation Assays: MTT, WST, and Resazurin. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2017; Volume 1601, pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCray, P.B.; Pewe, L.; Wohlford-Lenane, C.; Hickey, M.; Manzel, L.; Shi, L.; Netland, J.; Jia, H.P.; Halabi, C.; Sigmund, C.D.; et al. Lethal Infection of K18- HACE2 Mice Infected with Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.K.W.; Pan, Y.; Cheng, S.M.S.; Hui, K.P.Y.; Krishnan, P.; Liu, Y.; Ng, D.Y.M.; Wan, C.K.C.; Yang, P.; Wang, Q.; et al. Molecular Diagnosis of a Novel Coronavirus (2019-NCoV) Causing an Outbreak of Pneumonia. Clin. Chem. 2020, 66, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corman, V.M.; Landt, O.; Kaiser, M.; Molenkamp, R.; Meijer, A.; Chu, D.K.W.; Bleicker, T.; Brünink, S.; Schneider, J.; Schmidt, M.L.; et al. Detection of 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-NCoV) by Real-Time RT-PCR. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes-Correa, M.C.; Salomão, M.C.; Ghilardi, F.; Tozetto-Mendoza, T.R.; Santos Villas-Boas, L.; de Paula, A.V.; Paiao, H.G.O.; da Costa, A.C.; Leal, F.E.; de Barros Coscelli Ferraz, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Detection and Culture in Different Biological Specimens from Immunocompetent and Immunosuppressed COVID-19 Patients Infected with Two Different Viral Strains. Viruses 2023, 15, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurtop, E.; Villarroel, P.M.S.; Pastorino, B.; Ninove, L.; Drexler, J.F.; Roca, Y.; Gake, B.; Dubot-Peres, A.; Grard, G.; Peyrefitte, C.; et al. Combination of ELISA Screening and Seroneutralisation Tests to Expedite Zika Virus Seroprevalence Studies. Virol. J. 2018, 15, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendel, S.; Kutner, J.M.; Machado, R.; Fontão-Wendel, R.; Bub, C.; Fachini, R.; Yokoyama, A.; Candelaria, G.; Sakashita, A.; Achkar, R.; et al. Screening for SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Convalescent Plasma in Brazil: Preliminary Lessons from a Voluntary Convalescent Donor Program. Transfusion 2020, 60, 2938–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendrone-Junior, A.; Dinardo, C.L.; Ferreira, S.C.; Nishya, A.; Salles, N.A.; de Almeida Neto, C.; Hamasaki, D.T.; Facincani, T.; de Oliveira Alves, L.B.; Machado, R.R.G.; et al. Correlation between SARS-COV-2 Antibody Screening by Immunoassay and Neutralizing Antibody Testing. Transfusion 2021, 61, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villas-Boas, L.S.; Paula, A.V.; Silva, A.R.D., Jr.; Paiao, H.G.O.; Tozetto-Mendoza, T.R.; Manuli, E.R.; Leal, F.E.; Ferraz, A.B.C.; Sabino, E.C.; Bierrenbach, A.L.; et al. Absence of Neutralizing Antibodies against the Omicron SARS-CoV-2 Variant in Convalescent Sera from Individuals Infected with the Ancestral SARS-CoV-2 Virus or Its Gamma Variant. Clinics 2022, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chidekel, A.; Shaffer, T.H. 3. Cultured Human Airway Epithelial Cells (Calu-3): A Model of Human Respiratory Function, Structure, and Inflammatory Responses. Crit. Care Res. Pract. 2010, 2010, 394578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halfmann, P.J.; Iida, S.; Iwatsuki-Horimoto, K.; Maemura, T.; Kiso, M.; Scheaffer, S.M.; Darling, T.L.; Joshi, A.; Loeber, S.; Singh, G.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Virus Causes Attenuated Disease in Mice and Hamsters. Nature 2022, 603, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberca-Custodio, R.W.; Faustino, L.D.; Gomes, E.; Nunes, F.P.B.; Siqueira, M.K.; Labrada, A.; Almeida, R.R.; Camara, N.O.S.; Fonseca, D.M.; Russo, M. Allergen-Specific Immunotherapy with Liposome Containing CpG-ODN in Murine Model of Asthma Relies on MyD88 Signaling in Dendritic Cells Allergen-Specific Immunotherapy with Liposome Containing CpG-ODN in Murine Model of Asthma Relies on MyD88 Signaling in Dendritic Cells. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirotti, L.; Custódio, R.W.A.; Gomes, E.; Rammauro, F.; de Araujo, E.F.; Calich, V.L.G.; Russo, M. CPG-ODN Shapes Alum Adjuvant Activity Signaling via MyD88 and Il-10. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, A.; Azharuddin, M.; Cardona, M.E.; Devito, C.; von Castelmur, E.; Wehlin, A.; Pietras, Z.; Sunnerhagen, M.; Selegård, R.; Aili, D.; et al. Intranasal Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 Immunization with Lipid Adjuvants Provides Systemic and Mucosal Immune Response against SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike and Nucleocapsid Protein. Vaccines 2022, 10, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, G.; Battiany, J.; Poeck, H.; Wagner, M.; Kerkmann, M.; Lubenow, N.; Rothenfusser, S.; Endres, S. Rational Design of New CpG Oligonucleotides That Combine B Cell Activation with High IFN-α Induction in Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2003, 33, 1633–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollmer, J.; Weeratna, R.; Payette, P.; Jurk, M.; Schetter, C.; Laucht, M.; Wader, T.; Tluk, S.; Liu, M.; Davis, H.L.; et al. Characterization of Three CpG Oligodeoxynucleotide Classes with Distinct Immunostimulatory Activities. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firmino-Cruz, L.; dos-Santos, J.S.; da Fonseca-Martins, A.M.; Oliveira-Maciel, D.; Guadagnini-Perez, G.; Roncaglia-Pereira, V.A.; Dumard, C.H.; Guedes-da-Silva, F.H.; Vicente Santos, A.C.; Alvim, R.G.F.; et al. Intradermal Immunization of SARS-CoV-2 Original Strain Trimeric Spike Protein Associated to CpG and AddaS03 Adjuvants, but Not MPL, Provide Strong Humoral and Cellular Response in Mice. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Hernandez, T.; Rhyme, M.S.; Cork, A.J.; Jones, S.; Segui-Perez, C.; Brunner, L.; Richter, J.; Petrovsky, N.; Lawrenz, M.; Goldblatt, D.; et al. Vaccine-Induced Th1-Type Response Protects against Invasive Group a Streptococcus Infection in the Absence of Opsonizing Antibodies. mBio 2020, 11, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyaka, P.N. Inducing Mucosal IgA: A Challenge for Vaccine Adjuvants and Delivery Systems. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandtzaeg, P. Mucosal Immunity: Induction, Dissemination, and Effector Functions. Scand. J. Immunol. 2009, 70, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hand, T.W.; Reboldi, A. Annual Review of Immunology Production and Function of Immunoglobulin A. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 39, 695–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.F.; Meng, W.; Chen, L.; Ding, L.; Feng, J.; Perez, J.; Ali, A.; Sun, S.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Y.; et al. Neutralizing Antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern Including Delta and Omicron in Subjects Receiving MRNA-1273, BNT162b2, and Ad26.COV2.S Vaccines. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 5678–5690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diallo, B.K.; Chasaide, C.N.; Wong, T.Y.; Schmitt, P.; Lee, K.S.; Weaver, K.; Miller, O.; Cooper, M.; Jazayeri, S.D.; Damron, F.H.; et al. Intranasal COVID-19 Vaccine Induces Respiratory Memory T Cells and Protects K18-HACE Mice against SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Vaccines 2023, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, B.S.; Picece, V.C.T.M.; Baillet, J.; Gale, E.C.; Powelll, A.E.; Saouaf, O.M.; Yan, J.; Lopez Hernandez, H.; Appel, E.A. Nanoparticle-Conjugated TLR9 Agonists Improve the Potency, Durability, and Breadth of COVID-19 Vaccines. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| Actb | 5′-GAA GAT CAT TGC TCC TC-3′ | 5′-CCT GCT TGC TGA TCC ACA TC-3′ |
| Il1b | 5′-CAG GCA GGC AGT ATC ACT CA-3′ | 5′-AGC TCA TAT GGG TCC GAC AG-3′ |
| Il6 | 5′-TAG TCC TTC CTA CCC CAA TTT CC-3′ | 5′-TTG GTC CTT AGC CAC TCC TTC-3′ |
| Tnf | 5′-TGT AGC CCA CGT CGT AGC AAA-3′ | 5′GGC TCA GCC ACT CCA GCT G-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Russo, M.; Mendes-Corrêa, M.C.; Lins, B.B.; Kersten, V.; Pernambuco Filho, P.C.A.; Martins, T.R.; Tozetto-Mendoza, T.R.; Vilas Boas, L.S.; Gomes, B.M.; Dati, L.M.M.; et al. Intranasal Liposomal Formulation of Spike Protein Adjuvanted with CpG Protects and Boosts Heterologous Immunity of hACE2 Transgenic Mice to SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1732. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11111732
Russo M, Mendes-Corrêa MC, Lins BB, Kersten V, Pernambuco Filho PCA, Martins TR, Tozetto-Mendoza TR, Vilas Boas LS, Gomes BM, Dati LMM, et al. Intranasal Liposomal Formulation of Spike Protein Adjuvanted with CpG Protects and Boosts Heterologous Immunity of hACE2 Transgenic Mice to SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Vaccines. 2023; 11(11):1732. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11111732
Chicago/Turabian StyleRusso, Momtchilo, Maria Cássia Mendes-Corrêa, Bruna B. Lins, Victor Kersten, Paulo C. A. Pernambuco Filho, Toni Ricardo Martins, Tânia Regina Tozetto-Mendoza, Lucy Santos Vilas Boas, Brisa Moreira Gomes, Livia Mendonça Munhoz Dati, and et al. 2023. "Intranasal Liposomal Formulation of Spike Protein Adjuvanted with CpG Protects and Boosts Heterologous Immunity of hACE2 Transgenic Mice to SARS-CoV-2 Infection" Vaccines 11, no. 11: 1732. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11111732
APA StyleRusso, M., Mendes-Corrêa, M. C., Lins, B. B., Kersten, V., Pernambuco Filho, P. C. A., Martins, T. R., Tozetto-Mendoza, T. R., Vilas Boas, L. S., Gomes, B. M., Dati, L. M. M., Duarte-Neto, A. N., Reigado, G. R., Frederico, A. B. T., de Brito e Cunha, D. R. d. A., de Paula, A. V., da Silva, J. I. G., Vasconcelos, C. F. M., Chambergo, F. S., Nunes, V. A., ... Mirotti, L. (2023). Intranasal Liposomal Formulation of Spike Protein Adjuvanted with CpG Protects and Boosts Heterologous Immunity of hACE2 Transgenic Mice to SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Vaccines, 11(11), 1732. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11111732









