Oxidative Stress in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: Putative Pathways to Hearing System Impairment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
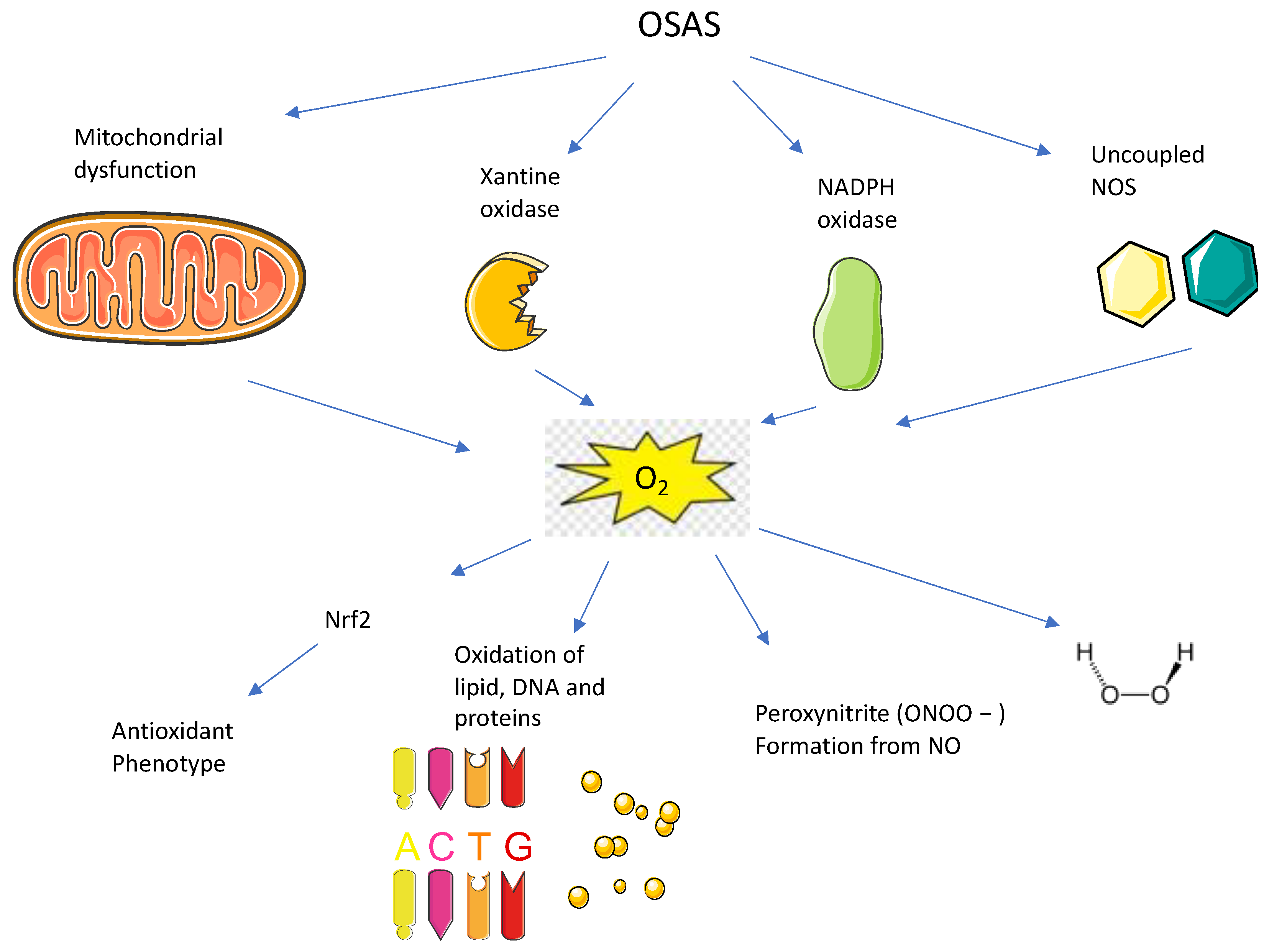
4.1. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and ROS
4.2. Hypoxia and HIF-α
4.3. OSAS, miRNAs, and Auditory System
4.4. OSAS and Interleukins
4.5. Oxidative Stress and Auditory System
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
5.1. High-Frequency Pure-Tone Audiometry
5.2. The Role of Antioxidant Therapy
5.3. Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Young, T.; Evans, L.; Finn, L.; Palta, M. Estimation of the clinically diagnosed proportion of sleep apnea syndrome in middle-aged men and women. Sleep 1997, 20, 705–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuvat, N.; Tanriverdi, H.; Armutcu, F. The relationship between obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and obesity: A new perspective on the pathogenesis in terms of organ crosstalk. Clin. Respir. J. 2020, 14, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodson, B.T.; Franco, R. Physiology of sleep disordered breathing. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2007, 40, 691–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapur, V.K.; Auckley, D.H.; Chowdhuri, S.; Kuhlmann, D.C.; Mehra, R.; Ramar, K.; Harrod, C.G. Clinical Practice Guideline for Diag-nostic Testing for Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea: An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2017, 13, 479–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S.P.; Schneider, H.; Schwartz, A.R.; Smith, P.L. Adult obstructive sleep apnea: Pathophysiology and diagnosis. Chest 2007, 132, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushida, C.A.; Littner, M.R.; Morgenthaler, T.; Alessi, C.A.; Bailey, D.; Friedman, L.; Hirshkowitz, M.; Kapen, S.; Kramer, M.; Lee-Chiong, T.; et al. Practice parameters for the indications for polysomnography and related procedures: An update for 2005. Sleep 2005, 28, 499–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboussouan, L.S.; Golish, J.A.; Wood, B.G.; Dinner, D.S. Dynamic pharyngoscopy in predicting outcome in uvulopalatopharyngoplasty. Laringoscope 1985, 95, 1483–1487. [Google Scholar]
- Croft, C.B.; Pringle, M. Sleep nasendoscopy: A technique of assessment in snoring and obstructive sleep apnoea. Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci. 1991, 16, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, M.B.; Reddy, R.P.; White, D.R.; Discolo, C.M.; Overdyk, F.J.; Nguyen, S.A. A trial of drug-induced sleep endoscopy in the surgical management of sleep-disordered breathing. Laryngoscope 2013, 123, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kezirian, E.J.; Hohenhorst, W.; de Vries, N. Drug-induced sleep endoscopy: The VOTE classification. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2011, 268, 1233–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loube, D.I.; Gay, P.C.; Strohl, K.P.; Pack, A.I.; White, D.P.; Collop, N.A. Indications for positive airway pressure treatment of adult obstructive sleep apnea patients: A consensus statement. Chest 1999, 115, 863–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.R.; White, D.P.; Malhotra, A.; Stanchina, M.L.; Ayas, N.T. Continuous positive airway pressure therapy for treating sleepiness in a diverse popu-lation with obstructive sleep apnea: Results of a meta-analysis. Arch. Intern. Med. 2003, 163, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randerath, W.J.; Verbraecken, J.; Andreas, S.; Bettega, G.; Boudewyns, A.; Hamans, E.; Jalbert, F.; Paoli, J.R.; Sanner, B.; Smith, I.; et al. Non-CPAP therapies in obstructive sleep apnoea. Eur. Respir. J. 2001, 37, 1000–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutsourelakis, I.; Safiruddin, F.; Ravesloot, M.; Zakynthinos, S.; de Vries, N. Surgery for obstructive sleep apnea: Sleep endoscopy determinants of out-come. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 2587–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofaso, F.; Coste, A.; d’Ortho, M.P.; Zerah-Lancner, F.; Delclaux, C.; Goldenberg, F.; Harf, A. Nasal obstruction as a risk factor for sleep apnoea syndrome. Eur. Respir. J. 2000, 16, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, M.; Tanyeri, H.; Lim, J.W.; Landsberg, R.; Vaidyanathan, K.; Caldarelli, D. Effect of improved nasal breathing on obstructive sleep apnea. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2000, 122, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, S. Pharyngeal surgery for obstructive sleep apnea and snoring. In Snoring and Obstructive Sleep Apnea; Fairbanks, D.N.F., Ed.; Raven Press: New York, NY, USA, 1987; pp. 101–128. [Google Scholar]
- Cahali, M.B. Lateral pharyngoplasty: A new treatment for obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome. Laryngoscope 2003, 113, 1961–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minni, A.; Cialente, F.; Ralli, M.; Colizza, A.; Lai, Q.; Placentino, A.; Franco, M.; Rossetti, V.; De Vincentiis, M. Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty and barbed reposition pharyngoplasty with and without hyoid suspension for obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome: A comparison of long-term functional results. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2020, 21, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minni, A.; Visconti, I.C.; Colizza, A.; Cavalcanti, L.; Gilardi, A.; de Vincentiis, M. Long-Term Functional Results of Barbed Reposition Pharyngoplasty Vs. Hyoid Suspension for Obstructive Sleep Apnea Hypopnea Syndrome. In Barbed Pharyngoplasty and Sleep Disordered Breathing; Vicini, C., Salamanca, F., Iannella, G., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Swizerland, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, S.; Woodson, B.T.; Clark, J.L.; Wittig, R. Laser midline glossectomy as a treatment for obstructive sleep apnea. Laryngoscope 1991, 101, 805–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechien, J.R.; Chiesa-Estomba, C.M.; Fakhry, N.; Saussez, S.; Badr, I.; Ayad, T.; Chekkoury-Idrissi, Y.; Melkane, A.E.; Bahgat, A.; Crevier-Buchman, L.; et al. Surgical, clinical, and functional outcomes of transoral robotic surgery used in sleep surgery for obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Head Neck 2021, 43, 2216–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavie, L.; Lavie, P. Molecular mechanisms of cardiovascular disease in OSAHS: The oxidative stress link. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 33, 1467–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavie, L. Oxidative stress and inflammation in OSA. Eur. Respir. Monogr. 2010, 50, 360–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meliante, P.G.; Zoccali, F.; Cascone, F.; Di Stefano, V.; Greco, A.; de Vincentiis, M.; Petrella, C.; Fiore, M.; Minni, A.; Barbato, C. Molecular Pathology, Oxidative Stress, and Biomarkers in Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto-Urata, M.; Urata, S.; Fujimoto, C.; Yamasoba, T. Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Acquired Inner Ear Disorders. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiuyang, F.; Tao, W.; Yong, L.; Lin, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wan, J.; Fan, S. Auditory Deficits in Patients With Mild and Moderate Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: A Speech Syllable Evoked Auditory Brainstem Response Study. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 12, 58–65. [Google Scholar]
- Gozeler, M.S.; Sengoz, F. Auditory Function of Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: A Study. Eurasian J. Med. 2020, 52, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinosi, M.C.; D’Amico, F.; Passàli, G.; Cingi, C.; Rodriguez, H.; Passàli, D. Hearing loss in mild OSAS and simple snoring patients. Otolaryngol. Polska 2017, 71, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martines, F.; Ballacchino, A.; Sireci, F.; Mucia, M.; La Mattina, E.; Rizzo, S.; Salvago, P. Audiologic profile of OSAS and simple snoring patients: The effect of chronic nocturnal intermittent hypoxia on auditory function. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2015, 273, 1419–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casale, M.; Vesperini, E.; Potena, M.; Pappacena, M.; Bressi, F.; Baptista, P.K.; Salvinelli, F. Is obstructive sleep apnea syndrome a risk factor for auditory pathway? Sleep Breath 2012, 16, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Su, J.; Kong, D.; Pang, J.; Kang, J. Gender, nocturnal hypoxia, and arousal influence brainstem auditory evoked potentials in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath. 2016, 20, 1239–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iriz, A.; Duzlu, M.; Kokturk, O.; Kemaloğlu, Y.K.; Cihat Eravcı, F.; Küükünal, I.S.; Karamert, R. The effect of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome on the central auditory system. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 48, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deniz, M.; Ersözlü, T. Evaluation of the changes in the hearing system over the years among patients with OSAS using a CPAP device. Cranio 2022, 40, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, S.; Jax, T.; Evers, S.; Hennersdorf, M.; Schwalen, A.; Strauer, B.E. Altered Blood Rheology in Obstructive Sleep Apnea as a Mediator of Cardiovascular Risk. Cardiology 2005, 104, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernáth, I.; McNamara, P.; Szternák, N.; Szakács, Z.; Köves, P.; Terray-Horváth, A.; Vida, Z. Hyperviscosity as a possible cause of positive acoustic evoked potential findings in patients with sleep apnea: A dual electrophysiological and hemorheological study. Sleep Med. 2009, 10, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekin, S.; Turan, M.; Arısoy, A.; Gunbatar, H.; Sunnetcioglu, A.; Asker, S.; Yıldız, H. Is there a relationship between Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) and hearing loss? Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 2, 3124–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.J.; Ju, H.M.; Lee, S.H.; Kwak, S.H.; Kang, M.J.; Yoon, J.-H.; Kim, C.-H.; Cho, H.-J. Damage of Inner Ear Sensory Hair Cells via Mitochondrial Loss in a Murine Model of Sleep Apnea With Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia. Sleep 2017, 40, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, S.; Taylor, C.T.; McNicholas, W.T. Selective activation of inflammatory pathways by intermittent hypoxia in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Circulation 2005, 112, 2660–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.J.; Song, L. Role of mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in sensorineural hearing loss. Heart Res. 2023, 434, 108783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, T.G.A.; Monsanto, R.D.C.; Amaral, J.B.D.; Oyama, L.M.; Maza, P.K.; Penido, N.D.O. Evaluation of Oxidative-Stress Pathway and Recovery of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 25, e428–e432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.I.; Kim, Y.R.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, U.K. Mitochondrial redox system: A key target of antioxidant therapy to prevent acquired sen-sorineural hearing loss. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1176881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacedonia, D.; Carpagnano, G.E.; Crisetti, E.; Cotugno, G.; Palladino, G.P.; Patricelli, G.; Sabato, R.; Barbaro, M.P.F. Mitochondrial DNA alteration in obstructive sleep apnea. Respir. Res. 2015, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, P.; Peng, Y.; Ouyang, R. Role of Oxidative Stress in the Neurocognitive Dys-function of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 9626831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.A.; Wei, Y.; Sowers, J.R. Role of mitochondrial dysfunction in insulin resistance. Circ. Res. 2008, 102, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, M.P. How mitochondria produce reactive oxygen species. Biochem. J. 2009, 417, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mladenov, M.; Lubomirov, L.; Grisk, O.; Avtanski, D.; Mitrokhin, V.; Sazdova, I.; Keremidarska-Markova, M.; Danailova, Y.; Nikolaev, G.; Konakchieva, R.; et al. Oxidative Stress, Reductive Stress and Antioxidants in Vascular Pathogenesis and Aging. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B.; Gutteridge, J.M.C. Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine, 4th ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Dröge, W. Free Radicals in the Physiological Control of Cell Function. Physiol. Rev. 2002, 82, 47–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, R.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, N.; Wang, X.; He, Y.; Yue, H.; Yin, Q. Pathophysiological mecha-nisms and therapeutic approaches in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stl, P.S.; Johansson, B. Abnormal mitochondria organization and oxidative activity in the palate muscles of long-term snorers with obstructive sleep apnea. Respiration 2012, 83, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, R.; Hummel, C.; Heinemann, S.; Seeger, W.; Grimminger, F. Serum Levels of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Are Elevated in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Severe Nighttime Hypoxia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Qian, Y.; Zou, J.; Yi, H.; Guan, J.; Yin, S. Association between Upper-airway Surgery and Ameliorative Risk Markers of Endothelial Function in Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lévy, P.; Kohler, M.; McNicholas, W.T.; Barbé, F.; McEvoy, R.D.; Somers, V.K.; Lavie, L.; Pépin, J.-L. Obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2015, 1, 15015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lino, D.; Freitas, I.; Meneses, G.; Martins, A.; Daher, E.; Rocha, J.; Junior, G.S. Interleukin-6 and adhesion molecules VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 as biomarkers of post-acute myocardial infarction heart failure. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2019, 52, e8658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Düger, M.; Seyhan, E.C.; Günlüoğlu, M.Z.; Bolatkale, M.; Ozgul, M.A.; Turan, D.; Uğur, E.; Ülfer, G. Does ischemia-modified albumin level predict severity of obstructive sleep apnea? Sleep Breath 2020, 25, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntalapascha, M.; Makris, D.; Kyparos, A.; Tsilioni, I.; Kostikas, K.; Gourgoulianis, K.; Kouretas, D.; Zakynthinos, E. Oxidative stress in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep Breath. 2012, 17, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lira, A.B.; de Sousa Rodrigues, C.F. Evaluation of oxidative stress markers in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and additional antioxidant therapy: A review article. Sleep Breath. 2016, 20, 1155–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, C.M.R.; Lima, A.M.J.; Ataide, L., Jr.; Lins, O.G.; Castro, C.M.M.; Bezerra, A.A.; de Oliveira, M.F.; Oliveira, J.R.M. Ob-structive sleep apnea severity correlates with cellular and plasma oxidative stress parameters and affective symptoms. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2012, 47, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabryelska, A.; Szmyd, B.; Szemraj, J.; Stawski, R.; Sochal, M.; Białasiewicz, P. Patients with obstructive sleep apnea present with chronic upregulation of serum HIF-1α protein. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2020, 16, 1761–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniaci, A.; Iannella, G.; Cocuzza, S.; Vicini, C.; Magliulo, G.; Ferlito, S.; Cammaroto, G.; Meccariello, G.; De Vito, A.; Nicolai, A.; et al. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Biomarker Expression in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, N.R.; Peng, Y.-J.; Nanduri, J. Hypoxia-inducible factors and obstructive sleep apnea. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 5042–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sies, H.; Jones, D.P. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) as pleiotropic physiological signalling agents. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 363–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, E.J. Hypoxia and aging. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.J.; Wu, C.; Lin, H.; Lee, I. Visfatin-induced expression of inflammatory mediators in human endothelial cells through the NF-kappaB pathway. Int. J. Obes. 2009, 33, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.P.; Kim, D.-Y.; Lee, Y.-G.; Lee, Y.-S.; Truong, X.T.; Lee, J.H.; Song, D.-K.; Kwon, T.K.; Park, S.; Jung, C.H.; et al. SREBP-1c impairs ULK1 sulfhydration-mediated autophagic flux to promote hepatic steatosis in high-fat-diet-fed mice. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 3820–3832.e3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Savransky, V.; Nanayakkara, A.; Smith, P.L.; O’Donnell, C.P.; Polotsky, V.Y. Hyperlipidemia and lipid peroxidation are dependent on the severity of chronic intermittent hypoxia. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 102, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niki, E. Lipid peroxidation: Physiological levels and dual biological effects. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 47, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliogiannis, P.; Fois, A.G.; Sotgia, S.; Mangoni, A.A.; Zinellu, E.; Pirina, P.; Carru, C.; Zinellu, A. Circulating malondialdehyde concentrations in patients with stable COPD: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomark. Med. 2018, 12, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pau, M.C.; Zinellu, E.; Fois, S.S.; Piras, B.; Pintus, G.; Carru, C.; Mangoni, A.A.; Fois, A.G.; Zinellu, A.; Pirina, P. Circulating Malondialdehyde Concentrations in Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis with Me-ta-Regression. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harki, O.; Tamisier, R.; Pépin, J.-L.; Bailly, S.; Mahmani, A.; Gonthier, B.; Salomon, A.; Vilgrain, I.; Faury, G.; Briançon-Marjollet, A. VE-cadherin cleavage in sleep apnoea: New insights into intermittent hypoxia-related endothelial permeability. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 58, 2004518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Du, Y.; Li, L.; Hu, C.; Zhang, J.; Qin, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, H. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Intermittent Hypoxia–Treated Red Blood Cells Impair Endothelial Function Through Regulating eNOS Phosphorylation and ET-1 Expres-sion. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2020, 35, 901–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbato, C. MicroRNA-Mediated Silencing Pathways in the Nervous System and Neu-rological Diseases. Cells 2022, 11, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wei, P.; Qin, Y.; Wie, Y. MicroRNA expression profiling and bioinformatics analysis of dysregulated microRNAs in ob-structive sleep apnea patients. Medicine 2007, 96, e7917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Chang, S.C.; Jin, J.; Gu, W.; Li, S. NLRP3 inflammasome mediates chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced renal injury implication of the microRNA-155/FOXO3a signaling pathway. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 9404–9415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meszaros, M.; Horvath, P.; Kis, A.; Kunos, L.; Tarnoki, A.D.; Tarnoki, D.L.; Lazar, Z.; Bikov, A. Circulating levels of clusterin and complement factor H in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Biomarkers Med. 2021, 15, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Chen, Z.; Qin, Y.; Wei, Y. MiR-664a-3p expression in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: A potential marker of atherosclerosis. Medicine 2018, 97, e9813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, R.; Dai, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Lin, Q. Endothelial cell autophagy in chronic intermittent hypoxia is impaired by miRNA-30a-mediated translational control of Beclin-1. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 4214–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Wang, K.; Tang, W.; Yu, L.; Cao, H.; Chi, W.; Wang, B. miR-34a-5p was involved in chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced autophagy of human coronary artery endothelial cells via Bcl-2/beclin 1 signal transduction pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 18871–18882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavie, L. Obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome—An oxidative stress disorder. Sleep Med. Rev. 2003, 7, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vgontzas, A.N.; Papanicolaou, D.A.; Bixler, E.O.; Kales, A.; Tyson, K.; Chrousos, G.P. Elevation of Plasma Cytokines in Disorders of Excessive Daytime Sleepiness: Role of Sleep Disturbance and Obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 1313–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszewska, E.; Pietrewicz, T.M.; Swiderska, M.; Jamiołkowski, J.; Chabowski, A. A Case-Control Study on the Changes in High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein and Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Levels with Surgical Treatment of OSAS. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinnusi, M.; Jaoude, P.; Kufel, T.; El-Solh, A.A. Toll-like receptor activity in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath 2013, 17, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.-T.; Chen, Y.-C.; Tseng, C.-C.; Chang, H.-C.; Su, M.-C.; Wang, T.-Y.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Zheng, Y.-X.; Chang, J.-C.; Chin, C.-H.; et al. Aberrant DNA methylation of the toll-like receptors 2 and 6 genes in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisele, H.-J.; Markart, P.; Schulz, R. Obstructive Sleep Apnea, Oxidative Stress, and Cardiovascular Disease: Evidence from Human Studies. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 608438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadasivam, K.; Patial, K.; Vijayan, V.K.; Ravi, K. Anti-oxidant treatment in obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Indian J. Chest Dis. Allied Sci. 2011, 53, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Macrea, M.; Martin, T.; Zagrean, L.; Jia, Z.; Misra, H. Role of leptin as antioxidant in obstructive sleep apnea: An in vitro study using electron paramagnetic resonance method. Sleep Breath 2013, 17, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, S.H.; Taylor, R.; Forge, A.; Schacht, J. Differential vulnerability of basal and apical hair cells is based on intrinsic sus-ceptibility to free radicals. Heart Res. 2001, 155, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patt, B.T.; Jarjoura, D.; Haddad, D.N.; Sen, C.K.; Roy, S.; Flavahan, S.; Khayat, R.N. Endothelial dysfunction in the microcirculation of patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 1540–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, A. Physiopathology of the cochlear microcirculation. Heart Res. 2011, 282, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivri, B.; Sezen, O.S.; Akbulut, S.; Coskuner, T. The effect of continuous positive airway pressure on middle ear pressure. Laryngoscope 2013, 123, 1300–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, K.; Akai, H.; Muramatsu, K. Effects of methionine and related compounds on plasma cholesterol level in rats fed a high cholesterol diet. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 1986, 32, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B.G.; Zhao, X.-Q.; Chait, A.; Fisher, L.D.; Cheung, M.C.; Morse, J.S.; Dowdy, A.A.; Marino, E.K.; Bolson, E.L.; Alaupovic, P.; et al. Simvastatin and Niacin, Antioxidant Vitamins, or the Combination for the Prevention of Coronary Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 1583–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Touyz, R.M.; Park, J.B.; Schiffrin, E.L. Antioxidant Effects of Vitamins C and E Are Associated With Altered Activation of Vascular NADPH Oxidase and Superoxide Dismutase in Stroke-Prone SHR. Hypertension 2001, 38, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, R.; Adhikari, S.; Patro, B.S.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Mukherjee, T. Free radical scavenging behavior of folic acid: Evidence for possible antioxidant activity. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2001, 30, 1390–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papucci, L.; Schiavone, N.; Witort, E.; Donnini, M.; Lapucci, A.; Tempestini, A.; Formigli, L.; Zecchi-Orlandini, S.; Orlandini, G.; Carella, G.; et al. Coenzyme Q10 Prevents Apoptosis by Inhibiting Mitochondrial Depolarization Independently of Its Free Radical Scavenging Property. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 28220–28228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, L.; Witt, E.H.; Tritschler, H.J. Alpha-lipoic acid as a biological antioxidant. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 1995, 19, 227–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.-X.; Yan, L.-J.; Lewith, G.; Liu, J.-P. Chinese herbal medicine for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A systematic review of randomised clinical trials. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2013, 38, 455–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya, H.; Koç, A.K.; Sayın, İ.; Güneş, S.; Altıntaş, A.; Yeğin, Y.; Kayhan, F.T. Vitamins A, C, and E and selenium in the treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2015, 272, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebe, M.; Eisele, H.J.; Weissmann, N.; Schaefer, C.; Tillmanns, H.; Seeger, W.; Schulz, R. Antioxidant Vitamin C Improves Endothelial Function in Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 897–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Study Title | Group/Patients | Age | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Qiuyang Fu, Tao Wang, Yong Liang et al.: Auditory Deficits in Patients with Mild and Moderate Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: A Speech Syllable Evoked Auditory Brainstem Response Study. Clin and Exp Otorhinol 12(1): 58–65 [26]. | 52 (31 OSAS + 21 ctrl) | 23 years to 39 years | 2019 |
| Mustafa Sitki Gozeler, Furkan Sengoz: Auditory Function of Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: A Study. Eur-asian J Med 52(2): 176-9 [27]. | 65 (35 OSAS + 30 ctrl) | 39 years to 48 years | 2020 |
| Spinosi MC, D’Amico F, Passali G, Cingi C, Rodriguez H, Passali D. Hearing loss in mild OSAS and simple snoring patients. Otolaryngol Pol. Apr 30;71(2):11–15 [28]. | 80 (50 OSAS + 30 ctrl) | 45 years to 65 years | 2017 |
| Martines F, Ballacchino A, Sireci F, Mucia M, La Mattina E, Rizzo S, Salvago P. Audiologic profile of OSAS and simple snoring patients: the effect of chronic nocturnal intermittent hypoxia on auditory function. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. Jun;273(6):1419-24 [29]. | 160 (100 OSAS + 60 ctrl) | 38 years to 55 years | 2016 |
| Manuele Casale, Emanuela Vesperini, Massimiliano Potena et al.: Is obstructive sleep apnea syndrome a risk factor for auditory pathway? Sleep Breath 16:413–417 [30]. | 60 (39 OSAS + 21 ctrl) | 31 years to 39 years | 2012 |
| Wei Wang, Jiao Su, Delei Kong et al.: Gender, nocturnal hypoxia, and arousal influence brainstem auditory evoked potentials in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath [31]. | 118 (84 OSAS + 34 ctrl) | 53 years to 60 years | 2016 |
| Ayşe Iriz, Mehmet Duzlu, Oğuz Kokturk et al.: The effect of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome on the central auditory system. Turk J Med Sci; 48: 5–9 [32]. | 31 (21 OSAS + 10 ctrl) | 47 years to 55 years | 2018 |
| Deniz, Ersözlü T. Evaluation of the changes in the hearing system over the years among patients with OSAS using a CPAP device. Cranio. 40(6):524–527 [33]. | 22 (OSAS under CPAP treatment) | 56 years to 67 years | 2022 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mastino, P.; Rosati, D.; de Soccio, G.; Romeo, M.; Pentangelo, D.; Venarubea, S.; Fiore, M.; Meliante, P.G.; Petrella, C.; Barbato, C.; et al. Oxidative Stress in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: Putative Pathways to Hearing System Impairment. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1430. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12071430
Mastino P, Rosati D, de Soccio G, Romeo M, Pentangelo D, Venarubea S, Fiore M, Meliante PG, Petrella C, Barbato C, et al. Oxidative Stress in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: Putative Pathways to Hearing System Impairment. Antioxidants. 2023; 12(7):1430. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12071430
Chicago/Turabian StyleMastino, Pierluigi, Davide Rosati, Giulia de Soccio, Martina Romeo, Daniele Pentangelo, Stefano Venarubea, Marco Fiore, Piero Giuseppe Meliante, Carla Petrella, Christian Barbato, and et al. 2023. "Oxidative Stress in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: Putative Pathways to Hearing System Impairment" Antioxidants 12, no. 7: 1430. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12071430
APA StyleMastino, P., Rosati, D., de Soccio, G., Romeo, M., Pentangelo, D., Venarubea, S., Fiore, M., Meliante, P. G., Petrella, C., Barbato, C., & Minni, A. (2023). Oxidative Stress in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: Putative Pathways to Hearing System Impairment. Antioxidants, 12(7), 1430. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12071430








