Specialized Large Language Model Outperforms Neurologists at Complex Diagnosis in Blinded Case-Based Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
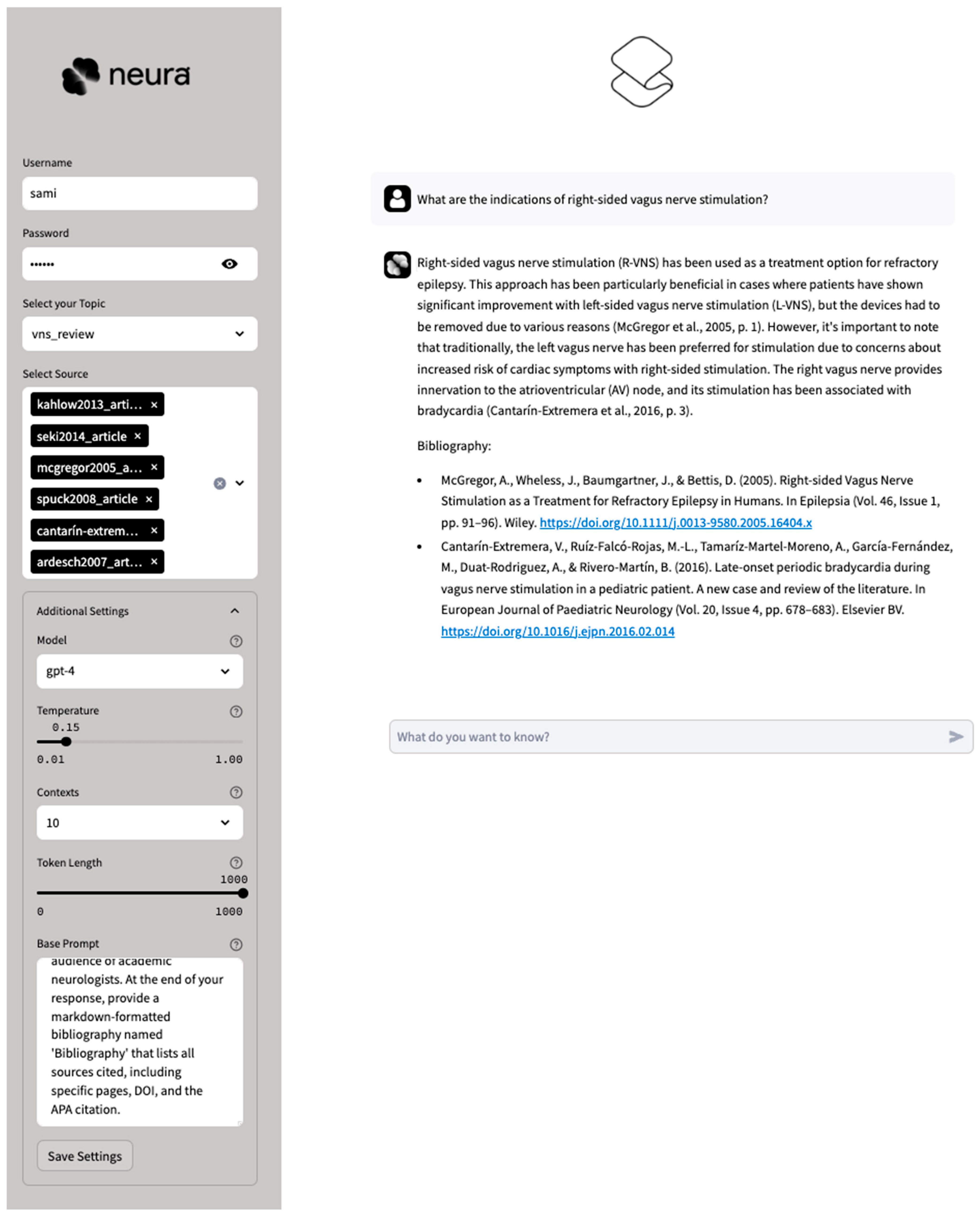
2.1. AI System
2.2. Diagnostic Challenges
2.3. Statistical Analysis
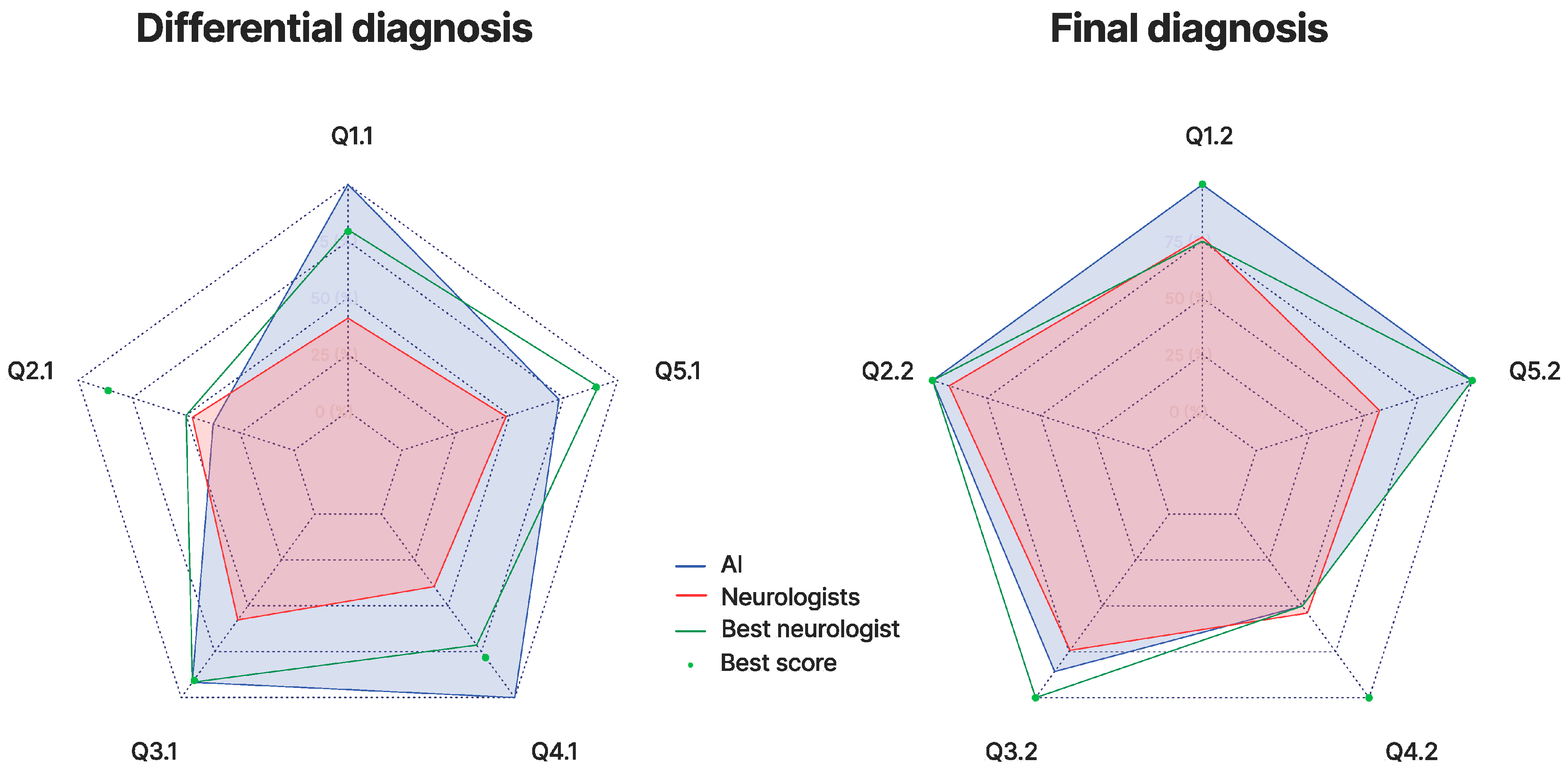
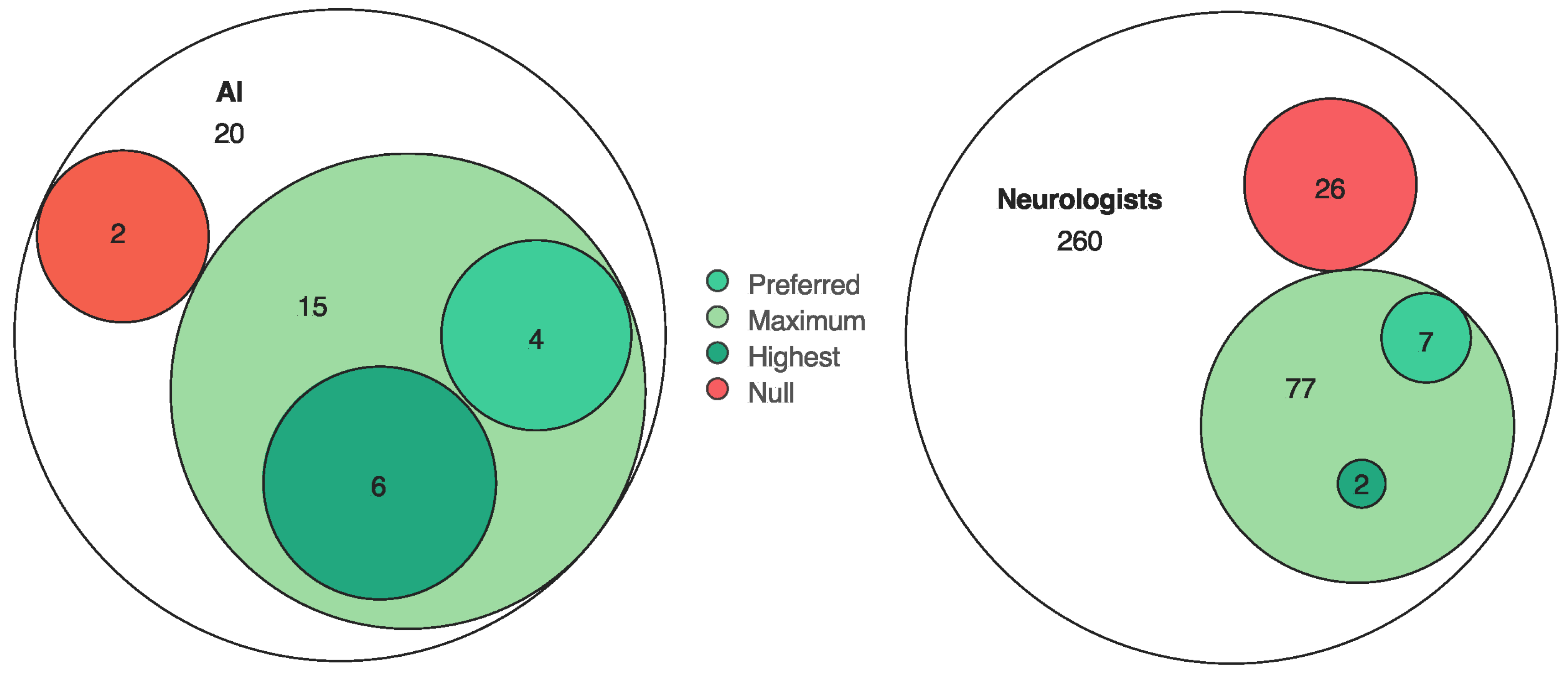
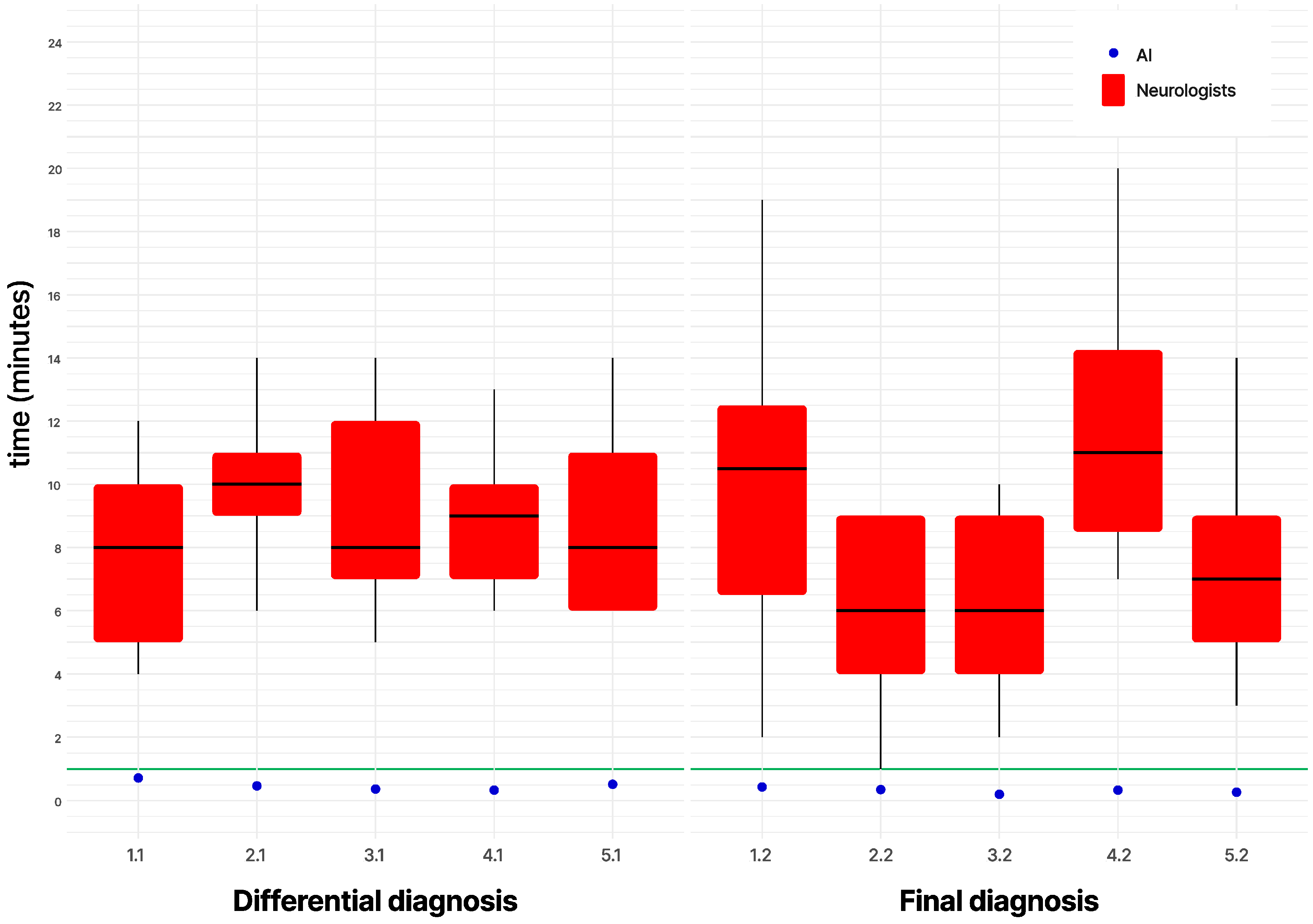
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Rationale
4.2. Limitations
4.3. Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| LLM | Large language model |
| RAG | Retrieval-augmented generation |
References
- Yu, K.H.; Beam, A.L.; Kohane, I.S. Artificial intelligence in healthcare. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 2, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Cao, X.; Huang, C.; Liu, E.; Qian, S.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Dong, F.; Zhang, J.; et al. Artificial intelligence: A powerful paradigm for scientific research. Innovation 2021, 2, 100179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radford, A.; Narasimhan, K.; Salimans, T.; Sutskever, I. Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training. Preprint 2018. Available online: https://cdn.openai.com/research-covers/language-unsupervised/language_understanding_paper.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.-W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achiam, J.; Adler, S.; Agarwal, S.; Ahmad, L.; Akkaya, I.; Aleman, F.L.; Almeida, D.; Altenschmidt, J.; Altman, S.; McGrew, B.; et al. GPT-4 Technical Report. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.08774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beam, A.L.; Drazen, J.M.; Kohane, I.S.; Leong, T.Y.; Manrai, A.K.; Rubin, E.J. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1220–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, C.; Zhao, X.; Lu, J.; Deng, C.; Zheng, C.; Wang, J.; Chowdhury, T.; Li, Y.; Cui, H.; Zhao, L.; et al. Domain Specialization as the Key to Make Large Language Models Disruptive: A Comprehensive Survey. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.18703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strubell, E.; Ganesh, A.; McCallum, A. Energy and Policy Considerations for Deep Learning in NLP. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.02243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, K.; Azizi, S.; Tu, T.; Singhal, K.; Azizi, S.; Tu, T.; Mahdavi, S.S.; Wei, J.; Chung, H.W.; Natarajan, V.; et al. Large language models encode clinical knowledge. Nature 2023, 620, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, Z.C. The Mythos of Model Interpretability. Queue 2018, 16, 31–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Altosaar, J.; Ranganath, R. ClinicalBERT: Modeling Clinical Notes and Predicting Hospital Readmission. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.05342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.F.; Lin, K.; Hewitt, J.; Paranjape, A.; Bevilacqua, M.; Petroni, F.; Liang, P. Lost in the Middle: How Language Models Use Long Contexts (Version 3). arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.03172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, P.; Perez, E.; Piktus, A.; Petroni, F.; Karpukhin, V.; Goyal, N.; Küttler, H.; Lewis, M.; Yih, W.-T.; Rocktäschel, T.; et al. Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.11401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolov, T.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.; Dean, J. Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1301.3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokorny, J. NoSQL databases. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Information Integration and Web-based Applications and Services, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 5–7 December 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taipalus, T. Vector database management systems: Fundamental concepts, use-cases, and current challenges. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.11322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.H. Adams and Victor’s Principles of Neurology; American Association of Neuropathologists, Inc.: Littleton, CO, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Brazis, P.W.; Masdeu, J.C.; Biller, J. Localization in Clinical Neurology, 6th ed.; Wolters Kluwer Health Adis (ESP): Waltham, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 1–668. [Google Scholar]
- Jankovic, J.; Mazziotta, J.C.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Newman, N.J. Bradley’s Neurology in Clinical Practice; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, P.E. Cooper PE. DeJong’s The Neurologic Examination. 2005. Sixth edition. By William W. Campbell. Published by Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins. 671 pages. C$140 approx. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 32, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, L.P.; Pedley, T.A.; Merritt, H.H. Merritt’s Neurology; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Edition MMP. Neurologic Disorders. 2023. Available online: https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/neurologic-disorders (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- Wikipedia. Category: Neurological Disorders. 2023. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:Neurological_disorders_%E2%80%8C (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- Lun, R.; Niznick, N.; Padmore, R.; Mack, J.; Shamy, M.; Stotts, G.; Blacquiere, D. Clinical Reasoning: Recurrent strokes secondary to unknown vasculopathy. Neurology 2020, 94, e2396–e2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, A.W.; Kiernan, C.L.; Huvard, M.J.; Vargas, A.; Zeidman, L.A.; Moss, H.E. Clinical Reasoning: An unusual diagnostic triad. Susac syndrome, or retinocochleocerebral vasculopathy. Neurology 2015, 85, e17–e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Wallach, A.I.; Rosales, D.; Margiewicz, S.E.; Belmont, H.M.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Minen, M.T. Clinical Reasoning: A 50-year-old woman with SLE and a tumefactive lesion. Neurology 2017, 89, e140–e145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, Y.; Elkhider, H.; Masangkay, N.; Lotia, M. Clinical Reasoning: A 65-year-old man with asymmetric weakness and paresthesias. Neurology 2019, 93, 856–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, P.; Scott, B. Clinical Reasoning: A 55-Year-Old Man with Odd Behavior and Abnormal Movements. Neurology 2021, 97, 1090–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Evans, L.; Hughes, T. Diagnostic aids: The Surgical Sieve revisited. Clin Teach. 2017, 14, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, T.H.; Cheatham, M.; Medenilla, A.; Sillos, C.; De Leon, L.; Elepaño, C.; Madriaga, M.; Aggabao, R.; Diaz-Candido, G.; Tseng, V.; et al. Performance of ChatGPT on USMLE: Potential for AI-assisted medical education using large language models. PLoS Digit. Health 2023, 2, e0000198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, M.C.; Wick, W.; Venkataramani, V. Performance of Large Language Models on a Neurology Board-Style Examination. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2346721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhal, K.; Tu, T.; Gottweis, J.; Sayres, R.; Wulczyn, E.; Amin, M.; Hou, L.; Clark, K.; Pfohl, S.R.; Cole-Lewis, H.; et al. Towards Expert-Level Medical Question Answering with Large Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.09617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, P.P. ChatGPT: A comprehensive review on background, applications, key challenges, bias, ethics, limitations and future scope. Internet Things Cyber-Phys. Syst. 2023, 3, 121–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.D.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A. Language Models are Few-Shot Learners. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.14165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touvron, H.; Martin, L.; Stone, K.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Llama 2: Open Foundation and Fine-Tuned Chat Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.09288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, A.Q.; Sablayrolles, A.; Mensch, A.; Bamford, C.; Chaplot, D.S.; de las Casas, D.; Bressand, F.; Lengyel, G.; Lample, G.; Saulnier, L.; et al. Mistral 7B. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.06825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Du, M.; Song, R.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. A Survey on Fairness in Large Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.10149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Fikri Aji, A. Style Over Substance: Evaluation Biases for Large Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.03025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, K. GPT-4 is here: What scientists think. arXiv 2023, 615, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louie, P.; Wilkes, R. Representations of race and skin tone in medical textbook imagery. Soc. Sci. Med. 2018, 202, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belyaeva, A.; Cosentino, J.; Hormozdiari, F.; Eswaran, K.; Shetty, S.; Corrado, G.; Carroll, A.; McLean, C.Y.; Furlotte, N.A. Multimodal LLMs for health grounded in individual-specific data. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.09018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, C.; Wu, M.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Liu, B.; Du, Z.; Shi, S.; Tu, Z. Macaw-LLM: Multi-Modal Language Modeling with Image, Audio, Video, and Text Integration. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.09093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F. On the Measure of Intelligence. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.01547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, L.; Tong, M.; Kaufmann, M.; Balesni, M.; Cooper Stickland, A.; Korbak, T.; Evans, O. The Reversal Curse: LLMs trained on “A is B” fail to learn “B is A”. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.12288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziri, N.; Lu, X.; Sclar, M.; Li, X.L.; Jiang, L.; Lin, B.Y.; Welleck, S.; West, P.; Bhagavatula, C.; Le Bras, R.; et al. Faith and Fate: Limits of Transformers on Compositionality. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.18654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, R.T.; Yao, S.; Friedman, D.; Hardy, M.; Griffiths, T.L. Embers of Autoregression: Understanding Large Language Models Through the Problem They are Trained to Solve. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.13638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.; Palmarini, A.B.; Moskvichev, A. Comparing Humans, GPT-4, and GPT-4V On Abstraction and Reasoning Tasks. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.09247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallegos, I.O.; Rossi, R.A.; Barrow, J.; Tanjim, M.M.; Kim, S.; Dernoncourt, F.; Yu, T.; Zhang, R.; Ahmed, N.K. Bias and Fairness in Large Language Models: A Survey. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.00770. Available online: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2023arXiv230900770G (accessed on 1 September 2023). [CrossRef]
- Daroff, R.B.; Jankovic, J.; Mazziotta, J.C.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Bradley, W.G. Bradley’s Neurology in Clinical Practice; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 149, 237, 304, 334, 338, 564, 569, 570, 1051, 1061, 1067, 1075, 1181, 1192, 1223, 1256, 1257, 1294, 1361, 1828, 1890, 2243, 2312, 2323–2325, 2330, 2337, 2339, 2341. ISBN 0323339166. [Google Scholar]
- Rowland, L.P.; Pedley, T.A.; Merritt, H.H. Merritt’s Neurology; Wolters Kluwer: Alphen aan den Rijn, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 854, 690, 1180, 1348, 1445, 1472. ISBN 145119336X. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreri, A.J.; Campo, E.; Seymour, J.F.; Willemze, R.; Ilariucci, F.; Ambrosetti, A.; Zucca, E.; Rossi, G.; López-Guillermo, A.; Pavlovsky, M.A.; et al. Intravascular lymphoma: Clinical presentation, natural history, management and prognostic factors in a series of 38 cases, with special emphasis on the ‘cutaneous variant’. Br. J. Haematol. 2004, 127, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ropper, A.; Samuels, M.; Klein, J. Adams and Victor’s Principles of Neurology, 10th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 889, 1224, 1543, 2032. ISBN 978-0071794794. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, H.H.; Danek, A.; Walker, R.H. Neuroacanthocytosis Syndromes. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2011, 6, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Case Summary | Neurological Field | Final Diagnosis | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | An 84-year-old Chinese woman with recurrent focal deficits, cognitive decline, multifocal cerebral artery constriction, and bilateral infarctions. | Neurovascular/neuro-oncology | Intravascular lymphoma |
| Case 2 | A 44-year-old woman with hypothyroidism presenting with cognitive decline, headaches, confusion, and progressive multifocal white matter lesions. | CNS inflammation diseases | Susac disease |
| Case 3 | A 50-year-old woman with systemic lupus erythematosus presenting with acute progressive left-sided weakness and sensory deficits, with imaging showing rapidly worsening right-hemispheric lesions. | Demyelinating diseases | Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) |
| Case 4 | A 65-year-old man with diabetes presenting with progressive asymmetric weakness, sensory deficits, areflexia, and weight loss. | PNS inflammation diseases | Neurosarcoidosis |
| Case 5 | A 55-year-old man with extensive psychiatric history presenting with subacute-on-chronic cognitive decline, dysphagia, involuntary hyperkinetic movements, gait instability, and chronic transaminitis. | Movement disorders | Neuroacanthocytosis |
| Initial Presentation | Differential Diagnosis (Tier 1) | Ancillary Exams and Results | Final Diagnosis (Tier 2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Evaluators awarded points (max 1 each) for justified differential diagnoses:
|
| Neuroacanthocytosis (3 points awarded). (Alternative, less accurate diagnosis, Huntington’s: 1 point.) Penalties possible for aberrant/harmful conclusions. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barrit, S.; Torcida, N.; Mazeraud, A.; Boulogne, S.; Benoit, J.; Carette, T.; Carron, T.; Delsaut, B.; Diab, E.; Kermorvant, H.; et al. Specialized Large Language Model Outperforms Neurologists at Complex Diagnosis in Blinded Case-Based Evaluation. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040347
Barrit S, Torcida N, Mazeraud A, Boulogne S, Benoit J, Carette T, Carron T, Delsaut B, Diab E, Kermorvant H, et al. Specialized Large Language Model Outperforms Neurologists at Complex Diagnosis in Blinded Case-Based Evaluation. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(4):347. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040347
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarrit, Sami, Nathan Torcida, Aurelien Mazeraud, Sebastien Boulogne, Jeanne Benoit, Timothée Carette, Thibault Carron, Bertil Delsaut, Eva Diab, Hugo Kermorvant, and et al. 2025. "Specialized Large Language Model Outperforms Neurologists at Complex Diagnosis in Blinded Case-Based Evaluation" Brain Sciences 15, no. 4: 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040347
APA StyleBarrit, S., Torcida, N., Mazeraud, A., Boulogne, S., Benoit, J., Carette, T., Carron, T., Delsaut, B., Diab, E., Kermorvant, H., Maarouf, A., Maldonado Slootjes, S., Redon, S., Robin, A., Hadidane, S., Harlay, V., Tota, V., Madec, T., Niset, A., ... Carron, R. (2025). Specialized Large Language Model Outperforms Neurologists at Complex Diagnosis in Blinded Case-Based Evaluation. Brain Sciences, 15(4), 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040347






