Abstract
Studies have demonstrated that the α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid (AMPA) receptor is essential to drug addiction. In this study, we explored the influence of GluR2-3Y, an interfering peptide to prevent the endocytosis of AMPA receptors containing the GluR2 subunit, on morphine-seeking behavior in the rat self-administration model. After self-administration was established, the rats received intravenous injections of GluR2-3Y during the extinction sessions. There were no significant differences in both active and inactive pokes compared to the control group of rats that received GluR2-3S, indicating that GluR2-3Y has no significant influences on the extinction of morphine self-administration. The other two groups of rats were trained, extinguished, and reinstated by repeated morphine priming (respectively, called Prime 1, Prime 2, and Prime 3). Only one intravenous injection of GluR2-3Y was performed before Prime 1. Compared to the control group, GluR2-3Y did not affect Prime 1, but significantly attenuated the morphine-seeking behavior during repeated morphine-primed reinstatement, indicating an inhibitory after effect of GluR2-3Y on morphine-seeking behavior in rats. The long-term depression (LTD) in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) shell was also assessed. Pretreatment with GluR2-3Y altered the ability of LTD induction to the level of that in the naive group, while pretreatment with GluR2-3S had no effects on LTD. Our results demonstrated that the intravenous injection of GluR2-3Y, to block the endocytosis of AMPA receptors, inhibited the reinstatement of morphine-seeking behavior, which may be induced by modulating the neuronal plasticity in the NAc shell of rats.
1. Introduction
Addiction is thought to be a chronically relapsing disease/disorder. The process of drug addiction exploits the reward-related learning and memory systems [1] and involves mechanisms of synaptic plasticity [2,3,4]. For instance, exposure to different drugs of abuse induces changes in long-term potentiation (LTP) or long-term depression (LTD), two main forms of Hebbian synaptic plasticity, in the neural circuits underlying reward-related learning such as the nucleus accumbens (NAc) [5,6] and hippocampus [7]. Meanwhile, altering the synaptic plasticity in these brain regions also influences addiction behavior [8,9,10].
It is well known that different types of glutamate receptors play important and specific roles in synaptic transmission and plasticity [11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21]. The AMPA receptor, one of the three types of ionotropic glutamate receptors (iGluRs), is integral to synaptic plasticity [22,23,24] and is involved in opioid addiction [25,26,27,28,29]. For example, after a single morphine injection, the mRNA levels of AMPA receptor subunits were significantly reduced three days later but enhanced three weeks later in the NAc core [30]. The AMPA receptor GluR1 subunit on the dendrite membrane in the basolateral amygdala (BLA) increased in morphine self-administering rats [31]. The surface expression of the AMPA receptors changed in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) upon repeated morphine administration [32]. Acute or chronic morphine administration produced region-specific changes in the subcellular distribution of the GluR1 subunit in the rat ventral tegmental area (VTA) [33]. Overexpression of the GluR1 subunits or knockdown of the GluR2 subunits in the central amygdala (CeA) facilitated the acquisition of morphine-induced conditioned place preference (CPP) [34].
Among the subunits of the AMPA receptor, GluR2 regulates synaptic plasticity by controlling Ca2+ influx [35,36]. The presence of the GluR2 subunit in the heteromeric AMPA receptor is Ca2+-impermeable. An early study by Van den Oever and colleagues found that preventing GluR2 endocytosis decreased cue-induced heroin-seeking behavior [37]. However, its specific role in relapse to opioids is still not clear, especially the synaptic changes that take place after morphine priming, which may lead to the resumption of drug seeking, have not yet been studied.
GluR2-3Y is a GluR2-derived interfering peptide that contains tyrosine residues and acts as a competitive inhibitor of tyrosine phosphorylation. The accumulated evidence shows that GluR2-3Y blocks the endocytosis of the AMPA receptors containing GluR2 and the induction of LTD [38,39,40,41]. Besides, many studies have demonstrated that GluR2-3Y influences the process of learning and memory and addictive behavior induced by different drugs of abuse. For example, both the systemic and intra-NAc infusion of GluR2-3Y prevented the expression of amphetamine-induced behavioral sensitization in the rat [39]. Pretreatment of GluR2-3Y inhibited the acquisition and reinstatement of morphine CPP in rats [42], indicating the AMPA receptor endocytosis is a target for the treatment of opioid addiction and GluR2-3Y is of great value in the treatment.
Therefore, in the present study, using GluR2-3Y, we explored the effect of inhibiting AMPA receptor endocytosis on the reinstatement of drug-seeking behavior induced by morphine priming in a repeated priming model. We also studied the involvement of LTD induced in the NAc shell in the process.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
Male Sprague–Dawley rats (220–250 g) were afforded one week of acclimation before use. The rats were housed under a reverse cycle (12 h light/dark) with food and water ad libitum, except for the morphine self-administration (SA) training when they received a 20 g ration of rat chow daily.
2.2. Drugs
Morphine hydrochloride injection (Shenyang First Pharmaceutical Factory, Shenyang, China) was diluted with sterile saline to obtain a 1 mg/mL dose. GluR2-3Y (YGRKKRRQRRR-YKEGYNVYG) and scrambled control peptide GluR2-3S (YGRKKRRQRRR-VYKYGGYNE) (GL Biochem, Shanghai, China) were dissolved in sterile saline.
2.3. Surgery
Under sodium pentobarbital anesthesia (75 mg/kg, i.p.), a silastic catheter was implanted in the right jugular vein. After surgery, the catheter was flushed with heparinized saline (100 IU/mL, 0.4 mL) daily. The rats were allowed to recover for 7 to 10 days after surgery.
2.4. Morphine SA, Extinction, and Relapse Tests
2.4.1. Apparatus
The SA setup consisted of 16 operant chambers (29 × 29 × 26 cm; AniLab, Ningbo, China). Each chamber was located in a sound-proof opaque box equipped with exhaust fans and which had a white house light for illumination. There were two holes, and a blue cue light was placed inside each hole. A speaker was used to provide audio cues. Each rat was placed in a chamber daily, and the catheter was connected to a pump-driven syringe. The data were collected with AniLab software (AniLab, Ningbo, China).
2.4.2. Acquisition
The rats were trained to perform morphine self-administration (0.3 mg/kg/100-µL injection) on a fixed ratio 1 (FR1) schedule in daily 3 h sessions during their dark cycle. The house light was turned on at the beginning of each session and indicated the availability of morphine. Poking the nose into the active hole caused an infusion of morphine (5 s) and simultaneously caused a 5 s compound audiovisual cue, which meant that the blue light placed inside the hole lit up and the speaker sounded. Poking the nose into the inactive hole had no consequences. The injection of morphine was followed by a 15 s time out, during which time the house light was turned off, and the nose pokes were ineffective.
2.4.3. Extinction
Extinction sessions were conducted for three hours once daily. The procedures for the extinction sessions were identical to the training sessions, except that morphine was not available.
2.4.4. Relapse
On the test day, the rats were injected with 5 mg/kg of morphine intraperitoneally and immediately placed in the operant cages. The procedures for the relapse session were the same as the extinction session.
2.4.5. Behavior Experiment 1: Effect of Intravenous Pretreatment with GluR2-3Y on the Extinction of Morphine SA
The rats were trained to self-administer morphine for 14 days, followed by 21 consecutive extinction sessions. The 14 rats were administered with GluR2-3Y (n = 7) or GluR2-3S (n = 7) (1.5 nmol/g body weight, i.v.) 60 min before the extinction sessions for the first 19 days.
2.4.6. Behavior Experiment 2: Effect of Intravenous Pretreatment with GluR2-3Y on the Morphine-Primed Reinstatement of Drug Seeking
Another two groups of rats were used. The rats remained in morphine SA training until they met an acquisition criterion that required the average infusion over three consecutive training days to vary by less than 15%. Once the rats met this criterion, the extinction procedures were instituted on the following day. The rats remained in extinction until the active pokes and inactive pokes were both less than 10 for three consecutive days. Twenty-four hours after meeting this criterion, 17 rats were reinstated with morphine (5 mg/kg, i.p.) for Prime 1. GluR2-3Y (n = 8) or GluR2-3S (n = 9) (1.5 nmol/g body weight) was intravenously injected 60 min before morphine Prime 1 (a three-hour session). The extinction procedures were instituted for at least three days, and after meeting the extinction criterion, Prime 2 (a three-hour session) was performed 24 h later. Then, the extinction procedures were instituted for at least another three days, and Prime 3 (a three-hour session) was performed after meeting the extinction criterion.
2.5. Electrophysiological Studies
2.5.1. Slice Preparation
Twenty rats were used. The number of rats in the naive group, GluR2-3Y, and GluR2-3S was eight, six, and six, respectively. Slices were prepared as described previously with minor modifications [43]. One day after meeting the extinction criterion, the rats were anesthetized with sodium pentobarbital (75 mg/kg, i.p.) and decapitated. The brain was quickly removed into an ice-cold cutting solution containing (mM) 87 NaCl, 2.5 KCl, 7 MgCl2, 0.5 CaCl2, 1.25 NaH2PO4, 25 NaHCO3, 15 glucose, and 90 sucrose and cooled for 3–5 min. Then, 300-μm sagittal slices were cut on a vibratome (Leica VT 1000 S, Heidelberg, Germany) in the ice-cold cutting solution. Immediately after cutting, the slices were stored for 45 min at 33 °C in artificial cerebrospinal fluid (ACSF) containing (mM) 125 NaCl, 2.5 KCl, 1 MgCl2, 2 CaCl2, 1.25 NaH2PO4, 25 NaHCO3, and 10 glucose, and were equilibrated with 95% O2/5% CO2. The slices were then stored at room temperature until recording.
2.5.2. Patch Clamp
Recordings were conducted in a chamber superfused continuously with carbonated ACSF. The superfusion medium contained bicuculline (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA, ten μM) to block the GABAA receptors. Whole-cell recordings were performed from visualized neurons in the NAc shell. Glass microelectrodes (resistance 4–6 MΩ) were filled with a solution containing (mM) 122.5 Cs-gluconate, 17.5 CsCl, 2 MgCl2, 10 HEPES, 0.5 EGTA, 4 ATP, and osmolarity 300–310 mOsm. The pH was adjusted to 7.2–7.4 with CsOH. The data were recorded with a Heka EPC10 amplifier (Heka, Reutlingen, Germany).
2.5.3. LTD Recordings
Synaptic currents were evoked by stimulating the prelimbic cortical synaptic inputs via a constant-voltage pulse (1 ms) delivered through a concentric bipolar electrode (FHC, Bowdoinham, ME, USA). Synaptic responses were evoked at 0.067 Hz, except during the induction of LTD. After 10 min of stable baseline recording, LTD was triggered by pairing low-frequency stimulation (1 Hz, 480 pulses) while holding the cells at −40 mV.
2.6. Data Analysis
We analyzed the data with Prism GraphPad (version 8). Data from the SA and electrophysiological recordings were analyzed with one-way or repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) with a Bonferroni post-test. The critical value for statistical significance was set at p < 0.05. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Intravenous GluR2-3Y Injection on the Extinction of Morphine SA
After 14 days of training, the rats that acquired morphine SA were divided into two groups for extinction. One group received intravenous injections of GluR2-3Y (1.5 nmol/g body weight, n = 7), and the other group received intravenous injections of GluR2-3S (1.5 nmol/g body weight, n = 7) as a control. For the 14 days of SA training, a three-way analysis of variance revealed a significant session effect (F 13, 156 = 2.616; p < 0.01) and nose poke effect (F 1, 12 = 31.80; p < 0.001), with no significant group effect (F 1, 12 = 3.177; p = 0.100) or group × nose poke × session interaction (F 13, 156 = 0.877; p = 0.579). No significant difference was found for the nose pokes in the two groups (Figure 1b).
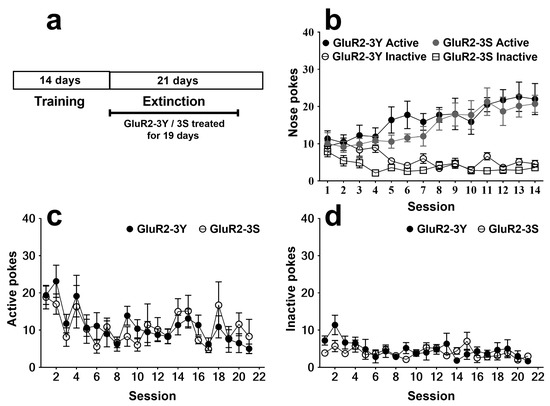
Figure 1.
Intravenous injection of GluR2-3Y has no effect on the extinction of morphine SA. (a) Experimental protocol. (b) Active and inactive pokes during morphine SA training. (c) Active pokes during extinction sessions. (d) Inactive pokes during extinction sessions. Data are expressed as mean ± s.e.m. (n = 7 per group).
The effects of GluR2-3Y given just before 19 daily extinction sessions are shown in Figure 1c, d. The rats that received the GluR2-3Y treatment showed no significant difference in both active pokes (F 1, 240 = 0.003; p > 0.05; Figure 1c) and inactive pokes (F 1, 240 = 1.32; p > 0.05; Figure 1d) compared to the rats that received the GluR2-3S injection, indicating that GluR2-3Y had no significant influences on extinction.
3.2. Effects of Injection of GluR2-3Y on Morphine-Seeking Behavior during Repeated Morphine-Primed Reinstatement
The rats that met the extinction criterion were divided into two groups with no significant differences for the nose pokes (F 1, 15 = 0.40, p > 0.05 for the last training day, F 1, 15 = 1.11, p > 0.05 for the last extinction day; Figure 2b). The rats received intravenous injections of GluR2-3Y (n = 8) or GluR2-3S (n = 9), then were reinstated with morphine. As shown in Figure 2c, GluR2-3Y did not affect Prime 1 (F 1, 15 = 0.09, p > 0.05). To determine whether there were after effects of GluR2-3Y or not, Prime 2 and Prime 3 progressed, and interestingly, significant attenuation effects were found in both Prime 2 and Prime 3 (F 1, 15 = 5.91, p < 0.05 for Prime 2, F 1, 15 = 8.98, p < 0.01 for Prime 3; Figure 2d, e). The Bonferroni post-test showed GluR2-3Y significantly attenuated the active pokes (t 15 = 3.14, p < 0.01 for Prime 2, t 15 = 3.84, p < 0.01 for Prime 3), but not the inactive pokes (t 15 = 0.36, p > 0.05 for Prime 2, t 15 = 0.50, p > 0.05 for Prime 3). Combining the data from the three reinstatement tests, we found GluR2-3Y attenuated morphine-primed morphine-seeking behavior during repeated morphine-primed reinstatement (F 1, 15 = 4.71, p < 0.05).
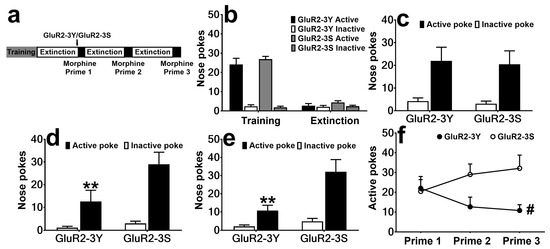
Figure 2.
Intravenous injection of GluR2-3Y attenuates morphine-induced morphine-seeking. (a) Experimental protocol. (b) Active and inactive pokes during morphine SA training and extinction, showing the last day of training and extinction. (c–e) Nose pokes during the morphine Prime 1, Prime 2, and Prime 3 sessions. (f) Active pokes during the three reinstatement sessions. # indicates a significant difference between the GluR2-3Y and GluR2-3S groups, and ** p < 0.01 indicates significant differences in the Bonferroni post-test pairwise comparison vs. the active pokes of the GluR2-3S group. Data are expressed as mean ± s.e.m. (n = 8–9 per group).
3.3. Influences of GluR2-3Y on the LTD in NAc Shell Neurons before Morphine-Primed Reinstatement
To determine the involvement of synaptic plasticity underlying the attenuating effect of GluR2-3Y on repeated morphine-primed reinstatement, we explored the changes in LTD induced in the NAc shell. Another group of rats was used, and GluR2-3Y and GluR2-3S were injected as before. After reaching the extinction criterion, the rats were anesthetized and decapitated for brain slice preparation (Figure 3a).
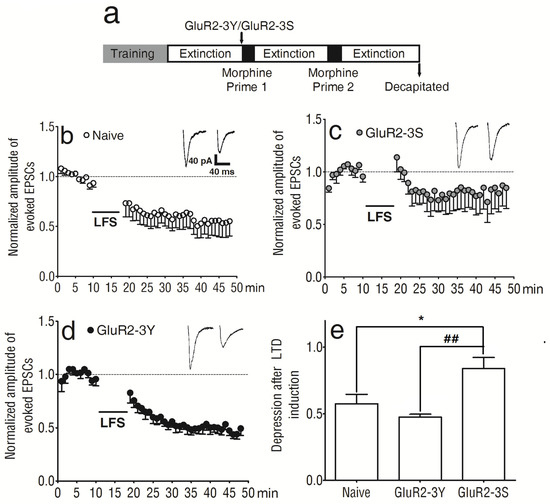
Figure 3.
Intravenous injection of GluR2-3Y altered LTD in the NAc shell. (a) Experimental protocol. (b) Expression of LTD in the NAc of naive rats. (c) Expression of LTD in the NAc of animals treated with GluR2-3S. (d) Expression of LTD in the NAc of animals treated with GluR2-3Y. (e) Bar graphs summarizing the data for the last 5 min of LTD induction from experiments such as those shown in (b–d). ## p < 0.01 versus the GluR2-3S group, * p < 0.05 versus the naive group (Bonferroni post-test). Data are expressed as mean ± s.e.m. (n = 6–8 per group).
LTD induction was recorded in the NAc shell of naive rats (Figure 3b), as well as those pretreated with GluR2-3S (Figure 3c) or GluR2-3Y (Figure 3d). All the data were normalized to the average value of the evoked EPSCs before LTD induction. The last 5 min of LTD induction showed significant differences between the 3 groups (F 2, 99 = 7.31, p < 0.01; Figure 3e); there were significant differences between the naive and GluR2-3S-pretreated rats (t99 = 2.86, p < 0.05) and between the GluR2-3Y- and GluR2-3S-pretreated rats (t99 = 3.68, p < 0.01; Figure 3e). The amplitude of the normalized evoked EPSCs was 57.44 ± 7.09% in the naive rats (n = 8), 47.53 ± 2.17% in the GluR2-3Y-treated rats (n = 6), and 83.88 ± 8.29% in the GluR2-3S-treated rats (n = 6). The data indicated that GluR2-3Y attenuated the morphine-primed morphine-seeking behavior. This inhibitory effect may be associated with its influence on the synaptic plasticity in the NAc shell, but GluR2-3S did not have the same effect.
4. Discussion
Morphine and other opioid drugs are widely used to treat pain, but their clinical usefulness is limited by tolerance and dependence [44]. To develop effective therapies for morphine addiction, it is crucial to prevent relapse. The drug, the cue associated with the drug of abuse, and stress all induce relapse [45,46,47]. Here, we showed that inhibiting the endocytosis of AMPA receptors with the interfering peptide GluR2-3Y attenuated the reinstatement of morphine-seeking behavior induced by repeated morphine-priming in rats trained to morphine SA, but had no effect on extinction. Furthermore, we found that the LTD induction in the NAc shell of rats returns to the normal level as the naive rats as a result of pretreatment with GluR2-3Y. So, the rescue of LTD in the NAc shell might contribute to the reduction in morphine-seeking behavior. The data demonstrated that GluR2-3Y is a potential candidate for treating opioid addiction, especially the prevention of relapse.
Previous studies have shown that drugs of abuse influence the glutamate system and synaptic plasticity [22,23,48]. For instance, cocaine changes the release of glutamate in several brain areas [49,50], and exposure to cocaine or morphine alters the expression of the AMPA receptors in the prefrontal cortex (PFC) [32], the VTA [33], and the NAc [51,52,53]. For opioid addiction, reinstatement by either heroin or cue increases extracellular glutamate in the NAc core in the self-administration rats [54]. Moreover, chronic morphine administration induces a decrease in the surface AMPA receptor GluR1 subunit in particular types of neurons in rats’ NAc shell and NAc core [55]. However, our results suggested that the endocytosis of GluR2 was not involved in the extinction of morphine self-administration, consistent with the previous finding on morphine-conditioned place preference (mCPP) [25].
Besides, an earlier study showed that GluR2-3Y decreases cue-induced heroin reinstatement [37]. Here, we showed that the infusion of GluR2-3Y reduced the reinstatement in a delayed and persistent manner in our repeated priming model, which suggests the possible effect of GluR2 endocytosis on morphine-induced relapse. However, inconsistent with the effect of GluR2-3Y on cue-induced heroin reinstatement, morphine Prime 1 was not affected. These differences may be due to differences in the ways of induction. One previous study demonstrated that low-dose risperidone can attenuate cue-induced but not heroin-induced reinstatement [56]. Similarly, another study showed that ketanserin can attenuate cue-induced but not cocaine-induced reinstatement [57]. These studies suggested that cue-induced and drug-induced reinstatement have different mechanisms, which need to continue to be explored.
The reasons why Prime 2 and Prime 3 were affected by intravenous injections of GluR2-3Y may be explained by the widely accepted hypothesis that addiction is a pathological process that involves plasticity mechanisms related to the glutamate system, similar to those implicated in neuronal models of learning and memory [58,59,60,61]. When exposed to the drug use-related cue/context or the drug itself, the memories of the drug experience are retrieved, leading to drug seeking. During the reinstatement induced by morphine priming, a small dose of morphine triggers the drug-seeking behavior, which might be due to the activation of the association between drug-use experience and drug-seeking behavior. While established memory will be labile and, then, sensitive to disruption [62]. Milekic et al. found that established morphine-conditioned place preference was persistently disrupted if protein synthesis was blocked after the re-presentation of a conditioning session, and this effect required the re-experience of both the conditioning context and the drug [63]. Rao-Ruiz et al. found that contextual fear memory recall induced acute hippocampal AMPAR endocytosis [64], suggesting that GluR2 plays a crucial role in memory reconsolidation. So, the finding that GluR2-3Y injection attenuated morphine-seeking behavior during repeated morphine-primed reinstatement sessions may be due to GluR2-3Y interfering with the memory reconsolidation after the first morphine-primed reinstatement. The effects of intravenous GluR2-3Y injection on the extinction after Prime 1 and Prime 2 also support this supposition (Figure S1). The time course and the relationship between reinstatement and memory reconsolidation need more research.
Previous studies on drug addiction underscore the importance of the NAc in the development of drug seeking, extinction, and relapse [65,66,67]. The NAc shell, an area that processes reward-related incentives [55], is critically involved in the reward effect [68,69]. Moreover, the enhancement of control over behavior by psychostimulants depends on the shell [70,71]. Although LaLumiere and colleagues indicated that the glutamate receptors in the NAc core play an essential role in heroin reinstatement [54], Peters and colleagues also identified that inhibition of the shell induced cocaine-seeking in extinguished rats [72]. Here, we demonstrated the critical function of the NAc shell in morphine-induced reinstatement. In addition, memory reconsolidation seems to be involved in neuroplasticity [73]. Other evidence indicates the role of AMPARs endocytosis and LTD in behavioral sensitization [39,74]. Therefore, we hypothesized that the plasticity of the NAc shell was related to the activation of an association between morphine-use experience and morphine-seeking behavior, and our observations fit within this conceptual framework.
There are several limitations to this study. Firstly, we only tested male rats; thus, how GluR2-3Y may be involved in the priming of morphine SA in female animals is not known. Secondly, we did not record the other behavioral parameters, such as the latency to poke, and the timeline of poking among the length of the session; if GluR2-3Y affects these parameters needs to be further investigated.
5. Conclusions
Our results showed that relapse induced by morphine priming can be persistently disrupted by the intravenous injection of GluR2-3Y. This effect may be due to a change of LTD in the NAc shell. This finding suggests that GluR2-3Y influenced the synaptic plasticity in the NAc shell and interfered with the morphine-induced reconsolidation of memories related to morphine SA, therefore inhibiting the late reinstatement of morphine-seeking behavior.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/brainsci13040590/s1, Figure S1: Effects of intravenous GluR2-3Y injection on extinction after Prime.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.Z., Z.L. and L.Y.; methodology, J.Z., X.L. and Z.L.; validation, Z.L., J.Z. and X.L.; formal analysis, Z.L. and J.Z.; data curation, Z.L., J.Z., X.L. and X.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.L. and J.Z.; writing—review and editing, Z.L. and J.Z.; supervision, L.Y.; funding acquisition, Z.L. and J.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 31871111, Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS, grant number 2020088, the Scientific and Technological Innovation Programs of Higher Education Institutions in Shanxi, grant number 2022L341, and the Basic Research Fund of People’s Public Security University of China, grant number 2016JKF01314.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Research Ethics Review Board of the Institute of Psychology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (A15016).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hyman, S.E. Addiction: A disease of learning and memory. Am. J. Psychiatry 2005, 162, 1414–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luscher, C.; Malenka, R.C. Drug-evoked synaptic plasticity in addiction: From molecular changes to circuit remodeling. Neuron 2011, 69, 650–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauer, J.A.; Malenka, R.C. Synaptic plasticity and addiction. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 844–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gipson, C.D.; Kupchik, Y.M.; Kalivas, P.W. Rapid, transient synaptic plasticity in addiction. Neuropharmacology 2014, 76 Pt B, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Kalivas, P.W. Reduced LTP and LTD in prefrontal cortex synapses in the nucleus accumbens after heroin self-administration. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 16, 1165–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, B.L.; Oscar-Berman, M.; Kaplan, G.B. Opioid-induced structural and functional plasticity of medium-spiny neurons in the nucleus accumbens. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 120, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Dong, Z.; Jia, Y.; Mao, R.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, L.; Cao, J. Opioid addiction and withdrawal differentially drive long-term depression of inhibitory synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Moussawi, K.; Zhou, W.; Toda, S.; Kalivas, P.W. Heroin relapse requires long-term potentiation-like plasticity mediated by NMDA2b-containing receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 19407–19412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polter, A.M.; Bishop, R.A.; Briand, L.A.; Graziane, N.M.; Pierce, R.C.; Kauer, J.A. Poststress block of kappa opioid receptors rescues long-term potentiation of inhibitory synapses and prevents reinstatement of cocaine seeking. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 76, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Cheng, Y.; Roltsch Hellard, E.; Wang, X.; Lu, J.; Gao, X.; Huang, C.C.Y.; Wei, X.Y.; Ji, J.Y.; Wang, J. Bidirectional and long-lasting control of alcohol-seeking behavior by corticostriatal LTP and LTD. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luscher, C.; Xia, H.; Beattie, E.C.; Carroll, R.C.; von Zastrow, M.; Malenka, R.C.; Nicoll, R.A. Role of AMPA receptor cycling in synaptic transmission and plasticity. Neuron 1999, 24, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.K.; Barbarosie, M.; Kameyama, K.; Bear, M.F.; Huganir, R.L. Regulation of distinct AMPA receptor phosphorylation sites during bidirectional synaptic plasticity. Nature 2000, 405, 955–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, R.C.; Beattie, E.C.; von Zastrow, M.; Malenka, R.C. Role of AMPA receptor endocytosis in synaptic plasticity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malinow, R.; Malenka, R.C. AMPA receptor trafficking and synaptic plasticity. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 25, 103–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessels, H.W.; Malinow, R. Synaptic AMPA receptor plasticity and behavior. Neuron 2009, 61, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoletti, P.; Bellone, C.; Zhou, Q. NMDA receptor subunit diversity: Impact on receptor properties, synaptic plasticity and disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collingridge, G.L.; Isaac, J.T.; Wang, Y.T. Receptor trafficking and synaptic plasticity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 5, 952–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polenghi, A.; Nieus, T.; Guazzi, S.; Gorostiza, P.; Petrini, E.M.; Barberis, A. Kainate Receptor Activation Shapes Short-Term Synaptic Plasticity by Controlling Receptor Lateral Mobility at Glutamatergic Synapses. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsanov, M.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Synaptic plasticity in the adult visual cortex is regulated by the metabotropic glutamate receptor, mGluR5. Exp. Brain Res. 2009, 199, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wong, T.P.; Pozza, M.F.; Lingenhoehl, K.; Wang, Y.; Sheng, M.; Auberson, Y.P.; Wang, Y.T. Role of NMDA receptor subtypes in governing the direction of hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Science 2004, 304, 1021–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manahan-Vaughan, D.; Braunewell, K.H. The metabotropic glutamate receptor, mGluR5, is a key determinant of good and bad spatial learning performance and hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Cereb. Cortex 2005, 15, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiamulera, C.; Piva, A.; Abraham, W.C. Glutamate receptors and metaplasticity in addiction. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2021, 56, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Huijstee, A.N.; Mansvelder, H.D. Glutamatergic synaptic plasticity in the mesocorticolimbic system in addiction. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, B.D.; Kashima, D.T.; Manz, K.M.; Grueter, C.A.; Grueter, B.A. Synaptic Plasticity in the Nucleus Accumbens: Lessons Learned from Experience. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 2114–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billa, S.K.; Sinha, N.; Rudrabhatla, S.R.; Moron, J.A. Extinction of morphine-dependent conditioned behavior is associated with increased phosphorylation of the GluR1 subunit of AMPA receptors at hippocampal synapses. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Tian, X.; Guo, X.; He, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Z.J. AMPA receptor positive allosteric modulators attenuate morphine tolerance and dependence. Neuropharmacology 2018, 137, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.N.; Jing, X.; Li, M.; Deng, H.; Jiang, T.; Xiong, K.Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.F.; Wang, Q.J. Corydaline and l-tetrahydropalmatine attenuate morphine-induced conditioned place preference and the changes in dopamine D(2) and GluA1 AMPA receptor expression in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 884, 173397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Brownstein, A.J.; Buonora, M.; Niikura, K.; Ho, A.; Correa da Rosa, J.; Kreek, M.J.; Ott, J. Self administration of oxycodone alters synaptic plasticity gene expression in the hippocampus differentially in male adolescent and adult mice. Neuroscience 2015, 285, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Liang, J.; Zheng, X.; Bai, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Xing, X. Altered phosphorylation of GluA1 in the striatum is associated with locomotor sensitization induced by exposure to increasing doses of morphine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 702, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, E.H.; Wardeh, G.; Smit, A.B.; Schoffelmeer, A.N. Morphine causes a delayed increase in glutamate receptor functioning in the nucleus accumbens core. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 511, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, M.J.; Kruzich, P.J.; Colago, E.E.; Kreek, M.J.; Pickel, V.M. Increased AMPA GluR1 receptor subunit labeling on the plasma membrane of dendrites in the basolateral amygdala of rats self-administering morphine. Synapse 2005, 58, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mickiewicz, A.L.; Napier, T.C. Repeated exposure to morphine alters surface expression of AMPA receptors in the rat medial prefrontal cortex. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2011, 33, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, D.A.; Lessard, A.A.; Chan, J.; Colago, E.E.; Zhou, Y.; Schlussman, S.D.; Kreek, M.J.; Pickel, V.M. Region-specific changes in the subcellular distribution of AMPA receptor GluR1 subunit in the rat ventral tegmental area after acute or chronic morphine administration. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 9670–9681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.Q.; Wang, W.; Hou, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, J.; Pan, Z.Z. Central amygdala GluA1 facilitates associative learning of opioid reward. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 1577–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Agopyan, N.; Miu, P.; Xiong, Z.; Henderson, J.; Gerlai, R.; Taverna, F.A.; Velumian, A.; MacDonald, J.; Carlen, P.; et al. Enhanced LTP in mice deficient in the AMPA receptor GluR2. Neuron 1996, 17, 945–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, D.H.; Royle, G.; Kolaj, M.; Vissel, B.; Randic, M. Enhanced LTP of primary afferent neurotransmission in AMPA receptor GluR2-deficient mice. Pain 2008, 136, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Oever, M.C.; Goriounova, N.A.; Li, K.W.; Van der Schors, R.C.; Binnekade, R.; Schoffelmeer, A.N.; Mansvelder, H.D.; Smit, A.B.; Spijker, S.; De Vries, T.J. Prefrontal cortex AMPA receptor plasticity is crucial for cue-induced relapse to heroin-seeking. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, G.; Ju, W.; Liu, L.; Wyszynski, M.; Lee, S.H.; Dunah, A.W.; Taghibiglou, C.; Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Wong, T.P.; et al. Tyrosine phosphorylation of GluR2 is required for insulin-stimulated AMPA receptor endocytosis and LTD. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 1040–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brebner, K.; Wong, T.P.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Campsall, P.; Gray, S.; Phelps, L.; Phillips, A.G.; Wang, Y.T. Nucleus accumbens long-term depression and the expression of behavioral sensitization. Science 2005, 310, 1340–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, G.L.; Wang, Y.T.; Floresco, S.B.; Phillips, A.G. Disruption of AMPA receptor endocytosis impairs the extinction, but not acquisition of learned fear. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 2416–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, C.J.; Russell, K.; Titterness, A.K.; Wang, Y.T.; Christie, B.R. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the GluR2 subunit is required for long-term depression of synaptic efficacy in young animals in vivo. Hippocampus 2007, 17, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.J.; Zhang, J.J.; Yu, L.C. GluR2-3Y Inhibits the Acquisition and Reinstatement of Morphine-Induced Conditioned Place Preference in Rats. Neurosci. Bull. 2016, 32, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.D.; Zhang, J.J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, L.C. Inhibitory effects of calcitonin gene-related peptide on long-term potentiation induced in hippocampal slices of rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 494, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, K.A.; Akil, H. Inhibition of morphine tolerance and dependence by the NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801. Science 1991, 251, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiner, D.J.; Fredriksson, I.; Lofaro, O.M.; Bossert, J.M.; Shaham, Y. Relapse to opioid seeking in rat models: Behavior, pharmacology and circuits. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantsch, J.R.; Baker, D.A.; Funk, D.; Le, A.D.; Shaham, Y. Stress-Induced Reinstatement of Drug Seeking: 20 Years of Progress. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 335–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalev, U.; Grimm, J.W.; Shaham, Y. Neurobiology of relapse to heroin and cocaine seeking: A review. Pharmacol. Rev. 2002, 54, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzschentke, T.M.; Schmidt, W.J. Glutamatergic mechanisms in addiction. Mol. Psychiatry 2003, 8, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, S.; Simms, D.; McDaniel, W.C.; Gallagher, J.P. Chronic cocaine enhances gamma-aminobutyric acid and glutamate release by altering presynaptic and not postsynaptic gamma-aminobutyric acidB receptors within the rat dorsolateral septal nucleus. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997, 280, 129–137. [Google Scholar]
- Miguens, M.; Del Olmo, N.; Higuera-Matas, A.; Torres, I.; Garcia-Lecumberri, C.; Ambrosio, E. Glutamate and aspartate levels in the nucleus accumbens during cocaine self-administration and extinction: A time course microdialysis study. Psychopharmacology 2008, 196, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudreau, A.C.; Wolf, M.E. Behavioral sensitization to cocaine is associated with increased AMPA receptor surface expression in the nucleus accumbens. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 9144–9151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemby, S.E.; Tang, W.; Muly, E.C.; Kuhar, M.J.; Howell, L.; Mash, D.C. Cocaine-induced alterations in nucleus accumbens ionotropic glutamate receptor subunits in human and non-human primates. J. Neurochem. 2005, 95, 1785–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, M.A.; Schmidt, E.F.; Choi, K.H.; Schad, C.A.; Whisler, K.; Simmons, D.; Karanian, D.A.; Monteggia, L.M.; Neve, R.L.; Self, D.W. Extinction-induced upregulation in AMPA receptors reduces cocaine-seeking behaviour. Nature 2003, 421, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaLumiere, R.T.; Kalivas, P.W. Glutamate release in the nucleus accumbens core is necessary for heroin seeking. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 3170–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, M.J.; Lane, D.A.; Colago, E.E.; Chan, J.; Schlussman, S.D.; Zhou, Y.; Kreek, M.J.; Pickel, V.M. Chronic administration of morphine is associated with a decrease in surface AMPA GluR1 receptor subunit in dopamine D1 receptor expressing neurons in the shell and non-D1 receptor expressing neurons in the core of the rat nucleus accumbens. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 210, 750–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.; Chen, W.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, W. Low dose risperidone attenuates cue-induced but not heroin-induced reinstatement of heroin seeking in an animal model of relapse. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 16, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmeister, J.J.; Lungren, E.M.; Kirschner, K.F.; Neisewander, J.L. Differential roles of 5-HT receptor subtypes in cue and cocaine reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 2004, 29, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mameli, M.; Bellone, C.; Brown, M.T.; Luscher, C. Cocaine inverts rules for synaptic plasticity of glutamate transmission in the ventral tegmental area. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 414–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourgeaud, L.; Mato, S.; Bouchet, D.; Hemar, A.; Worley, P.F.; Manzoni, O.J. A single in vivo exposure to cocaine abolishes endocannabinoid-mediated long-term depression in the nucleus accumbens. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 6939–6945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keralapurath, M.M.; Briggs, S.B.; Wagner, J.J. Cocaine self-administration induces changes in synaptic transmission and plasticity in ventral hippocampus. Addict. Biol. 2017, 22, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafenbreidel, M.; Rafa Todd, C.; Mueller, D. Infralimbic GluN2A-Containing NMDA Receptors Modulate Reconsolidation of Cocaine Self-Administration Memory. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 1113–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nader, K.; Schafe, G.E.; Le Doux, J.E. Fear memories require protein synthesis in the amygdala for reconsolidation after retrieval. Nature 2000, 406, 722–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milekic, M.H.; Brown, S.D.; Castellini, C.; Alberini, C.M. Persistent disruption of an established morphine conditioned place preference. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 3010–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao-Ruiz, P.; Rotaru, D.C.; van der Loo, R.J.; Mansvelder, H.D.; Stiedl, O.; Smit, A.B.; Spijker, S. Retrieval-specific endocytosis of GluA2-AMPARs underlies adaptive reconsolidation of contextual fear. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 1302–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasanetz, F.; Deroche-Gamonet, V.; Berson, N.; Balado, E.; Lafourcade, M.; Manzoni, O.; Piazza, P.V. Transition to addiction is associated with a persistent impairment in synaptic plasticity. Science 2010, 328, 1709–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachtell, R.K.; Choi, K.H.; Simmons, D.L.; Falcon, E.; Monteggia, L.M.; Neve, R.L.; Self, D.W. Role of GluR1 expression in nucleus accumbens neurons in cocaine sensitization and cocaine-seeking behavior. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 27, 2229–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conrad, K.L.; Tseng, K.Y.; Uejima, J.L.; Reimers, J.M.; Heng, L.J.; Shaham, Y.; Marinelli, M.; Wolf, M.E. Formation of accumbens GluR2-lacking AMPA receptors mediates incubation of cocaine craving. Nature 2008, 454, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loweth, J.A.; Singer, B.F.; Baker, L.K.; Wilke, G.; Inamine, H.; Bubula, N.; Alexander, J.K.; Carlezon, W.A., Jr.; Neve, R.L.; Vezina, P. Transient overexpression of alpha-Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in the nucleus accumbens shell enhances behavioral responding to amphetamine. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodd-Henricks, Z.A.; McKinzie, D.L.; Li, T.K.; Murphy, J.M.; McBride, W.J. Cocaine is self-administered into the shell but not the core of the nucleus accumbens of Wistar rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 303, 1216–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, J.A.; Olmstead, M.C.; Burns, L.H.; Robbins, T.W.; Everitt, B.J. Dissociation in effects of lesions of the nucleus accumbens core and shell on appetitive pavlovian approach behavior and the potentiation of conditioned reinforcement and locomotor activity by D-amphetamine. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 2401–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, R.; Robbins, T.W.; Everitt, B.J. Differential control over cocaine-seeking behavior by nucleus accumbens core and shell. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, J.; LaLumiere, R.T.; Kalivas, P.W. Infralimbic prefrontal cortex is responsible for inhibiting cocaine seeking in extinguished rats. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 6046–6053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tronson, N.C.; Taylor, J.R. Molecular mechanisms of memory reconsolidation. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.T. Probing the role of AMPAR endocytosis and long-term depression in behavioural sensitization: Relevance to treatment of brain disorders, including drug addiction. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153 (Suppl. S1), S389–S395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).