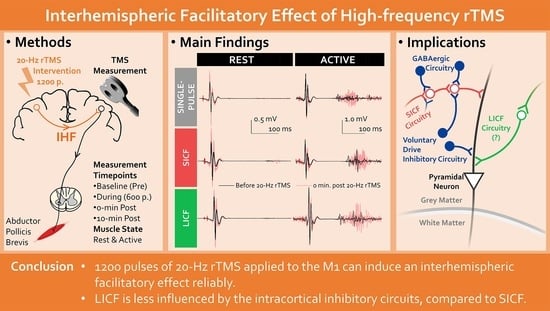
Interhemispheric Facilitatory Effect of High-Frequency rTMS: Perspective from Intracortical Facilitation and Inhibition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Participants
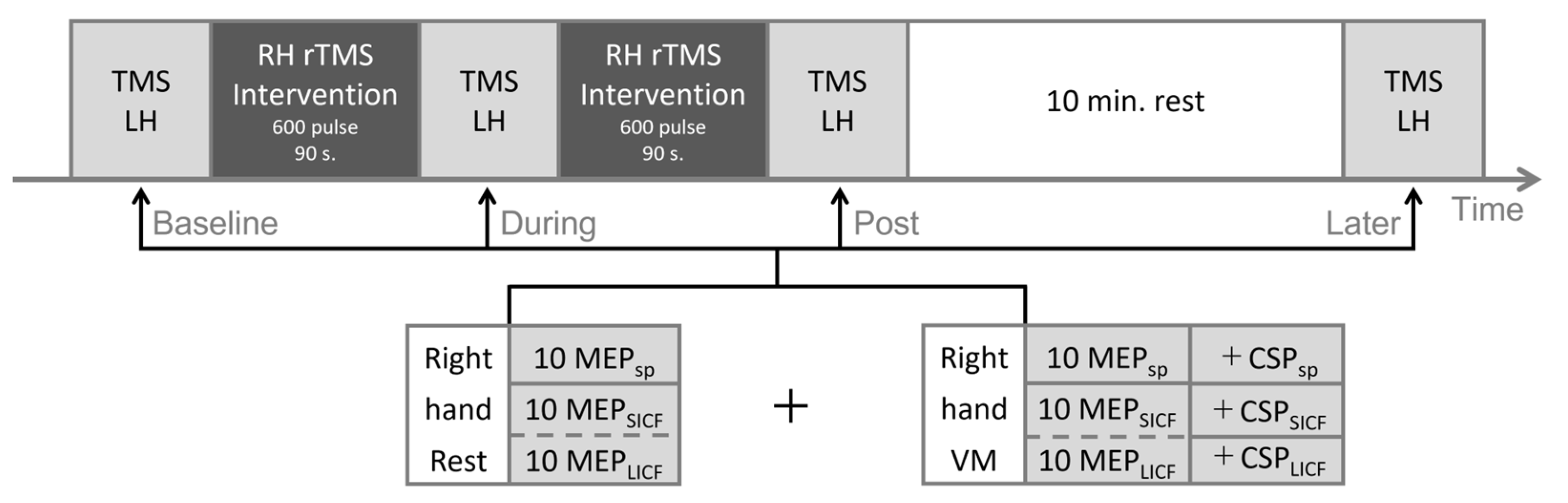
2.3. Protocol
2.4. TMS Parameters
2.4.1. TMS Equipment and Basic Configuration
2.4.2. Measurement: Single-Pulse TMS
2.4.3. Measurement: Paired-Pulse TMS
2.4.4. Intervention: Repetitive TMS
2.5. EMG Recording
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
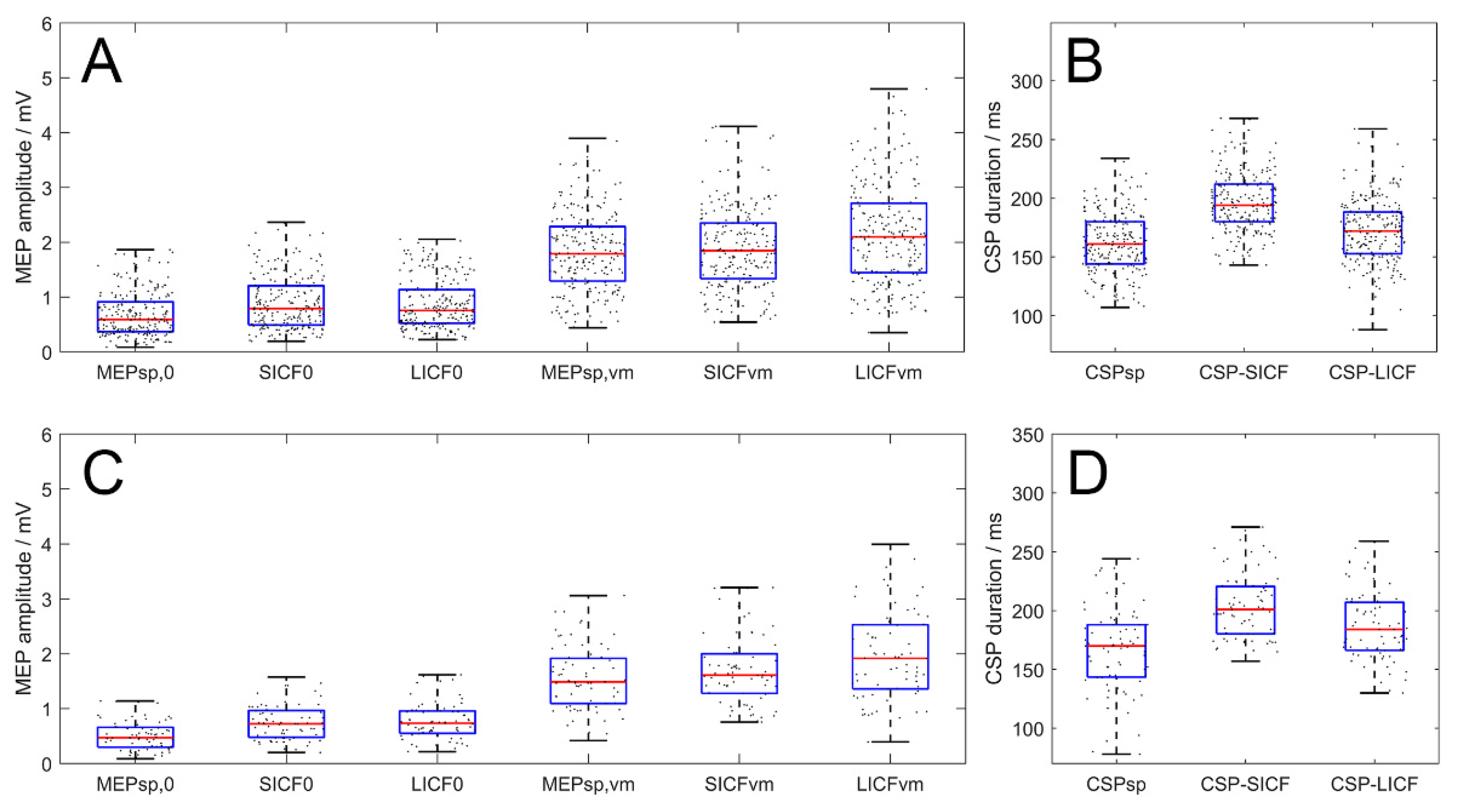
3.1. Baseline Measurements
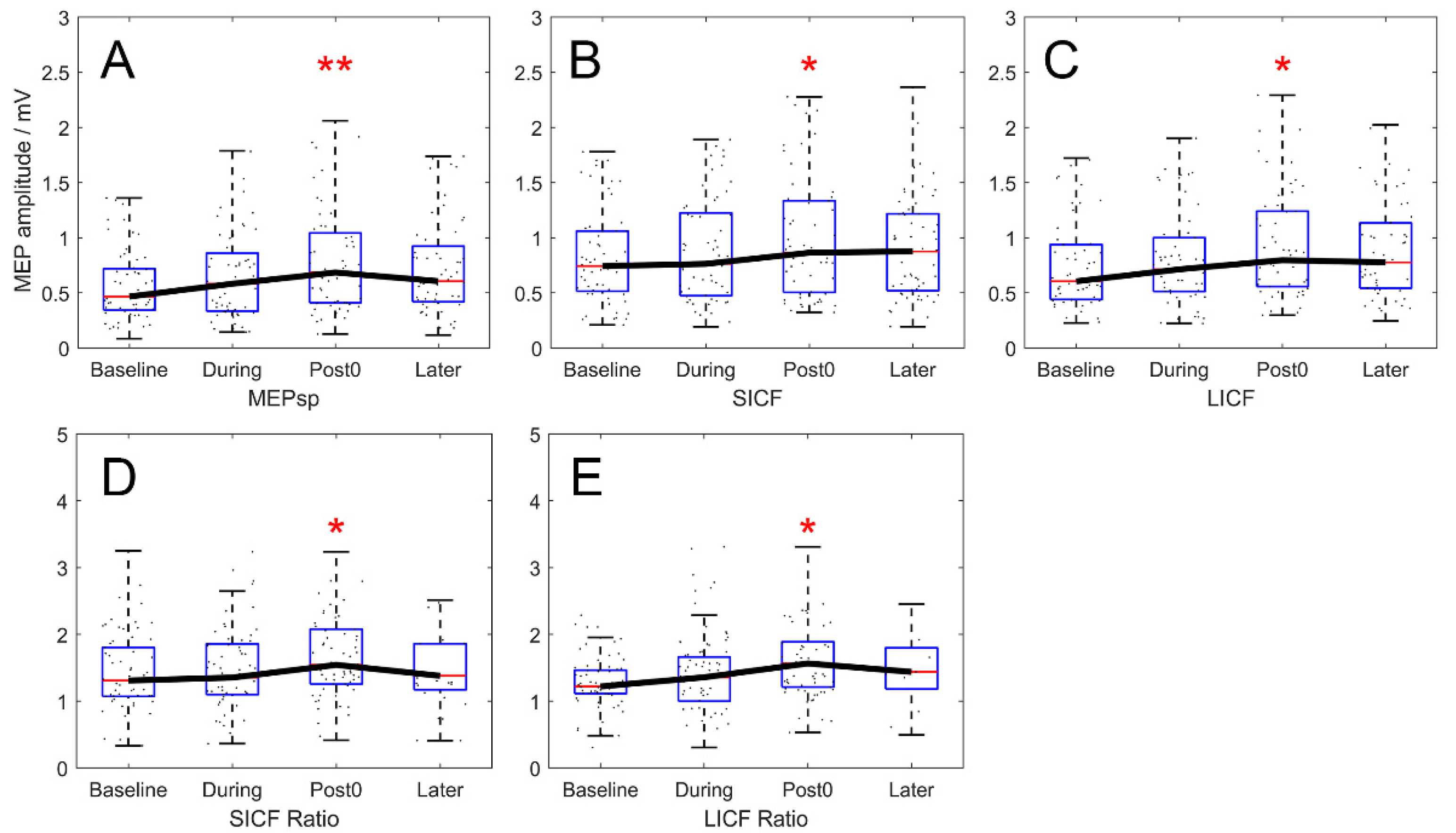
3.2. Interhemispheric ICF Modulation by rTMS
3.3. Interhemispheric ICI Modulation by rTMS
3.4. Paradigm-Wise Effects of Rest and VM
3.5. Parameter-Wise Test–Retest Reliability
4. Discussion
4.1. Interhemispheric Facilitatory Effects of 20-Hz rTMS
4.2. Modulation of ICF by 20-Hz rTMS
4.3. Modulation of ICI by 20-Hz rTMS
4.4. Attributes of ICI and ICF
4.5. Limitation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Caglayan, A.B.; Beker, M.C.; Caglayan, B.; Yalcin, E.; Caglayan, A.; Yulug, B.; Hanoglu, L.; Kutlu, S.; Doeppner, T.R.; Hermann, D.M. Acute and post-acute neuromodulation induces stroke recovery by promoting survival signaling, neurogenesis, and pyramidal tract plasticity. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davis, P.; Gaitanis, J. Neuromodulation for the treatment of epilepsy: A review of current approaches and future directions. Clin. Ther. 2020, 42, 1140–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGirr, A.; Berlim, M.T. Clinical Usefulness of Therapeutic Neuromodulation for Major Depression: A Systematic Meta-Review of Recent Meta-Analyses. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 41, 485–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, R.B.C.; Galvão, S.C.B.; Frederico, L.M.P.; Amaral, N.S.L.; Carneiro, M.I.S.; de Moura Filho, A.G.; Piscitelli, D.; Monte-Silva, K. Cortical and spinal excitability changes after repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation combined to physiotherapy in stroke spastic patients. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 40, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polania, R.; Nitsche, M.A.; Ruff, C.C. Studying and modifying brain function with non-invasive brain stimulation. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, A.T.; Jalinous, R.; Freeston, I.L. Non-invasive magnetic stimulation of human motor cortex. Lancet 1985, 325, 1106–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, S.-I. Investigation of Human Motor Control Using Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation. Jpn. J. Rehabil. Med. 2001, 38, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, A.R.; Snow, N.J.; Alcock, L.R.; Ploughman, M. Probing the Brain–Body Connection Using Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS): Validating a Promising Tool to Provide Biomarkers of Neuroplasticity and Central Nervous System Function. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, P.M.; Burke, D.; Chen, R.; Cohen, L.G.; Daskalakis, Z.; Di Iorio, R.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Ferreri, F.; Fitzgerald, P.B.; George, M.S.; et al. Non-invasive electrical and magnetic stimulation of the brain, spinal cord, roots and peripheral nerves: Basic principles and procedures for routine clinical and research application. An updated report from an IFCN Committee. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 1071–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujirai, T.; Caramia, M.D.; Rothwell, J.C.; Day, B.L.; Thompson, P.D.; Ferbert, A.; Wroe, S.; Asselman, P.; Marsden, C.D. Corticocortical inhibition in human motor cortex. J. Physiol. 1993, 471, 501–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemann, U.L.F.; Rothwell, J.C.; Ridding, M.C. Interaction between intracortical inhibition and facilitation in human motor cortex. J. Physiol. 1996, 496, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemann, U. I-waves in motor cortex revisited. Exp. Brain Res. 2020, 238, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Lazzaro, V.; Rothwell, J.C. Corticospinal activity evoked and modulated by non-invasive stimulation of the intact human motor cortex. J. Physiol. 2014, 592, 4115–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegel, P.; Niemann, N.; Rothwell, J.C.; Leukel, C. Evidence for a subcortical contribution to intracortical facilitation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2018, 47, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udupa, K.; Ni, Z.; Gunraj, C.; Chen, R. Effect of long interval interhemispheric inhibition on intracortical inhibitory and facilitatory circuits. J. Physiol. 2010, 588, 2633–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorsler, A.; Bäumer, T.; Weiller, C.; Münchau, A.; Liepert, J. Interhemispheric effects of high and low frequency rTMS in healthy humans. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2003, 114, 1800–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, P.K.; Hanajima, R.; Gunraj, C.A.; Li, J.-Y.; Wagle-Shukla, A.; Morgante, F.; Chen, R. Effect of Low-Frequency Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation on Interhemispheric Inhibition. J. Neurophysiol. 2005, 94, 1668–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fitzgerald, P.B.; Fountain, S.; Daskalakis, Z.J. A comprehensive review of the effects of rTMS on motor cortical excitability and inhibition. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2006, 117, 2584–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroff, O.A.C. Book review: GABA and glutamate in the human brain. Neuroscientist 2002, 8, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, S.; Beaulé, V.; Proulx, S.; De Beaumont, L.; Marjańska, M.; Doyon, J.; Pascual-Leone, A.; Lassonde, M.; Théoret, H. Relationship between transcranial magnetic stimulation measures of intracortical inhibition and spectroscopy measures of GABA and glutamate+ glutamine. J. Neurophysiol. 2013, 109, 1343–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuypers, K.; Marsman, A. Transcranial magnetic stimulation and magnetic resonance spectroscopy: Opportunities for a bimodal approach in human neuroscience. Neuroimage 2021, 224, 117394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldfield, R.C. The assessment and analysis of handedness: The Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 1971, 9, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Hallett, M.; Rossini, P.M.; Pascual-Leone, A. Screening questionnaire before TMS: An update. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2011, 1222, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, S.; Antal, A.; Bestmann, S.; Bikson, M.; Brewer, C.; Brockmoller, J.; Carpenter, L.L.; Cincotta, M.; Chen, R.; Daskalakis, J.D.; et al. Safety and recommendations for TMS use in healthy subjects and patient populations, with updates on training, ethical and regulatory issues: Expert Guidelines. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2021, 132, 269–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Chang, W.H.; Cho, J.W.; Youn, J.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, Y.-H. Efficacy of cumulative high-frequency rTMS on freezing of gait in Parkinson’s disease. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2015, 33, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perez, M.A.; Cohen, L.G. Mechanisms underlying functional changes in the primary motor cortex ipsilateral to an active hand. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 5631–5640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derosiere, G.; Alexandre, F.; Bourdillon, N.; Mandrick, K.; Ward, T.E.; Perrey, S. Similar scaling of contralateral and ipsilateral cortical responses during graded unimanual force generation. Neuroimage 2014, 85, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, A.; Belvisi, D.; Iezzi, E.; Mari, F.; Inghilleri, M.; Berardelli, A. Effects of attention on inhibitory and facilitatory phenomena elicited by paired-pulse transcranial magnetic stimulation in healthy subjects. Exp. Brain Res. 2008, 186, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, A.; Gilio, F.; Iezzi, E.; Frasca, V.; Inghilleri, M.; Berardelli, A. Attention influences the excitability of cortical motor areas in healthy humans. Exp. Brain Res. 2007, 182, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.A.; Thickbroom, G.W.; Mastaglia, F.L. Transcranial magnetic stimulation mapping of the motor cortex in normal subjects: The representation of two intrinsic hand muscles. J. Neurol. Sci. 1993, 118, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saatlou, F.H.; Rogasch, N.C.; McNair, N.A.; Biabani, M.; Pillen, S.D.; Marshall, T.R.; Bergmann, T.O. MAGIC: An open-source MATLAB toolbox for external control of transcranial magnetic stimulation devices. Brain Stimul. Basic Transl. Clin. Res. Neuromodulation 2018, 11, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Cros, D.; Curra, A.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Lefaucheur, J.P.; Magistris, M.R.; Mills, K.; Rosler, K.M.; Triggs, W.J.; Ugawa, Y.; et al. The clinical diagnostic utility of transcranial magnetic stimulation: Report of an IFCN committee. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 504–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasem, H.; Fujiyama, H.; Rurak, B.K.; Vallence, A.-M. Good test–retest reliability of a paired-pulse transcranial magnetic stimulation protocol to measure short-interval intracortical facilitation. Exp. Brain Res. 2020, 238, 2711–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaseghi, B.; Zoghi, M.; Jaberzadeh, S. Inter-pulse interval affects the size of single-pulse TMS-induced motor evoked potentials: A reliability study. Basic Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 6, 44. [Google Scholar]
- Di Lazzaro, V.; Oliviero, A.; Profice, P.; Saturno, E.; Pilato, F.; Insola, A.; Mazzone, P.; Tonali, P.; Rothwell, J.C. Comparison of descending volleys evoked by transcranial magnetic and electric stimulation in conscious humans. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1998, 109, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biabani, M.; Aminitehrani, M.; Zoghi, M.; Farrell, M.; Egan, G.; Jaberzadeh, S. The effects of transcranial direct current stimulation on short-interval intracortical inhibition and intracortical facilitation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 29, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thickbroom, G.W.; Byrnes, M.L.; Edwards, D.J.; Mastaglia, F.L. Repetitive paired-pulse TMS at I-wave periodicity markedly increases corticospinal excitability: A new technique for modulating synaptic plasticity. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2006, 117, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opie, G.M.; Sasaki, R.; Hand, B.J.; Semmler, J.G. Modulation of motor cortex plasticity by repetitive paired-pulse TMS at late I-wave intervals is influenced by intracortical excitability. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cash, R.F.H.; Dar, A.; Hui, J.; De Ruiter, L.; Baarbé, J.; Fettes, P.; Peters, S.; Fitzgerald, P.B.; Downar, J.; Chen, R. Influence of inter-train interval on the plastic effects of rTMS. Brain Stimul. 2017, 10, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, F.; Keenan, J.P.; Tormos, J.M.; Topka, H.; Pascual-Leone, A. Interindividual variability of the modulatory effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on cortical excitability. Exp. Brain Res. 2000, 133, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corneal, S.F.; Butler, A.J.; Wolf, S.L. Intra-and intersubject reliability of abductor pollicis brevis muscle motor map characteristics with transcranial magnetic stimulation. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 1670–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Säisänen, L.; Pirinen, E.; Teitti, S.; Könönen, M.; Julkunen, P.; Määttä, S.; Karhu, J. Factors influencing cortical silent period: Optimized stimulus location, intensity and muscle contraction. J. Neurosci. Methods 2008, 169, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cash, R.F.H.; Benwell, N.M.; Murray, K.; Mastaglia, F.L.; Thickbroom, G.W. Neuromodulation by paired-pulse TMS at an I-wave interval facilitates multiple I-waves. Exp. Brain Res. 2009, 193, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akoglu, H. User’s guide to correlation coefficients. Turk. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 18, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Hanajima, R.; Shirota, Y.; Ohminami, S.; Tsutsumi, R.; Terao, Y.; Ugawa, Y.; Hirose, S.; Miyashita, Y.; Konishi, S. Bidirectional effects on interhemispheric resting-state functional connectivity induced by excitatory and inhibitory repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2014, 35, 1896–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, W.-K.; You, S.H.; Ko, M.-H.; Kim, S.T.; Park, C.-H.; Park, J.-W.; Ohn, S.H.; Hallett, M.; Kim, Y.-H. High frequency rTMS modulation of the sensorimotor networks: Behavioral changes and fMRI correlates. Neuroimage 2008, 39, 1886–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nettekoven, C.; Volz, L.J.; Kutscha, M.; Pool, E.-M.; Rehme, A.K.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Fink, G.R.; Grefkes, C. Dose-dependent effects of theta burst rTMS on cortical excitability and resting-state connectivity of the human motor system. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 6849–6859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimomura, T.; Fujiki, M.; Ohba, H.; Kochiyma, T.; Sugita, K.; Matsuta, H.; Kawasaki, Y.; Oonishi, K.; Fudaba, H.; Kamida, T. Contralateral Negative Bold Responses in the Motor Network during Subthreshold High-Frequency Interleaved TMS-fMRI over the Human Primary Motor Cortex. J. Neurol. Neurophysiol. 2018, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebner, H.R.; Peller, M.; Willoch, F.; Minoshima, S.; Boecker, H.; Auer, C.; Drzezga, A.; Conrad, B.; Bartenstein, P. Lasting cortical activation after repetitive TMS of the motor cortex: A glucose metabolic study. Neurology 2000, 54, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Potter, T.; Wang, J.; Shi, Z.; Wang, C.; Yang, L.; Chan, R.; Zhang, Y. Cortical hemodynamic response and connectivity modulated by sub-threshold high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jing, H.; Takigawa, M. Observation of EEG coherence after repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2000, 111, 1620–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliviero, A.; Strens, L.H.A.; Lazzaro, V.; Tonali, P.A.; Brown, P. Persistent effects of high frequency repetitive TMS on the coupling between motor areas in the human. Exp. Brain Res. 2003, 149, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, Y. Receptor subtypes involved in callosally-induced postsynaptic potentials in rat frontal agranular cortex in vitro. Exp. Brain Res. 1992, 88, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, F.; Manzoni, T. The neurotransmitters and postsynaptic actions of callosally projecting neurons. Behav. Brain Res. 1994, 64, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Sommer, M.; Tergau, F.; Paulus, W. Lasting influence of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on intracortical excitability in human subjects. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 287, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malcolm, M.P.; Paxton, R.J. High-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation effects on motor intracortical neurophysiology: A sham-controlled investigation. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 32, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.H.; Shin, J.E.; Jeong, Y.-S.; Shin, H.-I. Changes in motor cortical excitability induced by high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of different stimulation durations. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyke, K.; Kim, S.; Jackson, G.M.; Jackson, S.R. Reliability of single and paired pulse transcranial magnetic stimulation parameters across eight testing sessions. Brain Stimul. 2018, 11, 1393–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.C.; Yuan, S.; DeVries, W.H.; Armstrong, N.M.; Korte, J.E.; Sahlem, G.L.; Carpenter, L.L.; George, M.S. NMDA-receptor agonist reveals LTP-like properties of 10-Hz rTMS in the human motor cortex. Brain Stimul. Basic Transl. Clin. Res. Neuromodulation 2021, 14, 619–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, S.K.; Huber, R.; Massimini, M.; Peterson, M.J.; Ferrarelli, F.; Tononi, G. A direct demonstration of cortical LTP in humans: A combined TMS/EEG study. Brain Res. Bull. 2006, 69, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jesus, D.R.; de Souza Favalli, G.P.; Hoppenbrouwers, S.S.; Barr, M.S.; Chen, R.; Fitzgerald, P.B.; Daskalakis, Z.J. Determining optimal rTMS parameters through changes in cortical inhibition. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2014, 125, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daskalakis, Z.J.; Möller, B.; Christensen, B.K.; Fitzgerald, P.B.; Gunraj, C.; Chen, R. The effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on cortical inhibition in healthy human subjects. Exp. Brain Res. 2006, 174, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, S.; Gilio, F.; Pedace, F.; Ozkaynak, S.; Inghilleri, M.; Manfredi, M.; Berardelli, A. Changes in the cortical silent period after repetitive magnetic stimulation of cortical motor areas. Exp. Brain Res. 2000, 135, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreifuss, J.J.; Kelly, J.S.; Krnjević, K. Cortical inhibition and γ-aminobutyric acid. Exp. Brain Res. 1969, 9, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortu, E.; Deriu, F.; Suppa, A.; Tolu, E.; Rothwell, J.C. Effects of volitional contraction on intracortical inhibition and facilitation in the human motor cortex. J. Physiol. 2008, 586, 5147–5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, M.; Rothwell, J.C. The cortical silent period: Intrinsic variability and relation to the waveform of the transcranial magnetic stimulation pulse. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004, 115, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, S.; Onishi, H.; Sugawara, K.; Kirimoto, H.; Suzuki, M.; Tamaki, H. Modulation of the cortical silent period elicited by single-and paired-pulse transcranial magnetic stimulation. BMC Neurosci. 2013, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silbert, B.I.; Thickbroom, G.W. Conditioning the cortical silent period with paired transcranial magnetic stimulation. Brain Stimul. 2013, 6, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Gunraj, C.; Chen, R. Short interval intracortical inhibition and facilitation during the silent period in human. J. Physiol. 2007, 583, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Gunraj, C.; Wagle-Shukla, A.; Udupa, K.; Mazzella, F.; Lozano, A.M.; Chen, R. Direct demonstration of inhibitory interactions between long interval intracortical inhibition and short interval intracortical inhibition. J. Physiol. 2011, 589, 2955–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Branscheidt, M.; Schambra, H.; Steiner, L.; Widmer, M.; Diedrichsen, J.; Goldsmith, J.; Lindquist, M.; Kitago, T.; Luft, A.R.; et al. Rethinking interhemispheric imbalance as a target for stroke neurorehabilitation. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 85, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huber, L.; Handwerker, D.A.; Jangraw, D.C.; Chen, G.; Hall, A.; Stüber, C.; Gonzalez-Castillo, J.; Ivanov, D.; Marrett, S.; Guidi, M.; et al. High-Resolution CBV-fMRI Allows Mapping of Laminar Activity and Connectivity of Cortical Input and Output in Human M1. Neuron 2017, 96, 1253–1263.e1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, R.; Baltar, A.; Berenguer-Rocha, M.; Shirahige, L.; Rocha, S.; Fonseca, A.; Piscitelli, D.; Monte-Silva, K. Intrahemispheric EEG: A New Perspective for Quantitative EEG Assessment in Poststroke Individuals. Neural Plast. 2021, 2021, 5664647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, D.; Izumi, S.-I. Interhemispheric Facilitatory Effect of High-Frequency rTMS: Perspective from Intracortical Facilitation and Inhibition. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12080970
Tian D, Izumi S-I. Interhemispheric Facilitatory Effect of High-Frequency rTMS: Perspective from Intracortical Facilitation and Inhibition. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(8):970. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12080970
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Dongting, and Shin-Ichi Izumi. 2022. "Interhemispheric Facilitatory Effect of High-Frequency rTMS: Perspective from Intracortical Facilitation and Inhibition" Brain Sciences 12, no. 8: 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12080970
APA StyleTian, D., & Izumi, S.-I. (2022). Interhemispheric Facilitatory Effect of High-Frequency rTMS: Perspective from Intracortical Facilitation and Inhibition. Brain Sciences, 12(8), 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12080970