Intradermal Vaccination against Influenza with a STING-Targeted Nanoparticle Combination Adjuvant Induces Superior Cross-Protective Humoral Immunity in Swine Compared with Intranasal and Intramuscular Immunization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Vaccine Preparation
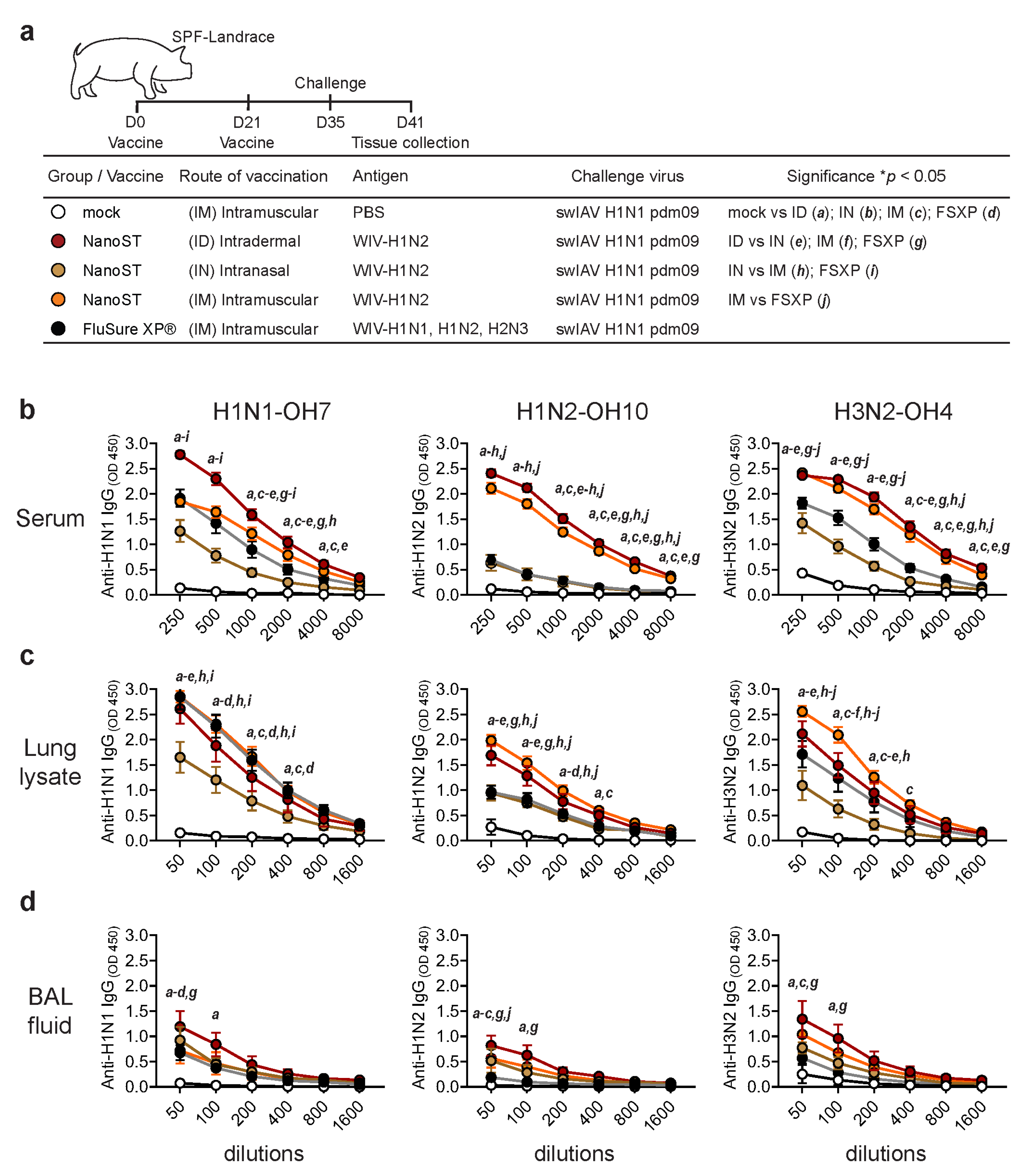
2.2. Animals
2.3. Cross-Reactive Antibody Analysis
2.4. Influenza-Specific Antibody-Secreting Cell Analysis
2.5. Preparation of Erythrocyte Suspension and Antigen
2.6. Hemagglutination Inhibition (HI) Titers
2.7. Quantification of Viral Load
2.8. Virus Neutralization Titers
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Intradermal Vaccination with WIV/NanoST Induces Systemic and Mucosal Cross-Reactive Antibodies
3.2. Intradermal Vaccination with WIV/NanoST Induces a Potent Cross-Reactive Mucosal IgA Response in the Respiratory System of Challenged Pigs
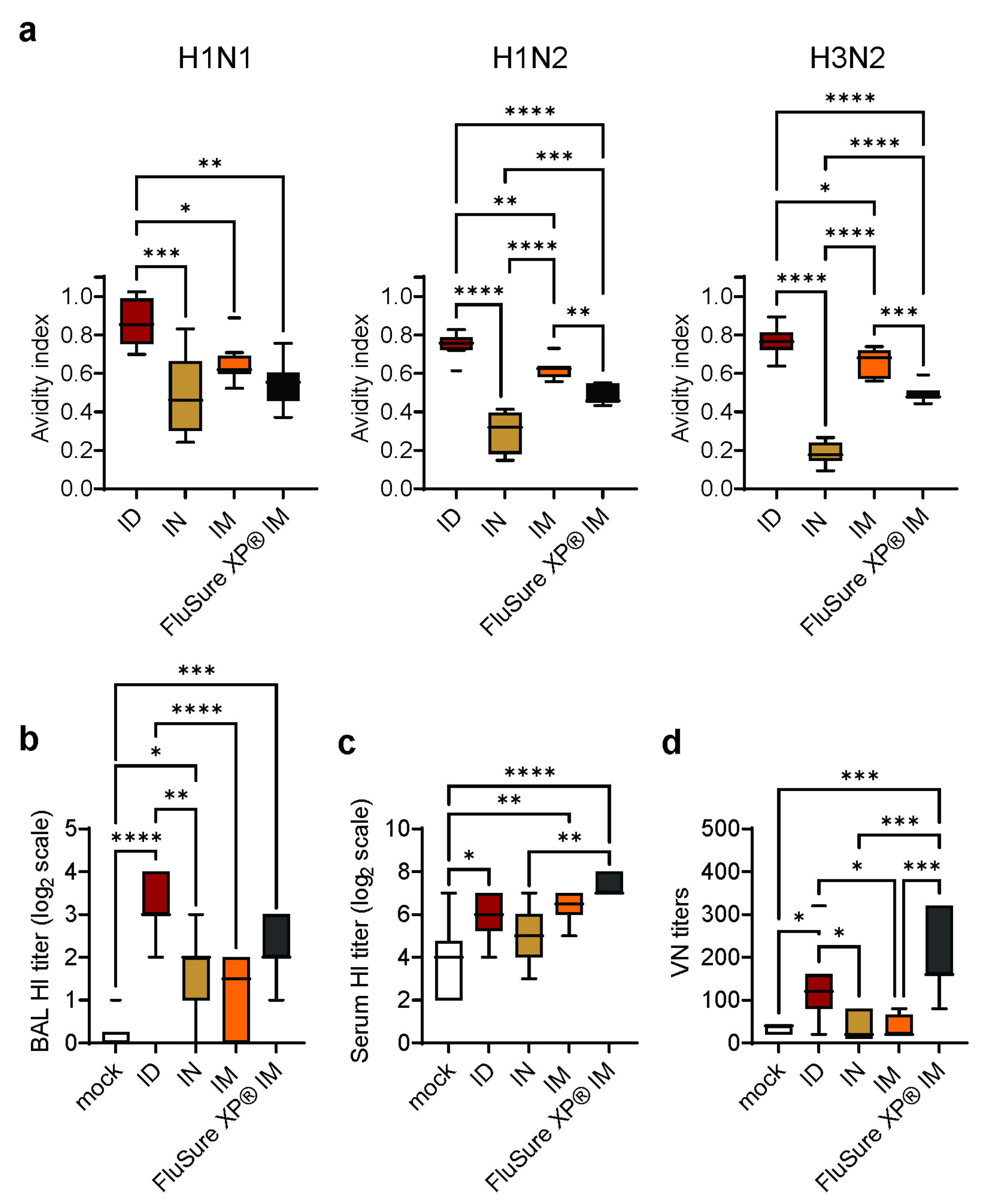
3.3. Intradermal Vaccination with WIV/NanoST Induces Cross-Reactive and Qualitative Immunological Memory
3.4. Intradermal Vaccination with WIV/NanoST Induces Functional Antibodies against Influenza
3.5. Intradermal Vaccination with WIV/NanoST Protects against Challenges with Heterologous SwIAV
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morens, D.M.; Taubenberger, J.K.; Fauci, A.S. Rethinking next-generation vaccines for coronaviruses, influenzaviruses, and other respiratory viruses. Cell Host Microbe 2023, 31, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mena, I.; Nelson, M.I.; Quezada-Monroy, F.; Dutta, J.; Cortes-Fernandez, R.; Lara-Puente, J.H.; Castro-Peralta, F.; Cunha, L.F.; Trovao, N.S.; Lozano-Dubernard, B.; et al. Origins of the 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic in swine in Mexico. eLife 2016, 5, e16777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, M.I.; Vincent, A.L. Reverse zoonosis of influenza to swine: New perspectives on the human-animal interface. Trends Microbiol. 2015, 23, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meurens, F.; Summerfield, A.; Nauwynck, H.; Saif, L.; Gerdts, V. The pig: A model for human infectious diseases. Trends Microbiol. 2012, 20, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Poucke, S.G.; Nicholls, J.M.; Nauwynck, H.J.; Van Reeth, K. Replication of avian, human and swine influenza viruses in porcine respiratory explants and association with sialic acid distribution. Virol. J. 2010, 7, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.K.; Chang, J.; Arendsee, Z.W.; Venkatesh, D.; Souza, C.K.; Kimble, J.B.; Lewis, N.S.; Davis, C.T.; Vincent, A.L. Swine Influenza A Viruses and the Tangled Relationship with Humans. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2021, 11, a038737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandbulte, M.R.; Spickler, A.R.; Zaabel, P.K.; Roth, J.A. Optimal Use of Vaccines for Control of Influenza A Virus in Swine. Vaccines 2015, 3, 22–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, H.E.; Aramouni, M.; Coward, V.; Ramsay, A.; Kelly, M.; Morgan, S.; Tchilian, E.; Canini, L.; Woolhouse, M.E.J.; Gilbert, S.; et al. Vaccine-mediated protection of pigs against infection with pandemic H1N1 2009 swine influenza A virus requires a close antigenic match between the vaccine antigen and challenge virus. Vaccine 2019, 37, 2288–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Chit, A.; Soobiah, C.; Hallett, D.; Meier, G.; Chen, M.H.; Tashkandi, M.; Bauch, C.T.; Loeb, M. Comparing influenza vaccine efficacy against mismatched and matched strains: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauger, P.C.; Vincent, A.L.; Loving, C.L.; Lager, K.M.; Janke, B.H.; Kehrli, M.E., Jr.; Roth, J.A. Enhanced pneumonia and disease in pigs vaccinated with an inactivated human-like (delta-cluster) H1N2 vaccine and challenged with pandemic 2009 H1N1 influenza virus. Vaccine 2011, 29, 2712–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajao, D.S.; Chen, H.; Perez, D.R.; Sandbulte, M.R.; Gauger, P.C.; Loving, C.L.; Shanks, G.D.; Vincent, A. Vaccine-associated enhanced respiratory disease is influenced by haemagglutinin and neuraminidase in whole inactivated influenza virus vaccines. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, C.K.; Rajao, D.S.; Sandbulte, M.R.; Lopes, S.; Lewis, N.S.; Loving, C.L.; Gauger, P.C.; Vincent, A.L. The type of adjuvant in whole inactivated influenza a virus vaccines impacts vaccine-associated enhanced respiratory disease. Vaccine 2018, 36, 6103–6110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kappes, M.A.; Sandbulte, M.R.; Platt, R.; Wang, C.; Lager, K.M.; Henningson, J.N.; Lorusso, A.; Vincent, A.L.; Loving, C.L.; Roth, J.A.; et al. Vaccination with NS1-truncated H3N2 swine influenza virus primes T cells and confers cross-protection against an H1N1 heterosubtypic challenge in pigs. Vaccine 2012, 30, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, A.L.; Ma, W.; Lager, K.M.; Richt, J.A.; Janke, B.H.; Sandbulte, M.R.; Gauger, P.C.; Loving, C.L.; Webby, R.J.; Garcia-Sastre, A. Live attenuated influenza vaccine provides superior protection from heterologous infection in pigs with maternal antibodies without inducing vaccine-associated enhanced respiratory disease. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 10597–10605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Zeller, M.A.; Li, G.; Harmon, K.M.; Zhang, J.; Hoang, H.; Anderson, T.K.; Vincent, A.L.; Gauger, P.C. Detection of live attenuated influenza vaccine virus and evidence of reassortment in the U.S. swine population. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2020, 32, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Mencia, A.; Bi, L.; Taylor, A.; Yao, Y.; HogenEsch, H. Dendrimer-like alpha-d-glucan nanoparticles activate dendritic cells and are effective vaccine adjuvants. J. Control Release 2015, 204, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, S.; Lu, F.; Ghimire, S.; Renu, S.; Lakshmanappa, Y.S.; Hogshead, B.T.; Ragland, D.; HogenEsch, H.; Renukaradhya, G.J. Corn-derived alpha-D-glucan nanoparticles as adjuvant for intramuscular and intranasal immunization in pigs. Nanomedicine 2019, 16, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, V.; Hernandez-Franco, J.F.; Yadagiri, G.; Bugybayeva, D.; Dolatyabi, S.; Feliciano-Ruiz, N.; Schrock, J.; Hanson, J.; Ngunjiri, J.; HogenEsch, H.; et al. A split influenza vaccine formulated with a combination adjuvant composed of alpha-D-glucan nanoparticles and a STING agonist elicits cross-protective immunity in pigs. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, V.; Renu, S.; Feliciano-Ruiz, N.; Han, Y.; Ramesh, A.; Schrock, J.; Dhakal, S.; HogenEsch, H.; Renukaradhya, G.J. Intranasal Delivery of Inactivated Influenza Virus and Poly(I:C) Adsorbed Corn-Based Nanoparticle Vaccine Elicited Robust Antigen-Specific Cell-Mediated Immune Responses in Maternal Antibody Positive Nursery Pigs. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 596964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Franco, J.F.; Mosley, Y.C.; Franco, J.; Ragland, D.; Yao, Y.; HogenEsch, H. Effective and Safe Stimulation of Humoral and Cell-Mediated Immunity by Intradermal Immunization with a Cyclic Dinucleotide/Nanoparticle Combination Adjuvant. J. Immunol. 2021, 206, 700–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrales, L.; Glickman, L.H.; McWhirter, S.M.; Kanne, D.B.; Sivick, K.E.; Katibah, G.E.; Woo, S.R.; Lemmens, E.; Banda, T.; Leong, J.J.; et al. Direct Activation of STING in the Tumor Microenvironment Leads to Potent and Systemic Tumor Regression and Immunity. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 1018–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Sun, L.; Chen, Z.J. Regulation and function of the cGAS-STING pathway of cytosolic DNA sensing. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhun, A.S.; Haaheim, L.R.; Nostbakken, J.K.; Ebensen, T.; Chichester, J.; Yusibov, V.; Guzman, C.A.; Cox, R.J. Intranasal c-di-GMP-adjuvanted plant-derived H5 influenza vaccine induces multifunctional Th1 CD4+ cells and strong mucosal and systemic antibody responses in mice. Vaccine 2011, 29, 4973–4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, P.; Wu, M.X. Natural STING Agonist as an “Ideal” Adjuvant for Cutaneous Vaccination. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 2183–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa, D.A.; Beatty, P.R.; Reiner, G.L.; Sivick, K.E.; Hix Glickman, L.; Dubensky, T.W., Jr.; Harris, E. Cyclic Dinucleotide-Adjuvanted Dengue Virus Nonstructural Protein 1 Induces Protective Antibody and T Cell Responses. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, S.; Hiremath, J.; Bondra, K.; Lakshmanappa, Y.S.; Shyu, D.L.; Ouyang, K.; Kang, K.I.; Binjawadagi, B.; Goodman, J.; Tabynov, K.; et al. Biodegradable nanoparticle delivery of inactivated swine influenza virus vaccine provides heterologous cell-mediated immune response in pigs. J. Control Release 2017, 247, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artiaga, B.L.; Yang, G.; Hutchinson, T.E.; Loeb, J.C.; Richt, J.A.; Lednicky, J.A.; Salek-Ardakani, S.; Driver, J.P. Rapid control of pandemic H1N1 influenza by targeting NKT-cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauger, P.C.; Loving, C.L.; Vincent, A.L. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for detection of serum or mucosal isotype-specific IgG and IgA whole-virus antibody to influenza A virus in swine. In Animal Influenza Virus; Spackman, E., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 303–312. [Google Scholar]
- Spackman, E.; Sitaras, I. Hemagglutination Inhibition Assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2123, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, S.; Goodman, J.; Bondra, K.; Lakshmanappa, Y.S.; Hiremath, J.; Shyu, D.L.; Ouyang, K.; Kang, K.I.; Krakowka, S.; Wannemuehler, M.J.; et al. Polyanhydride nanovaccine against swine influenza virus in pigs. Vaccine 2017, 35, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauger, P.C.; Vincent, A.L. Serum Virus Neutralization Assay for Detection and Quantitation of Serum Neutralizing Antibodies to Influenza A Virus in Swine. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2123, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slifka, M.K.; Antia, R.; Whitmire, J.K.; Ahmed, R. Humoral immunity due to long-lived plasma cells. Immunity 1998, 8, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radbruch, A.; Muehlinghaus, G.; Luger, E.O.; Inamine, A.; Smith, K.G.; Dorner, T.; Hiepe, F. Competence and competition: The challenge of becoming a long-lived plasma cell. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Geyer, A.; Saif, L.J. Short-term immunoglobulin A B-cell memory resides in intestinal lymphoid tissues but not in bone marrow of gnotobiotic pigs inoculated with Wa human rotavirus. Immunology 2001, 103, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulupuri, P.; Zimmerman, J.J.; Hermann, J.; Johnson, C.R.; Cano, J.P.; Yu, W.; Dee, S.A.; Murtaugh, M.P. Antigen-specific B-cell responses to porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budroni, S.; Buricchi, F.; Cavallone, A.; Bourguignon, P.; Caubet, M.; Dewar, V.; D’Oro, U.; Finco, O.; Garcon, N.; El Idrissi, M.; et al. Antibody avidity, persistence, and response to antigen recall: Comparison of vaccine adjuvants. NPJ Vaccines 2021, 6, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, A.L.; Perez, D.R.; Rajao, D.; Anderson, T.K.; Abente, E.J.; Walia, R.R.; Lewis, N.S. Influenza A virus vaccines for swine. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 206, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsi, A.; Ansaldi, F.; de Florentiis, D.; Ceravolo, A.; Parodi, V.; Canepa, P.; Coppelli, M.; Icardi, G.; Durando, P. Cross-protection against drifted influenza viruses: Options offered by adjuvanted and intradermal vaccines. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2013, 9, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, I.F.; Zhang, A.J.; To, K.K.; Chan, J.F.; Li, P.; Wong, T.L.; Zhang, R.; Chan, T.C.; Chan, B.C.; Wai, H.H.; et al. Topical imiquimod before intradermal trivalent influenza vaccine for protection against heterologous non-vaccine and antigenically drifted viruses: A single-centre, double-blind, randomised, controlled phase 2b/3 trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, X. Adjuvantation of Influenza Vaccines to Induce Cross-Protective Immunity. Vaccines 2021, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, C.C.L.; Daniels, C.S.; Garcia, R.; Milward, F.; Nation, T. Needle-free injection technology in swine: Progress toward vaccine efficacy and pork quality. J. Swine Health Prod. 2008, 16, 254–261. [Google Scholar]
- Dalmau, A.; Sanchez-Matamoros, A.; Molina, J.M.; Xercavins, A.; Varvaro-Porter, A.; Munoz, I.; Moles, X.; Baulida, B.; Fabrega, E.; Velarde, A.; et al. Intramuscular vs. Intradermic Needle-Free Vaccination in Piglets: Relevance for Animal Welfare Based on an Aversion Learning Test and Vocalizations. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 715260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temple, D.; Jimenez, M.; Escribano, D.; Martin-Valls, G.; Diaz, I.; Manteca, X. Welfare Benefits of Intradermal Vaccination of Piglets. Animals 2020, 10, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salman, M.; Lin, H.; Suntisukwattana, R.; Watcharavongtip, P.; Jermsutjarit, P.; Tantituvanont, A.; Nilubol, D. Intradermal needle-free injection prevents African Swine Fever transmission, while intramuscular needle injection does not. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madapong, A.; Saeng-Chuto, K.; Tantituvanont, A.; Nilubol, D. Safety of PRRSV-2 MLV vaccines administrated via the intramuscular or intradermal route and evaluation of PRRSV transmission upon needle-free and needle delivery. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutwiri, G.; Gerdts, V.; van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk, S.; Auray, G.; Eng, N.; Garlapati, S.; Babiuk, L.A.; Potter, A. Combination adjuvants: The next generation of adjuvants? Expert. Rev. Vaccines 2011, 10, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubensky, T.W., Jr.; Kanne, D.B.; Leong, M.L. Rationale, progress and development of vaccines utilizing STING-activating cyclic dinucleotide adjuvants. Ther. Adv. Vaccines 2013, 1, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaolis, D.K.; Means, T.K.; Yang, D.; Takahashi, M.; Yoshimura, T.; Muraille, E.; Philpott, D.; Schroeder, J.T.; Hyodo, M.; Hayakawa, Y.; et al. Bacterial c-di-GMP is an immunostimulatory molecule. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 2171–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meric-Bernstam, F.; Sweis, R.F.; Hodi, F.S.; Messersmith, W.A.; Andtbacka, R.H.I.; Ingham, M.; Lewis, N.; Chen, X.; Pelletier, M.; Chen, X.; et al. Phase I Dose-Escalation Trial of MIW815 (ADU-S100), an Intratumoral STING Agonist, in Patients with Advanced/Metastatic Solid Tumors or Lymphomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, M.C.; Crespo, M.P.; Abraham, W.; Moynihan, K.D.; Szeto, G.L.; Chen, S.H.; Melo, M.B.; Mueller, S.; Irvine, D.J. Nanoparticulate STING agonists are potent lymph node-targeted vaccine adjuvants. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 2532–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junkins, R.D.; Gallovic, M.D.; Johnson, B.M.; Collier, M.A.; Watkins-Schulz, R.; Cheng, N.; David, C.N.; McGee, C.E.; Sempowski, G.D.; Shterev, I.; et al. A robust microparticle platform for a STING-targeted adjuvant that enhances both humoral and cellular immunity during vaccination. J. Control Release 2018, 270, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, P.; Yu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Lu, M.; Sun, Z.; Jiang, S.; Lu, L.; Wu, M.X. Pulmonary surfactant-biomimetic nanoparticles potentiate heterosubtypic influenza immunity. Science 2020, 367, eaau0810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garland, K.M.; Sheehy, T.L.; Wilson, J.T. Chemical and Biomolecular Strategies for STING Pathway Activation in Cancer Immunotherapy. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 5977–6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Franco, J.F.; Xie, S.; Thimmapuram, J.; Ragland, D.; HogenEsch, H. Mechanism of activation of porcine dendritic cells by an a-D-glucan nanoparticle adjuvant and a nanoparticle/poly(I:C) combination adjuvant. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 990900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Patel, G.B.; Hu, S.; Chen, W. Induction of mucosal immunity through systemic immunization: Phantom or reality? Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2016, 12, 1070–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Co-Rives, I.; Chen, A.Y.; Moore, A.C. Skin-Based Vaccination: A Systematic Mapping Review of the Types of Vaccines and Methods Used and Immunity and Protection Elicited in Pigs. Vaccines 2023, 11, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Luduec, J.B.; Debeer, S.; Piras, F.; Andreoni, C.; Boudet, F.; Laurent, P.; Kaiserlian, D.; Dubois, B. Intradermal vaccination with un-adjuvanted sub-unit vaccines triggers skin innate immunity and confers protective respiratory immunity in domestic swine. Vaccine 2016, 34, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelli, P.; Saleri, R.; Cavalli, V.; De Angelis, E.; Ferrari, L.; Benetti, M.; Ferrarini, G.; Merialdi, G.; Borghetti, P. Systemic and local immune response in pigs intradermally and intramuscularly injected with inactivated Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae vaccines. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 168, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinkora, M.; Sinkorova, J. B cell lymphogenesis in swine is located in the bone marrow. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 5023–5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benner, R.; Hijmans, W.; Haaijman, J.J. The bone marrow: The major source of serum immunoglobulins, but still a neglected site of antibody formation. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1981, 46, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lemke, A.; Kraft, M.; Roth, K.; Riedel, R.; Lammerding, D.; Hauser, A.E. Long-lived plasma cells are generated in mucosal immune responses and contribute to the bone marrow plasma cell pool in mice. Mucosal Immunol. 2016, 9, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, D. Instructing durable humoral immunity for COVID-19 and other vaccinable diseases. Immunity 2022, 55, 945–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medzhitov, R.; Schneider, D.S.; Soares, M.P. Disease tolerance as a defense strategy. Science 2012, 335, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, A.; Foxman, E.F.; Molony, R.D. Early local immune defences in the respiratory tract. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, I.S.; Baeten, D.L.P.; den Dunnen, J. The inflammatory function of human IgA. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 1041–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Peng, B.; Chang, H.; Zhang, R.; Lu, F.; Wang, F.; Fang, F.; Chen, Z. Intranasal Immunization of Mice to Avoid Interference of Maternal Antibody against H5N1 Infection. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernandez-Franco, J.F.; Yadagiri, G.; Patil, V.; Bugybayeva, D.; Dolatyabi, S.; Dumkliang, E.; Singh, M.; Suresh, R.; Akter, F.; Schrock, J.; et al. Intradermal Vaccination against Influenza with a STING-Targeted Nanoparticle Combination Adjuvant Induces Superior Cross-Protective Humoral Immunity in Swine Compared with Intranasal and Intramuscular Immunization. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11111699
Hernandez-Franco JF, Yadagiri G, Patil V, Bugybayeva D, Dolatyabi S, Dumkliang E, Singh M, Suresh R, Akter F, Schrock J, et al. Intradermal Vaccination against Influenza with a STING-Targeted Nanoparticle Combination Adjuvant Induces Superior Cross-Protective Humoral Immunity in Swine Compared with Intranasal and Intramuscular Immunization. Vaccines. 2023; 11(11):1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11111699
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernandez-Franco, Juan F., Ganesh Yadagiri, Veerupaxagouda Patil, Dina Bugybayeva, Sara Dolatyabi, Ekachai Dumkliang, Mithilesh Singh, Raksha Suresh, Fatema Akter, Jennifer Schrock, and et al. 2023. "Intradermal Vaccination against Influenza with a STING-Targeted Nanoparticle Combination Adjuvant Induces Superior Cross-Protective Humoral Immunity in Swine Compared with Intranasal and Intramuscular Immunization" Vaccines 11, no. 11: 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11111699
APA StyleHernandez-Franco, J. F., Yadagiri, G., Patil, V., Bugybayeva, D., Dolatyabi, S., Dumkliang, E., Singh, M., Suresh, R., Akter, F., Schrock, J., Renukaradhya, G. J., & HogenEsch, H. (2023). Intradermal Vaccination against Influenza with a STING-Targeted Nanoparticle Combination Adjuvant Induces Superior Cross-Protective Humoral Immunity in Swine Compared with Intranasal and Intramuscular Immunization. Vaccines, 11(11), 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11111699








