Improving the Sensitivity of Task-Based Multi-Echo Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging via T2* Mapping Using Synthetic Data-Driven Deep Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Multi-Echo fMRI Signal Model
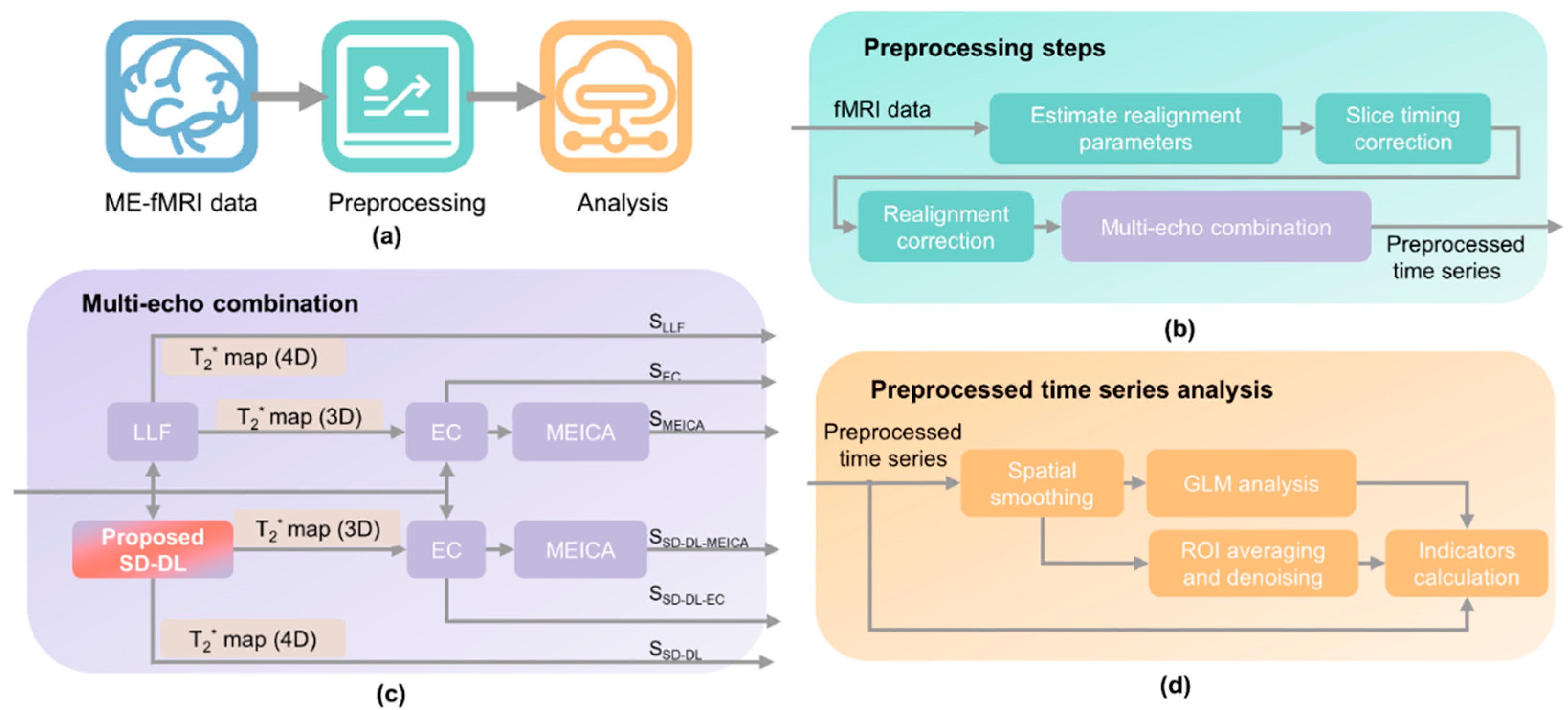
2.2. Data Processing Pipeline
2.3. T2* Mapping and Multi-Echo Combination
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. MRI Protocol
2.6. Evaluation Indicators
3. Results
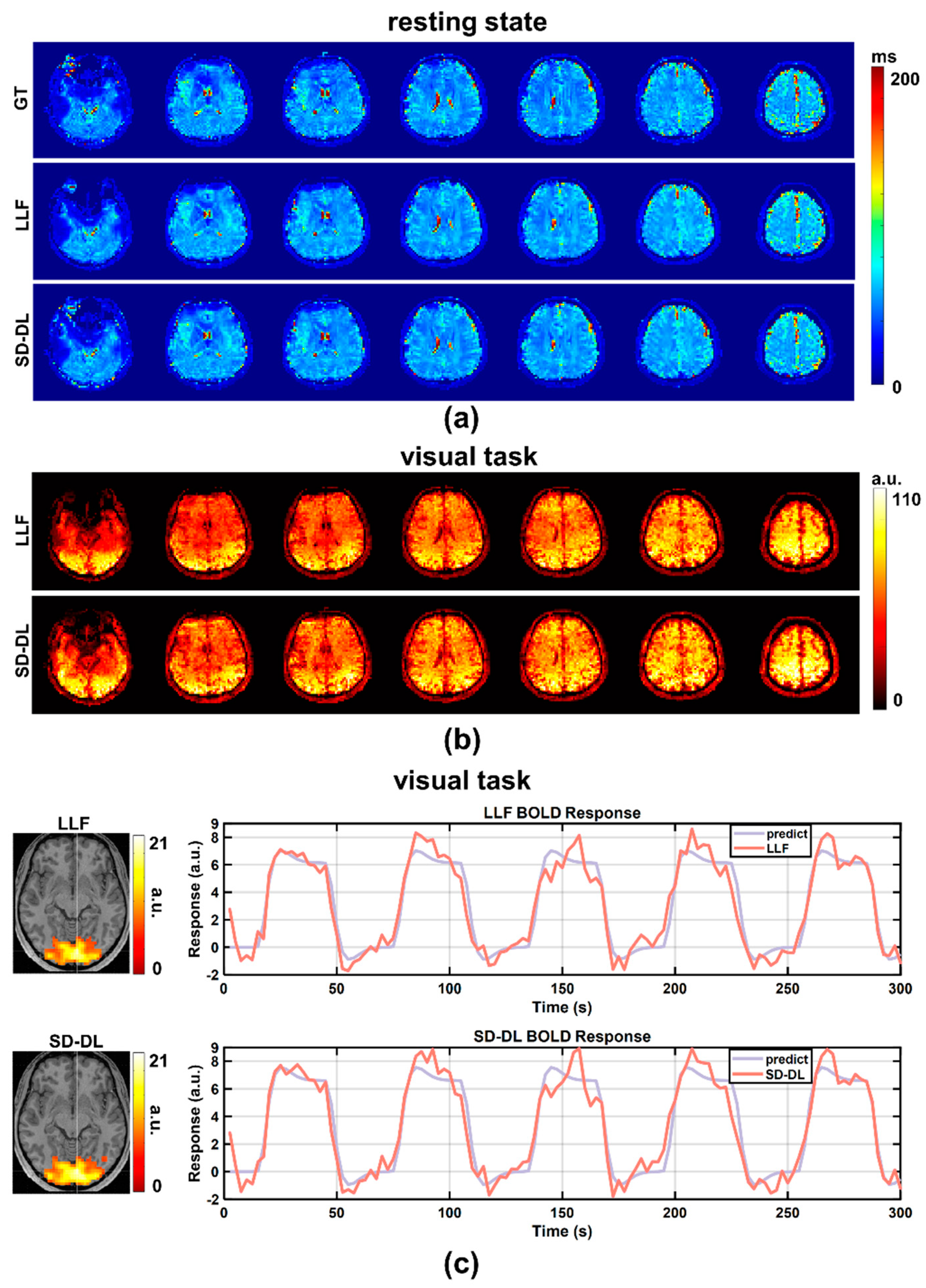
3.1. Results of Simulation Experiments
3.2. Results of Visual Stimulation Task Data
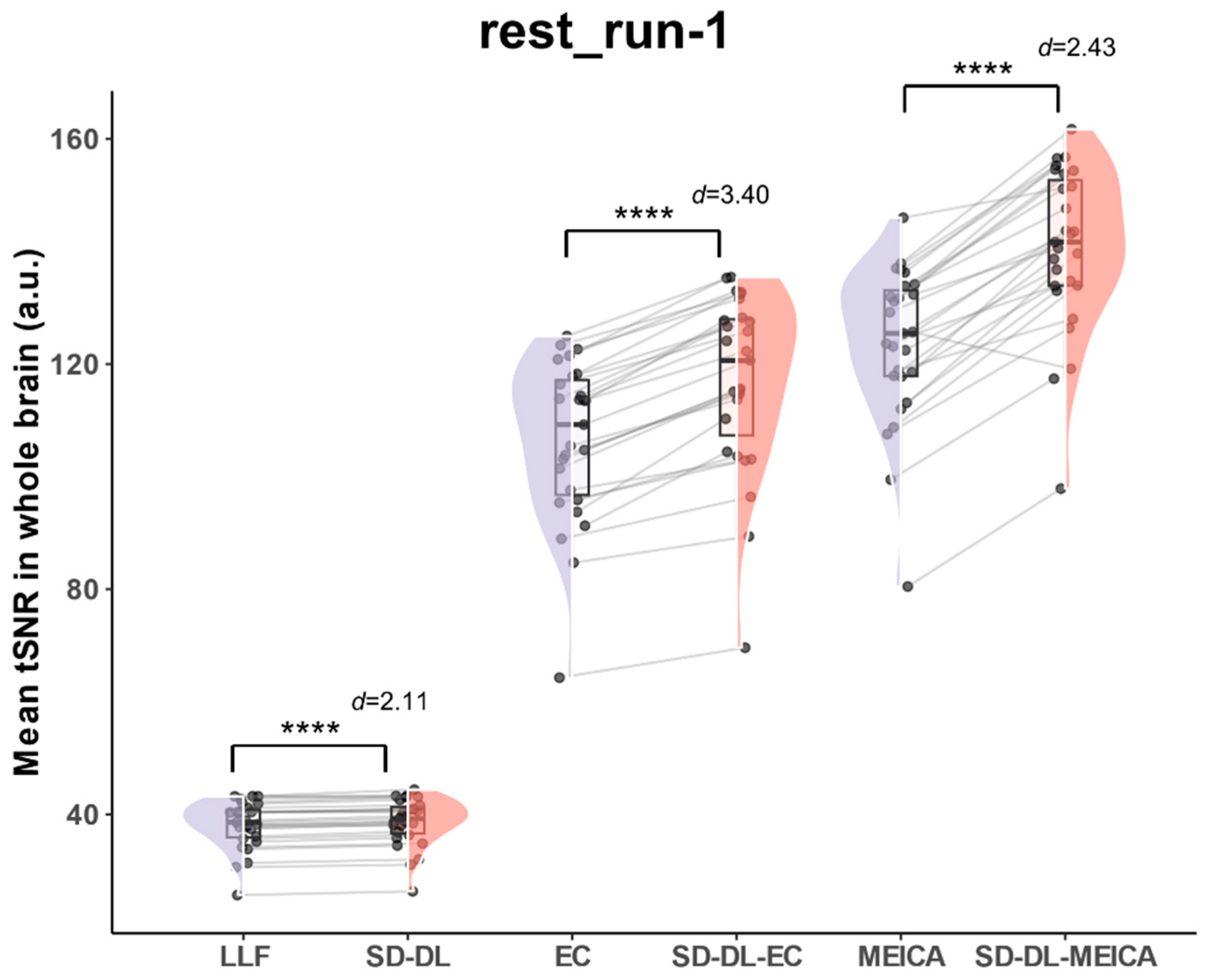
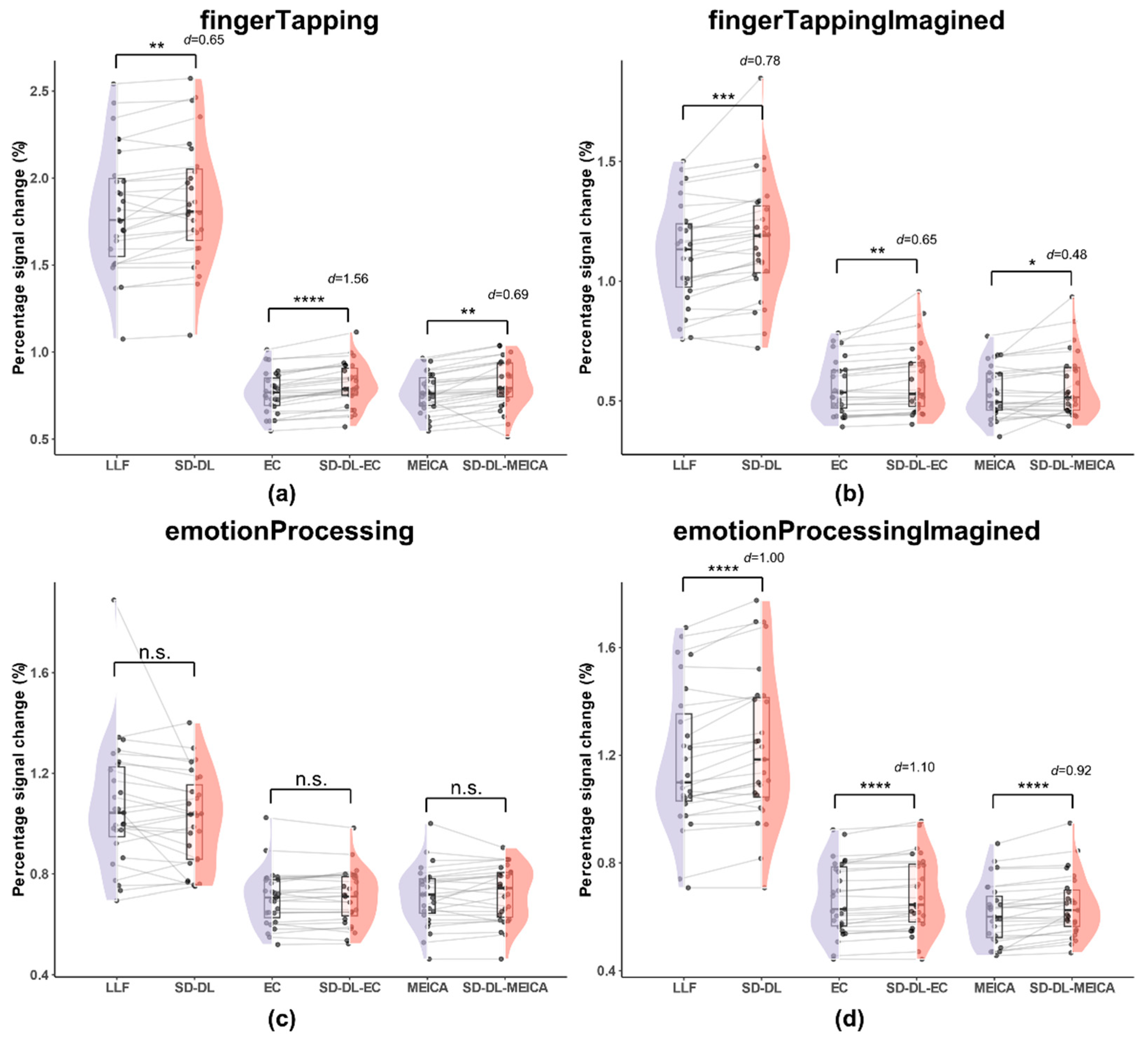
3.3. Results of rt-ME-fMRI Dataset
3.3.1. tSNR
3.3.2. Percentage Signal Change
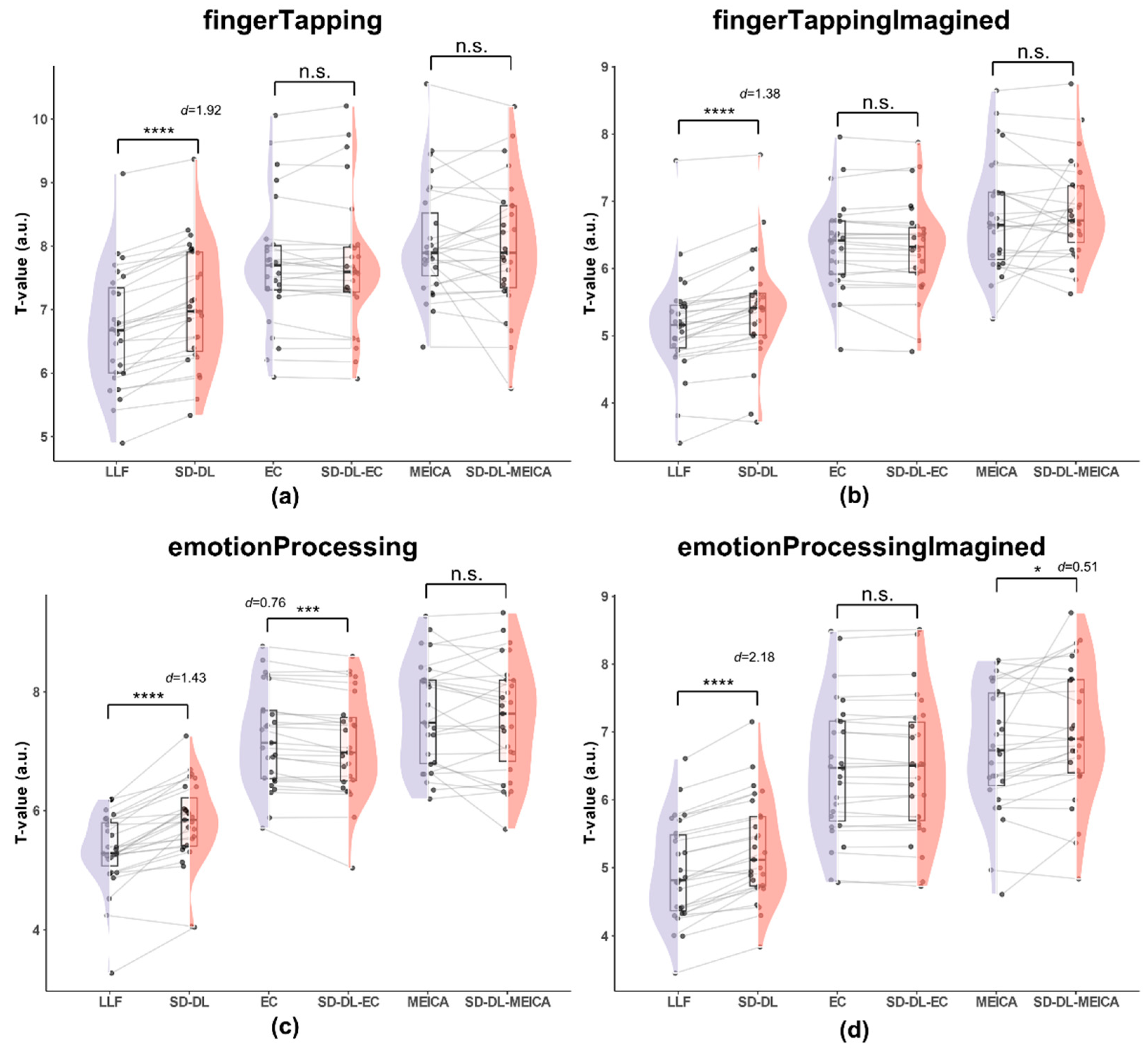
3.3.3. T-Values
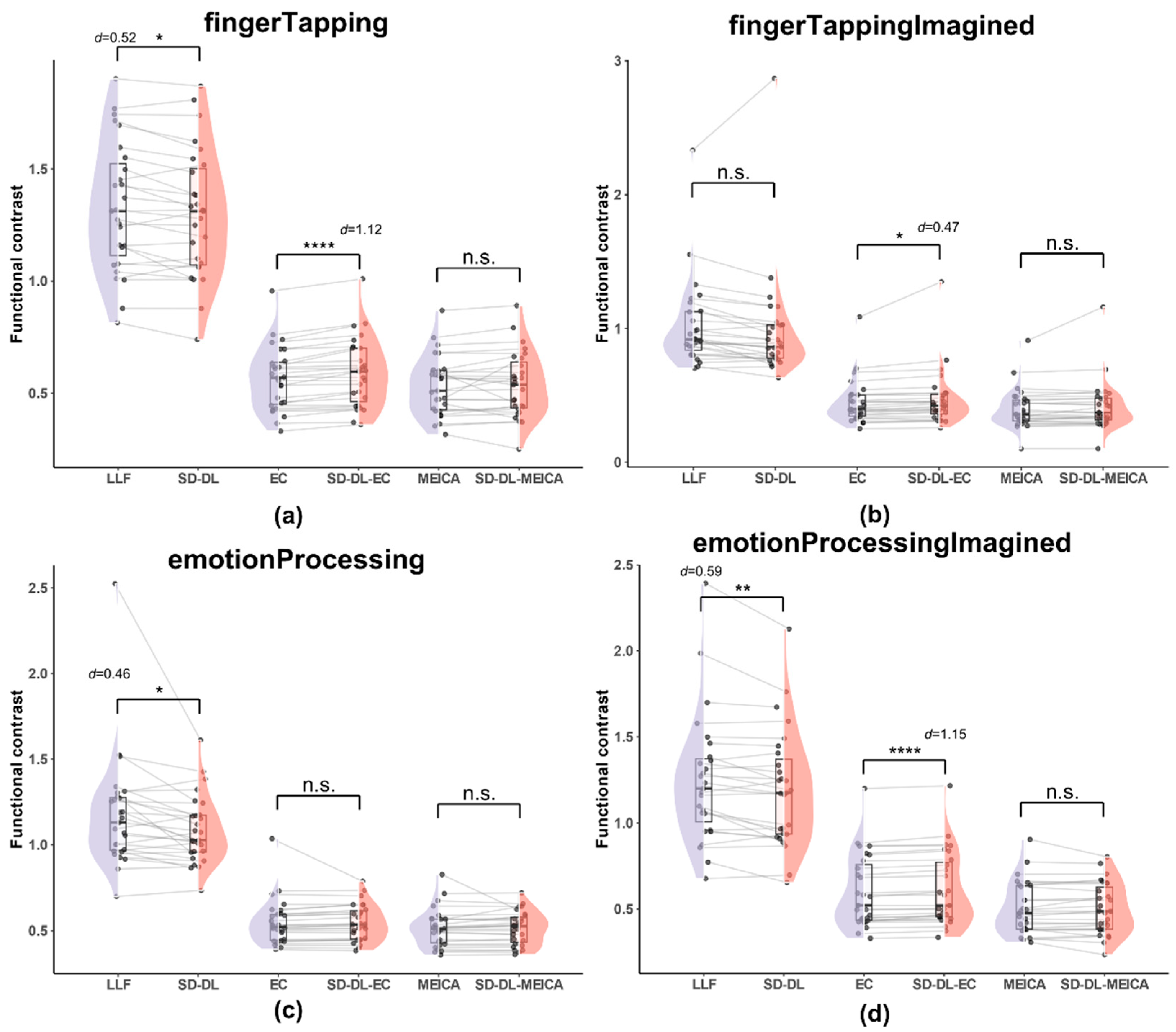
3.3.4. Functional Contrast
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vaidya, M.V.; Lazar, M.; Deniz, C.M.; Haemer, G.G.; Chen, G.; Bruno, M.; Sodickson, D.K.; Lattanzi, R.; Collins, C.M. Improved detection of fMRI activation in the cerebellum at 7T with dielectric pads extending the imaging region of a commercial head coil. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 48, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.H.; Miller, I.; Lai, S.; Xiong, J.; Fox, P.T. Quantitative assessment of blood inflow effects in functional MRI signals. Magn. Reson. Med. 1996, 36, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logothetis, N.K. MR imaging in the non-human primate: Studies of function and of dynamic connectivity. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2003, 13, 630–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posse, S.; Wiese, S.; Gembris, D.; Mathiak, K.; Kessler, C.; Grosse-Ruyken, M.-L.; Elghahwagi, B.; Richards, T.; Dager, S.R.; Kiselev, V.G. Enhancement of BOLD-contrast sensitivity by single-shot multi-echo functional MR imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 1999, 42, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poser, B.A.; Versluis, M.J.; Hoogduin, J.M.; Norris, D.G. BOLD contrast sensitivity enhancement and artifact reduction with multiecho EPI: Parallel-acquired inhomogeneity-desensitized fMRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2006, 55, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poser, B.A.; Norris, D.G. Investigating the benefits of multi-echo EPI for fMRI at 7 T. Neuroimage 2009, 45, 1162–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, J.D.; Barnes, K.A.; Snyder, A.Z.; Schlaggar, B.L.; Petersen, S.E. Spurious but systematic correlations in functional connectivity MRI networks arise from subject motion. Neuroimage 2012, 59, 2142–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satterthwaite, T.D.; Wolf, D.H.; Loughead, J.; Ruparel, K.; Elliott, M.A.; Hakonarson, H.; Gur, R.C.; Gur, R.E. Impact of in-scanner head motion on multiple measures of functional connectivity: Relevance for studies of neurodevelopment in youth. Neuroimage 2012, 60, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dijk, K.R.A.; Sabuncu, M.R.; Buckner, R.L. The influence of head motion on intrinsic functional connectivity MRI. Neuroimage 2012, 59, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.M.; Lewis, B.K.; Ruttimann, U.E.; Ye, F.Q.; Sinnwell, T.M.; Yang, Y.H.; Duyn, J.H.; Frank, J.A. Investigation of low frequency drift in fMRI signal. Neuroimage 1999, 9, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pais-Roldán, P.; Biswal, B.; Scheffler, K.; Yu, X. Identifying Respiration-Related Aliasing Artifacts in the Rodent Resting-State fMRI. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birn, R.M.; Diamond, J.B.; Smith, M.A.; Bandettini, P.A. Separating respiratory-variation-related neuronal-activity-related fluctuations in fluctuations from fMRI. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 1536–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianciardi, M.; Fukunaga, M.; van Gelderen, P.; Horovitz, S.G.; de Zwart, J.A.; Shmueli, K.; Duyn, J.H. Sources of functional magnetic resonance imaging signal fluctuations in the human brain at rest: A 7 T study. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2009, 27, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glover, G.H.; Li, T.Q.; Ress, D. Image-based method for retrospective correction of physiological motion effects in fMRI: RETROICOR. Magn. Reson. Med. 2000, 44, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, M.; Marecek, R.; Krajcovicová, L.; Slavícek, T.; Kaspárek, T.; Zemánková, P.; Ríha, P.; Mikl, M. Evaluation of different cerebrospinal fluid and white matter fMRI filtering strategies-Quantifying noise removal and neural signal preservation. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2019, 40, 1114–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.T.; Glover, G.H.; Meyer, C.H. Discrimination of Large Venous Vessels in Time-Course Spiral Blood-Oxygen-Level-Dependent Magnetic-Resonance Functional Neuroimaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 1995, 33, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, P.; Inati, S.J.; Evans, J.W.; Luh, W.M.; Bandettini, P.A. Differentiating BOLD and non-BOLD signals in fMRI time series using multi-echo EPI. Neuroimage 2012, 60, 1759–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, J.D.; Plitt, M.; Gotts, S.J.; Kundu, P.; Voon, V.; Bandettini, P.A.; Martin, A. Ridding fMRI data of motion-related influences: Removal of signals with distinct spatial and physical bases in multiecho data. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E2105–E2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dipasquale, O.; Sethi, A.; Lagana, M.M.; Baglio, F.; Baselli, G.; Kundu, P.; Harrison, N.A.; Cercignani, M. Comparing resting state fMRI de-noising approaches using multi- and single-echo acquisitions. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, P.; Santin, M.D.; Bandettini, P.A.; Bullmore, E.T.; Petiet, A. Differentiating BOLD and non-BOLD signals in fMRI time series from anesthetized rats using multi-echo EPI at 11.7 T. Neuroimage 2014, 102, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heunis, S.; Breeuwer, M.; Caballero-Gaudes, C.; Hellrung, L.; Huijbers, W.; Jansen, J.F.; Lamerichs, R.; Zinger, S.; Aldenkamp, A.P. The effects of multi-echo fMRI combination and rapid T2*-mapping on offline and real-time BOLD sensitivity. Neuroimage 2021, 238, 118244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, P.; Voon, V.; Balchandani, P.; Lombardo, M.V.; Poser, B.A.; Bandettini, P.A. Multi-echo fMRI: A review of applications in fMRI denoising and analysis of BOLD signals. Neuroimage 2017, 154, 59–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beissner, F.; Baudrexel, S.; Volz, S.; Deichmann, R. Dual-echo EPI for non-equilibrium fMRI-Implications of different echo combinations and masking procedures. Neuroimage 2010, 52, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Castillo, J.; Panwar, P.; Buchanan, L.C.; Caballero-Gaudes, C.; Handwerker, D.A.; Jangraw, D.C.; Zachariou, V.; Inati, S.; Roopchansingh, V.; Derbyshire, J.A.; et al. Evaluation of multi-echo ICA denoising for task based fMRI studies: Block designs, rapid event-related designs, and cardiac-gated fMRI. Neuroimage 2016, 141, 452–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glover, G.H.; Lemieux, S.K.; Drangova, M.; Pauly, J.M. Decomposition of inflow and blood oxygen level-dependent (BOLD) effects with dual-echo spiral gradient-recalled echo (GRE) fMRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 1996, 35, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speck, O.; Ernst, T.; Clang, L. Biexponential modeling of multigradient-echo MRI data of the brain. Magn. Reson. Med. 2001, 45, 1116–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciani, L.; Pfeiffer, J.C.; Hort, J.; Head, K.; Bush, D.; Taylor, A.J.; Spiller, R.C.; Francis, S.; Gowland, P.A. Improved methods for fMRI studies of combined taste and aroma stimuli. J. Neurosci. Methods 2006, 158, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, Z.S.; Glen, D.R.; Chen, G.; Beauchamp, M.S.; Desai, R.; Cox, R.W. A new method for improving functional-to-structural MRI alignment using local Pearson correlation. Neuroimage 2009, 44, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, M.V.; Auyeung, B.; Holt, R.J.; Waldman, J.; Ruigrok, A.N.V.; Mooney, N.; Bullmore, E.T.; Baron-Cohen, S.; Kundu, P. Improving effect size estimation and statistical power with multi-echo fMRI and its impact on understanding the neural systems supporting mentalizing. Neuroimage 2016, 142, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olafsson, V.; Kundu, P.; Wong, E.C.; Bandettini, P.A.; Liu, T.T. Enhanced identification of BOLD-like components with multi-echo simultaneous multi-slice (MESMS) fMRI and multi-echo ICA. Neuroimage 2015, 112, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Yang, Q.; Lin, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, P.; Cai, S.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Z.; Kang, T.; Cai, C. Learning from synthetic data for reference-free Nyquist ghost correction and parallel imaging reconstruction of echo planar imaging. Med. Phys. 2023, 50, 2135–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.Q.; Lin, Y.H.; Wang, J.C.; Bao, J.F.; Wang, X.Y.; Ma, L.C.; Zhou, Z.H.; Yang, Q.Z.; Cai, S.H.; He, H.J.; et al. Model-Based SyntheTic Data-Driven Learning (MOST-DL): Application in Single-Shot T-2 Mapping with Severe Head Motion Using Overlapping-Echo Acquisition. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2022, 41, 3167–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, Q.; Fan, L.; Yu, S.; Sun, L.; Cai, C.; Ding, X. Towards Better Generalization Using Synthetic Data: A Domain Adaptation Framework for T2 Mapping via Multiple Overlapping-Echo Acquisition. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2024, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, J. Statistical Parametric Mapping. Available online: https://github.com/spm/spm12 (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- Shorten, C.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. A survey on Image Data Augmentation for Deep Learning. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; Bandettini, P.A.; Bottenhorn, K.L.; Caballero-Gaudes, C.; Dowdle, L.T.; DuPre, E.; Gonzalez-Castillo, J.; Handwerker, D.; Heunis, S.; Kundu, P.; et al. ME-ICA/Tedana: 0.0.12. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/6461353 (accessed on 14 May 2024).
- Kundu, P.; Brenowitz, N.D.; Voon, V.; Worbe, Y.; Vertes, P.E.; Inati, S.J.; Saad, Z.S.; Bandettini, P.A.; Bullmore, E.T. Integrated strategy for improving functional connectivity mapping using multiecho fMRI. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16187–16192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DuPre, E.; Salo, T.; Ahmed, Z.; Bandettini, P.A.; Bottenhorn, K.L.; Caballero-Gaudes, C.; Dowdle, L.T.; Gonzalez-Castillo, J.; Heunis, S.; Kundu, P. TE-dependent analysis of multi-echo fMRI with tedana. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heunis, S.; Breeuwer, M.; Caballero-Gaudes, C.; Hellrung, L.; Huijbers, W.; Jansen, J.F.A.; Lamerichs, R.; Zinger, S.; Aldenkamp, A.P. rt-me-fMRI: A task and resting state dataset for real-time, multi-echo fMRI methods development and validation. F1000Research 2021, 10, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, L.; Bollmann, S.; Diaconescu, A.O.; Hutton, C.; Heinzle, J.; Iglesias, S.; Hauser, T.U.; Sebold, M.; Manjaly, Z.M.; Pruessmann, K.P.; et al. The PhysIO Toolbox for Modeling Physiological Noise in fMRI Data. J. Neurosci. Methods 2017, 276, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan Henuis, R.G. fMRwhy. Available online: https://github.com/jsheunis/fMRwhy (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- Pernet, C.R. Misconceptions in the use of the General Linear Model applied to functional MRI: A tutorial for junior neuro-imagers. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Ma, L.; Zhou, Z.; Bao, J.; Yang, Q.; Huang, H.; Cai, S.; He, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhong, J.; et al. Rapid high-fidelity T2* mapping using single-shot overlapping-echo acquisition and deep learning reconstruction. Magn. Reson. Med. 2023, 89, 2157–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Yang, Q.; Qian, S.; Dong, J.; Cai, S.; Chen, Z.; Cai, C. Improving the Sensitivity of Task-Based Multi-Echo Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging via T2* Mapping Using Synthetic Data-Driven Deep Learning. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14080828
Zhao Y, Yang Q, Qian S, Dong J, Cai S, Chen Z, Cai C. Improving the Sensitivity of Task-Based Multi-Echo Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging via T2* Mapping Using Synthetic Data-Driven Deep Learning. Brain Sciences. 2024; 14(8):828. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14080828
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yinghe, Qinqin Yang, Shiting Qian, Jiyang Dong, Shuhui Cai, Zhong Chen, and Congbo Cai. 2024. "Improving the Sensitivity of Task-Based Multi-Echo Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging via T2* Mapping Using Synthetic Data-Driven Deep Learning" Brain Sciences 14, no. 8: 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14080828
APA StyleZhao, Y., Yang, Q., Qian, S., Dong, J., Cai, S., Chen, Z., & Cai, C. (2024). Improving the Sensitivity of Task-Based Multi-Echo Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging via T2* Mapping Using Synthetic Data-Driven Deep Learning. Brain Sciences, 14(8), 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14080828







