Deficits in Key Brain Network for Social Interaction in Individuals with Schizophrenia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Assessments
2.2.1. Schizophrenia Symptom Assessment
2.2.2. Social Functioning Assessment
2.3. MRI Acquisition and Preprocessing
2.3.1. Image Data Acquisition
2.3.2. Image Data Processing
2.3.3. Region of Interest
2.3.4. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and Clinical Data
3.2. ALFF, fALFF and ReHo Differences of Key Brain Regions between Two Groups
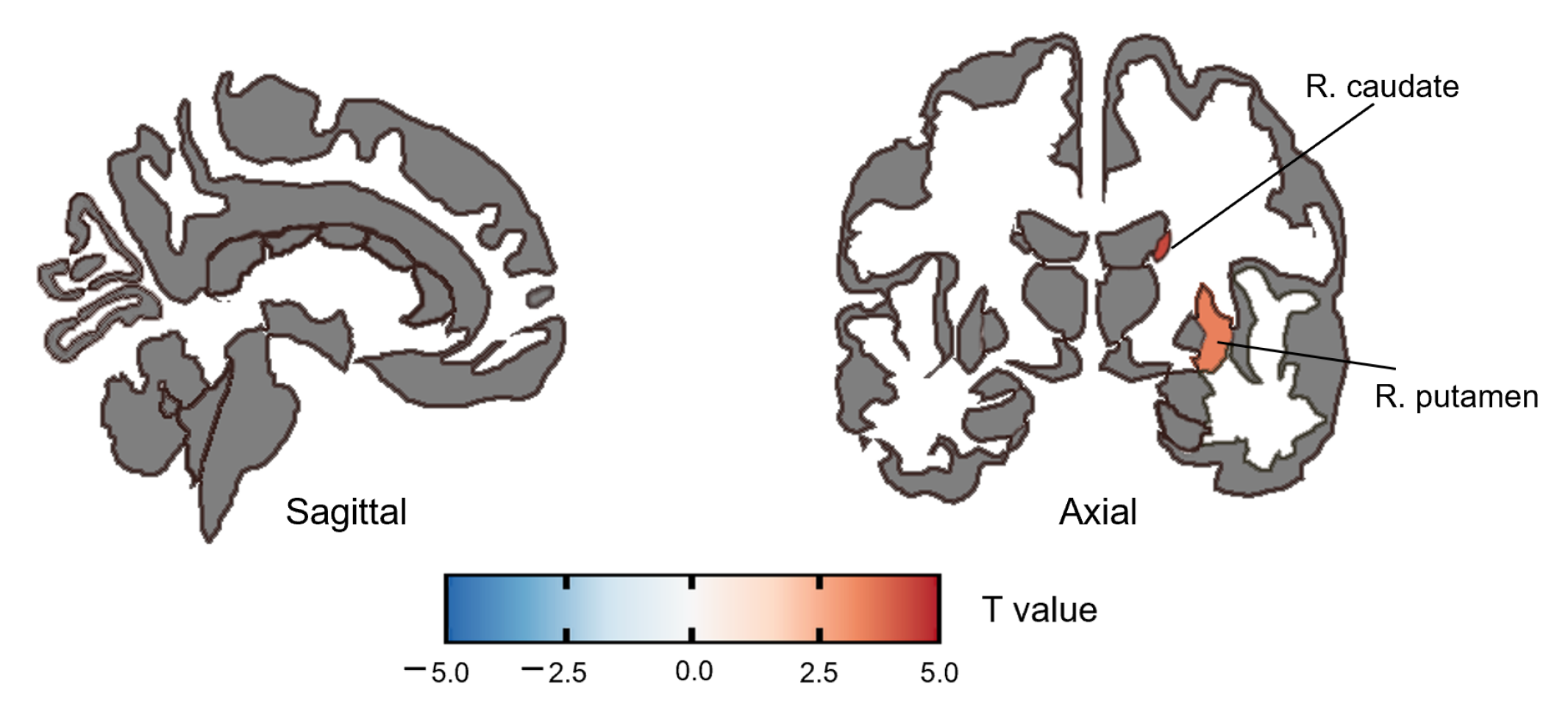
3.2.1. ALFF Group Difference
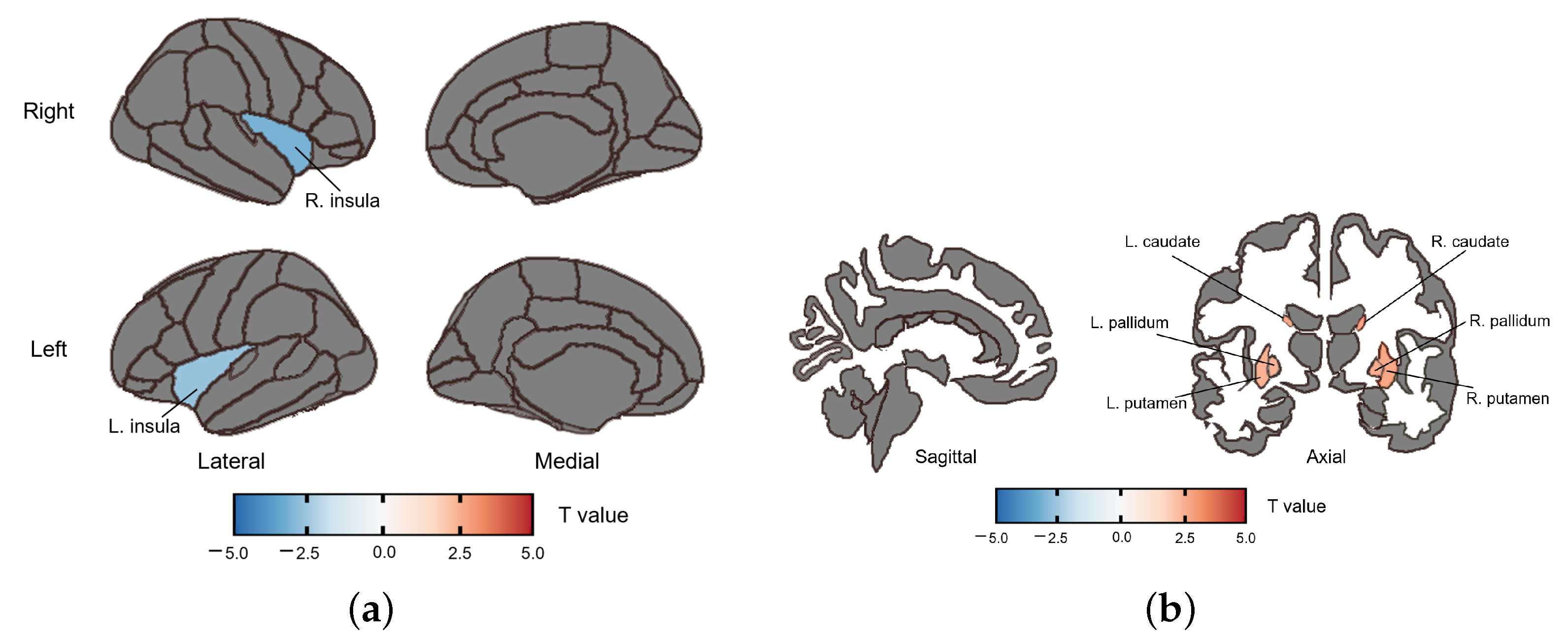
3.2.2. fALFF Group Difference
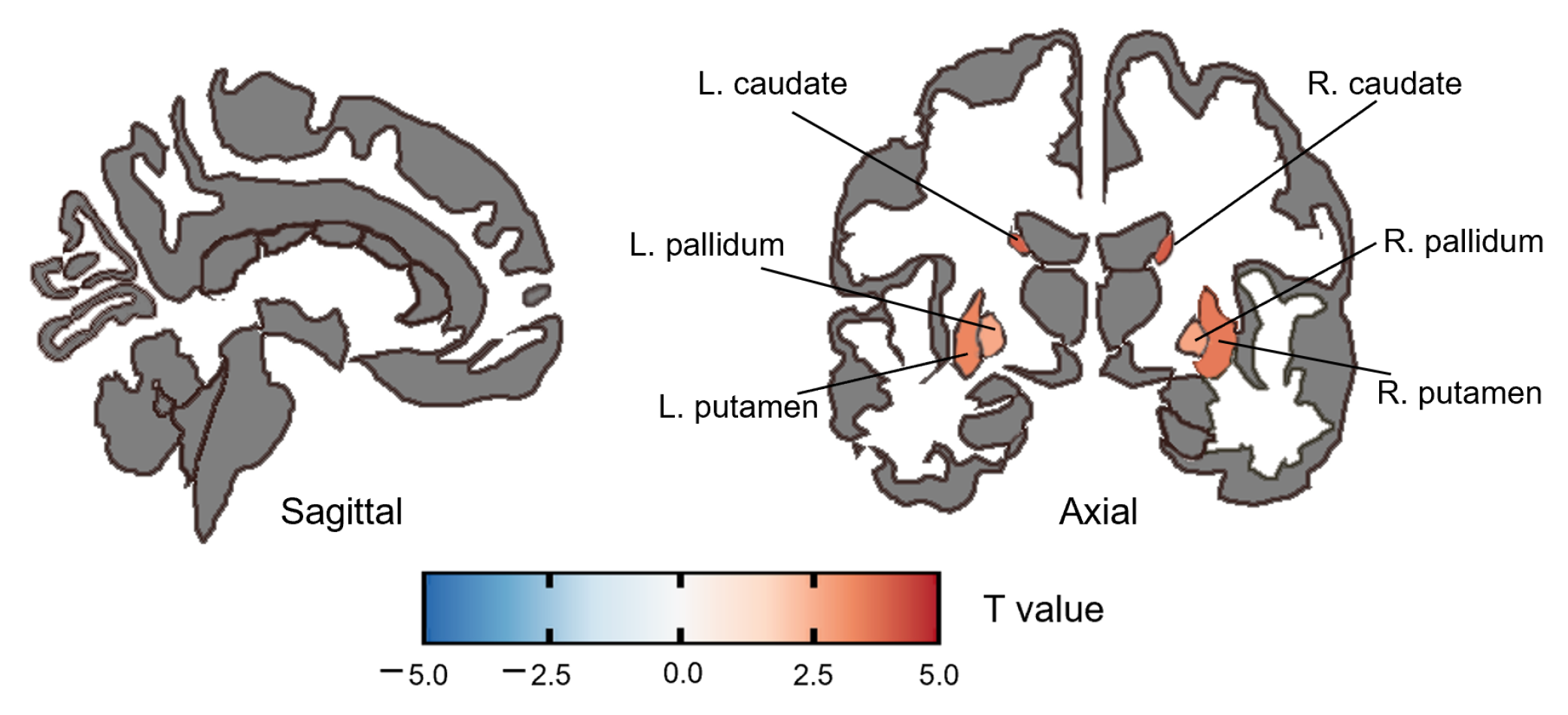
3.2.3. ReHo Group Difference
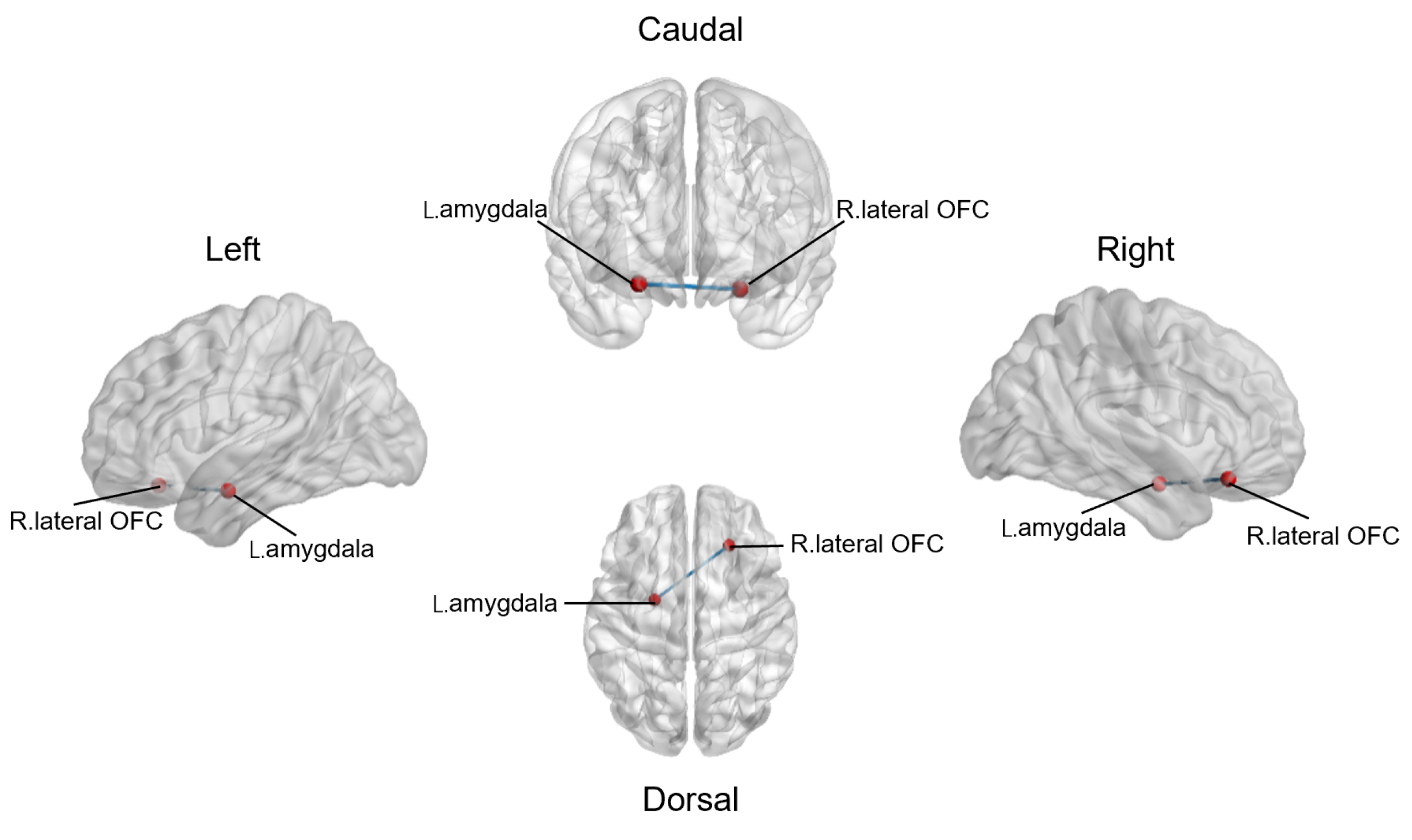
3.3. Altered Resting-State Functional Connections between Reward Network and Emotional Salience Network
4. Discussion
4.1. Altered ALFF, fALFF and ReHo in the SZ Group
4.2. Altered Functional Connectivity in the SZ Group
4.3. The Correlation between ALFF, fALFF, ReHo, rs-fc and Symptom Severity or Social Functioning
4.4. Limitations and Future Studies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jauhar, S.; Johnstone, M.; McKenna, P.J. Schizophrenia. Lancet 2022, 399, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatric Association (APA). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5™, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charernboon, T. Interplay among positive and negative symptoms, neurocognition, social cognition, and functioning in clinically stable patients with schizophrenia: A network analysis. F1000Res 2021, 10, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gromann, P.M.; Heslenfeld, D.J.; Fett, A.K.; Joyce, D.W.; Shergill, S.S.; Krabbendam, L. Trust versus paranoia: Abnormal response to social reward in psychotic illness. Brain 2013, 136, 1968–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mow, J.L.; Gandhi, A.; Fulford, D. Imaging the “social brain” in schizophrenia: A systematic review of neuroimaging studies of social reward and punishment. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 118, 704–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campellone, T.R.; Sanchez, A.H.; Kring, A.M. Defeatist Performance Beliefs, Negative Symptoms, and Functional Outcome in Schizophrenia: A Meta-analytic Review. Schizophr. Bull. 2016, 42, 1343–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favrod, J.; Nguyen, A.; Chaix, J.; Pellet, J.; Frobert, L.; Fankhauser, C.; Ismailaj, A.; Brana, A.; Tamic, G.; Suter, C.; et al. Improving Pleasure and Motivation in Schizophrenia: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Psychother. Psychosom. 2019, 88, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventura, J.; Subotnik, K.L.; Gitlin, M.J.; Gretchen-Doorly, D.; Ered, A.; Villa, K.F.; Hellemann, G.S.; Nuechterlein, K.H. Negative symptoms and functioning during the first year after a recent onset of schizophrenia and 8 years later. Schizophr. Res. 2015, 161, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vita, A.; Barlati, S. Recovery from schizophrenia: Is it possible? Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2018, 31, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchino, T.; Okubo, R.; Takubo, Y.; Aoki, A.; Wada, I.; Hashimoto, N.; Ikezawa, S.; Nemoto, T. Mediation Effects of Social Cognition on the Relationship between Neurocognition and Social Functioning in Major Depressive Disorder and Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.F. Impact of cognitive and social cognitive impairment on functional outcomes in patients with schizophrenia. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2016, 77 (Suppl. 2), 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkham, A.E.; Penn, D.L.; Green, M.F.; Buck, B.; Healey, K.; Harvey, P.D. The social cognition psychometric evaluation study: Results of the expert survey and RAND panel. Schizophr. Bull. 2014, 40, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, M.F.; Horan, W.P.; Lee, J. Nonsocial and social cognition in schizophrenia: Current evidence and future directions. World Psychiatry 2019, 18, 146–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahera, G.; Herrera, S.; Reinares, M.; Benito, A.; Rullas, M.; Gonzalez-Cases, J.; Vieta, E. Hostile attributions in bipolar disorder and schizophrenia contribute to poor social functioning. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2015, 131, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibaudeau, E.; Rae, J.; Raucher-Chene, D.; Bougeard, A.; Lepage, M. Disentangling the Relationships Between the Clinical Symptoms of Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders and Theory of Mind: A Meta-analysis. Schizophr. Bull. 2023, 49, 255–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redcay, E.; Warnell, K.R. A Social-Interactive Neuroscience Approach to Understanding the Developing Brain. Adv. Child Dev. Behav. 2018, 54, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, S.N.; Knutson, B. The reward circuit: Linking primate anatomy and human imaging. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 4–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Hairston, J.; Schrier, M.; Fan, J. Common and distinct networks underlying reward valence and processing stages: A meta-analysis of functional neuroimaging studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2011, 35, 1219–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitton, A.E.; Treadway, M.T.; Pizzagalli, D.A. Reward processing dysfunction in major depression, bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2015, 28, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangopadhyay, P.; Chawla, M.; Dal Monte, O.; Chang, S.W.C. Prefrontal-amygdala circuits in social decision-making. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberlin, L.E.; Victoria, L.W.; Ilieva, I.; Dunlop, K.; Hoptman, M.J.; Avari, J.; Alexopoulos, G.S.; Gunning, F.M. Comparison of Functional and Structural Neural Network Features in Older Adults with Depression with vs. without Apathy and Association With Response to Escitalopram: Secondary Analysis of a Nonrandomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2224142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Hu, Y.; Gu, H.; Salmeron, B.J.; Adinoff, B.; Stein, E.A.; Yang, Y. Salience and default mode network dysregulation in chronic cocaine users predict treatment outcome. Brain 2017, 140, 1513–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeley, W.W.; Menon, V.; Schatzberg, A.F.; Keller, J.; Glover, G.H.; Kenna, H.; Reiss, A.L.; Greicius, M.D. Dissociable intrinsic connectivity networks for salience processing and executive control. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 2349–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somerville, L.H.; Heatherton, T.F.; Kelley, W.M. Anterior cingulate cortex responds differentially to expectancy violation and social rejection. Nat. Neurosci. 2006, 9, 1007–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Braun, C.; Enck, P. How the brain reacts to social stress (exclusion)—A scoping review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 80, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, I.R.; Plotzker, A.; Ezzyat, Y. The Enigmatic temporal pole: A review of findings on social and emotional processing. Brain 2007, 130, 1718–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robison, A.J.; Thakkar, K.N.; Diwadkar, V.A. Cognition and Reward Circuits in Schizophrenia: Synergistic, Not Separate. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 87, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.K.; Lee, J.S.; Shin, Y.B.; Kim, H.E.; Kim, B.H.; Kim, J.J. The relationship between ambivalence, alexithymia, and salience network dysfunction in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2021, 310, 111271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rademacher, L.; Krach, S.; Kohls, G.; Irmak, A.; Gründer, G.; Spreckelmeyer, K.N. Dissociation of neural networks for anticipation and consumption of monetary and social rewards. Neuroimage 2010, 49, 3276–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.M.; Somerville, L.H.; Li, J.; Ruberry, E.J.; Libby, V.; Glover, G.; Voss, H.U.; Ballon, D.J.; Casey, B.J. Behavioral and neural properties of social reinforcement learning. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 13039–13045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, G.P.; Waltz, J.A.; Gold, J.M. A review of reward processing and motivational impairment in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2014, 40 (Suppl. 2), S107–S116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Fan, L.; Qiu, C.; Jiang, T. Prefrontal cortex and the dysconnectivity hypothesis of schizophrenia. Neurosci. Bull. 2015, 31, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Chen, C.; Rong, B.; Wan, Q.; Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, H. Resting-state functional connectivity of salience network in schizophrenia and depression. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, Y.F.; He, Y.; Zhu, C.Z.; Cao, Q.J.; Sui, M.Q.; Liang, M.; Tian, L.X.; Jiang, T.Z.; Wang, Y.F. Altered baseline brain activity in children with ADHD revealed by resting-state functional MRI. Brain Dev. 2007, 29, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Q.H.; Zhu, C.Z.; Yang, Y.; Zuo, X.N.; Long, X.Y.; Cao, Q.J.; Wang, Y.F.; Zang, Y.F. An improved approach to detection of amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (ALFF) for resting-state fMRI: Fractional ALFF. J. Neurosci. Methods 2008, 172, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Lu, Y.; He, Y.; Tian, L. Regional homogeneity approach to fMRI data analysis. Neuroimage 2004, 22, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Zhang, R.; Wen, L.; Jiang, F.; Mao, H.; Yan, W.; Xie, S.; Pan, X. Alterations in Spontaneous Brain Activity in Drug-Naïve First-Episode Schizophrenia: An Anatomical/Activation Likelihood Estimation Meta-Analysis. Psychiatry Investig. 2022, 19, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, T.; Wang, W.; Hei, G.; Yang, Y.; Long, Y.; Wang, X.; Xiao, J.; Huang, Y.; Song, X.; Xu, X.; et al. Identifying and revealing different brain neural activities of cognitive subtypes in early course schizophrenia. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 983995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Xu, W.; Zhang, R.; Yan, W.; Ma, W.; Xie, S.; Zhou, M. Regional Homogeneity Brain Alterations in Schizophrenia: An Activation Likelihood Estimation Meta-Analysis. Psychiatry Investig. 2021, 18, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, B.F.; Goldstein, R.B.; Saha, T.D.; Chou, S.P.; Jung, J.; Zhang, H.; Pickering, R.P.; Ruan, W.J.; Smith, S.M.; Huang, B.; et al. Epidemiology of DSM-5 Alcohol Use Disorder: Results From the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions III. JAMA Psychiatry 2015, 72, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leucht, S.; Samara, M.; Heres, S.; Patel, M.X.; Furukawa, T.; Cipriani, A.; Geddes, J.; Davis, J.M. Dose Equivalents for Second-Generation Antipsychotic Drugs: The Classical Mean Dose Method. Schizophr. Bull. 2015, 41, 1397–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, S.R.; Fiszbein, A.; Opler, L.A. The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 1987, 13, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, G.; Hesdon, B.; Wild, D.; Cookson, R.; Farina, C.; Sharma, V.; Fitzpatrick, R.; Jenkinson, C. Self-report quality of life measure for people with schizophrenia: The SQLS. Br. J. Psychiatry 2000, 177, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R.W. AFNI: Software for analysis and visualization of functional magnetic resonance neuroimages. Comput. Biomed. Res. 1996, 29, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, P.A.; Saad, Z.S. FATCAT: (an efficient) Functional and Tractographic Connectivity Analysis Toolbox. Brain Connect 2013, 3, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, J.D.; Barnes, K.A.; Snyder, A.Z.; Schlaggar, B.L.; Petersen, S.E. Spurious but systematic correlations in functional connectivity MRI networks arise from subject motion. Neuroimage 2012, 59, 2142–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischl, B.; Salat, D.H.; Busa, E.; Albert, M.; Dieterich, M.; Haselgrove, C.; van der Kouwe, A.; Killiany, R.; Kennedy, D.; Klaveness, S.; et al. Whole brain segmentation: Automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron 2002, 33, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desikan, R.S.; Ségonne, F.; Fischl, B.; Quinn, B.T.; Dickerson, B.C.; Blacker, D.; Buckner, R.L.; Dale, A.M.; Maguire, R.P.; Hyman, B.T.; et al. An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 968–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Guo, Z.; Cao, H.; Li, H.; Hu, X.; Cheng, L.; Li, J.; Liu, R.; Xu, Y. Altered asymmetries of resting-state MRI in the left thalamus of first-episode schizophrenia. Chronic Dis. Transl. Med. 2022, 8, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liao, J.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Yan, J.; Zhang, D.; Yan, H.; Yue, W. Altered Resting-State Brain Activity in Schizophrenia and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Compared With Non-psychiatric Controls: Commonalities and Distinctions Across Disorders. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 681701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, M.E.; Bollu, P.C.; Tadi, P. Neuroanatomy, Nucleus Caudate. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing Copyright© 2022; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Balleine, B.W.; Delgado, M.R.; Hikosaka, O. The Role of the Dorsal Striatum in Reward and Decision-Making. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 8161–8165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, D.; Rademacher, L.; Gabay, A.S.; Taylor, R.; Richey, J.A.; Smith, D.V.; Goerlich, K.S.; Nawijn, L.; Cremers, H.R.; Wilson, R.; et al. Mapping social reward and punishment processing in the human brain: A voxel-based meta-analysis of neuroimaging findings using the social incentive delay task. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 122, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Zhu, J.; Liu, X.; Pu, C.; Lai, Y.; Chen, L.; Yu, X.; Hong, N. Structural and functional brain abnormalities in schizophrenia: A cross-sectional study at different stages of the disease. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 83, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, J.J.; Cordeiro, S.A.; Weber, M.A.; Friederich, H.C.; Wolf, R.C.; Weisbrod, M.; Kaiser, S. Reward System Dysfunction as a Neural Substrate of Symptom Expression Across the General Population and Patients With Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2015, 41, 1370–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Chen, Q.; Wang, W.; Desrivières, S.; Quinlan, E.B.; Jia, T.; Macare, C.; Robert, G.H.; Cui, J.; Guedj, M.; et al. Association of a Schizophrenia-Risk Nonsynonymous Variant With Putamen Volume in Adolescents: A Voxelwise and Genome-Wide Association Study. JAMA Psychiatry 2019, 76, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirschner, M.; Schmidt, A.; Hodzic-Santor, B.; Burrer, A.; Manoliu, A.; Zeighami, Y.; Yau, Y.; Abbasi, N.; Maatz, A.; Habermeyer, B.; et al. Orbitofrontal-Striatal Structural Alterations Linked to Negative Symptoms at Different Stages of the Schizophrenia Spectrum. Schizophr. Bull. 2021, 47, 849–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, K.J.M.; Chen, Q.; Jaffe, A.E.; Stolz, J.M.; Collado-Torres, L.; Huuki-Myers, L.A.; Burke, E.E.; Arora, R.; Feltrin, A.S.; Barbosa, A.R.; et al. Analysis of the caudate nucleus transcriptome in individuals with schizophrenia highlights effects of antipsychotics and new risk genes. Nat. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 1559–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Tang, X.; You, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Yu, M. Altered Patterns of the Fractional Amplitude of Low-Frequency Fluctuation and Functional Connectivity Between Deficit and Non-Deficit Schizophrenia. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Solís, A.; Vives-Gilabert, Y.; Portella, M.J.; Rabella, M.; Grasa, E.M.; Roldán, A.; Keymer-Gausset, A.; Molins, C.; Núñez-Marín, F.; Gómez-Ansón, B.; et al. Altered amplitude of low frequency fluctuations in schizophrenia patients with persistent auditory verbal hallucinations. Schizophr. Res. 2017, 189, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasquoine, P.G. Contributions of the insula to cognition and emotion. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2014, 24, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhuo, C.; Xu, L.; Liu, F.; Qin, W.; Yu, C. Altered Coupling Between Resting-State Cerebral Blood Flow and Functional Connectivity in Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2017, 43, 1363–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylie, K.P.; Tregellas, J.R. The role of the insula in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2010, 123, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavigne, K.M.; Menon, M.; Woodward, T.S. Functional Brain Networks Underlying Evidence Integration and Delusions in Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2020, 46, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, N.F.; Li Hui Chong, P.; Lee, D.R.; Chew, Q.H.; Chen, G.; Sim, K. The Amygdala in Schizophrenia and Bipolar Disorder: A Synthesis of Structural MRI, Diffusion Tensor Imaging, and Resting-State Functional Connectivity Findings. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 2019, 27, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walther, S.; Lefebvre, S.; Conring, F.; Gangl, N.; Nadesalingam, N.; Alexaki, D.; Wüthrich, F.; Rüter, M.; Viher, P.V.; Federspiel, A.; et al. Limbic links to paranoia: Increased resting-state functional connectivity between amygdala, hippocampus and orbitofrontal cortex in schizophrenia patients with paranoia. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2021, 272, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anticevic, A.; Tang, Y.; Cho, Y.T.; Repovs, G.; Cole, M.W.; Savic, A.; Wang, F.; Krystal, J.H.; Xu, K. Amygdala connectivity differs among chronic, early course, and individuals at risk for developing schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2014, 40, 1105–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledoux, J.E. Emotion circuits in the brain. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 23, 155–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, D.J.; Kunkel, L.; Weiss, A.P.; Goff, D.C.; Wright, C.I.; Shin, L.M.; Rauch, S.L.; Hootnick, J.; Heckers, S.J.S.R. Increased medial temporal lobe activation during the passive viewing of emotional and neutral facial expressions in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2006, 82, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Grace, A. Inhibitory Modulation of Orbitofrontal Cortex on Medial Prefrontal Cortex-Amygdala Information Flow. Cereb. Cortex 2018, 28, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torregrossa, M.M.; Quinn, J.J.; Taylor, J.R. Impulsivity, compulsivity, and habit: The role of orbitofrontal cortex revisited. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 63, 253–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcalonan, K.; Brown, V.J. Orbital prefrontal cortex mediates reversal learning and not attentional set shifting in the rat. Behav. Brain Res. 2003, 146, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wake, S.J.; Izuma, K. A common neural code for social and monetary rewards in the human striatum. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2017, 12, 1558–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellucci, G.; Chernyak, S.V.; Goodyear, K.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Krueger, F. Neural signatures of trust in reciprocity: A coordinate-based meta-analysis. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2017, 38, 1233–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeiffer, U.J.; Schilbach, L.; Timmermans, B.; Kuzmanovic, B.; Georgescu, A.L.; Bente, G.; Vogeley, K. Why we interact: On the functional role of the striatum in the subjective experience of social interaction. Neuroimage 2014, 101, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redcay, E.; Velnoskey, K.R.; Rowe, M.L. Perceived communicative intent in gesture and language modulates the superior temporal sulcus. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2016, 37, 3444–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheon, E.J.; Male, A.G.; Gao, B.; Adhikari, B.M.; Edmond, J.T.; Hare, S.M.; Belger, A.; Potkin, S.G.; Bustillo, J.R.; Mathalon, D.H.; et al. Five negative symptom domains are differentially associated with resting state amplitude of low frequency fluctuations in Schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2023, 329, 111597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yao, J.; Lv, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Lei, J.; Li, Y.; Sui, Y. Aberrant Functional Connectivity of the Orbitofrontal Cortex Is Associated With Excited Symptoms in First-Episode Drug-Naive Patients With Schizophrenia. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 922272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birchwood, M.; Smith, J.; Cochrane, R.; Wetton, S.; Copestake, S. The Social Functioning Scale. The development and validation of a new scale of social adjustment for use in family intervention programmes with schizophrenic patients. Br. J. Psychiatry 1990, 157, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreeraj, V.S.; Shivakumar, V.; Bhalerao, G.V.; Kalmady, S.V.; Narayanaswamy, J.C.; Venkatasubramanian, G. Resting-state functional connectivity correlates of antipsychotic treatment in unmedicated schizophrenia. Asian J. Psychiatry 2023, 82, 103459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, K.D.; Cheung, C.K.; Choi, W. Cyberostracism: Effects of being ignored over the Internet. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 2000, 79, 748–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, P.; Bitsch, F.; Nagels, A.; Straube, B.; Falkenberg, I. Frontal hypoactivation and alterations in the reward-system during humor processing in patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorders. Schizophr. Res. 2018, 202, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalesky, A.; Fornito, A.; Bullmore, E.T. Network-based statistic: Identifying differences in brain networks. Neuroimage 2010, 53, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Brain Region | Side | Brain Network |
|---|---|---|
| caudate | R | reward network |
| L | reward network | |
| putamen | R | reward network |
| L | reward network | |
| pallidum | R | reward network |
| L | reward network | |
| amygdala | R | reward network; emotional salience network |
| L | reward network; emotional salience network | |
| caudal anterior cingulate | R | reward network |
| L | reward network | |
| lateral OFC | R | reward network; emotional salience network |
| L | reward network; emotional salience network | |
| medial OFC | R | reward network; emotional salience network |
| L | reward network; emotional salience network | |
| posterior cingulate | R | emotional salience network |
| L | emotional salience network | |
| rostral anterior cingulate | R | reward network |
| L | reward network | |
| insula | R | reward network; emotional salience network |
| L | reward network; emotional salience network |
| Items | SZ(n = 30) | HC(n = 30) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (male/female), n | 22/8 | 17/13 | 1.83 | 0.18 |
| Age (years), M(SD) | 46.70 (6.47) | 47.47 (14.15) | −0.27 | 0.79 |
| Education (years), M(SD) | 12.23 (2.80) | 10.50 (4.41) | 1.82 | 0.08 |
| Duration of illness (months), M(SD) | 214.12 (104.32) | n/a | ||
| Medication dosage (OL eq.), M(SD) | 14.34 (7.44) | n/a | ||
| PANSS, M(SD) | ||||
| Positive | 14.00 (4.83) | n/a | ||
| Negative | 21.63 (4.55) | n/a | ||
| General | 34.47 (8.03) | n/a | ||
| Total | 70.10 (13.93) | n/a |
| Brain Region | Side | t | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SZ > HC | ||||
| caudate | R | 4.40 | <0.001 | 0.001 |
| putamen | R | 3.50 | <0.001 | 0.009 |
| Brain Region | Side | t | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SZ > HC | ||||
| caudate | R | 2.732 | 0.008 | 0.038 |
| L | 2.708 | 0.009 | 0.038 | |
| putamen | R | 2.717 | 0.009 | 0.038 |
| L | 2.506 | 0.015 | 0.038 | |
| pallidum | R | 2.629 | 0.011 | 0.038 |
| L | 2.518 | 0.015 | 0.038 | |
| SZ < HC | ||||
| insula | R | −3.082 | 0.003 | 0.038 |
| L | −2.608 | 0.012 | 0.038 |
| Brain Region | Side | t | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SZ > HC | ||||
| caudate | R | 4.048 | <0.001 | 0.002 |
| L | 3.987 | <0.001 | 0.002 | |
| putamen | R | 3.601 | <0.001 | 0.004 |
| L | 3.393 | 0.001 | 0.006 | |
| pallidum | R | 2.761 | 0.008 | 0.030 |
| L | 2.697 | 0.009 | 0.030 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, C.; Zhang, C.; Li, Q.; Shao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Li, C.; Fan, Q. Deficits in Key Brain Network for Social Interaction in Individuals with Schizophrenia. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13101403
Wu Y, Wang H, Li C, Zhang C, Li Q, Shao Y, Yang Z, Li C, Fan Q. Deficits in Key Brain Network for Social Interaction in Individuals with Schizophrenia. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(10):1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13101403
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yiwen, Hongyan Wang, Chuoran Li, Chen Zhang, Qingfeng Li, Yang Shao, Zhi Yang, Chunbo Li, and Qing Fan. 2023. "Deficits in Key Brain Network for Social Interaction in Individuals with Schizophrenia" Brain Sciences 13, no. 10: 1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13101403
APA StyleWu, Y., Wang, H., Li, C., Zhang, C., Li, Q., Shao, Y., Yang, Z., Li, C., & Fan, Q. (2023). Deficits in Key Brain Network for Social Interaction in Individuals with Schizophrenia. Brain Sciences, 13(10), 1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13101403






