Whole Proteome-Based Therapeutic Targets Annotation and Designing of Multi-Epitope-Based Vaccines against the Gram-Negative XDR-Alcaligenes faecalis Bacterium
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Proteome Subtraction
2.2. Putative Immune Epitope Predictions in the Target Proteins
2.3. Target-Specific Multi-Epitope-Based Vaccine Designs against A. faecalis
2.4. Molecular Docking and Interaction Analysis
2.5. In Silico Cloning of the MEVCs (Multi-Epitope-Based Vaccine Constructs)
2.6. Immune Simulation
3. Results
3.1. Target Proteins Annotation for A. faecalis
3.2. Immunogenic Epitopes Prediction for Target Proteins
3.3. Target-Specific Design of Peptide-Based MEVCs
3.4. Modelling and Validation of Target-Specific Peptide-Based MEVCs
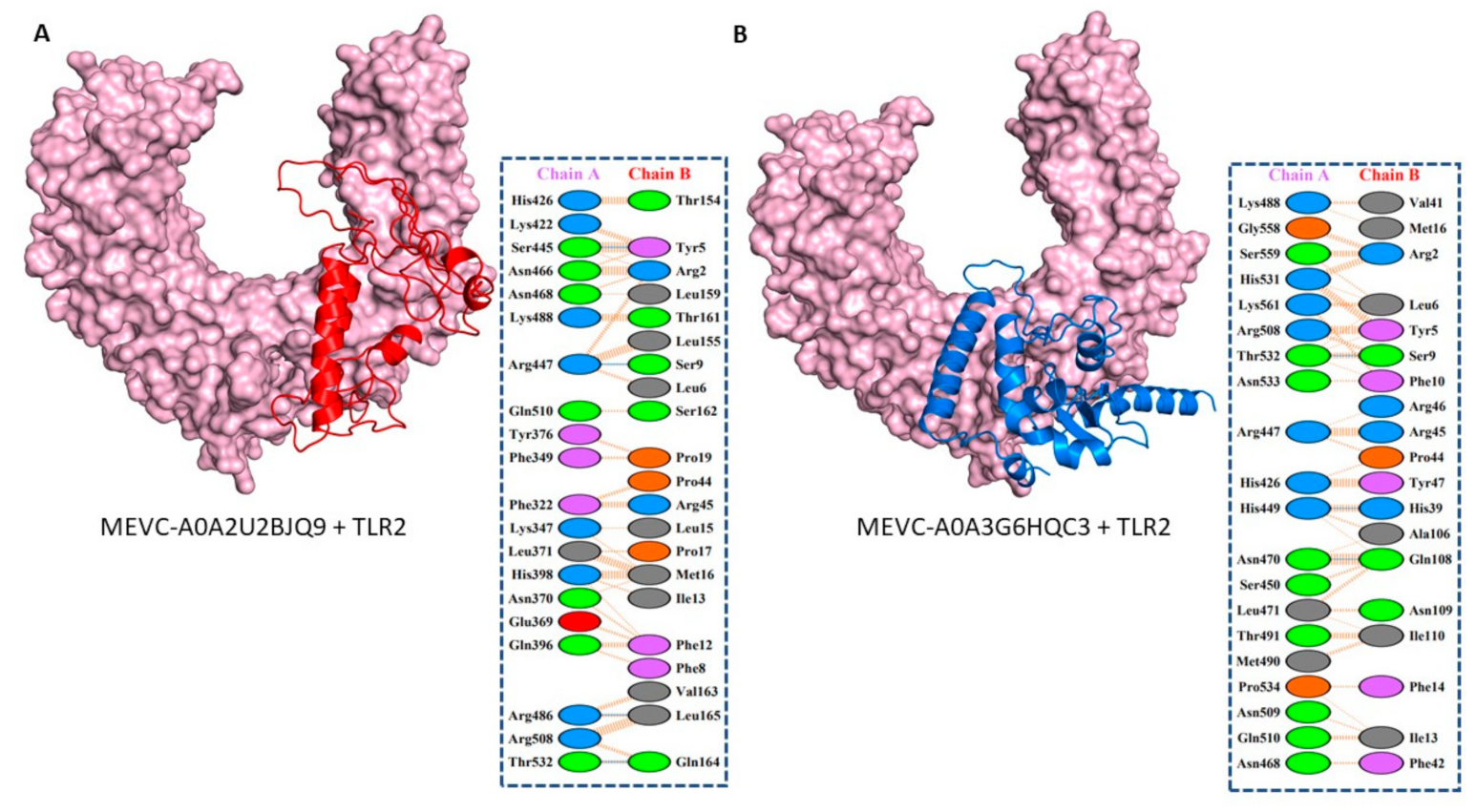
3.5. Molecular Docking and Interaction Analysis of the Designed MEVCs with Human TLR2
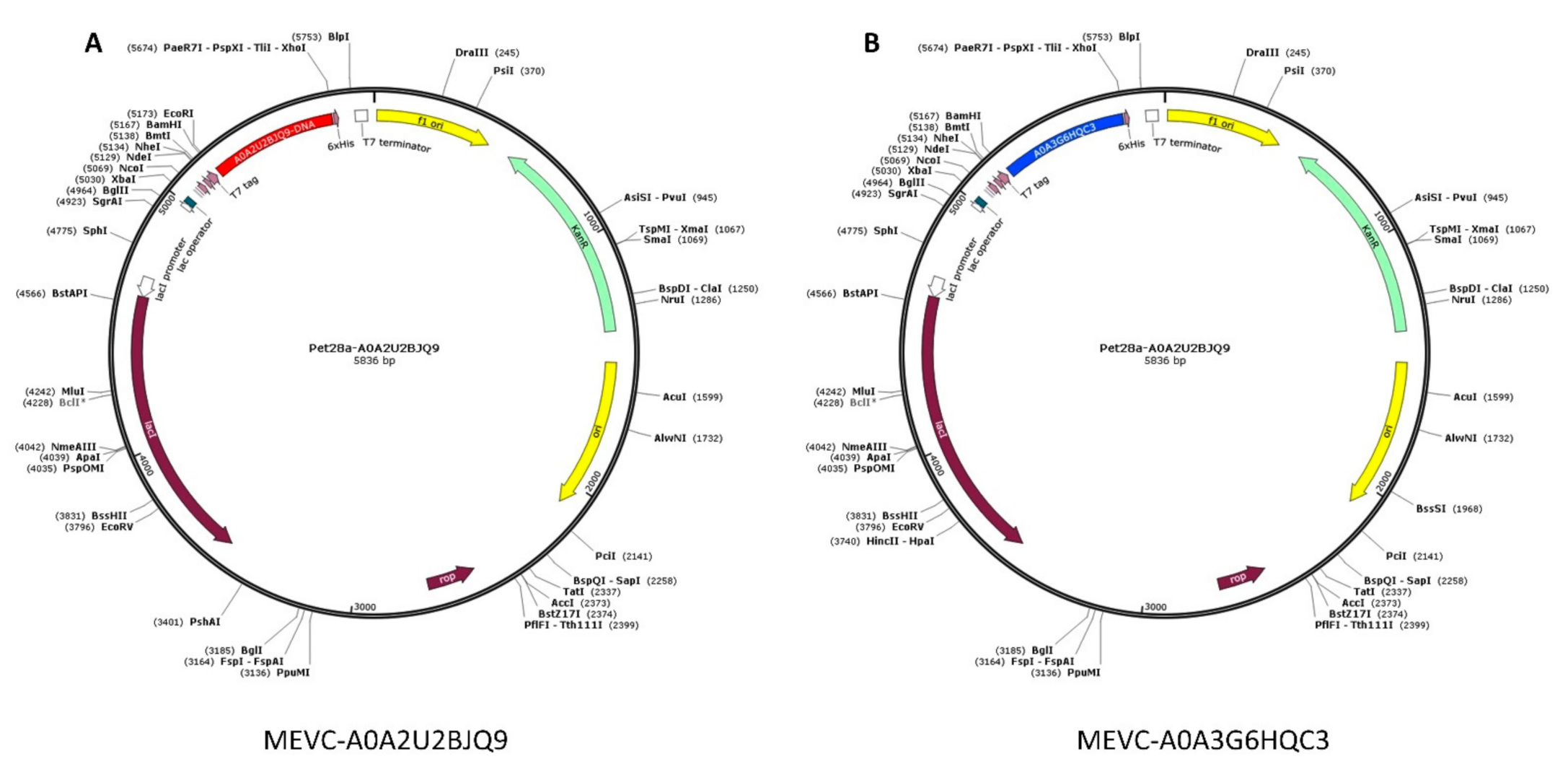
3.6. In Silico Cloning Design of WP-MEVC
3.7. Immune Simulation of the Proposed Vaccine
3.8. Limitations of the Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.; Giske, C.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizet, J.; Bizet, C. Strains of Alcaligenes faecalis from clinical material. J. Infect. 1997, 35, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, F.; Karami, P.; Zarei, O.; Kosari, F.; Alikhani, M.Y.; Zandkarimi, E.; Zarandi, E.R.; Taheri, M. Prevalence of common nosocomial infections and evaluation of antibiotic resistance patterns in patients with secondary infections in Hamadan, Iran. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, A.; Mirza, S.A.; Keating, C.; Ali, S.; Campos, L.C. Indigenous Bacillus paramycoides spp. and Alcaligenes faecalis: Sustainable solution for bioremediation of hospital wastewater. Environ. Technol. 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C. Diabetic foot ulcer with Alcaligenes faecalis infection. Dubai Diabetes Endocrinol. J. 2020, 26, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papen, H.; Von Berg, R.; Hinkel, I.; Thoene, B.; Rennenberg, H. Heterotrophic nitrification by Alcaligenes faecalis: NO2−, NO3−, N2O, and NO production in exponentially growing cultures. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1989, 55, 2068–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharali, P.; Das, S.; Konwar, B.; Thakur, A. Crude biosurfactant from thermophilic Alcaligenes faecalis: Feasibility in petro-spill bioremediation. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2011, 65, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttigarn, A.; Wang, Y.-T. Arsenite oxidation by Alcaligenes faecalis strain O1201. J. Environ. Eng. 2005, 131, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, H.-S.; Hirai, M.; Shoda, M. Characteristics of ammonium removal by heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification by Alcaligenes faecalis No. 4. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2005, 100, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neerackal, G.M.; Ndegwa, P.M.; Joo, H.-S.; Wang, X.; Frear, C.S.; Harrison, J.H.; Beutel, M.W. Potential application of Alcaligenes faecalis strain No. 4 in mitigating ammonia emissions from dairy wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 206, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, O.A.; Ali, S.S.; Azab, M.; El-Shouny, W.A.; Sun, J.; Mahmoud, Y.A.-G. Exploring new marine bacterial species, Alcaligenes faecalis Alca F2018 valued for bioconversion of shrimp chitin to chitosan for concomitant biotechnological applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 196, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C. Extensively drug-resistant Alcaligenes faecalis infection. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naas, T.; Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P. Minor extended-spectrum β-lactamases. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2008, 14, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavuncuoglu, F.; Unal, A.; Oguzhan, N.; Tokgoz, B.; Oymak, O.; Utas, C. First reported case of Alcaligenes faecalis peritonitis. Perit. Dial. Int. 2010, 30, 118–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warthen, R.O. Alcaligenes faecalis meningitis complicated by hydrocephalus in a premature twin: Report of Case; Intramuscular Chloramphenicol Therapy. AMA Am. J. Dis. Child. 1952, 84, 729–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordi, R.; Yusuf, E.; Onemu, S.; Igeleke, C.; Odjadjare, E. The prevalence of Alcaligenes faecalis in bacteremia, meningitis and wound sepsis in a tertiary health care institution in western part of Nigeria. Int. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 2, 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Sherman, J.D.; Ingall, D.; Wiener, J.; Pryles, C.V. Alcaligenes faecalis infection in the newborn. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1960, 100, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliaperumal, S.; Srinivasan, R.; Gupta, A.; Parija, S. Postoperative endophthalmitis due to an unusual pathogen: Alcaligenes faecalis. Eye 2006, 20, 968–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Verma, M.; Chhatwal, J.; Varughese, P. Neonatal conjunctivitis: A profile. Indian Pediatrics 1994, 31, 1357–1361. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Zakhari, R.; Suhail, M.; Ataallah, B.; Aljammali, S.; Grigos, A. Rare but Fatal Case of Cavitary Pneumonia Caused by Alcaligenes Faecalis. Cureus 2020, 12, e8934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tena, D.; Fernández, C.; Lago, M.R. Alcaligenes faecalis: An unusual cause of skin and soft tissue infection. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 68, 128–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basharat, Z.; Yasmin, A.; He, T.; Tong, Y. Genome sequencing and analysis of Alcaligenes faecalis subsp. phenolicus MB207. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsueh, P.-R.; Chen, M.-L.; Sun, C.-C.; Chen, W.-H.; Pan, H.-J.; Yang, L.-S.; Chang, S.-C.; Ho, S.-W.; Lee, C.-Y.; Hsieh, W.-C. Antimicrobial drug resistance in pathogens causing nosocomial infections at a university hospital in Taiwan, 1981–1999. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, S.S.; Panigrahi, P.K.; Roy, R.; Nandi, K.; Das, S. Endophthalmitis caused by Alcaligenes faecalis: A case series. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2013, 21, 446–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir ul Qamar, M.; Shokat, Z.; Muneer, I.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Javed, H.; Anwar, F.; Bari, A.; Zahid, B.; Saari, N. Multiepitope-based subunit vaccine design and evaluation against respiratory syncytial virus using reverse vaccinology approach. Vaccines 2020, 8, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Khan, S.; Saleem, S.; Nizam-Uddin, N.; Mohammad, A.; Khan, T.; Ahmad, S.; Arshad, M.; Ali, S.S.; Suleman, M. Immunogenomics guided design of immunomodulatory multi-epitope subunit vaccine against the SARS-CoV-2 new variants, and its validation through in silico cloning and immune simulation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 133, 104420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, B.; Wang, J.; Sun, H.; Lu, Z.; Chen, L.; Lan, M.; Xu, J.; Pan, J.; Shi, J. In silico analyses and experimental validation of the MHC class-I restricted epitopes of Ebolavirus GP. Int. Immunol. 2022, 28, 465–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann-Leitner, E.S.; Chaudhury, S.; Steers, N.J.; Sabato, M.; Delvecchio, V.; Wallqvist, A.S.; Ockenhouse, C.F.; Angov, E. Computational and experimental validation of B and T-cell epitopes of the in vivo immune response to a novel malarial antigen. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, A.S. In silico analysis and experimental validation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific proteins and peptides of Mycobacterium tuberculosis for immunological diagnosis and vaccine development. Med. Princ. Pract. 2013, 22, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consortium, U. UniProt: A worldwide hub of protein knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D506–D515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.S.; Chen, Y.C.; Lu, C.H.; Hwang, J.K. Prediction of protein subcellular localization. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2006, 64, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahram, A.; Herbordt, M.C. NCBI BLASTP on high-performance reconfigurable computing systems. ACM Trans. Reconfigurable Technol. Syst. 2015, 7, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Niu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, W. CD-HIT: Accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3150–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Godzik, A. Cd-hit: A fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1658–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doytchinova, I.A.; Flower, D.R. VaxiJen: A server for prediction of protective antigens, tumour antigens and subunit vaccines. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Patiyal, S.; Dhall, A.; Pande, A.; Arora, C.; Raghava, G.P. AlgPred 2.0: An improved method for predicting allergenic proteins and mapping of IgE epitopes. Brief. Bioinform. 2020, 24, bbaa294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stranzl, T.; Larsen, M.V.; Lundegaard, C.; Nielsen, M. NetCTLpan: Pan-specific MHC class I pathway epitope predictions. Immunogenetics 2010, 62, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Ponomarenko, J.; Zhu, Z.; Tamang, D.; Wang, P.; Greenbaum, J.; Lundegaard, C.; Sette, A.; Lund, O.; Bourne, P.E. Immune epitope database analysis resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W525–W530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanda, S.K.; Vir, P.; Raghava, G.P. Designing of interferon-gamma inducing MHC class-II binders. Biol. Direct 2013, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Raghava, G.P.S. Prediction methods for B-cell epitopes. In Immunoinformatics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 387–394. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, S.; Raghava, G.P.S. Prediction of continuous B-cell epitopes in an antigen using recurrent neural network. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2006, 65, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.; Khan, A.; Nasir, S.N.; Ahmad, S.; Ali, S.S.; Wei, D.-Q. CytomegaloVirusDb: Multi-Omics knowledge database for Cytomegaloviruses. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 135, 104563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, T.; Khan, A.; Wei, D.-Q. MMV-db: Vaccinomics and RNA-based therapeutics database for infectious hemorrhagic fever-causing mammarenaviruses. Database 2021, 2021, baab063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvizpour, S.; Pourseif, M.M.; Razmara, J.; Rafi, M.A.; Omidi, Y. Epitope-based vaccine design: A comprehensive overview of bioinformatics approaches. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.E.; Chivian, D.; Baker, D. Protein structure prediction and analysis using the Robetta server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W526–W531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiederstein, M.; Sippl, M.J. ProSA-web: Interactive web service for the recognition of errors in three-dimensional structures of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W407–W410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskowski, R.; MacArthur, M.; Thornton, J. PROCHECK: Validation of Protein-Structure Coordinates. In International Tables for Crystallography; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/iucr/itc/Fa/ch25o2v0001/sec25o2o6/ (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. In The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Humana Press: Clifton, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 571–607. [Google Scholar]
- Invernizzi, R.; Lloyd, C.M.; Molyneaux, P.L. Respiratory microbiome and epithelial interactions shape immunity in the lungs. Immunology 2020, 160, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, G.; Wang, E.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhu, F.; Li, D.; Hou, T. HawkDock: A web server to predict and analyze the protein–protein complex based on computational docking and MM/GBSA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W322–W330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huminiecki, L.; Bicknell, R. In silico cloning of novel endothelial-specific genes. Genome Res. 2000, 10, 1796–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrees, M.; Noorani, M.Y.; Altaf, K.U.; Alatawi, E.A.; Aba Alkhayl, F.F.; Allemailem, K.S.; Almatroudi, A.; Ali Khan, M.; Hamayun, M.; Khan, T. Core-Proteomics-Based Annotation of Antigenic Targets and Reverse-Vaccinology-Assisted Design of Ensemble Immunogen against the Emerging Nosocomial Infection-Causing Bacterium Elizabethkingia meningoseptica. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grote, A.; Hiller, K.; Scheer, M.; Münch, R.; Nörtemann, B.; Hempel, D.C.; Jahn, D. JCat: A novel tool to adapt codon usage of a target gene to its potential expression host. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W526–W531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapin, N.; Lund, O.; Castiglione, F. Immune system simulation online. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2013–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delves, P.J.; Roitt, I.M. The immune system. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y. Omics-based systems vaccinology for vaccine target identification. Drug Dev. Res. 2012, 73, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawal, K.; Sinha, R.; Abbasi, B.A.; Chaudhary, A.; Nath, S.K.; Kumari, P.; Preeti, P.; Saraf, D.; Singh, S.; Mishra, K. Identification of vaccine targets in pathogens and design of a vaccine using computational approaches. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, T.; Abdullah, M.; Toor, T.F.; Almajhdi, F.N.; Suleman, M.; Iqbal, A.; Ali, L.; Khan, A.; Waheed, Y.; Wei, D.-Q. Evaluation of the Whole Proteome of Achromobacter xylosoxidans to Identify Vaccine Targets for mRNA and Peptides-Based Vaccine Designing Against the Emerging Respiratory and Lung Cancer-Causing Bacteria. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 825876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boes, D.M.; Godoy-Hernandez, A.; McMillan, D.G. Peripheral Membrane Proteins: Promising therapeutic targets across domains of life. Membranes 2021, 11, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, A.R.; Yerbury, J.J.; Poon, S.; Wilson, M.R. Therapeutic targets in extracellular protein deposition diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 2855–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Pinilla, C.; Valmori, D.; Martin, R.; Simon, R. Application of support vector machines for T-cell epitopes prediction. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1978–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Shahid, F.; Tahir ul Qamar, M.; Rehman, H.U.; Abbasi, S.W.; Sajjad, W.; Ismail, S.; Alrumaihi, F.; Allemailem, K.S.; Almatroudi, A.; et al. Immuno-informatics analysis of PAKISTAN-based HCV subtype-3a for chimeric polypeptide vaccine design. Vaccines 2021, 9, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, R.A.; MacArthur, M.W.; Moss, D.S.; Thornton, J.M. PROCHECK: A program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1993, 26, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Ahmad, S.; Ismail, S.; Afsheen, Z.; Khurram, M.; Tahir ul Qamar, M.; AlSuhaymi, N.; Alsugoor, M.H.; Allemailem, K.S. Towards A Novel Multi-Epitopes Chimeric Vaccine for Simulating Strong Immune Responses and Protection against Morganella morganii. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naz, S.; Ahmad, S.; Abbasi, S.W.; Ismail, S.; Waseem, S.; ul Qamar, M.T.; Almatroudi, A.; Ali, Z. Identification of immunodominant epitopes in allelic variants VK210 and VK247 of Plasmodium Vivax Circumsporozoite immunogen. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 96, 105120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, I.; Ahmad, S.; Abbasi, S.W.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Shahid, F.; ul Qamar, M.T.; Rehman, A.; Allemailem, K.S. Designing of a multi-epitopes-based peptide vaccine against rift valley fever virus and its validation through integrated computational approaches. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 141, 105151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gul, S.; Ahmad, S.; Ullah, A.; Ismail, S.; Khurram, M.; ul Qamar, M.T.; Hakami, A.R.; Alkhathami, A.G.; Alrumaihi, F.; Allemailem, K.S. Designing a Recombinant Vaccine against Providencia rettgeri Using Immunoinformatics Approach. Vaccines 2022, 10, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Accession ID (UniProt) | Prioritized Proteins | Antigenicity Scores | Allergenicity Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| A0A2U2BJQ9 | Hcp1 family type VI secretion system effector | 1 | Non-Allergen |
| A0A3G6HQC3 | Uncharacterized protein | 0.93 | Non-Allergen |
| A0A3G6HK40 | Uncharacterized protein | 0.87 | Non-Allergen |
| Accession ID (UniProt) | Epitope | Number of Epitopes | Peptide Sequences | Antigenicity Scores | Allergenicity Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0A3G6HQC3 | T-cell | 2 | QAARVKQQY KAGGEQVEY | 0.93 0.75 | Non-allergens |
| A0A3G6HQC3 | B-cell | 2 | MSSGGGGGQGKANFND CKAGGEQVEYSKITLE | 2.7 1.3 | Non-allergens |
| A0A3G6HQC3 | HTL | 2 | ESVMVNYSFQAARVK SKITLEEVLVTSVQL | 0.8 0.5 | Non-allergens |
| A0A2U2BJQ9 | T-cell | 2 | ETEGVAIGY NASLNGLNY | 0.95 0.89 | Non-allergen |
| A0A2U2BJQ9 | B-cell | 2 | DGNENVALGRDAGQNI HWNVEAPTDGKEGGNT | 0.5 2.2 | Non-allergens |
| A0A2U2BJQ9 | HTL | 2 | VAEFNSSIAVGREAQ NGSFAYNGGQHSSLK | 0.5 0.79 | Non-allergens |
| Vaccine Name | Peptide Sequences | Amino Acids (Number) | Molecular Weight (kd) | Theoretical pI | Aliphatic Index | Hydropathicity (GRAVY) | Antigenicity Score | Antigenicity Status | Allergenicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEVC-A0A2U2BJQ9 | MRVLYLLFSFLFIFLMPLPGVFGGIGDPVTCLKSGAICHPVFCPRRKQIGTCGLPGTKCCKKPEAAKQAARVKQQYAAYKAGGEQVEY GPGPGMSSGGGGGQGKANFND GPGPGCKAGGEQVEYSKITLEKKESVMVNYSFQAARVKKKSKITLEEVLVTSVQL | 165 | 17.5 kd | 9.41 | 72.67 | −0.145 | 1.16 | Antigen | Non-Allergen |
| MEVC-A0A3G6HQC3 | MRVLYLLFSFLFIFLMPLPGVFGGIGDPVTCLKSGAICHPVFCPRRYKQIGTCGLPGTKCCKKPEAAKETEGVAIGYAAYNASLNGLNYPGPGDGNENVALGRDAGQNIGPGPGHWNVEAPTDGKEGGNTKKVAEFNSSIAVGREAQKKNGSFAYNGGQHSSLK | 165 | 17.2 kd | 8.91 | 69.21 | −0.251 | 0.97 | Antigen | Non-Allergen |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alharbi, M.; Alshammari, A.; Alasmari, A.F.; Alharbi, S.; Tahir ul Qamar, M.; Abbasi, S.W.; Shaker, B.; Ahmad, S. Whole Proteome-Based Therapeutic Targets Annotation and Designing of Multi-Epitope-Based Vaccines against the Gram-Negative XDR-Alcaligenes faecalis Bacterium. Vaccines 2022, 10, 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10030462
Alharbi M, Alshammari A, Alasmari AF, Alharbi S, Tahir ul Qamar M, Abbasi SW, Shaker B, Ahmad S. Whole Proteome-Based Therapeutic Targets Annotation and Designing of Multi-Epitope-Based Vaccines against the Gram-Negative XDR-Alcaligenes faecalis Bacterium. Vaccines. 2022; 10(3):462. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10030462
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlharbi, Metab, Abdulrahman Alshammari, Abdullah F. Alasmari, Saud Alharbi, Muhammad Tahir ul Qamar, Sumra Wajid Abbasi, Bilal Shaker, and Sajjad Ahmad. 2022. "Whole Proteome-Based Therapeutic Targets Annotation and Designing of Multi-Epitope-Based Vaccines against the Gram-Negative XDR-Alcaligenes faecalis Bacterium" Vaccines 10, no. 3: 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10030462
APA StyleAlharbi, M., Alshammari, A., Alasmari, A. F., Alharbi, S., Tahir ul Qamar, M., Abbasi, S. W., Shaker, B., & Ahmad, S. (2022). Whole Proteome-Based Therapeutic Targets Annotation and Designing of Multi-Epitope-Based Vaccines against the Gram-Negative XDR-Alcaligenes faecalis Bacterium. Vaccines, 10(3), 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10030462









