Dietary Mg Supplementation Decreases Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Vascular Dysfunction in an Experimental Model of Metabolic Syndrome with Renal Failure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. In Vivo Experiments
Animals and Surgical Procedures
2.2. Blood Pressure (BP) Measurements
2.3. Blood Chemistry
2.4. Evaluation of Oxidative Stress
2.5. Real-Time PCR
2.6. Protein Extracts and Western Blot
2.7. Proteomic Studies by DIA-SWATH in Aortic Tissue
2.7.1. Sample Preparation
2.7.2. Mass Spectrometry
2.7.3. Data Analysis
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Biochemical Parameters
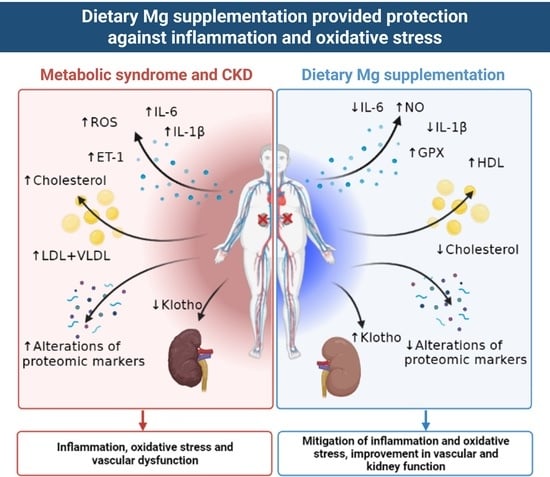
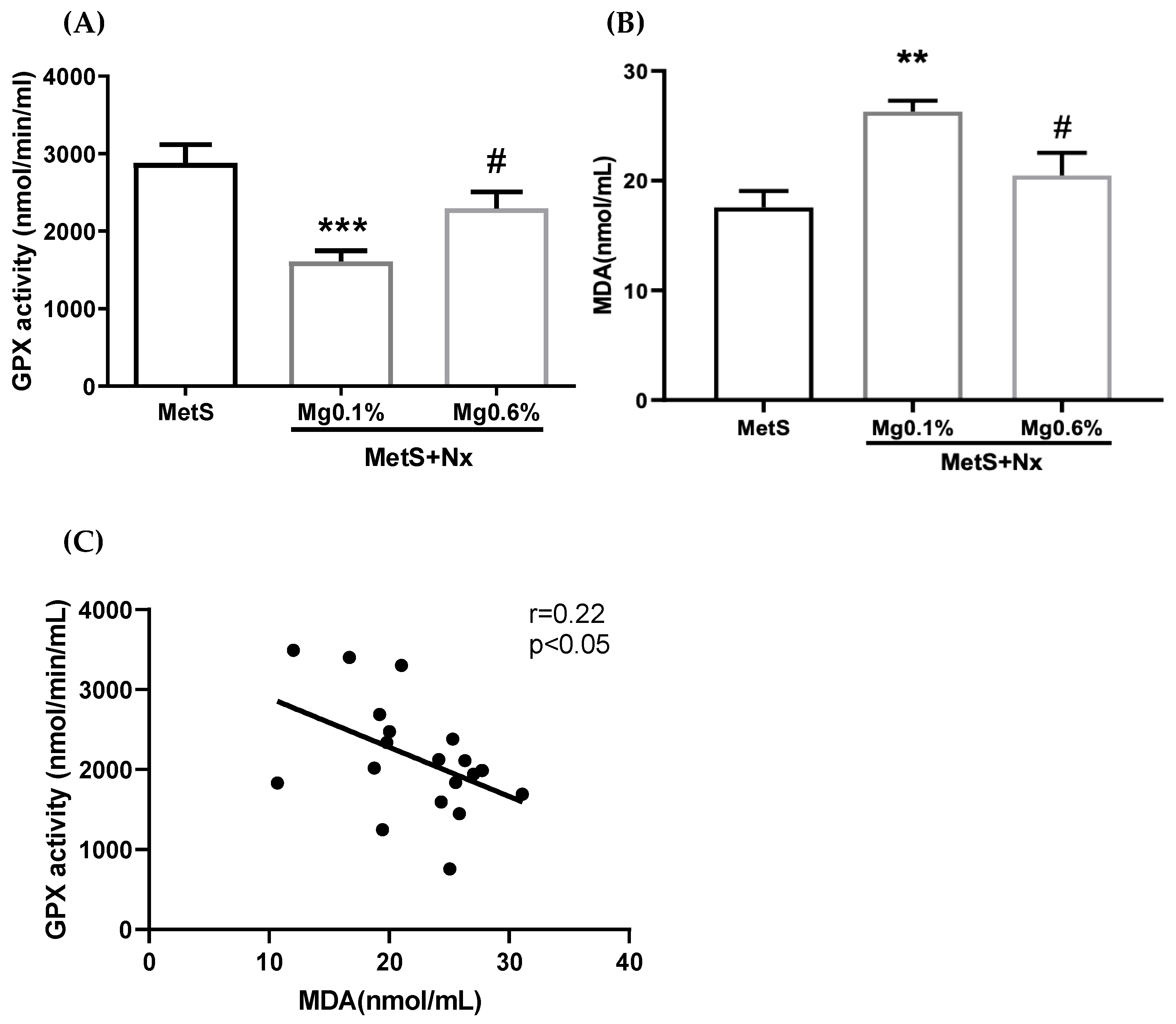
3.2. Dietary Mg Supplementation Reduced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Rats with MetS and CKD
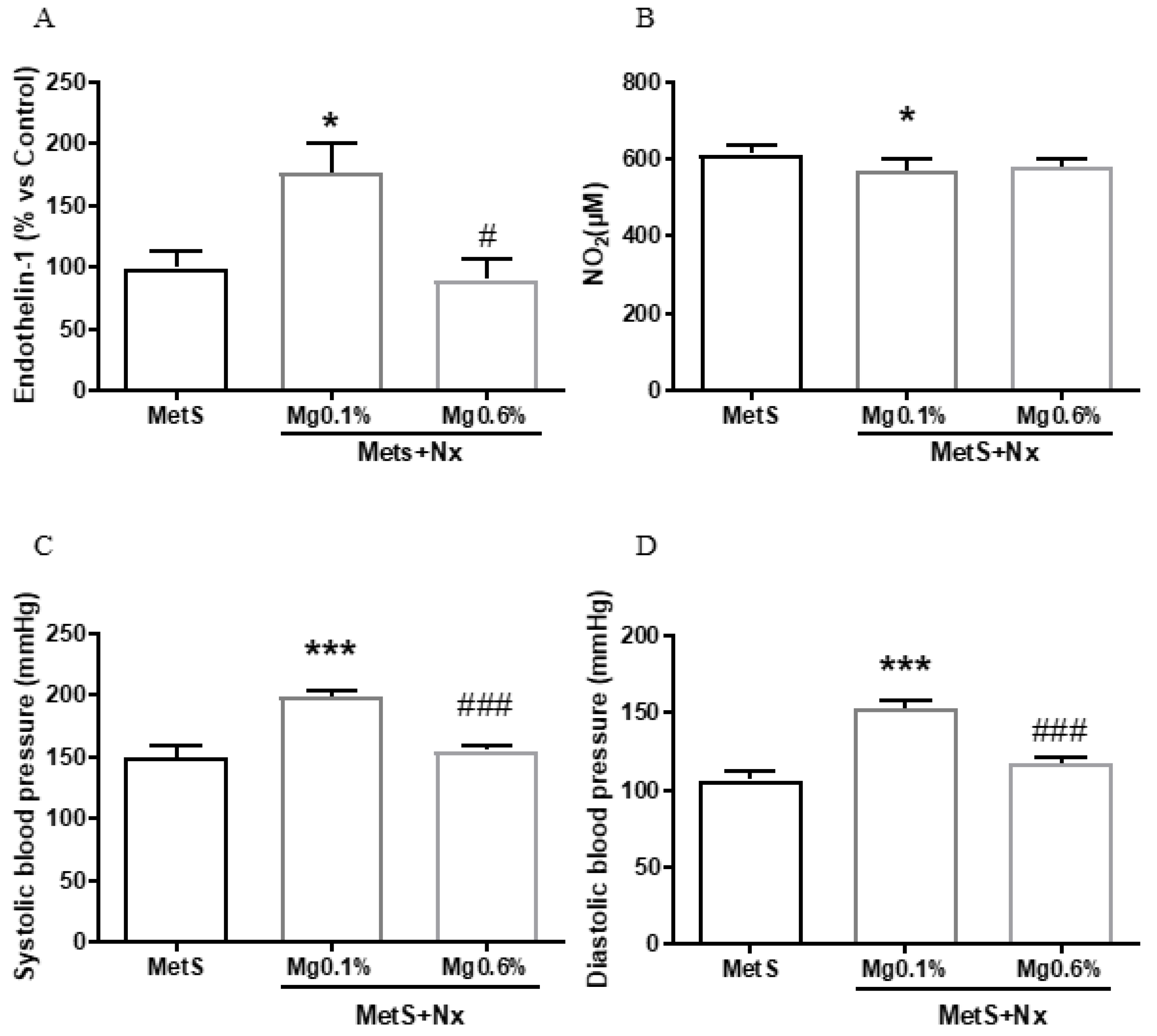
3.3. Dietary Mg Supplementation Prevented Endothelial Dysfunction in Rats with MetS and CKD
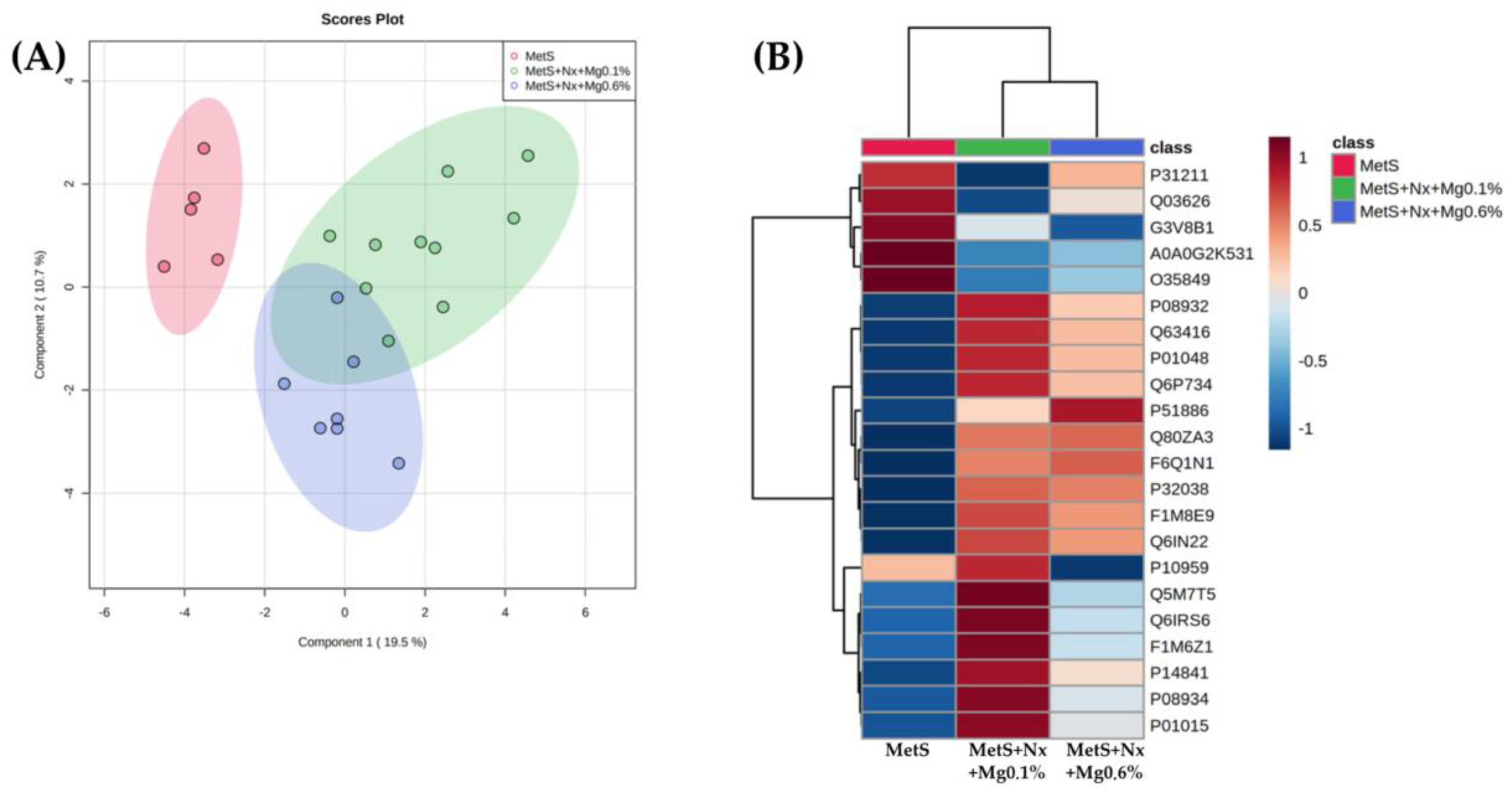
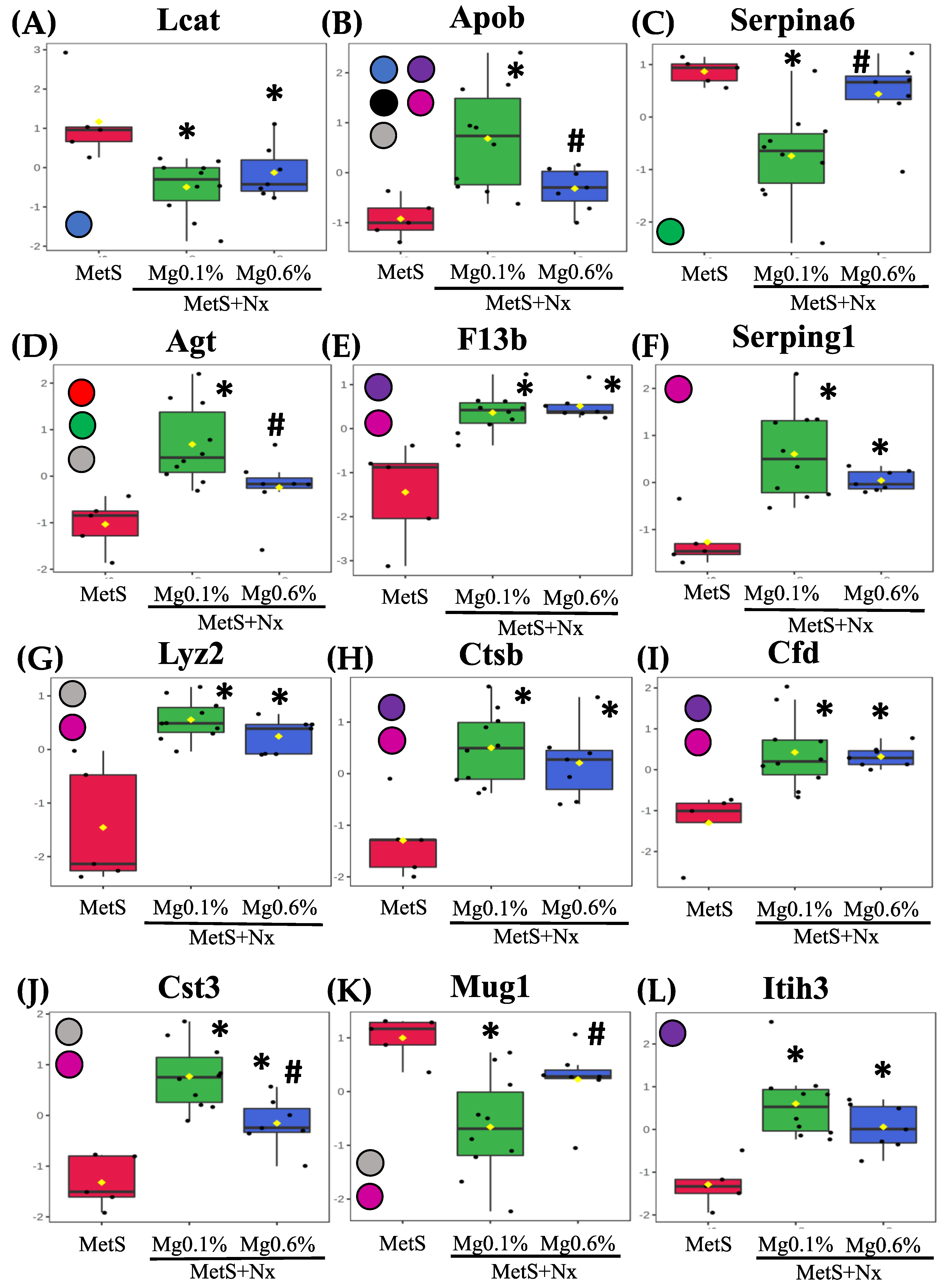
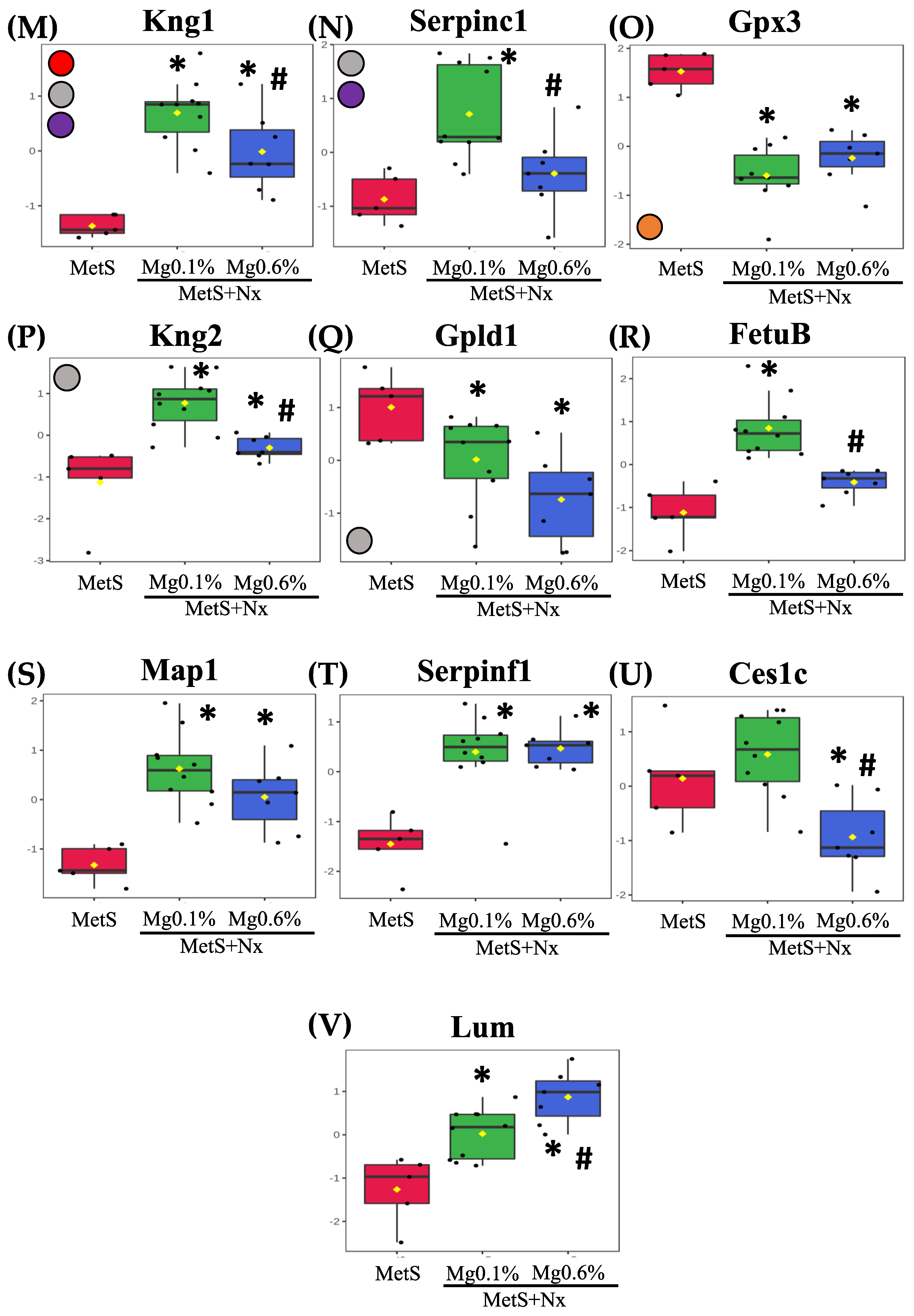
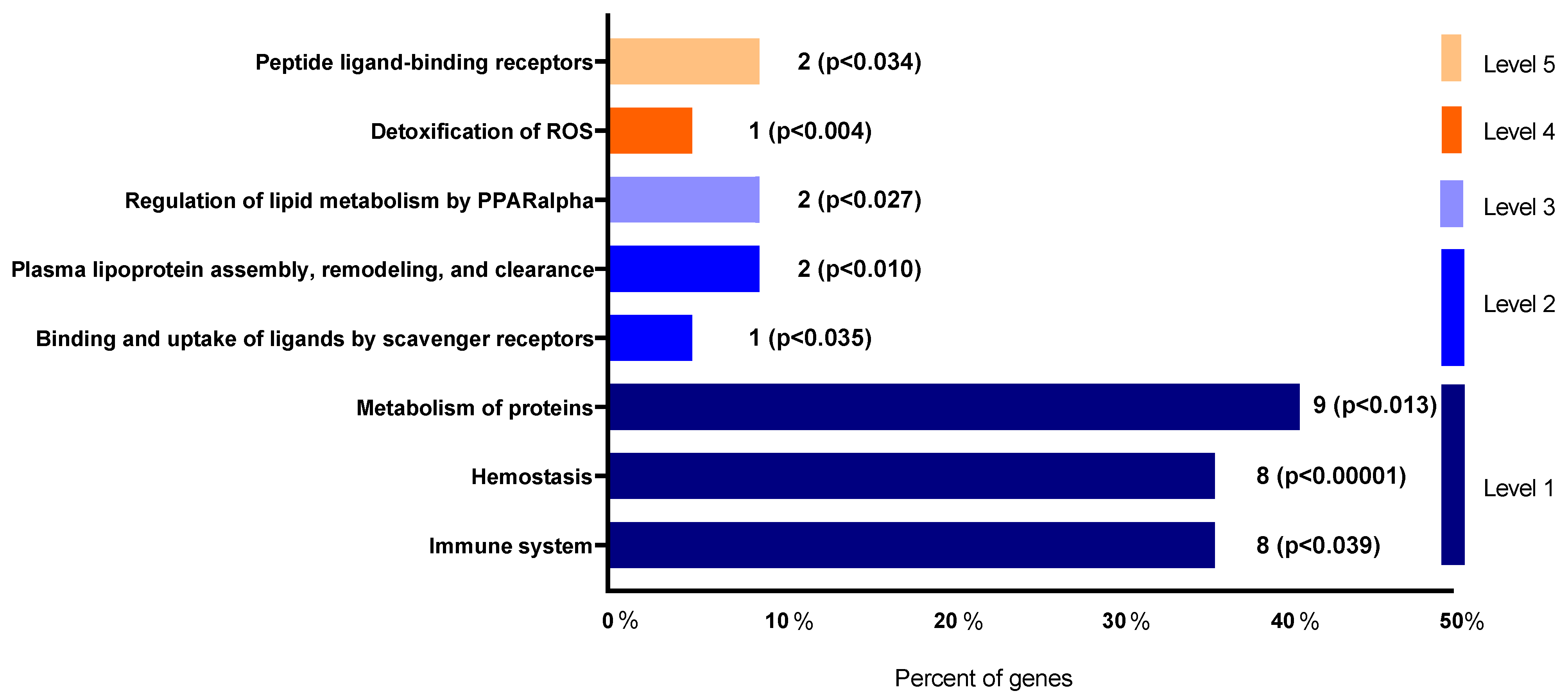
3.4. Dietary Mg Supplementation Altered Proteomic Markers of MetS, CKD and Vascular Dysfunction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rochlani, Y.; Pothineni, N.V.; Kovelamudi, S.; Mehta, J.L. Metabolic Syndrome: Pathophysiology, Management, and Modulation by Natural Compounds. Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 11, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gami, A.S.; Witt, B.J.; Howard, D.E.; Erwin, P.J.; Gami, L.A.; Somers, V.K.; Montori, V.M. Metabolic Syndrome and Risk of Incident Cardiovascular Events and Death: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Longitudinal Studies. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 49, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mottillo, S.; Filion, K.B.; Genest, J.; Joseph, L.; Pilote, L.; Poirier, P.; Rinfret, S.; Schiffrin, E.L.; Eisenberg, M.J. The Metabolic Syndrome and Cardiovascular Risk a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 56, 1113–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tirandi, A.; Carbone, F.; Montecucco, F.; Liberale, L. The Role of Metabolic Syndrome in Sudden Cardiac Death Risk: Recent Evidence and Future Directions. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2022, 52, e13693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhan-Vague, I.; Alessi, M.C.; Mavri, A.; Morange, P.E. Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1, Inflammation, Obesity, Insulin Resistance and Vascular Risk. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2003, 1, 1575–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahba, I.M.; Mak, R.H. Obesity and Obesity-Initiated Metabolic Syndrome: Mechanistic Links to Chronic Kidney Disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 2, 550–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández-Sánchez, A.; Madrigal-Santillán, E.; Bautista, M.; Esquivel-Soto, J.; Morales-González, Á.; Esquivel-Chirino, C.; Durante-Montiel, I.; Sánchez-Rivera, G.; Valadez-Vega, C.; Morales-González, J.A. Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 3117–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gobal, F.; Deshmukh, A.; Shah, S.; Mehta, J.L. Triad of Metabolic Syndrome, Chronic Kidney Disease, and Coronary Heart Disease with a Focus on Microalbuminuria Death by Overeating. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 2303–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steven, S.; Frenis, K.; Oelze, M.; Kalinovic, S.; Kuntic, M.; Jimenez, M.T.B.; Vujacic-Mirski, K.; Helmstädter, J.; Kröller-Schön, S.; Münzel, T.; et al. Vascular Inflammation and Oxidative Stress: Major Triggers for Cardiovascular Disease. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 7092151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maslov, L.N.; Naryzhnaya, N.V.; Boshchenko, A.A.; Popov, S.V.; Ivanov, V.V.; Oeltgen, P.R. Is Oxidative Stress of Adipocytes a Cause or a Consequence of the Metabolic Syndrome? J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol. 2018, 15, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podkowińska, A.; Formanowicz, D. Chronic Kidney Disease as Oxidative Stress- and Inflammatory-Mediated Cardiovascular Disease. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapa, S.F.; Di Iorio, B.R.; Campiglia, P.; Heidland, A.; Marzocco, S. Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Chronic Kidney Disease-Potential Therapeutic Role of Minerals, Vitamins and Plant-Derived Metabolites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agharazii, M.; St-Louis, R.; Gautier-Bastien, A.; Ung, R.V.; Mokas, S.; Larivière, R.; Richard, D.E. Inflammatory Cytokines and Reactive Oxygen Species as Mediators of Chronic Kidney Disease-Related Vascular Calcification. Am. J. Hypertens. 2015, 28, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silverstein, D.M. Inflammation in Chronic Kidney Disease: Role in the Progression of Renal and Cardiovascular Disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2009, 24, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnieri, G.; Zanetti, M.; Vinci, P.; Cattin, M.R.; Pirulli, A.; Barazzoni, R. Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2010, 20, S19–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, G.R. Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease: Current Status and Future Directions. World J. Nephrol. 2014, 3, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Tan, W.; Pan, X.; Tian, E.; Wu, Z.; Yang, J. Metabolic Syndrome-Related Kidney Injury: A Review and Update. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 904001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, G.; Sehgal, A.R.; Kashyap, S.R.; Srinivas, T.R.; Kirwan, J.P.; Navaneethan, S.D. Metabolic Syndrome and Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 2364–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Locatelli, F.; Pozzoni, P.; Del Vecchio, L. Renal Manifestations in the Metabolic Syndrome. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, S81–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malpuech-Brugère, C.; Nowacki, W.; Daveau, M.; Gueux, E.; Linard, C.; Rock, E.; Lebreton, J.P.; Mazur, A.; Rayssiguier, Y. Inflammatory Response Following Acute Magnesium Deficiency in the Rat. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2000, 1501, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheltova, A.A.; Kharitonova, M.V.; Iezhitsa, I.N.; Spasov, A.A. Magnesium Deficiency and Oxidative Stress: An Update. Biomedicine 2016, 6, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazur, A.; Maier, J.A.M.; Rock, E.; Gueux, E.; Nowacki, W.; Rayssiguier, Y. Magnesium and the Inflammatory Response: Potential Physiopathological Implications. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 458, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharitonova, M.; Iezhitsa, I.; Zheltova, A.; Ozerov, A.; Spasov, A.; Skalny, A. Comparative Angioprotective Effects of Magnesium Compounds. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2015, 29, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altura, B.M.; Altura, B.T. Magnesium and Cardiovascular Biology: An Important Link between Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Atherogenesis. Cell. Mol. Biol. Res. 1995, 41, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Del Gobbo, L.C.; Imamura, F.; Wu, J.H.Y.; De Oliveira Otto, M.C.; Chiuve, S.E.; Mozaffarian, D. Circulating and Dietary Magnesium and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 98, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dinicolantonio, J.J.; Liu, J.; O’Keefe, J.H. Magnesium for the Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease. Open Heart 2018, 5, e000775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lipsky, M.S.; Mendelson, M.; Havas, S.; Miller, M. American Medical Association Guide to Preventing and Treating Heart Disease: Essential Information You and Your Family Need to Know about Having a Healthy Heart, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, S.Y.; Choi, W.S.; Ock, S.M.; Kim, C.M.; Kim, D.H. Dietary Magnesium Intake and Metabolic Syndrome in the Adult Population: Dose-Response Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression. Nutrients 2014, 6, 6005–6019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarrafzadegan, N.; Khosravi-Boroujeni, H.; Lotfizadeh, M.; Pourmogaddas, A.; Salehi-Abargouei, A. Magnesium Status and the Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrition 2016, 32, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakaguchi, Y.; Iwatani, H.; Hamano, T.; Tomida, K.; Kawabata, H.; Kusunoki, Y.; Shimomura, A.; Matsui, I.; Hayashi, T.; Tsubakihara, Y.; et al. Magnesium Modifies the Association between Serum Phosphate and the Risk of Progression to End-Stage Kidney Disease in Patients with Non-Diabetic Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrè, S.; Li, X.; Adams-Huet, B.; Maalouf, N.M.; Sakhaee, K.; Toto, R.D.; Moe, O.W.; Neyra, J.A. Low Serum Magnesium Is Associated with Faster Decline in Kidney Function: The Dallas Heart Study Experience. J. Investig. Med. 2019, 67, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diaz-Tocados, J.M.; Peralta-Ramirez, A.; Rodríguez-Ortiz, M.E.; Raya, A.I.; Lopez, I.; Pineda, C.; Herencia, C.; Montes de Oca, A.; Vergara, N.; Steppan, S.; et al. Dietary Magnesium Supplementation Prevents and Reverses Vascular and Soft Tissue Calcifications in Uremic Rats. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 1084–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralser, M.; Vowinckel, J.; Capuano, F.; Campbell, K.; Deery, M.J.; Lilley, K.S. The Beauty of Being (Label)-Free: Sample Preparation Methods for SWATH-MS and next-Generation Targeted Proteomics. F1000Research 2014, 2, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara, N.; De Mier, M.V.P.-R.; Rodelo-Haad, C.; Revilla-González, G.; Membrives, C.; Díaz-Tocados, J.M.; Martínez-Moreno, J.M.; Torralbo, A.I.; Herencia, C.; Rodríguez-Ortiz, M.E.; et al. The Direct Effect of Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 on Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Phenotype and Function. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2022, Volume, gfac220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Baltanás, R.; Encarnación Rodríguez-Ortiz, M.; Canalejo, A.; Díaz-Tocados, J.M.; Herencia, C.; Leiva-Cepas, F.; Torres-Peña, J.D.; Ortíz-Morales, A.; Muñoz-Castañeda, J.R.; Rodríguez, M.; et al. Magnesium Supplementation Reduces Inflammation in Rats with Induced Chronic Kidney Disease. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 51, e13561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitin, J.C.; Bhamre, S.; Tham, D.M.; Cohen, H.J. Extracellular Glutathione Peroxidase Is Secreted Basolaterally by Human Renal Proximal Tubule Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2002, 283, F20–F28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Worley, B.L.; Phaëton, R.; Hempel, N. Extracellular Glutathione Peroxidase GPx3 and Its Role in Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, T.; Shimada, K.; Sato, O.; Kotani, K.; Kume, A.; Sumiyoshi, K.; Sato, Y.; Ohmura, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Mokuno, H.; et al. Circulating Malondialdehyde-Modified LDL and Atherogenic Lipoprotein Profiles Measured by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. Atherosclerosis 2005, 179, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastre, C.; Rubio-Navarro, A.; Buendiá, I.; Goḿez-Guerrero, C.; Blanco, J.; Mas, S.; Egido, J.; Blanco-Colio, L.M.; Ortiz, A.; Moreno, J.A. Hyperlipidemia-Associated Renal Damage Decreases Klotho Expression in Kidneys from ApoE Knockout Mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuro-o, M. Klotho as a Regulator of Oxidative Stress and Senescence. Biol. Chem. 2008, 389, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Yang, H.; Guo, X.; Sun, Y. Klotho Attenuates Angiotensin II-induced Cardiotoxicity through Suppression of Necroptosis and Oxidative Stress. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.Y.; Ma, H.X. Significant Roles of Anti-Aging Protein Klotho and Fibroblast Growth Factor23 in Cardiovascular Disease. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2015, 12, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keles, N.; Dogan, B.; Kalcik, M.; Caliskan, M.; Keles, N.N.; Aksu, F.; Bulut, M.; Kostek, O.; Isbilen, B.; Yilmaz, Y.; et al. Is Serum Klotho Protective against Atherosclerosis in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus? J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2016, 30, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.A.I.; Larsson, A.; Lind, L.; Larsson, T.E. Circulating Fibroblast Growth Factor-23 Is Associated with Vascular Dysfunction in the Community. Atherosclerosis 2009, 205, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, S.M.; Fineman, J.R. Oxidative and Nitrosative Stress in Pediatric Pulmonary Hypertension: Roles of Endothelin-1 and Nitric Oxide. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2006, 45, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaskonen, T.; Mervaala, E.; Seppänen-Laakso, T.; Karppanen, H. Diet Enrichment with Calcium and Magnesium Enhances the Cholesterol-Lowering Effect of Plant Sterols in Obese Zucker Rats. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2001, 11, 158–167. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, J.; Jain, A.; Bhamra, R.; Rathi, V.; Dhingra, A.K. The Mechanistic Role of Different Mediators in the Pathophysiology of Nephropathy: A Review. Curr. Drug Targets 2022, 24, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, A.A.; Bankier, S.; Altmaier, E.; Barnes, C.L.K.; Clark, D.W.; Ermel, R.; Friedrich, N.; Van der Harst, P.; Joshi, P.K.; Karhunen, V.; et al. Variation in the SERPINA6/SERPINA1 Locus Alters Morning Plasma Cortisol, Hepatic Corticosteroid Binding Globulin Expression, Gene Expression in Peripheral Tissues, and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 66, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behbodikhah, J.; Ahmed, S.; Elyasi, A.; Kasselman, L.J.; De Leon, J.; Glass, A.D.; Reiss, A.B. Apolipoprotein B and Cardiovascular Disease: Biomarker and Potential Therapeutic Target. Metabolites 2021, 11, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lygirou, V.; Latosinska, A.; Makridakis, M.; Mullen, W.; Delles, C.; Schanstra, J.P.; Zoidakis, J.; Pieske, B.; Mischak, H.; Vlahou, A. Plasma Proteomic Analysis Reveals Altered Protein Abundances in Cardiovascular Disease. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz Ocaranza, M.; Riquelme, J.A.; García, L.; Jalil, J.E.; Chiong, M.; Santos, R.A.S.; Lavandero, S. Counter-Regulatory Renin-Angiotensin System in Cardiovascular Disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, H.; Cassis, L.A.; Kooi, C.W.V.; Daugherty, A. Structure and Functions of Angiotensinogen. Hypertens. Res. 2016, 39, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roxborough, H.E.; Mercer, C.; McMaster, D.; Maxwell, A.P.; Young, I.S. Plasma Glutathione Peroxidase Activity Is Reduced in Haemodialysis Patients. Nephron 1999, 81, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, P.; Abbott, M.; Abdi, M.; Fucci, Q.A.; Chauhan, N.; Mistri, M.; Proctor, B.; Chin, M.; Wang, B.; Yin, W.; et al. Pre-Clinical Model of Severe Glutathione Peroxidase-3 Deficiency and Chronic Kidney Disease Results in Coronary Artery Thrombosis and Depressed Left Ventricular Function. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rhaleb, N.E.; Yang, X.P.; Carretero, O.A. The Kallikrein-Kinin System as a Regulator of Cardiovascular and Renal Function. Compr. Physiol. 2011, 1, 971–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, X.; Liu, D.; Song, H.; Tian, X.; Yan, C.; Han, Y. Overexpression of Kininogen-1 Aggravates Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in DOX-Induced Cardiotoxicity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 550, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taglieri, N.; Koenig, W.; Kaski, J.C. Cystatin C and Cardiovascular Risk. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 1932–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balta, S.; Demirkol, S.; Ay, S.A.; Cakar, M.; Sarlak, H.; Celik, T. Serum Cystatin-C Levels Correlate with Endothelial Dysfunction in Patients with the Metabolic Syndrome. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 274, 200–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalise, U.; Daseke, M.J.; Kalusche, W.J.; Konfrst, S.R.; Rodriguez-Paar, J.R.; Flynn, E.R.; Cook, L.M.; Becirovic-Agic, M.; Lindsey, M.L. Macrophages Secrete Murinoglobulin-1 and Galectin-3 to Regulate Neutrophil Degranulation after Myocardial Infarction. Mol. Omics 2022, 18, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Jin, F.; Hao, Y.; Li, H.; Tang, T.; Wang, H.; Yan, W.; Dai, K. Magnesium and the Risk of Cardiovascular Events: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gröber, U.; Schmidt, J.; Kisters, K. Magnesium in Prevention and Therapy. Nutrients 2015, 7, 8199–8226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bo, S.; Pisu, E. Role of Dietary Magnesium in Cardiovascular Disease Prevention, Insulin Sensitivity and Diabetes. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2008, 19, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syauqy, A.; Hsu, C.Y.; Lee, H.A.; Rau, H.H.; Chao, J.C.J. Association between Dietary Patterns and Kidney Function Parameters in Adults with Metabolic Syndrome: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2020, 13, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sham -MetS | MetS+Nx +Mg0.1% | MetS+Nx +Mg0.6% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.52 ± 0.1 | 1.59 ± 0.2 * | 0.99 ± 0.1 *# |
| Phosphate (mg/dL) | 8.75 ± 0.35 | 13.05 ± 0.9 * | 10.63 ± 0.4 *# |
| Magnesium (mg/dL) | 2.30 ± 0.2 | 3.97 ± 0.3 * | 6.24 ± 0.8 *# |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 269 ± 54.5 | 426.7 ± 34.5 * | 297.7 ± 35.1 |
| FGF23 (pg/mL) | 692.5 ± 32.2 | 2275 ± 270.1 *** | 1229 ± 142.1 ## |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) * | 256.2 ± 19.5 | 326 ± 13.5 ** | 285.3 ± 19.6# |
| HDL (mg/dL) * | 67.06 ± 0.6 | 64.05 ± 7.6 | 82.7 ± 5.6 *# |
| No-HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) * | 189.1 ± 19.8 | 256.6 ± 14 ** | 202.6 ± 14.9# |
| Urine phosphate (mg/24 h) | 2.98 ± 0.4 | 24,97 ± 2.3 * | 12.11 ± 0.8 *# |
| Urine magnesium (mg/24 h) | 7.08 ± 1.3 | 3.37 ± 0.2 * | 8.02 ± 0.9 # |
| Protein Accession | Gene | Protein | F Value | p Value | -LOG(10) | FDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0A0G2K531 | Gpx3 | Glutathione peroxidase 3 | 27.743 | 0.00 | 56.366 | 0.0005 |
| P14841 | Cst3 | Cystatin-C | 22.699 | 0.00 | 50.362 | 0.0008 |
| Q6IRS6 | Fetub | Fetuin B | 21.764 | 0.00 | 49.145 | 0.0008 |
| P08932 | Kng1 | Kininogen-1 | 19.747 | 0.00 | 46.394 | 0.0010 |
| F1M8E9 | Lyz2 | Lysozyme | 19.449 | 0.00 | 45.972 | 0.0010 |
| Q80ZA3 | Serpinf1 | Alpha-2 antiplasmin | 17.566 | 0.00 | 43.197 | 0.0014 |
| F6Q1N1 | F13b | Coagulation factor XIII B chain | 17.432 | 0.00 | 42.992 | 0.0014 |
| P51886 | Lum | Lumican | 16.253 | 0.00 | 41.145 | 0.0019 |
| P08934 | Kng2 | Kininogen-2 | 15.403 | 0.00 | 3.976 | 0.0023 |
| P01048 | Map1 | T-kininogen 1 | 14.581 | 0.00 | 38.375 | 0.0028 |
| Q63416 | Itih3 | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H3 | 12.493 | 0.00 | 34.634 | 0.0061 |
| Q6P734 | Serping1 | Plasma protease C1 inhibitor | 11,91 | 0.00 | 33.525 | 0.0072 |
| Q6IN22 | Ctsb | Cathepsin B | 10.841 | 0.00 | 31.412 | 0.0108 |
| P32038 | Cfd | Complement factor D | 10.397 | 0.00 | 30.502 | 0.0124 |
| P31211 | Serpina6 | Corticosteroid-binding globulin | 96.864 | 0.00 | 29.001 | 0.0164 |
| P01015 | Agt | Angiotensinogen | 93.701 | 0.00 | 28.315 | 0.0180 |
| Q5M7T5 | Serpinc1 | Antithrombin-III | 85.016 | 0.00 | 26.371 | 0.0265 |
| Q03626 | Mug1 | Murinoglobulin-1 | 81.335 | 0.00 | 25.518 | 0.0284 |
| P10959 | Ces1c | Carboxylesterase 1C | 80.811 | 0.00 | 25.396 | 0.0284 |
| F1M6Z1 | Apob | Apolipoprotein B-100 | 80.625 | 0.00 | 25.352 | 0.0284 |
| O35849 | Lcat | Phosphatidylcholine-sterol acyltransferase | 76.767 | 0.00 | 24.435 | 0.0334 |
| G3V8B1 | Gpld1 | Phosphatidylinositol-glycan-specific phospholipase D | 70.004 | 0.01 | 22.778 | 0.0468 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López-Baltanás, R.; Rodríguez-Ortiz, M.E.; Díaz-Tocados, J.M.; Martinez-Moreno, J.M.; Membrives, C.; Rodelo-Haad, C.; Pendón Ruiz de Mier, M.V.; Rodríguez, M.; Canalejo, A.; Almadén, Y.; et al. Dietary Mg Supplementation Decreases Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Vascular Dysfunction in an Experimental Model of Metabolic Syndrome with Renal Failure. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12020283
López-Baltanás R, Rodríguez-Ortiz ME, Díaz-Tocados JM, Martinez-Moreno JM, Membrives C, Rodelo-Haad C, Pendón Ruiz de Mier MV, Rodríguez M, Canalejo A, Almadén Y, et al. Dietary Mg Supplementation Decreases Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Vascular Dysfunction in an Experimental Model of Metabolic Syndrome with Renal Failure. Antioxidants. 2023; 12(2):283. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12020283
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez-Baltanás, Rodrigo, María E. Rodríguez-Ortiz, Juan M. Díaz-Tocados, Julio M. Martinez-Moreno, Cristina Membrives, Cristian Rodelo-Haad, M. Victoria Pendón Ruiz de Mier, Mariano Rodríguez, Antonio Canalejo, Yolanda Almadén, and et al. 2023. "Dietary Mg Supplementation Decreases Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Vascular Dysfunction in an Experimental Model of Metabolic Syndrome with Renal Failure" Antioxidants 12, no. 2: 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12020283
APA StyleLópez-Baltanás, R., Rodríguez-Ortiz, M. E., Díaz-Tocados, J. M., Martinez-Moreno, J. M., Membrives, C., Rodelo-Haad, C., Pendón Ruiz de Mier, M. V., Rodríguez, M., Canalejo, A., Almadén, Y., & Muñoz-Castañeda, J. R. (2023). Dietary Mg Supplementation Decreases Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Vascular Dysfunction in an Experimental Model of Metabolic Syndrome with Renal Failure. Antioxidants, 12(2), 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12020283