MicroRNA Profile of Lung Tumor Tissues Is Associated with a High Risk Plasma miRNA Signature
Abstract
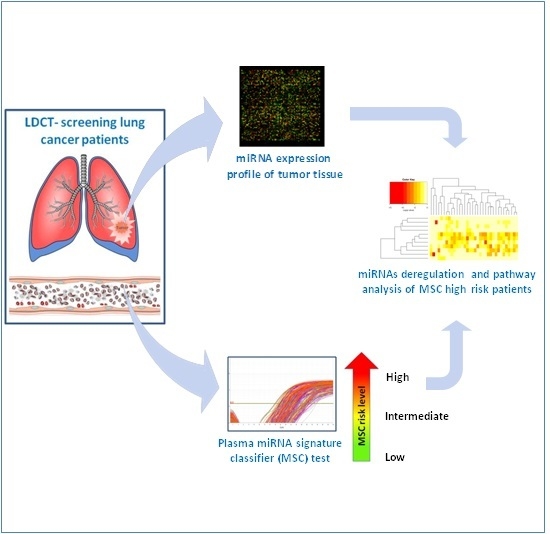
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients’ Characteristics
2.2. MicroRNA Profiling in Plasma Samples
2.3. MicroRNA Profiling in Tumor Tissue Samples
2.4. Statistical and Bioinformatics Analyses
2.5. Pathways Enrichment Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Characteristics and Prognostic Value of the miRNA Signature Classifier (MSC)
3.2. MicroRNA Expression in Tumor Tissue Associated with MSC Risk Level
3.3. Pathway Enrichment Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.; Ma, J.; Zou, Z.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2014, 64, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaswamy, S.; Tamayo, P.; Rifkin, R.; Mukherjee, S.; Yeang, C.H.; Angelo, M.; Ladd, C.; Reich, M.; Latulippe, E.; Mesirov, J.P.; et al. Multiclass cancer diagnosis using tumor gene expression signatures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 15149–15154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanaihara, N.; Caplen, N.; Bowman, E.; Seike, M.; Kumamoto, K.; Yi, M.; Stephens, R.M.; Okamoto, A.; Yokota, J.; Tanaka, T.; et al. Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.; Griffiths-Jones, S.; Ashurst, J.L.; Bradley, A. Identification of mammalian microRNA host genes and transcription units. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1902–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krol, J.; Loedige, I.; Filipowicz, W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garzon, R.; Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNAs in Cancer. Annu. Rev. Med. 2009, 60, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeri, M.; Pastorino, U.; Sozzi, G. Role of microRNAs in lung cancer: microRNA signatures in cancer prognosis. Cancer J. 2012, 18, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, F.; Nicassio, F.; Marzi, M.; Belloni, E.; Dall’olio, V.; Bernard, L.; Pelosi, G.; Maisonneuve, P.; Veronesi, G.; di Fiore, P.P. A serum circulating miRNA diagnostic test to identify asymptomatic high-risk individuals with early stage lung cancer. EMBO Mol. Med. 2011, 3, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortez, M.A.; Bueso-Ramos, C.; Ferdin, J.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K.; Calin, G.A. MicroRNAs in body fluids—The mix of hormones and biomarkers. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turchinovich, A.; Weiz, L.; Langheinz, A.; Burwinkel, B. Characterization of extracellular circulating microRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 7223–7233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroyo, J.D.; Chevillet, J.R.; Kroh, E.M.; Ruf, I.K.; Pritchard, C.C.; Gibson, D.F.; Mitchell, P.S.; Bennett, C.F.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Stirewalt, D.L.; et al. Argonaute2 complexes carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles in human plasma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5003–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeri, M.; Sestini, S.; Fortunato, O.; Verri, C.; Suatoni, P.; Pastorino, U.; Sozzi, G. Recent advances of microRNA-based molecular diagnostics to reduce false-positive lung cancer imaging. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2015, 15, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sozzi, G.; Boeri, M.; Rossi, M.; Verri, C.; Suatoni, P.; Bravi, F.; Roz, L.; Conte, D.; Grassi, M.; Sverzellati, N.; et al. Clinical Utility of a Plasma-Based miRNA Signature Classifier Within Computed Tomography Lung Cancer Screening: A Correlative MILD Trial Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeri, M.; Verri, C.; Conte, D.; Roz, L.; Modena, P.; Facchinetti, F.; Calabro, E.; Croce, C.M.; Pastorino, U.; Sozzi, G. MicroRNA signatures in tissues and plasma predict development and prognosis of computed tomography detected lung cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3713–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sestini, S.; Boeri, M.; Marchiano, A.; Pelosi, G.; Galeone, C.; Verri, C.; Suatoni, P.; Sverzellati, N.; La, V.C.; Sozzi, G.; et al. Circulating microRNA signature as liquid-biopsy to monitor lung cancer in low-dose computed tomography screening. Oncotarget 2015, 20, 32868–32877. [Google Scholar]
- Fortunato, O.; Boeri, M.; Moro, M.; Verri, C.; Mensah, M.; Conte, D.; Caleca, L.; Roz, L.; Pastorino, U.; Sozzi, G. Mir-660 is downregulated in lung cancer patients and its replacement inhibits lung tumorigenesis by targeting MDM2-p53 interaction. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastorino, U.; Bellomi, M.; Landoni, C.; de Fiori, E.; Arnaldi, P.; Picchio, M.; Pelosi, G.; Boyle, P.; Fazio, F. Early lung-cancer detection with spiral CT and positron emission tomography in heavy smokers: 2-year results. Lancet 2003, 362, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, O.; Boeri, M.; Verri, C.; Conte, D.; Mensah, M.; Suatoni, P.; Pastorino, U.; Sozzi, G. Assessment of circulating microRNAs in plasma of lung cancer patients. Molecules 2014, 19, 3038–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Simon, R. BRB-ArrayTools Data Archive for human cancer gene expression: A unique and efficient data sharing resource. Cancer Inform. 2008, 6, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dinse, G.E.; Lagakos, S.W. Nonparametric estimation of lifetime and disease onset distributions from incomplete observations. Biometrics 1982, 38, 921–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachos, I.S.; Kostoulas, N.; Vergoulis, T.; Georgakilas, G.; Reczko, M.; Maragkakis, M.; Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Prionidis, K.; Dalamagas, T.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. DIANA miRPath v.2.0: Investigating the combinatorial effect of microRNAs in pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W498–W504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dweep, H.; Gretz, N. miRWalk2.0: A comprehensive atlas of microRNA-target interactions. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhang, S.; Wu, N.; Wu, L.; Wang, C.; Lin, Y. Overexpression of miR-499–5p inhibits non-small cell lung cancer proliferation and metastasis by targeting VAV3. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.C.; Li, S.J.; Zhang, F.; Pan, J.Y.; Wang, L.; Yang, C.L.; Xi, Y.Y.; Li, D.J. Hsa-miR-329 exerts tumor suppressor function through down-regulation of MET in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 16, 21510–21527. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Shan, C.; Kong, G.; Du, Y.; Ye, L.; Zhang, X. MicroRNA-520e suppresses growth of hepatoma cells by targeting the NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK). Oncogene 2012, 31, 3607–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Liu, Y.W.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Q.; Li, J.-J.; Huang, A.; Qi, S.T.; Lu, Y.-T. MiR-519a functions as a tumor suppressor in glioma by targeting the oncogenic STAT3 pathway. J. Neurooncol. 2016, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Zhu, X.; Dou, Y. The miR-302/367 cluster: A comprehensive update on its evolution and functions. Open Biol. 2015, 5, 150138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanyam, D.; Lamouille, S.; Judson, R.L.; Liu, J.Y.; Bucay, N.; Derynck, R.; Blelloch, R. Multiple targets of miR-302 and miR-372 promote reprogramming of human fibroblasts to induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Clinico-Pathological Charachteristics | Trial INT-IEO N = 19 | |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||
| Male | 12 | (63.2%) |
| Female | 7 | (36.8%) |
| Age (years) | 57.5 ± 5.6 (s.d.) | |
| Smoking habit (Pack-Years index) | 60.3 ± 23.8 (s.d.) | |
| Histotype | ||
| ADC (adenocarcinoma) | 14 | (73.7%) |
| SCC (squamous carcinoma) | 3 | (15.8%) |
| other | 2 | (10.5%) |
| Stage | ||
| Ia-Ib | 12 | (63.2%) |
| II-III-IV | 7 | (36.8%) |
| Status at 5 years | ||
| Alive | 11 | (57.9%) |
| Dead | 8 | (42.1%) |
| MSC risk level | ||
| High | 12 | (63.2%) |
| Intermediate & Low | 7 | (36.8%) |
| MicroRNA | Parametric p-Value | Permutation p-Value | Geom Mean of MSC H Patients | Geom Mean of MSC I & L Patients | Fold-Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-mir-210-prec | 0.0003 | 9.00 × 10‒4 | 782.18 | 1474.27 | 0.53 |
| hsa-mir-520e | 0.0003 | 8.00 × 10‒4 | 382.79 | 528.74 | 0.72 |
| hsa-mir-520h | 0.0006 | 4.00 × 10‒4 | 712.74 | 485.72 | 1.47 |
| hsa-mir-7-2-prec | 0.0009 | 0.0011 | 762.86 | 1107.25 | 0.69 |
| hsa-mir-329-3p | 0.0017 | 0.0016 | 299.35 | 277.83 | 1.08 |
| hsa-mir-520f-3p | 0.002 | 0.0016 | 304.94 | 274.83 | 1.11 |
| hsa-mir-511-5p | 0.002 | 8.00 × 10‒4 | 339.84 | 306.75 | 1.11 |
| hsa-mir-521 | 0.0021 | 5.00 × 10‒4 | 746.92 | 525.49 | 1.42 |
| hsa-mir-15a-prec | 0.0032 | 0.0031 | 390.85 | 489.14 | 0.8 |
| hsa-mir-518c-5p | 0.004 | 0.0055 | 353.1 | 418.94 | 0.84 |
| hsa-mir-147-prec | 0.005 | 0.0049 | 401.67 | 457.29 | 0.88 |
| hsa-mir-302d-3p | 0.0054 | 0.0038 | 299.31 | 274.01 | 1.09 |
| hsa-mir-499a-5p | 0.0058 | 0.0049 | 1726.93 | 1028.1 | 1.68 |
| hsa-mir-125a-prec | 0.0062 | 0.0055 | 364.76 | 435.28 | 0.84 |
| hsa-mir-138-2-prec | 0.0067 | 0.008 | 893.27 | 1298.2 | 0.69 |
| hsa-mir-519a-3p | 0.0068 | 0.0036 | 2117.4 | 1501.89 | 1.41 |
| hsa-mir-509-3p | 0.0099 | 0.0065 | 1204.47 | 908.23 | 1.33 |
| KEGG Pathway | p-Value | #Genes | #miRNAs |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | 3.66 × 10‒15 | 51 | 6 |
| Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | 8.99 × 10‒9 | 40 | 6 |
| Hepatitis B | 1.68 × 10‒14 | 35 | 5 |
| Axon guidance | 3.39 × 10‒14 | 22 | 5 |
| Chronic myeloid leukemia | 5.98 × 10‒13 | 24 | 5 |
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | 1.49 × 10‒12 | 67 | 5 |
| Pancreatic cancer | 2.24 × 10‒11 | 23 | 5 |
| Transcriptional misregulation in cancer | 5.40 × 10‒9 | 34 | 5 |
| ErbB signaling pathway | 1.35 × 10‒11 | 25 | 4 |
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | 2.21 × 10‒11 | 23 | 4 |
| TGF-beta signaling pathway | 1.34 × 10‒9 | 17 | 4 |
| Non-small cell lung cancer | 3.53 × 10‒8 | 15 | 4 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fortunato, O.; Verri, C.; Pastorino, U.; Sozzi, G.; Boeri, M. MicroRNA Profile of Lung Tumor Tissues Is Associated with a High Risk Plasma miRNA Signature. Microarrays 2016, 5, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/microarrays5030018
Fortunato O, Verri C, Pastorino U, Sozzi G, Boeri M. MicroRNA Profile of Lung Tumor Tissues Is Associated with a High Risk Plasma miRNA Signature. Microarrays. 2016; 5(3):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/microarrays5030018
Chicago/Turabian StyleFortunato, Orazio, Carla Verri, Ugo Pastorino, Gabriella Sozzi, and Mattia Boeri. 2016. "MicroRNA Profile of Lung Tumor Tissues Is Associated with a High Risk Plasma miRNA Signature" Microarrays 5, no. 3: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/microarrays5030018
APA StyleFortunato, O., Verri, C., Pastorino, U., Sozzi, G., & Boeri, M. (2016). MicroRNA Profile of Lung Tumor Tissues Is Associated with a High Risk Plasma miRNA Signature. Microarrays, 5(3), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/microarrays5030018