Intraoperative Cerebral Hemodynamic Monitoring during Carotid Endarterectomy via Diffuse Correlation Spectroscopy and Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
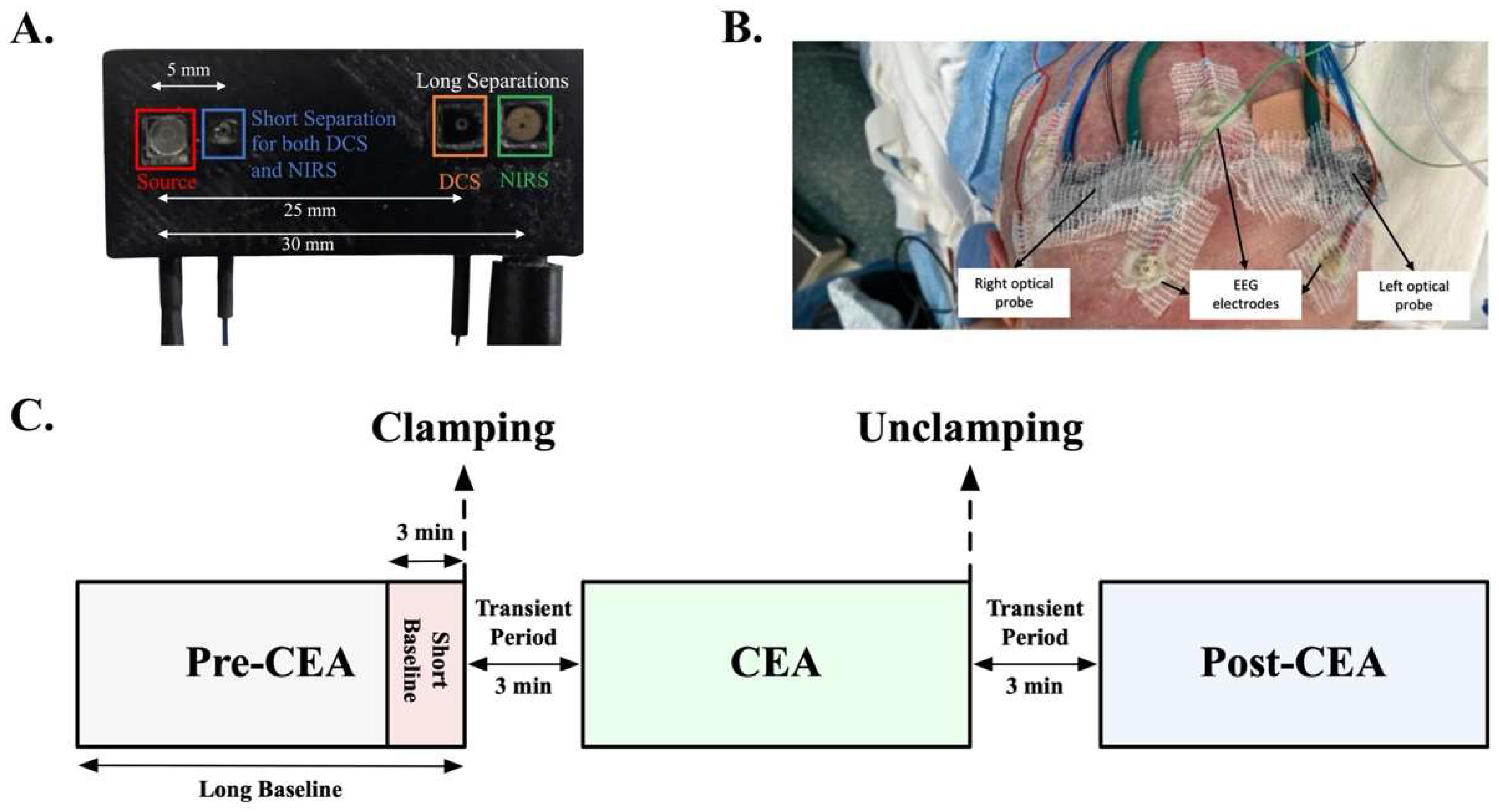
2.1. Study Patients and Procedure
2.2. Optical Instrument and Clinical Auxiliary Signals
2.3. Analysis of Cerebral Blood Flow Index and Oxygenation
2.4. Estimation of Cerebral Autoregulation and Cerebrovascular Resistance
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
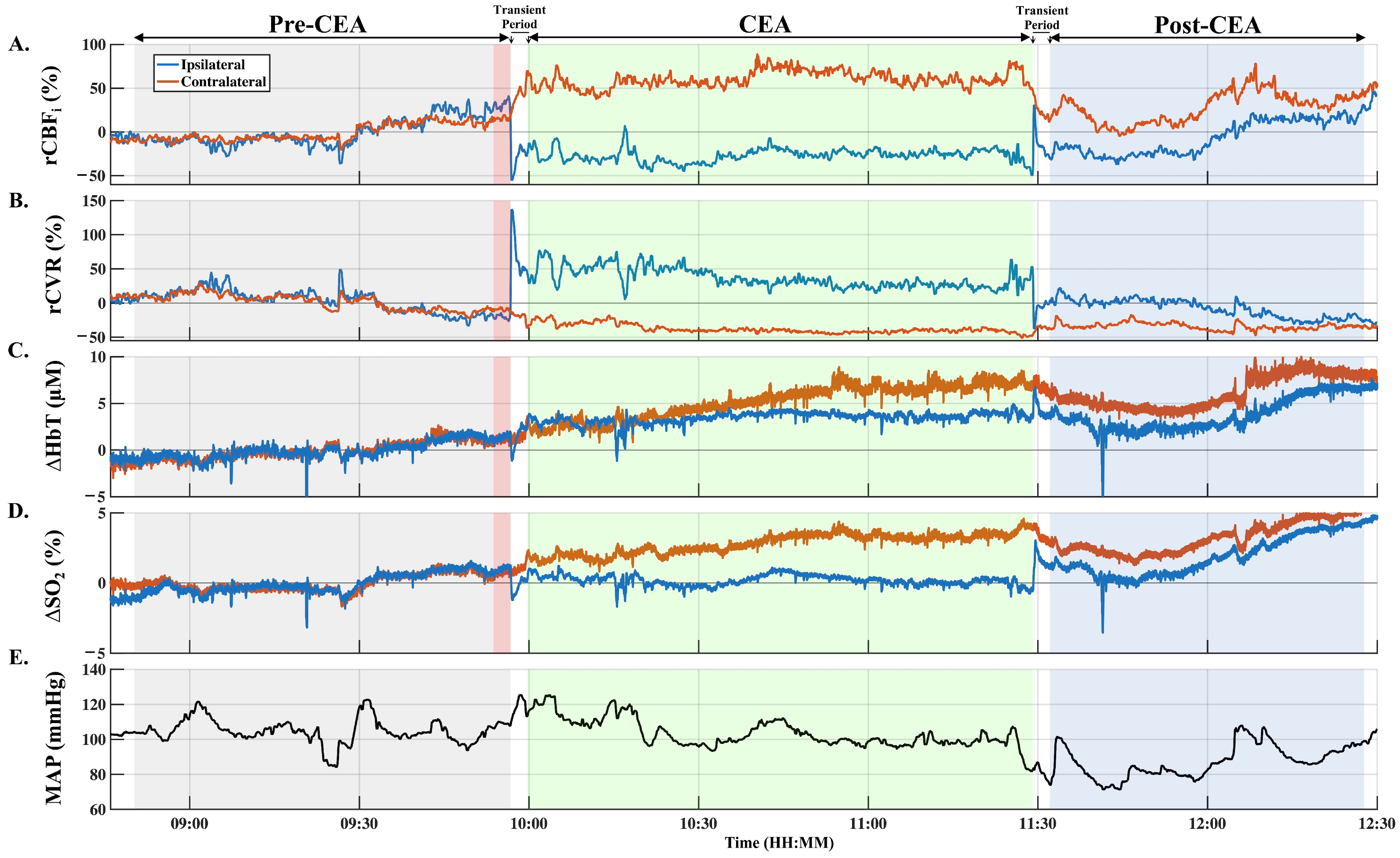
3.1. Intraoperative Hemodynamic Changes
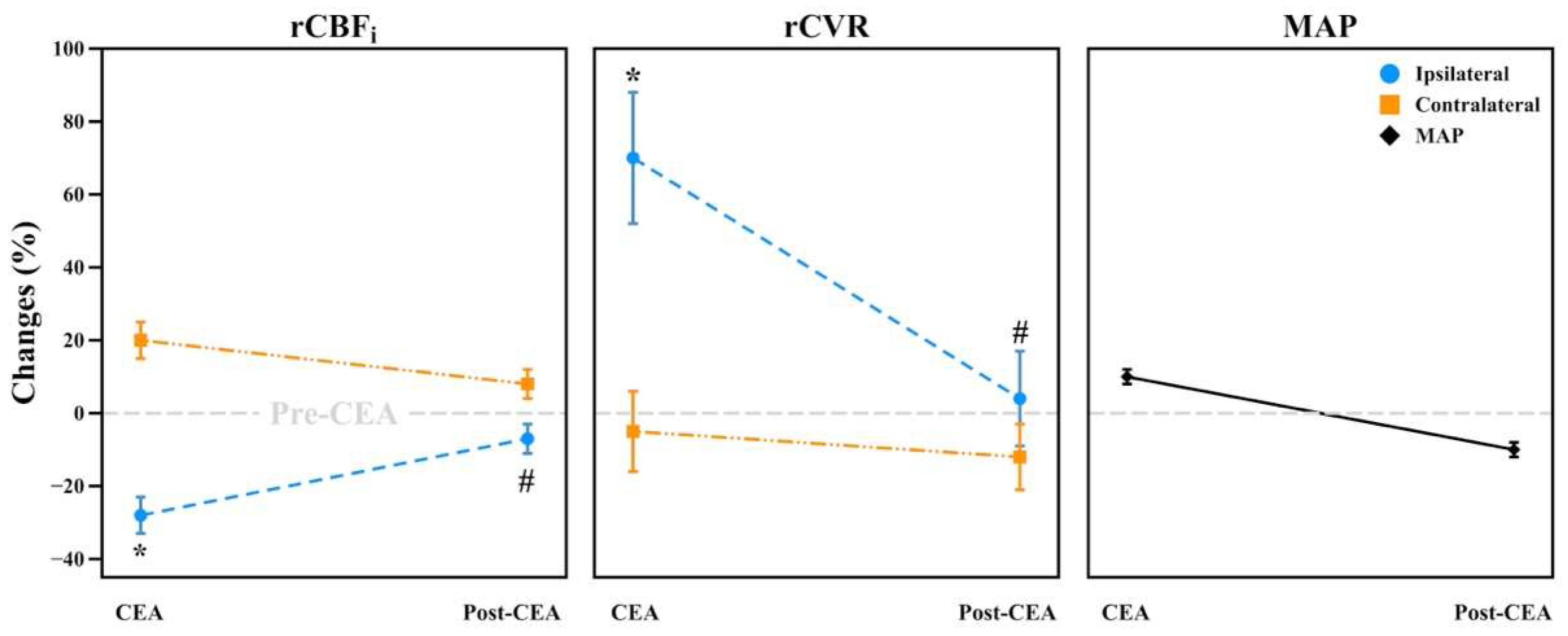
3.2. Quantification of Transient Ipsilateral Changes in rCBFi, ∆HbT, and ∆SO2
3.3. Intraoperative Hemodynamic Changes during CEA and Post-CEA Phases
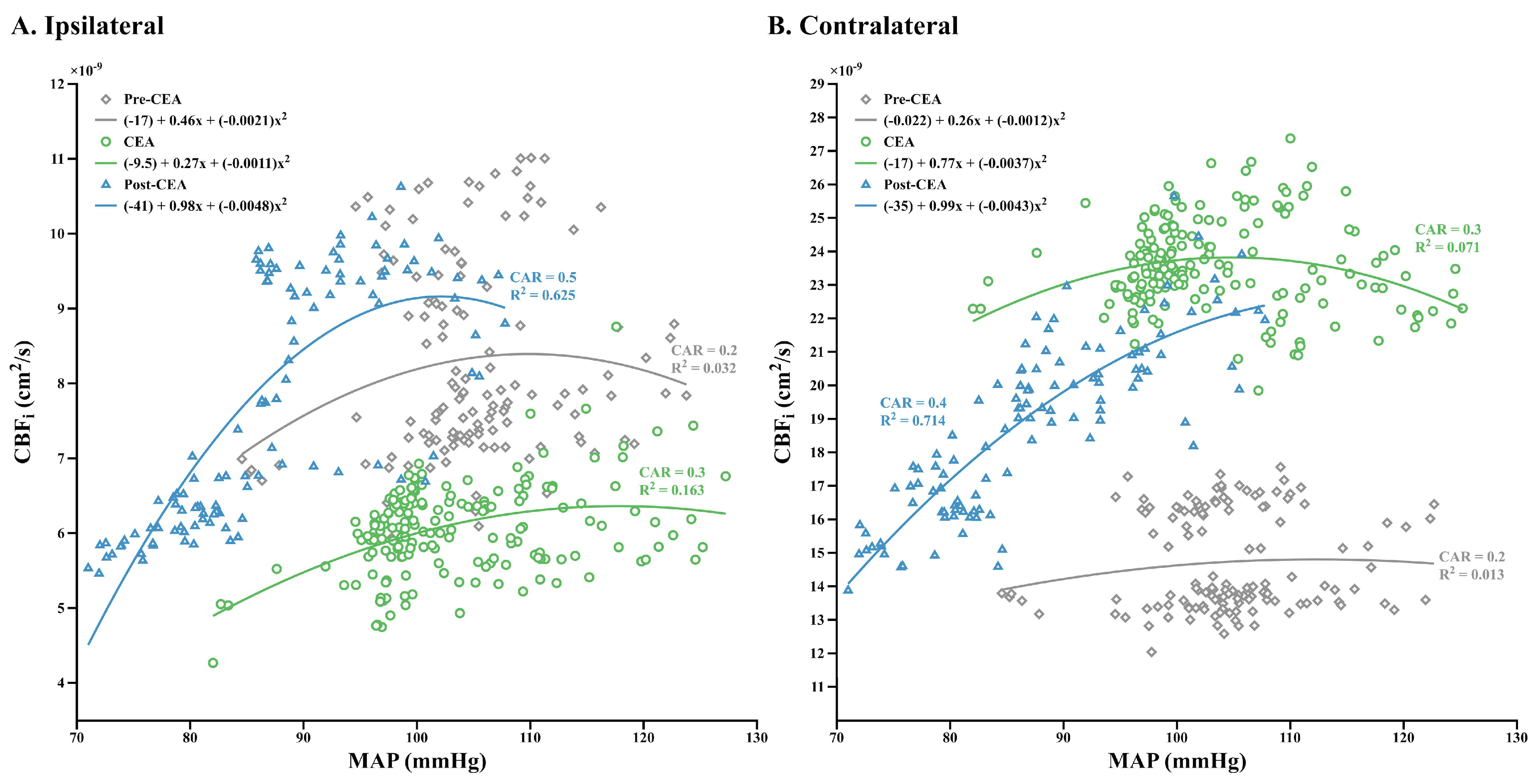
3.4. Relationship between CBFi and MAP, and Dynamic CAR Changes
3.5. Perioperative Complications
4. Discussion
4.1. Clamp- and Unclamp-Induced Transient Hemodynamic Changes
4.2. Intraoperative Changes in CBFi and CVR
4.3. Dynamic CAR Indices
4.4. Hemodynamic Changes in the Superficial Compartment
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Howell, S.J. Carotid Endarterectomy. Br. J. Anaesth. 2007, 99, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, J.R.; Pikula, A.; Nguyen, T.N.; Nien, Y.L.; Norbash, A.; Babikian, V.L. Cerebral Collateral Circulation in Carotid Artery Disease. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2009, 5, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrselja, Z.; Brkic, H.; Mrdenovic, S.; Radic, R.; Curic, G. Function of Circle of Willis. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 34, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cursi, M.; Meraviglia, M.V.; Fanelli, G.F.; Chiesa, R.; Tirelli, A.; Comi, G.; Minicucci, F. Electroencephalographic Background Desynchronization during Cerebral Blood Flow Reduction. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2005, 116, 2577–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moritz, S.; Kasprzak, P.; Arlt, M.; Taeger, K.; Metz, C. Accuracy of Cerebral Monitoring in Detecting Cerebral Ischemia during Carotid Endarterectomy: A Comparison of Transcranial Doppler Sonography, Near-Infrared Spectroscopy, Stump Pressure, and Somatosensory Evoked Potentials. Anesthesiology 2007, 107, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowed, D.W.; Houlden, D.A.; Burkholder, L.M.; Taylor, A.B. Comparison of Monitoring Techniques for Intraoperative Cerebral Ischemia. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2004, 31, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloan, T.B. Anesthetic Effects on Electrophysiologic Recordings. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1998, 15, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, C.; Vriens, E.M.; Eikelboom, B.C.; Vermeulen, F.E.; van Gijn, J.; Ackerstaff, R.G. Carotid Endarterectomy with Transcranial Doppler and Electroencephalographic Monitoring. A Prospective Study in 130 Operations. Stroke 1993, 24, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belardi, P.; Lucertini, G.; Ermirio, D. Stump Pressure and Transcranial Doppler for Predicting Shunting in Carotid Endarterectomy. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2003, 25, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Spencer, M.P.; Thomas, G.I.; Nicholls, S.C.; Sauvage, L.R. Detection of Middle Cerebral Artery Emboli during Carotid Endarterectomy Using Transcranial Doppler Ultrasonography. Stroke 1990, 21, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edlow, B.L.; Kim, M.N.; Durduran, T.; Zhou, C.; Putt, M.E.; Yodh, A.G.; Greenberg, J.H.; Detre, J.A. The Effects of Healthy Aging on Cerebral Hemodynamic Responses to Posture Change. Physiol. Meas. 2010, 31, 477–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennekamp, C.W.; Bots, M.L.; Kappelle, L.J.; Moll, F.L.; de Borst, G.J. The Value of Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Measured Cerebral Oximetry during Carotid Endarterectomy in Perioperative Stroke Prevention. A Review. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2009, 38, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delpy, D.T.; Cope, M.; van der Zee, P.; Arridge, S.; Wray, S.; Wyatt, J. Estimation of Optical Pathlength through Tissue from Direct Time of Flight Measurement. Phys. Med. Biol. 1988, 33, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, S.; Nakahara, I.; Higashi, T.; Iwamuro, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Ando, M.; Takezawa, M.; Kira, J.I. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy in Carotid Artery Stenting Predicts Cerebral Hyperperfusion Syndrome. Neurology 2009, 72, 1512–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigamonti, A.; Scandroglio, M.; Minicucci, F.; Magrin, S.; Carozzo, A.; Casati, A. A Clinical Evaluation of Near-Infrared Cerebral Oximetry in the Awake Patient to Monitor Cerebral Perfusion during Carotid Endarterectomy. J. Clin. Anesth. 2005, 17, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubhofer, G.; Plöchl, W.; Skolka, M.; Czerny, M.; Ehrlich, M.; Lassnigg, A. Comparing Doppler Ultrasonography and Cerebral Oximetry as Indicators for Shunting in Carotid Endarterectomy. Anesth. Analg. 2000, 91, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugliese, F.; Ruberto, F.; Tosi, A.; Martelli, S.; Bruno, K.; Summonti, D.; D’Alio, A.; Diana, B.; Anile, M.; Panico, A. Regional Cerebral Saturation versus Transcranial Doppler during Carotid Endarterectomy under Regional Anaesthesia. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2009, 26, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrini, L.; Magnoni, F.; Sensi, L.; Pisano, E.; Ballestrazzi, M.S.; Cirelli, M.R.; Pilato, A. Is Near-Infrared Spectroscopy a Reliable Method to Evaluate Clamping Ischemia during Carotid Surgery? Stroke Res. Treat. 2012, 2012, 156975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mille, T.; Tachimiri, M.E.; Klersy, C.; Ticozzelli, G.; Bellinzona, G.; Blangetti, I.; Pirrelli, S.; Lovotti, M.; Odero, A. Near Infrared Spectroscopy Monitoring during Carotid Endarterectomy: Which Threshold Value Is Critical? Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2004, 27, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, J.; Green, D.; Slim, H.; Tiwari, A.; Brown, J.; Rashid, H. The Role of Cerebral Oximetry in Combination with Awake Testing in Patients Undergoing Carotid Endarterectomy under Local Anaesthesia. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2011, 41, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Durduran, T.; Choe, R.; Baker, W.B.; Yodh, A.G. Diffuse Optics for Tissue Monitoring and Tomography. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2010, 73, 076701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boas, D.A.; Yodh, A.G. Spatially Varying Dynamical Properties of Turbid Media Probed with Diffusing Temporal Light Correlation. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1997, 14, 192–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durduran, T.; Yu, G.; Burnett, M.G.; Detre, J.A.; Greenberg, J.H.; Wang, J.; Zhou, C.; Yodh, A.G. Diffuse Optical Measurement of Blood Flow, Blood Oxygenation, and Metabolism in a Human Brain during Sensorimotor Cortex Activation. Opt. Lett. 2004, 29, 1766–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durduran, T.; Zhou, C.; Edlow, B.L.; Yu, G.; Choe, R.; Kim, M.N.; Cucchiara, B.L.; Putt, M.E.; Shah, Q.; Kasner, S.E.; et al. Transcranial Optical Monitoring of Cerebrovascular Hemodynamics in Acute Stroke Patients. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 3884–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial Collaborators (NASCET). Beneficial Effect of Carotid Endarterectomy in Symptomatic Patients with High-Grade Carotid Stenosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 325, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carp, S.A.; Farzam, P.; Redes, N.; Hueber, D.M.; Franceschini, M.A. Combined Multi-Distance Frequency Domain and Diffuse Correlation Spectroscopy System with Simultaneous Data Acquisition and Real-Time Analysis. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 3993–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selb, J.J.; Boas, D.A.; Chan, S.-T.; Evans, K.C.; Buckley, E.M.; Carp, S.A. Sensitivity of Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Diffuse Correlation Spectroscopy to Brain Hemodynamics: Simulations and Experimental Findings during Hypercapnia. Neurophotonics 2014, 1, 015005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carp, S.; Tamborini, D.; Mazumder, D.; Wu, K.C.; Robinson, M.; Stephens, K.; Shatrovoy, O.; Lue, N.; Ozana, N.; Blackwell, M.; et al. Diffuse Correlation Spectroscopy Measurements of Blood Flow Using 1064 Nm Light. J. Biomed. Opt. 2020, 25, 097003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prahl, S. Tabulated Molar Extinction Coefficient for Hemoglobin in Water. Nature 1999, 401, 788–791. Available online: http://omlc.ogi.edu/spectra/hemoglobin/summary.html (accessed on 30 July 2022).
- Wolthuis, R.; van Aken, M.; Fountas, K.; Robinson, J.S., Jr.; Bruining, H.A.; Puppels, G.J. Determination of Water Concentration in Brain Tissue by Raman Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 3915–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Kibler, K.K.; Benni, P.B.; Easley, R.B.; Czosnyka, M.; Smielewski, P.; Koehler, R.C.; Shaffner, D.H.; Brady, K.M. Cerebrovascular Reactivity Measured by Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Stroke 2009, 40, 1820–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunwoo, J.; Chalacheva, P.; Khaleel, M.; Shah, P.; Sposto, R.; Kato, R.M.; Detterich, J.; Zeltzer, L.K.; Wood, J.C.; Coates, T.D.; et al. A Novel Cross-Correlation Methodology for Assessing Biophysical Responses Associated with Pain. J. Pain Res. 2018, 11, 2207–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorrentino, E.; Budohoski, K.P.; Kasprowicz, M.; Smielewski, P.; Matta, B.; Pickard, J.D.; Czosnyka, M. Critical Thresholds for Transcranial Doppler Indices of Cerebral Autoregulation in Traumatic Brain Injury. Neurocrit. Care 2011, 14, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zweifel, C.; Dias, C.; Smielewski, P.; Czosnyka, M. Continuous Time-Domain Monitoring of Cerebral Autoregulation in Neurocritical Care. Med. Eng. Phys. 2014, 36, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Cheng, R.; Dong, L.; Ryan, S.J.; Saha, S.P.; Yu, G. Cerebral Monitoring during Carotid Endarterectomy Using Near-Infrared Diffuse Optical Spectroscopies and Electroencephalogram. Phys. Med. Biol. 2011, 56, 3015–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartkamp, M.J.; van der Grond, J.; van Everdingen, K.J.; Hillen, B.; Mali, W.P.T.M. Circle of Willis Collateral Flow Investigated by Magnetic Resonance Angiography. Stroke 1999, 30, 2671–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, N.H.; Ortega-Gutierrez, S.; Reccius, A.; Masurkar, A.; Huang, A.; Marshall, R.S. Dynamic Cerebral Autoregulation Is Transiently Impaired for One Week after Large-Vessel Acute Ischemic Stroke. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2015, 39, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Ji, Z.; Lin, Z.; Pan, S.; Yin, J. Cerebral Autoregulation Is Heterogeneous in Different Stroke Mechanism of Ischemic Stroke Caused by Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stenosis. Brain Behav. 2020, 11, e01907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrini, P.; Cardia, A.; Fraser, K.; Lanzino, G. A Microsurgical Study of the Anatomy and Course of the Ophthalmic Artery and Its Possibly Dangerous Anastomoses. J. Neurosurg. 2007, 106, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaisti, K.K.; Långsjö, J.W.; Aalto, S.; Oikonen, V.; Sipilä, H.; Teräs, M.; Hinkka, S.; Metsähonkala, L.; Scheinin, H. Effects of Sevoflurane, Propofol, and Adjunct Nitrous Oxide on Regional Cerebral Blood Flow, Oxygen Consumption, and Blood Volume in Humans. Anesthesiology 2003, 99, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Patient | Sex | Measurement Type | Optical Modality | Measurement Duration | Clamp Duration | Ipsilateral Stenosis | Contralateral Stenosis | Shunt | Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F | Unilateral | DCS | 2 h, 52 min | 48 min | 70–89% | No stenosis | No | MCS |
| 2 | M | Unilateral | DCS | 2 h, 29 min | 53 min | 70–89% | 1–19% | No | MCS |
| 3 | F | Unilateral | DCS | 2 h, 20 min | 1 h, 4 min | 20–49% | No stenosis | No | MCS |
| 4 | F | Unilateral | DCS | 3 h, 58 min | 1 h, 19 min | 70–89% | 20–49% | No | MCS |
| 5 | M | Unilateral | DCS | 2 h, 19 min | 1 h, 1 min | 90–99% | 1–19% | Yes | SH |
| 6 | M | Unilateral | DCS | 3 h, 53 min | 40 min | 1–19% | 1–19% | No | MCS |
| 7 | M | Unilateral | DCS | 3 h, 17 min | 1 h, 17 min | 20–49% | 1–19% | No | MCS |
| 8 | M | Bilateral | DCS | 3 h, 34 min | 58 min | 70–89% | 70–99% | No | SCS |
| 9 | F | Bilateral | DCS | 3 h, 14 min | 52 min | 70–89% | No stenosis | No | MCS |
| 10 | F | Bilateral | DCS | 2 h, 48 min | 55 min | 70–89% | 1–19% | Yes | SH |
| 11 | M | Bilateral | DCS-NIRS | 2 h, 48 min | 1 h, 5 min | 70–89% | 20–49% | Yes | SH |
| 12 | M | Bilateral | DCS-NIRS | 2 h, 25 min | 1 h, 3 min | 70–89% | No stenosis | No | MCS |
| 13 | F | Bilateral | DCS-NIRS | 1 h, 35 min | 37 min | 70–89% | No stenosis | No | MCS |
| 14 | F | Bilateral | DCS-NIRS | 2 h, 27 min | 1 h, 3 min | 20–49% | 1–19% | No | MCS |
| 15 | F | Bilateral | DCS-NIRS | 2 h, 33 min | 49 min | 70–89% | 1–19% | No | MCS |
| 16 | M | Bilateral | DCS-NIRS | 1 h, 53 min | 46 min | 50–69% | 100% | No | SCS |
| 17 | M | Bilateral | DCS-NIRS | 2 h, 47 min | 1 h, 1 min | 70–89% | 1–19% | No | MCS |
| 18 | M | Bilateral | DCS-NIRS | 2 h, 55 min | 1 h, 4 min | 70–89% | 20–49% | No | MCS |
| 19 | F | Bilateral | DCS-NIRS | 2 h, 11 min | 43 min | 70–89% | 50–69% | No | SCS |
| 20 | F | Bilateral | DCS-NIRS | 2 h, 24 min | 56 min | 50–69% | 1–19% | Yes | SH |
| 21 | M | Bilateral | DCS-NIRS | 4 h, 4 min | 1 h, 34 min | 70–89% | No stenosis | No | MCS |
| 22 | M | Bilateral | DCS-NIRS | 2 h, 57 min | 1 h, 4 min | 50–69% | 50–69% | Yes | SH |
| 23 | M | Bilateral | DCS-NIRS | 1 h, 15 min | 53 min | 70–89% | 70–89% | No | SCS |
| 24 | M | Bilateral | DCS-NIRS | 2 h, 2 min | 56 min | 70–89% | 50–69% | No | SCS |
| MCS (n = 14) | SCS (n = 5) | SH (n = 5) | |||||||
| Age, years (mean ± SD) Range | 69 ± 10 53–90 | 69 ± 5 64–74 | 65 ± 2 62–68 | ||||||
| Comorbid Disease | |||||||||
| Hypertension | 71% | 80% | 100% | ||||||
| Diabetes-Mellitus | 50% | 20% | 20% | ||||||
| Coronary Disease | 35% | 0% | 20% | ||||||
| Hyperlipidemia | 50% | 40% | 40% | ||||||
| Afib | 21% | 0% | 0% | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaya, K.; Zavriyev, A.I.; Orihuela-Espina, F.; Simon, M.V.; LaMuraglia, G.M.; Pierce, E.T.; Franceschini, M.A.; Sunwoo, J. Intraoperative Cerebral Hemodynamic Monitoring during Carotid Endarterectomy via Diffuse Correlation Spectroscopy and Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12081025
Kaya K, Zavriyev AI, Orihuela-Espina F, Simon MV, LaMuraglia GM, Pierce ET, Franceschini MA, Sunwoo J. Intraoperative Cerebral Hemodynamic Monitoring during Carotid Endarterectomy via Diffuse Correlation Spectroscopy and Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(8):1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12081025
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaya, Kutlu, Alexander I. Zavriyev, Felipe Orihuela-Espina, Mirela V. Simon, Glenn M. LaMuraglia, Eric T. Pierce, Maria Angela Franceschini, and John Sunwoo. 2022. "Intraoperative Cerebral Hemodynamic Monitoring during Carotid Endarterectomy via Diffuse Correlation Spectroscopy and Near-Infrared Spectroscopy" Brain Sciences 12, no. 8: 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12081025
APA StyleKaya, K., Zavriyev, A. I., Orihuela-Espina, F., Simon, M. V., LaMuraglia, G. M., Pierce, E. T., Franceschini, M. A., & Sunwoo, J. (2022). Intraoperative Cerebral Hemodynamic Monitoring during Carotid Endarterectomy via Diffuse Correlation Spectroscopy and Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Brain Sciences, 12(8), 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12081025






