Dexmedetomidine Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Sympathetic Activation and Sepsis via Suppressing Superoxide Signaling in Paraventricular Nucleus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Rats
2.2. Septic Animal Model
2.3. General Procedures
2.4. RSNA Recording
2.5. PVN Microinjection
2.6. Heart Rate Variability
2.7. PVN Preparation for Measurements
2.8. Measurement of Superoxide Level and NADPH Oxidase Activity
2.9. Detection of Superoxide Production in Brain Slice
2.10. Measurements with Commercial Kits
2.11. Quantitative RT-PCR
2.12. Western Blot
2.13. Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining
2.14. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.15. Chemicals
2.16. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
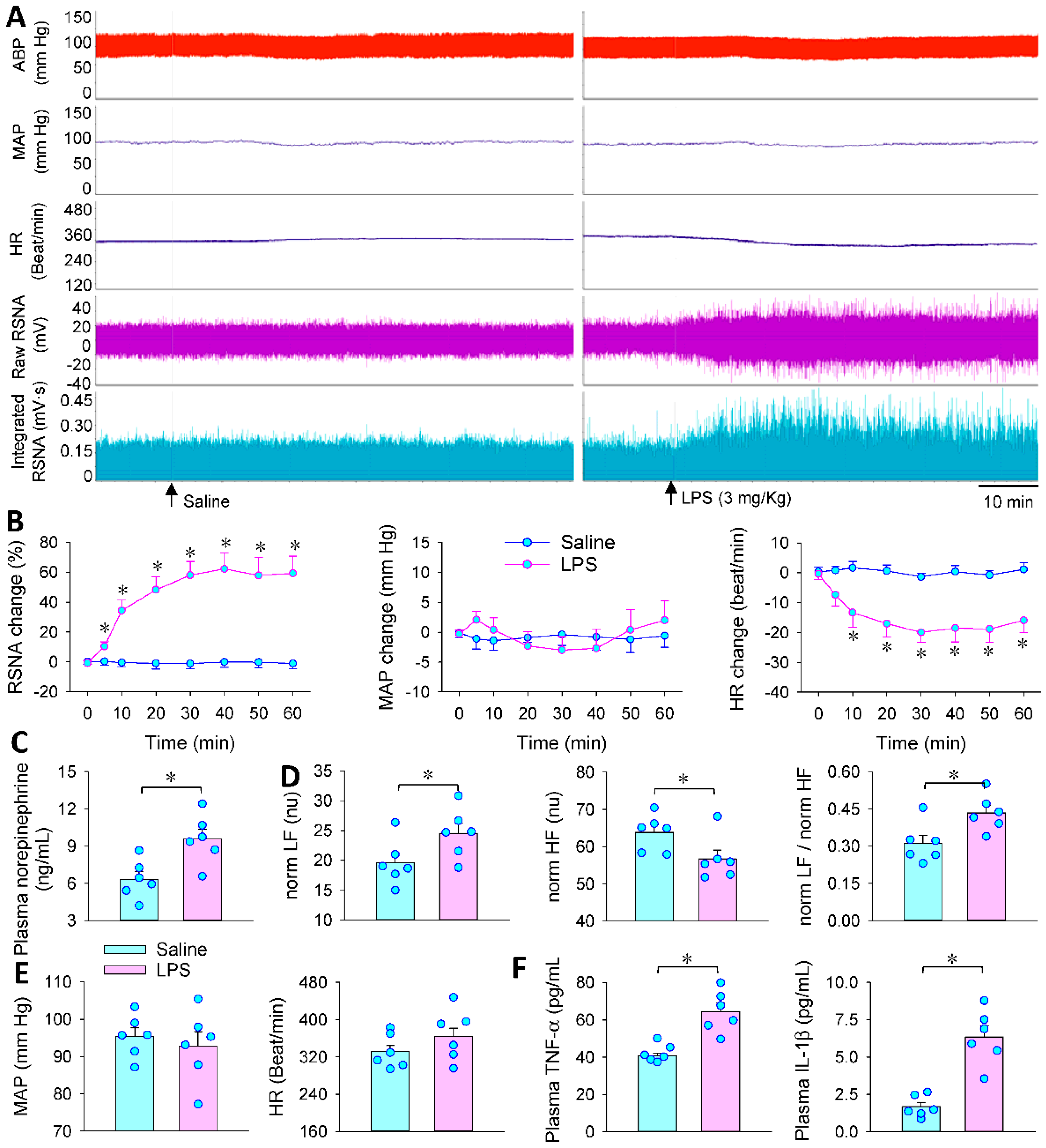
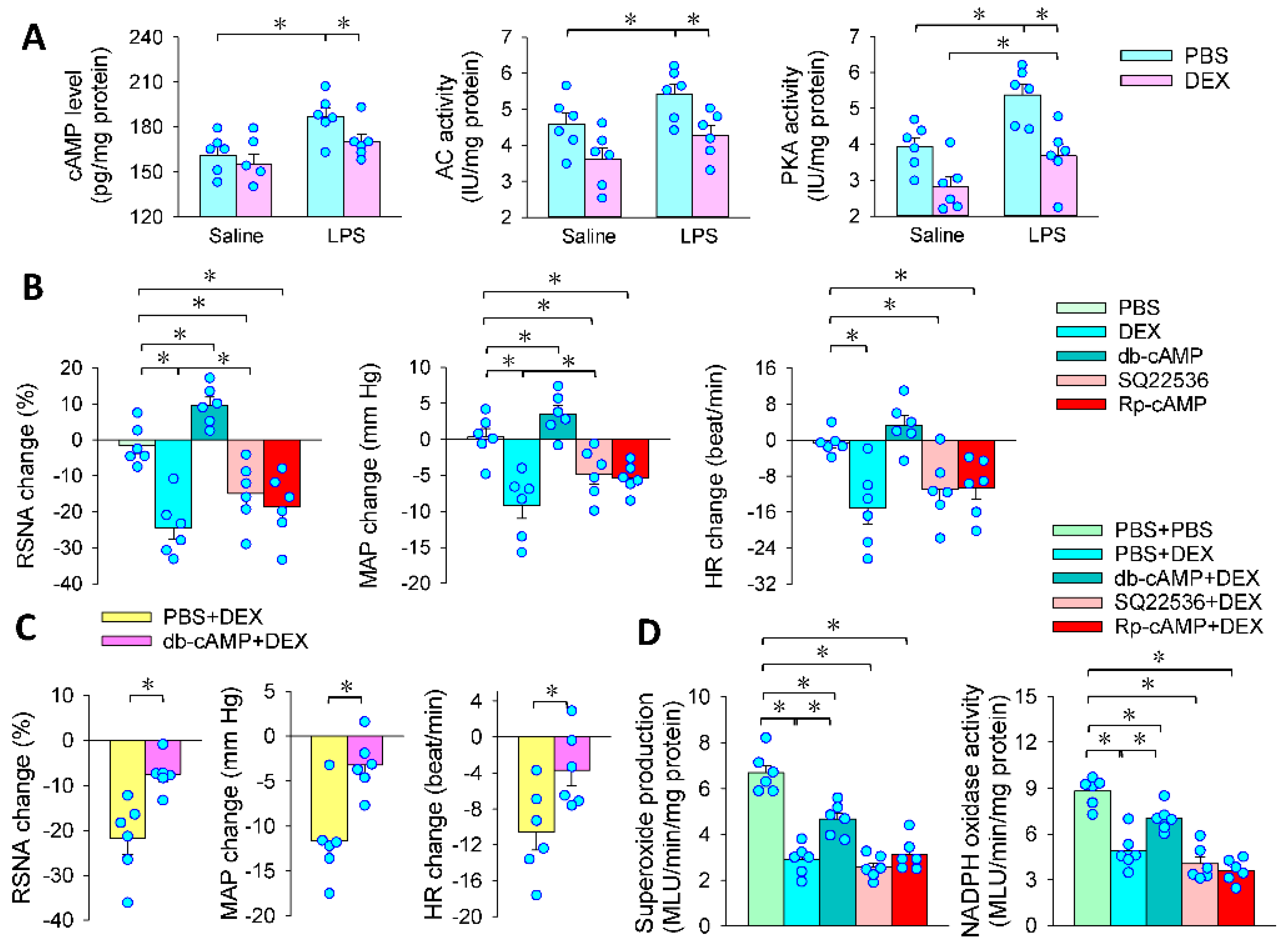
3.1. LPS-Induced Sympathetic Activation
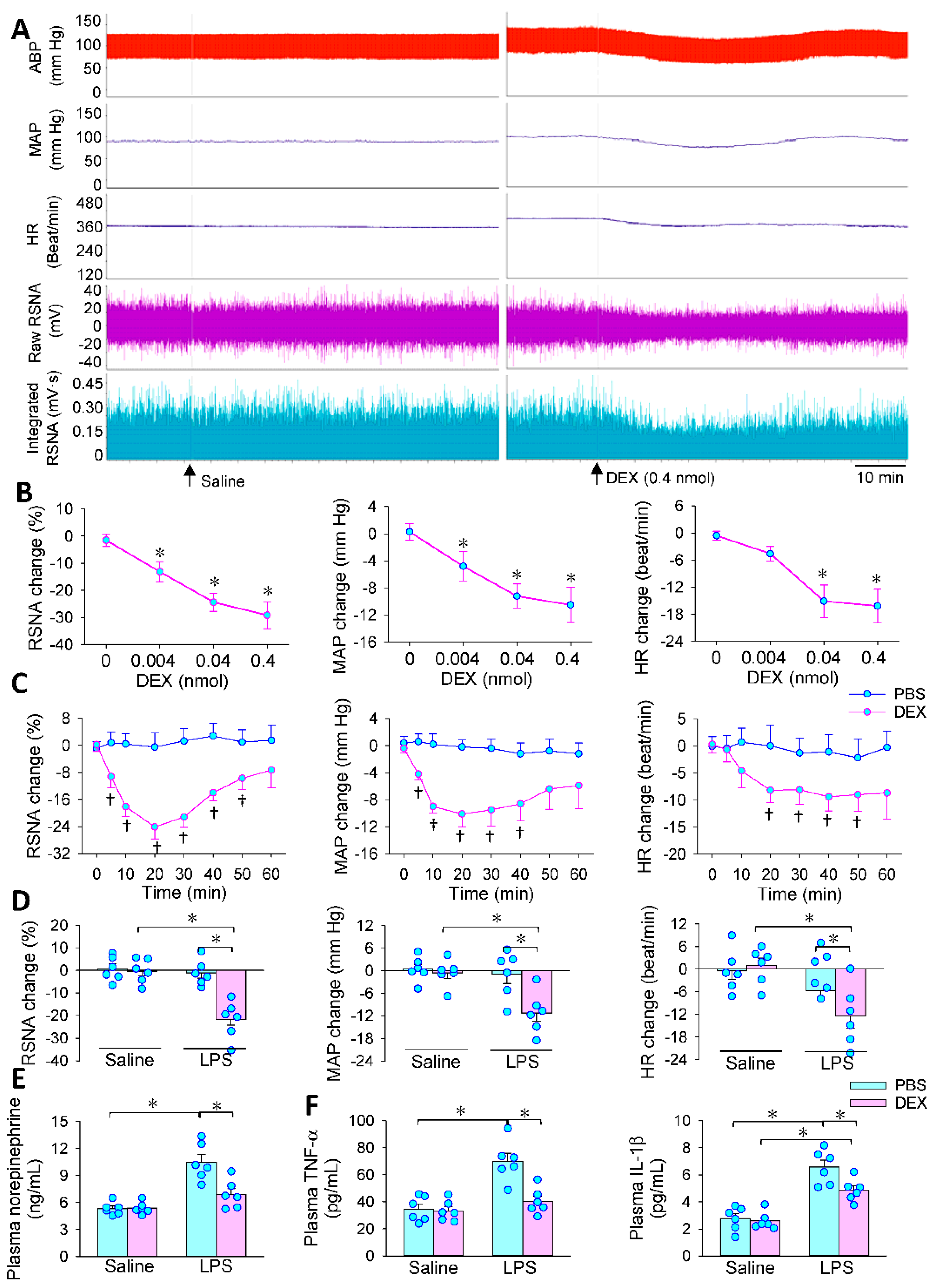
3.2. Effects of PVN Microinjection of DEX on LPS-Induced RSNA, MAP and HR Changes
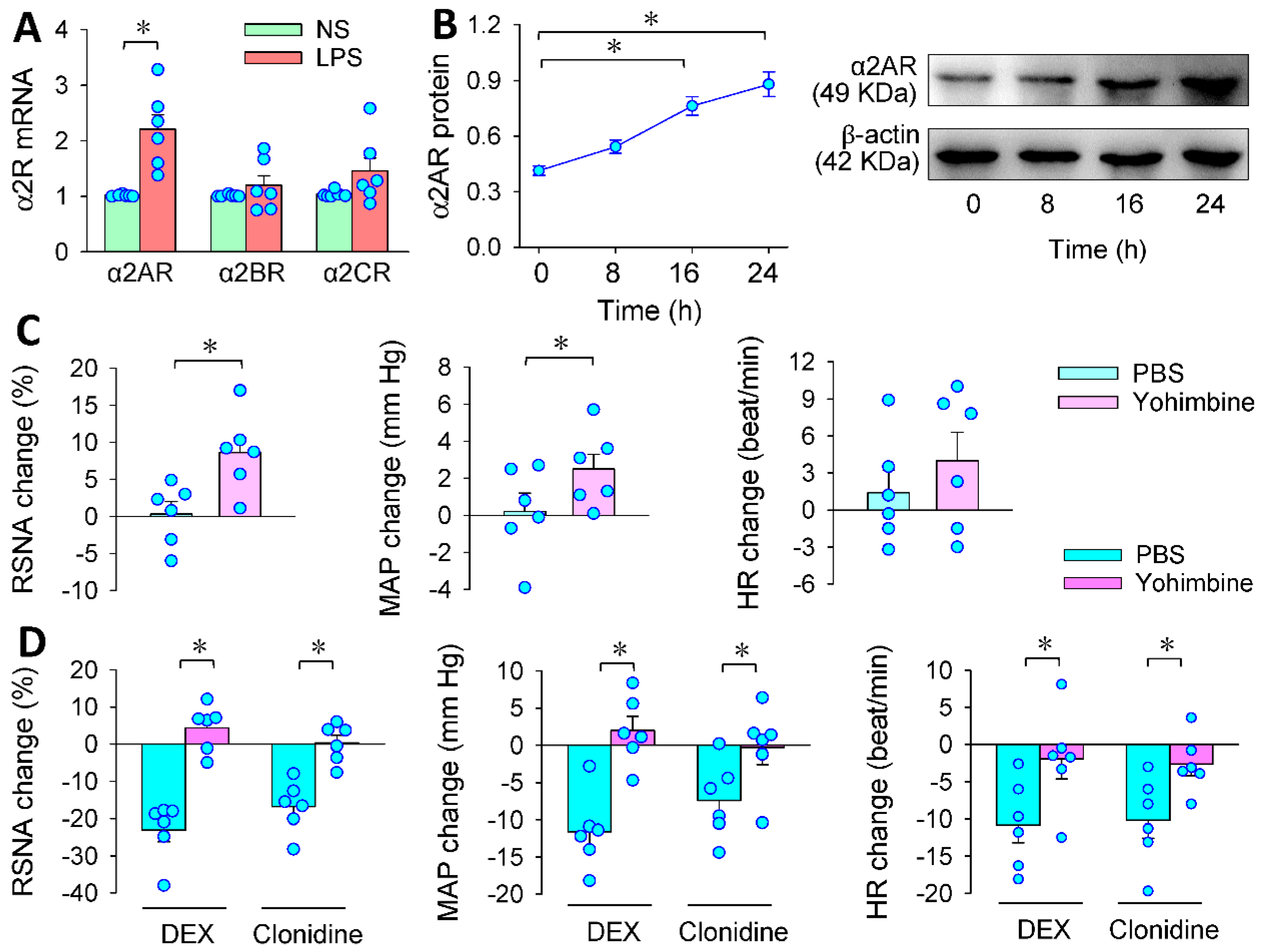
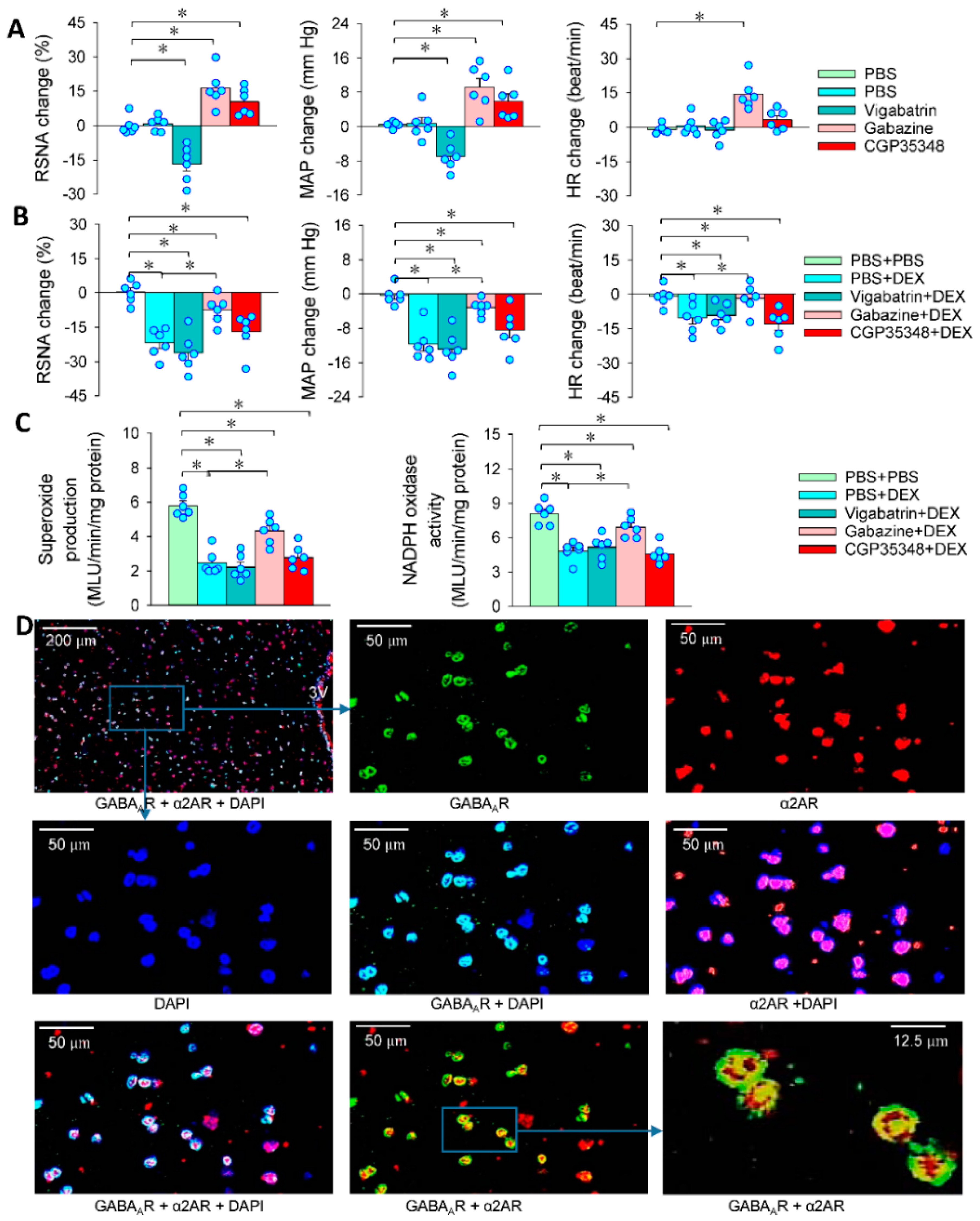
3.3. α2R in the PVN Mediates the Effects of PVN Microinjection of DEX
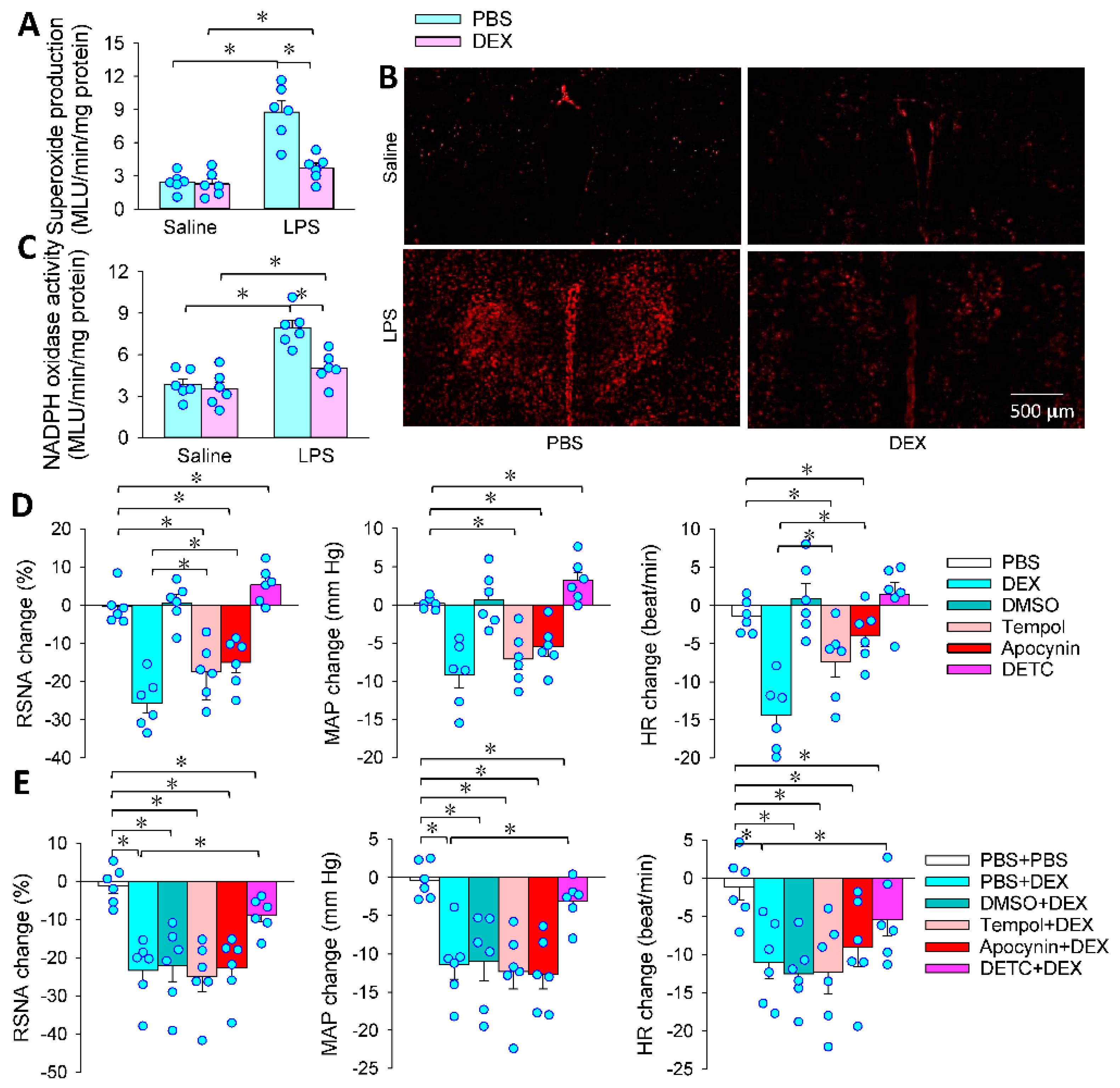
3.4. Superoxide in the PVN Mediates the Effects of PVN Microinjection of DEX
3.5. Intracellular cAMP Signaling Contributes to the Effects of PVN Microinjection of DEX
3.6. GABA in the Effects of DEX in PVN
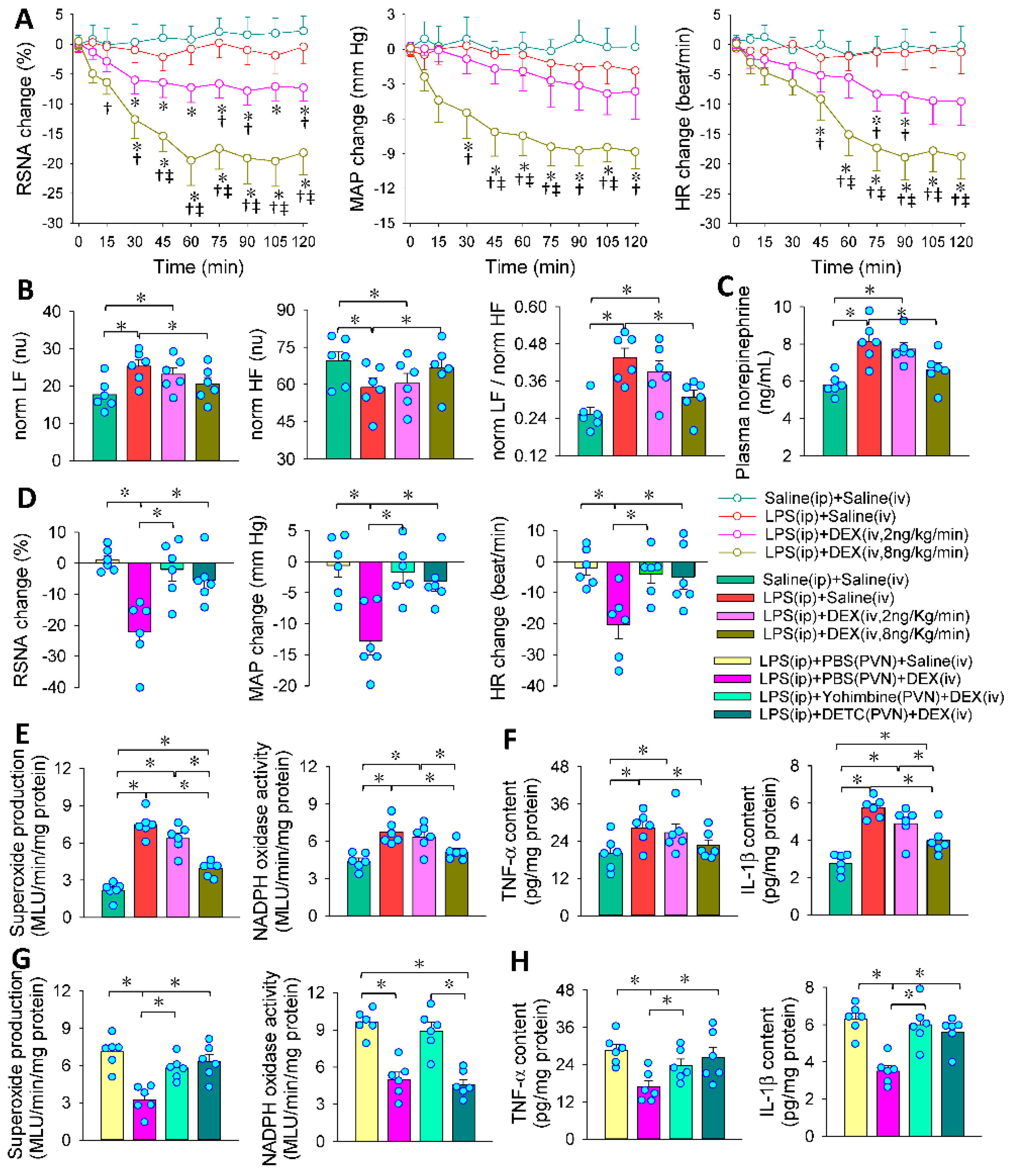
3.7. PVN in the Roles of Intravenous DEX in Inhibiting Sympathetic Activation
3.8. PVN in the Roles of Intravenous DEX in Attenuating Systemic Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Organ Injury
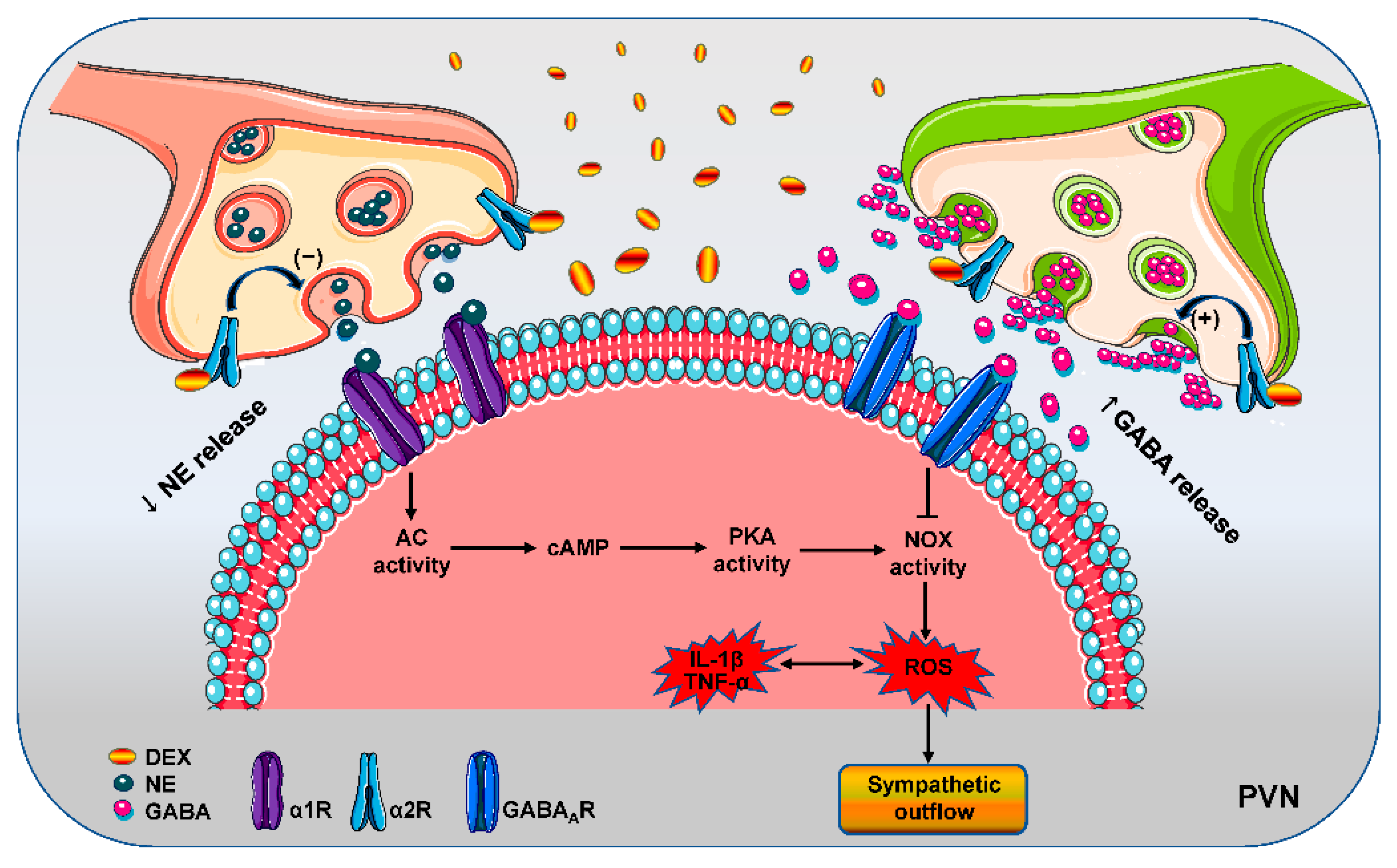
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choudhary, R. Sepsis Management, Controversies, and Advancement in Nanotechnology: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e22112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, C.; Zheng, F.; Xu, T.; Wu, N.; Tong, Y.; Xiong, X.Q.; Zhou, Y.B.; Wang, J.J.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.H.; et al. Norepinephrine acting on adventitial fibroblasts stimulates vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation via promoting small extracellular vesicle release. Theranostics 2022, 12, 4718–4733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo, L.P.; Maricato, J.T.; Guereschi, M.G.; Takenaka, M.C.; Nascimento, V.M.; de Melo, F.M.; Quintana, F.J.; Brum, P.C.; Basso, A.S. The Sympathetic Nervous System Mitigates CNS Autoimmunity via β2-Adrenergic Receptor Signaling in Immune Cells. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 3120–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miksa, M.; Wu, R.; Zhou, M.; Wang, P. Sympathetic excitotoxicity in sepsis: Pro-inflammatory priming of macrophages by norepinephrine. Front. Biosci. 2005, 10, 2217–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zhou, M.; Chaudry, I.H.; Wang, P. Norepinephrine-induced hepatocellular dysfunction in early sepsis is mediated by activation of alpha2-adrenoceptors. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2001, 281, G1014–G1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Yang, S.; Koo, D.J.; Ornan, D.A.; Chaudry, I.H.; Wang, P. The role of Kupffer cell α2-adrenoceptors in norepinephrine-induced TNF-alpha production. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1537, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martelli, D.; Yao, S.T.; McKinley, M.J.; McAllen, R.M. Neural control of inflammation by the greater splanchnic nerves. Temperature 2014, 1, 14–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Suzuki, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Okuda, J.; Kurazumi, T.; Suhara, T.; Ueda, T.; Nagata, H.; Morisaki, H. Sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction and β-adrenergic blockade therapy for sepsis. J. Intensive Care 2017, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, C.N.; Calzavacca, P.; Ishikawa, K.; Langenberg, C.; Wan, L.; Ramchandra, R.; Bellomo, R. Novel targets for sepsis-induced kidney injury: The glomerular arterioles and the sympathetic nervous system. Exp. Physiol. 2012, 97, 1168–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.Z.; Wu, J.M.; Hu, G.M.; Gu, H.J.; Feng, Y.N.; Wang, S.X.; Cong, W.W.; Li, M.Z.; Xu, W.L.; Song, Y.; et al. α1-AR overactivation induces cardiac inflammation through NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.S.; Tong, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Ye, C.; Wu, N.; Xiong, X.Q.; Wang, J.J.; Han, Y.; Zhou, Y.B.; Zhang, F.; et al. MiR155-5p in adventitial fibroblasts-derived extracellular vesicles inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation via suppressing angiotensin-converting enzyme expression. J. Extracell. Vesicles. 2020, 9, 1698795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, C.; Zheng, F.; Nan, W.; Zhu, G.Q.; Li, X.Z. Extracellular vesicles in vascular remodeling. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 2191–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofer, S.; Steppan, J.; Wagner, T.; Funke, B.; Lichtenstern, C.; Martin, E.; Graf, B.M.; Bierhaus, A.; Weigand, M.A. Central sympatholytics prolong survival in experimental sepsis. Crit. Care 2009, 13, R11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.J.; Ma, H.J.; Shao, J.Y.; Pan, H.L.; Li, D.P. Impaired Hypothalamic Regulation of Sympathetic Outflow in Primary Hypertension. Neurosci. Bull. 2019, 35, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dampney, R.A.; Michelini, L.C.; Li, D.P.; Pan, H.L. Regulation of sympathetic vasomotor activity by the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus in normotensive and hypertensive states. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2018, 315, H1200–H1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.W.; Xiong, X.Q.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.H.; Kang, Y.M.; Zhu, G.Q. Cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex and its implications for sympathetic activation in chronic heart failure and hypertension. Acta Physiol. 2015, 213, 778–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanick, W.J.; Polo-Parada, L.; Dantzler, H.A.; Kline, D.D. Activation of alpha-1 adrenergic receptors increases cytosolic calcium in neurones of the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2019, 31, e12791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjurmina, O.A.; Goldstein, D.S.; Palkovits, M.; Kopin, I.J. Alpha2-adrenoceptor-mediated restraint of norepinephrine synthesis, release, and turnover during immobilization in rats. Brain Res. 1999, 826, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proudman, R.G.W.; Akinaga, J.; Baker, J.G. The affinity and selectivity of α-adrenoceptor antagonists, antidepressants and antipsychotics for the human α2A, αB, and α2C-adrenoceptors and comparison with human α1 and β−adrenoceptors. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2022, 10, e00936. [Google Scholar]
- Gavras, I.; Manolis, A.J.; Gavras, H. The alpha2 -adrenergic receptors in hypertension and heart failure: Experimental and clinical studies. J. Hypertens. 2001, 19, 2115–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawada, T.; Nishikawa, T.; Hayama, Y.; Li, M.; Zheng, C.; Uemura, K.; Saku, K.; Miyamoto, T.; Sugimachi, M. Quantitative assessment of the central versus peripheral effect of intravenous clonidine using baroreflex equilibrium diagrams. J. Physiol. Sci. 2021, 71, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lankadeva, Y.R.; Shehabi, Y.; Deane, A.M.; Plummer, M.P.; Bellomo, R.; May, C.N. Emerging benefits and drawbacks of α2-adrenoceptor agonists in the management of sepsis and critical illness. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 1407–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dardalas, I.; Stamoula, E.; Rigopoulos, P.; Malliou, F.; Tsaousi, G.; Aidoni, Z.; Grosomanidis, V.; Milonas, A.; Papazisis, G.; Kouvelas, D.; et al. Dexmedetomidine effects in different experimental sepsis in vivo models. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 856, 172401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unnerstall, J.R.; Kopajtic, T.A.; Kuhar, M.J. Distribution of α 2 agonist binding sites in the rat and human central nervous system: Analysis of some functional, anatomic correlates of the pharmacologic effects of clonidine and related adrenergic agents. Brain Res. 1984, 319, 69–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamibayashi, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Mammoto, T.; Yamatodani, A.; Sumikawa, K.; Yoshiya, I. Role of the vagus nerve in the antidysrhythmic effect of dexmedetomidine on halothane/epinephrine dysrhythmias in dogs. Anesthesiology 1995, 83, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerink, M.A.S.; Struys, M.M.R.F.; Hannivoort, L.N.; Barends, C.R.M.; Absalom, A.R.; Colin, P. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Dexmedetomidine. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 56, 893–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhu, R.; Liu, Q.; Fei, J.; Wang, S. Anti-inflammatory activity of curcumin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles in IL-1β transgenic mice subjected to the lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis. Biomaterials 2015, 53, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasa, T.; Matsuzaki, T.; Yano, K.; Mayila, Y.; Irahara, M. Prenatal undernutrition decreases the anorectic response to septic doses of lipopolysaccharides in adulthood in male rats. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2018, 69, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, F.; Li, J. Changes of plasma glutamine concentration and hepatocyte membrane system N transporters expression in early endotoxemia. J. Surg. Res. 2011, 166, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Zheng, F.; Wang, J.X.; Wang, X.L.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.H.; Kang, Y.M.; Zhu, G.Q. Dysregulation of the excitatory renal reflex in the sympathetic activation of spontaneously hypertensive rat. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 673950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Chen, A.D.; Zhou, H.; Wang, J.J.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.H.; Kang, Y.M.; Zhu, G.Q. Chemical stimulation of renal tissue induces sympathetic activation and pressor response via hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. Neurosci. Bull. 2020, 36, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.Z.; Du, X.L.; Gao, Y.; Wang, J.X.; Wang, X.L.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.H.; Zhu, G.Q.; et al. Impact of Selective Renal Afferent Denervation on Oxidative Stress and Vascular Remodeling in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Zheng, F.; Li, N.; Han, Y.; Xiong, X.Q.; Wang, J.J.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.H.; Zhu, G.Q.; Zhou, Y.B. RND3 attenuates oxidative stress and vascular remodeling in spontaneously hypertensive rat via inhibiting ROCK1 signaling. Redox. Biol. 2021, 48, 102204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Zheng, F.; Ye, C.; Chen, A.D.; Wang, J.J.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.H.; Kang, Y.M.; Zhu, G.Q. Angiotensin type 1 receptors and superoxide anion production in hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus contribute to capsaicin-induced excitatory renal reflex and sympathetic activation. Neurosci. Bull. 2020, 36, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Li, K.; Su, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tang, X.; Xing, Y.; Xu, Y.; Dai, X.; Teng, J.; et al. Dexmedetomidine promotes lipopolysaccharide-induced differentiation of cardiac fibroblasts and collagen I/III synthesis through α2A adrenoreceptor-mediated activation of the PKC-p38-Smad2/3 signaling pathway in mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Caraveo, A.; Sayd, A.; Maus, S.R.; Caso, J.R.; Madrigal, J.L.M.; Garcia-Bueno, B.; Leza, J.C. Lipopolysaccharide enters the rat brain by a lipoprotein-mediated transport mechanism in physiological conditions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blandizzi, C. Enteric alpha-2 adrenoceptors: Pathophysiological implications in functional and inflammatory bowel disorders. Neurochem. Int. 2007, 51, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saia, R.S.; Oliveira-Pelegrin, G.R.; da Silva, M.E.; Aguila, F.A.; Antunes-Rodrigues, J.; Rocha, M.J.; Carnio, E.C. Neonatal endotoxin exposure changes neuroendocrine, cardiovascular function and mortality during polymicrobial sepsis in adult rats. Regul. Pept. 2011, 169, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.W.; Qiao, W.L.; Li, Q.; Wei, S.; Liu, T.T.; Qiu, C.Y.; Hu, W.P. Suppression of P2X3 receptor-mediated currents by the activation of α2A-adrenergic receptors in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. CNS. Neurosci. Ther. 2022, 28, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Goldfien, A.; Roberts, J.M. Alpha adrenergic stimulation reduces cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate generation in rabbit myometrium by two mechanisms. Biol. Reprod. 1988, 39, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotecchia, S.; Stanasila, L.; Diviani, D. Protein-protein interactions at the adrenergic receptors. Curr. Drug Targets. 2012, 13, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Cui, B.P.; Zhang, L.L.; Sun, H.J.; Liu, T.Y.; Zhu, G.Q. Melanocortin 3/4 receptors in paraventricular nucleus modulates sympathetic outflow and blood pressure. Exp. Physiol. 2013, 98, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kc, P.; Dick, T.E. Modulation of cardiorespiratory function mediated by the paraventricular nucleus. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2010, 174, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derbenev, A.V.; Smith, B.N. Dexamethasone rapidly increases GABA release in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus via retrograde messenger-mediated enhancement of TRPV1 activity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.P.; Atnip, L.M.; Chen, S.R.; Pan, H.L. Regulation of synaptic inputs to paraventricular-spinal output neurons by alpha2 adrenergic receptors. J. Neurophysiol. 2005, 93, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Su, Q.; Yu, X.J.; Wang, X.M.; Peng, B.; Bai, J.; Li, H.B.; Li, Y.; Xia, W.J.; Fu, L.Y.; Liu, K.L.; et al. Na+/K+-ATPase α2 isoform elicits rac1-dependent oxidative stress and TLR4-induced inflammation in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus in high salt-induced hypertension. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes-Pires, M.E.; Frade-Guanaes, J.O.; Quinlan, G.J. Clotting dysfunction in sepsis: A role for ROS and potential for therapeutic intervention. Antioxidants 2021, 11, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, S.T. Dexmedetomidine may produce extra protective effects on sepsis-induced diaphragm injury. Chin. Med. J. 2015, 128, 1407–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Xi, R.; Liu, J.; Peng, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Zheng, X.; Xu, X. TAS2R16 Activation Suppresses LPS-Induced Cytokine Expression in Human Gingival Fibroblasts. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 726546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Hong, Q.; Tan, H.L.; Xiao, C.R.; Gao, Y. Ferulic acid prevents LPS-induced up-regulation of PDE4B and stimulates the cAMP/CREB signaling pathway in PC12 cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2016, 37, 1543–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, L.L., Jr.; Almeida, R.L.; David, R.B.; De Paula, P.M.; Andrade, C.A.; Menani, J.V. Participation of α2 -adrenoceptors in sodium appetite inhibition during sickness behaviour following administration of lipopolysaccharide. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 1607–1616. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, E.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Choi, W.S.; Lee, M.H. Toll-like receptor 4-mediated cAMP production up-regulates B-cell activating factor expression in Raw264.7 macrophages. Exp. Cell Res. 2011, 317, 2447–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aurelian, L.; Warnock, K.T.; Balan, I.; Puche, A.; June, H. TLR4 signaling in VTA dopaminergic neurons regulates impulsivity through tyrosine hydroxylase modulation. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitti, N.; Etgen, A.M. Progesterone depression of norepinephrine-stimulated cAMP accumulation in hypothalamic slices. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 1989, 5, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, B.N.; Minneman, K.P. Multiple adrenergic receptor subtypes controlling cyclic AMP formation: Comparison of brain slices and primary neuronal and glial cultures. J. Neurochem. 1991, 56, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.H.; Lee, H.W.; Kang, E.A.; Song, M.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Ryu, P.D. Microglial activation induced by LPS mediates excitation of neurons in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus projecting to the rostral ventrolateral medulla. BMB Rep. 2021, 54, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xiao, H.; Shen, J.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Y. Different roles of β-arrestin and the PKA pathway in mitochondrial ROS production induced by acute β-adrenergic receptor stimulation in neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 489, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, D.C.; Fauconnier, J.; Yamada, T.; Lacampagne, A.; Zhang, S.J.; Katz, A.; Westerblad, H. Mitochondrial production of reactive oxygen species contributes to the β-adrenergic stimulation of mouse cardiomycytes. J. Physiol. 2011, 589, 1791–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.W. Pu-Erh tea and GABA attenuates oxidative stress in kainic acid-induced status epilepticus. J. Biomed. Sci. 2011, 18, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, H.; Lee, H.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y. Protective effect of gamma-aminobutyric acid against oxidative stress by inducing phase II enzymes in C2C12 myoblast cells. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Shi, Z.; Xie, C.; Gong, W.; Hu, Z.; Peng, Y. A novel mechanism of Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) protecting human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) against H2O2-induced oxidative injury. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 217, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawazoe, Y.; Miyamoto, K.; Morimoto, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Fuke, A.; Hashimoto, A.; Koami, H.; Beppu, S.; Katayama, Y.; Itoh, M.; et al. Effect of Dexmedetomidine on Mortality and Ventilator-Free Days in Patients Requiring Mechanical Ventilation With Sepsis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2017, 317, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, C.G.; Mailloux, P.T.; Devlin, J.W.; Swan, J.T.; Sanders, R.D.; Anzueto, A.; Jackson, J.C.; Hoskins, A.S.; Pun, B.T.; Orun, O.M.; et al. Dexmedetomidine or Propofol for Sedation in Mechanically Ventilated Adults with Sepsis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1424–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Mei, Q.; Dai, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, H. Use of dexmedetomidine in patients with sepsis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials. Ann. Intensive Care 2022, 12, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bo, J.-H.; Wang, J.-X.; Wang, X.-L.; Jiao, Y.; Jiang, M.; Chen, J.-L.; Hao, W.-Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.-H.; Ma, Z.-L.; et al. Dexmedetomidine Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Sympathetic Activation and Sepsis via Suppressing Superoxide Signaling in Paraventricular Nucleus. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11122395
Bo J-H, Wang J-X, Wang X-L, Jiao Y, Jiang M, Chen J-L, Hao W-Y, Chen Q, Li Y-H, Ma Z-L, et al. Dexmedetomidine Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Sympathetic Activation and Sepsis via Suppressing Superoxide Signaling in Paraventricular Nucleus. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(12):2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11122395
Chicago/Turabian StyleBo, Jin-Hua, Jing-Xiao Wang, Xiao-Li Wang, Yang Jiao, Ming Jiang, Jun-Liu Chen, Wen-Yuan Hao, Qi Chen, Yue-Hua Li, Zheng-Liang Ma, and et al. 2022. "Dexmedetomidine Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Sympathetic Activation and Sepsis via Suppressing Superoxide Signaling in Paraventricular Nucleus" Antioxidants 11, no. 12: 2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11122395
APA StyleBo, J.-H., Wang, J.-X., Wang, X.-L., Jiao, Y., Jiang, M., Chen, J.-L., Hao, W.-Y., Chen, Q., Li, Y.-H., Ma, Z.-L., & Zhu, G.-Q. (2022). Dexmedetomidine Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Sympathetic Activation and Sepsis via Suppressing Superoxide Signaling in Paraventricular Nucleus. Antioxidants, 11(12), 2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11122395








