Abstract
Lung cancer (LC) constitutes an important cause of death among patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). Both diseases may share pathobiological mechanisms related to oxidative damage and cellular senescence. In this study, the potential value of leucocyte telomere length, a hallmark of aging, and 8-OHdG concentrations, indicative of oxidative DNA damage, as risk biomarkers of LC was evaluated in COPD patients three years prior to LC diagnosis. Relative telomere length measured using qPCR and serum levels of 8-OHdG were determined at the baseline in 99 COPD smokers (33 with LC and 66 age-matched COPD without LC as controls). Of these, 21 COPD with LC and 42 controls had the biomarkers measured 3 years before. Single nucleotide variants (SNVs) in TERT, RTEL, and NAF1 genes were also determined. COPD cases were evaluated, which showed greater telomere length (p < 0.001) and increased serum 8-OHdG levels (p = 0.004) three years prior to LC diagnosis compared to the controls. This relationship was confirmed at the time of LC diagnosis. No significant association was found between the studied SNVs in cases vs. controls. In conclusion, this preliminary study shows that longer leucocyte telomere length and increased 8-OHdG serum levels can be useful as early biomarkers of the risk for future lung cancer development among COPD patients.
1. Introduction
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and lung cancer (LC) are major public health problems, being the third- and fifth-leading causes of death worldwide [1]. Both diseases are thought to result from an interaction between the genome and the surrounding environment [2]. There is significant evidence that an enhanced inflammatory response due to noxious particles and gases contributes to the frequent association between COPD and LC [3]. Tobacco exposure is the most common risk factor for COPD and LC, with lung cancer incidence being 2–5 times that of smokers without COPD [3,4]. LC also constitutes an important cause of death among patients with COPD [5]. This suggests that both diseases may share mechanisms, with oxidative stress playing a central pathobiological role [2,6]. Oxidative stress leads to DNA damage and impairs an adequate repair process, leading to cellular senescence [7]. This suggests that changes in oxidative stress and senescence markers could help to define the pathobiological processes at an earlier stage of LC development.
Telomere shortening is frequently used as a biomarker of cellular senescence. The main function of telomeres is to protect chromosomes from end-to-end fusions, misrepair, and degradation [8]. Telomeres shorten with each cell division until they reach a critically short length when they trigger apoptosis or cellular senescence [9]. Contradictory results relate telomere length and LC in studies that measured telomere length at the time of LC diagnosis; some studies found shorter telomeres in relation to LC [10,11], while others have reported longer telomeres [12,13,14]. However, few studies have evaluated the relationship between telomere length and LC risk before diagnosis. Doherty et al. found that short telomere length was associated with an increased risk of death from cancer [11], while Shen et al. reported longer telomeres in relation to LC risk in the peripheral white blood cells of male smokers [12]. No study has investigated the dynamic change of telomere length over time in relation to LC development among patients with COPD.
Telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) encodes the catalytic subunit of telomerase, an enzyme that maintains telomere ends while acting with an RNA component (TERC) in the process of adding telomeric nucleotide repeats (TTAGGG). Telomerase expression is higher in progenitor and cancer cells in contrast with the absent or low levels found in normal somatic cells [15]. Multiple genetic and epigenetic mechanisms are proposed to be involved in the telomerase reactivation that occurs in relation to oncogenesis [16]. RTEL1 (Regulator of Telomere Length 1) is an essential helicase required for telomere integrity; it has multiple roles in the control and maintenance of telomere length and sites of mitotic DNA damage, being involved in the repair of DSBs (double strands breaks). It was also reported to have a tumor-suppressive function [17]. Nuclear assembly factor 1 (NAF1) is another key factor in telomerase biogenesis [15].
A few single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) in TERT, RTEL1, and NAF1 genes are reported to associate with long telomeres [18,19], suggesting that they may be associated with an increased risk of cancer, as shown for rs2736100 in the TERT gene that is associated with an increased risk of adenocarcinoma [19].
On the other hand, other markers related to oxidative damage could help characterize this scenario. Aoshiba et al. (2012) suggested that the DNA damage caused by long-term smoking accumulates over the years before COPD and lung cancer develop [20]. Oxidative stress may damage DNA in different forms, as is the case for the change of genomic bases to species like 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG), which leads to DNA hypomethylation and subsequent genomic instability [21]. In this line, higher concentrations of 8-OHdG were reported in the lung tissue and peripheral blood mononuclear cells of COPD smokers [22]. Although increased levels of 8-OHdG are associated with cancers such as hepatocellular carcinoma, breast cancer, colorectal cancer, and prostate cancer [23], there are still controversies regarding this marker. To our knowledge, 8-OHdG as a potential non-invasive biomarker of LC risk in COPD patients, before LC diagnosis, has not been explored.
We hypothesized that leucocyte telomere length and serum levels of 8-OHdG could be risk markers of LC in smoker patients with COPD. We prospectively evaluated the potential value of these markers in COPD patients three years prior to LC diagnosis compared to COPD smokers without LC during the same observation period, with the latter group serving as controls. Secondary single nucleotide polymorphisms in the TERT, RTEL1, and NAF1 genes were analyzed in relation to telomere length.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
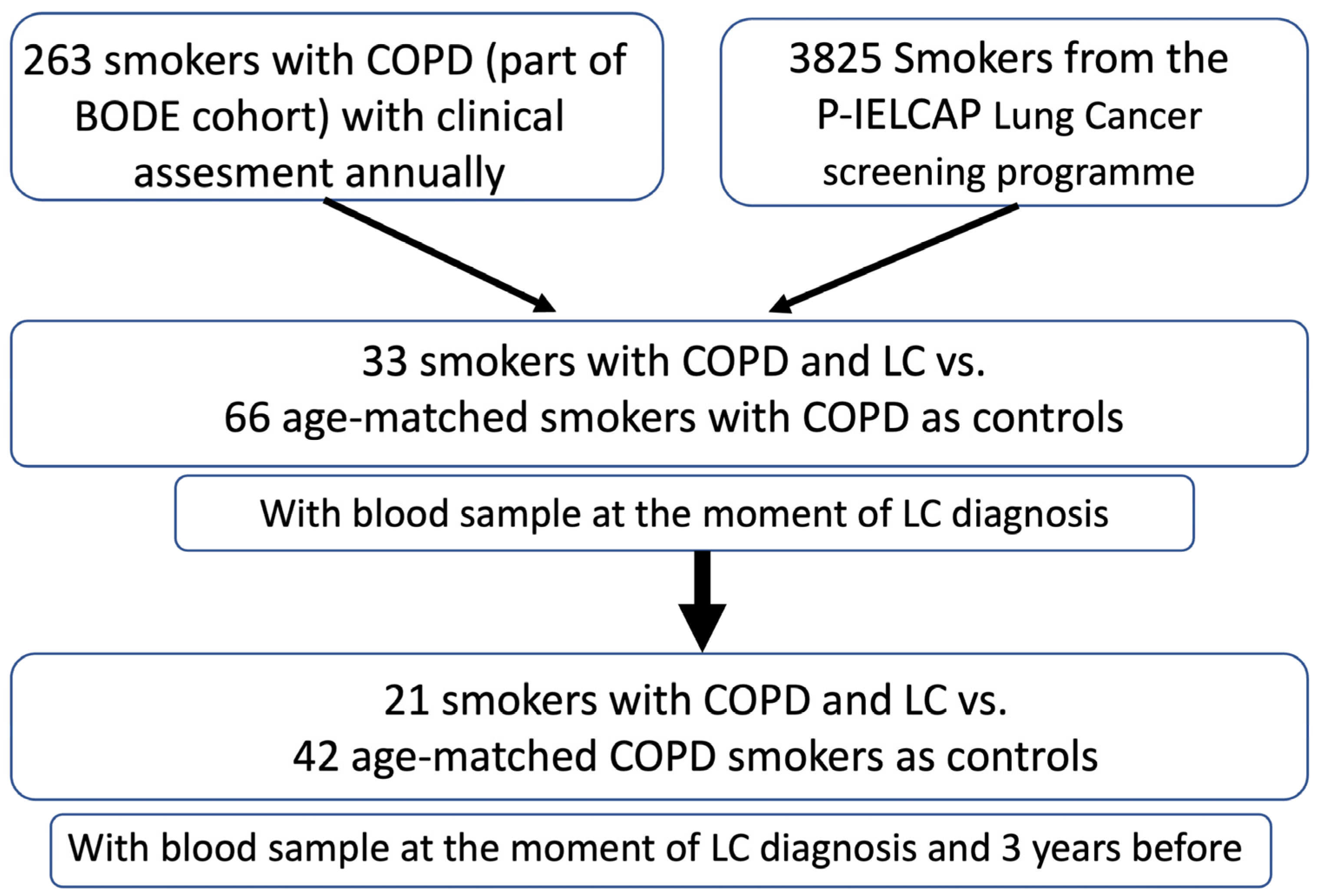
A total of 263 smokers with a COPD diagnosis were included in this study. The participants belonged to two cohorts: 1—patients screened at the Hospital Universitario La Candelaria, Tenerife, Spain (Tenerife-cohort), part of the BODE cohort, with an annual follow-up as detailed previously [24]; and 2—patients screened at the P-IELCAP, Pamplona-International early-detection program (3825 individuals) [25]. Of these patients, 33 developed LC during the mean 72 months of follow-up and were enrolled in the study (13 in Tenerife and 20 in the Pamplona cohort). Of these patients, 21 had blood samples obtained at two time points—at LC diagnosis and 3 years before. The latter time point was set up to coincide with sampling and as a point close to the time of diagnosis but early enough to anticipate the development and progression of cancer. As controls, we included 66 COPD patients who did not develop LC during the follow-up period and who were age- and gender-matched with cases (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Consort diagram illustrating the selection and assessment of patients and controls included in this study.
Briefly, patient inclusion criteria were age, >40 years; smoking history, >15 pack-years; and post-bronchodilator FEV1/FVC ratio, <0.70. Patients were clinically stable for at least 6 weeks at the time of evaluation. Pulmonary function, measured according to ATS-ERS guidelines [26,27], dyspnea [28], the BODE Index [29], and the Charlson Index [30], was measured annually. All-cause mortality was recorded. Patients received inhaled respiratory therapy as recommended by the international guidelines [26,27]. The presence of emphysema at the baseline was determined using criteria established by the Fleischner Society [31]. Patients were excluded from the study if they had uncontrolled co-morbidities such as malignancy at the baseline, asthma, pulmonary fibrosis, or pulmonary diseases other than COPD.
The study was approved by the institutional review board of HUNSC (PI14/12). All participants provided written informed consent.
2.2. Telomere Length Measurement
DNA was extracted from whole blood using the QIAamp DNA Mini Kit (GE Healthcare, Chicago, IL, USA). Telomere length and albumin (reference gene) were measured in triplicate in each sample using a qPCR-based protocol as described previously [32]. Two control DNA samples were assayed per run as a normalizing factor. Also, calibrator samples were assayed on each PCR plate to control for inter-plate and intra-plate coefficients of variance (CV).
Telomere length was calculated as a ratio of telomere to albumin. The T/S ratio for an experimental DNA sample is T (the number of nanograms of the standard DNA that matches the experimental sample for the copy number of the telomere template) divided by S (the number of nanograms of the standard DNA that matches the experimental sample for copy number of the albumin single-copy gene) [33]. T/S ratios were calculated using the “∆∆Cp with efficiency correction” method [34]. Conversion of the T/S ratio to base pair was calculated for every subject based on the equation y = 1114.58 + 10,373.13 × x of the correlation analysis, where x is the T/S ratio as previously determined [32].
2.3. Measurement of 8-Hydroxy-2′Deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) in Serum
Serum/plasma concentrations of 8-OHdG were determined using a commercial sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit—STA-320 OxiSelect™ Oxidative DNA Damage ELISA Kit (CellsBiolab, Inc. San Diego, CA, USA). Absorbance was read on a spectrophotometer (EnSpire Perkin Elmer, PerkinElmer, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) using 450 nm as the primary wavelength.
2.4. TERT, RTEL, and NAF SNV Genotyping
Genotyping was performed on genomic blood DNA samples obtained from the studied patients included in this study. The SNVs were assessed using Taqman® assays (TERT A__rs2736100_C, RTEL1 A___rs755017_G, and NAF1 A___rs7675998_G) (ThermoFisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) employing a Quant 5™ Real-Time PCR System (ThermoFisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). The SNVs were selected according to a review of the scientific literature regarding their influence on telomere length, the minor allele frequencies of the variants in European populations, and the availability of genotyping methodologies.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
For characterizing the sample, we used the following summary statistics: relative frequency of each category, 50th percentiles (5–95th), and non-scale normal and mean ± SD, as appropriate. The comparison between cases and controls was carried out using Pearson’s Chi-square, Mann–Whitney U, Wilcoxon, ANOVA, Fisher Exact, and Kruskal–Wallis tests. The correlations between variables were estimated using the Spearman or Pearson correlation tests. Relative telomere length (T/S) was inversely correlated with age, so all subsequent analyses were adjusted by this variable. The biomarker analysis was performed at two time points—at the point of LC diagnosis and 3 years before (median follow-up = 36 months).
Cases and controls were age- and gender-matched. Using the Cox multivariate analysis, the following covariates were included: smoking status (pack years), BMI, Kco, the Charlson Index, and the presence of emphysema (based on a visual score using CT scans). The sensitivity and specificity of relative telomere length (T/S) and 8-OHdG levels for distinguishing those patients who developed lung cancer early were determined by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. The associations between SNPs and clinical data were tested using unconditional logistic regression while adjusting for sex and pack years smoked. The Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium was tested for each of the SNPs using Fisher’s exact test. Haplotype blocks were constructed using Haploview v.4.1 [35] and SNPSTAT software (https://www.snpstats.net/start.htm) [36].
SPSS 26.0 IBM Co and R software (https://www.r-project.org/) were used for all statistical analyses, and two-tailed p-values < 0.05 were considered significant.
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Findings
The clinical characteristics of the 33 patients with COPD who developed LC, and the 66 controls with COPD and no cancer, are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Demographical and clinical characteristics at the baseline of COPD patients who developed lung cancer (LC) during follow-up monitoring and those who did not.
Patients had a mean age of 63 years, were mainly men (85%), and included heavy smokers, although the proportion of active smokers was slightly lower in the COPD patients who developed LC. Most of the COPD patients (90%) had moderate airway obstruction. Smokers with COPD and LC presented higher FEV1 and lower KCO values but a similar percentage of emphysema as visualized using CT scans than the COPD controls. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) was the primary LC histological subtype, as follows: 61% adenocarcinoma, 27% squamous carcinoma, 3% microcytic carcinoma, and two cases of undifferentiated carcinoma.
3.2. Changes over Time
The clinical characteristics of the 21 COPD patients who developed LC and the 42 who did not and had the biomarker measurements are shown in Table 2 and Table S1. For similar age and gender, patients who developed LC had higher FEV1 but slightly lower KCO values, with all other parameters being similar.

Table 2.
Demographical and clinical characteristics of smoking COPD patients that did and did not develop lung cancer (LC) during follow-up monitoring, three years before diagnosis.
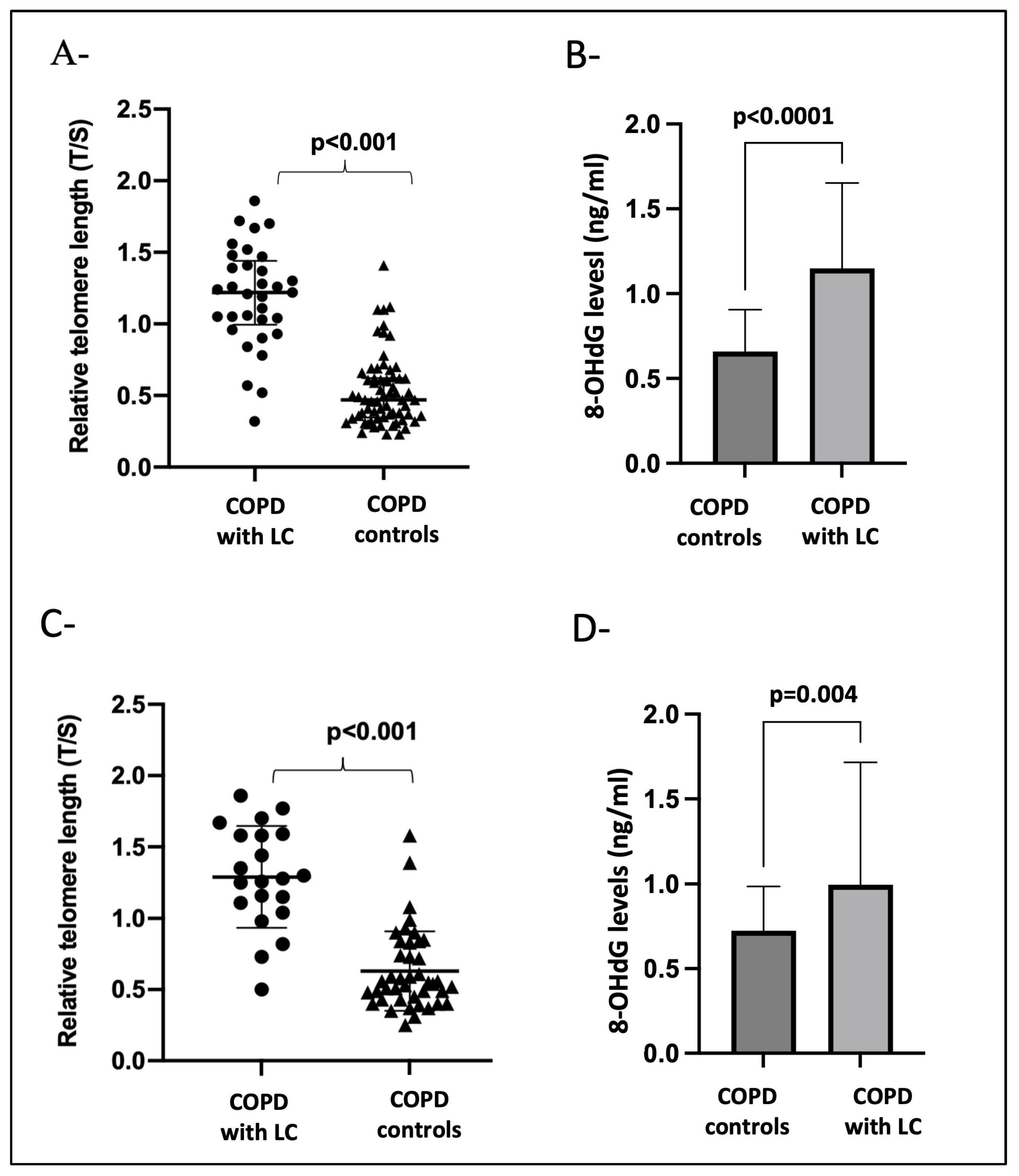
At the time of LC diagnosis and after adjusting for age, pack years of smoking, BMI, and emphysema (Figure 2A,B), the patients with COPD that developed LC had longer telomeres (p < 0.001) and increased 8-OHdG levels (p < 0.0001) compared with the COPD cases without LC. Importantly, longer telomere length (p < 0.001) and increased 8-OHdG levels (p = 0.004) could be detected three years before LC diagnosis when compared to the COPD controls who did not develop LC (Figure 2C,D).
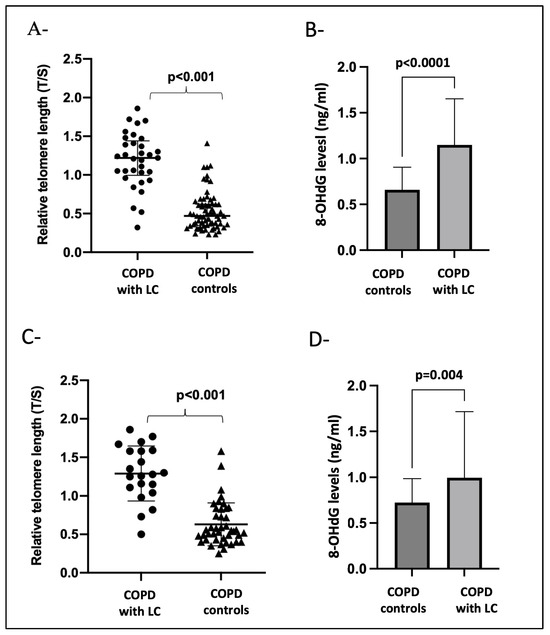
Figure 2.
Panels (A,B) show the biomarker differences between COPD-with-LC patients (n = 33) at the time of diagnosis and age- and gender-matched COPD controls (n = 66). (A) T/S, leukocyte relative telomere length; (B) 8-OHdG levels in serum. Panels (C,D) show the biomarker differences between COPD patients with LC (n = 21) three years before diagnosis versus COPD patients (n = 42) that did not develop LC during follow-up monitoring. (C) T/S, leukocyte relative telomere length; (D) 8-OHdG levels in serum. A p-value < 0.05 was considered significant.
An increased risk of developing LC in COPD patients was found in relation to telomere length (T/S) and 8-OHdG levels independently of smoking habit, BMI, or the presence of emphysema (Table 3). The combined effect of telomere length (T/S) and 8-OHdG levels did not significantly increase the risk.

Table 3.
Association between the studied biomarkers and lung cancer risk in smokers with COPD three years before LC diagnosis.
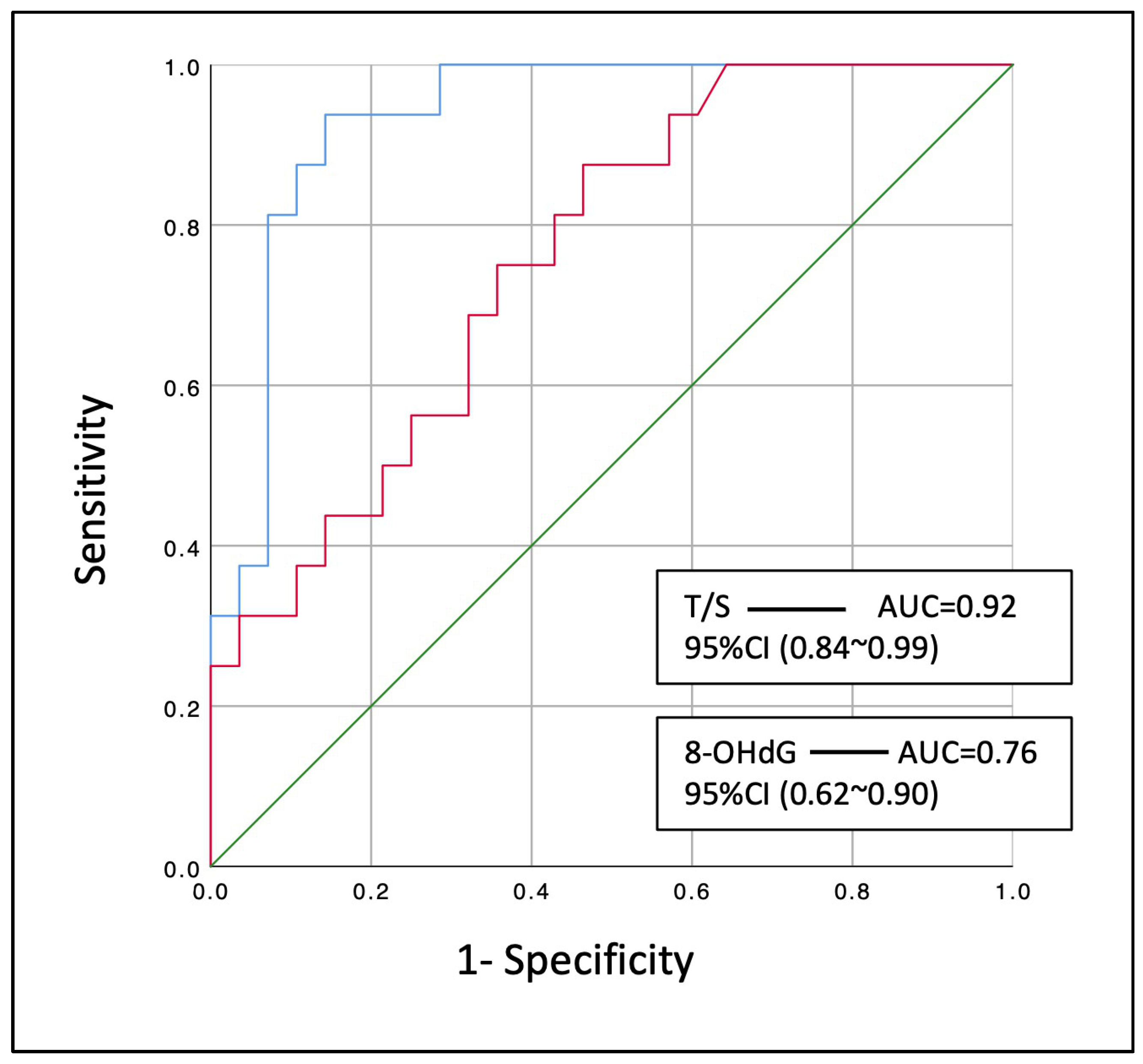
The sensitivity analysis revealed that relative telomere length (T/S) [AUC: 0.92 (95% CI: 0.84–0.99), p < 0.001] could significantly discriminate those smokers with COPD that developed LC within the next three years from the control smokers that did not (Figure 3). In the same way, the marker of oxidative DNA damage (8-OHdG) [AUC: 0.76 (95% CI: 0.62~0.90), p = 0.004] could modestly discriminate these patients from the COPD controls.
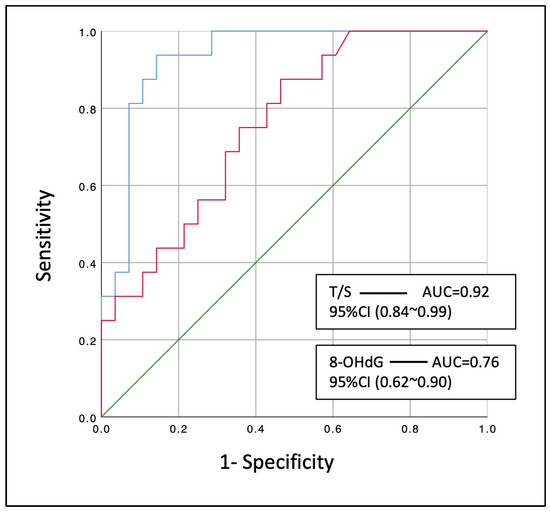
Figure 3.
Diagnostic performance of leucocyte relative telomere length (T/S) and serum 8-OHdG at discriminating smoking COPD patients that developed lung cancer within the next three years. Blue line: T/S, relative telomere length; Red line: 8-OHdG levels; AUC: area under the curve; 95% CI: 95% confidence interval.
3.3. TERT, RTEL1, and NAF1 Single Nucleotide Variants
The allele and genotype frequencies of TERT, RTEL1, and NAF1 SNVs are presented in Table 4. The genotypic frequencies of all gene single-nucleotide variants were accomplished with Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium. There were no significant differences in the genotype frequencies between the COPD-with-LC and COPD control groups (p > 0.05), even after correction for multiple comparisons. Global haplotypes (C-A-G; TERT–RTEL1-NAF1) did not differ in their frequency distribution between the analyzed groups (controls = 0.4223 vs. cases = 0.3125; p = 0.9).

Table 4.
Distribution of TERT, RTEL1, and NAF1 genetic variants in COPD patients with LC and COPD cases without LC as controls included in this study.
4. Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first prospective study exploring the relationships between leukocyte telomere length, serum/plasma concentrations of 8-OHdG, and LC risk in COPD patients 3 years prior to LC diagnosis. This preliminary study has several important findings: First, longer leucocyte telomeres were observed in COPD patients prior to the diagnosis of LC when compared to age-matched COPD patients who did not develop LC during the same period of observation. Second, increased levels of 8-OHdG were detected in the serum/plasma of the COPD patients who developed LC three years prior to diagnosis.
4.1. Telomere Length
In human somatic cells, telomeres progressively shorten at a rate of 50–200 bp with each cell division [37]. In previous studies, we found accelerated telomere shortening in COPD patients followed for 10 years (183 bp per year) compared to smoking controls of the same age and sex and without COPD [32].
In this study, we found that COPD patients who developed LC during follow-up monitoring had longer telomeres than individuals with COPD who did not. Telomeres are thought to be involved in the initiation and progression of cancers [38]. Telomerase activity can promote tumor development by ensuring the maintenance of telomere length above a critical short threshold to prevent senescence or apoptosis [39], although this may also increase the risk of acquiring genetic abnormalities. Telomerase is aberrantly expressed in more than 90% of human cancers [40]. In addition to this, there is another mechanism for telomere elongation, known as “alternative telomere lengthening” or ALT, which has been documented in 10–15% of cancers [41].
Many studies have reported an association between increased telomere length and the risk of various cancers, including melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, glioma, lymphoma, urogenital cancer, and lung cancer [42,43,44]. These results are supported by a genetic basis through studies, where certain gene variants modulate telomere length, with alleles segregating with long telomeres associated with the increased risk of different diseases. This is the case for SNVs near the TERT, RTEL1, and NAF1 genes, which show differential effects on telomere length. For these SNVs, one of the alleles that promotes short telomeres strongly associates with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, while the other long-telomere alleles associate with LC [44]. However, none of the studied alleles at these variants are significantly associated with lung cancer, at least in the studied COPD cohort. Further studies regarding genetics and epigenetic mechanisms are needed to elucidate these findings. In our study, longer telomeres maintained their length for years in individuals with COPD who developed LC during follow-up monitoring. Our results are supported by a metanalysis from three cohorts of smokers and non-smokers, where a significant association between longer leukocyte telomere length and risk of LC—particularly adenocarcinoma—was found [45]. Our findings agree with other studies that reported an association between longer leucocyte telomeres and LC [13,14] independently of the presence of COPD or emphysema [14] but, importantly, extends across previous cross-sectional research when evaluating longitudinal potential markers of LC risk as early as 3 years prior to diagnosis. Our group previously evaluated a potential profile of microRNAs as risk markers of cancer development and found a signature of two miRNAs (miR-1246 and miR-206) with a moderate capacity of detection [46]. This new marker has a strong capacity to discriminate those patients with COPD who are at increased risk of developing lung cancer.
4.2. 8-OHdG Serum/Plasma Levels
Oxidative DNA damage (8-OHdG formation), along with the impaired induction of hOGG1, has been studied in the lungs of COPD patients. Increased 8-OHdG levels in DNA from peripheral blood were reported to be associated with poor lung function in smoking COPD patients in contrast to hOGG1 induction [22]. Another study observed that urinary excretion levels of 8-OHdG were significantly higher in smokers than in subjects who had never smoked, confirming oxidative damage. Importantly, these levels were also found to be significantly increased in lung cancer patients, although decreasing with a higher severity of disease [47]. An et al. (2019) found that the expression of 8-OHdG by immunohistochemistry in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) tissue was associated with a good prognosis (never smoked, low T category, or negative lymph node) [48]. All these results highlight the importance of studying this biomarker longitudinally in well-characterized cohorts to unravel possible controversies. Our study extends these observations by showing higher levels of 8-OHdG 3 years before the diagnosis of LC, further strengthening the association of this biomarker with COPD smokers and subsequent LC development.
Our study has some limitations. Firstly, and perhaps most importantly, the sample size may be considered small compared to some cross-sectional studies. However, this may not hold for a prospective study like ours, where a large, very well-characterized cohort of COPD patients was included and who were followed for a long period, thereby allowing the monitoring of the development and diagnosis of LC. Secondly, telomere length was measured in leucocytes and, therefore, our findings may not reflect the process occurring in the whole lung. It is already known that telomere length in blood correlates well with telomere length in the lung tissue of COPD patients [49], with similar rates of shortening between different tissues [50]. In addition, blood has the advantage of being a non-invasive, easy-to-access biological sample that allows the analysis of large cohorts of individuals. Third, we did not investigate other markers of aging and DNA damage alongside telomere length and 8-OHdG. Current evidence indicates that COPD may be due to accelerated lung aging, where accumulations of senescent cells persist in the lung tissue and release multiple inflammatory mediators and ROS [51]. The measurement of markers of immunosenescence could help to deeply characterize this complex scenario and its impact and contribution to immunosenescence, oxidative balance, and related inflammaging in COPD patients in relation to LC development. Lastly, we are aware that pharmacological treatment is an important factor that may alter the oxidative balance; however, the patients included in this study only received inhaled respiratory therapy as recommended by international guidelines, and none of these treatments have been shown to effectively modify the oxidative balance [52].
On the other hand, this study has several strengths, including the fact that the COPD patients proceeded from two different centers, with the biomarker measures that precede the diagnosis of LC identified in both samples. Finally, these findings provide a new perspective on LC screening. Until now, only the use of low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) screening has been shown to improve survival in older smoking subjects [53]. The addition of complementary biomarkers to other clinical data may help refine the risk-stratification process of cancer screening for subjects at risk of LC development [54].
In conclusion, our results suggest that longer leucocyte telomere length and increased 8-OHdG serum levels may serve as early biological markers of future lung cancer development among COPD patients, which can be employed along with traditional methods to help define LC risk during the screening of patients.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/antiox13020156/s1, Table S1: Comparison of clinical characteristics of smoking patients with COPD and lung cancer (LC) at the time of LC diagnosis and three years before.
Author Contributions
E.C.-L. and C.C. participated in the study conception and design, analysis and interpretation, and drafting of the manuscript, and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. A.D.-d.-B., L.M.M., A.O. and J.J.Z. participated in data analysis and interpretation. A.D.-d.-B., D.M., F.G. and A.R.-S. participated in data acquisition. B.C. participated in the interpretation of the results and helped draft the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III (PI 12/00355); the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF), the Spanish Respiratory Society, SEPAR (PI 13/007) and Menarini Laboratory S.A. (2018); Cabildo de Tenerife, Tenerife 2030, FDCAN, MEDI (Agustín de Betancourt program), and Consorcio Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Enfermedades Infecciosas CIBERINFEC (CB21/13/00100), Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Spain.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Hospital Universitario La Candelaria, Tenerife, Spain (PI55/17, CHUNSC-2018-29).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article and its Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the IUETSPC and SEGAI at the University of La Laguna for the use of infrastructure, equipment, and facilities.
Conflicts of Interest
Elizabeth Córdoba-Lanús, Luis M. Montuenga, Angélica Domínguez de-Barros, Alexis Oliva, Delia Mayato, Ana Remírez-Saenz, Francisca Gonzalvo, and Javier J. Zulueta declare not to have any financial or personal conflicts of interests. Ciro Casanova has received speaker or consulting fees from AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Menarini, and Novartis; and research grants from GlaxoSmithKline, Menarini, and AstraZeneca in the last 3 years. Bartolomé Celli declares having received compensation for advisory boards and consultation fees from GlaxoSmithKline, Boehringer-Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Sanofi-Aventis, CHIESI, Menarini, and Gala Therapeutics; and declares not to have shares or interests in any company, neither has he received or had any relationship with money from the tobacco industry.
References
- WHO. Leading Causes of Death Globally. 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death (accessed on 3 November 2023).
- Celli, B. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and lung cancer: Common pathogenesis, shared clinical challenges. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2012, 9, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GOLD. Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease-2022 Report. 2022. Available online: https://goldcopd.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/GOLD-REPORT-2022-v1.0-12Nov2021_WMV.pdf (accessed on 3 November 2023).
- Álvarez, F.V.; Trueba, I.M.; Sanchis, J.B.; López-Rodó, L.M.; Suárez, P.M.R.; Escuín, J.S.d.C.; Barreiro, E.; Pintado, M.H.B.; Vicente, C.D.; Aldeyturriaga, J.F.; et al. Executive summary of the SEPAR recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2016, 52, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestbo, J.; Hurd, S.S.; Agustí, A.G.; Jones, P.W.; Vogelmeier, C.; Anzueto, A.; Barnes, P.J.; Fabbri, L.M.; Martinez, F.J.; Nishimura, M.; et al. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: GOLD executive summary. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 347–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parris, B.A.; O’Farrell, H.E.; Fong, K.M.; Yang, I.A. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and lung cancer: Common pathways for pathogenesis. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11 (Suppl. S17), S2155–S2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisi, J. Aging, cellular senescence, and cancer. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013, 75, 685–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernadotte, A.; Mikhelson, V.M.; Spivak, I.M. Markers of cellular senescence. Telomere shortening as a marker of cellular senescence. Aging 2016, 8, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capper, R.; Britt-Compton, B.; Tankimanova, M.; Rowson, J.; Letsolo, B.; Man, S.; Haughton, M.; Baird, D.M. The nature of telomere fusion and a definition of the critical telomere length in human cells. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 2495–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.S.; Choi, Y.Y.; Lee, W.K.; Choi, J.E.; Cha, S.I.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, C.H.; Kam, S.; Jung, T.H.; Park, J.Y. Telomere length and the risk of lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99, 1385–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, J.A.; Grieshober, L.; Houck, J.R.; Barnett, M.J.; Tapsoba, J.D.; Thornquist, M.; Wang, C.Y.; Goodman, G.E.; Chen, C. Telomere Length and Lung Cancer Mortality among Heavy Smokers. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2018, 27, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Cawthon, R.; Rothman, N.; Weinstein, S.J.; Virtamo, J.; Hosgood, H.D., 3rd; Hu, W.; Lim, U.; Albanes, D.; Lan, Q. A prospective study of telomere length measured by monochrome multiplex quantitative PCR and risk of lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2011, 73, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, Q.; Cawthon, R.; Gao, Y.; Hu, W.; Hosgood, H.D., 3rd; Barone-Adesi, F.; Ji, B.T.; Bassig, B.; Chow, W.H.; Shu, X.; et al. Longer telomere length in peripheral white blood cells is associated with risk of lung cancer and the rs2736100 (CLPTM1L-TERT) polymorphism in a prospective cohort study among women in China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de-Torres, J.P.; Sanchez-Salcedo, P.; Bastarrika, G.; Alcaide, A.B.; Pío, R.; Pajares, M.J.; Campo, A.; Berto, J.; Montuenga, L.; Del Mar Ocon, M.; et al. Telomere length, COPD and emphysema as risk factors for lung cancer. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1601521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.C.; Cech, T.R. Human telomerase: Biogenesis, tracking, recruitment, and activation. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthel, F.P.; Wei, W.; Tang, M.; Martinez-Ledesma, E.; Hu, X.; Amin, S.B.; Akdemir, K.C.; Seth, S.; Song, X.; Wang, Q.; et al. Systematic analysis of telomere length and somatic alterations in 31 cancer types. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, L.J.; Youds, J.L.; Ward, J.D.; McIlwraith, M.J.; O’Neil, N.J.; Petalcorin, M.I.; Martin, J.S.; Collis, S.J.; Cantor, S.B.; Auclair, M.; et al. RTEL1 maintains genomic stability by suppressing homologous recombination. Cell 2008, 135, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codd, V.; Nelson, C.P.; Albrecht, E.; Mangino, M.; Deelen, J.; Buxton, J.L.; Hottenga, J.J.; Fischer, K.; Esko, T.; Surakka, I.; et al. Identification of seven loci affecting mean telomere length and their association with disease. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, M.T.; Chatterjee, N.; Yu, K.; Goldin, L.R.; Goldstein, A.M.; Rotunno, M.; Mirabello, L.; Jacobs, K.; Wheeler, W.; Yeager, M.; et al. A genome-wide association study of lung cancer identifies a region of chromosome 5p15 associated with risk for adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 85, 679–691, Erratum in Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 88, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoshiba, K.; Zhou, F.; Tsuji, T.; Nagai, A. DNA damage as a molecular link in the pathogenesis of COPD in smokers. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 39, 1368–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziech, D.; Franco, R.; Pappa, A.; Panayiotidis, M.I. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) induced genetic and epigenetic alterations in human carcinogenesis. Mutat. Res. 2011, 711, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wu, H.; Zhao, J.; Wu, X.; Zhao, J.; Ning, Q.; Xu, Y.; Xie, J. Feasibility of 8-OHdG formation and hOGG1 induction in PBMCs for assessing oxidative DNA damage in the lung of COPD patients. Respirology 2014, 19, 1183–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelic, M.D.; Mandic, A.D.; Maricic, S.M.; Srdjenovic, B.U. Oxidative stress and its role in cancer. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2021, 17, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, C.; de Torres, J.P.; Aguirre-Jaíme, A.; Pinto-Plata, V.; Marin, J.M.; Cordoba, E.; Baz, R.; Cote, C.; Celli, B.R. The progression of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is heterogeneous: The experience of the BODE cohort. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 184, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesa-Guzmán, M.; González, J.; Alcaide, A.B.; Bertó, J.; de-Torres, J.P.; Campo, A.; Seijo, L.M.; Ocón, M.M.; Pueyo, J.C.; Bastarrika, G.; et al. Surgical Outcomes in a Lung Cancer-Screening Program Using Low Dose Computed Tomography. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2021, 57, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Thoracic Society Statement. Lung function testing: Selection of reference values and interpretative strategies. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1991, 144, 1202–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macintyre, N.; Crapo, R.O.; Viegi, G.; Johnson, D.C.; van der Grinten, C.P.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.; Enright, P.; et al. Standardisation of the single-breath determination of carbon monoxide uptake in the lung. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 720–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahler, D.A.; Wells, C.K. Evaluation of clinical methods for rating dyspnea. Chest 1988, 93, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celli, B.R.; Cote, C.G.; Marin, J.M.; Casanova, C.; Montes de Oca, M.; Mendez, R.A.; Pinto Plata, V.; Cabral, H.J. The body-mass index, airflow obstruction, dyspnea, and exercise capacity index in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, M.; Szatrowski, T.P.; Peterson, J.; Gold, J. Validation of a combined comorbidity index. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1994, 47, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, D.A.; Austin, J.H.; Hogg, J.C.; Grenier, P.A.; Kauczor, H.U.; Bankier, A.A.; Barr, R.G.; Colby, T.V.; Galvin, J.R.; Gevenois, P.A.; et al. CT-Definable Subtypes of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Statement of the Fleischner Society. Radiology 2015, 277, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Córdoba-Lanús, E.; Cazorla-Rivero, S.; García-Bello, M.A.; Mayato, D.; Gonzalvo, F.; Ayra-Plasencia, J.; Celli, B.; Casanova, C. Telomere length dynamics over 10-years and related outcomes in patients with COPD. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawthon, R.M. Telomere length measurement by a novel monochrome multiplex quantitative PCR method. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barrett, J.C.; Fry, B.; Maller, J.; Daly, M.J. Haploview: Analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solé, X.; Guinó, E.; Valls, J.; Iniesta, R.; Moreno, V. SNPStats: A web tool for the analysis of association studies. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1928–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greider, C.W.; Blackburn, E.H. The telomere terminal transferase of Tetrahymena is a ribonucleoprotein enzyme with two kinds of primer specificity. Cell 1987, 51, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heaphy, C.M.; Meeker, A.K. The potential utility of telomere-related markers for cancer diagnosis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 1227–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesus, B.B.; Blasco, M.A. Telomerase at the intersection of cancer and aging. Trends Genet. 2013, 29, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shay, J.W.; Bacchetti, S. A survey of telomerase activity in human cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 1997, 33, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, T.M.; Englezou, A.; Dalla-Pozza, L.; Dunham, M.A.; Reddel, R.R. Evidence for an alternative mechanism for maintaining telomere length in human tumors and tumor-derived cell lines. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 1271–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telomeres Mendelian Randomization Collaboration; Haycock, P.C.; Burgess, S.; Nounu, A.; Zheng, J.; Okoli, G.N.; Bowden, J.; Wade, K.H.; Timpson, N.J.; Evans, D.M.; et al. Association between Telomere Length and Risk of Cancer and Non-Neoplastic Diseases: A Mendelian Randomization Study. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 636–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rode, L.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Bojesen, S.E. Long telomeres and cancer risk among 95,568 individuals from the general population. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 45, 1634–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, E.J.; Luncsford, P.J.; Armanios, M. Long telomeres and cancer risk: The price of cellular immortality. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 3474–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seow, W.J.; Cawthon, R.M.; Purdue, M.P.; Hu, W.; Gao, Y.T.; Huang, W.Y.; Weinstein, S.J.; Ji, B.T.; Virtamo, J.; Hosgood, H.D., 3rd; et al. Telomere length in white blood cell DNA and lung cancer: A pooled analysis of three prospective cohorts. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 4090–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdoba-Lanús, E.; Domínguez de-Barros, A.; Oliva, A.; Mayato, D.; Gonzalvo, F.; Remírez-Sanz, A.; Zulueta, J.J.; Celli, B.; Casanova, C. Circulating miR-206 and miR-1246 as Markers in the Early Diagnosis of Lung Cancer in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, T.; Shoji, F.; Baba, H.; Koga, T.; Shiraishi, T.; Orita, H.; Kohno, H. Significance of the urinary 8-OHdG level as an oxidative stress marker in lung cancer patients. Lung Cancer 2009, 63, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, A.R.; Kim, K.M.; Park, H.S.; Jang, K.Y.; Moon, W.S.; Kang, M.J.; Lee, Y.C.; Kim, J.H.; Chae, H.J.; Chung, M.J. Association between Expression of 8-OHdG and Cigarette Smoking in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2019, 53, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saferali, A.; Lee, J.; Sin, D.D.; Rouhani, F.N.; Brantly, M.L.; Sandford, A.J. Longer telomere length in COPD patients with α1-antitrypsin deficiency independent of lung function. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniali, L.; Benetos, A.; Susser, E.; Kark, J.D.; Labat, C.; Kimura, M.; Desai, K.; Granick, M.; Aviv, A. Telomeres shorten at equivalent rates in somatic tissues of adults. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, M.A.; Chotirmall, S.H. The Impact of Immunosenescence on Pulmonary Disease. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 692546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzola, M.; Page, C.P.; Wedzicha, J.A.; Celli, B.R.; Anzueto, A.; Matera, M.G. Use of thiols and implications for the use of inhaled corticosteroids in the presence of oxidative stress in COPD. Respir. Res. 2023, 24, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Koning, H.J.; van der Aalst, C.M.; de Jong, P.A.; Scholten, E.T.; Nackaerts, K.; Heuvelmans, M.A.; Lammers, J.J.; Weenink, C.; Yousaf-Khan, U.; Horeweg, N.; et al. Reduced Lung-Cancer Mortality with Volume CT Screening in a Randomized Trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, M.; Ajona, D.; Seijo, L.M.; Sanz, J.; Valencia, K.; Corral, J.; Mesa-Guzmán, M.; Pío, R.; Calvo, A.; Lozano, M.D.; et al. Molecular biomarkers in early stage lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 1165–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).