Evaluation of Mild Cognitive Impairment through Perientorhinal/Hippocampal Imaging and Comprehensive Neuropsychological and Psychophysical Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Single domain amnesic MCI: this is a rare form that only involves memory and correlates with the evolution of Alzheimer’s disease;
- (2)
- Multiple domain amnesic MCI represents the prevalent form, in which memory is compromised together with one or more different cognitive domains;
- (3)
- Non-amnesic single domain MCI exclusively involves the cognitive domain, except memory;
- (4)
- Non-amnesic multiple domain MCI, in which two or more cognitive domains are involved, except memory.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Perientorhinal/Hippocampal MRI
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion and Limits of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hallett, M.; Aybek, S.; Dworetzky, B.A.; McWhirter, L.; Staab, J.P.; Stone, J. Functional Neurological Disorder: New Subtypes and Shared Mechanisms. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, S.; Reisberg, B.; Zaudig, M.; Petersen, R.C.; Ritchie, K.; Broich, K.; Belleville, S.; Brodaty, H.; Bennett, D.; Chertkow, H.; et al. Mild Cognitive Impairment. Lancet 2006, 367, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, N.L.; Unverzagt, F.; LaMantia, M.A.; Khan, B.A.; Boustani, M.A. Risk Factors for the Progression of Mild Cognitive Impairment to Dementia. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2013, 29, 873–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-X.; Liang, N.; Li, X.-L.; Yang, S.-H.; Wang, Y.-P.; Shi, N.-N. Diagnosis and Treatment for Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review of Clinical Practice Guidelines and Consensus Statements. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 719849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephan, B.C.M.; Hunter, S.; Harris, D.; Llewellyn, D.J.; Siervo, M.; Matthews, F.E.; Brayne, C. The Neuropathological Profile of Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI): A Systematic Review. Mol. Psychiatry 2012, 17, 1056–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davatzikos, C.; Bhatt, P.; Shaw, L.M.; Batmanghelich, K.N.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Prediction of MCI to AD Conversion, via MRI, CSF Biomarkers, and Pattern Classification. Neurobiol. Aging 2011, 32, 2322.e19–2322.e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasper, S.; Bancher, C.; Eckert, A.; Förstl, H.; Frölich, L.; Hort, J.; Korczyn, A.D.; Kressig, R.W.; Levin, O.; Palomo, M.S.M. Management of Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI): The Need for National and International Guidelines. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 21, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verghese, J.; De Sanctis, P.; Ayers, E. Everyday Function Profiles in Prodromal Stages of MCI: Prospective Cohort Study. Alzheimers Dement. 2023, 19, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Festari, C.; Massa, F.; Cotta Ramusino, M.; Gandolfo, F.; Nicolosi, V.; Orini, S.; Aarsland, D.; Agosta, F.; Babiloni, C.; Boada, M.; et al. European Consensus for the Diagnosis of MCI and Mild Dementia: Preparatory Phase. Alzheim. Dement. 2023, 19, 1729–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetsuka, S. Depression and Dementia in Older Adults: A Neuropsychological Review. Aging Dis. 2021, 12, 1920–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walla, P.; Duregger, C.; Deecke, L.; Dal-Bianco, P. Dysfunctional Incidental Olfaction in Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI): An Electroencephalography (EEG) Study. Brain Sci. 2011, 1, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Invitto, S.; Piraino, G.; Ciccarese, V.; Carmillo, L.; Caggiula, M.; Trianni, G.; Nicolardi, G.; Di Nuovo, S.; Balconi, M. Potential Role of OERP as Early Marker of Mild Cognitive Impairment. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devanand, D.P.; Michaels-Marston, K.S.; Liu, X.; Pelton, G.H.; Padilla, M.; Marder, K.; Bell, K.; Stern, Y.; Mayeux, R. Olfactory Deficits in Patients With Mild Cognitive Impairment Predict Alzheimer’s Disease at Follow-Up. Am. J. Psychiatry 2000, 157, 1399–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, P.L.; Murphy, C. Olfactory Measures as Predictors of Conversion to Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapuis, J.; Cohen, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, S.; Xu, F.; Wilson, D.A. Lateral Entorhinal Modulation of Piriform Cortical Activity and Fine Odor Discrimination. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 13449–13459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzi, A.; Sobel, N. Olfactory Perception as a Compass for Olfactory Neural Maps. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2011, 15, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettenmann, B.; Hummel, C.; Stefan, H.; Kobal, G. Multiple Olfactory Activity in the Human Neocortex Identified by Magnetic Source Imaging. Chem. Senses 1997, 22, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pilly, P.K.; Grossberg, S. How Do Spatial Learning and Memory Occur in the Brain? Coordinated Learning of Entorhinal Grid Cells and Hippocampal Place Cells. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2012, 24, 1031–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franjic, D.; Skarica, M.; Ma, S.; Arellano, J.I.; Tebbenkamp, A.T.N.; Choi, J.; Xu, C.; Li, Q.; Morozov, Y.M.; Andrijevic, D.; et al. Transcriptomic Taxonomy and Neurogenic Trajectories of Adult Human, Macaque, and Pig Hippocampal and Entorhinal Cells. Neuron 2022, 110, 452–469.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
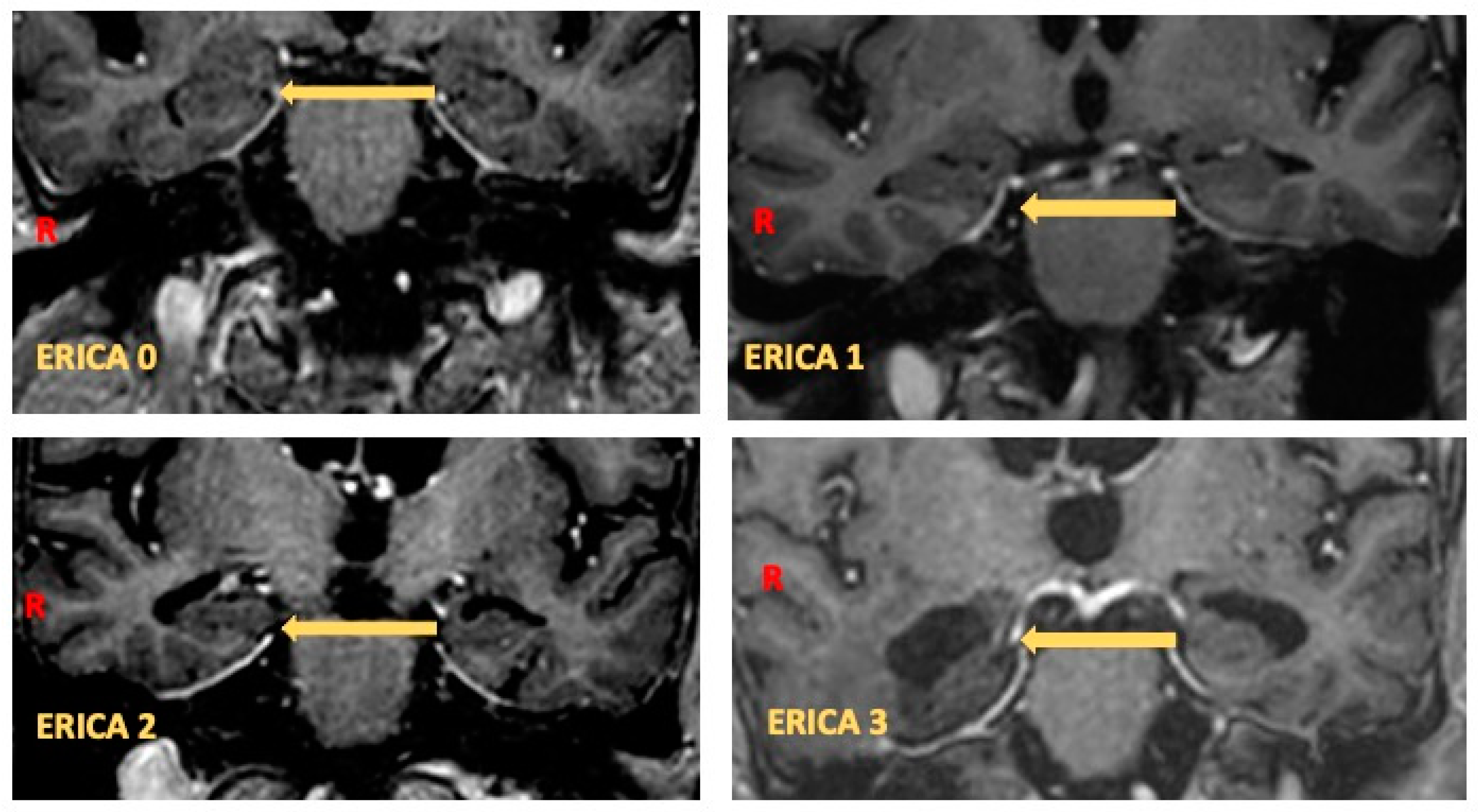
- Enkirch, S.J.; Traschütz, A.; Müller, A.; Widmann, C.N.; Gielen, G.H.; Heneka, M.T.; Jurcoane, A.; Schild, H.H.; Hattingen, E. The ERICA Score: An MR Imaging-Based Visual Scoring System for the Assessment of Entorhinal Cortex Atrophy in Alzheimer Disease. Radiology 2018, 288, 226–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischl, B.; Stevens, A.A.; Rajendran, N.; Yeo, B.T.T.; Greve, D.N.; Van Leemput, K.; Polimeni, J.R.; Kakunoori, S.; Buckner, R.L.; Pacheco, J.; et al. Predicting the Location of Entorhinal Cortex from MRI. NeuroImage 2009, 47, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Convertino, L.; Bush, D.; Zheng, F.; Adams, R.A.; Burgess, N. Reduced Grid-like Theta Modulation in Schizophrenia. Brain 2023, 146, 2191–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortier-Lebel, O.; Hudon, É.; Boller, B.; Frasnelli, J. Chemosensation in Anxiety: The Trigeminal System Matters. Chem. Senses 2023, 48, bjad010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Pozo, A.; Frosch, M.P.; Masliah, E.; Hyman, B.T. Neuropathological Alterations in Alzheimer Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2011, 1, a006189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesteruk, T.; Nesteruk, M.; Styczyńska, M.; Barcikowska-Kotowicz, M.; Walecki, J. Radiological Evaluation of Strategic Structures in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment and Early Alzheimer’s Disease. Pol. J. Radiol. 2016, 81, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battista, P.; Salvatore, C.; Castiglioni, I. Optimizing Neuropsychological Assessments for Cognitive, Behavioral, and Functional Impairment Classification: A Machine Learning Study. Behav. Neurol. 2017, 2017, 1850909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traschütz, A.; Enkirch, S.J.; Polomac, N.; Widmann, C.N.; Schild, H.H.; Heneka, M.T.; Hattingen, E. The Entorhinal Cortex Atrophy Score Is Diagnostic and Prognostic in Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. JAD 2020, 75, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpinelli Mazzi, M.; Iavarone, A.; Russo, G.; Musella, C.; Milan, G.; D’Anna, F.; Garofalo, E.; Chieffi, S.; Sannino, M.; Illario, M.; et al. Mini-Mental State Examination: New Normative Values on Subjects in Southern Italy. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2020, 32, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiewel, N.A.; Wisdom, N.M.; Bradshaw, M.R.; Pastorek, N.J.; Strutt, A.M. A Retrospective Review of Digit Span-Related Effort Indicators in Probable Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2012, 26, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, M.; Gerace, C.; Ruggeri, M.; Blundo, C. Various Faces of the Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test (RAVLT): Comments to the Manuscript “Normative Data beyond the Total Scores: A Process Score Analysis of the Rey’s 15 Words Test in Healthy Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease” by Gasparini and Colleagues. Neurol. Sci. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arce, T.; McMullen, K. The Corsi Block-Tapping Test: Evaluating Methodological Practices with an Eye towards Modern Digital Frameworks. Comput. Hum. Behav. Rep. 2021, 4, 100099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barncord, S.W.; Wanlass, R.L. The Symbol Trail Making Test: Test Development and Utility as a Measure of Cognitive Impairment. Appl. Neuropsychol. 2001, 8, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, T.; Sekinger, B.; Wolf, S.R.; Pauli, E.; Kobal, G. “Sniffin” Sticks’. Olfactory Performance Assessed by the Combined Testing of Odor Identification, Odor Discrimination and Olfactory Threshold. Chem. Senses 1997, 22, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horner, M.D.; Teichner, G.; Kortte, K.B.; Harvey, R.T. Construct Validity of the Babcock Story Recall Test. Appl. Neuropsychol. 2002, 9, 114–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appollonio, I.; Leone, M.; Isella, V.; Piamarta, F.; Consoli, T.; Villa, M.; Forapani, E.; Russo, A.; Nichelli, P. The Frontal Assessment Battery (FAB): Normative Values in an Italian Population Sample. Neurol. Sci. 2005, 26, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Invitto, S.; Boscolo-Rizzo, P.; Fantin, F.; Bonifati, D.M.; de Filippis, C.; Emanuelli, E.; Frezza, D.; Giopato, F.; Caggiula, M.; Schito, A.; et al. Exploratory Study on Chemosensory Event-Related Potentials in Long COVID-19 and Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Common Pathway? Bioengineering 2023, 10, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, E.; Kim, Y.-K. Neuroinflammation-Associated Alterations of the Brain as Potential Neural Biomarkers in Anxiety Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Fonseca, J.A.; Gosselink, K.L. Tauopathy and Neurodegeneration: A Role for Stress. Neurobiol. Stress. 2018, 9, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milligan Armstrong, A.; Porter, T.; Quek, H.; White, A.; Haynes, J.; Jackaman, C.; Villemagne, V.; Munyard, K.; Laws, S.M.; Verdile, G.; et al. Chronic Stress and Alzheimer’s Disease: The Interplay between the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis, Genetics and Microglia. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2021, 96, 2209–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, S.; Puentes, F.; Baker, D.; van der Valk, P. Inflammation in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Immunology 2010, 129, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, M.F. The Relationship Between Anxiety and Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. Rep. 2021, 5, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botto, R.; Callai, N.; Cermelli, A.; Causarano, L.; Rainero, I. Anxiety and Depression in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review of Pathogenetic Mechanisms and Relation to Cognitive Decline. Neurol. Sci. Off. J. Ital. Neurol. Soc. Ital. Soc. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2022, 43, 4107–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.-F.; Wang, H.-X.; Wu, J.-J.; Yao, W.; Hao, C.-F.; Pei, J.-J. Depressive Symptoms and Cognitive Impairment: A 10-Year Follow-up Study from the Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe. Eur. Psychiatry J. Assoc. Eur. Psychiatr. 2021, 64, e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirza, S.S.; Ikram, M.A.; Bos, D.; Mihaescu, R.; Hofman, A.; Tiemeier, H. Mild Cognitive Impairment and Risk of Depression and Anxiety: A Population-Based Study. Alzheimer’s Dementia J. Alzheimer’s Assoc. 2017, 13, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettema, J.M.; Prescott, C.A.; Myers, J.M.; Neale, M.C.; Kendler, K.S. The Structure of Genetic and Environmental Risk Factors for Anxiety Disorders in Men and Women. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2005, 62, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, E.; Salchner, P.; Aldag, J.M.; Salomé, N.; Singewald, N.; Landgraf, R.; Wigger, A. Genetic Predisposition to Anxiety-Related Behavior Determines Coping Style, Neuroendocrine Responses, and Neuronal Activation during Social Defeat. Behav. Neurosci. 2006, 120, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toloraia, K.; Meyer, A.; Beltrani, S.; Fuhr, P.; Lieb, R.; Gschwandtner, U. Anxiety, Depression, and Apathy as Predictors of Cognitive Decline in Patients With Parkinson’s Disease-A Three-Year Follow-Up Study. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 792830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salzman, C. Do Benzodiazepines Cause Alzheimer’s Disease? Am. J. Psychiatry 2020, 177, 476–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frosolini, A.; Parrino, D.; Fabbris, C.; Fantin, F.; Inches, I.; Invitto, S.; Spinato, G.; Filippis, C. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Confirmed Olfactory Bulb Reduction in Long COVID-19: Literature Review and Case Series. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Test | Statistic | p |
|---|---|---|
| MMSE | 2.6 | 0.46 |
| TMT-A | 2.05 | 0.56 |
| TMT-B | 0.81 | 0.84 |
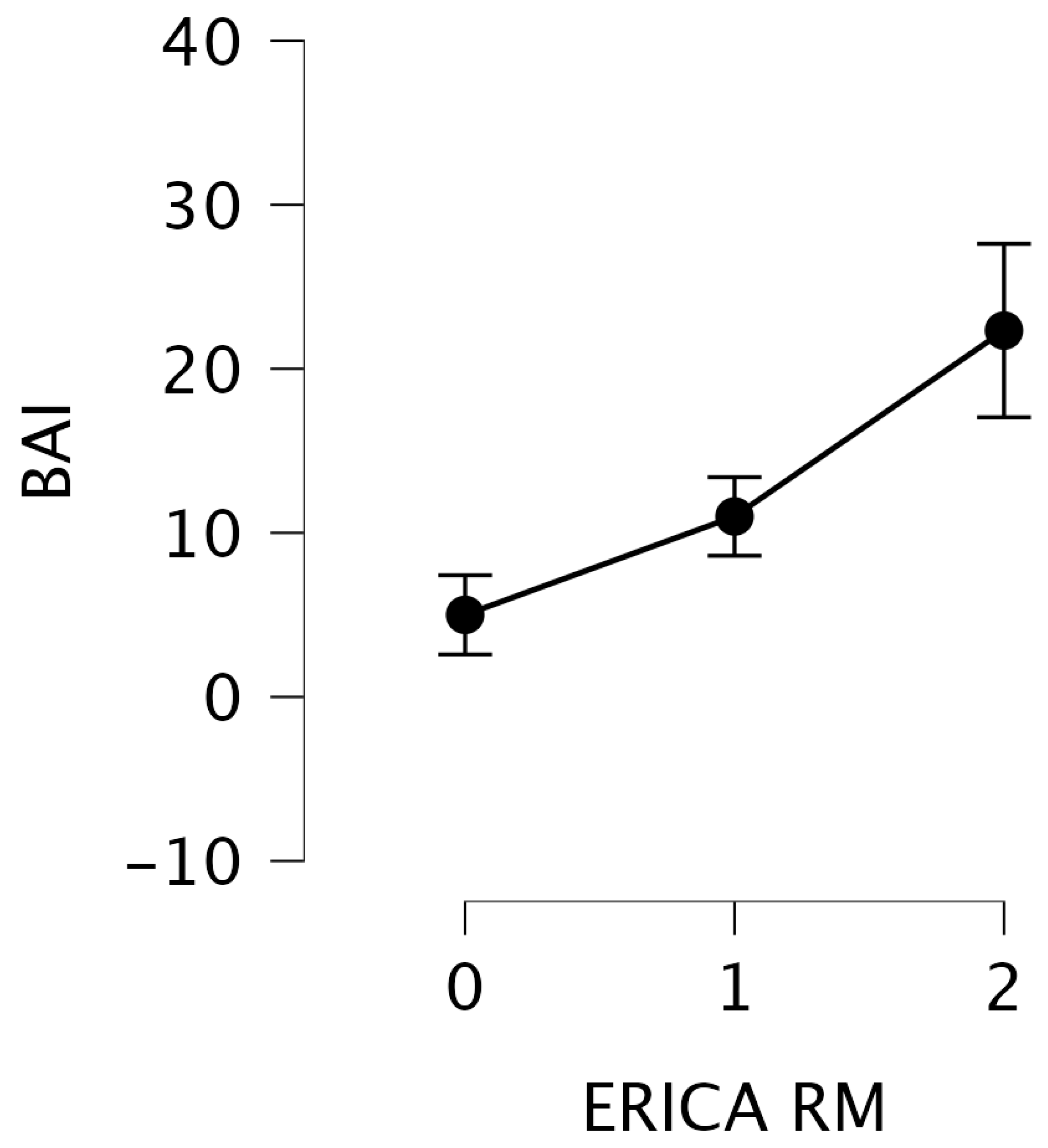
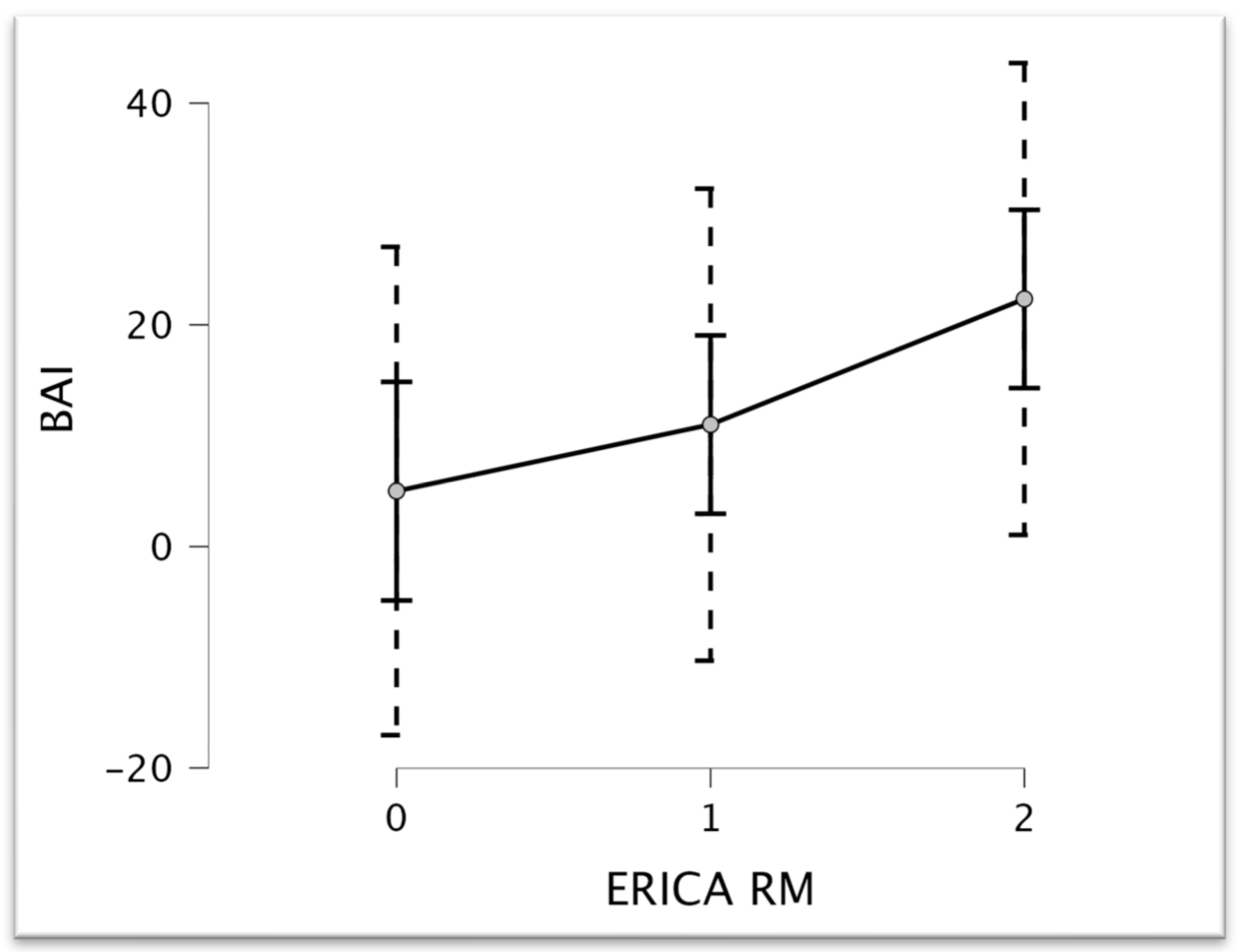
| BAI | 9.62 | 0.008 |
| ADL | 7.24 | 0.06 |
| IADL | 2.77 | 0.43 |
| 15 Ray W IMM | 1.29 | 0.73 |
| 15 Ray W Diff | 3.09 | 0.38 |
| Prose Memory | 1.14 | 0.77 |
| Test | F | p | η2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| BDI | 0.651 | 0.542 | 0.115 |
| Corsi | 1.417 | 0.252 | 0.096 |
| Digit Span | 1.482 | 0.231 | 0.086 |
| FAB | 0.774 | 0.515 | 0.055 |
| Fonemic Fluency | 0.402 | 0.752 | 0.029 |
| G8 | 0.049 | 0.737 | 0.536 |
| Prose Memory | 0.29 | 0.832 | 0.023 |
| Raven’s Matrices | 2.672 | 0.060 | 0.160 |
| Rey’s Pic Diff | 0.051 | 0.984 | 0.004 |
| Rey’s Pic Imm | 0.407 | 0.749 | 0.030 |
| Semantic Fluency | 0.051 | 0.984 | 0.004 |
| Sniffing | 1.323 | 0.279 | 0.081 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Invitto, S.; Boscolo-Rizzo, P.; Spinato, G.; Trinchera, G.; Accogli, G.; Ciccarese, V.; Saba, L.; Caggiula, M.; Barbagallo, G.; Pauciulo, A.; et al. Evaluation of Mild Cognitive Impairment through Perientorhinal/Hippocampal Imaging and Comprehensive Neuropsychological and Psychophysical Assessment. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14070697
Invitto S, Boscolo-Rizzo P, Spinato G, Trinchera G, Accogli G, Ciccarese V, Saba L, Caggiula M, Barbagallo G, Pauciulo A, et al. Evaluation of Mild Cognitive Impairment through Perientorhinal/Hippocampal Imaging and Comprehensive Neuropsychological and Psychophysical Assessment. Brain Sciences. 2024; 14(7):697. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14070697
Chicago/Turabian StyleInvitto, Sara, Paolo Boscolo-Rizzo, Giacomo Spinato, Giuseppe Trinchera, Giuseppe Accogli, Vincenzo Ciccarese, Luca Saba, Marcella Caggiula, Gaetano Barbagallo, Alfredo Pauciulo, and et al. 2024. "Evaluation of Mild Cognitive Impairment through Perientorhinal/Hippocampal Imaging and Comprehensive Neuropsychological and Psychophysical Assessment" Brain Sciences 14, no. 7: 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14070697
APA StyleInvitto, S., Boscolo-Rizzo, P., Spinato, G., Trinchera, G., Accogli, G., Ciccarese, V., Saba, L., Caggiula, M., Barbagallo, G., Pauciulo, A., & de Tommaso, M. (2024). Evaluation of Mild Cognitive Impairment through Perientorhinal/Hippocampal Imaging and Comprehensive Neuropsychological and Psychophysical Assessment. Brain Sciences, 14(7), 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14070697









