Clinicopathological Phenotype and Genetics of X-Linked Dystonia–Parkinsonism (XDP; DYT3; Lubag)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Clinical Phenotype
3. Neuroimaging
4. Treatments
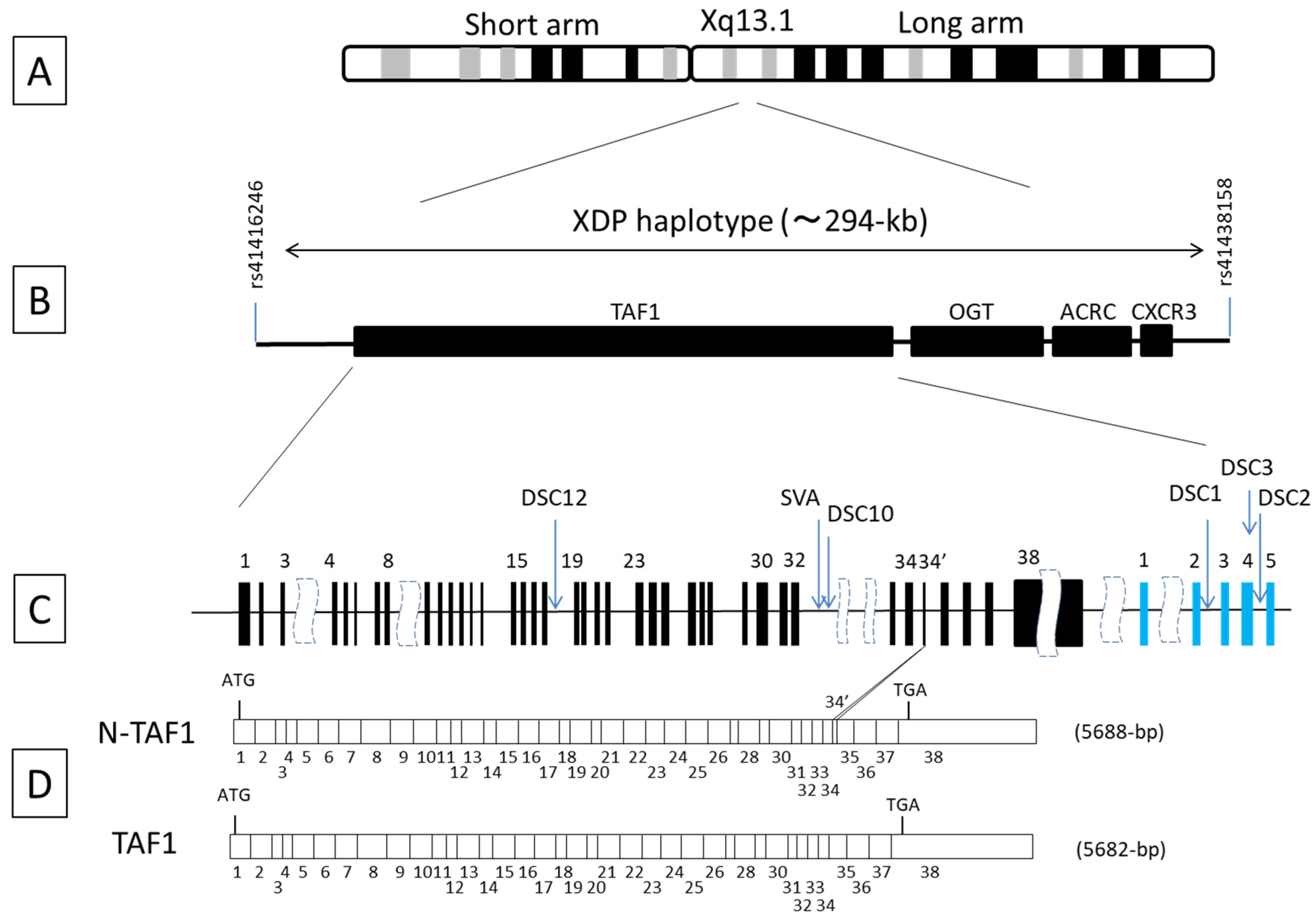
5. Genetics
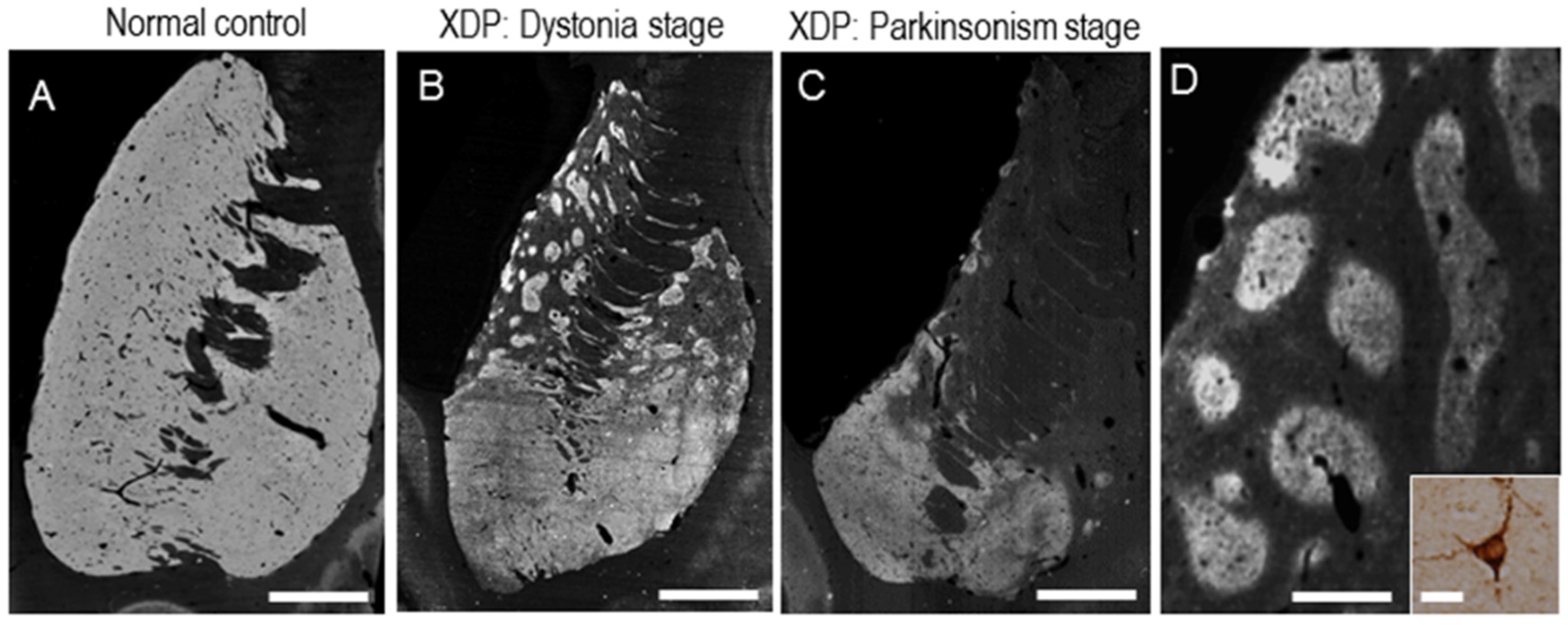
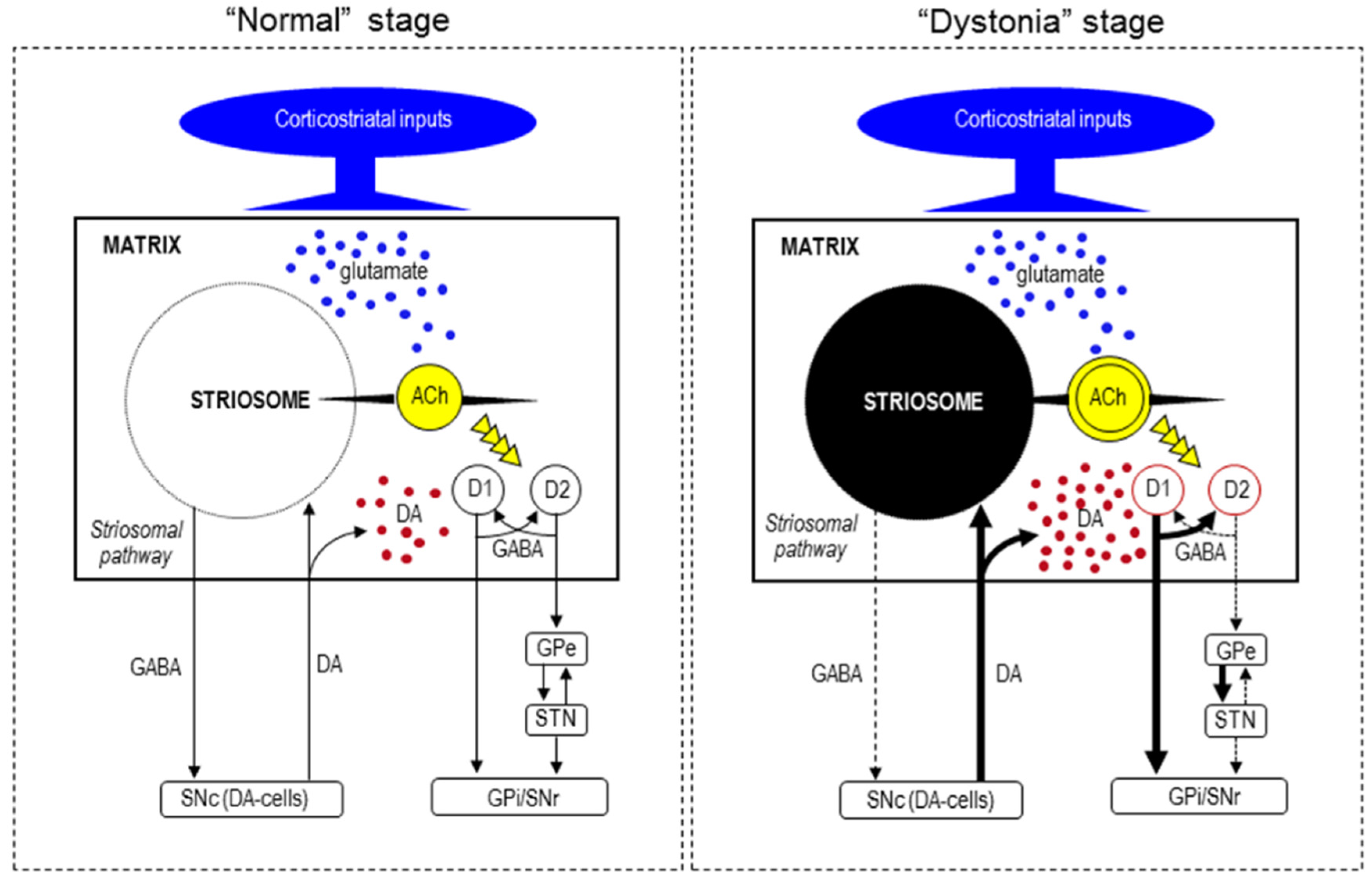
6. Functional Pathology
7. Pathogenesis of Striatal Neurodegeneration
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, L.V.; Pascasio, F.M.; Fuentes, F.D.; Viterbo, G.H. Torsion dystonia in Panay, Philippines. Adv. Neurol. 1976, 14, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Müller, U. The monogenic primary dystonias. Brain 2009, 132, 2005–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.V.; Rivera, C.; Teleg, R.A.; Dantes, M.B.; Pasco, P.M.; Jamora, R.D.; Arancillo, J.; Villareal-Jordan, R.F.; Rosales, R.L.; Demaisip, C.; et al. The unique phenomenology of sex-linked dystonia parkinsonism (XDP, DYT3, “Lubag”). Int. J. Neurosci. 2011, 121 (Suppl. 1), 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolte, D.; Niemann, S.; Müller, U. Specific sequence changes in multiple transcript system DYT3 are associated with X-linked dystonia parkinsonism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 10347–10352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo, A.; Westenberger, A.; Lee, L.V.; Brænne, I.; Liu, T.; Vater, I.; Rosales, R.; Jamora, R.D.; Pasco, P.M.; Cutiongco-Dela Paz, E.M.; et al. New insights into the genetics of X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism (XDP, DYT3). Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 23, 1334–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wassarman, D.A.; Sauer, F. TAFII250: A transcription toolbox. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 2895–2902. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Waters, C.H.; Faust, P.L.; Powers, J.; Vinters, H.; Moskowitz, C.; Nygaard, T.; Hunt, A.L.; Fahn, S. Neuropathology of lubag (x-linked dystonia parkinsonism). Mov. Disord. 1993, 8, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, S.; Lee, L.V.; Munoz, E.L.; Tooyama, I.; Tamiya, G.; Makino, S.; Ando, S.; Dantes, M.B.; Yamada, K.; Matsumoto, S.; et al. Functional anatomy of the basal ganglia in X-linked recessive dystonia-parkinsonism. Ann. Neurol. 2005, 58, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, S.; Kawarai, T.; Morigaki, R.; Okita, S.; Koizumi, H.; Nagahiro, S.; Munoz, E.L.; Lee, L.V.; Kaji, R. Defects in the striatal neuropeptide Y system in X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism. Brain 2013, 136 Pt 5, 1555–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.V.; Maranon, E.; Demaisip, C.; Peralta, O.; Borres-Icasiano, R.; Arancillo, J.; Rivera, C.; Munoz, E.; Tan, K.; Reyes, M.T. The natural history of sex-linked recessive dystonia parkinsonism of Panay, Philippines (XDP). Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2002, 9, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, R.L. X-linked dystonia parkinsonism: Clinical phenotype, genetics and therapeutics. J. Mov. Disord. 2010, 3, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo, A.; Lee, L.V.; Bruggemann, N.; Freimann, K.; Kaiser, F.J.; Jamora, R.D.; Rosales, R.L.; Klein, C.; Westenberger, A. Woman with X-linked recessive dystonia-parkinsonism: Clue to the epidemiology of parkinsonism in filipino women? JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 1177–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evidente, V.G.; Nolte, D.; Niemann, S.; Advincula, J.; Mayo, M.C.; Natividad, F.F.; Müller, U. Phenotypic and molecular analyses of X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism (“Lubag”) in women. Arch. Neurol. 2004, 61, 1956–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evidente, V.G.H. X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism. In Genereviews(r); Pagon, R.A., Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Wallace, S.E., Amemiya, A., Bean, L.J.H., Bird, T.D., Ledbetter, N., Mefford, H.C., Smith, R.J.H., et al., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Rosales, R.L.; Santos, M.M.; Ng, A.R.; Teleg, R.; Dantes, M.; Lee, L.V.; Fernandez, H.H. The broadening application of chemodenervation in X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism (part 1): Muscle afferent block versus botulinum toxin-a in cervical and limb dystonias. Int. J. Neurosci. 2011, 121 (Suppl. 1), 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamora, R.D.; Ledesma, L.K.; Domingo, A.; Cenina, A.R.; Lee, L.V. Nonmotor features in sex-linked dystonia parkinsonism. Neurodegener. Dis. Manag. 2014, 4, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, L.L.; Kellison, I.L.; Fernandez, H.H.; Okun, M.S.; Bowers, D. Neuropsychological profile of a filipino gentleman with X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism: A case report of Lubag disease. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2009, 23, 100–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadia, P.M.; Lim, S.Y.; Lozano, A.M.; Adams, J.R.; Poon, Y.Y.; Torres Diaz, C.V.; Moro, E. Bilateral pallidal stimulation for X-linked dystonia parkinsonism. Arch. Neurol. 2010, 67, 1012–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemmotsu, N.; Price, C.C.; Oyama, G.; Okun, M.S.; Foote, K.D.; Howe, L.L.; Bowers, D. Pre- and post- gpi dbs neuropsychological profiles in a case of X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2011, 25, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beste, C.; Mückschel, M.; Rosales, R.; Domingo, A.; Lee, L.; Ng, A.; Klein, C.; Münchau, A. Striosomal dysfunction affects behavioral adaptation but not impulsivity-evidence from X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beste, C.; Mückschel, M.; Rosales, R.; Domingo, A.; Lee, L.; Ng, A.; Klein, C.; Münchau, A. Dysfunctions in striatal microstructure can enhance perceptual decision making through deficits in predictive coding. Brain Struct. Funct. 2017, 24, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friston, K. A theory of cortical responses. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 815–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morigaki, R.; Nakataki, M.; Kawarai, T.; Lee, L.V.; Teleg, R.A.; Tabuena, M.D.; Mure, H.; Sako, W.; Pasco, P.M.; Nagahiro, S.; et al. Depression in X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism: A case-control study. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2013, 19, 844–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasco, P.M.; Ison, C.V.; Munoz, E.L.; Magpusao, N.S.; Cheng, A.E.; Tan, K.T.; Lo, R.W.; Teleg, R.A.; Dantes, M.B.; Borres, R.; et al. Understanding XDP through imaging, pathology, and genetics. Int. J. Neurosci. 2011, 121 (Suppl. 1), 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eidelberg, D.; Takikawa, S.; Dhawan, V.; Chaly, T.; Robeson, W.; Dahl, R.; Margouleff, D.; Moeller, J.R.; Patlak, C.S.; Fahn, S. Striatal 18F-dopa uptake: Absence of an aging effect. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1993, 13, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evidente, V.G.H.; Santiago, J.; Fugoso, L.; Natividad, F.F. In Fluorine 18fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) brain imaging findings in symptomatic and asymptomatic carriers of X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism (“Lubag”). Mov. Disord. 2002, 21 (Suppl. 15), S626. [Google Scholar]
- Tackenberg, B.; Metz, A.; Unger, M.; Schimke, N.; Passow, S.; Hoeffken, H.; Hoffmann, G.F.; Müller, U.; Nolte, D.; Oertel, W.H.; et al. Nigrostriatal dysfunction in X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism (DYT3). Mov. Disord. 2007, 22, 900–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brüggemann, N.; Rosales, R.L.; Waugh, J.L.; Blood, A.J.; Domingo, A.; Heldmann, M.; Jamora, R.D.; Münchau, A.; Münte, T.F.; Lee, L.V.; et al. Striatal dysfunction in X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism is associated with disease progression. Eur. J. Neurol. 2017, 24, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falardeau, P. Functional dinstinctions of dopamine D2Long and D2Short receptors. In Dopamine Receptors and Transporters; Niznik, H.B., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 323–342. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, U.; Rosales, R.; Rocco, A.; Westenberger, A.; Domingo, A.; Go, C.L.; Brüggemann, N.; Klein, C.; Lee, L.V.; Dressler, D. Sonographic alteration of substantia nigra is related to parkinsonism-predominant course of X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2017, 37, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evidente, V.G. Zolpidem improves dystonia in “Lubag” or X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism syndrome. Neurology 2002, 58, 662–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evidente, V.G.; Advincula, J.; Esteban, R.; Pasco, P.; Alfon, J.A.; Natividad, F.F.; Cuanang, J.; Luis, A.S.; Gwinn-Hardy, K.; Hardy, J.; et al. Phenomenology of “Lubag” or X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism. Mov. Disord. 2002, 17, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evidente, V.G.; Lyons, M.K.; Wheeler, M.; Hillman, R.; Helepolelei, L.; Beynen, F.; Nolte, D.; Müller, U.; Starr, P.A. First case of X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism (“Lubag”) to demonstrate a response to bilateral pallidal stimulation. Mov. Disord. 2007, 22, 1790–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Torres, I.; Limousin, P.; Tisch, S.; Page, R.; Pinto, A.; Foltynie, T.; Bhatia, K.P.; Hariz, M.I.; Zrinzo, L. Early and marked benefit with GPi DBS for Lubag syndrome presenting with rapidly progressive life-threatening dystonia. Mov. Disord. 2009, 24, 1710–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyama, G.; Fernandez, H.H.; Foote, K.D.; Zeilman, P.; Hwynn, N.; Jacobson, C.E.; Malaty, I.A.; Rodriguez, R.L.; Okun, M.S. Differential response of dystonia and parkinsonism following globus pallidus internus deep brain stimulation in X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism (Lubag). Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2010, 88, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar, J.A.; Vesagas, T.S.; Jamora, R.D.; Teleg, R.A.; Ledesma, L.; Rosales, R.L.; Fernandez, H.H.; Lee, L.V. The promise of deep brain stimulation in X-linked dystonia parkinsonism. Int. J. Neurosci. 2011, 121 (Suppl. 1), 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitmer, D.; de Solages, C.; Hill, B.C.; Yu, H.; Bronte-Stewart, H. Resting beta hypersynchrony in secondary dystonia and its suppression during pallidal deep brain stimulation in DYT3+ Lubag dystonia. Neuromodulation 2013, 16, 200–205; discussion 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.J.; Sarwar, A.I.; Jankovic, J.; Viswanathan, A. Bilateral pallidal deep brain stimulation for X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism. World Neurosurg. 2014, 82, 241.e1–241.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tronnier, V.M.; Domingo, A.; Moll, C.K.; Rasche, D.; Mohr, C.; Rosales, R.; Capetian, P.; Jamora, R.D.; Lee, L.V.; Münchau, A.; et al. Biochemical mechanisms of pallidal deep brain stimulation in X-linked dystonia parkinsonism. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2015, 21, 954–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Németh, A.H.; Nolte, D.; Dunne, E.; Niemann, S.; Kostrzewa, M.; Peters, U.; Fraser, E.; Bochukova, E.; Butler, R.; Brown, J.; et al. Refined linkage disequilibrium and physical mapping of the gene locus for X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism (DYT3). Genomics 1999, 60, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.V.; Munoz, E.L.; Tan, K.T.; Reyes, M.T. Sex linked recessive dystonia parkinsonism of Panay, Philippines (XDP). Mol. Pathol. 2001, 54, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kawarai, T.; Pasco, P.M.; Teleg, R.A.; Kamada, M.; Sakai, W.; Shimozono, K.; Mizuguchi, M.; Tabuena, D.; Orlacchio, A.; Izumi, Y.; et al. Application of long-range polymerase chain reaction in the diagnosis of X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism. Neurogenetics 2013, 14, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasco, P.M.; Kawarai, T.; Silao, C.L.; Canson, D.M.; Lee, L.V.; Kaji, R. Validation of a PCR-based test for the genetic diagnosis of Filipino patients with X-linked dystonia pakinsonism (XDP). Acta Medic. Philipp. 2015, 49, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Jambaldorj, J.; Makino, S.; Munkhbat, B.; Tamiya, G. Sustained expression of a neuron-specific isoform of the Taf1 gene in development stages and aging mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 425, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino, S.; Kaji, R.; Ando, S.; Tomizawa, M.; Yasuno, K.; Goto, S.; Matsumoto, S.; Tabuena, M.D.; Maranon, E.; Dantes, M.; et al. Reduced neuron-specific expression of the TAF1 gene is associated with X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 80, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo, A.; Amar, D.; Grütz, K.; Lee, L.V.; Rosales, R.; Brüggemann, N.; Jamora, R.D.; Cutiongco-Dela Paz, E.; Rolfs, A.; Dressler, D.; et al. Evidence of TAF1 dysfunction in peripheral models of X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3205–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, N.; Hendriks, W.T.; Dhakal, J.; Vaine, C.A.; Liu, C.; Shin, D.; Shin, K.; Wakabayashi-Ito, N.; Dy, M.; Multhaupt-Buell, T.; et al. Decreased N-TAF1 expression in X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism patient-specific neural stem cells. Dis. Model. Mech. 2016, 9, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzfeld, T.; Nolte, D.; Grznarova, M.; Hofmann, A.; Schultze, J.L.; Muller, U. X-linked dystonia parkinsonism syndrome (xdp, lubag): Disease-specific sequence change dsc3 in taf1/dyt3 affects genes in vesicular transport and dopamine metabolism. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, I.; Sbodio, J.I.; Harraz, M.M.; Tyagi, R.; Grima, J.C.; Albacarys, L.K.; Hubbi, M.E.; Xu, R.; Kim, S.; Paul, B.D.; et al. Huntington’s disease: Neural dysfunction linked to inositol polyphosphate multikinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 9751–9756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Rawe, J.A.; Wu, Y.; Dorfel, M.J.; Rope, A.F.; Au, P.Y.; Parboosingh, J.S.; Moon, S.; Kousi, M.; Kosma, K.; Smith, C.S.; et al. TAF1 variants are associated with dysmorphic features, intellectual disability, and neurological manifestations. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 97, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostertag, E.M.; Goodier, J.L.; Zhang, Y.; Kazazian, H.H., Jr. SVA elements are nonautonomous retrotransposons that cause disease in humans. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2003, 73, 1444–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilund, K.R.; Yi, M.; Campagna, F.; Arca, M.; Zuliani, G.; Fellin, R.; Ho, Y.K.; Garcia, J.V.; Hobbs, H.H.; Cohen, J.C. Molecular mechanisms of autosomal recessive hypercholesterolemia. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2002, 11, 3019–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, K.; Nakahori, Y.; Miyake, M.; Matsumura, K.; Kondo-Iida, E.; Nomura, Y.; Segawa, M.; Yoshioka, M.; Saito, K.; Osawa, M.; et al. An ancient retrotransposal insertion causes Fukuyama-type congenital muscular dystrophy. Nature 1998, 394, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, L.; Ran, F.A.; Cox, D.; Lin, S.; Barretto, R.; Habib, N.; Hsu, P.D.; Wu, X.; Jiang, W.; Marraffini, L.A.; et al. Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science 2013, 339, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brüggemann, N.; Heldmann, M.; Klein, C.; Domingo, A.; Rasche, D.; Tronnier, V.; Rosales, R.L.; Jamora, R.D.; Lee, L.V.; Münte, T.F. Neuroanatomical changes extend beyond striatal atrophy in X-linked dystonia parkinsonism. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2016, 31, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crittenden, J.R.; Graybiel, A.M. Basal ganglia disorders associated with imbalances in the striosome and matrix compartments. Front. Neuroanat. 2011, 5, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crittenden, J.R.; Tillberg, P.W.; Riad, M.H.; Shima, Y.; Gerfen, C.R.; Curry, J.; Housman, D.E.; Nelson, S.B.; Boyden, E.S.; Graybiel, A.M. Striosome-dendron bouquets highlight a unique striatonigral circuit targeting dopamine-containing neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 11318–11323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koizumi, H.; Morigaki, R.; Okita, S.; Nagahiro, S.; Kaji, R.; Nakagawa, M.; Goto, S. Response of striosomal opioid signaling to dopamine depletion in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rat model of Parkinson’s disease: A potential compensatory role. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskow Jaunarajs, K.L.; Bonsi, P.; Chesselet, M.F.; Standaert, D.G.; Pisani, A. Striatal cholinergic dysfunction as a unifying theme in the pathophysiology of dystonia. Prog. Neurobiol. 2015, 127–128, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amemori, K.; Gibb, L.G.; Graybiel, A.M. Shifting responsibly: The importance of striatal modularity to reinforcement learning in uncertain environments. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2011, 5, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albin, R.L.; Reiner, A.; Anderson, K.D.; Penny, J.B.; Young, A.B. Striatal and nigral neuron subpopulations in rigid Huntington’s disease: Implications for the functional anatomy of chorea and rigid-akinesia. Ann. Neurol. 1990, 27, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rüb, U.; Vonsattel, J.P.; Heinsen, H.; Korf, H.W. The neuropathology of Huntington’s disease: Classical findings, recent developments and correlation to functional neuroanatomy. Adv. Anat. Embryol. Cell. Biol. 2015, 217, 1–146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vaine, C.A.; Shin, D.; Liu, C.; Hendriks, W.T.; Dhakal, J.; Shin, K.; Sharma, N.; Bragg, D.C. X-linked Dystonia-Parkinsonism patient cells exhibit altered signaling via nuclear factor-kappa B. Neurobiol. Dis. 2017, 100, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decressac, M.; Prestoz, L.; Veran, J.; Cantereau, A.; Jaber, M.; Gaillard, A. Neuropeptide Y stimulates proliferation, migration and differentiation of neural precursors from the subventricular zone in adult mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2009, 34, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morigaki, R.; Goto, S. Striatal vulnerability in Huntington’s disease: Neuroprotection versus neurotoxicity. Brain Sci. 2017, 7, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kawarai, T.; Morigaki, R.; Kaji, R.; Goto, S. Clinicopathological Phenotype and Genetics of X-Linked Dystonia–Parkinsonism (XDP; DYT3; Lubag). Brain Sci. 2017, 7, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci7070072
Kawarai T, Morigaki R, Kaji R, Goto S. Clinicopathological Phenotype and Genetics of X-Linked Dystonia–Parkinsonism (XDP; DYT3; Lubag). Brain Sciences. 2017; 7(7):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci7070072
Chicago/Turabian StyleKawarai, Toshitaka, Ryoma Morigaki, Ryuji Kaji, and Satoshi Goto. 2017. "Clinicopathological Phenotype and Genetics of X-Linked Dystonia–Parkinsonism (XDP; DYT3; Lubag)" Brain Sciences 7, no. 7: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci7070072
APA StyleKawarai, T., Morigaki, R., Kaji, R., & Goto, S. (2017). Clinicopathological Phenotype and Genetics of X-Linked Dystonia–Parkinsonism (XDP; DYT3; Lubag). Brain Sciences, 7(7), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci7070072






