Downregulation of GABAARα1 Aggravates Comorbidity of Epilepsy and Migraine via the TLR4 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Grouping
2.2. Surgical Procedures
2.3. Establish LiCl-Pilocarpine Rat Epilepsy Model
2.4. Establish Migraine Model with Inflammatory Soup
2.5. Head-Scratching and Pain Threshold Recording
2.6. Drug Application
2.7. Western Blotting
2.8. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.9. Co-Immunoprecipitation
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
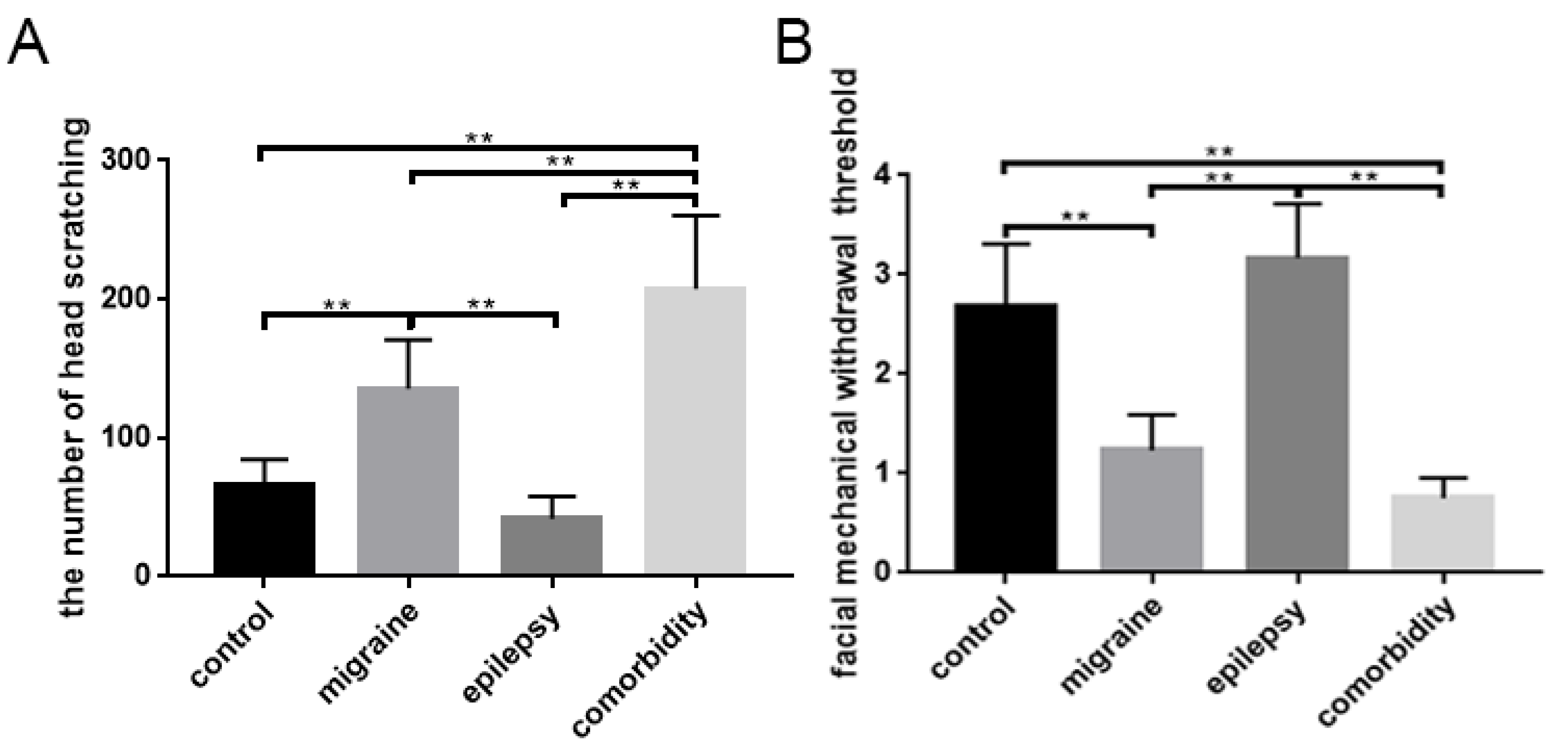
3.1. Changes in Behavioral Responses
3.2. Pilocarpine and Inflammatory Soup Disrupt TLR4 and GABAARα1 Expression Levels in Brain Tissue
3.3. Epilepsy–Migraine Comorbidity Leads to an Increase of Microglia
3.4. GABAARα1 Binds TLR4 and Regulates Its Expression
3.5. Activates GABAARα1 or Interferes with TLR4 Activity, Affecting Behavior in Comorbid Rats
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oakley, C.B.; Kossoff, E.H. Migraine and epilepsy in the pediatric population. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2014, 18, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipton, R.B.; Bigal, M.E. Migraine: Epidemiology, impact, and risk factors for progression. Headache 2005, 45 (Suppl. S1), S3–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwedt, T.J. Chronic migraine. BMJ 2014, 348, g1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Comorbidity in Adults with Epilepsy—United States. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2013, 62, 849–853. [Google Scholar]
- Lipton, R.B.; Ottman, R.; Ehrenberg, B.L.; Hauser, W.A. Comorbidity of migraine: The connection between migraine and epilepsy. Neurology 1994, 44 (Suppl. S7), S28–S32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leniger, T.; von den Driesch, S.; Isbruch, K.; Diener, H.C.; Hufnagel, A. Clinical characteristics of patients with comorbidity of migraine and epilepsy. Headache 2003, 43, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salma, Z.; Hanen, H.K.; Salma, S.; Olfa, H.; Nouha, F.; Mariem, D.; Chokri, M. Headaches and their relationships to epileptic seizures. Epilepsy Behav. 2019, 90, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, X.; Qiu, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; He, S.; Lai, W.; Peng, A.; Ning, M.; et al. Relationship between right-to-left shunt and migraine in patients with epilepsy: A single-centre, cross-sectional study in China. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e024144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanner, A.M. Management of psychiatric and neurological comorbidities in epilepsy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haerian, B.S.; Baum, L.; Kwan, P.; Cherny, S.S.; Shin, J.G.; Kim, S.E.; Han, B.G.; Tan, H.J.; Raymond, A.A.; Tan, C.T.; et al. Contribution of GABRG2 Polymorphisms to Risk of Epilepsy and Febrile Seizure: A Multicenter Cohort Study and Meta-analysis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 5457–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çavuş, I.; Romanyshyn, J.C.; Kennard, J.T.; Farooque, P.; Williamson, A.; Eid, T.; Spencer, S.S.; Duckrow, R.; Dziura, J.; Spencer, D.D. Elevated basal glutamate and unchanged glutamine and GABA in refractory epilepsy: Microdialysis study of 79 patients at the yale epilepsy surgery program. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 80, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Hu, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Du, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, F.; Wang, X. Association of Microtubule Dynamics with Chronic Epilepsy. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 5013–5024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mele, M.; Aspromonte, M.C.; Duarte, C.B. Downregulation of GABAA Receptor Recycling Mediated by HAP1 Contributes to Neuronal Death in In Vitro Brain Ischemia. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.Y.; Guan, B.J.; Wang, Y.J.; Hatzoglou, M.; Mu, T.W. L-type Calcium Channel Blockers Enhance Trafficking and Function of Epilepsy-associatedalpha1(D219N) Subunits of GABA(A) Receptors. ACS Chem. Biol. 2015, 10, 2135–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguila, M.R.; Rebbeck, T.; Leaver, A.M.; Lagopoulos, J.; Brennan, P.C.; Hubscher, M.; Refshauge, K.M. The Association Between Clinical Characteristics of Migraine and Brain GABA Levels: An Exploratory Study. J. Pain 2016, 17, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, K.; Woller, S.A.; Miller, Y.I.; Yaksh, T.L.; Wallace, M.; Beaton, G.; Chakravarthy, K. Targeting toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4)-an emerging therapeutic target for persistent pain states. Pain 2018, 159, 1908–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aderem, A.; Ulevitch, R.J. Toll-like receptors in the induction of the innate immune response. Nature 2000, 406, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, G.M.; Medzhitov, R. Control of adaptive immune responses by Toll-like receptors. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2002, 14, 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Zhou, H.R.; Wang, S.; Liu, C.Y.; Qin, G.C.; Fu, Q.Q.; Zhou, J.Y.; Chen, L.X. NR2B-Tyr phosphorylation regulates synaptic plasticity in central sensitization in a chronic migraine rat model. J. Headache Pain 2018, 19, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Xiao, Z.; Zhu, F.; He, X.; Lu, Z. A new comorbidity model and the common pathological mechanisms of migraine and epilepsy. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 2286–2295. [Google Scholar]
- Racine, R.J. Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation. II. Motor seizure. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1972, 32, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Erum, J.; Van Dam, D.; De Deyn, P.P. PTZ-induced seizures in mice require a revised Racine scale. Epilepsy Behav. 2019, 95, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, S.; Fang, H.; Dang, E.; Xue, K.; Zhang, J.Y.; Li, B.; Qiao, H.J.; Cao, T.Y.; Zhuang, Y.C.; Shen, S.X.; et al. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Promote Inflammatory Responses in Psoriasis via Activating Epidermal TLR4/IL-36R Crosstalk. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleason, N.R.; Gallos, G.; Zhang, Y.; Emala, C.W. The GABAA agonist muscimol attenuates induced airway constriction in guinea pigs in vivo. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 106, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethmann, K.; Fritschy, J.M.; Brandt, C.; Löscher, W. Antiepileptic drug resistant rats differ from drug responsive rats in GABA A receptor subunit expression in a model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurobiol. Dis. 2008, 31, 169–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arain, F.M.; Boyd, K.L.; Gallagher, M.J. Decreased viability and absence-like epilepsy in mice lacking or deficient in the GABAA receptor α1 subunit. Epilepsia 2012, 53, e161–e165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubé, C.M.; Ravizza, T.; Hamamura, M.; Zha, Q.; Keebaugh, A.; Fok, K.; Andres, A.L.; Nalcioglu, O.; Obenaus, A.; Vezzani, A.; et al. Epileptogenesis provoked by prolonged experimental febrile seizures: Mechanisms and biomarkers. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 7484–7494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzani, A.; Moneta, D.; Conti, M.; Richichi, C.; Ravizza, T.; De Luigi, A.; De Simoni, M.G.; Sperk, G.; Andell-Jonsson, S.; Lundkvist, J.; et al. Powerful anticonvulsant action of IL-1 receptor antagonist on intracerebral injection and astrocytic overexpression in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 11534–11539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolkowska, D.; Banks, C.N.; Dhir, A.; Inceoglu, B.; Sanborn, J.R.; McCoy, M.R.; Bruun, D.A.; Hammock, B.D.; Lein, P.J.; Rogawski, M.A. Characterization of seizures induced by acute and repeated exposure to tetramethylenedisulfotetramine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 341, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, V.T. New theories in the pathogenesis of menstrual migraine. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2008, 12, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, L.R.; Hutchinson, M.R.; Ledeboer, A.; Wieseler-Frank, J.; Milligan, E.D.; Maier, S.F. Norman Cousins Lecture. Glia as the “bad guys”: Implications for improving clinical pain control and the clinical utility of opioids. Brain Behav. Immun. 2007, 21, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraz, M.; Herdenberg, C.; Holmlund, C.; Henriksson, R.; Hedman, H. A protein interaction network centered on leucine-rich repeats and immunoglobulin-like domains 1 (LRIG1) regulates growth factor receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 3421–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, R.W. GABAA receptor: Positive and negative allosteric modulators. Neuropharmacology 2018, 136 Pt A, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, H.T.; Duan, L.; Niu, L.; Yuan, G.Q.; Dai, J.Q.; Hou, B.R.; Pan, Y.W. HDAC4 gene silencing alleviates epilepsy by inhibition of GABA in a rat model. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2019, 15, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKernan, R.M.; Whiting, P.J. Which GABAA-receptor subtypes really occur in the brain? Trends Neurosci. 1996, 19, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crepeau, A.Z. Migralepsy: A borderland of wavy lines. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2014, 14, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantegazza, M.; Cestèle, S. Pathophysiological mechanisms of migraine and epilepsy: Similarities and differences. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 667, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolay, H.; Reuter, U.; Dunn, A.K.; Huang, Z.; Boas, D.A.; Moskowitz, M.A. Intrinsic brain activity triggers trigeminal meningeal afferents in a migraine model. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okun, E.; Griffioen, K.J.; Mattson, M.P. Toll-like receptor signaling in neural plasticity and disease. Trends Neurosci. 2011, 34, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zusso, M.; Lunardi, V.; Franceschini, D.; Pagetta, A.; Lo, R.; Stifani, S.; Frigo, A.C.; Giusti, P.; Moro, S. Ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin attenuate microglia inflammatory response via TLR4/NF-kB pathway. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.W.; Yu, L.; Hua, R.; Zhao, X.P.; Qin, X.; Zhang, Y.M. Spinal toll-like receptor 4-mediated signalling pathway contributes to visceral hypersensitivity induced by neonatal colonic irritation in rats. Eur. J. Pain 2015, 19, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Luo, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhang, X.; Fu, J. Curcumin inhibits LPS-induced neuroinflammation by promoting microglial M2 polarization via TREM2/TLR4/NF-κB pathways in BV2 cells. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 116, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobieski, C.; Christian, C.A. Developmental Inflammation Takes a Toll: Early Immune Responses Increase Seizure Susceptibility via Astrocytic TLR4 Signaling. Epilepsy Curr. 2017, 17, 370–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | Day 4 | Day 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control group (n = 6) | Surgery + PBS (I.P) (2:00 pm) | Saline (S.C) (08:00 am) PBS (I.P) (08:30 am) | PBS (08:30 am) | PBS (08:30 am) | PBS (08:30 am) |
| Migraine group (n = 6) | Surgery PBS (I.P) | Saline (S.C) (08:00 am) PBS (I.P) (08:30 am) | IS (08:30 am) | IS (08:30 am) | IS (08:30 am) |
| Epilepsy group (n = 6) | Surgery LiCl (I.P) | Atropine (S.C) (08:00 am) PILO (I.P) (08:30 am) | PBS (08:30 am) | PBS (08:30 am) | PBS (08:30 am) |
| Comorbidity group (n = 6) | Surgery LiCl (I.P) | Atropine (S.C) (08:00 am) PILO (I.P) (08:30 am) | IS (08:30 am) | IS (08:30 am) | IS (08:30 am) |
| Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | Day 4 | Day 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comorbidity group (n = 3) | Surgery + LiCl (I.P) (2:00 pm) | DMSO) (07:00 am) + Sterile distilled water (08:00 am) (I.P) + PILO (I.P) (08:30 am) | DMSO (07:00 am) + Sterile distilled water (08:00 am) (I.P) + IS (08:30 am) | DMSO (07:00 am) + Sterile distilled water (08:00 am) (I.P) + IS (08:30 am) | DMSO (07:00 am) + Sterile distilled water (08:00 am) (I.P) + IS (08:30 am) |
| Comorbidity +TAK-242 group (n = 3) | Surgery + LiCl (I.P) (2:00 pm) | TAK-242 (07:00 am) + Sterile distilled water (08:00 am) (I.P) + PILO (I.P) (08:30 am) | TAK-242 (07:00 am) + Sterile distilled water (08:00 am) (I.P) + IS (08:30 am) | TAK-242 (07:00 am) + Sterile distilled water (08:00 am) (I.P) + IS (08:30 am) | TAK-242 (07:00 am) + Sterile distilled water (08:00 am) (I.P) + IS (08:30 am) |
| Comorbidity + Muscimol group (n = 3) | Surgery + LiCl (I.P) (2:00 pm) | DMSO (07:00 am) + Muscimol (08:00 am) (I.P) + PILO (I.P) (08:30 am) | DMSO (07:00 am) + Muscimol (08:00 am) (I.P) + IS (08:30 am) | DMSO (07:00 am) + Muscimol (08:00 am) (I.P) + IS (08:30 am) | DMSO (07:00 am) + Muscimol (08:00 am) (I.P) + IS (08:30 am) |
| Control Group (n = 6) | Migraine Group (n = 6) | Epilepsy Group (n = 6) | Comorbidity Group (n = 6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| the amount of head scratching | 66.33 ± 18.21 (times) | 135.50 ± 35.35 (times) | 41.83 ± 16.13 (times) | 207.67 ± 52.78 (times) |
| facial mechanical withdrawal threshold (square root transformation) | 2.68 ± 0.63 (√g) | 1.23 ± 0.36 (√g) | 3.16 ± 0.55 (√g) | 0.75 ± 0.20 (√g) |
| Epilepsy Group (n = 3) | Epilepsy + TAK-242 Group (n = 3) | Epilepsy + Muscimol Group (n = 3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| The latency of epilepsy | 1338.0 ± 372.04 (s) | 1172.0 ± 244.83 (s) | 3083.0 ± 208.62 (s) |
| Racine scale level of epilepsy | 4.67 ± 0.58 (level) | 4.33 ± 0.58 (level) | 3.33 ± 0.58 (level) |
| Comorbidity Group (n = 3) | Comorbidity + TAK-242 Group (n = 3) | Comorbidity + Muscimol Group (n = 3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| The amount of head scratching | 271.67 ± 23.46 (times) | 96.67 ± 23.71 (times) | 91.33 ± 11.15 (times) |
| Facial mechanical withdrawal threshold (square root transformation) | 0.71 ± 0.14 (√g) | 3.07 ± 0.71 (√g) | 3.42 ± 0.78 (√g) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.; Ding, M.; Gong, Q.; Xiao, Z. Downregulation of GABAARα1 Aggravates Comorbidity of Epilepsy and Migraine via the TLR4 Signaling Pathway. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12111436
Lin Y, Ding M, Gong Q, Xiao Z. Downregulation of GABAARα1 Aggravates Comorbidity of Epilepsy and Migraine via the TLR4 Signaling Pathway. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(11):1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12111436
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yao, Man Ding, Qiaoyu Gong, and Zheman Xiao. 2022. "Downregulation of GABAARα1 Aggravates Comorbidity of Epilepsy and Migraine via the TLR4 Signaling Pathway" Brain Sciences 12, no. 11: 1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12111436
APA StyleLin, Y., Ding, M., Gong, Q., & Xiao, Z. (2022). Downregulation of GABAARα1 Aggravates Comorbidity of Epilepsy and Migraine via the TLR4 Signaling Pathway. Brain Sciences, 12(11), 1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12111436





