Abstract
The absent decline in cancer mortality rates is primarily due to moderate therapeutic efficacy and intrinsic or acquired tumor cell resistance toward treatments. Combining different oncology treatments increases therapy success and decreases the chance of refractory tumor cells. Therefore, combination cancer treatments are the principal paradigm of 21st-century oncology. Physical modalities such as radiotherapy have a long-standing tradition in such combination treatments. In the last decade, another physical principle emerged as a promising anticancer agent: cold gas plasma. This partially ionized gas, operated at about body temperature, emits multiple bioactive components, including reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (ROS/RNS). This technology’s multi-ROS/RNS nature cannot be phenocopied by other means, and it capitalizes on the vulnerability of tumor cells within metabolic and redox signaling pathways. Many cancer models exposed to mono or combination gas plasma treatments have shown favorable results, and first cancer patients have benefited from cold gas plasma therapy. The main findings and proposed mechanisms of action are summarized. Considering the specific application modes, this review identifies promising gas plasma combination therapies within guideline-directed treatment schemes for several tumor entities. In conclusion, gas plasmas may become a potential (neo)adjuvant therapy to existing treatment modalities to help improve the efficacy of oncological treatments.
1. Intoduction
Despite progress in diagnostic techniques and therapeutic approaches in oncology, the global cancer burden is still increasing and constitutes the leading cause of death worldwide [1]. Although cancer mortality rates have gradually improved among Western countries, cancer incidences are rising for the majority of malignancies. Moreover, the efficacy of many oncological treatments is insufficient and steadily results in therapy failures. Intrinsic or acquired resistances further lead to tumor relapses that cause poor patient prognosis. Multimodal combination approaches are proposed as the most promising innovation in the fight against cancer since they comprise the simultaneous or sequential administration of multiple therapy options, exploiting different mechanisms of action to achieve an augmented efficacy. Additionally, the risk of tumor resistance is reduced, and the severity of toxic side effects can be alleviated since a combination of complementary treatment techniques can sensitize tumor cells, lowering the required therapeutic dosage of the second treatment to obtain the same or stronger antitumor effect [2,3]. For example, a phase II clinical trial investigating a combinatory approach of curcuminoids with concurrent chemotherapy demonstrated improved efficacy paralleled by reduced adverse events and increased quality of life in patients compared to monotherapy [4].
Cold physical plasma, an oxidative stress-inducing multicomponent system, has been suggested as a novel adjuvant therapy tool as it has shown promising potential for anticancer treatment [5] and even more powerful tumor toxicity in combination with other therapeutic options like radiotherapy, chemotherapy, or nanoparticles [6,7,8]. Due to its highly reactive nature, gas plasma can prime tumor cells for additional treatments and elicits cell physiological changes like the upregulation of drug transporters or immunogenic cell death markers, which can lead to enhanced toxicity of co-therapies by elevated intracellular accumulation of chemotherapeutic agents (e.g., doxorubicin) or efficacy of immunotherapies, respectively [8,9]. Simultaneously, it shows prominent tumor selectivity that enables evidently good tissue tolerability and low side effects, rendering gas plasma a promising technology to sensitize cancer cells in the context of combination therapies and thus revolutionizing multimodal anticancer concepts.
This review summarizes the main findings of combining cold physical plasma with other oncological approaches and current preclinical progress across several cancer types. Furthermore, the translation of such combination strategies in prospective medical applications, potential future objectives, and limitations that need to be addressed for successful clinical implementation are discussed.
2. Gas Plasma Technology
Gas plasma, also known in physics as physical plasma, is a partially ionized gas composed of various bioactive components like reactive species, light (VIS, UV), thermal radiation, and electromagnetic fields (Figure 1). It is generated by applying external energy, usually in the form of an electric field, to excite gas molecules [10]. The applied electric field energizes electrons that can collide with gas molecules of the ambient air, creating new charged particles. Leap innovations, a few decades ago, facilitated the generation of plasmas at atmospheric pressure into the ambient air while remaining at about body temperature. This enabled the use of cold plasma for biomedical and clinical applications [11]. Due to the potent antimicrobial activity of gas plasma exposure [12,13], the technology was soon tested for the treatment of chronic, non-healing wounds and ulcers, as these are often heavily infected with microorganisms of different kinds [14,15]. Intriguingly, early clinical investigations were successful in reducing microbial burden in wounds and facilitated their healing [16,17], leading to the approval of several medical gas plasma devices in Europe for dermatology applications [18]. Thus, multiple risk assessment studies have demonstrated and validated the safety and good tissue tolerability of this therapeutic tool. Due to its high tumor selectivity [19,20,21], the plasma application causes merely low side effects, being primarily restricted to the local treatment area. No mutagenic, genotoxic [22], or long-term side effects were observed in animal experiments [23], and irritation assays using the in ovo HET-CAM egg model revealed no significantly higher irritative potential compared to conventional therapeutic agents, e.g., cisplatin, but instead a notably better reversibility of induced irritative pattern [24].
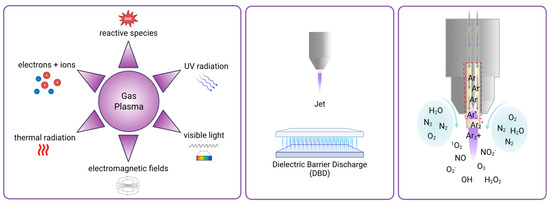
Figure 1.
Gas plasmas’ main biologically active components, device types, and exemplary principle of ROS production. Gas plasma is composed of various physical and chemical gas plasma components with biological activity (left). Gas plasma for medical applications is commonly generated with either atmospheric pressure plasma jets, in which a feed gas (e.g., helium or argon) flowing through a nozzle is excited by applying high voltage, or with dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) devices, where ambient air is excited between two electrodes. Representative drawings of the two device types are shown here (middle). Reactive species causing biological effects like singlet oxygen, superoxide, ozone, nitric oxide, nitrate, hydroxyl radical, and hydrogen peroxide are generated by the reaction of excited gas molecules (e.g., argon gas in a jet device, red square) with oxygen, nitrogen, and water molecules from ambient air (right).
Standard methods to generate such gas plasmas for clinical use include dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) [25], where electrical discharge occurs in ambient air between two electrodes separated by an insulating dielectric barrier, and jet discharge, where a working gas (such as helium or argon) flows through a nozzle or capillary and generates a plasma plume by applying high voltage [26] (Figure 1). Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (ROS/RNS) of various types produced by gas plasmas were found to be significant components mediating biological effects in gas plasma, independent of the gas plasma device geometry being jet-like or DBDs [27]. Major ROS are, for instance, superoxide (O2−), singlet oxygen (1O2), ozone (O3), hydroxyl radical (•OH), and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Major RNS are, for example, nitric oxide (NO) and nitrite (NO2−) [28] (Figure 1). As most RNS contain reactive oxygen, ROS/RNS will be abbreviated as ROS from hereon. Next to its supportive properties for wound healing, it was shown that gas plasma is also able to confer cytotoxicity based on dose-dependent opposing effects, which are explained by the concept of hormesis [29]. In cells and tissues, it is known that ROS can lead to oxidative eustress and distress [30]. Oxidative eustress is essential to cell viability, differentiation, and proliferation [31]. On the contrary, excess ROS apparent in oxidative distress causes cell damage or even death by triggering downstream effects, including DNA strand breaks, oxidation of proteins and lipids, resulting in activation of apoptotic pathways [32]. The potential of gas plasma to treat cancer was shown in recent years for a number of different tumor entities, including breast cancer, colorectal cancer, glioblastoma, leukemia, lung cancer, melanoma, and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) in vitro and in vivo, as reviewed before [33].
The induced cell death modality of apoptosis is mainly reported to be the cause of gas plasma-mediated anticancer effects, visible in, e.g., caspase 3 and 7 activation [34], mitochondrial membrane potential loss [35], or histone 2AX phosphorylation (yH2AX) [36,37]. Nevertheless, further types of cell death were found to be induced, such as ferroptosis [38,39], pyroptosis [40], and autophagy [41]. Another mode of action observed in gas plasma-mediated cancer cell death is the modulation of immunogenicity. Hallmarks of immunogenic cell death (ICD), like ATP secretion [42] or HMGB1 externalization [43,44], have been shown to be induced upon plasma treatment in vitro and in vivo. Despite broad preclinical evidence, plasma cancer treatment is still lacking clinical studies. So far, only five clinical trials investigating gas plasma for the treatment of cancer or precancerous lesions registered on ClinicalTrials.gov have been completed (Table 1). The completed trials on plasma treatment of cervical intraepithelial neoplasias (CIN) [45], anal intraepithelial neoplasias (AIN) [46], actinic keratosis lesions [47], and combination with tumor resection [48] could already show promising anticancer actions of gas plasma while being safe without serious adverse events.

Table 1.
Clinical trials registered on ClinicalTrials.gov that mention the utilization of medical gas plasma technology to treat cancer.
3. Combination Treatment with Gas Plasmas in Experimental Models
Gas plasma emerged as a cancer treatment and has been proven effective. It has broadened its application via various therapies in oncology. Furthermore, cold gas plasma exposure can display local and/or systemic properties. The former indicates that gas plasma could be directly used locally on tumor entities like melanoma, while the latter points to gas plasma-driven immune-related mechanisms [5] and/or gas plasma-treated liquid (PTL) used to flush larger body cavities such as the peritoneum [49]. Several in vitro and in vivo studies (Table 2) combining gas plasma technology with other systemic or local anticancer approaches are available, and significant findings are summarized in the following sections.
Although surgery serves as the preferred first-line therapy, particularly for early or mid-stage tumors, advanced disease stages require multimodal therapies to eradicate local malignancies and metastatic lesions [50,51]. Systemic therapies have the benefit of reaching primary tumors and metastases at almost all body sites through the blood circulation. Still, they are often associated with severe side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, and impaired immunity [52]. In contrast, local therapies directly impose their action in an often spatiotemporally controlled manner onto the treatment sites. Even if the clinical discipline of oncology has evolved multidisciplinary and partially highly successful treatment regimes, existing or new challenges arise with those, such as drug resistance triggering therapy failures and long-term treatment duration, as well as adverse events reducing a patient’s quality of life [53], continuously motivating the search for innovative anticancer treatments. Implementation of cold physical plasma as a medical adjuvant could bridge known shortcomings of insufficient treatment options in a synergistic or additive manner. Gas plasma-induced oxidation of cell membranes could increase the membrane permeability, promoting uptake of applied therapeutic agents [54,55] and sensitization of tumor cells for the following treatments [56]. Furthermore, a plethora of redox-regulated signaling pathways are initiated that can lead to augmented expression of drug-relevant transporters, which in turn facilitate the enhanced intracellular accumulation of chemotherapeutics. By stimulating immunogenic cancer cell death, plasma additionally mounts the antitumor immunity, not only tackling tumor metastasis but also recurrences. Patients could tremendously benefit from the integration of gas plasma in multimodal concepts, as it has the potential to optimize therapeutic efficacy, improve therapy outcomes, and decrease the required dose of toxic treatment approaches, e.g., chemotherapy, mitigating undesired side effects.

Table 2.
Studies on combining gas plasmas with anticancer treatment modalities. Anticancer treatments combined with gas plasma treatment are sorted alphabetically. BT = biologicals (e.g., virotherapy, hormone therapy, and non-checkpoint antibody therapy); CT = chemotherapy; EA = experimental agents; ECT = electrochemotherapy; HT = hyperthermia; IT = immunotherapy (including checkpoint antibody therapy); NP = nanoparticle; PDT = photodynamic therapy; PEF = pulsed electric fields; RT = radiotherapy; and TT = targeted therapy.
Table 2.
Studies on combining gas plasmas with anticancer treatment modalities. Anticancer treatments combined with gas plasma treatment are sorted alphabetically. BT = biologicals (e.g., virotherapy, hormone therapy, and non-checkpoint antibody therapy); CT = chemotherapy; EA = experimental agents; ECT = electrochemotherapy; HT = hyperthermia; IT = immunotherapy (including checkpoint antibody therapy); NP = nanoparticle; PDT = photodynamic therapy; PEF = pulsed electric fields; RT = radiotherapy; and TT = targeted therapy.
| Combined Anticancer Treatment | Type of Cancer | Agent/Clinically Relevant | Gas Plasma Source | Study Model | Additive/Synergistic Effect | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BT | Melanoma | Cell starvation/yes | kINPen (Ar) | In vivo: Syngeneic | Yes | [57] |
| BT | Breast | Melittin/yes | kINPen (Ar) | In ovo: TUM-CAM | Yes | [58] |
| CT | Melanoma | Cyclophosphamide/no | Jet (He) | In vivo: Syngeneic | Yes | [59] |
| CT | Melanoma | Dacarbazine/yes | Jet (Ar) | In vivo: Syngeneic | Yes | [60] |
| CT | Melanoma | Bleomycin/yes Dacarbazine/yes Paclitaxel/yes | Jet (Ar) | In vitro | Yes | [61] |
| CT | Melanoma | Doxorubicin/yes Epirubicin/yes Oxaliplatin/yes | kINPen (Ar) | In vitro | Yes | [8] |
| CT | Melanoma | Doxorubicin/yes | DBD | In vitro | Yes | [62] |
| CT | OSCC | Cisplatin/yes | P500-SM (Ar) | In vitro | Yes | [63] |
| CT | HNSCC | Cisplatin/yes | SMD | In vitro | Yes | [64] |
| CT | Breast | Doxorubicin/yes | Jet (He) | In vitro | Yes | [65] |
| CT | Breast | Doxorubicin | Jet (Ar) | In vitro | Yes | [66] |
| CT | Breast | Paclitaxel/yes | DBD | In vitro | Yes | [67] |
| CT | Glioma | Temozolomide/yes | Jet (He) | In vitro | Yes | [68] |
| CT | Glioma | Temozolomide/yes | kINPen (Ar) | In vitro | Yes | [69] |
| CT | Glioma | Temozolomide/yes | DBD | In vitro | Yes | [70] |
| CT | Glioma | Temozolomide/yes | SMD | In vitro | Yes | [71] |
| CT | Glioma | Topotecan/no | Glow charge/spark discharge (Air) | In vitro | Yes | [72] |
| CT | Endometrial, Gastric | Cisplatin/yes | Unknown (Ar) | In vivo: Xenograft | Yes Yes | [73] |
| CT | Liver | Cisplatin/yes | DBD | In vitro | Yes | [74] |
| CT | Pancreas | Gemcitabine/yes Cisplatin/yes | kINPen (Ar) | In ovo: TUM-CAM | Yes Yes | [75] |
| CT | Pancreas | Gemcitabine/yes | Plasma gun (He) | In vitro | Yes | [76] |
| CT | Bladder | Cisplatin/yes Methotrexate/yes Adriamycin/yes paclitaxel/yes | Jet (He) | In vitro | Yes | [77] |
| CT | Ovary | Cisplatin/yes | Jet (Ar) | In vitro | Yes | [78] |
| CT | Prostate (Bone Metastasis) | Doxorubicin/yes | kINPen (Ar) | In vitro | Yes | [79] |
| CT | Ewing Sarcoma | Doxorubicin/yes Vincristine/yes | kINPen (Ar) | In vitro | Yes Yes | [80] |
| CT | Ewing Sarcoma | Methotrexate/yes Cisplatin/yes | kINPen (Ar) | In vitro | Yes | [37] |
| CT | Osteosarcoma | Salinomycin/no | Jet (He) | In vivo: Syngeneic | Yes | [81] |
| EA | Melanoma, SCC | Sm837/no, IS112/no | kINPen (Ar) | In vivo: Xenograft | Yes | [82] |
| EA | Melanoma | ADDA 5/no | kINPen (Ar) | In vitro | Yes | [83] |
| EA | Melanoma | Curcumin/no | Jet (Ar) | In vitro | No | [84] |
| EA | Melanoma | Salinomycin/no | Jet (Ar) | In vitro | Yes | [81] |
| EA | Breast | Pluronic F127/no | Jet (He) | In vivo: Syngeneic | Yes | [85] |
| EA | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | Chloroquine/no | Jet (He) | In vitro | Yes | [86] |
| EA | Glioma | Auranofin/no | kINPen (Ar) | In vivo: Syngeneic | Yes | [87] |
| EA | Glioma | Vitamin C/no | kINPen (Ar) | In vivo: Xenograft | Yes | [88] |
| EA | Glioma | Pyrazolopyrimidinone/no | DBD | In vitro | Yes | [89] |
| EA | Acute Lymphoid Leukemia | Sulfasalazine/no | PN-120TPG (Ar) | In vitro | Yes | [90] |
| ECT | Melanoma | ECT bleomycin/yes | Jet (Ar), DBD | In vivo: Syngeneic | Yes | [91] |
| ECT | Fibrosarcoma | ECT bleomycin/yes | PMJ (He) | In vivo: Syngeneic | Yes | [92] |
| HT | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | Hyperthermia/yes | Unknown (Ar) | In vitro | Yes | [93] |
| IT | Melanoma | Anti-PD-L1/no | Jet (He) | In vivo: Syngeneic | Yes | [94] |
| IT and EA | Melanoma | Pembrolizumab/yes, A-1210477/no, Carvedilol/no, Cozymasei/no, SBI-0206965/no, Navitoclax/no | kINPen (Ar) | In vivo: Syngeneic | Yes | [95] |
| NP | Melanoma | Nanoparticle/no (Si, Ag, FeO, CeO2, TiO2, FeTiO2) | kINPen (Ar) | In vitro | Yes | [96] |
| NP | Melanoma | Anti-NEU gold nanoparticle/no | DBD | In vitro | Yes | [97] |
| NP | Melanoma | p-FAK gold nanoparticle/no | DBD | In vitro | Yes | [98] |
| NP | Melanoma | Anti-FAK gold nanoparticle/no | Unknown (Air) | In vitro | Yes | [99] |
| NP | Melanoma | Silver nanoparticle/no | pm-rf-APGD | In vitro | Yes | [100] |
| NP | Breast | Iron particle/no | Jet (He) | In vitro | Yes | [101] |
| NP | Breast | Nanoparticle/no | Unknown | In vitro | Yes | [102] |
| NP | Colon | Gold nanoparticle/no | Jet (He) | In vitro | Yes | [103] |
| NP | Glioma | Gold nanoparticle/no | DBD | In vitro | Yes | [104] |
| NP | Glioma | Silver nanoparticle/no | DBD | In vitro | Yes | [105] |
| NP | Glioma | Gold nanoparticle/no | Jet (He) | In vitro | Yes | [106] |
| NP | Glioma | Gold quantum dots/no | Jet (Air) | In vitro | Yes | [107] |
| NP | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | Iron oxide-based magnetic nanoparticle/no | Jet (He) | In vitro | Yes | [108] |
| NP and BT | Melanoma | Silymarin nanoemulsion/no | DBD | In vitro | Yes | [109] |
| NP and BT | Melanoma | Silymarin nanoemulsion/no | DBD | In vivo: Xenograft | Yes | [110] |
| NP and CT | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | Paclitaxel-loaded magnetic nanoparticles | Jet (He) | In vitro | Yes | [111] |
| NP and PDT | Melanoma | Photodynamic therapy (nanoparticle)/yes | Unknown | In vitro | Yes | [112] |
| PDT | Colon | Photodynamic therapy/yes | Jet (He) | In vitro | Yes | [113] |
| PDT | Glioma | Photodynamic therapy/yes | Jet (He) | In vitro | Yes | [113] |
| PDT | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | Photodynamic therapy/yes | Jet (He) | In vitro | Yes | [114] |
| PEF | Pancreas | Pulsed electric field/no | Jet (He) | In vitro | Yes | [115] |
| RT | Melanoma | Radiation/yes | kINPen (Ar) | In vitro | Yes | [116] |
| RT | Hepatoblastoma | Radiation/yes | Jet (Ar + O2) | In vivo: Xenograft | No | [6] |
| RT and TT | Breast | Radiation therapy/yes Olaparib/yes | Jet (He) | In vitro | Yes | [117] |
3.1. Systemic Agents
3.1.1. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapies are traditional anticancer treatments using synthetic or extracted elements, which will circulate through the body fluid by intravenous or oral medication and then enter cells to interfere with cellular metabolism. Chemotherapy is classified into alkylating agents, antimetabolites, hormones and antagonists, natural products, and miscellaneous [118], and it is known to mainly hamper DNA and RNA synthesis and disrupt mitosis [119]. Current gas plasma combinations with chemotherapy all show synergistic effects in at least one cell line. So far, clinically relevant chemotherapies investigated only involve three categories: alkylating agents, antimetabolites, and natural products.
In alkylating agents, cyclophosphamide combination points out that the synergistic effect is associated with activation of p53 and Bax/Bcl-2 markers by plasma via enhancing ROS levels [59]. Dacarbazine combination showed a synergistic effect in melanoma cells in vitro and in vivo [60] and an 18% increased anticancer effect [61] in glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) cell lines in vitro, but the regulation mechanisms were not unraveled yet. Oxaliplatin [8] does not display a pronounced synergistic effect in the melanoma cell line. Cisplatin combinations are widely investigated in seven studies (Table 2), showing combinatorial effects, but still focus on phenotypic effects such as cell death [63,64,75] or cell cycle arrest [75], lacking mechanistic investigations. For temozolomide (TMZ), gas plasma could improve GBM cell sensitivity towards TMZ chemotherapy in 06-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT)-positive TMZ-resistant cells [71]. Further, gas plasma augmented TMZ cytotoxicity by ROS-mediated DNA damage, visible in the induction of H2AX phosphorylation [68] and increased 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) and 8-Oxo-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-oxodG) levels after inhibiting antioxidative glutathione (GSH)/glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) signaling [69]. Regarding antimetabolites, methotrexate displays poor anticancer selectivity [77], and gemcitabine is initially being sought for combination with gas plasmas or plasma-treated liquids against pancreatic cancer [75,76], both of which have not yet revealed underlying mechanisms. Among natural products, salinomycin and plasma-treated infusion cooperatively promoted disruption of the mitochondrial network [81]. Further, a synergistic toxicity with doxorubicin was connected to improved drug uptake by SLC22A16 upregulation [8] or decreased drug efflux via downregulation of drug-resistance-associated ABCC1 (MRP1), ABCB1 (MDR1), and ABCG2 (BCRP1) upon plasma treatment [79]. Other natural products (bleomycin [61], paclitaxel [61,67,77], vincristine [80]) show a lack of mechanism exploration.
Based on the above studies, gas plasma could be an interesting tool for overcoming drug resistance, and, if applied locally to a tumor, it might decrease the dosage of chemotherapies. Notably, most of these studies focused on alkylating agents and natural products, and future research could also extend to other drugs. However, chemotherapy resistance and its side effects have emerged as prominent issues in patients, and it is necessary to pursue effective means to resolve them.
3.1.2. Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy primarily anchors at molecular loci via specific molecules binding, and is generally divided into two classes: small-molecule inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) [120]. Small molecules can be further categorized into tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), poly ADP ribose polymerase (PARP) inhibitors, proteasome inhibitors (PIs), and cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitors [121]. Targeted therapy should be distinguished from immunotherapy, especially with regard to mAbs. According to their mechanism of action, mAbs can be broadly classified into two groups: those exerting antitumor effects by directly targeting tumor-related molecules (targeted therapy) and those modulating the immune system by checkpoint inhibition [122]. The latter will be discussed in the immunotherapy section.
In essence, commonly used targeted sites include HER (human epidermal growth factor receptor) 2, EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor), and VEGFR (vascular-endothelial growth factor receptor) [123]. These sites can be targeted by mAbs, like trastuzumab [124] or cetuximab, or TKIs like sorafenib [125,126]. For instance, gas plasma-mediated toxicity has been shown in lung cancer cell growth through the VEGF/VEGFR2/RAS axis [127] and in hepatocellular carcinoma via enhanced autophagy and the EGFR/p-JUK/BIRC6/LC3B axis [128]. A combination of cetuximab and plasma was shown to inhibit the invasion/migration of oral squamous cell carcinoma (oSCC) cells through NF-kappaB signaling regulation [129]. Synergy between TKIs and oxidative stress was reported in a study using hydrogen peroxide in colorectal cancer [130], suggesting gas plasma to be an interesting approach to combine with targeted therapies. Interestingly, gas plasma-mediated ROS were also shown to impact the targeted tyrosine kinase proteins themself by introducing oxidative posttranslational modifications (oxPTMs), which might lead to altered structure and catalytic function [131]. If these modifications synergize with TKIs’ inhibitory effects or instead lower their effectiveness, it remains to be investigated. For CDK inhibitors, a combination of an indirubin derivative (KD87) with gas plasma-treated medium was shown to induce G2/M arrest and apoptosis via AhR pathway activation [132]. As a PARP inhibitor, olaparib shows a synergistic effect with plasma [117], but no further research was conducted to clarify the underlying pathway. Among PIs, plasma could increase the sensitivity of myeloma cells to bortezomib [133] to achieve an anticancer effect. Due to their overlap with the above-mentioned plasma combination approaches, TKIs and mAbs may serve as promising entry points for further investigations.
Next to synergizing mechanisms of action, drugs such as TKIs could be affected by gas plasma exposure, potentially altering their activity. This was seen in a study using 37 gas plasma-treated TKIs, showing mainly a reduction in TKI toxicity but also an increased toxicity for five compounds [134]. Such alterations can be induced by gas plasma-mediated oxidation of specific structures of the drug molecules, e.g., at the warhead groups necessary for the binding to the targeted kinase. Another interesting approach is the activation of prodrugs, which was, for example, shown for fenretinide via gas plasma-induced oxidation [135]. This way, gas plasma could be used as a tool to induce on-site activation of prodrugs, e.g., in superficial tumors, reducing off-target effects.
3.1.3. Immunotherapy
Although gas plasma was first tested in cancer patients in the mid-2010s [136], clinical combination therapies of gas plasma and immunotherapy have not been reported (Table 2). In general, immunotherapies are classified as either passive or active [137]. Often, immunotherapies act via tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cells, lymphokine-activated killer cells (LAK), cytokine-induced killer cells (CIK), and antibody-based immune checkpoint inhibition (ICI) like CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L1 [138]. It was previously proposed from preclinical models that gas plasma should not be used as monotherapy but instead combined with immunotherapy to improve anticancer effects [139,140]. A promising approach is to functionalize the tumor microenvironment (TME) by enhancing the local function of anticancer immunity, for instance, by inducing immunogenic cell death (ICD) and triggering the influx and activity of antitumor leukocytes [5]. For example, gas plasma-treated skin cancer cells showed a higher susceptibility to NK-cell-induced tumor cell lysis than untreated skin cancer cells [141]. Gas plasma treatment was further shown to enhance tumor infiltration with T-cells and dendritic cells (DCs) in treated tumors and in an abscopal way in vivo [9] and increase phagocytosis of cancer cells by DCs [142].
Two studies have demonstrated synergistic effects combining gas plasma treatment with ICI. A combination of gas plasma anti-PD-L1 in a syngeneic melanoma model in vivo resulted in improved tumor reduction and increased TILs [94]. This finding is supported by a second study combining pembrolizumab (anti-PD-1) for the first time with an improved atmospheric pressure argon plasma jet routinely applied in dermatology [95]. The underlying mechanism involved gas plasma-induced oxidative stress triggering ICD, characterized by the release of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), which consequently attracted antigen-presenting cells (APCs). No studies have been performed combining anti-CTLA-4 with gas plasma yet. Given the promising approaches stated above, more research is expected in combining immunotherapies with gas plasma technology in immuno-oncology.
3.1.4. Nanoparticles
Nanoparticles have been considered promising since they were first proposed in 1959 [143]. Different from standard therapies, nanoparticles function as drug carriers and effective agents simultaneously, and their roles in cancer have been reviewed elsewhere before [144]. Their effectiveness depends on particle diameter, shape, types, elasticity, superficial structures, and chemical modifications [145,146]. Nanoparticles can be used in biomedicine for drug delivery and biological imaging due to their large surface-to-volume ratio, enabling the attachment of cargos like fluorophores, drugs, or antibodies, as well as a deep tissue penetration [147,148]. Generally, nanoparticles can enter cells through endocytosis and non-endocytosis-mediated passive penetration [149]. They can lower drug toxicity through enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effects. In contrast, the safety of nanoparticles themselves remains controversial [150]. Encouragingly, reports suggest combined effects of gas plasma and nanoparticle exposure, including silymarin nanoemulsion and Pluronic F127 (Table 2). Interestingly, intracellular ROS generation was described for different types of nanoparticles, like metallic oxide NPs and silica particles [151], which could combine with gas plasma-generated extracellular ROS [28]. Combined toxicity was found in melanoma [96], while gas plasma exposure of the particles also affects the melanoma toxicity of the latter [100]. This was suggested due to a decreased nanoparticle size and modified surface structure in response to gas plasma exposure [105,152]. At the same time, elevated PLGA (Poly Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid) film hydrophilicity was indicated as an effector in improved combined toxicity [153], along with increased nanoparticle uptake via enhanced clathrin-dependent endocytosis [154]. On the cellular level, gas plasma may alter cell membrane permeability and nanoparticle accumulation [106,155]. Owing to multiple nanoparticle synthesis ways, nanoparticles can have cores and shells [102]. Thus, a drug–nanoparticle–gas plasma triple combination would be possible. Consequently, drug release speed could be more flexible by controlling the nanoparticle surface versus volume ratio [156]. Hence, nanoparticle–gas plasma combination could extend drug retention periods in vivo and enhance their intracellular concentrations [157]. Moreover, significant differences between various metal properties were found between Au and Ag nanoparticles combined with gas plasma [104,105]. For instance, gold nanoparticles are essentially non-toxic but notably enhance anticancer effects when combined with gas plasma exposure [97]. Similar findings were also made for nanoparticles coated with antibodies targeting FAK when combined with gas plasma treatment [99]. However, gold nanoparticles and gas plasma combination treatment also promoted the degradation of HER2/Neu and FAK1 [98], complicating potential therapeutic applications and mechanisms of action. At the same time, metals could be key to enhancing gas plasma-derived reactive species and anticancer toxicity via, e.g., the Fenton reaction [158]. For instance, iron-oxide magnetic nanoparticles were found to promote EGFR downregulation via suppressing pERK and pAKT in synergy with gas plasma exposure involving enhanced •OH generation catalyzed by Fe2+/Fe3+ [108]. As both pathways are essential for cancer survival and metastasis [159,160], targeted approaches combining nanoparticles and gas plasma exposure might be promising, depending on the tumor type and location. More in vivo studies are required to substantiate such concepts scientifically. Current nanoparticle combinations with gas plasma can be classified into two classes: metallic nanoparticles and nanoparticle-mediated drug delivery. It is also worthwhile to explore the synergy between non-metallic nanoparticles and gas plasma in future studies.
3.2. Local Treatment Modalities
Several local treatment modalities, many of which are based on principles from physics, can be combined with gas plasma therapy [161]. A selection of such approaches is given in the following, with some showing promising results in vitro and in vivo (Table 2).
3.2.1. Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy is an anticancer treatment that utilizes, e.g., X-rays, gamma rays, and neutrons. Radiotherapies are classified into external beam radiation therapy (EBRT) and internal radiation therapy. Radiotherapy directly induces DNA damage through ionizing radiation (IR) or indirectly promotes molecules adjacent to DNA to take up high-energy, thus generating reactive oxygen species, damaging DNA [162]. This involves, for instance, X-ray repair cross-complementing 1 (XRCC1) [163], p53 transcription factor, and genomic instabilities [164]. With the widespread application of radiotherapy, radio-resistance has emerged as a principal barrier [163]. It was proposed that radio-resistance is related to multiple factors, including altered DNA damage repair (DDR) regulatory molecules, cell cycle redistribution signalings, apoptosis escape, tumor microenvironment, cancer stem cells (CSCs), metabolic reprogramming, exosomes, and ferroptosis [165]. Additionally, normal tissue is also being influenced by high-dose irradiation rays, which leads to acute and late side effects [166], suggesting a need for reduced radiotherapy doses when the therapy is combined with other treatments. Recent research combined gas plasma with radiotherapy in murine melanoma cells, showing that the sequence of the treatments matters and that gas plasma exposure may sensitize tumor cells to radiotherapy and render them more immunogenic [116]. Enhanced toxicity was also found in breast cancer cell lines exposed to combined gas plasma and radiation therapy [117]. Interestingly, immortalized normal prostate cells would be less affected than prostate cancer cell lines in gas plasma-treated liquid and radiotherapy combination treatment [167]. This indicates that gas plasma could serve as one of the potential choices for radiotherapy amelioration in minimizing irradiation dosage and circumventing radio-resistance in the future, provided that ways are found for gas plasma to reach in-patient tumor sites. Few in vivo studies have reported on the relationship between combined gas plasma and radiation application. One was on melanoma, suggesting combined effects to be based on ROS generation, cell cycle arrest, and apoptosis induction involving radiation-derived DNA damage [6]. In general, gas plasma and radiation share common features, such as ROS production from intracellular and extracellular environments [168,169]. From a redox chemistry perspective, it has been suggested that gas plasma displays a similar reactive species chemistry pattern to X-rays [170]. Gas plasma could also be used not only to combine with radiotherapy for anticancer effects but also to contribute to tissue healing due to the radiotherapy-induced damage in non-tumor tissue [171]. In addition, radiotherapy was suggested to provide stimuli for enhanced efficacy of anticancer vaccines [172], which could also be achieved using gas plasma-derived reactive species production [173,174]. More in vivo studies and clinical data are awaited to verify or falsify the hypothesized promising nature of combined radio- and gas plasma therapy.
3.2.2. Pulsed Electric Fields (PEFs) and Electrochemotherapy (ECT)
In 1991, electrochemotherapy (ECT) was first introduced into clinical use [175]. In ECT, pulsed electric fields (PEFs) are applied throughout the tumor tissue, thus enhancing membrane permeability to facilitate drug penetration into the cell [176]. Electrochemotherapy usually employs bleomycin and cisplatin [177] and is mainly implemented in treating superficial tumors. Mechanistically, ECT generally comprises toxicity in tumor cells and reflexive vasoconstriction triggered by high-voltage pulses [178]. However, restricted by PEFs, ECT is considered below temperatures for ablathermia to avoid heating injury. Chemotherapy concentrations required for anticancer effects can be reduced up to 50-fold when using ECT [179]. Recently, gas plasma was combined with electrochemotherapy against melanoma growth in vitro and in vivo, suggesting that combined applications are superior to single treatment [91]. Conjoined with ECT, gas plasma-treated PBS is also effective in LPB sarcoma cell-implanted mice [92]. The presumed mechanisms of action are numerous, including partially overlapping mechanisms of cell apoptosis, enhanced membrane permeability induced by lipid peroxidation, intracellular calcium increase by PEF, and intracellular ROS concentration elevation by gas plasma [180]. Similar to the microsecond PEF (μsPEF) in ECT, a more intensified nanosecond PEF (nsPEF) can stimulate extra- and intracellular ROS production [181,182] like gas plasma, which was found to act synergistically with gas plasma exposure in vitro [183]. Reports on the clinical combination of both medical technologies in cancer patients are yet to be awaited to drive this scientific concept further.
3.2.3. Photodynamic Therapy
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) usually adopts photosensitizers to modify oxygen using external light and to release reactive species toward tissue, including tumors [184]. PDT can be sorted into acute and fractionated PDT based on treatment patterns. Its anticancer effect can be attributed to photodynamic reactions. Photodynamic reactions involve type 1-generating O2•− and type 2-producing 1O2, essential in anticancer effects [185]. These mechanisms include direct tumor cell destruction by inducing apoptosis and necrosis, tumor-supply vessel impairment from coagulation, and immune response activation [186]. Owing to photosensitizer dark toxicity [187] and dependency on the aerobic nature of the TME [188], some studies consider gas plasma to combine with PDT to avoid shortcomings, such as PDT resistance [189]. Gas plasma PDT integrating with polymeric nanoparticles showed enhanced anticancer effects in cervical cancer cells [7], and these improved results are also observed in lung cancer cells [114] and melanoma cells [112]. This synergy could be attributed to several factors. At first, gas plasma could be a light source to activate photosensitizers [112]. It was demonstrated that PDT could be stimulated by the overlap between gas plasma emission spectrum peaks and photosensitizer absorption spectrum peaks [190]. In this case, it is necessary to balance the duration of gas plasma irradiation, intensity, and wavelength range of various gases to comply with the photosensitizer type. Secondly, gas plasma and PDT would superimpose into a doubled-ROS-effect, and gas plasma-derived ROS/RNS could expand the toxicity onto tumor cells. Moreover, gas plasma could decrease PDT dependency on oxygen due to its exogenous property and tissue oxygenation improvement [191,192]. Lastly, PDT-mediated thermal effects could increase tumor cell membrane permeability, thus fostering more gas plasma-derived ROS to penetrate cancer cells [113]. In summary, current research lays the foundations for the joint usage of gas plasma and PDT, but solid in vivo trials are scarce to further substantiate the approach. Promising inventions like oxygen-independent PDT will provide more possibilities for clinical and research applications, also when combined with gas plasma exposure.
3.2.4. Hyperthermia
Hyperthermia is one medical treatment to eradicate tumor tissue by adopting above-body temperature and classified into long-term low-temperature (~40–41 °C) and moderate-temperature (~42–45 °C) hyperthermia [193]. Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) is a commonly used anticancer treatment that lavages the abdominal cavity with heated chemotherapy drugs. When the temperature is above 37 °C, cell membrane fluidity increases, and its permeability and cytoskeleton arrangements are affected, hindering tumor cell movement, intracellular signal transduction, and tumor growth and metastasis [194]. Nevertheless, hyperthermia is rarely used alone and is usually combined with other therapies, and it was previously suggested that it could be combined with gas plasma-treated (oxidized) liquids [49]. Currently, gas plasma is regarded as an effective means to integrate with hyperthermia and display a profound synergistic effect. In U937 cells, gas plasma promoted apoptosis through cytoskeleton changes caused by hyperthermia [195]. A similar effect was also found in 3D bladder tumor spheroids [196]. Moreover, gas plasma-generated H2O2 was found to decrease TRPM2 membrane receptor activation thresholds by heat from hyperthermia to induce cell death [93]. These in vitro experiments indicate the joint usage possibility of gas plasma and hyperthermia, both on how to generate gas plasma and achieve hyperthermia, but in vivo studies are awaited to unravel the full potential of this combination.
3.2.5. Hydrosurgery
When conventional surgery is combined with gas plasma, such a combination is regarded as a sequential regimen. Therefore, the ideal surgery type that can serve as a combination therapy with gas plasma is hydrosurgery. Hydrosurgery uses high-pressure saline (0.9% sodium chloride) jets that cut tissue with less thermal stress compared to electrosurgical approaches and can be used to remove tumors via pure, pulsed, and abrasive modes [197]. Hydrosurgery has been shown to have tissue-selective separation effects for nerve and vessel protection due to their intrinsically high proportions of collagens and elastic fibers [198]. However, in some cases, hydrosurgical cutting was observed postoperatively with enhanced tissue adhesion. Here, gas plasma-treated cell culture medium (also sometimes referred to as plasma-activated medium, PAM) has been suggested to modify the adhesion properties of cells [199]. In addition, it was demonstrated that a plasma-treated cell culture medium could reduce the expression and secretion of pro-adhesive cytokines and extracellular matrix proteins in peritoneal fibroblasts [200]. Moreover, A431 cell adhesion properties were also inhibited by an oxidant-loaded cell culture medium, showing downregulation of CD44, hyaluronan synthase 2 (HAS2), HAS3, and hyaluronidases [201]. Generally, approaches using gas plasma-treated cell culture medium are experimental and not clinically relevant. However, this can be increased using liquids approved for humans, such as sodium chloride and Ringer’s lactate [49]. Along such lines, gas plasma-treated water (PTW) might alleviate postsurgical pain [202], promote excision healing, and avoid relapse of residual tumor tissue on margins [48]. There are two issues to be resolved: one is to find the most appropriate liquid and gas plasma source types, and the other is the flow speed effect in operation in hydrosurgery. Nevertheless, the combination of gas plasma with hydrosurgery holds great potential and may produce an underlying anticancer effect. All these mentioned combination treatments can be envisioned to be used together with medical gas plasma technology (Figure 2).

Figure 2.
Potential combination treatments using medical gas plasma technology.
4. Bridging the Gap from Gas Plasma Medicine to Oncology in Patients
The number of experimental publications on gas plasma cancer treatment has increased recently, whereas clinical translational research has progressed only slowly [5]. This may have been due to gas plasma heterogeneity related to the application form (DBD [203], Jet [204]), working gas (helium, argon, air), air humidity [24], and many other factors [205]. In addition, there is the notion that gas plasma therapy may be most effective when combined with other local or systemic treatment modalities, such as immunotherapy [5]. Moreover, so far, medical experiences in gas plasma therapy against invasive tumors mainly pertain to the palliative setting [136]. Moreover, the treatment should be designed individually, depending on multiple factors, e.g., staging, tumor biology, mutational load, immune status, and the patient’s fitness. In addition, it is conceded that oxidative stress and related signaling, e.g., via Nrf2 (Figure 3), are prime hallmarks of gas plasma cancer treatment [5]. Despite some promising in vitro and in vivo results, the limited penetration depth [206] of gas plasma presumably requires repeated therapy of solid tumors [20,207], which would qualify skin cancer well for this therapy (Figure 4). Nevertheless, more than 100 known cancer entities exist. In the following, we will review potential oncology gas plasma applications to the deadliest cancers [208].

Figure 3.
Potential mechanism of action on clonal selection through oxidative stress. Image is adapted from ref. [209].

Figure 4.
Current and future approaches to use and combine medical gas plasma technology in oncology. Image is adapted from ref. [5].
4.1. Melanoma
With increased depth, the skin layers comprise the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. In general, skin cancers originate from corresponding cellular sites like stratum basale-derived melanoma, basal cell cancer, and stratum spinosum-derived squamous cell cancer. This section will focus on melanoma; its conclusion could be a referential recommendation for other skin cancer types. At an early stage, surgical resection is considered the first-line treatment. As cancer progresses, it is hard to achieve complete resection (R0), limited by cosmetic or functional factors [210]. To reduce residual tumors, it is inevitable to introduce multiple therapies. At the same time, surgical removal of melanoma could be followed by intraoperative gas plasma treatment of tumor resection margins to reduce the risk of relapse. Molecularly, melanoma progression relates to PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK pathways [211]. Thus, downstream BRAF and MEK protein-blocking agents are recommended as adjuvant therapies with surgery to eradicate lesions. Even if chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy are applied as complementary means, drug resistance and side effects frequently occur in melanoma [212]. Gas plasma was previously suggested as an adjuvant experimental melanoma treatment. For instance, gas plasma was shown to induce G361 melanoma cell autophagy when combined with silymarin nanoemulsion. This stimulated PI3K/mTOR and EGFR pathways [109] and inhibited proliferation via HGF/c-MET regulation [110], which indicates that gas plasma shares a common signaling pathway with the above treatments. In addition, combined with doxorubicin, gas plasma augmented the anticancer effect synergistically [62]. Another set of studies indicated that the AhR pathway is activated under gas plasma exposure when combined with indirubin derivatives [132]. Moreover, we could previously show that, in B16-F10-bearing C57BL/6 mice, argon gas plasma exposure potently combined with imiquimod, a Toll-like receptor (TLR) 7 and 8 agonist [173]. Moreover, we also showed the combination treatment effects of gas plasma exposure against these melanoma cells with radiotherapy [116].
4.2. Lung Cancer and Bronchial Carcinoma
Small cell (SCLC) and non-small cell (NSCLC) are the primary lung and bronchial carcinoma categories. Owing to malignancy discrepancy, chemotherapy combination regimens are often considered in all stages of SCLC, usually based on platinum (carboplatin or cisplatin) or etoposide [213]. At the same time, NSCLC requires surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy as first-line therapy at early stages 1–3. Metastatic stage 4 recommendations relate to platinum-based chemotherapy or immunotherapy, such as gefitinib, used against cancers with activated EGFR mutations [214]. Lung cancer etiology generally involves multiple mechanisms, like ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase) gene rearrangement, and current treatments are based on such tumor-specific changes. Typically, little research is available on gas plasma treatment against lung cancer. In vitro, studies suggested that the anticancer effects of gas plasma may be associated with autophagy [86] and EGFR signaling [108], and only relatively few gas plasma studies focus on NSCLC in in vitro models yet. Moreover, combining gas plasma and recommended therapies in in vivo models lacks experimental proof. Song and colleagues [215] introduced plasma-treated liquid by oral gavage to tumors and suggested that drinking this liquid can reduce the lung cancer growth of tumors with partially extreme sizes. Oral administration routes are unusual for lung cancer treatment. Even though the author team reports on anticancer effects, the findings should be interpreted with care, as there is no logical explanation for how the gas plasma-derived reactive species can be retained if taken up into the highly antioxidative bloodstream from the colon without being degraded in the liver (first-pass effect) for subsequent delivery to the lung tissue. More feasible would be a gas plasma implementation via nebulized plasma-treated liquid or bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) to target lung cancer.
4.3. Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal cancer can originate from the colon and rectum. In colon cancer, two major types of surgeries (colectomy and colostomy) are recommended, and adjuvant therapy includes chemotherapy or immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy as determined by biomarkers such as mismatch repair deficiency (dMMR). Likewise, surgery is preferable in rectal cancer, and chemotherapy with FOLFOX or CAPEOX is recommended as first-line treatment in the metastatic stage [216]. RAS, BRAF, HER2, and POLE/POLD-1 mutations could guide treatment choices in colorectal cancers that have not been resected. Several studies have suggested the role of gas plasma in colorectal cancer treatment. For instance, gas plasma elevated intracellular ROS to induce cell death, presumably via upregulation of Nox2 [217]. Moreover, gas plasma induced apoptosis via TRAIL and its death receptor 5 (DR5) in TRAIL-resistant colorectal cancer cells [218]. Combined with PDT [113,190], synergistic anticancer effects have been demonstrated in HT-29 cells. Single gas plasma exposure was suggested to involve mitochondrial pathways, which are key to its effects [219]. Nevertheless, no in vivo studies are available where colorectal cancers were treated directly at their appearance site (i.e., on the colon in an orthotopic model). Similarly, clinical experience of gas plasma exposure in colorectal cancer patients is not reported. As opposed to direct gas plasma exposure, it was indicated a few years ago that the peritoneal lavage of gas plasma-treated liquids [49] could effectively reduce metastatic colorectal cancer [43]. This was found for different, clinically employed liquids and is mechanistically mainly based on the presence of H2O2 in such liquids [220,221]. Another option would be employing gas plasma devices fitting into free endoscope channels, allowing gas plasma exposure inside the body. While technical concepts for such devices have been published [222], experimental in vivo anticancer effects in colorectal tumor models have not. Along similar lines, there are no reports on in vivo combination gas plasma treatment with pharmacological or immunotherapeutic intervention.
4.4. Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic cancer therapies list surgical resection as a preferred option [223]. First-line and second-line treatments are integrated into advanced or metastatic stage regimens based on body status rated by the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) score system. For late-stage patients, FOLFIRINOX (5-fluorouracil, folinic acid, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin) and gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel are regarded as the mainstream choice [224] but are limited to the deadliest form of pancreatic cancer, PDAC (pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma), having a poor prognosis [225]. Recently, oxidative stress [226] has been put forward as a new therapeutic target in PDAC, so gas plasma, a new and pleiotropic ROS source, has been tested in different pancreatic cell models. Hattori and colleagues [227] revealed that gas plasma-treated cell culture medium could activate caspases 3 and 7 and have a lethal effect on PDAC cell lines compared with normal pancreatic cells. Furthermore, gas plasma-treated PDAC cells were found to have altered inflammatory profiles and interfered with macrophage cluster formation in RAW 264.7 [228], related to the tumor-associated environment (TME) [229]. In addition to macrophages, tumor-supportive pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs) with immunosuppressive function may interfere with the toxicity and immunogenicity of gas plasma-treated PBS [230]. Gas plasma-treated cell culture medium was also found to reduce peritoneal carcinomatosis of PDAC effectively in vivo and supported the influx of immune cells into the tumor [231,232]. One of the few studies that combined gas plasma exposure (with treated Ringer’s lactate) with chemotherapy (cisplatin and gemcitabine) was tested in four pancreatic cancer cell lines in vitro and in ovo (a semi-in vivo model [233]), showing sound combined anticancer effects [75]. Notably, we thoroughly studied the metastasis risk effects of gas plasma-treated pancreatic cancer cells in different models and could not identify any increased risk due to the treatment [234].
4.5. Breast Cancer
Breast cancer treatments rely on multidisciplinary coordination, and corresponding therapies have evolved in diverse directions, including surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, endocrine therapy (e.g., estrogen-receptor-directed tamoxifen) [235], HER2-directed trastuzumab [236], and biological therapy. Notwithstanding, the 5-year survivorship in metastatic type and triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is 26% [237] and 12% [238], respectively. In addition, drug-resistance issues emerge, rendering several therapies partially inefficient in the course of the treatment [239]. In such transition stages, metastasis, TNBC, and drug resistance are perceived as core issues in developing new therapies. For breast cancer, radiotherapy was previously suggested to induce abscopal effects [240]. Similarly, gas plasma exposure has been demonstrated to induce abscopal effects in mice that carried syngeneic 4T1 tumors on both flanks, which was accompanied by an enhanced influx of T-cells, such as TH17, suggesting elevated anticancer immunity via gas plasma exposure [9]. Besides direct gas plasma treatment of tumors, a previous study also found reduced postsurgical tumor recurrence if the resection margins of the primary tumors were exposed to gas plasma [241]. For TNBC, gas plasma was associated with a selective anticancer effect, presumably via hyperactivation of MAPK/JNK (mitogen-activated protein kinase/c-Jun NH 2-terminal kinase) and NF-κB (nuclear factor k-light-chain enhancer of activated B-cells) pathways [242]. Another study suggested gas plasma treatment in TNBC leads to downregulated BCL2A1 (Bcl-2-related protein A1) expression [243]. At the same time, one report speculated that gas plasma susceptibility relates to the expression of ER/PR (estrogen receptor/progesterone receptor) on HER2-positive breast cancer cells [244]. Notably, gas plasma was suggested to decrease breast cancer cell drug resistance [245]. Specifically, it was revealed that gas plasma recuperated paclitaxel-resistant MCF-7 cell sensitivity to chemotherapy via regulating drug resistance-associated genes. 4T1 breast cells also showed improved doxorubicin uptake levels when exposed to gas plasma [246]. In addition, gas plasma treatment was suggested to modify breast cancer stemness by regulating the AQP3/FOXO1 axis and inducing cell apoptosis through ERK inhibition and activation of p38-MAPK based on adulteration from HO/H2O2 [247]. Despite the above inspiring research, there is still very little known about effective in vivo combination treatments of anti-breast cancer drugs with gas plasma exposure. In contrast, studies on using gas plasma directly in breast cancer patients are absent. The only report concerning the latter pertains to a patient trial to prevent radiation-induced damage in the skin of breast cancer patients within an intrapatient-randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial to reduce radiation-mediated side effects rather than treating the cancer [171,248]. Of note, we were the first to recently test patient-derived breast cancer tissue exposed to gas plasma ex vivo, demonstrating increased cytotoxicity [249,250], which holds some promises for future research.
4.6. Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer treatments are categorized into the risk group or staging system. The former adopts active surveillance as the first option [251]. The latter consists of localized and metastatic types, or early-stage and advanced-stage. Surgery and radiation therapy are preferred for early-stage prostate tumors, and hormone therapy combined with non-hormonal therapy is more favored for advanced stages. With the hormonal therapy resistance rate increasing along with side effects like postoperative urinary incontinence or erectile dysfunction [252] and androgen deprivation therapy (ADT)-associated osteoporosis [253], it is required to pursue alternative and low-invasive treatments for long-term survival of prostate cancer patients. A previous study suggested that DNA structure, cell viability, and colony-forming ability are debilitated by gas plasma, followed by necrotic death in BPH-1 and PC-3 cell lines, which primarily verifies the feasibility of gas plasma application on prostate cancer [254]. Subsequent parameter optimization achieved selective antitumor effects [255] associated with G0/G1 cell cycle arrest via activation of MAPK and NF-κB pathways [256]. However, no clinical efforts have been published on this topic so far. The crucial point is how gas plasma successfully targets the lesion and what dosage would be maximally effective at minimal invasiveness. At present, it is speculated that gas plasma could reach the prostate through a cryoprobe-like device based on transrectal ultrasound-guided percutaneous radical (TRUS) cryosurgical ablation [257]. Following this concept, more surgical approaches could serve as references to place gas plasmas inside the prostate and other cancer tissues, such as transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) and high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU).
4.7. Urothelial (Bladder) Cancer
Bladder cancer is, with more than 550,000 new cases annually, among the second most frequent malignancies of the urogenital tract [258]. Sophisticated diagnosis and stage-adapted treatments are required to treat bladder cancer. Due to its high tumor mutational burden (TMB) (fourth highest average mutation rate among cancers), multimodal treatments are usually required, including surgery, (cisplatin) chemotherapy, and immune checkpoint inhibitors [259]. Regardless of the treatment, about one-third of the patients develop aggressive, muscle-invasive bladder cancer with a metastatic risk and mortality, leading to a five-year survival of less than 50% [260]. Almost all bladder cancers are urothelial carcinomas (also called transitional cell carcinoma), with the latter originating generally from the urethra, bladder, ureters, renal pelvis, and some other organs. Treatment side effects and poor prognosis required novel therapy approaches, and gas plasma exposure was tested in several studies as a potential new treatment modality. In vitro, gas plasma treatment was shown to induce urothelial cancer cell death, regardless of the plasma jet source operated by, e.g., argon [261], helium [77], or gas plasma-treated cell culture medium [262,263]. It has been noted that gas plasma exposure modifies the intracellular glutathione levels and mitochondrial function of bladder cancer cells [261,264]. It was also found that epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition fostered the sensitivity of bladder cancer cells to gas plasma exposure [265]. With regard to combination treatments, there has been a promising in vitro study combining hyperthermia with gas plasma-treated liquid to reduce the growth of 3D bladder cancer spheroids [196], while argon plasma jet exposure also reduced bladder cancer spheroid growth [261]. Another striking study combined gas plasma bladder treatment with four different antitumor drugs (cisplatin, methotrexate, adriamycin, and paclitaxel), identifying partially promising additive anticancer effects of the combination therapy [77]. In vivo, a decline in bladder cancer growth was observed when employing gas plasma-treated saline [266]. In vivo combination treatments with gas plasma exposure are not documented. Notably, we have recently investigated, for the first time, patient-derived urothelial cancer tissue exposed to a clinically approved (medical device) atmospheric pressure argon plasma jet ex vivo, finding more apoptosis and altered gene expression signatures from transcriptomic analysis [261]. Concerning the application of gas plasma, gas plasma-treated liquids that could be used to flush the urogenital tract could be a viable option, perhaps in combination with chemotherapy or targeted therapy. In addition, endoscopy is frequently used in urology and gynecology, and local bladder cancer tissue could be directly treated with endoscopic gas plasma devices, which have already been partly developed [267].
4.8. Liver Cancer and Malignancies of Intrahepatic Bile Duct
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) are regarded as the common types of liver cancer. Early-stage tumors require surgery as the first-line treatment option, while systemic therapy is indicated as the recommended treatment with disease progression. Best supportive care, including palliative care, is the last resort for patients who are diagnosed with liver cancer in the advanced stage. Recently, liver cancer and cholangiocellular carcinoma have been increasingly studied in the context of plasma medicine. For instance, it has been shown in vitro that SK-HEP-1 tumor cells more easily detach following gas plasma treatment when compared to non-malignant cells [268] and that enhanced intracellular ROS were detected [269]. In addition, gas plasma-treated cell culture medium induced apoptosis in HepG2 to a higher extent than in a non-malignant cell line [270]. Similar findings were reported in other hepatic [269] and biliary cancer cells in vitro models [271]. Notably, gas plasma exposure was found to be toxic in both drug-sensitive and drug-resistant liver cancer cells [272] and gas plasma-treated medium potently combined with cisplatin in vitro [74]. In vivo anticancer effects of gas plasma exposure were recently shown in a cholangiocarcinoma mouse model, demonstrating reduced tumor size and growth [271]. Liver cancer still lacks in vivo gas plasma studies to support the general feasibility of the concept. The liver and gallbladder belong to intraperitoneal organs, and the bile duct opening is located at the ampulla of Vater, through which endoscopic gas plasma exposure would be feasible to reach, e.g., cholangiocarcinoma. This proof of concept was recently performed by adding a plasma catheter and successfully applying it to the porcine cholangiocarcinoma model [273]. Similarly, HCC gas plasma treatment improvement could be grounded on existing surgery techniques like radiofrequency ablation (RFA) [274]. In brief, gas plasma applications for hepatobiliary cancer are in their infancy. More preclinical experiments in combination with other treatments and the employment of sophisticated animal models are still needed, apart from the few in vitro studies.
4.9. Leukemia
Leukemia originates from blood or marrow and is classified into acute myeloid leukemia (AML), chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL), and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Primarily, AML treatments are discussed, for they are the primary type in adults. Relevant treatments depend on the complex mutation category and consist of targeted therapy, chemotherapy, and corresponding side effects, like immune suppression accompanying them. In early studies, exposure time-related cytotoxic effects of different gas plasma devices were tested on leukemia cells, e.g., jets [275,276], DBD [277], and gliding arc discharge (GAD) [278]. Further research suggests that gas plasma can reduce leukemia cell viability in AML [279], induce cell apoptosis in CML [280] and ALL [281], and decrease metabolic activity in CLL [282], accompanied by changes in redox-related oxidative stress responses [283,284] as well as small RNA profiles [285]. Hence, there would be sufficient in vitro data in gas plasma experiments for future testing of this method using in vivo leukemia models. However, a significant hurdle is how gas plasma could target cells mainly located in a fluid (blood and bone marrow). As things stand, two strategies may be adopted for the clinical application of gas plasma against leukemia. The first is partially treating leukemia cells and re-injecting or infusing them into the blood circulation in the sense of a vaccine [174]. Yet, the TMB of leukemia is relatively low [286], and antigen accessibility of APCs and T-cells is not a significant obstacle in leukemia as a blood-based disease, indicating that this approach may not be too successful. The second scheme is to eliminate leukemia cells ex vivo. This idea has been around in the community for about ten years already, and, recently, the first study appeared to successfully gas plasma-treat primary leukemia cells from CLL patients’ blood [282]. The vision is to generate an extracorporeal circulation device equipped with gas plasma exposure to inactivate leukemia cells on the fly. Although, in principle, it is feasible, the central issue of this approach is twofold. First, we had previously investigated gas plasma-treated non-malignant (proband-derived) immune cells extensively. The main findings have been reviewed before [287] and can be summarized to (i) a very high susceptibility of all lymphocyte subpopulations (including T-cells, NK-cells, NKT-cells, and B-cells) to gas plasma exposure (although lymphocyte activation reduced toxic effects significantly) [288]; (ii) monocytes are generally more robust than lymphocytes, but both non-malignant lymphocytes and monocytes are significantly more sensitive to gas plasma-induced toxicity than their leukemia cell line counterparts [289]; (iii) myeloid and lymphoid leukemia cell lines are generally more sensitive to gas plasma-mediated toxicity compared to those of solid tumor origin, which exemplifies even more how sensitive primary immune cells are [290]; (iv) neutrophils generated extracellular traps (NETs) upon gas plasma treatment [291] that could pose a complication of gas plasma-treated leukemia-containing leukocyte apheresis products; (v) blood is a strong buffer for gas plasma-derived oxidants [292,293]; (vi) gas plasma exposure activates platelets, which could lead to thrombogenic reactions [294]; (vii) gas plasma potently leads to blood clotting (hemostasis) in murine [295] and human blood [296] independent of the gas plasma device used [297]; and (viii) no combination treatments of gas plasma with anti-leukemia drugs have been described so far that could further motivate any future clinical application. These potential adverse reactions including potential coagulation complications imply that much more research and gas plasma source fine tuning are required to facilitate gas plasma exposure against leukemia treatment.
4.10. Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) is one group of lymphocyte cancers originating from the lymph system (e.g., spleen). Given its heterogeneity, NHLs are classified into multiple subtypes requiring various treatment strategies. As the most common type, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) therapies are mentioned and quoted as representatives to explain further the dilemma that NHL encounters. In DLBCL, various molecular differences and mutations determine corresponding subtypes. Therapeutic effects on 30–40% of DLBCL are still hindered [298], with hopes of relying on R-CHOP, which has been recommended as the first-line treatment. Other novel therapies are constantly designed on linker compound concepts like bispecific T-cell engagers (BiTEs) or antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs) for refractory types [299]. At present, no study explores the gas plasma anti-tumor effect on NHL. However, ROS have been studied in the field of NHL. Most studies reveal high ROS levels related to lymphoma pathogenesis and progression, including follicular lymphoma harboring higher peroxiredoxin levels associated with prolonged survival [300]. Mantle cell lymphomas show ROS exhaustion leading to apoptosis via interference with NADPH oxidase two expression [301]. In DLBCL, thioredoxin levels were found to be elevated, and its inhibition suppressed cell growth and modulated drug-resistant gene expression [302]. Moreover, GPX4 overexpression was shown to inhibit ROS-induced cell death and indicated poor prognosis in patients [303]. Given NHL subtype diversity and the absence of gas plasma-related studies, this cancer entity currently lacks promise through this experimental therapy modality.
4.11. High-Grade Glioma
Gliomas are a group of primary brain tumors that arise from neuroglial stem or progenitor cells and rank among the most common subtypes of this tumor entity [304]. Based on their considerable variation in the degree of malignancy, gliomas are categorized into low-grade (WHO grade 1–2) and high-grade (grade 3 and 4) tumors, with the latter showing higher recurrence rates and lower survival outcomes [305]. Although surgical resection is rarely curative as glioma cells extensively invade the surrounding brain parenchyma, it mitigates symptoms from tumor burden and enhances the efficacy of adjuvant therapies [306]. Since high-grade gliomas are highly heterogeneous in cytology and genetic signature, the clinical response of individual tumors may significantly differ, rendering treatment additionally challenging [307] and frequently causing therapy failures [308]. Therefore, strong research efforts are being made to define novel therapeutic avenues against GBM. Plasma medicine displays a bright prospect of innovative treatments in ongoing brain cancer research. First in vitro studies on using gas plasma technology were conducted more than a decade ago in T89G cells, showing jet plasma inhibitory effects on GBM growth and clonogenicity [309], which was suggested to be regulated via AKT1 and ERK1/2 signaling [310] in gas plasma-treated GBM cells. Gas plasma parameters can also be optimized towards GBM killing [311], which is effective against 3D GBM spheroids [312], and was indicated to reduce GBM migration and EMT [313]. Notably, several reports are available studying the combination treatment effects of gas plasma with anti-GBM drugs. For instance, TMZ-resistant glioma cells showed restored chemosensitivity following gas plasma exposure [71,314]. Gas plasma treatment also potently combined with TMZ cytotoxicity by inhibiting the GSH/GPX4 pathway [69]. Intriguingly, vitamin C showed a synergic anticancer effect with gas plasma-generated H2O2 against glioma [88]. Gas plasma was also suggested to increase the uptake of gold nanoparticles into GBM cells [106], providing synergistic toxicity [315]. Importantly, gas plasma-treated PBS and DBD treatment combined with auranofin induce ICD in GBM cells [87]. Thus, the gas plasma anticancer potential can be attributed to intrinsic cytotoxicity, drug sensitivity restoration, and synergy with guideline therapies. A recent study also suggested that electromagnetic fields produced by gas plasma devices contribute to anti-GBM effects [316]. Strikingly, we recently were the first to show in patient-derived glioblastoma tissue that apoptosis is elicited following gas plasma exposure [317]. There are several potential treatment modalities for employing gas plasma to treat brain tumors. First, gas plasma could treat the resection margins of surgically reduced tumors, which inactivates cancer cells and potentially induces ICD to promote anticancer immunity [318]. Second, gas plasma-treated liquids or hydrogels could be used to lavage tumor sites or section margins or be injected into the tissue. For the latter, intranasal delivery [319] with a gas plasma-treated pharmaceutical formulation could be an option. Potentially, intraventricular catheter systems, as Ommaya reservoirs, which are sometimes used for the administration of chemotherapeutics, could be used as a delivery route for gas plasma access. In general, while ample in vitro data is available [61,68,89,310,320], there is no convincing (orthotopic) in vivo evidence to support gas plasma-assisted brain tumor treatment. Nevertheless, given the high mortality of GBM and early data with patient-derived tumors, gas plasma remains a promising therapy modality.
4.12. Esophagus Cancer
Esophageal cancer is categorized into esophageal and esophagogastric cancers. Tumor treatment discussion focuses on the typical type of squamous cell cancer. Due to cancer’s proximity to cardiopulmonary structures, surgery will inevitably face more risk, and postoperative complications like dysphagia may occur. Once its progression proceeds into the metastatic stage, systemic therapies are the preferred option. A typical gas plasma application in esophageal cancer is argon plasma coagulation (APC, a hotter tissue-necrotic plasma)-assisted surgical removal [321]. However, only a few studies explored the efficacy and mechanisms of action of gas plasma exposure on esophageal cancer. Cold direct gas plasma treatment showed cytotoxic effects in KYSE-30 in vitro [322]. It was proposed [323] that enhanced ROS could inhibit cancer stem cells despite the cancer progression association with ROS. Other experiments also demonstrated the anticancer role of ROS on esophageal cells [324]. We recently provided the first evidence of ex vivo gas plasma exposure toxicity in patient-derived esophageal cancer [250]. Gas plasma application in esophageal cancer has several directions. Firstly, it could adopt the argon plasma coagulation (APC) device model and integrate itself into an entity by adjusting parameters. Secondly, plasma-treated liquid would be a relatively feasible means to contact cancer lesions orally, but more data are still needed to support this concept. Overall, esophageal cancer research on gas plasma should be combined with existing technical advantages.
4.13. Other Cancers
While this review has focused primarily on the deadliest cancers that have been thoroughly investigated regarding gas plasma combination therapies, it is essential to acknowledge that many other cancer entities—such as endometrial cancer, gastric cancer, hepatoblastoma, myeloma, ovarian cancer, sarcomas, and squamous cell carcinomas (SCC) (Table 2)—have been less frequently studied. Except for SCC, little preliminary research exists for these tumor types that examined the application of cold physical plasma in combination with a second treatment method. Especially rare sarcomas and pediatric tumors remain largely unexplored and lack research in the context of gas plasma and its implementation in multimodal treatment strategies. This gap highlights an essential field for future investigations, as expanding gas plasma applications across a broader range of malignancies could potentially improve therapeutic options. We therefore encourage further research efforts to explore the efficacy and mechanisms of gas plasma treatment in these underrepresented cancer entities.
5. Challenges in Gas Plasma Combination Therapy
Applied as monotherapy, gas plasma is considered a minimally invasive and well-tolerated treatment technique without severe side effects due to high tumor selectivity [18]. Accredited medical devices are routinely used in clinical dermatology [310]. However, safety assessments regarding its promising combinatory potential with other therapy options are entirely lacking, and in addition, several other challenges need to be addressed prior to clinical translation. First, it is necessary to define the most effective treatment regime, e.g., plasma application time point and duration, that exploits the optimal synergistic window for the simultaneous or sequential administration of additional therapies. For example, to harness the full potential of plasma-generated transient oxidation by the temporary burst of ROS/RNS, it is critical to exactly coordinate the treatment sequence and precisely tune treatment parameters. Thus, plasma treatment prior to radiation therapy exerted stronger antitumoral efficacy compared to the opposite sequence [116]. In a comparable context, plasma can mediate drug inactivation via oxidative modification [134]. Hence, the full spectrum of redox interactions between plasma-induced ROS/RNS and administered therapeutic agents or other therapy forms should be unraveled before clinical usage to avoid antagonism or efficacy loss. A third major obstacle is to elucidate which combination approach is rational for what kind of malignancy, as tumor entities demonstrated varying gas plasma sensitivities in previous studies [290]. For instance, combining gas plasma with a specific treatment modality may only be feasible in a few cancer types, as its combination with bleomycin evidently showed enhanced survival reduction in melanoma cells but no significant impact in glioblastoma cell lines compared with the drug monotherapy [61]. Lastly, these tumor insensitivities, either intrinsic or acquired, need to be extensively investigated to identify underlying mechanisms and potential ways to prevent or overcome these for an optimized treatment outcome. In this light, a previous study reported on the correlation between metabolic turnover rate and absolute expression levels of aquaporins and NOX members with gas plasma resistance [290]. Furthermore, molecular biological comparison of wild-type and plasma-resistant skin cancer cells revealed not only an adapted antioxidative capacity, increased G2-phase cycle arrest, and diminished pro-inflammatory profile but also diminished immunogenicity of plasma-resistant cancer cells. Besides markedly upregulation of immunosuppressive markers in vivo, transcriptome analysis showed strong and significant correlation of IL1R2 with the gas plasma resistance [325]. These defense mechanisms could also promote insusceptibility towards other tumor toxic treatments, emphasizing the urgent necessity for their imperative discovery.
6. Conclusions and Outlook
Only five completed studies noted in ClinicalTrials.gov explored gas plasma application on cancer or precancerous lesions (Table 1). Before proceeding with more clinical studies, for many tumors, it remains to be explored what combination of treatment modalities and gas plasma source types and parameters would be optimal to provide convincing effects in patients. A notion favoring the further investigation of medical gas plasma technology in oncology is that several existing therapeutic modalities involve ROS elevation, e.g., radiodynamic treatment (RDT) [326], sonodynamic therapy (SDT) [327], electrodynamic therapy (EDT) [328], and chemodynamic therapy (CDT) [329]. The anticancer effect might be intensified when gas plasma integrates the above treatments. A second aspect is integrating medical techniques with gas plasma, thus making gas plasma more accessible to cancer, which involves new administration methods such as endoscopy and gas plasma device reengineering. In general, it seems preferable to administer gas plasma along natural anatomical orifices unless there is an artificial opening like a stoma during colostomy. A third aspect is how gas plasma reaches the target: penetration depth, membranous entrance, and ROS half-life. It has been proposed that more than 80% RNS and less than 5% ROS can penetrate 500 µm tissue [330], and the penetration rate is less than 1% in 1 mm of tissue [331]. As another mechanism of action, gas plasma-derived reactive species may induce lipid peroxidation to enhance the entry of further reactive species [332,333]. It is also one of the main questions whether short-lived species produced by direct gas plasma treatment are required for tissue anticancer effects, or if long-lived species suffice [5,334]. Substantial research has successfully elaborated synergies of gas plasma with other therapies, and multiple mechanisms regulate such synergies. However, insufficient preclinical proof often bottlenecks synergistic gas plasma clinical translation in oncology, but the promising effects of gas plasma monotherapies in dozens of in vivo trials and a few clinical investigations generate hope for convincing future concepts and applications in gas plasma oncology.
Funding
L.Y. is a supported fellow of the Chinese Scholarship Council (CSC, China), A.M. is a fellow of the Local State (Mecklenburg-Western-Pomerania, Germany) Graduate Academy, E.F. is supported by the Mehdorn Foundation (Germany), D.S. is a Medical Scientist Fellow of the Rostock Academy of Science (RAS, Rostock University Medical Center, Germany), and R.C. is financially supported by the German Research Foundation (DFG, project number 543338827).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Apalla, Z.; Lallas, A.; Sotiriou, E.; Lazaridou, E.; Ioannides, D. Epidemiological trends in skin cancer. Dermatol. Pract. Concept. 2017, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winther, S.B.; Liposits, G.; Skuladottir, H.; Hofsli, E.; Shah, C.H.; Poulsen, L.O.; Ryg, J.; Osterlund, P.; Berglund, A.; Qvortrup, C.; et al. Reduced-dose combination chemotherapy (S-1 plus oxaliplatin) versus full-dose monotherapy (S-1) in older vulnerable patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (NORDIC9): A randomised, open-label phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 376–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat Mokhtari, R.; Homayouni, T.S.; Baluch, N.; Morgatskaya, E.; Kumar, S.; Das, B.; Yeger, H. Combination therapy in combating cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 38022–38043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahi, Y.; Saadat, A.; Beiraghdar, F.; Hosseini Nouzari, S.M.; Jalalian, H.R.; Sahebkar, A. Antioxidant effects of bioavailability-enhanced curcuminoids in patients with solid tumors: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 6, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeschus, S. Medical gas plasma technology: Roadmap on cancer treatment and immunotherapy. Redox Biol. 2023, 65, 102798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Xu, C.; Tu, Y.; Zhou, J. Non-thermal plasma inhibits tumor growth and proliferation and enhances the sensitivity to radiation in vitro and in vivo. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 3405–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, J.H.; Kim, Y.J. Photodynamic and Cold Atmospheric Plasma Combination Therapy Using Polymeric Nanoparticles for the Synergistic Treatment of Cervical Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagwal, S.K.; Pasqual-Melo, G.; Bodnar, Y.; Gandhirajan, R.K.; Bekeschus, S. Combination of chemotherapy and physical plasma elicits melanoma cell death via upregulation of SLC22A16. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdikia, H.; Saadati, F.; Freund, E.; Gaipl, U.S.; Majidzadeh, A.K.; Shokri, B.; Bekeschus, S. Gas plasma irradiation of breast cancers promotes immunogenicity, tumor reduction, and an abscopal effect in vivo. Oncoimmunology 2020, 10, 1859731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrads, H.; Schmidt, M. Plasma generation and plasma sources. Plasma Sources Sci. T 2000, 9, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, A.; Lindequist, U.; Weltmann, K.D.; Wilke, C.; von Woedtke, T. Plasma Medicine—Its perspective for wound therapy. GMS Krankenhaushygiene Interdiszip. 2008, 3, Doc16. [Google Scholar]
- Weltmann, K.D.; Brandenburg, R.; von Woedtke, T.; Ehlbeck, J.; Foest, R.; Stieber, M.; Kindel, E. Antimicrobial treatment of heat sensitive products by miniaturized atmospheric pressure plasma jets (APPJs). J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 194008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weltmann, K.D.; Brandenburg, R.; Ehlbeck, J.; Foest, R.; Kindel, E.; Stieber, M.; von Woedtke, T. Plasma decontamination at atmospheric pressure—Basics and applications. In Proceedings of the 35th IEEE International Conference on Plasma Science (ICOPS 2008), Karlsruhe, Germany, 15–19 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- O’Meara, S.M.; Cullum, N.A.; Majid, M.; Sheldon, T.A. Systematic review of antimicrobial agents used for chronic wounds. Br. J. Surg. 2001, 88, 4–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filius, P.M.; Gyssens, I.C. Impact of increasing antimicrobial resistance on wound management. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2002, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isbary, G.; Morfill, G.; Schmidt, H.U.; Georgi, M.; Ramrath, K.; Heinlin, J.; Karrer, S.; Landthaler, M.; Shimizu, T.; Steffes, B.; et al. A first prospective randomized controlled trial to decrease bacterial load using cold atmospheric argon plasma on chronic wounds in patients. Br. J. Dermatol. 2010, 163, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulrich, C.; Kluschke, F.; Patzelt, A.; Vandersee, S.; Czaika, V.A.; Richter, H.; Bob, A.; von Hutten, J.; Painsi, C.; Hugel, R.; et al. Clinical use of cold atmospheric pressure argon plasma in chronic leg ulcers: A pilot study. J. Wound Care 2015, 24, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekeschus, S.; von Woedtke, T.; Emmert, S.; Schmidt, A. Medical gas plasma-stimulated wound healing: Evidence and mechanisms. Redox Biol. 2021, 46, 102116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liedtke, K.R.; Diedrich, S.; Pati, O.; Freund, E.; Flieger, R.; Heidecke, C.D.; Partecke, L.I.; Bekeschus, S. Cold Physical Plasma Selectively Elicits Apoptosis in Murine Pancreatic Cancer Cells In Vitro and In Ovo. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 5655–5663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqual-Melo, G.; Nascimento, T.; Sanches, L.J.; Blegniski, F.P.; Bianchi, J.K.; Sagwal, S.K.; Berner, J.; Schmidt, A.; Emmert, S.; Weltmann, K.D.; et al. Plasma Treatment Limits Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Development In Vitro and In Vivo. Cancers 2020, 12, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Preston, R.; Ogawa, T.; Uemura, M.; Shumulinsky, G.; Valle, B.L.; Pirini, F.; Ravi, R.; Sidransky, D.; Keidar, M.; Trink, B. Cold atmospheric plasma treatment selectively targets head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 34, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wende, K.; Bekeschus, S.; Schmidt, A.; Jatsch, L.; Hasse, S.; Weltmann, K.D.; Masur, K.; von Woedtke, T. Risk assessment of a cold argon plasma jet in respect to its mutagenicity. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2016, 798–799, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, A.; Woedtke, T.V.; Stenzel, J.; Lindner, T.; Polei, S.; Vollmar, B.; Bekeschus, S. One Year Follow-Up Risk Assessment in SKH-1 Mice and Wounds Treated with an Argon Plasma Jet. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berner, J.; Herold, L.; Martinet, A.; Miebach, L.; von Woedke, T.; Weltmann, K.D.; Emmert, S.; Boeckmann, L.; Bekeschus, S. Reactive Species Risk Assessment Using Optimized HET-CAM Safety Evaluation of Feed Gas-Modified Gas Plasma Technology and Anticancer Drugs. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 34480–34495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Dubey, S.; Dabholkar, N.; Narayan Pal, U.; Singhvi, G.; Kumar Sharma, N.; Puri, A.; Kesharwani, P. Emerging innovations in cold plasma therapy against cancer: A paradigm shift. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 2425–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weltmann, K.D.; Kindel, E.; von Woedtke, T.; Hähnel, M.; Stieber, M.; Brandenburg, R. Atmospheric-pressure plasma sources: Prospective tools for plasma medicine. Pure Appl. Chem. 2010, 82, 1223–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Nguyen, L.N.; Akter, M.; Park, G.; Choi, E.H.; Kaushik, N.K. Impact of ROS Generated by Chemical, Physical, and Plasma Techniques on Cancer Attenuation. Cancers 2019, 11, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privat-Maldonado, A.; Schmidt, A.; Lin, A.; Weltmann, K.D.; Wende, K.; Bogaerts, A.; Bekeschus, S. ROS from Physical Plasmas: Redox Chemistry for Biomedical Therapy. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 9062098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, M.P. Hormesis defined. Ageing Res. Rev. 2008, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sies, H.; Jones, D.P. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) as pleiotropic physiological signalling agents. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Bio 2020, 21, 363–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sies, H. Hydrogen peroxide as a central redox signaling molecule in physiological oxidative stress: Oxidative eustress. Redox Biol. 2017, 11, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mates, J.M.; Segura, J.A.; Alonso, F.J.; Marquez, J. Oxidative stress in apoptosis and cancer: An update. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 1649–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeschus, S.; Saadati, F.; Emmert, S. The potential of gas plasma technology for targeting breast cancer. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022, 12, e1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Xu, Y.; Cui, Q.; Liu, D.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Feng, M.; Liang, R.; Chen, H.; et al. Cold atmospheric plasma as a potential tool for multiple myeloma treatment. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 18002–18017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.J.; Kim, K.I.; Kim, G.; Moon, E.; Yang, S.S.; Lee, J.S. Atmospheric-pressure plasma jet induces apoptosis involving mitochondria via generation of free radicals. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.W.; Kang, S.U.; Shin, Y.S.; Kim, K.I.; Seo, S.J.; Yang, S.S.; Lee, J.S.; Moon, E.; Baek, S.J.; Lee, K.; et al. Non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma induces apoptosis in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma: Involvement of DNA-damage-triggering sub-G(1) arrest via the ATM/p53 pathway. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 545, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsch, A.; Qarqash, S.; Römer, S.; Schoon, J.; Singer, D.; Bekeschus, S.; Ekkernkamp, A.; Wassilew, G.I.; Tzvetkov, M.V.; Haralambiev, L. Effective combination of cold physical plasma and chemotherapy against Ewing sarcoma cells in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, T.; Shi, L.; Toyokuni, S. Non-thermal plasma as a simple ferroptosis inducer in cancer cells: A possible role of ferritin. Pathol. Int. 2018, 68, 442–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, Y.; Toyokuni, S. Induction of cancer cell-specific ferroptosis by non-thermal plasma exposure. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 59, 110501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, G.; Yu, K.N.; Yang, M.; Peng, S.; Ma, J.; Qin, F.; Cao, W.; Cui, S.; Nie, L.; et al. Cold atmospheric plasma induces GSDME-dependent pyroptotic signaling pathway via ROS generation in tumor cells. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, N.; Liu, W.; Nakamura, K.; Yoshida, K.; Ikeda, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Mizuno, M.; Toyokuni, S.; Hori, M.; Kikkawa, F.; et al. Plasma-activated medium promotes autophagic cell death along with alteration of the mTOR pathway. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.G.; Xiang, B.; Merlino, D.J.; Baybutt, T.R.; Sahu, J.; Fridman, A.; Snook, A.E.; Miller, V. Non-thermal plasma induces immunogenic cell death in vivo in murine CT26 colorectal tumors. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1484978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, E.; Liedtke, K.R.; van der Linde, J.; Metelmann, H.R.; Heidecke, C.D.; Partecke, L.I.; Bekeschus, S. Physical plasma-treated saline promotes an immunogenic phenotype in CT26 colon cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troitskaya, O.; Golubitskaya, E.; Biryukov, M.; Varlamov, M.; Gugin, P.; Milakhina, E.; Richter, V.; Schweigert, I.; Zakrevsky, D.; Koval, O. Non-Thermal Plasma Application in Tumor-Bearing Mice Induces Increase of Serum HMGB1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M.; Arnholdt, M.; Hissnauer, A.; Fischer, I.; Schonfisch, B.; Andress, J.; Gerstner, S.; Dannehl, D.; Bosmuller, H.; Staebler, A.; et al. Tissue-preserving treatment with non-invasive physical plasma of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia-a prospective controlled clinical trial. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1242732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Pokomandy, A.; Rouleau, D.; Lalonde, R.; Beauvais, C.; de Castro, C.; Coutlee, F. Human Immunodeficiency and Papilloma Virus Research Group (HIPVIRG) Study Group Argon plasma coagulation treatment of anal high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions in men who have sex with men living with HIV: Results of a 2-year prospective pilot study. HIV Med. 2018, 19, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, P.C.; Miller, V.; Fridman, G.; Lin, A.; Fridman, A. Successful treatment of actinic keratoses using nonthermal atmospheric pressure plasma: A case series. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 76, 349–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canady, J.; Murthy, S.R.K.; Zhuang, T.; Gitelis, S.; Nissan, A.; Ly, L.; Jones, O.Z.; Cheng, X.; Adileh, M.; Blank, A.T.; et al. The First Cold Atmospheric Plasma Phase I Clinical Trial for the Treatment of Advanced Solid Tumors: A Novel Treatment Arm for Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freund, E.; Bekeschus, S. Gas Plasma-Oxidized Liquids for Cancer Treatment: Preclinical Relevance, Immuno-Oncology, and Clinical Obstacles. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2021, 5, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lango, M.N. Multimodal treatment for head and neck cancer. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 89, 43–52, viii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terlizzi, M.; Bossi, A. High-risk Locally Advanced Prostate Cancer: Multimodal Treatment Is the Key. Eur. Urol. Open Sci. 2022, 38, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.; Lavery, A.; Turkington, R.C. An overview of acute gastrointestinal side effects of systemic anti-cancer therapy and their management. Best. Pr. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2020, 48–49, 101691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X. Drug resistance and combating drug resistance in cancer. Cancer Drug Resist. 2019, 2, 141–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, C.; Nitsch, A.; Erb, H.H.H.; Egger, E.K.; Haralambiev, L.; Eggers, B.; Kramer, F.-J.; Weiss, M.; Mustea, A.; Stope, M.B. Non-Invasive Physical Plasma Enhances the Membrane Permeability to Low Molecular Weight Compounds and Subsequently Leads to the Loss of Cellular ATP and the Devitalization of Epithelial Cancer Cells. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacoby, J.M.; Strakeljahn, S.; Nitsch, A.; Bekeschus, S.; Hinz, P.; Mustea, A.; Ekkernkamp, A.; Tzvetkov, M.V.; Haralambiev, L.; Stope, M.B. An Innovative Therapeutic Option for the Treatment of Skeletal Sarcomas: Elimination of Osteo- and Ewing’s Sarcoma Cells Using Physical Gas Plasma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernier, P.T.; Levine, Z.A.; Wu, Y.H.; Joubert, V.; Ziegler, M.J.; Mir, L.M.; Tieleman, D.P. Electroporating fields target oxidatively damaged areas in the cell membrane. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golpour, M.; Alimohammadi, M.; Sohbatzadeh, F.; Fattahi, S.; Bekeschus, S.; Rafiei, A. Cold atmospheric pressure plasma treatment combined with starvation increases autophagy and apoptosis in melanoma in vitro and in vivo. Exp. Dermatol. 2022, 31, 1016–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, P.; Kumar, N.; Hammerschmid, D.; Privat-Maldonado, A.; Dewilde, S.; Bogaerts, A. Synergistic Effects of Melittin and Plasma Treatment: A Promising Approach for Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2019, 11, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadati, F.; Mahdikia, H.; Abbaszadeh, H.A.; Abdollahifar, M.A.; Khoramgah, M.S.; Shokri, B. Comparison of Direct and Indirect cold atmospheric-pressure plasma methods in the B(16)F(10) melanoma cancer cells treatment. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimohammadi, M.; Golpur, M.; Sohbatzadeh, F.; Hadavi, S.; Bekeschus, S.; Niaki, H.A.; Valadan, R.; Rafiei, A. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Is a Potent Tool to Improve Chemotherapy in Melanoma In Vitro and In Vivo. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daeschlein, G.; Hillmann, A.; Gumbel, D.; Sicher, C.; von Podewils, S.; Stope, M.B.; Junger, M. Enhanced Anticancer Efficacy by Drug Chemotherapy and Cold Atmospheric Plasma Against Melanoma and Glioblastoma Cell Lines In Vitro. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2018, 2, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pefani-Antimisiari, K.; Athanasopoulos, D.K.; Marazioti, A.; Sklias, K.; Rodi, M.; de Lastic, A.L.; Mouzaki, A.; Svarnas, P.; Antimisiaris, S.G. Synergistic effect of cold atmospheric pressure plasma and free or liposomal doxorubicin on melanoma cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.M.; Jeong, Y.I.; Kook, M.S.; Kim, B.H. Combinatorial Effect of Cold Atmosphere Plasma (CAP) and the Anticancer Drug Cisplatin on Oral Squamous Cell Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, T.F.; Probst, F.A.; Troeltzsch, M.; Schwenk-Zieger, S.; Zimmermann, J.L.; Morfill, G.; Becker, S.; Harreus, U.; Welz, C. Primary cold atmospheric plasma combined with low dose cisplatin as a possible adjuvant combination therapy for HNSCC cells-an in-vitro study. Head. Face Med. 2022, 18, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirpour, S.; Ghomi, H.; Piroozmand, S.; Nikkhah, M.; Tavassoli, S.H.; Azad, S.Z. The Selective Characterization of Nonthermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet on Treatment of Human Breast Cancer and Normal Cells. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2014, 42, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedian, S.; Hekmat, A.; Tackallou, S.H.; Ghoranneviss, M. The Impacts of Prepared Plasma-Activated Medium (PAM) Combined with Doxorubicin on the Viability of MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells: A New Cancer Treatment Strategy. Rep. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2022, 10, 640–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihai, C.T.; Mihaila, I.; Pasare, M.A.; Pintilie, R.M.; Ciorpac, M.; Topala, I. Cold Atmospheric Plasma-Activated Media Improve Paclitaxel Efficacy on Breast Cancer Cells in a Combined Treatment Model. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 1995–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjika, E.; Pal-Ghosh, S.; Kirschner, M.E.; Lin, L.; Sherman, J.H.; Stepp, M.A.; Keidar, M. Combination therapy of cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) with temozolomide in the treatment of U87MG glioblastoma cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, P.; Kumar, N.; Privat-Maldonado, A.; Smits, E.; Bogaerts, A. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Increases Temozolomide Sensitivity of Three-Dimensional Glioblastoma Spheroids via Oxidative Stress-Mediated DNA Damage. Cancers 2021, 13, 1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, G.E.; Casey, A.; Milosavljevic, V.; Liu, Y.; Howe, O.; Cullen, P.J.; Curtin, J.F. Non-thermal atmospheric plasma induces ROS-independent cell death in U373MG glioma cells and augments the cytotoxicity of temozolomide. Brit J. Cancer 2016, 114, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koritzer, J.; Boxhammer, V.; Schafer, A.; Shimizu, T.; Klampfl, T.G.; Li, Y.F.; Welz, C.; Schwenk-Zieger, S.; Morfill, G.E.; Zimmermann, J.L.; et al. Restoration of sensitivity in chemo-resistant glioma cells by cold atmospheric plasma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro Lopes, B.; O’Neill, L.; Bourke, P.; Boehm, D. Combined Effect of Plasma-Activated Water and Topotecan in Glioblastoma Cells. Cancers 2023, 15, 4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, J.I.; Tanaka, H.; Ishikawa, K.; Sakakita, H.; Ikehara, Y.; Hori, M. Plasma-activated medium (PAM) kills human cancer-initiating cells. Pathol. Int. 2018, 68, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tang, T.; Lee, H.J.; Song, K. Selective Anti-Cancer Effects of Plasma-Activated Medium and Its High Efficacy with Cisplatin on Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Cancer Stem Cell Characteristics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liedtke, K.R.; Freund, E.; Hermes, M.; Oswald, S.; Heidecke, C.D.; Partecke, L.I.; Bekeschus, S. Gas Plasma-Conditioned Ringer’s Lactate Enhances the Cytotoxic Activity of Cisplatin and Gemcitabine in Pancreatic Cancer In Vitro and In Ovo. Cancers 2020, 12, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brulle, L.; Vandamme, M.; Ries, D.; Martel, E.; Robert, E.; Lerondel, S.; Trichet, V.; Richard, S.; Pouvesle, J.M.; Le Pape, A. Effects of a non thermal plasma treatment alone or in combination with gemcitabine in a MIA PaCa2-luc orthotopic pancreatic carcinoma model. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.S.; Li, B.; Xu, S.D.; Liu, D.X.; Zhang, H.; Xu, D.H.; Guo, L.; Kong, M.G. Study of the anticancer effects of a helium plasma jet combined with four anticancer drugs on 3D bladder tumour spheroids. Plasma Process Polym. 2021, 18, 2000226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Kim, S.W.; Jung, M.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, K.S.; Suh, D.S.; Kim, K.H.; Choi, E.H.; Kim, J.; Kwon, B.S. Plasma-activated medium inhibits cancer stem cell-like properties and exhibits a synergistic effect in combination with cisplatin in ovarian cancer. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 182, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateu-Sanz, M.; Ginebra, M.P.; Tornin, J.; Canal, C. Cold atmospheric plasma enhances doxorubicin selectivity in metastasic bone cancer. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 189, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsch, A.; Qarqash, S.; Romer, S.; Schoon, J.; Ekkernkamp, A.; Niethard, M.; Reichert, J.C.; Wassilew, G.I.; Tzvetkov, M.V.; Haralambiev, L. Enhancing the Impact of Chemotherapy on Ewing Sarcoma Cells through Combination with Cold Physical Plasma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, T.; Suzuki-Karasaki, M.; Suzuki-Karasaki, M.; Ichikawa, J.; Ochiai, T.; Yoshida, Y.; Haro, H.; Suzuki-Karasaki, Y. Combined Anticancer Effect of Plasma-Activated Infusion and Salinomycin by Targeting Autophagy and Mitochondrial Morphology. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 593127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeckmann, L.; Berner, J.; Kordt, M.; Lenz, E.; Schafer, M.; Semmler, M.L.; Frey, A.; Sagwal, S.K.; Rebl, H.; Miebach, L.; et al. Synergistic effect of cold gas plasma and experimental drug exposure exhibits skin cancer toxicity in vitro and in vivo. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 57, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhirajan, R.K.; Rodder, K.; Bodnar, Y.; Pasqual-Melo, G.; Emmert, S.; Griguer, C.E.; Weltmann, K.D.; Bekeschus, S. Cytochrome C oxidase Inhibition and Cold Plasma-derived Oxidants Synergize in Melanoma Cell Death Induction. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, Z.; Mehrabanjoubani, P.; Rafiei, A.; Biparva, P.; Kardan, M. Combined Effect of Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Curcumin in Melanoma Cancer. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 1969863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Cao, X.; Shen, B.; Chen, Z.; Chen, G. Injectable cold atmospheric plasma-activated immunotherapeutic hydrogel for enhanced cancer treatment. Biomaterials 2023, 300, 122189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrakova, E.; Biryukov, M.; Troitskaya, O.; Gugin, P.; Milakhina, E.; Semenov, D.; Poletaeva, J.; Ryabchikova, E.; Novak, D.; Kryachkova, N.; et al. Chloroquine Enhances Death in Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cells Exposed to Cold Atmospheric Plasma Jet. Cells 2023, 12, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loenhout, J.; Freire Boullosa, L.; Quatannens, D.; De Waele, J.; Merlin, C.; Lambrechts, H.; Lau, H.W.; Hermans, C.; Lin, A.; Lardon, F.; et al. Auranofin and Cold Atmospheric Plasma Synergize to Trigger Distinct Cell Death Mechanisms and Immunogenic Responses in Glioblastoma. Cells 2021, 10, 2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Song, X.; Yang, F.; Wang, J.; Sun, M.; Liu, G.; Ahmad, N.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, G.; et al. Combined effects of vitamin C and cold atmospheric plasma-conditioned media against glioblastoma via hydrogen peroxide. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2023, 194, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Charleton, C.; Devine, R.W.; Kelada, M.; Walsh, J.M.D.; Conway, G.E.; Gunes, S.; Mondala, J.R.M.; Tian, F.; Tiwari, B.; et al. Enhanced pyrazolopyrimidinones cytotoxicity against glioblastoma cells activated by ROS-Generating cold atmospheric plasma. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 224, 113736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniruzzaman, R.; Rehman, M.U.; Zhao, Q.L.; Jawaid, P.; Mitsuhashi, Y.; Imaue, S.; Fujiwara, K.; Ogawa, R.; Tomihara, K.; Saitoh, J.I.; et al. Roles of intracellular and extracellular ROS formation in apoptosis induced by cold atmospheric helium plasma and X-irradiation in the presence of sulfasalazine. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 129, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daeschlein, G.; Scholz, S.; Lutze, S.; Arnold, A.; von Podewils, S.; Kiefer, T.; Tueting, T.; Hardt, O.; Haase, H.; Grisk, O.; et al. Comparison between cold plasma, electrochemotherapy and combined therapy in a melanoma mouse model. Exp. Dermatol. 2013, 22, 582–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.-H. Enhancement of Electrochemotherapy by Non-Thermal Plasma-Treated Liquids: Protocol Design and Proof of Concept. Doctoral Dissertation, Université Paris-Saclay, Gif-sur-Yvette, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ishii, R.; Kamiya, T.; Hara, H.; Adachi, T. Hyperthermia synergistically enhances cancer cell death by plasma-activated acetated Ringer’s solution. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 693, 108565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chen, Z.; Wen, D.; Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Zeng, Y.; Dotti, G.; Wirz, R.E.; Gu, Z. Transdermal cold atmospheric plasma-mediated immune checkpoint blockade therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 3687–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miebach, L.; Melo-Zainzinger, G.; Freund, E.; Clemen, R.; Cecchini, A.L.; Bekeschus, S. Medical Gas Plasma Technology Combines with Antimelanoma Therapies and Promotes Immune-Checkpoint Therapy Responses. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2303183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeschus, S. Combined Toxicity of Gas Plasma Treatment and Nanoparticles Exposure in Melanoma Cells In Vitro. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.B.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, U.K.; Hong, J.W.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, G.C. Targeting NEU Protein in Melanoma Cells with Non-Thermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma and Gold Nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2015, 11, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.B.R.; Choi, J.H.; Hong, J.W.; Song, K.W.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, U.K.; Kim, G.C. Selective Killing of Melanoma Cells With Non-Thermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma and p-FAK Antibody Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 14, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.C.; Kim, G.J.; Park, S.R.; Jeon, S.M.; Seo, H.J.; Iza, F.; Lee, J.K. Air plasma coupled with antibody-conjugated nanoparticles: A new weapon against cancer. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 032005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzimitrowicz, A.; Bielawska-Pohl, A.; diCenzo, G.C.; Jamroz, P.; Macioszczyk, J.; Klimczak, A.; Pohl, P. Pulse-Modulated Radio-Frequency Alternating-Current-Driven Atmospheric-Pressure Glow Discharge for Continuous-Flow Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Evaluation of Their Cytotoxicity toward Human Melanoma Cells. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, A.; Irani, S.; Mirfakhraie, R. Combination of cold atmospheric plasma and iron nanoparticles in breast cancer: Gene expression and apoptosis study. Onco Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 5911–5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Lee, S.J.; Castro, N.J.; Yan, D.; Keidar, M.; Zhang, L.G. Synergistic Effect of Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Drug Loaded Core-shell Nanoparticles on Inhibiting Breast Cancer Cell Growth. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, S.; Shahmirani, Z.; Atyabi, S.M.; Mirpoor, S. Induction of growth arrest in colorectal cancer cells by cold plasma and gold nanoparticles. Arch. Med. Sci. 2015, 11, 1286–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Liu, K.; Manaloto, E.; Casey, A.; Cribaro, G.P.; Byrne, H.J.; Tian, F.; Barcia, C.; Conway, G.E.; Cullen, P.J.; et al. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Induces ATP-Dependent Endocytosis of Nanoparticles and Synergistic U373MG Cancer Cell Death. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manaloto, E.; Gowen, A.A.; Lesniak, A.; He, Z.; Casey, A.; Cullen, P.J.; Curtin, J.F. Cold atmospheric plasma induces silver nanoparticle uptake, oxidative dissolution and enhanced cytotoxicity in glioblastoma multiforme cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 689, 108462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.Q.; Rajjoub, K.; Sherman, J.; Canady, J.; Recek, N.; Yan, D.Y.; Bian, K.; Murad, F.; Keidar, M. Cold Plasma Accelerates the Uptake of Gold Nanoparticles Into Glioblastoma Cells. Plasma Process Polym. 2015, 12, 1364–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, N.K.; Kaushik, N.; Wahab, R.; Bhartiya, P.; Linh, N.N.; Khan, F.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A.; Choi, E.H. Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Gold Quantum Dots Exert Dual Cytotoxicity Mediated by the Cell Receptor-Activated Apoptotic Pathway in Glioblastoma Cells. Cancers 2020, 12, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yu, H.; Ding, D.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Keidar, M.; Zhang, W. Cold atmospheric plasma and iron oxide-based magnetic nanoparticles for synergetic lung cancer therapy. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 130, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, M.; Adhikari, B.; Ghimire, B.; Baboota, S.; Choi, E.H. Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Silymarin Nanoemulsion Activate Autophagy in Human Melanoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, M.; Kaushik, N.; Ghimire, B.; Adhikari, B.; Baboota, S.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A.; Wahab, R.; Lee, S.J.; Kaushik, N.K.; Choi, E.H. Cold atmospheric plasma and silymarin nanoemulsion synergistically inhibits human melanoma tumorigenesis via targeting HGF/c-MET downstream pathway. Cell Commun. Signal 2019, 17, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Ding, D.; Gong, X.; Keidar, M.; Zhang, W. Paclitaxel-Loaded Core-Shell Magnetic Nanoparticles and Cold Atmospheric Plasma Inhibit Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Growth. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 43462–43471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Geilich, B.M.; Keidar, M.; Webster, T.J. Killing malignant melanoma cells with protoporphyrin IX-loaded polymersome-mediated photodynamic therapy and cold atmospheric plasma. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 4117–4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ara, E.S.; Noghreiyan, A.V.; Sazgarnia, A. Evaluation of photodynamic effect of Indocyanine green (ICG) on the colon and glioblastoma cancer cell lines pretreated by cold atmospheric plasma. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2021, 35, 102408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami-Gadallo, L.; Ghoranneviss, M.; Ataie-Fashtami, L.; Pouladian, M.; Sardari, D. Enhancement of cancerous cells treatment by applying cold atmospheric plasma and photo dynamic therapy simultaneously. Clin. Plasma Med. 2017, 7–8, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Oshin, E.A.; Guo, S.; Scott, M.; Li, X.; Mangiamele, C.; Heller, R. Synergistic effects of an atmospheric pressure plasma jet and pulsed electric field on cells and skin. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. IEEE Nucl. Plasma Sci. Soc. 2021, 49, 3317–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqual-Melo, G.; Sagwal, S.K.; Freund, E.; Gandhirajan, R.K.; Frey, B.; von Woedtke, T.; Gaipl, U.; Bekeschus, S. Combination of Gas Plasma and Radiotherapy Has Immunostimulatory Potential and Additive Toxicity in Murine Melanoma Cells in Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafontaine, J.; Boisvert, J.S.; Glory, A.; Coulombe, S.; Wong, P. Synergy between Non-Thermal Plasma with Radiation Therapy and Olaparib in a Panel of Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Cancers 2020, 12, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Antineoplastic Agents. In LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury; National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mollaei, M.; Hassan, Z.M.; Khorshidi, F.; Langroudi, L. Chemotherapeutic drugs: Cell death- and resistance-related signaling pathways. Are they really as smart as the tumor cells? Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 101056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, D.E. Targeted therapies: A new generation of cancer treatments. Am. Fam. Physician 2008, 77, 311–319. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.T.; Tan, Y.J.; Oon, C.E. Molecular targeted therapy: Treating cancer with specificity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 834, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, P.E.; Caenepeel, S.; Wu, L.C. Targeted Therapy and Checkpoint Immunotherapy Combinations for the Treatment of Cancer. Trends Immunol. 2016, 37, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebacher, N.A.; Stacy, A.E.; Porter, G.M.; Merlot, A.M. Clinical development of targeted and immune based anti-cancer therapies. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajria, D.; Chandarlapaty, S. HER2-amplified breast cancer: Mechanisms of trastuzumab resistance and novel targeted therapies. Expert. Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2011, 11, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, T.; Ohba, M.; Ohmori, T. Molecular-Targeted Therapies for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and Its Resistance Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, L.M.; Hicklin, D.J. VEGF-targeted therapy: Mechanisms of anti-tumour activity. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, J.; Chen, J.; Song, W. Low Temperature Plasma Suppresses Lung Cancer Cells Growth via VEGF/VEGFR2/RAS/ERK Axis. Molecules 2022, 27, 5934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Cai, L.; Dai, X. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Conveys Selectivity Against Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells via Triggering EGFR(Tyr1068)-Mediated Autophagy. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 895106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.W.; Kang, S.U.; Shin, Y.S.; Seo, S.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Yang, S.S.; Lee, J.S.; Moon, E.; Lee, K.; Kim, C.H. Combination of NTP with cetuximab inhibited invasion/migration of cetuximab-resistant OSCC cells: Involvement of NF-kappaB signaling. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, E.; Liedtke, K.R.; Miebach, L.; Wende, K.; Heidecke, A.; Kaushik, N.K.; Choi, E.H.; Partecke, L.I.; Bekeschus, S. Identification of Two Kinase Inhibitors with Synergistic Toxicity with Low-Dose Hydrogen Peroxide in Colorectal Cancer Cells in vitro. Cancers 2020, 12, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulan, P.; Wende, K.; von Woedtke, T.; Weltmann, K.D.; Bekeschus, S.; Clemen, R. Oxidative modifications control aberrant tyrosine kinase activity. Biointerphases 2024, 19, 061004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebl, H.; Sawade, M.; Hein, M.; Bergemann, C.; Wende, M.; Lalk, M.; Langer, P.; Emmert, S.; Nebe, B. Synergistic effect of plasma-activated medium and novel indirubin derivatives on human skin cancer cells by activation of the AhR pathway. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Luo, X.; Xu, Y.; Cui, Q.; Yang, Y.; Liu, D.; Chen, H.; Kong, M.G. The effects of cold atmospheric plasma on cell adhesion, differentiation, migration, apoptosis and drug sensitivity of multiple myeloma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 473, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulan, P.; Wende, M.; Bekeschus, S.; Lalk, M.; Wende, K. Activity Alterations of 37 Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Upon kINPen Plasma Exposure in A549 Lung Cancer Cells. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2024, 8, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Singer, D.; Potlitz, F.; Nasri, Z.; von Woedtke, T.; Link, A.; Bekeschus, S.; Wende, K. Cold Physical Plasma-Mediated Fenretinide Prodrug Activation Confers Additive Cytotoxicity in Epithelial Cells. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metelmann, H.R.; Seebauer, C.; Rutkowski, R.; Schuster, M.; Bekeschus, S.; Metelmann, P. Treating cancer with cold physical plasma: On the way to evidence-based medicine. Contrib. Plasm. Phys. 2018, 58, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Vacchelli, E.; Bravo-San Pedro, J.M.; Buque, A.; Senovilla, L.; Baracco, E.E.; Bloy, N.; Castoldi, F.; Abastado, J.P.; Agostinis, P.; et al. Classification of current anticancer immunotherapies. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 12472–12508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterfield, L.H.; Najjar, Y.G. Immunotherapy combination approaches: Mechanisms, biomarkers and clinical observations. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 24, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, M.; Daniels, L.; Lin, A.; Krebs, F.C.; Snook, A.E.; Bekeschus, S.; Bowne, W.B.; Miller, V. Non-Thermal Plasma-Induced Immunogenic Cell Death in Cancer: A Topical Review. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2019, 52, 423001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeschus, S.; Clemen, R. Plasma, cancer, immunity. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2022, 55, 473003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemen, R.; Heirman, P.; Lin, A.; Bogaerts, A.; Bekeschus, S. Physical Plasma-Treated Skin Cancer Cells Amplify Tumor Cytotoxicity of Human Natural Killer (NK) Cells. Cancers 2020, 12, 3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miebach, L.; Freund, E.; Horn, S.; Niessner, F.; Sagwal, S.K.; von Woedtke, T.; Emmert, S.; Weltmann, K.D.; Clemen, R.; Schmidt, A.; et al. Tumor cytotoxicity and immunogenicity of a novel V-jet neon plasma source compared to the kINPen. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleem, A.; Javaid, M.; Singh, R.P.; Rab, S.; Suman, R. Applications of nanotechnology in medical field: A brief review. Glob. Health J. 2023, 7, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austria, E.; Bilek, M.; Varamini, P.; Akhavan, B. Breaking biological barriers: Engineering polymeric nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Nano Today 2025, 60, 102552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, Y.; Yi, X.; Wibowo, D.; Yang, G.; Middelberg, A.P.J.; Gao, H.; Zhao, C.X. Nanoparticle elasticity regulates phagocytosis and cancer cell uptake. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salatin, S.; Maleki Dizaj, S.; Yari Khosroushahi, A. Effect of the surface modification, size, and shape on cellular uptake of nanoparticles. Cell Biol. Int. 2015, 39, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fuente, J.M.; Grazu, V. Nanobiotechnology: Inorganic Nanoparticles vs. Organic Nanoparticles; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Gavas, S.; Quazi, S.; Karpinski, T.M. Nanoparticles for Cancer Therapy: Current Progress and Challenges. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadi, S.; Serpooshan, V.; Tao, W.; Hamaly, M.A.; Alkawareek, M.Y.; Dreaden, E.C.; Brown, D.; Alkilany, A.M.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Mahmoudi, M. Cellular uptake of nanoparticles: Journey inside the cell. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4218–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfram, J.; Zhu, M.; Yang, Y.; Shen, J.; Gentile, E.; Paolino, D.; Fresta, M.; Nie, G.; Chen, C.; Shen, H.; et al. Safety of Nanoparticles in Medicine. Curr. Drug Targets 2015, 16, 1671–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdal Dayem, A.; Hossain, M.K.; Lee, S.B.; Kim, K.; Saha, S.K.; Yang, G.M.; Choi, H.Y.; Cho, S.G. The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in the Biological Activities of Metallic Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.L.; Chen, S.H.; Feng, W.R.; Chen, W.X.; Yang, S.Z. Surface modification of the nanoparticles by an atmospheric room-temperature plasma fluidized bed. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 3915–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasirci, N.; Endogan, T.; Vardar, E.; Kiziltay, A.; Hasirci, V. Effect of oxygen plasma on surface properties and biocompatibility of PLGA films. Surf. Interface Anal. 2010, 42, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Liu, K.; Scally, L.; Manaloto, E.; Gunes, S.; Ng, S.W.; Maher, M.; Tiwari, B.; Byrne, H.J.; Bourke, P.; et al. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Stimulates Clathrin-Dependent Endocytosis to Repair Oxidised Membrane and Enhance Uptake of Nanomaterial in Glioblastoma Multiforme Cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmirani, Z.; Irani, S.; Atyabi, S.M.; Mirpour, S.; Shadpour, S.; Ghorannevis, M.; Joupari, M.D. Effect of cold atmospheric pressure plasma and gold nanoparticles on cell viability. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2014, 4, 3108–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Lim, L.K.; Phua, Y.; Hua, J.; Wang, C.H. Electrohydrodynamic atomization for biodegradable polymeric particle production. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2006, 302, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Kasinathan, A.; Ganesan, R.; Balasubramanian, A.; Bhaskaran, J.; Suresh, S.; Srinivasan, R.; Aravind, K.B.; Sivalingam, N. Curcumin induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest via the activation of reactive oxygen species-independent mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in Smad4 and p53 mutated colon adenocarcinoma HT29 cells. Nutr. Res. 2018, 51, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterbourn, C.C. Toxicity of iron and hydrogen peroxide: The Fenton reaction. Toxicol. Lett. 1995, 82–83, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.M.; Rodriguez, Y.A.R.; Jeong, K.; Ahn, E.E.; Lim, S.S. Targeting focal adhesion kinase in cancer cells and the tumor microenvironment. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menard, S.; Casalini, P.; Campiglio, M.; Pupa, S.M.; Tagliabue, E. Role of HER2/neu in tumor progression and therapy. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 2965–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagwal, S.K.; Bekeschus, S. ROS Pleiotropy in Melanoma and Local Therapy with Physical Modalities. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6816214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ruysscher, D.; Niedermann, G.; Burnet, N.G.; Siva, S.; Lee, A.W.; Hegi-Johnson, F. Radiotherapy toxicity. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.P.; Zheng, C.C.; Huang, Y.N.; He, M.L.; Xu, W.W.; Li, B. Molecular mechanisms of chemo- and radiotherapy resistance and the potential implications for cancer treatment. MedComm 2021, 2, 315–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskar, R.; Dai, J.; Wenlong, N.; Yeo, R.; Yeoh, K.W. Biological response of cancer cells to radiation treatment. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2014, 1, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, T. Molecular mechanisms of tumor resistance to radiotherapy. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, H.B.; Coleman, C.N.; Anscher, M.S.; McBride, W.H. Effects of radiation on normal tissue: Consequences and mechanisms. Lancet Oncol. 2003, 4, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, J.C.; Suchowerska, N.; Rogers, L.J.; Lo, H.; Choong, E.S.; McKenzie, D.R. Plasma activated liquid synergistically enhances response to radiation for improved cancer therapy. Plasma Process Polym. 2022, 19, 2200026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.O.; Lee, M.H.; Kim, G.H.; Kim, E.H. Quantitation of the ROS production in plasma and radiation treatments of biotargets. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, K.; Qi, F.; Kobayashi, J. Potential relationship between the biological effects of low-dose irradiation and mitochondrial ROS production. J. Radiat. Res. 2018, 59, ii91–ii97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, W.G.; Schaper, L.; Muir, M.; Currell, F.J. The Effect of Electrical Discharges in the Cell Media on Their Viability and DNA Damage and Comparison with the Effect of X-Rays. Plasma Med. 2012, 2, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dejonckheere, C.S.; Torres-Crigna, A.; Layer, J.P.; Layer, K.; Wiegreffe, S.; Sarria, G.R.; Scafa, D.; Koch, D.; Leitzen, C.; Koksal, M.A.; et al. Non-Invasive Physical Plasma for Preventing Radiation Dermatitis in Breast Cancer: A First-In-Human Feasibility Study. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, T. Radiation as an In Situ Auto-Vaccination: Current Perspectives and Challenges. Vaccines 2019, 7, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeschus, S.; Clemen, R.; Niessner, F.; Sagwal, S.K.; Freund, E.; Schmidt, A. Medical Gas Plasma Jet Technology Targets Murine Melanoma in an Immunogenic Fashion. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1903438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemen, R.; Bekeschus, S. ROS Cocktails as an Adjuvant for Personalized Antitumor Vaccination? Vaccines 2021, 9, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belehradek, M.; Domenge, C.; Luboinski, B.; Orlowski, S.; Belehradek, J., Jr.; Mir, L.M. Electrochemotherapy, a new antitumor treatment. First clinical phase I-II trial. Cancer 1993, 72, 3694–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domenge, C.; Orlowski, S.; Luboinski, B.; De Baere, T.; Schwaab, G.; Belehradek, J., Jr.; Mir, L.M. Antitumor electrochemotherapy: New advances in the clinical protocol. Cancer 1996, 77, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, N.; Friebe, M. Electrochemotherapy: A Review of Current Status, Alternative IGP Approaches, and Future Perspectives. J. Healthc. Eng. 2019, 2019, 2784516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, L.M. Bases and rationale of the electrochemotherapy. Ejc Suppl. 2006, 4, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoneva, I.; Semkova, S.; Bakalova, R.; Zhelev, Z.; Nuss, P.; Staneva, G.; Nikolova, B. Electroporation, electrochemotherapy and electro-assisted drug delivery in cancer. A state-of-the-art review. Biophys. Chem. 2022, 286, 106819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, C.M.; Steuer, A.; Stoffels, I.; von Woedtke, T.; Weltmann, K.-D.; Bekeschus, S.; Kolb, J.F. Combination of cold plasma and pulsed electric fields—A rationale for cancer patients in palliative care. Clin. Plasma Med. 2019, 16, 100096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakhomova, O.N.; Khorokhorina, V.A.; Bowman, A.M.; Rodaite-Riseviciene, R.; Saulis, G.; Xiao, S.; Pakhomov, A.G. Oxidative effects of nanosecond pulsed electric field exposure in cells and cell-free media. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2012, 527, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan, N.R.; Munawar, T.; Sheehan, M.C.; Fujimori, M.; Vista, W.R.; Wimmer, T.; Gutta, N.B.; Solomon, S.B.; Srimathveeravalli, G. Electrolysis products, reactive oxygen species and ATP loss contribute to cell death following irreversible electroporation with microsecond-long pulsed electric fields. Bioelectrochemistry 2024, 155, 108579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, C.M.; Kolb, J.F.; Bekeschus, S. Combined In Vitro Toxicity and Immunogenicity of Cold Plasma and Pulsed Electric Fields. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai, D.L.; Lee, J.; Nguyen, D.L.; Kim, Y.P. Tailoring photosensitive ROS for advanced photodynamic therapy. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowski, S.; Knap, B.; Przystupski, D.; Saczko, J.; Kedzierska, E.; Knap-Czop, K.; Kotlinska, J.; Michel, O.; Kotowski, K.; Kulbacka, J. Photodynamic therapy—Mechanisms, photosensitizers and combinations. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 1098–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, R.R.; Moghissi, K. Photodynamic Therapy (PDT): PDT Mechanisms. Clin. Endosc. 2013, 46, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlanda, J.; Kiesslich, T.; Engelhardt, V.; Krammer, B.; Plaetzer, K. Comparative in vitro study on the characteristics of different photosensitizers employed in PDT. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2010, 100, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, L.; Huang, M.; Zeng, S.; Zheng, J.; Peng, S.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Li, S. Innovative strategies for photodynamic therapy against hypoxic tumor. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 18, 100775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, A.; Di Venosa, G.; Hasan, T.; Al, B. Mechanisms of resistance to photodynamic therapy. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 2486–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vejdani Noghreiyan, A.; Imanparast, A.; Shayesteh Ara, E.; Soudmand, S.; Vejdani Noghreiyan, V.; Sazgarnia, A. In-vitro investigation of cold atmospheric plasma induced photodynamic effect by Indocyanine green and Protoporphyrin IX. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2020, 31, 101822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collet, G.; Robert, E.; Lenoir, A.; Vandamme, M.; Darny, T.; Dozias, S.; Kieda, C.; Pouvesle, J.M. Plasma jet-induced tissue oxygenation: Potentialities for new therapeutic strategies. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2014, 23, 012005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Liebelt, G.; Niessner, F.; von Woedtke, T.; Bekeschus, S. Gas plasma-spurred wound healing is accompanied by regulation of focal adhesion, matrix remodeling, and tissue oxygenation. Redox Biol. 2021, 38, 101809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habash, R.W.; Bansal, R.; Krewski, D.; Alhafid, H.T. Thermal therapy, part 1: An introduction to thermal therapy. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 34, 459–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Weng, S.; Yu, L.; Zhu, N.; Yang, M.; Yuan, Y. The Role of Hyperthermia in the Multidisciplinary Treatment of Malignant Tumors. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 1534735419876345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moniruzzaman, R.; Rehman, M.U.; Zhao, Q.L.; Jawaid, P.; Takeda, K.; Ishikawa, K.; Hori, M.; Tomihara, K.; Noguchi, K.; Kondo, T.; et al. Cold atmospheric helium plasma causes synergistic enhancement in cell death with hyperthermia and an additive enhancement with radiation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.S.; Xu, S.D.; Wang, Z.F.; Xu, D.H.; Guo, L.; Liu, D.X.; Kong, M.G.; Rong, M.Z. Antitumor effects of hyperthermia with plasma-treated solutions on 3D bladder tumor spheroids. Plasma Process Polym. 2021, 18, 2100070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-Sola, M.; Sureda-Vidal, H.; Altimiras-Roset, J.; Fontsere-Candell, E.; Gonzalez-Martinez, V.; Espaulella-Panicot, J.; Falanga, V.; Otero-Vinas, M. Hydrosurgery as a safe and efficient debridement method in a clinical wound unit. J. Wound Care 2017, 26, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.F.; Zhao, J.Q.; Yan, H.; Yu, W.L.; Yin, L. Waterjet machining of biological tissues in medical surgeries: From soft tissue dissection to bone cutting. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 107, 529–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Bekeschus, S.; von Woedtke, T.; Hasse, S. Cell migration and adhesion of a human melanoma cell line is decreased by cold plasma treatment. Clin. Plasma Med. 2015, 3, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holl, M.; Rasch, M.L.; Becker, L.; Keller, A.L.; Schultze-Rhonhof, L.; Ruoff, F.; Templin, M.; Keller, S.; Neis, F.; Kessler, F.; et al. Cell Type-Specific Anti-Adhesion Properties of Peritoneal Cell Treatment with Plasma-Activated Media (PAM). Biomedicines 2022, 10, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golz, A.C.; Bergemann, C.; Hildebrandt, F.; Emmert, S.; Nebe, B.; Rebl, H. Selective adhesion inhibition and hyaluronan envelope reduction of dermal tumor cells by cold plasma-activated medium. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2023, 17, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusakci-Seker, B.; Ozdemır, H. Assessment of pain perception after conventional frenectomy with application of cold atmospheric plasma. East. J. Med. 2020, 25, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenburg, R. Dielectric barrier discharges: Progress on plasma sources and on the understanding of regimes and single filaments. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2017, 26, 053001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, J.; Brandenburg, R.; Weltmann, K.D. Atmospheric pressure plasma jets: An overview of devices and new directions. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2015, 24, 064001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, S.; van Gessel, A.F.H.; Verreycken, T.; Bruggeman, P. Power dissipation, gas temperatures and electron densities of cold atmospheric pressure helium and argon RF plasma jets. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2011, 20, 065010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partecke, L.I.; Evert, K.; Haugk, J.; Doering, F.; Normann, L.; Diedrich, S.; Weiss, F.U.; Evert, M.; Huebner, N.O.; Guenther, C.; et al. Tissue tolerable plasma (TTP) induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binenbaum, Y.; Ben-David, G.; Gil, Z.; Slutsker, Y.Z.; Ryzhkov, M.A.; Felsteiner, J.; Krasik, Y.E.; Cohen, J.T. Cold Atmospheric Plasma, Created at the Tip of an Elongated Flexible Capillary Using Low Electric Current, Can Slow the Progression of Melanoma. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekeschus, S. Acquired cancer tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance: ROS as critical determinants. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.J.; Shin, T.M.; Sobanko, J.F.; Sharkey, J.M.; Grunyk, J.W.; Elenitsas, R.; Chu, E.Y.; Capell, B.C.; Ming, M.E.; Etzkorn, J.R. Risk factors for positive or equivocal margins after wide local excision of 1345 cutaneous melanomas. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 77, 333–340 e331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Hmada, Y.; Brodell, R.T.; Kharouf, N.; Flanagan, T.W.; Alamodi, A.A.; Hassan, S.Y.; Shalaby, H.; Hassan, S.L.; Haikel, Y.; Megahed, M.; et al. Mechanisms of Melanoma Progression and Treatment Resistance: Role of Cancer Stem-like Cells. Cancers 2024, 16, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbe, C.; Amaral, T.; Peris, K.; Hauschild, A.; Arenberger, P.; Basset-Seguin, N.; Bastholt, L.; Bataille, V.; Brochez, L.; Del Marmol, V.; et al. European consensus-based interdisciplinary guideline for melanoma. Part 2: Treatment—Update 2024. Eur. J. Cancer 2025, 215, 115153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundstrom, S.; Bremnes, R.M.; Kaasa, S.; Aasebo, U.; Hatlevoll, R.; Dahle, R.; Boye, N.; Wang, M.; Vigander, T.; Vilsvik, J.; et al. Cisplatin and etoposide regimen is superior to cyclophosphamide, epirubicin, and vincristine regimen in small-cell lung cancer: Results from a randomized phase III trial with 5 years’ follow-up. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 4665–4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzoli, C.G.; Baker, S., Jr.; Temin, S.; Pao, W.; Aliff, T.; Brahmer, J.; Johnson, D.H.; Laskin, J.L.; Masters, G.; Milton, D.; et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline update on chemotherapy for stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 6251–6266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.H.; Attri, P.; Ku, S.K.; Han, I.; Bogaerts, A.; Choi, E.H. Cocktail of reactive species generated by cold atmospheric plasma: Oral administration induces non-small cell lung cancer cell death. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2021, 54, 185202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, V.K.; Kennedy, E.B.; Baxter, N.N.; Benson, A.B., 3rd; Cercek, A.; Cho, M.; Ciombor, K.K.; Cremolini, C.; Davis, A.; Deming, D.A.; et al. Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: ASCO Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 678–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishaq, M.; Evans, M.D.; Ostrikov, K.K. Atmospheric pressure gas plasma-induced colorectal cancer cell death is mediated by Nox2-ASK1 apoptosis pathways and oxidative stress is mitigated by Srx-Nrf2 anti-oxidant system. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1843, 2827–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishaq, M.; Han, Z.J.; Kumar, S.; Evans, M.D.M.; Ostrikov, K. Atmospheric-Pressure Plasma- and TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis in TRAIL-Resistant Colorectal Cancer Cells. Plasma Process Polym. 2015, 12, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mang, X.; Li, X.; Cai, Z.; Tan, F. Cold atmospheric plasma induces apoptosis in human colon and lung cancer cells through modulating mitochondrial pathway. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 915785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miebach, L.; Freund, E.; Clemen, R.; Kersting, S.; Partecke, L.I.; Bekeschus, S. Gas plasma-oxidized sodium chloride acts via hydrogen peroxide in a model of peritoneal carcinomatosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2200708119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miebach, L.; Freund, E.; Cecchini, A.L.; Bekeschus, S. Conductive Gas Plasma Treatment Augments Tumor Toxicity of Ringer’s Lactate Solutions in a Model of Peritoneal Carcinomatosis. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, J.; Nishime, T.M.C.; Glitsch, S.; Lühder, H.; Weltmann, K.D. On the development of a deployable cold plasma endoscope. Contrib. Plasm. Phys. 2018, 58, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, I.; Kleeff, J.; Bergmann, F.; Reiser, C.; Herpel, E.; Friess, H.; Schirmacher, P.; Buchler, M.W. Most pancreatic cancer resections are R1 resections. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 15, 1651–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizrahi, J.D.; Surana, R.; Valle, J.W.; Shroff, R.T. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2020, 395, 2008–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Dosso, S.; Siebenhuner, A.R.; Winder, T.; Meisel, A.; Fritsch, R.; Astaras, C.; Szturz, P.; Borner, M. Treatment landscape of metastatic pancreatic cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2021, 96, 102180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Useros, J.; Li, W.; Cabeza-Morales, M.; Garcia-Foncillas, J. Oxidative Stress: A New Target for Pancreatic Cancer Prognosis and Treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2017, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, N.; Yamada, S.; Torii, K.; Takeda, S.; Nakamura, K.; Tanaka, H.; Kajiyama, H.; Kanda, M.; Fujii, T.; Nakayama, G.; et al. Effectiveness of plasma treatment on pancreatic cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 1655–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khabipov, A.; Freund, E.; Liedtke, K.R.; Kading, A.; Riese, J.; van der Linde, J.; Kersting, S.; Partecke, L.I.; Bekeschus, S. Murine Macrophages Modulate Their Inflammatory Profile in Response to Gas Plasma-Inactivated Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Cancers 2021, 13, 2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasir, I.; McGuinness, C.; Poh, A.R.; Ernst, M.; Darcy, P.K.; Britt, K.L. Tumor macrophage functional heterogeneity can inform the development of novel cancer therapies. Trends Immunol. 2023, 44, 971–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loenhout, J.; Flieswasser, T.; Freire Boullosa, L.; De Waele, J.; Van Audenaerde, J.; Marcq, E.; Jacobs, J.; Lin, A.; Lion, E.; Dewitte, H.; et al. Cold Atmospheric Plasma-Treated PBS Eliminates Immunosuppressive Pancreatic Stellate Cells and Induces Immunogenic Cell Death of Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Cancers 2019, 11, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liedtke, K.R.; Bekeschus, S.; Kaeding, A.; Hackbarth, C.; Kuehn, J.P.; Heidecke, C.D.; von Bernstorff, W.; von Woedtke, T.; Partecke, L.I. Non-thermal plasma-treated solution demonstrates antitumor activity against pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liedtke, K.R.; Freund, E.; Hackbarth, C.; Heidecke, C.-D.; Partecke, L.-I.; Bekeschus, S. A myeloid and lymphoid infiltrate in murine pancreatic tumors exposed to plasma-treated medium. Clin. Plasma Med. 2018, 11, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miebach, L.; Berner, J.; Bekeschus, S. In ovo model in cancer research and tumor immunology. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1006064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeschus, S.; Freund, E.; Spadola, C.; Privat-Maldonado, A.; Hackbarth, C.; Bogaerts, A.; Schmidt, A.; Wende, K.; Weltmann, K.D.; von Woedtke, T.; et al. Risk Assessment of kINPen Plasma Treatment of Four Human Pancreatic Cancer Cell Lines with Respect to Metastasis. Cancers 2019, 11, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, C.; Pan, H.; Godwin, J.; Gray, R.; Arriagada, R.; Raina, V.; Abraham, M.; Medeiros Alencar, V.H.; Badran, A.; Bonfill, X.; et al. Long-term effects of continuing adjuvant tamoxifen to 10 years versus stopping at 5 years after diagnosis of oestrogen receptor-positive breast cancer: ATLAS, a randomised trial. Lancet 2013, 381, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis Phillips, G.D.; Li, G.; Dugger, D.L.; Crocker, L.M.; Parsons, K.L.; Mai, E.; Blattler, W.A.; Lambert, J.M.; Chari, R.V.; Lutz, R.J.; et al. Targeting HER2-positive breast cancer with trastuzumab-DM1, an antibody-cytotoxic drug conjugate. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 9280–9290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peart, O. Metastatic Breast Cancer. Radiol. Technol. 2017, 88, 519M–539M. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burguin, A.; Diorio, C.; Durocher, F. Breast Cancer Treatments: Updates and New Challenges. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Kiani, M.F.; Wang, B. Classification, Treatment Strategy, and Associated Drug Resistance in Breast Cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 2016, 16, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolberg, H.C.; Hoffmann, O.; Baumann, R. The Abscopal Effect: Could a Phenomenon Described Decades Ago Become Key to Enhancing the Response to Immune Therapies in Breast Cancer? Breast Care 2020, 15, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Obenchain, R.; Wen, D.; Li, H.; Wirz, R.E.; Gu, Z. Portable air-fed cold atmospheric plasma device for postsurgical cancer treatment. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg5686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Xu, X.; Zhang, S.; Cai, D.; Dai, X. Cold atmospheric plasma conveys selectivity on triple negative breast cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 124, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, S.R.K.; Cheng, X.; Zhuang, T.; Ly, L.; Jones, O.; Basadonna, G.; Keidar, M.; Canady, J. BCL2A1 regulates Canady Helios Cold Plasma-induced cell death in triple-negative breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, L.; Cheng, X.; Murthy, S.R.K.; Zhuang, T.; Jones, O.Z.; Basadonna, G.; Keidar, M.; Canady, J. Canady cold plasma conversion system treatment: An effective inhibitor of cell viability in breast cancer molecular subtypes. Clin. Plasma Med. 2020, 19–20, 100109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, H.; Ji, H.W.; Kim, H.W.; Yun, S.H.; Choi, E.H.; Kim, S.J. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Restores Paclitaxel Sensitivity to Paclitaxel-Resistant Breast Cancer Cells by Reversing Expression of Resistance-Related Genes. Cancers 2019, 11, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayarangan, V.; Delalande, A.; Dozias, S.; Pouvesle, J.M.; Robert, E.; Pichon, C. New insights on molecular internalization and drug delivery following plasma jet exposures. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 589, 119874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Attri, P.; Choi, E.H.; Uhm, H.S. Influence of water vapour with non-thermal plasma jet on the apoptosis of SK-BR-3 breast cancer cells. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 14670–14677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejonckheere, C.S.; Layer, J.P.; Nour, Y.; Layer, K.; Glasmacher, A.; Wiegreffe, S.; Fuhrmann, A.; Caglayan, L.; Grau, F.; Sarria, G.R.; et al. Non-invasive physical plasma for preventing radiation dermatitis in breast cancer: Results from an intrapatient-randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 44, 100699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, Z.; Saadati, F.; Mahdikia, H.; Freund, E.; Abbasvandi, F.; Shokri, B.; Zali, H.; Bekeschus, S. Antitumor Effects in Gas Plasma-Treated Patient-Derived Microtissues—An Adjuvant Therapy for Ulcerating Breast Cancer? Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadati, F.; Jahanbakhshi, F.; Mahdikia, H.; Abbasvandi, F.; Ghomi, H.; Yazdani, N.; Aghazadeh, K.; Emmert, S.; Bekeschus, S. Cold Physical Plasma Toxicity in Breast and Oral Squamous Carcinoma In Vitro and in Patient-Derived Cancer Tissue Ex Vivo. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A.A.; Shabir, U.; Mahmood, A.W.; Harrington, G.; Khan, M.; Ahmad, A.; Howlader, M.; Colan, N.; Shah, A.A.; Ghadersohi, S.; et al. The impact of NCCN-compliant multidisciplinary conference on the uptake of active surveillance among eligible patients with localized prostate cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2023, 41, 483.e21–483.e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malcolm, J.B.; Fabrizio, M.D.; Barone, B.B.; Given, R.W.; Lance, R.S.; Lynch, D.F.; Davis, J.W.; Shaves, M.E.; Schellhammer, P.F. Quality of life after open or robotic prostatectomy, cryoablation or brachytherapy for localized prostate cancer. J. Urol. 2010, 183, 1822–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, M.H.; Frost, M.; Abrahamsen, B.; Gerke, O.; Walter, S.; Lund, L. Osteoporosis and prostate cancer; a 24-month prospective observational study during androgen deprivation therapy. Scand. J. Urol. 2019, 53, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirst, A.M.; Simms, M.S.; Mann, V.M.; Maitland, N.J.; O’Connell, D.; Frame, F.M. Low-temperature plasma treatment induces DNA damage leading to necrotic cell death in primary prostate epithelial cells. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1536–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fofana, M.; Buñay, J.; Judée, F.; Baron, S.; Menecier, S.; Nivoix, M.; Perisse, F.; Vacavant, A.; Balandraud, X. Selective treatments of prostate tumor cells with a cold atmospheric plasma jet. Clin. Plasma Med. 2020, 17–18, 100098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, D.; Cai, D.; Ning, M.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Han, P.; Dai, X. Cold atmospheric plasma selectively induces G(0)/G(1) cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in AR-independent prostate cancer cells. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 5977–5986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirst, A.M.; Frame, F.M.; Maitland, N.J.; O’Connell, D. Low temperature plasma: A novel focal therapy for localized prostate cancer? BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 878319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamoun, A.; de Reynies, A.; Allory, Y.; Sjodahl, G.; Robertson, A.G.; Seiler, R.; Hoadley, K.A.; Groeneveld, C.S.; Al-Ahmadie, H.; Choi, W.; et al. A Consensus Molecular Classification of Muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2020, 77, 420–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witjes, J.A.; Bruins, H.M.; Cathomas, R.; Comperat, E.M.; Cowan, N.C.; Gakis, G.; Hernandez, V.; Linares Espinos, E.; Lorch, A.; Neuzillet, Y.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Muscle-invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer: Summary of the 2020 Guidelines. Eur. Urol. 2021, 79, 82–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, E.M.; Belay, S.; Li, W.; Aragon-Ching, J.B. Non-urothelial and urothelial variants of bladder cancer. Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2022, 33, 100661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelbrich, N.; Miebach, L.; Berner, J.; Freund, E.; Saadati, F.; Schmidt, A.; Stope, M.; Zimmermann, U.; Burchardt, M.; Bekeschus, S. Medical gas plasma augments bladder cancer cell toxicity in preclinical models and patient-derived tumor tissues. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 47, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, A.; Joh, H.M.; Bae, J.H.; Kim, S.J.; Chung, J.W.; Chung, T.H. Plasma-Activated Media Produced by a Microwave-Excited Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet Is Effective against Cisplatin-Resistant Human Bladder Cancer Cells In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuhara, H.; Szili, E.J.; Oh, J.-S.; Chiaki, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Kurabayashi, A.; Furihata, M.; Tsuda, M.; Furuta, H.; Lindsay, H.D.; et al. Oxidative Stress Pathways Linked to Apoptosis Induction by Low-Temperature Plasma Jet Activated Media in Bladder Cancer Cells: An In Vitro and In Vivo Study. Plasma 2022, 5, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares-da-Silva, E.; Pereira, E.; Pires, A.S.; Neves, A.R.; Braz-Guilherme, C.; Marques, I.A.; Abrantes, A.M.; Goncalves, A.C.; Caramelo, F.; Silva-Teixeira, R.; et al. Cold Atmospheric Plasma, a Novel Approach against Bladder Cancer, with Higher Sensitivity for the High-Grade Cell Line. Biol. 2021, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Zhou, R.; Thomas, P.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, R.; Mandal, S.; Jolly, M.K.; Richard, D.J.; Rehm, B.H.A.; Ostrikov, K.K.; et al. Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition Enhances Cancer Cell Sensitivity to Cytotoxic Effects of Cold Atmospheric Plasmas in Breast and Bladder Cancer Systems. Cancers 2021, 13, 2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Guo, B.; Chen, H.; Xu, D.; Kong, M.G. The Antitumor Effects of Plasma-Activated Saline on Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Cells In Vitro and In Vivo Demonstrate Its Feasibility as a Potential Therapeutic Approach. Cancers 2021, 13, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, J.; Nishime, T.M.C.; Bansemer, R.; Balazinski, M.; Wende, K.; Weltmann, K.D. Enhanced atmospheric pressure plasma jet setup for endoscopic applications. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2019, 52, 024005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gweon, B.; Kim, M.; Kim, D.B.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.; Jung, H.; Shin, J.H.; Choe, W. Differential responses of human liver cancer and normal cells to atmospheric pressure plasma. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 063701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolkova, B.; Lunova, M.; Lynnyk, A.; Uzhytchak, M.; Churpita, O.; Jirsa, M.; Kubinova, S.; Lunov, O.; Dejneka, A. Non-Thermal Plasma, as a New Physicochemical Source, to Induce Redox Imbalance and Subsequent Cell Death in Liver Cancer Cell Lines. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 52, 119–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Lu, X.; He, G. The selective effect of plasma activated medium in an in vitro co-culture of liver cancer and normal cells. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 121, 013302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaquero, J.; Judee, F.; Vallette, M.; Decauchy, H.; Arbelaiz, A.; Aoudjehane, L.; Scatton, O.; Gonzalez-Sanchez, E.; Merabtene, F.; Augustin, J.; et al. Cold-Atmospheric Plasma Induces Tumor Cell Death in Preclinical In Vivo and In Vitro Models of Human Cholangiocarcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lu, R.; Xian, Y.; Gan, L.; Lu, X.; Yang, X. Effects of atmospheric pressure cold plasma on human hepatocarcinoma cell and its 5-fluorouracil resistant cell line. Phys. Plasmas 2015, 22, 122006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decauchy, H.; Pavy, A.; Camus, M.; Fouassier, L.; Dufour, T. Cold plasma endoscopy applied to biliary ducts: Feasibility risk assessment on human-like and porcine models for the treatment of cholangiocarcinoma. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2022, 55, 455401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzulli, M.; Brandi, N.; Pecorelli, A.; Pastore, L.V.; Granito, A.; Martinese, G.; Tovoli, F.; Simonetti, M.; Dajti, E.; Colecchia, A.; et al. Segmental Distribution of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Cirrhotic Livers. Diagn. 2022, 12, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barekzi, N.; Laroussi, M. Dose-dependent killing of leukemia cells by low-temperature plasma. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 422002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundscherer, L.; Wende, K.; Ottmuller, K.; Barton, A.; Schmidt, A.; Bekeschus, S.; Hasse, S.; Weltmann, K.D.; Masur, K.; Lindequist, U. Impact of non-thermal plasma treatment on MAPK signaling pathways of human immune cell lines. Immunobiology 2013, 218, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, H.X.; Xue, Z.X.; Yin, H.J.; Niu, Q.; Chen, H.L. The relation between doses or post-plasma time points and apoptosis of leukemia cells induced by dielectric barrier discharge plasma. AIP Adv. 2015, 5, 127220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaser, S.A.; Ahmed, M.M.; El-Aragi, G.M.; Elhadry, A.A.; Said, Z.S. Cytogenetic and Biochemical Investigations of Cultured Leukemia Cells Exposed to Gliding Arc Discharges. Plasma Med. 2017, 7, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xu, D.; Ning, N.; Xu, Y.; Wang, B.; Cui, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, D.; Chen, H.; Kong, M.G. Effect of cold atmospheric plasma treatment on the metabolites of human leukemia cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.M.; El-Aragi, G.M.; Elhadary, A.M.A.; Said, Z.S. Promising Trial for Treatment of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Using Plasma Technology. Plasma Med. 2013, 3, 243–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Turrini, E.; Laurita, R.; Stancampiano, A.; Catanzaro, E.; Calcabrini, C.; Maffei, F.; Gherardi, M.; Colombo, V.; Fimognari, C. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Induces Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress Pathway Regulation in T-Lymphoblastoid Leukemia Cells. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 4271065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golpour, M.; Alimohammadi, M.; Mohseni, A.; Zaboli, E.; Sohbatzadeh, F.; Bekeschus, S.; Rafiei, A. Lack of Adverse Effects of Cold Physical Plasma-Treated Blood from Leukemia Patients: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeschus, S.; Schmidt, A.; Bethge, L.; Masur, K.; von Woedtke, T.; Hasse, S.; Wende, K. Redox Stimulation of Human THP-1 Monocytes in Response to Cold Physical Plasma. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 5910695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Rödder, K.; Hasse, S.; Masur, K.; Toups, L.; Lillig, C.H.; von Woedtke, T.; Wende, K.; Bekeschus, S. Redox-regulation of activator protein 1 family members in blood cancer cell lines exposed to cold physical plasma-treated medium. Plasma Process Polym. 2016, 13, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Xu, D.; Liu, Z.; Huang, C. Aberrant Expressional Profiling of Small RNA by Cold Atmospheric Plasma Treatment in Human Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Cells. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 809658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, T.N.; Schreiber, R.D. Neoantigens in cancer immunotherapy. Science 2015, 348, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeschus, S.; Seebauer, C.; Wende, K.; Schmidt, A. Physical plasma and leukocytes—Immune or reactive? Biol. Chem. 2018, 400, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeschus, S.; Kolata, J.; Muller, A.; Kramer, A.; Weltmann, K.-D.; Broker, B.; Masur, K. Differential Viability of Eight Human Blood Mononuclear Cell Subpopulations After Plasma Treatment. Plasma Med. 2013, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundscherer, L.; Bekeschus, S.; Tresp, H.; Hasse, S.; Reuter, S.; Weltmann, K.-D.; Lindequist, U.; Masur, K. Viability of Human Blood Leukocytes Compared with Their Respective Cell Lines after Plasma Treatment. Plasma Med. 2013, 3, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeschus, S.; Liebelt, G.; Menz, J.; Berner, J.; Sagwal, S.K.; Wende, K.; Weltmann, K.D.; Boeckmann, L.; von Woedtke, T.; Metelmann, H.R.; et al. Tumor cell metabolism correlates with resistance to gas plasma treatment: The evaluation of three dogmas. Free Radic. Bio Med. 2021, 167, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeschus, S.; Winterbourn, C.C.; Kolata, J.; Masur, K.; Hasse, S.; Broker, B.M.; Parker, H.A. Neutrophil extracellular trap formation is elicited in response to cold physical plasma. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 100, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeschus, S.; Poschkamp, B.; van der Linde, J. Medical gas plasma promotes blood coagulation via platelet activation. Biomaterials 2021, 278, 120433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.; Biscop, E.; Breen, C.; Butler, S.J.; Smits, E.; Bogaerts, A.; Jakovljevic, V. Critical Evaluation of the Interaction of Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species with Blood to Inform the Clinical Translation of Nonthermal Plasma Therapy. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striesow, J.; Wesche, J.; McKitterick, N.; Busch, L.M.; von Woedtke, T.; Greinacher, A.; Bekeschus, S.; Wende, K. Gas plasma-induced platelet activation corresponds to reactive species profiles and lipid oxidation. Free Radic. Bio Med. 2023, 207, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeschus, S.; Brüggemeier, J.; Hackbarth, C.; von Woedtke, T.; Partecke, L.-I.; van der Linde, J. Platelets are key in cold physical plasma-facilitated blood coagulation in mice. Clin. Plasma Med. 2017, 7–8, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeschus, S.; Brüggemeier, J.; Hackbarth, C.; Weltmann, K.-D.; von Woedtke, T.; Partecke, L.-I.; van der Linde, J. The feed gas composition determines the degree of physical plasma-induced platelet activation for blood coagulation. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2018, 27, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miebach, L.; Poschkamp, B.; van der Linde, J.; Bekeschus, S. Medical Gas Plasma-A Potent ROS-Generating Technology for Managing Intraoperative Bleeding Complications. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletto, S.; Novo, M.; Paruzzo, L.; Frascione, P.M.M.; Vitolo, U. Treatment strategies for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2022, 110, 102443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldfinger, M.; Cooper, D.L. Refractory DLBCL: Challenges and Treatment. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2022, 22, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peroja, P.; Haapasaari, K.M.; Mannisto, S.; Miinalainen, I.; Koivunen, P.; Leppa, S.; Karjalainen-Lindsberg, M.L.; Kuusisto, M.E.; Turpeenniemi-Hujanen, T.; Kuittinen, O.; et al. Total peroxiredoxin expression is associated with survival in patients with follicular lymphoma. Virchows Arch. 2016, 468, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, Y.; Miwa, H.; Ohno, T.; Haneda, M.; Hosokawa, Y.; Nitta, M.; Daibata, M. The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species In Apoptosis Induction of Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL); Inhibition of NADPH Oxidase 2 Induces Apoptosis In MCL. Blood 2010, 116, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Thompson, M.A.; Tamayo, A.T.; Zuo, Z.; Lee, J.; Vega, F.; Ford, R.J.; Pham, L.V. Over-expression of Thioredoxin-1 mediates growth, survival, and chemoresistance and is a druggable target in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncotarget 2012, 3, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinowaki, Y.; Kurata, M.; Ishibashi, S.; Ikeda, M.; Tatsuzawa, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Miura, O.; Kitagawa, M.; Yamamoto, K. Glutathione peroxidase 4 overexpression inhibits ROS-induced cell death in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Lab. Investig. 2018, 98, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeill, K.A. Epidemiology of Brain Tumors. Neurol. Clin. 2016, 34, 981–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, M.; Wick, W.; Aldape, K.; Brada, M.; Berger, M.; Pfister, S.M.; Nishikawa, R.; Rosenthal, M.; Wen, P.Y.; Stupp, R.; et al. Glioma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stummer, W.; van den Bent, M.J.; Westphal, M. Cytoreductive surgery of glioblastoma as the key to successful adjuvant therapies: New arguments in an old discussion. Acta Neurochir. 2011, 153, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, T. Understanding high grade glioma: Molecular mechanism, therapy and comprehensive management. Cancer Lett. 2013, 331, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Bent, M.J.; Carpentier, A.F.; Brandes, A.A.; Sanson, M.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Bernsen, H.J.; Frenay, M.; Tijssen, C.C.; Grisold, W.; Sipos, L.; et al. Adjuvant procarbazine, lomustine, and vincristine improves progression-free survival but not overall survival in newly diagnosed anaplastic oligodendrogliomas and oligoastrocytomas: A randomized European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer phase III trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 2715–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, N.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Han, Y.G.; Choi, E.H. Effect of jet plasma on T98G human brain cancer cells. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2013, 13, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, S.; Bien-Moller, S.; Marx, S.; Bekeschus, S.; Schroeder, H.W.S.; Mustea, A.; Stope, M.B. Devitalization of Glioblastoma Cancer Cells by Non-invasive Physical Plasma: Modulation of Proliferative Signalling Cascades. Anticancer Res. 2023, 43, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.Q.; Sherman, J.; Murphy, W.; Ratovitski, E.; Canady, J.; Keidar, M. The Effect of Tuning Cold Plasma Composition on Glioblastoma Cell Viability. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanigasekara, J.; Barcia, C.; Cullen, P.J.; Tiwari, B.; Curtin, J.F. Plasma induced reactive oxygen species-dependent cytotoxicity in glioblastoma 3D tumourspheres. Plasma Process Polym. 2022, 19, 2100157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Yuan, Q.; Chen, C.; Liu, G.; Zhong, Z.; Zhu, K.; Guo, J. Nanosecond pulsed cold atmospheric plasma jet suppresses proliferation and migration of human glioblastoma cells via apoptosis promotion and EMT inhibition. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2023, 747, 109757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Lin, L.; Soni, V.; Gjika, E.; Sherman, J.H.; Yan, D.; Keidar, M. Sensitization of glioblastoma cells to temozolomide by a helium gas discharge tube. Phys. Plasmas 2020, 27, 114502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.Q.; Murphy, W.; Recek, N.; Yan, D.Y.; Cvelbar, U.; Vesel, A.; Mozetic, M.; Canady, J.; Keidar, M.; Sherman, J.H. Synergistic effect of gold nanoparticles and cold plasma on glioblastoma cancer therapy. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2014, 47, 335402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolotukhin, D.B.; Horkowitz, A.; Keidar, M. Electromagnetic Nature of Distant Interaction of the Atmospheric Pressure Helium Plasma Discharge Tube with Glioblastoma Cancer Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 13597–13610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekeschus, S.; Ispirjan, M.; Freund, E.; Kinnen, F.; Moritz, J.; Saadati, F.; Eckroth, J.; Singer, D.; Stope, M.B.; Wende, K.; et al. Gas Plasma Exposure of Glioblastoma Is Cytotoxic and Immunomodulatory in Patient-Derived GBM Tissue. Cancers 2022, 14, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekeschus, S.; Roessler, K.; Kepp, O.; Freund, E. Gas Plasma Technology and Immunogenic Cell Death: Implications for Chordoma Treatment. Cancers 2025, 17, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, T.P.; Greenlee, M.H.W.; Kanthasamy, A.G.; Hsu, W.H. Mechanism of intranasal drug delivery directly to the brain. Life Sci. 2018, 195, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, G.E.; He, Z.; Hutanu, A.L.; Cribaro, G.P.; Manaloto, E.; Casey, A.; Traynor, D.; Milosavljevic, V.; Howe, O.; Barcia, C.; et al. Cold Atmospheric Plasma induces accumulation of lysosomes and caspase-independent cell death in U373MG glioblastoma multiforme cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawada, K.; Kawano, T.; Momma, K.; Fujiwara, J.; Nagal, K.; Nishikage, T.; Nakajima, Y.; Ogiya, K.; Tanaka, K.; Haruki, S.; et al. New argon plasma coagulation method for superficial esophageal carcinomas: Argon plasma coagulation-subepithelial ablation. Dig. Endosc. 2007, 19, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estarabadi, H.; Atyabi, S.A.; Tavakkoli, S.; Noormohammadi, Z.; Gholami, M.R.; Ghiaseddin, A.; Irani, S. Cold atmospheric plasma induced genotoxicity and cytotoxicity in esophageal cancer cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 1323–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Ye, X.; Wang, R.; Poon, K. Current research progress in the role of reactive oxygen species in esophageal adenocarcinoma. Transl. Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 1568–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhou, T.; Wang, S.; Bahetjan, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, X. Dehydrocostus lactone inhibits the proliferation of esophageal cancer cells in vivo and in vitro through ROS-mediated apoptosis and autophagy. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 170, 113453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berner, J.; Miebach, L.; Kordt, M.; Seebauer, C.; Schmidt, A.; Lalk, M.; Vollmar, B.; Metelmann, H.R.; Bekeschus, S. Chronic oxidative stress adaptation in head and neck cancer cells generates slow-cyclers with decreased tumour growth in vivo. Br. J. Cancer 2023, 129, 869–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hu, F.; Wu, M.; Tian, L.; Gong, F.; Zhong, X.; Chen, M.; Liu, Z.; Liu, B. Bioorthogonal Coordination Polymer Nanoparticles with Aggregation-Induced Emission for Deep Tumor-Penetrating Radio- and Radiodynamic Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2007888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.; Kim, J.H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Yoon, S.A.; Shin, J.; Sharma, A.; Lee, M.H.; Cheng, L.; Wu, J.; et al. Multifunctional sonosensitizers in sonodynamic cancer therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 3244–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, T.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Cheng, L.; Feng, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Han, G.; Liu, Z. Platinum Nanoparticles to Enable Electrodynamic Therapy for Effective Cancer Treatment. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1806803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Li, H.; Bu, W. A Forward Vision for Chemodynamic Therapy: Issues and Opportunities. Angew. Chem. 2023, 62, e202210415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Lu, X.; He, G. On the penetration depth of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species generated by a plasma jet through real biological tissue. Phys. Plasmas 2017, 24, 073506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Kuroeda, G.; Sei, R.; Yamaguchi, M.; Yoshinaga, R.; Yamashita, R.; Tasaki, H.; Koga, K.; Shiratani, M. Transportation of reactive oxygen species in a tissue phantom after plasma irradiation. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 57, 01AG01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striesow, J.; Nasri, Z.; von Woedtke, T.; Bekeschus, S.; Wende, K. Epilipidomics reveals lipid fatty acid and headgroup modification in gas plasma-oxidized biomembranes. Redox Biol. 2024, 77, 103343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusupov, M.; Wende, K.; Kupsch, S.; Neyts, E.C.; Reuter, S.; Bogaerts, A. Effect of head group and lipid tail oxidation in the cell membrane revealed through integrated simulations and experiments. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbanev, Y.; O’Connell, D.; Chechik, V. Non-Thermal Plasma in Contact with Water: The Origin of Species. Chemistry 2016, 22, 3496–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).