Differential Effects of Chronic Methamphetamine Treatment on High-Frequency Oscillations and Responses to Acute Methamphetamine and NMDA Receptor Blockade in Conscious Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
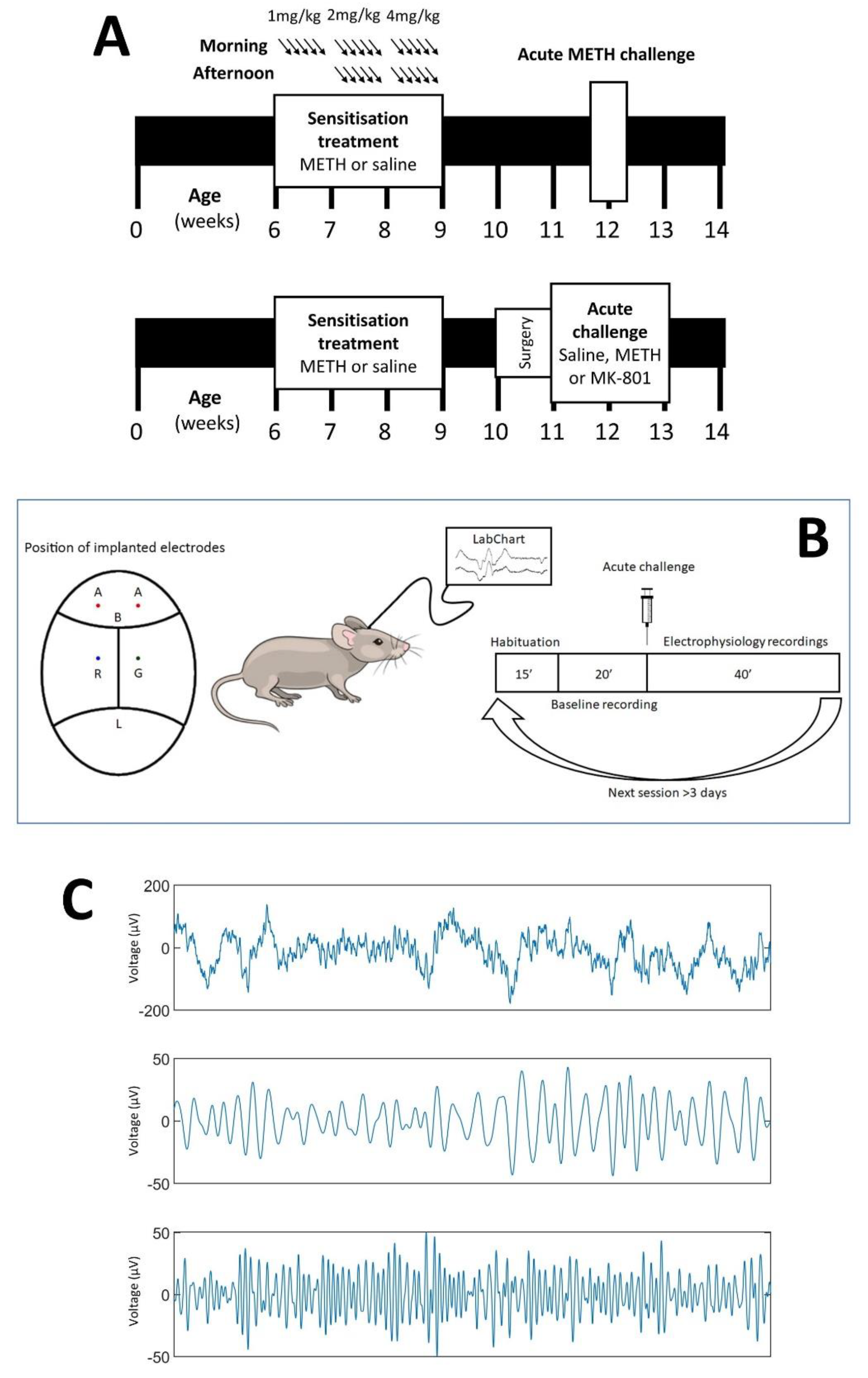
2.2. Chronic METH Exposure Paradigm
2.3. Validation of Sensitisation
2.4. Electrode Implantation Surgery
2.5. Electrophysiology Studies
2.6. Electrophysiology Analyses
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
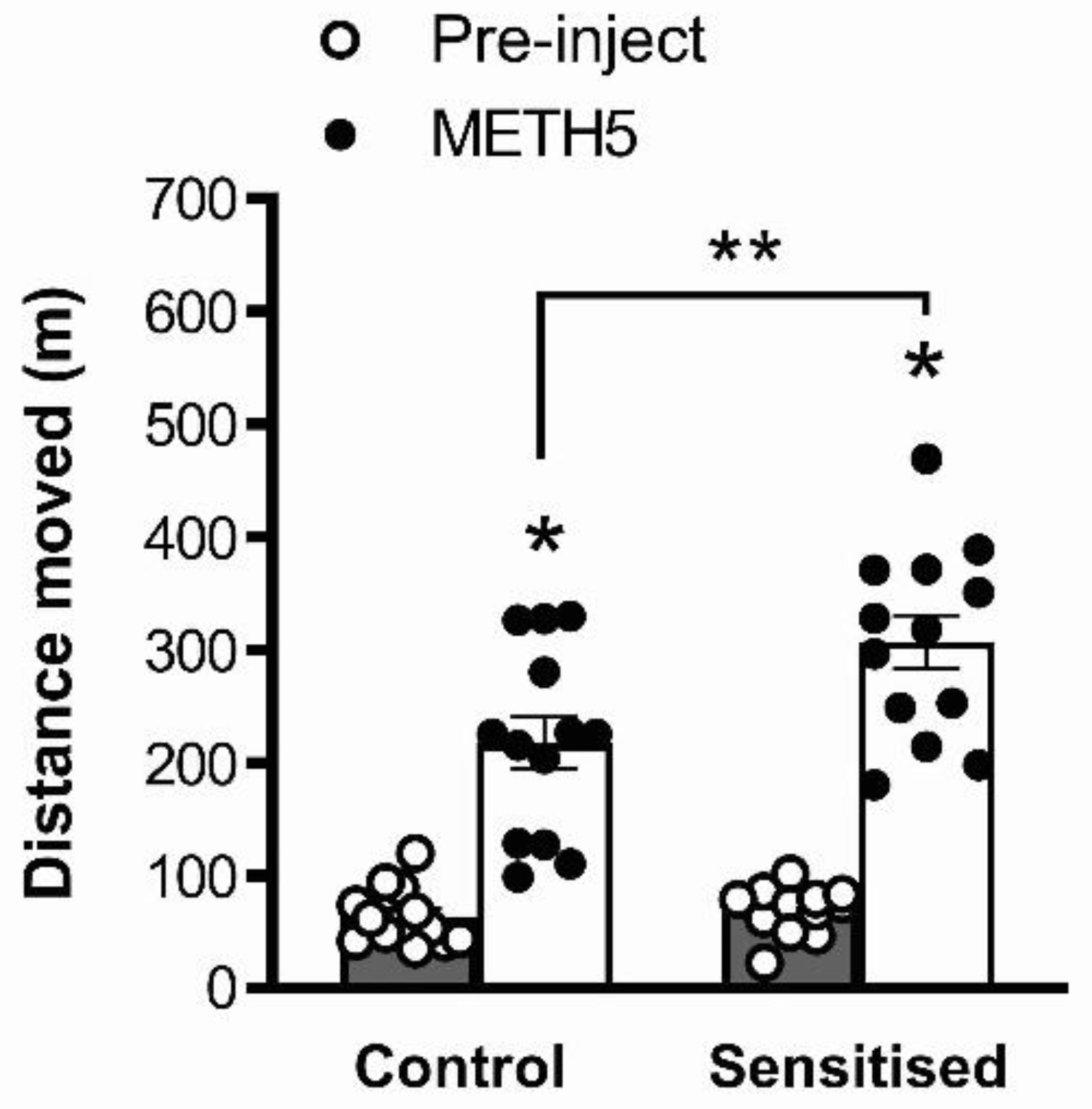
3.1. METH Pretreatment Results in Sensitisation of Acute METH-Induced Locomotor Hyperactivity
3.2. Ongoing Beta, but Not Gamma Power, Is Reduced by MK-801 and Acute METH
3.3. Auditory-Evoked Gamma Power, but Not Beta Power, Is Reduced by MK-801 and Acute METH
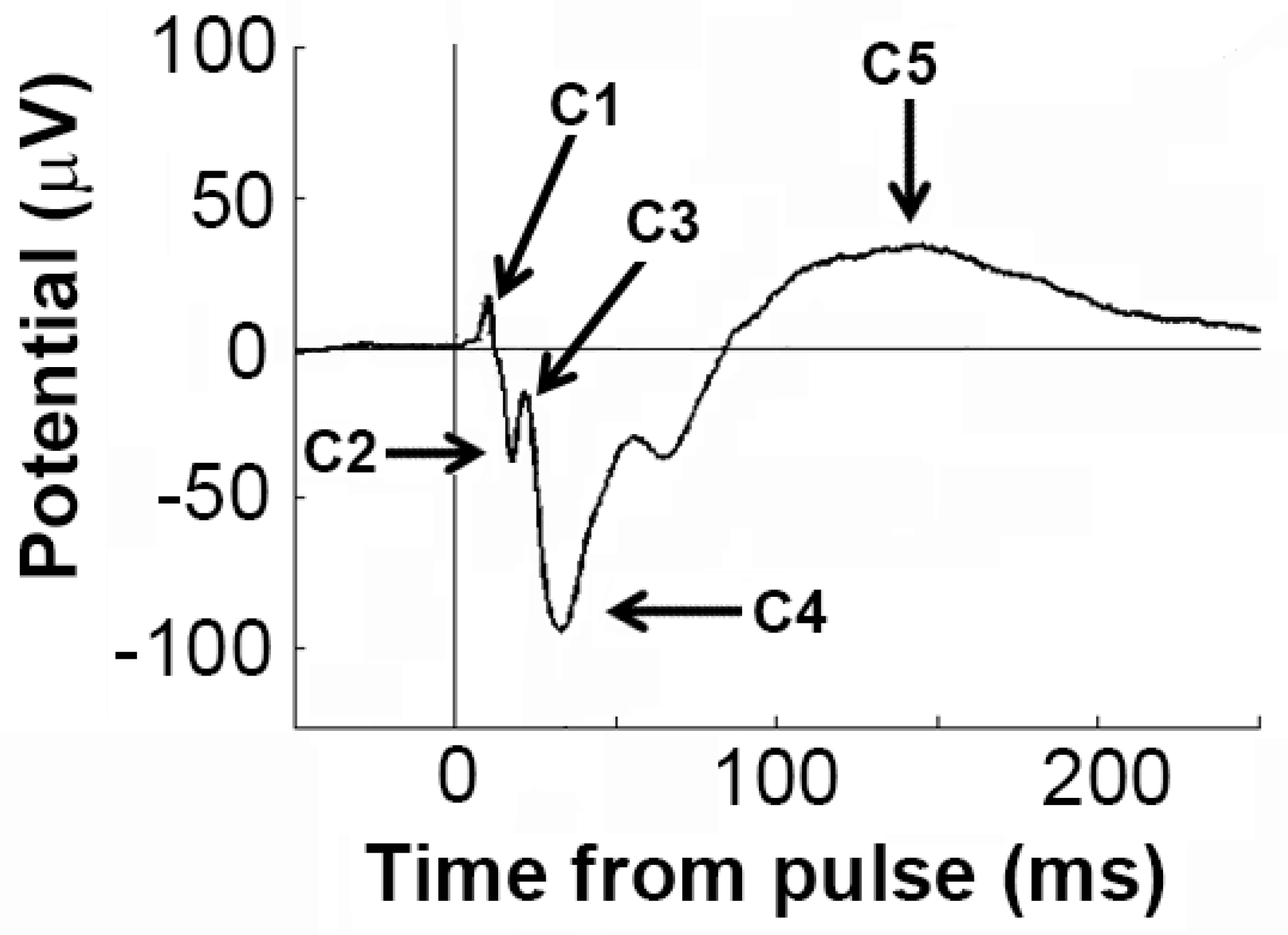
3.4. Effects of Sensitisation to METH and Acute Drug Challenges on ERP Components
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scott, J.C.; Woods, S.P.; Matt, G.E.; Meyer, R.A.; Heaton, R.K.; Atkinson, J.H.; Grant, I. Neurocognitive effects of methamphetamine: A critical review and meta-analysis. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2007, 17, 275–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vearrier, D.; Greenberg, M.I.; Miller, S.N.; Okaneku, J.T.; Haggerty, D.A. Methamphetamine: History, pathophysiology, adverse health effects, current trends, and hazards associated with the clandestine manufacture of methamphetamine. Dis. Mon. 2012, 58, 38–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleckenstein, A.E.; Volz, T.J.; Riddle, E.L.; Gibb, J.W.; Hanson, G.R. New insights into the mechanism of action of amphetamines. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2007, 47, 681–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volz, T.J.; Hanson, G.R.; Fleckenstein, A.E. The role of the plasmalemmal dopamine and vesicular monoamine transporters in methamphetamine-induced dopaminergic deficits. J. Neurochem. 2007, 101, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, R.C.; Kalivas, P.W. A circuitry model of the expression of behavioral sensitization to amphetamine-like psychostimulants. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 1997, 25, 192–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujike, H.; Sato, M. Clinical features of sensitization to methamphetamine observed in patients with methamphetamine dependence and psychosis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1025, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, A.H.; Mizuno, Y.; Volkow, N.D.; Howes, O.D. Association of stimulant use with dopaminergic alterations in users of cocaine, amphetamine, or methamphetamine: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry 2017, 74, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkow, N.D.; Chang, L.; Wang, G.J.; Fowler, J.S.; Franceschi, D.; Sedler, M.; Gatley, S.J.; Miller, E.; Hitzemann, R.; Ding, Y.S.; et al. Loss of dopamine transporters in methamphetamine abusers recovers with protracted abstinence. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 9414–9418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasner-Edwards, S.; Mooney, L.J. Methamphetamine psychosis: Epidemiology and management. CNS Drugs 2014, 28, 1115–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wearne, T.A.; Cornish, J.L. A comparison of methamphetamine-induced psychosis and schizophrenia: A review of positive, negative, and cognitive symptomatology. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laruelle, M. The role of endogenous sensitization in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia: Implications from recent brain imaging studies. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 2000, 31, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidenauer, A.; Bauer, M.; Sauerzopf, U.; Bartova, L.; Nics, L.; Pfaff, S.; Philippe, C.; Berroteran-Infante, N.; Pichler, V.; Meyer, B.M.; et al. On the relationship of first-episode psychosis to the amphetamine-sensitized state: A dopamine D2/3 receptor agonist radioligand study. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidenauer, A.; Bauer, M.; Sauerzopf, U.; Bartova, L.; Praschak-Rieder, N.; Sitte, H.H.; Kasper, S.; Willeit, M. Making Sense of: Sensitization in Schizophrenia. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alderson, H.L.; Semple, D.M.; Blayney, C.; Queirazza, F.; Chekuri, V.; Lawrie, S.M. Risk of transition to schizophrenia following first admission with substance-induced psychotic disorder: A population-based longitudinal cohort study. Psychol. Med. 2017, 47, 2548–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queirazza, F.; Semple, D.M.; Lawrie, S.M. Transition to schizophrenia in acute and transient psychotic disorders. Br. J. Psychiatry 2014, 204, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, K.G.; Uhlhaas, P.J. Neural oscillations as a translational tool in schizophrenia research: Rationale, paradigms and challenges. J. Psychopharmacol. 2015, 29, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hume, C.; Massey, S.; van den Buuse, M. The effect of chronic methamphetamine treatment on schizophrenia endophenotypes in heterozygous reelin mice: Implications for schizophrenia. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greening, D.W.; Notaras, M.; Chen, M.; Xu, R.; Smith, J.D.; Cheng, L.; Simpson, R.J.; Hill, A.F.; van den Buuse, M. Chronic methamphetamine interacts with BDNF Val66Met to remodel psychosis pathways in the mesocorticolimbic proteome. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 4431–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, E.E.; Halberstadt, A.L.; van den Buuse, M. BDNF-deficient mice show reduced psychosis-related behaviors following chronic methamphetamine. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 19, pyv116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, E.E.; van den Buuse, M. BDNF deficiency and young-adult methamphetamine induce sex-specific effects on prepulse inhibition regulation. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, E.E.; van den Buuse, M. Altered social cognition in male BDNF heterozygous mice and following chronic methamphetamine exposure. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 305, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, J.M.; Maxwell, C.R.; Ehrlichman, R.S.; Siegel, S.J. Event-related potentials (ERPs) in the study of schizophrenia: How preclinical ERP studies have contributed to our understanding of schizophrenia. In Handbook of Neurochemistry and Molecular Neurobiology; Lajtha, A., Javitt, D., Kantrowitz, J., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 525–543. [Google Scholar]
- Uhlhaas, P.J.; Singer, W. Abnormal neural oscillations and synchrony in schizophrenia. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlhaas, P.J.; Singer, W. Oscillations and neuronal dynamics in schizophrenia: The search for basic symptoms and translational opportunities. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 77, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Burgos, G.; Cho, R.Y.; Lewis, D.A. Alterations in cortical network oscillations and parvalbumin neurons in schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 77, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morra, J.T.; Glick, S.D.; Cheer, J.F. Cannabinoid receptors mediate methamphetamine induction of high frequency gamma oscillations in the nucleus accumbens. Neuropharmacology 2012, 63, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pinault, D. N-methyl d-aspartate receptor antagonists ketamine and MK-801 induce wake-related aberrant gamma oscillations in the rat neocortex. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 63, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xie, X.; Xing, H.; Yuan, X.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Wang, J.; Vreugdenhil, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, R.; et al. The modulation of gamma oscillations by methamphetamine in rat hippocampal slices. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janetsian, S.S.; Linsenbardt, D.N.; Lapish, C.C. Memory impairment and alterations in prefrontal cortex gamma band activity following methamphetamine sensitization. Psychopharmacology 2015, 232, 2083–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapish, C.C.; Chiang, J.; Wang, J.Z.; Phillips, A.G. Oscillatory power and synchrony in the rat forebrain are altered by a sensitizing regime of D-amphetamine. Neuroscience 2012, 203, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramlakhan, J.U.; Ma, M.; Zomorrodi, R.; Blumberger, D.M.; Noda, Y.; Barr, M.S. The role of gamma oscillations in the pathophysiology of substance use disorders. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, J.T.; Basu, A.; Benneyworth, M.; Balu, D.; Konopaske, G. Glutamatergic synaptic dysregulation in schizophrenia: Therapeutic implications. In Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 267–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Buuse, M. Modeling the positive symptoms of schizophrenia in genetically modified mice: Pharmacology and methodology aspects. Schizophr. Bull. 2010, 36, 246–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakami, T.; Jones, N.C.; Tolmacheva, E.A.; Gaudias, J.; Chaumont, J.; Salzberg, M.; O’Brien, T.J.; Pinault, D. NMDA receptor hypofunction leads to generalized and persistent aberrant gamma oscillations independent of hyperlocomotion and the state of consciousness. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, N.C.; Anderson, P.; Rind, G.; Sullivan, C.; van den Buuse, M.; O’Brien, T.J. Effects of aberrant gamma frequency oscillations on prepulse inhibition. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 17, 1671–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, L.E.; Anderson, P.; Frank, E.; Shaw, A.; Liu, S.; Huang, X.F.; Pinault, D.; Karl, T.; O’Brien, T.J.; Shannon Weickert, C.; et al. Neuregulin 1 expression and electrophysiological abnormalities in the Neuregulin 1 transmembrane domain heterozygous mutant mouse. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlichman, R.S.; Gandal, M.J.; Maxwell, C.R.; Lazarewicz, M.T.; Finkel, L.H.; Contreras, D.; Turetsky, B.I.; Siegel, S.J. N-methyl-d-aspartic acid receptor antagonist-induced frequency oscillations in mice recreate pattern of electrophysiological deficits in schizophrenia. Neuroscience 2009, 158, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaehne, E.J.; Ameti, D.; Paiva, T.; van den Buuse, M. Investigating the role of serotonin in methamphetamine psychosis: Unaltered behavioral effects of chronic methamphetamine in 5-HT1A knockout mice. Front. Psychiatry 2017, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonfeld, L.; Jaehne, E.J.; Ogden, A.R.; Spiers, J.G.; Hogarth, S.; van den Buuse, M. Differential effects of chronic adolescent glucocorticoid or methamphetamine on drug-induced locomotor hyperactivity and disruption of prepulse inhibition in adulthood in mice. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 117, 110552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulveda, M.; Manning, E.E.; Gogos, A.; Hale, M.; van den Buuse, M. Long-term effects of young-adult methamphetamine on dorsal raphe serotonin systems in mice: Role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Brain Res. 2021, 1762, 147428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, N.C.; Salzberg, M.R.; Kumar, G.; Couper, A.; Morris, M.J.; O’Brien, T.J. Elevated anxiety and depressive-like behavior in a rat model of genetic generalized epilepsy suggesting common causation. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 209, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, N.C.; Reddy, M.; Anderson, P.; Salzberg, M.R.; O’Brien, T.J.; Pinault, D. Acute administration of typical and atypical antipsychotics reduces EEG gamma power, but only the preclinical compound LY379268 reduces the ketamine-induced rise in gamma power. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012, 15, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolenko, E.; Hudson, M.R.; Nithianantharajah, J.; Jones, N.C. The mGluR2/3 agonist LY379268 reverses NMDA receptor antagonist effects on cortical gamma oscillations and phase coherence, but not working memory impairments, in mice. J. Psychopharmacol. 2019, 33, 1588–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, N.C.; Hudson, M.; Foreman, J.; Rind, G.; Hill, R.; Manning, E.E.; van den Buuse, M. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor haploinsufficiency impairs high-frequency cortical oscillations in mice. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2018, 48, 2816–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, M.R.; Rind, G.; O’Brien, T.J.; Jones, N.C. Reversal of evoked gamma oscillation deficits is predictive of antipsychotic activity with a unique profile for clozapine. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, M.R.; Jones, N.C. Deciphering the code: Identifying true gamma neural oscillations. Exp. Neurol 2022, 357, 114205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, M.R.; Hannan, A.J.; O’Brien, T.J.; Jones, N.C. High-frequency neuronal oscillatory abnormalities in the phospholipase C-beta1 knockout mouse model of schizophrenia. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019, 22, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, M.R.; Sokolenko, E.; O’Brien, T.J.; Jones, N.C. NMDA receptors on parvalbumin-positive interneurons and pyramidal neurons both contribute to MK-801 induced gamma oscillatory disturbances: Complex relationships with behaviour. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 134, 104625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, A.; Nakamura, J.P.; Hudson, M.; Jones, N.C.; Du, X.; Sundram, S.; Hill, R.A. Raloxifene recovers effects of prenatal immune activation on cognitive task-induced gamma power. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 110, 104448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizoguchi, H.; Yamada, K. Methamphetamine use causes cognitive impairment and altered decision-making. Neurochem. Int. 2019, 124, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potvin, S.; Pelletier, J.; Grot, S.; Hebert, C.; Barr, A.M.; Lecomte, T. Cognitive deficits in individuals with methamphetamine use disorder: A meta-analysis. Addict. Behav. 2018, 80, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamei, H.; Nagai, T.; Nakano, H.; Togan, Y.; Takayanagi, M.; Takahashi, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Yoshida, S.; Maeda, K.; Takuma, K.; et al. Repeated methamphetamine treatment impairs recognition memory through a failure of novelty-induced ERK1/2 activation in the prefrontal cortex of mice. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 59, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, T.; Takuma, K.; Dohniwa, M.; Ibi, D.; Mizoguchi, H.; Kamei, H.; Nabeshima, T.; Yamada, K. Repeated methamphetamine treatment impairs spatial working memory in rats: Reversal by clozapine but not haloperidol. Psychopharmacology 2007, 194, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrone, M.; Ratnayake, R.; De Oliveira, N.; Jaehne, E.J.; van den Buuse, M. Methamphetamine-induced locomotor sensitization in mice is not associated with deficits in a range of cognitive, affective and social behaviours: Interaction with brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) Val66Met genotype. Behav. Pharmacol. 2022, in press.
- Gross, A.; Joutsiniemi, S.L.; Rimon, R.; Appelberg, B. Correlation of symptom clusters of schizophrenia with absolute powers of main frequency bands in quantitative EEG. Behav. Brain Funct. 2006, 2, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Saletu, B.; Kufferle, B.; Anderer, P.; Grunberger, J.; Steinberger, K. EEG-brain mapping in schizophrenics with predominantly positive and negative symptoms. Comparative studies with remoxipride/haloperidol. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 1990, 1, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luck, S.J.; Mathalon, D.H.; O’Donnell, B.F.; Hamalainen, M.S.; Spencer, K.M.; Javitt, D.C.; Uhlhaas, P.J. A roadmap for the development and validation of event-related potential biomarkers in schizophrenia research. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 70, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amann, L.C.; Gandal, M.J.; Halene, T.B.; Ehrlichman, R.S.; White, S.L.; McCarren, H.S.; Siegel, S.J. Mouse behavioral endophenotypes for schizophrenia. Brain Res. Bull. 2010, 83, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, C.R.; Ehrlichman, R.S.; Liang, Y.; Trief, D.; Kanes, S.J.; Karp, J.; Siegel, S.J. Ketamine produces lasting disruptions in encoding of sensory stimuli. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 316, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silber, B.; Croft, R.; Camfield, D.A.; Downey, L.A.; Papafotiou, K.; Stough, C. The acute effects of d-amphetamine and d-methamphetamine on ERP components in humans. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012, 22, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, S.; Usall, J.; Cobo, J.; Labad, X.; Kulkarni, J. Gender differences in schizophrenia and first-episode psychosis: A comprehensive literature review. Schizophr. Res. Treat. 2012, 2012, 916198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaehne, E.J.; Smith, J.D.; van den Buuse, M. Analysis of striatum and brain levels reveals sex differences in conversion of methamphetamine to amphetamine in mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2022, 783, 136722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Chronic METH | Acute drug | Interaction | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | F | p | F | p | F | p | |
| Ongoing power | Beta | 0.050 | 0.826 | 23.70 | 0.000 | 2.255 | 0.122 |
| Gamma | 0.192 | 0.667 | 2.819 | 0.077 | 2.417 | 0.108 | |
| Evoked power | Beta | 0.153 | 0.701 | 0.307 | 0.687 | 0.760 | 0.476 |
| Gamma | 3.637 | 0.075 | 21.79 | 0.000 | 1.805 | 0.181 | |
| Amplitude | C1 | 0.528 | 0.478 | 1.374 | 0.268 | 0.795 | 0.461 |
| C2 | 0.187 | 0.672 | 2.170 | 0.143 | 3.060 | 0.066 | |
| C3 | 0.354 | 0.561 | 4.412 | 0.453 | 2.416 | 0.116 | |
| C4 | 2.024 | 0.174 | 7.510 | 0.002 | 2.396 | 0.107 | |
| C5 | 0.006 | 0.938 | 6.104 | 0.006 | 1.346 | 0.275 | |
| Latency | C1 | 3.634 | 0.075 | 1.009 | 0.376 | 0.617 | 0.546 |
| C2 | 0.507 | 0.487 | 14.93 | 0.000 | 0.802 | 0.461 | |
| C3 | 0.291 | 0.597 | 10.39 | 0.001 | 0.515 | 0.604 | |
| C4 | 0.060 | 0.810 | 2.064 | 0.144 | 1.313 | 0.283 | |
| C5 | 7.718 | 0.017 | 1.335 | 0.278 | 1.523 | 0.233 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hudson, M.R.; Foreman, J.; Rind, G.; Manning, E.E.; Jones, N.C.; van den Buuse, M. Differential Effects of Chronic Methamphetamine Treatment on High-Frequency Oscillations and Responses to Acute Methamphetamine and NMDA Receptor Blockade in Conscious Mice. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1503. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12111503
Hudson MR, Foreman J, Rind G, Manning EE, Jones NC, van den Buuse M. Differential Effects of Chronic Methamphetamine Treatment on High-Frequency Oscillations and Responses to Acute Methamphetamine and NMDA Receptor Blockade in Conscious Mice. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(11):1503. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12111503
Chicago/Turabian StyleHudson, Matthew R., Joshua Foreman, Gil Rind, Elizabeth E. Manning, Nigel C. Jones, and Maarten van den Buuse. 2022. "Differential Effects of Chronic Methamphetamine Treatment on High-Frequency Oscillations and Responses to Acute Methamphetamine and NMDA Receptor Blockade in Conscious Mice" Brain Sciences 12, no. 11: 1503. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12111503
APA StyleHudson, M. R., Foreman, J., Rind, G., Manning, E. E., Jones, N. C., & van den Buuse, M. (2022). Differential Effects of Chronic Methamphetamine Treatment on High-Frequency Oscillations and Responses to Acute Methamphetamine and NMDA Receptor Blockade in Conscious Mice. Brain Sciences, 12(11), 1503. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12111503






