Stable Isotope Ratio Analysis for the Authentication of Natural Antioxidant Curcuminoids from Curcuma longa (Turmeric)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Simultaneous Determination of the Three Curcuminoids Components
2.3. 14C Analysis
2.4. Stable Isotope Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
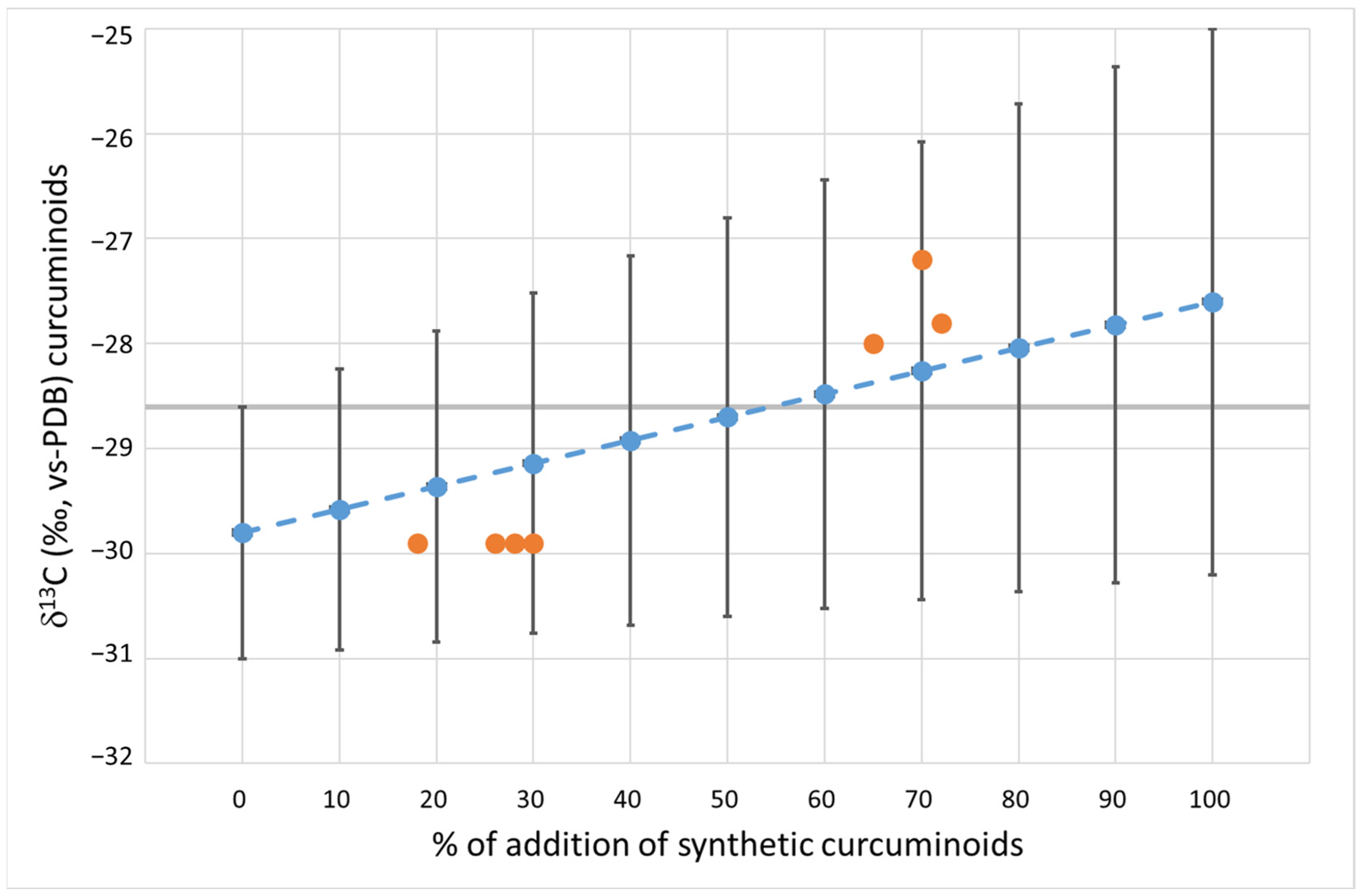
3.1. δ13C of Natural and Synthetic Curcuminoid Complex
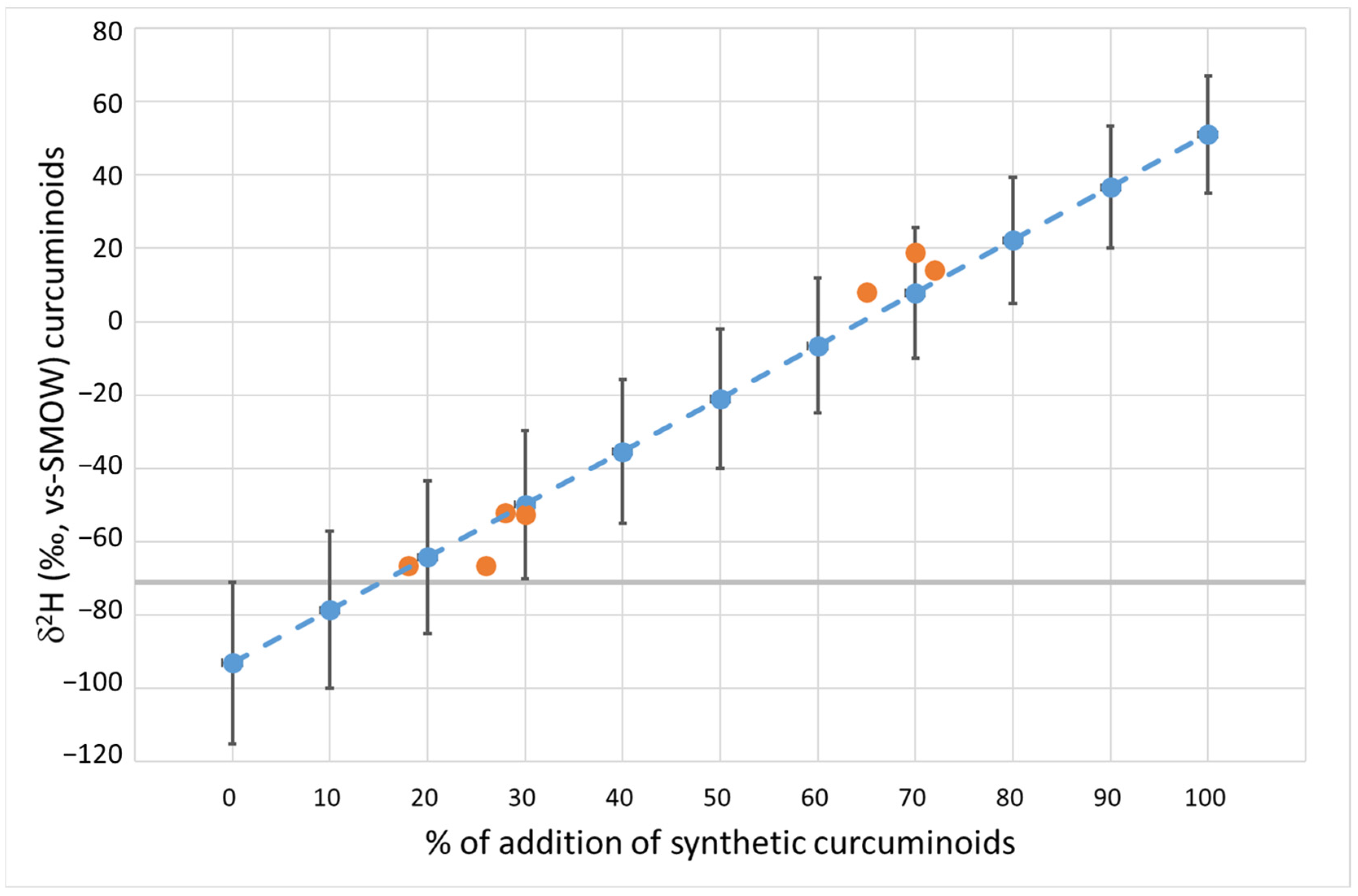
3.2. δ2H of Natural and Synthetic Curcuminoid Complex
3.3. Natural Curcuminoids Complex Spiked with Different Concentrations of Synthetic Curcuminoids
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hewlings, S.J.; Kalman, D.S. Curcumin: A Review of Its Effects on Human Health. Foods 2017, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christine, E.A.; André, D.G.; Benjamin, K.K.; Maxwell, B.G.A.; Séraphin, K.-C. Biochemical Composition of Two Zinziberaceae: Ginger (Zingiber officinale roscoe) and Turmeric (Curcuma longa). Asian Food Sci. J. 2021, 20, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowsalya, R.; Krishnaveni, M. Extraction and Antibacterial Studies of Curcumin. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 5, 317–321. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, S.; Kar, S.K. Curcuminoids: The Novel Molecules of Nature. In Herbs and Spices-New Processing Technologies; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, T.; Majid, F.; Eckl, V.; Morton Reynolds, C. Herbal Supplement Sales in US Increase by Record-Breaking 17.3% in 2020. Herb. Gram 2021, 131, 52–65. [Google Scholar]
- Nagpal, M.; Sood, S. Role of Curcumin in Systemic and Oral Health: An Overview. J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med. 2013, 4, 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, T.P.; Nyunt, M.S.Z.; Gao, Q.; Gwee, X.; Chua, D.Q.L.; Yap, K.B. Curcumin-Rich Curry Consumption and Neurocognitive Function from 4.5-Year Follow-Up of Community-Dwelling Older Adults (Singapore Longitudinal Ageing Study). Nutrients 2022, 14, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzanti, G.; Di Giacomo, S. Curcumin and Resveratrol in the Management of Cognitive Disorders: What Is the Clinical Evidence? Molecules 2016, 21, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, G.W.; Siddarth, P.; Li, Z.; Miller, K.J.; Ercoli, L.; Emerson, N.D.; Martinez, J.; Wong, K.-P.; Liu, J.; Merrill, D.A.; et al. Memory and Brain Amyloid and Tau Effects of a Bioavailable Form of Curcumin in Non-Demented Adults: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled 18-Month Trial. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2018, 26, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girme, A.; Saste, G.; Balasubramaniam, A.K.; Pawar, S.; Ghule, C.; Hingorani, L. Assessment of Curcuma longa Extract for Adulteration with Synthetic Curcumin by Analytical Investigations. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 191, 113603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhail, F.K.; Masood, U.; Sharma, A.; John, S.; Dhamoon, A. Turmeric Supplement Induced Hepatotoxicity: A Rare Complication of a Poorly Regulated Substance. Clin. Toxicol. 2020, 58, 216–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Food and Drug Administration. 2019. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/130730/download (accessed on 29 April 2022).
- Sarma, N.; Upton, R.; Rose, U.; Guo, D.-A.; Marles, R.; Khan, I.; Giancaspro, G. Pharmacopeial Standards for the Quality Control of Botanical Dietary Supplements in the United States. J. Diet. Suppl. 2021, 1, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gafner, S.; Blumenthal, M.; Foster, S.; Cardellina, J.; Khan, I.A.; Upton, R. Laboratory Guidance on Analytical Methods to Detect Adulterants in Commercial Botanical Materials: The next Phase of the ABC-AHP-NCNPR Botanical Adulterants Program. Planta Med. 2015, 81, OA35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
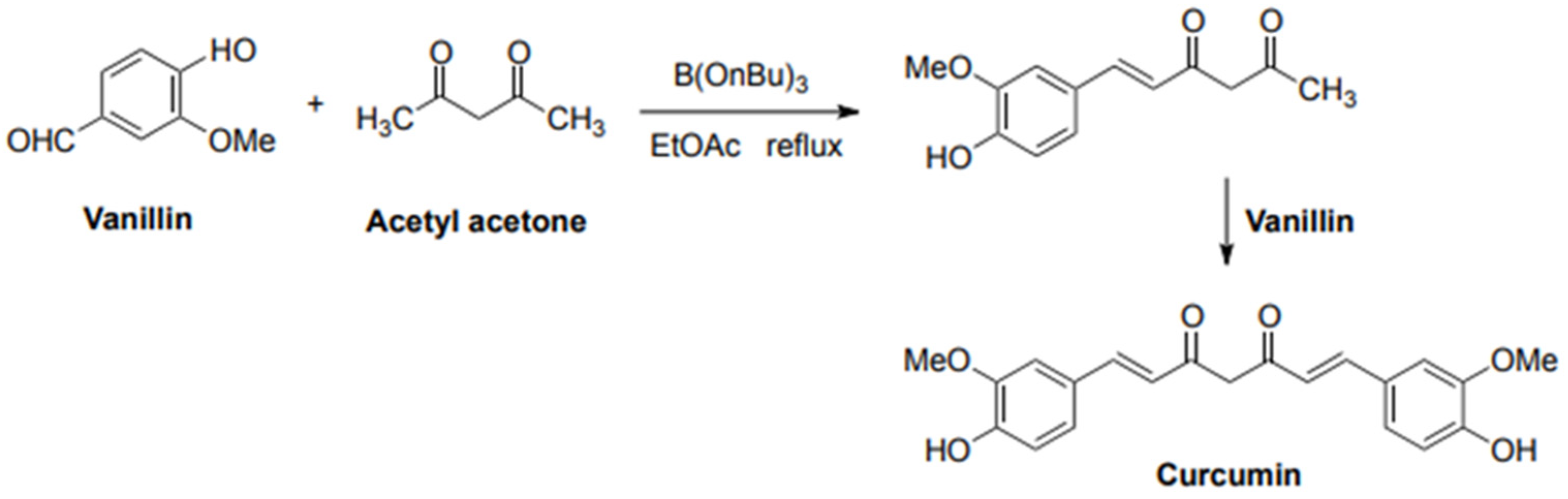
- Kita, T.; Imai, S.; Sawada, H.; Kumagai, H.; Seto, H. The Biosynthetic Pathway of Curcuminoid in Turmeric (Curcuma longa) as Revealed by 13C-Labeled Precursors. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2008, 72, 1789–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossmann, A. Determination of Stable Isotope Ratios in Food Analysis. Food Rev. Int. 2001, 17, 347–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leeuwen, K.A.; Prenzler, P.D.; Ryan, D.; Camin, F. Gas Chromatography-Combustion-Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry for Traceability and Authenticity in Foods and Beverages. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 814–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perini, M.; Pianezze, S.; Ziller, L.; Camin, F. Characterization of L-Theanine in Tea Extracts and Synthetic Products Using Stable Isotope Ratio Analysis. J. Food Drug Anal. 2021, 29, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, F.; Reniero, F.; Guillou, C.G.; Moreno, J.M.; Marinas, J.M.; Vanhaecke, F. 13C and 18O Isotopic Analysis to Determine the Origin of L-Tartaric Acid. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richling, E.; Höhn, C.; Weckerle, B.; Heckel, F.; Schreier, P. Authentication Analysis of Caffeine-Containing Foods via Elemental Analysis Combustion/pyrolysis Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry (EA-C/P-IRMS). Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2003, 216, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perini, M.; Carbone, G.; Camin, F. Stable Isotope Ratio Analysis for Authentication of Red Yeast Rice. Talanta 2017, 174, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perini, M.; Paolini, M.; Pace, R.; Camin, F. The Use of Stable Isotope Ratio Analysis to Characterise Saw Palmetto (Serenoa repens) Extract. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, M.H. Carbon Isotopes in Photosynthesis. Bioscience 1988, 38, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhou, W.; Xiong, X.; Wu, S.; Niu, Z.; Cheng, P.; Du, H.; Hou, Y. Stable Carbon Isotopic Characteristics of Fossil Fuels in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perini, M.; Pianezze, S.; Strojnik, L.; Camin, F. C and H Stable Isotope Ratio Analysis Using Solid-Phase Microextraction and Gas Chromatography-Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry for Vanillin Authentication. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1595, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passo, C.J.; Anderson, R.; Roberts, D.; Cook, G.T. Performance of the Packard Tri-Carb® 2770TR/SL Liquid Scintillation Analyzer for 14C Dating. Radiocarbon 1997, 40, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, P.K.; Panda, J.; Jogendra Kumar, Y.V.; Karunya Ranjitha, S. A Robust RP-HPLC Method for Determination of Turmeric Adulteration. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2020, 43, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN EN 16640:2017-08; Biobasierte Produkte_-Gehalt an Biobasiertem Kohlenstoff_-Bestimmung des Gehalts an Biobasiertem Kohlenstoff Mittels Radiokarbonmethode; Deutsche Fassung EN_16640:2017. Deutsches Institut für Normung: Berlin, Germany, 2017.
- Coplen, T.B. Guidelines and Recommended Terms for Expression of Stable-Isotope-Ratio and Gas-Ratio Measurement Results. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 25, 2538–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wassenaar, L.I.; Hobson, K.A.; Sisti, L. An Online Temperature-Controlled Vacuum-Equilibration Preparation System for the Measurement of δ2H Values of Non-Exchangeable-H and of δ18O Values in Organic Materials by Isotope-Ratio Mass Spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 29, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, P.K.; Larcher, R.; Camin, F.; Ziller, L.; Tonon, A.; Nardin, T.; Bontempo, L. Stable Isotope Ratios of Herbs and Spices Commonly Used as Herbal Infusions in the Italian Market. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 11925–11934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchese, J.A.; Ming, L.C.; Ducatti, C.; Broetto, F.; Silva, E.T.; Leonardo, M. Carbon Isotope Composition as a Tool to Control the Quality of Herbs and Medicinal Plants. Photosynthetica 2006, 44, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossmann, A.; Butzenlechner, M.; Schmidt, H.L. Evidence for a Nonstatistical Carbon Isotope Distribution in Natural Glucose. Plant Physiol. 1991, 96, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabon, H.J.J. A Synthesis of Curcumin and Related Compounds. Recl. Trav. Chim. Pays-Bas 1964, 83, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, A.-M.S.; Fromberg, A.; Frandsen, H.L. Authenticity and Traceability of Vanilla Flavors by Analysis of Stable Isotopes of Carbon and Hydrogen. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 10326–10331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greule, M.; Tumino, L.D.; Kronewald, T.; Hener, U.; Schleucher, J.; Mosandl, A.; Keppler, F. Improved Rapid Authentication of Vanillin Using δ13C and δ2H Values. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2010, 231, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, H.-W.; Epstein, S. Hydrogen and Carbon Isotopes of Petroleum and Related Organic Matter. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 1981, 45, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gat, J.R. Oxygen and Hydrogen Isotopes in the Hydrologic Cycle. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1996, 24, 225–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Veer, G.; Voerkelius, S.; Lorentz, G.; Heiss, G.; Hoogewerff, J.A. Spatial Interpolation of the Deuterium and Oxygen-18 Composition of Global Precipitation Using Temperature as Ancillary Variable. J. Geochem. Explor. 2009, 101, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Geographical Origin | % Curcumin | % Demethoxy Curcumin | % Didemethoxy Curcumin | Carbon 14 % | δ2H (‰. vs. V-SMOW) | δ13C (‰. vs. V-PDB) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synthetic | India | 79.0 | 17.0 | 3.9 | 0.0 | 52 | −26.4 |
| India | 78.0 | 18.0 | 3.9 | <2 | 58 | −26.3 | |
| India | 77.5 | 18.2 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 47 | −26.7 | |
| India | 77.6 | 17.8 | 3.9 | 5 | 42 | −29.0 | |
| India | 79.0 | 17.1 | 3.8 | 5 | 44 | −29.0 | |
| India | 78.0 | 18.1 | 3.7 | <2 | 62 | −28.4 | |
| Mean | 51 | −27.6 | |||||
| SD | 8 | 1.3 | |||||
| Natural | China | 78.7 | 11.2 | 1.4 | 90.0 | −108 | −30.2 |
| India | 76.2 | 13.8 | 2.2 | 96.2 | −86 | −30.7 | |
| China | 78.7 | 11.2 | 1.4 | 96.3 | −108 | −30.2 | |
| India | 71.4 | 16.4 | 2.9 | 97.2 | −83 | −29.3 | |
| China | 79.2 | 11.3 | 1.3 | 85.0 | −98 | −30.1 | |
| India | 71.4 | 16.4 | 2.9 | 97.2 | −86 | −29.4 | |
| India | 74.1 | 14.1 | 1.9 | 97.4 | −82 | −29.1 | |
| India | 74.2 | 14.4 | 2.7 | 97.9 | −92 | −29.8 | |
| India | 76.1 | 16.9 | 3.0 | 98.7 | −97 | −29.5 | |
| China | 71.7 | 15.7 | 7.2 | 99.7 | −95 | −30.6 | |
| China | 78.4 | 10.9 | 0.9 | 99.8 | −120 | −30.5 | |
| India | 78.5 | 14.6 | 1.3 | 100.3 | −86 | −29.0 | |
| India | 78.3 | 11.4 | 1.3 | 97.4 | −83 | −30.4 | |
| India | 76.4 | 12.4 | 2.3 | 97 | −84 | −30.4 | |
| China | 79.0 | 16.3 | 2.6 | 100.7 | −110 | −30.9 | |
| India | 72.0 | 16.0 | 2.8 | 97.8 | −83 | −29.4 | |
| India | 73.1 | 15.0 | 2.8 | 98.6 | −87 | −29.6 | |
| India | 75.6 | 12.0 | 2.6 | 99.7 | −90.2 | −28.9 | |
| China | 76.6 | 18.0 | 2.0 | 97.8 | −109.8 | −29.7 | |
| India | 78.9 | 15.0 | 1.9 | 98.3 | −87.5 | −29.1 | |
| India | 74.3 | 18.0 | 2.0 | 97.4 | −87.1 | −29.4 | |
| Mean | −93 | −29.8 | |||||
| SD | 11 | 0.6 | |||||
| Limit 95% | −71 | −28.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perini, M.; Pianezze, S.; Ziller, L.; Larcher, R.; Pace, R. Stable Isotope Ratio Analysis for the Authentication of Natural Antioxidant Curcuminoids from Curcuma longa (Turmeric). Antioxidants 2023, 12, 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12020498
Perini M, Pianezze S, Ziller L, Larcher R, Pace R. Stable Isotope Ratio Analysis for the Authentication of Natural Antioxidant Curcuminoids from Curcuma longa (Turmeric). Antioxidants. 2023; 12(2):498. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12020498
Chicago/Turabian StylePerini, Matteo, Silvia Pianezze, Luca Ziller, Roberto Larcher, and Roberto Pace. 2023. "Stable Isotope Ratio Analysis for the Authentication of Natural Antioxidant Curcuminoids from Curcuma longa (Turmeric)" Antioxidants 12, no. 2: 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12020498
APA StylePerini, M., Pianezze, S., Ziller, L., Larcher, R., & Pace, R. (2023). Stable Isotope Ratio Analysis for the Authentication of Natural Antioxidant Curcuminoids from Curcuma longa (Turmeric). Antioxidants, 12(2), 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12020498








