The Effects of Indoxyl Sulfate and Oxidative Stress on the Severity of Peripheral Nerve Dysfunction in Patients with Chronic Kidney Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Peripheral Nerve Function Assessment
2.2. Measurements of Biomarkers for Oxidative Stress, Endothelial Dysfunction, and Protein-Binding Uremic Toxins
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Patients
3.2. Clinical Score, NCS, and ESC in CKD
3.3. Effect of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxin and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors on Composite Amplitude Scores in Patients with CKD
3.4. Clinical Factors Are Significantly Associated with Composite Amplitude Scores in Patients with CKD
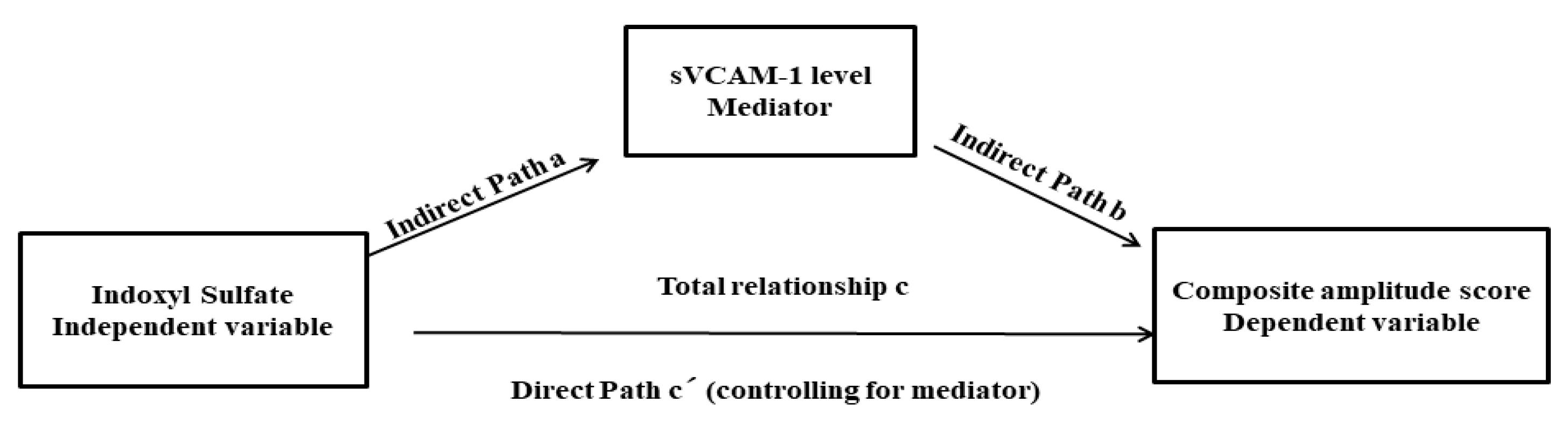
3.5. Mediation Analysis for Uremic Toxin (IS), the Severity of Peripheral Nerve Dysfunction (CAS), and Endothelial Dysfunction (sVCAM-1 Level)
4. Discussion
4.1. Major Findings of Our Study
4.2. The Pathophysiology of Protein-Binding Uremic Toxins
4.3. The Potential Pathogenesis of Protein-Binding Uremic Toxins in Peripheral Nerve Function
4.4. Electrophysiological Parameters and Clinical Scores in Patients with CKD
4.5. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2020, 395, 709–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruck, K.; Stel, V.S.; Gambaro, G.; Hallan, S.; Volzke, H.; Arnlov, J.; Kastarinen, M.; Guessous, I.; Vinhas, J.; Stengel, B.; et al. CKD Prevalence Varies across the European General Population. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 2135–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, R.; Issar, T.; Krishnan, A.V.; Pussell, B.A. Neurological complications in chronic kidney disease. JRSM Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016, 5, 2048004016677687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mambelli, E.; Barrella, M.; Facchini, M.G.; Mancini, E.; Sicuso, C.; Bainotti, S.; Formica, M.; Santoro, A. The prevalence of peripheral neuropathy in hemodialysis patients. Clin. Nephrol. 2012, 77, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asbury, A.K.; Victor, M.; Adams, R.D. Uremic polyneuropathy. Arch. Neurol. 1963, 8, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.R.; Cheng, B.C.; Huang, C.C.; Chiu, W.C.; Tsai, N.W.; Chen, J.F.; Lu, C.H. Correlation between kidney and peripheral nerve functions in Type 2 diabetes. QJM 2020, 113, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesfaye, S. Recent advances in the management of diabetic distal symmetrical polyneuropathy. J. Diabetes Investig. 2011, 2, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanholder, R.; Glorieux, G.; De Smet, R.; Lameire, N. New insights in uremic toxins. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2003, 63, S6–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, V.; Greene, T.; Pereira, A.A.; Wang, X.; Beck, G.J.; Kusek, J.W.; Collins, A.J.; Levey, A.S.; Sarnak, M.J. Glycosylated hemoglobin and mortality in patients with nondiabetic chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 3411–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.C.; Tomino, Y.; Lu, K.C. Impacts of Indoxyl Sulfate and p-Cresol Sulfate on Chronic Kidney Disease and Mitigating Effects of AST-120. Toxins 2018, 10, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, A.V.; Lin, C.S.-Y.; Kiernan, M.C. Activity-dependent excitability changes suggest Na+/K+ pump dysfunction in diabetic neuropathy. Brain 2008, 131, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, A.V.; Kiernan, M.C. Uremic neuropathy: Clinical features and new pathophysiological insights. Muscle Nerve 2007, 35, 273–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloan, G.; Selvarajah, D.; Tesfaye, S. Pathogenesis, diagnosis and clinical management of diabetic sensorimotor peripheral neuropathy. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 400–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Shi, J.; Ma, X.; Shi, D.; Qu, H. Effects of Microbiota-driven Therapy on Circulating Indoxyl Sulfate and P-cresyl Sulfate in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 13, 1267–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldiroli, L.; Armelloni, S.; Eskander, A.; Messa, P.; Rizzo, V.; Margiotta, E.; Cesari, M.; Vettoretti, S. Association between the uremic toxins indoxyl-sulfate and p-cresyl-sulfate with sarcopenia and malnutrition in elderly patients with advanced chronic kidney disease. Exp. Gerontol. 2021, 147, 111266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.J.; Wu, V.; Wu, P.C.; Wu, C.J. Meta-Analysis of the Associations of p-Cresyl Sulfate (PCS) and Indoxyl Sulfate (IS) with Cardiovascular Events and All-Cause Mortality in Patients with Chronic Renal Failure. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnier, L.; Colette, C. Glycemic variability: Should we and can we prevent it? Diabetes Care 2008, 31 (Suppl. S2), S150–S154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, A.; Barnett, C.; Katzberg, H.D.; Lovblom, L.E.; Perkins, B.A.; Bril, V. Toronto Clinical Neuropathy Score is valid for a wide spectrum of polyneuropathies. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 25, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eknoyan, G.; Hostetter, T.; Bakris, G.L.; Hebert, L.; Levey, A.S.; Parving, H.H.; Steffes, M.W.; Toto, R. Proteinuria and other markers of chronic kidney disease: A position statement of the national kidney foundation (NKF) and the national institute of diabetes and digestive and kidney diseases (NIDDK). Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2003, 42, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.C.; Zuo, L.; Chen, J.H.; Luo, Q.; Yu, X.Q.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.S.; Huang, S.M.; Wang, L.N.; Huang, W.; et al. Modified glomerular filtration rate estimating equation for Chinese patients with chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 2937–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, C.; Ferris III, F.L.; Klein, R.E.; Lee, P.P.; Agardh, C.D.; Davis, M.; Dills, D.; Kampik, A.; Pararajasegaram, R.; Verdaguer, J.T. Proposed international clinical diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema disease severity scales. Ophthalmology 2003, 110, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.R.; Chiu, W.C.; Huang, C.C.; Tsai, N.W.; Wang, H.C.; Lin, W.C.; Cheng, B.C.; Su, Y.J.; Su, C.M.; Hsiao, S.Y.; et al. HbA1C Variability Is Strongly Associated with the Severity of Peripheral Neuropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.R.; Chang, W.N.; Chang, H.W.; Tsai, N.W.; Lu, C.H. Effects of age, gender, height, and weight on late responses and nerve conduction study parameters. Acta Neurol. 2009, 18, 242–249. [Google Scholar]
- Mayaudon, H.; Miloche, P.O.; Bauduceau, B. A new simple method for assessing sudomotor function: Relevance in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. 2010, 36, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.-H.; Lin, H.-C.; Huang, C.-C.; Lin, W.-C.; Chen, H.-L.; Chang, H.-W.; Friedman, M.; Chen, C.T.; Tsai, N.-W.; Wang, H.-C. Increased circulating endothelial progenitor cells and anti-oxidant capacity in obstructive sleep apnea after surgical treatment. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 448, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-N.; Wu, I.-W.; Huang, Y.-F.; Peng, S.-Y.; Huang, Y.-C.; Ning, H.-C. Measuring serum total and free indoxyl sulfate and p-cresyl sulfate in chronic kidney disease using UPLC-MS/MS. J. Food Drug Anal. 2019, 27, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lano, G.; Burtey, S.; Sallee, M. Indoxyl Sulfate, a Uremic Endotheliotoxin. Toxins 2020, 12, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, R.M.; Kenny, D.A. The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1986, 51, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wager, T.D.; Davidson, M.L.; Hughes, B.L.; Lindquist, M.A.; Ochsner, K.N. Prefrontal-subcortical pathways mediating successful emotion regulation. Neuron 2008, 59, 1037–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Cao, X.; Zou, J.; Shen, B.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Lv, W.; Teng, J.; Ding, X. Indoxyl sulfate, a valuable biomarker in chronic kidney disease and dialysis. Hemodial. Int. 2017, 21, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.-H.; Wang, C.-P.; Chung, F.-M.; Huang, L.L.; Yu, T.-H.; Hung, W.-C.; Lu, L.-F.; Chen, P.-Y.; Luo, C.-H.; Lee, K.-T. Uremic retention solute indoxyl sulfate level is associated with prolonged QTc interval in early CKD patients. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijers, B.K.; De Loor, H.; Bammens, B.; Verbeke, K.; Vanrenterghem, Y.; Evenepoel, P. p-Cresyl sulfate and indoxyl sulfate in hemodialysis patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 1932–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, S.C.; Kuo, K.L.; Wu, C.C.; Tarng, D.C. Indoxyl sulfate: A novel cardiovascular risk factor in chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e005022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijers, B.K.; Claes, K.; Bammens, B.; de Loor, H.; Viaene, L.; Verbeke, K.; Kuypers, D.; Vanrenterghem, Y.; Evenepoel, P. p-Cresol and cardiovascular risk in mild-to-moderate kidney disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 1182–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, L.; Jourde-Chiche, N.; Faure, V.; Cerini, C.; Berland, Y.; Dignat-George, F.; Brunet, P. The uremic solute indoxyl sulfate induces oxidative stress in endothelial cells. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 1302–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumur, Z.; Niwa, T. Indoxyl sulfate inhibits nitric oxide production and cell viability by inducing oxidative stress in vascular endothelial cells. Am. J. Nephrol. 2009, 29, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumur, Z.; Shimizu, H.; Enomoto, A.; Miyazaki, H.; Niwa, T. Indoxyl sulfate upregulates expression of ICAM-1 and MCP-1 by oxidative stress-induced NF-kappaB activation. Am. J. Nephrol. 2010, 31, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Martin, R.; Hoeth, M.; Hofer-Warbinek, R.; Schmid, J.A. The transcription factor NF-kappa B and the regulation of vascular cell function. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, e83–e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marui, N.; Offermann, M.K.; Swerlick, R.; Kunsch, C.; Rosen, C.A.; Ahmad, M.; Alexander, R.W.; Medford, R.M. Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) gene transcription and expression are regulated through an antioxidant-sensitive mechanism in human vascular endothelial cells. J. Clin. Invest. 1993, 92, 1866–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jude, E.B.; Abbott, C.A.; Young, M.J.; Anderson, S.G.; Douglas, J.T.; Boulton, A.J. The potential role of cell adhesion molecules in the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetologia 1998, 41, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.M.; Crandall, J.; Hori, O.; Cao, R.; Lakatta, E. Elevated plasma levels of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) in diabetic patients with microalbuminuria: A marker of vascular dysfunction and progressive vascular disease. Br. J. Haematol. 1996, 92, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.Y.; Park, T.S. Role of inflammatory biomarkers in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J. Diabetes Investig. 2018, 9, 1016–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, P.C.; Doll, S.C.; Cromey, D.W. Pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy. Ann. Neurol. 1986, 19, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasti, D.B.; Mallipeddi, S.; Apparao, A.; Vengamma, B.; Sivakumar, V.; Kolli, S. A Clinical and Electrophysiological Study of Peripheral Neuropathies in Predialysis Chronic Kidney Disease Patients and Relation of Severity of Peripheral Neuropathy with Degree of Renal Failure. J. Neurosci. Rural Pract. 2017, 8, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Issar, T.; Walker, S.; Arnold, R.; Poynten, A.M.; Endre, Z.H.; Krishnan, A.V. Peripheral nerve morphology and intraneural blood flow in chronic kidney disease with and without diabetes. Muscle Nerve 2022, 65, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.R.; Huang, C.C.; Chiu, W.C.; Liu, R.T.; Tsai, N.W.; Wang, H.C.; Lin, W.C.; Cheng, B.C.; Su, Y.J.; Su, C.M.; et al. Sural nerve sensory response in diabetic distal symmetrical polyneuropathy. Muscle Nerve 2020, 61, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; Chang, C.H.; Sun, M.F.; Hsu, S.F.; Weng, C.S. DPP-4 inhibitor attenuates toxic effects of indoxyl sulfate on kidney tubular cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Diabetic CKD (n = 27) | Non-Diabetic CKD (n = 27) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline characteristics | |||
| Age (year) | 69.7 ± 12.4 | 67.0 ± 10.2 | 0.22 |
| Sex (male/female) | 16/11 | 18/9 | 0.57 |
| Diabetes duration (year) | 16.2 ± 11.1 | - | |
| Height (cm) | 163.3 ± 8.0 | 161.5 ± 8.3 | 0.42 |
| Body mass index | 26.5 ± 5.4 | 26.5 ± 5.4 | 0.11 |
| Waist circumstance (cm) | 96.8 ± 14.8 | 90.0 ± 10.3 | 0.10 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 140.5 ± 23.2 | 151.9 ± 25.6 | 0.09 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 75.3 ± 14.9 | 81.9 ± 16.5 | 0.13 |
| ACE inhibitor or angiotensin II receptor blocker | 20 | 22 | 0.51 |
| Beta-blocker | 13 | 13 | 1.0 |
| Calcium channel blocker | 18 | 14 | 0.27 |
| Diuretics | 8 | 1 | 0.02 |
| Alpha-blocker | 4 | 3 | 1.0 |
| Antiplatelet medications | 13 | 9 | 0.27 |
| Lipid-lowering medications | 22 | 15 | 0.04 |
| Diabetic CKD (n = 27) | Non-Diabetic CKD (n = 27) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peripheral blood studies | |||
| WBC counts (×103/mL) | 7.5 ± 2.5 | 6.0 ± 1.6 | 0.02 |
| RBC counts (×106/mL) | 4.0 ± 0.6 | 4.0 ± 1.0 | 0.93 |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 12.0 ± 1.7 | 12.0 ± 2.1 | 0.96 |
| Hematocrit | 36.0 ± 4.8 | 36.0 ± 6.8 | 0.98 |
| Platelet counts (×103/mL) | 236.2 ± 55.1 | 195.7 ± 55.5 | 0.02 |
| UACR (mg/g) | 258.9 (78.3, 1052.5) | 276.6 (18.0, 758.6) | 0.43 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 31.2 ± 9.8 | 30.6 ± 11.4 | 0.08 |
| Creatinine (mmol/L) | 2.0 ± 0.8 | 2.3 ± 0.7 | 0.1 |
| Albumin (mg/dL) | 4.5 ± 0.3 | 4.6 ± 0.3 | 0.49 |
| Total cholesterol l(mmol/L) | 160.9 ± 38.5 | 183.3 ± 57.8 | 0.11 |
| Triglyceride (mmol/L) | 117.5 ± 65.3 | 118.2 ± 53.7 | 0.97 |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 45.5 ± 11.0 | 47.5 ± 13.4 | 0.56 |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 88.3 ± 30.6 | 111.2 ± 44.8 | 0.03 |
| Glycohemoglobin (%) | 6.9 ± 1.1 | 5.5 ± 0.3 | <0.0001 * |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 6.6 ± 1.9 | 6.9 ± 1.5 | 0.57 |
| Calcium (mmol/L) | 9.3 ± 0.4 | 9.4 ± 0.4 | 0.48 |
| hs-CRP, mg/L | 2.2 ± 1.4 | 1.7 ± 1.0 | 0.47 |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 4.5 ± 0.8 | 4.5 ± 0.7 | 0.91 |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 139.7 ± 4.3 | 139.4 ± 3.5 | 0.78 |
| Phosphate (mmol/L) | 3.7 ± 0.8 | 3.6 ± 0.6 | 0.65 |
| CO2 | 29.2 ± 22.7 | 31.7 ± 24.6 | 0.74 |
| iPTH (pg/mL) | 125.5 ± 87.8 | 156.3 ± 94.0 | 0.6 |
| Biomarkers for endothelial dysfunction | |||
| sICAM-1 (ng/mL) | 242.2 ± 69.1 | 245.1 ± 29.6 | 0.93 |
| sVCAM-1 (ng/mL) | 1083.0 ± 259.5 | 971.1 ± 94.0 | 0.36 |
| Biomarkers for oxidative stress | |||
| TBARS, μmol/L | 13.4 ± 7.9 | 9.9 ± 2.6 | 0.09 |
| Thiols, μmol/L | 1.0 ± 0.5 | 1.1 ± 0.4 | 0.57 |
| Protein-bound uremic toxin | |||
| Free-form Indoxyl sulfate (μg/mL) | 0.24 ± 0.17 | 0.21 ± 0.15 | 0.54 |
| Free-form p-Cresol sulfate (μg/mL) | 0.50 ± 0.49 | 0.45 ± 0.41 | 0.73 |
| Total-form Indoxyl sulfate (μg/mL) | 4.0 ± 3.3 | 3.9 ± 2.3 | 0.88 |
| Total-form p-Cresol sulfate (μg/mL) | 11.6 ± 10.4 | 10.4 ± 9.8 | 0.65 |
| Diabetic CKD (n = 27) | Non-Diabetic CKD (n = 27) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Toronto Clinical Neuropathy Score | 5.7 ± 4.1 | 3.4 ± 3.0 | 0.02 * |
| Composite amplitude score | 5.3 ± 3.2 | 3.2 ± 2.8 | 0.008 * |
| Median nerve, motor | |||
| DML | 4.4 ± 0.6 | 4.1 ± 0.7 | 0.12 |
| CMAP | 8.5 ± 2.1 | 9.6 ± 2.9 | 0.12 |
| MNCV | 51.1 ± 4.3 | 52.9 ± 4.2 | 0.12 |
| Ulnar nerve, motor | |||
| DML | 3.1 ± 0.4 | 3.0 ± 0.4 | 0.17 |
| CMAP | 7.9 ± 2.3 | 9.8 ± 2.6 | 0.004 * |
| MNCV | 51.3 ± 5.5 | 54.6 ± 4.9 | 0.02 * |
| Peroneal nerve, | |||
| DML | 4.1 ± 0.6 | 3.8 ± 0.6 | 0.03 * |
| CMAP | 2.4 ± 1.8 | 4.2 ± 2.7 | 0.004 * |
| MNCV | 41.4 ± 4.3 | 46.0 ± 5.1 | 0.001 * |
| Tibial nerve | |||
| DML | 4.2 ± 0.6 | 4.0 ± 0.5 | 0.06 |
| CMAP | 7.4 ± 5.3 | 8.7 ± 4.3 | 0.29 |
| MNCV | 41.3 ± 5.3 | 44.5 ± 3.3 | 0.01 * |
| Median nerve, sensory | |||
| Latency | 3.3 ± 0.4 | 3.1 ± 0.5 | 0.04 * |
| SNAP | 23.2 ± 13.2 | 30.4 ± 15.6 | 0.06 |
| SNCV | 42.6 ± 5.8 | 46.2 ± 7.8 | 0.04 * |
| Ulnar nerve, sensory | |||
| Latency | 2.6 ± 0.4 | 2.4 ± 0.3 | 0.04 * |
| SNAP | 17.8 ± 12.2 | 27.7 ± 13.5 | 0.004 * |
| SNCV | 46.8 ± 6.4 | 49.8 ± 5.3 | 0.07 |
| Sural nerve | |||
| Latency | 3.1 ± 0.4 | 2.9 ± 0.3 | 0.07 |
| SNAP | 4.0 ± 2.7 | 9.9 ± 7.0 | 0.001 * |
| SNCV | 44.8 ± 4.8 | 48.3 ± 5.3 | 0.04 * |
| Sudoscan | |||
| Hand ESC, µS | 40.6 ± 19.7 | 45.7 ± 18.5 | 0.30 |
| Feet ESC, µS | 44.4 ± 18.2 | 48.4 ± 23.6 | 0.54 |
| Variables | Composite Amplitude Scores | |
|---|---|---|
| r | p-Value | |
| Age (year) | 0.27 | 0.04 * |
| Height (cm) | 0.18 | 0.23 |
| Body mass index | 0.12 | 0.43 |
| Waist circumstance (cm) | 0.14 | 0.39 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | −0.008 | 0.96 |
| UACR (mg/g) | 0.29 | 0.046 * |
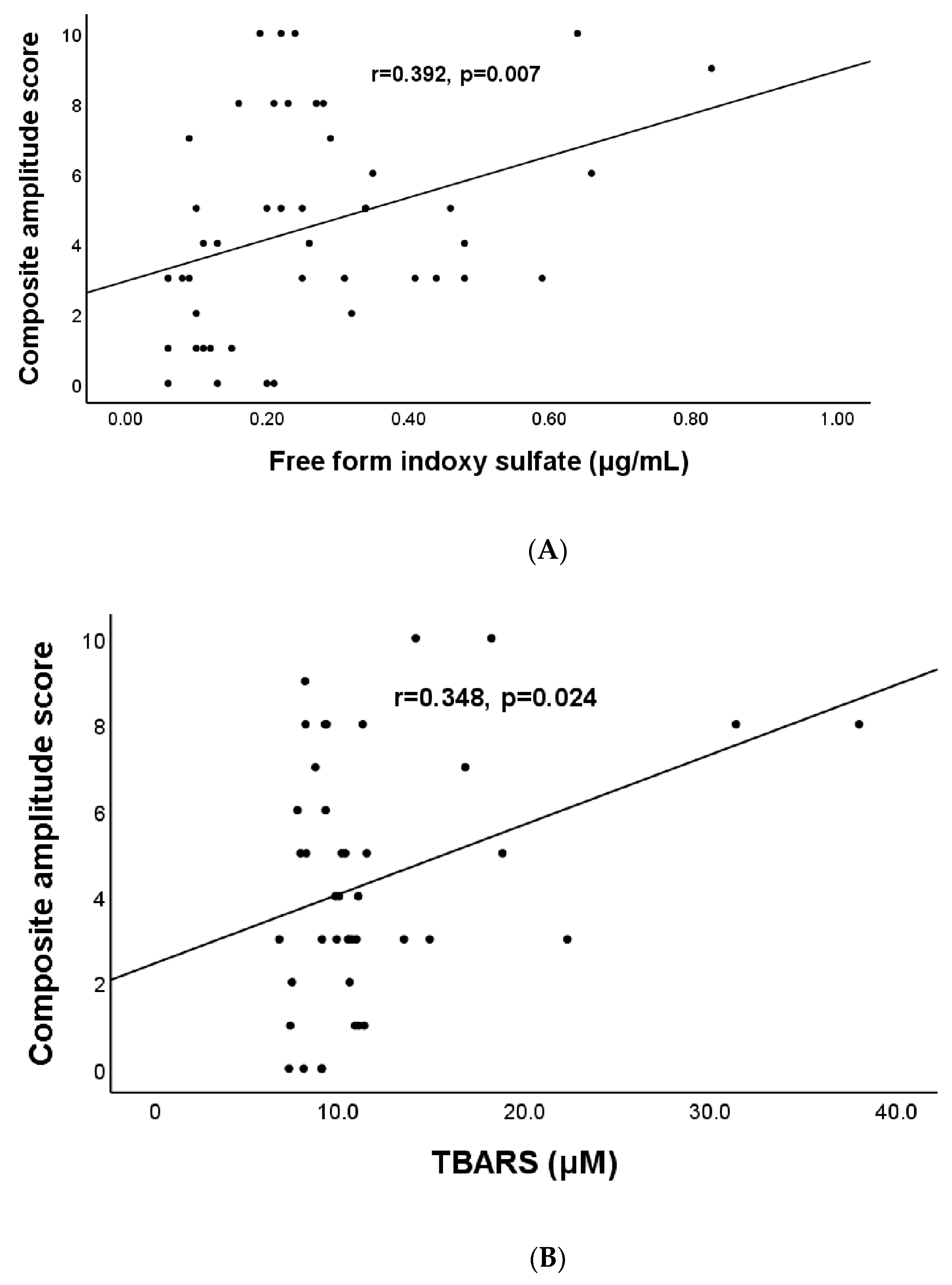
| Free-form Indoxyl sulfate (μg/mL) | 0.39 | 0.009 * |
| Free-form p-Cresol sulfate (μg/mL) | 0.26 | 0.10 |
| Total-form Indoxyl sulfate (μg/mL) | 0.28 | 0.07 |
| Total-form p-Cresol sulfate (μg/mL) | 0.31 | 0.05 |
| sICAM-1 (ng/mL) | 0.31 | 0.02 * |
| sVCAM-1 (ng/mL) | 0.44 | <0.0001 * |
| TBARS, μmol/L | 0.35 | 0.002 * |
| Thiols, μmol/L | −0.28 | 0.045 * |
| Total cholesterol(mmol/L) | −0.19 | 0.22 |
| Triglyceride(mmol/L) | −0.20 | 0.18 |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | −0.16 | 0.28 |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | −0.08 | 0.6 |
| Uric acid (mmol/L) | −0.04 | 0.8 |
| hs-CRP (mmol/L) | 0.18 | 0.3 |
| HbA1c (%) | 0.04 | 0.82 |
| Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Regression Coefficient | Standard Error | p-Value | |
| Constant | 0.56 | 0.94 | 0.56 |
| TBARS, μmol/L | 0.17 | 0.06 | 0.007 |
| Indoxyl sulfate (μg/mL) | 5.04 | 2.65 | 0.035 |
| Path Coefficient | Standard Error | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total effects (total relationship, path c) Ω | |||
| The relationship between the IS (independent variable) and CAS (dependent variable) | 7.87 | 2.50 | 0.003 |
| Direct effects, path c′ | |||
| The relationship between the IS (independent variable) and CAS (dependent variables) by including the sVCAM-1 (mediator) into the model | 5.06 | 2.56 | 0.45 |
| Indirect effect, path a | |||
| The effect of the IS (independent variable) on the sVCAM-1 (mediator) | 704.08 | 235.26 | 0.004 |
| Indirect effect, path b | |||
| The effect of the sVCAM-1 (mediator) on the CAS (dependent variable by controlling the effect for the IS (independent variable) | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, Y.-R.; Cheng, B.-C.; Lin, C.-N.; Chiu, W.-C.; Lin, T.-Y.; Chiang, H.-C.; Kuo, C.-E.A.; Huang, C.-C.; Lu, C.-H. The Effects of Indoxyl Sulfate and Oxidative Stress on the Severity of Peripheral Nerve Dysfunction in Patients with Chronic Kidney Diseases. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2350. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11122350
Lai Y-R, Cheng B-C, Lin C-N, Chiu W-C, Lin T-Y, Chiang H-C, Kuo C-EA, Huang C-C, Lu C-H. The Effects of Indoxyl Sulfate and Oxidative Stress on the Severity of Peripheral Nerve Dysfunction in Patients with Chronic Kidney Diseases. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(12):2350. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11122350
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Yun-Ru, Ben-Chung Cheng, Chia-Ni Lin, Wen-Chan Chiu, Ting-Yin Lin, Hui-Ching Chiang, Chun-En Aurea Kuo, Chih-Cheng Huang, and Cheng-Hsien Lu. 2022. "The Effects of Indoxyl Sulfate and Oxidative Stress on the Severity of Peripheral Nerve Dysfunction in Patients with Chronic Kidney Diseases" Antioxidants 11, no. 12: 2350. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11122350
APA StyleLai, Y.-R., Cheng, B.-C., Lin, C.-N., Chiu, W.-C., Lin, T.-Y., Chiang, H.-C., Kuo, C.-E. A., Huang, C.-C., & Lu, C.-H. (2022). The Effects of Indoxyl Sulfate and Oxidative Stress on the Severity of Peripheral Nerve Dysfunction in Patients with Chronic Kidney Diseases. Antioxidants, 11(12), 2350. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11122350







