Diagnostic Value of the Vestibular Autorotation Test in Menière’s Disease, Vestibular Migraine and Menière’s Disease with Migraine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Vestibular Autorotation Test (VAT)
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics of Patients
3.2. VAT Parameters in VM and MD Patients
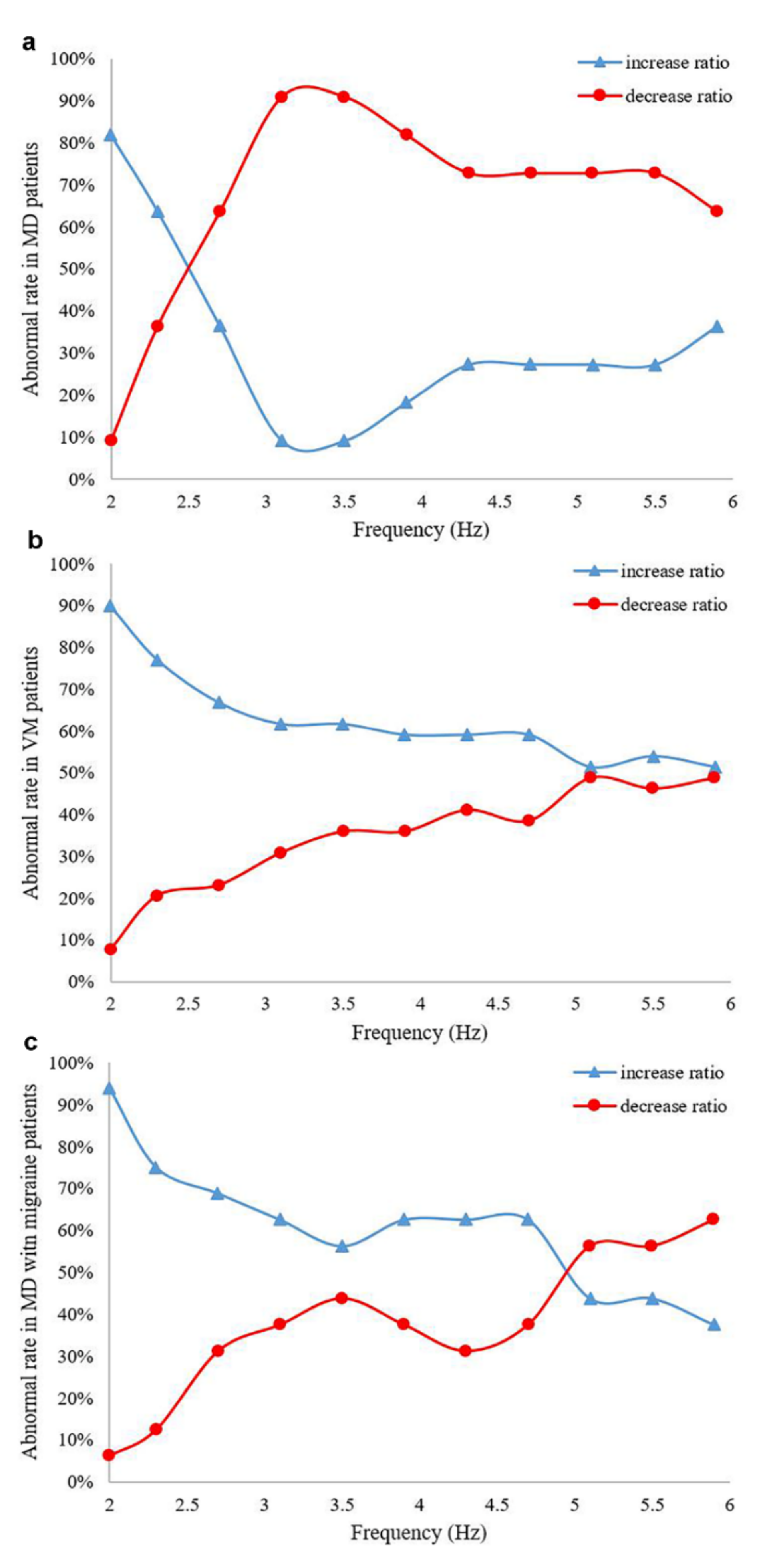
3.3. Comparison of Different Frequencies of Horizontal Gain in MD, VM and MD with Migraine Patients
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lopez-Escamez, J.A.; Carey, J.; Chung, W.-H.; Goebel, J.A.; Magnusson, M.; Mandalà, M.; Newman-Toker, D.E.; Strupp, M.; Suzuki, M.; Trabalzini, F.; et al. Diagnostic criteria for Menière’s disease. J. Vestib. Res. 2015, 25, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, T.; Pyykkö, I.; Arroll, M.A.; Casselbrant, M.L.; Foster, C.A.; Manzoor, N.F.; Megerian, C.A.; Naganawa, S.; Young, Y.-H. Menière’s disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2016, 2, 16028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Guo, Z.; Tian, E.; Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Kong, W. Menière disease subtyping: The direction of diagnosis and treatment in the future. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2022, 22, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Sanchez, J.M.; Lopez-Escamez, J.A. New insights into pathophysiology of vestibular migraine. Front. Neurol. 2015, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lempert, T.; Olesen, J.; Furman, J.; Waterston, J.; Seemungal, B.; Carey, J.; Bisdorff, A.; Versino, M.; Evers, S.; Newman-Toker, D. Vestibular migraine: Diagnostic criteria. J. Vestib. Res. 2012, 22, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neff, B.A.; Staab, J.; Eggers, S.D.; Carlson, M.L.; Schmitt, W.R.; Van Abel, K.M.; Worthington, D.K.; Beatty, C.W.; Driscoll, C.L.; Shepard, N.T. Auditory and vestibular symptoms and chronic subjective dizziness in patients with Ménière’s disease, vestibular migraine, and Ménière’s disease with concomitant vestibular migraine. Otol. Neurotol. 2012, 33, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Escamez, J.A.; Dlugaiczyk, J.; Jacobs, J.; Lempert, T.; Teggi, R.; von Brevern, M.; Bisdorff, A. Accompanying Symptoms Overlap during Attacks in Menière’s Disease and Vestibular Migraine. Front. Neurol. 2014, 5, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frejo, L.; Martin-Sanz, E.; Teggi, R.; Trinidad, G.; Soto-Varela, A.; Santos-Perez, S.; Manrique, R.; Perez, N.; Aran, I.; Almeida-Branco, M.; et al. Extended phenotype and clinical subgroups in unilateral Menière disease: A cross-sectional study with cluster analysis. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2017, 42, 1172–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frejo, L.; Soto-Varela, A.; Santos-Perez, S.; Aran, I.; Batuecas-Caletrio, A.; Perez-Guillen, V.; Perez-Garrigues, H.; Fraile, J.; Martin-Sanz, E.; Tapia, M.C.; et al. Clinical Subgroups in Bilateral Menière Disease. Front. Neurol. 2016, 7, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-U.; Kim, H.-J.; Choi, J.-Y.; Koo, J.-W.; Kim, J.-S. Evolution of caloric responses during and between the attacks of Menière’s disease. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 2913–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakley, B.W.; Barakat, N. Reliability of caloric testing. Ir. J. Med Sci. 2021, 190, 1571–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blödow, A.; Heinze, M.; Bloching, M.B.; Von Brevern, M.; Radtke, A.; Lempert, T. Caloric stimulation and video-head impulse testing in Ménière’s disease and vestibular migraine. Acta Otolaryngol. 2014, 134, 1239–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Escamez, J.A. Video Head-Impulse Testing vs Clinical Diagnosis of Vestibular Disorders. JAMA Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2019, 145, 561–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, M.N.; Garrison, D.B.; Kaylie, D.M. What is the potential clinical utility of vHIT when assessing adult patients with dizziness? Laryngoscope 2017, 127, 2689–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, L.E.; Blödow, A. Ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potential to air conducted sound stimulation and video head impulse test in acute vestibular neuritis. Otol. Neurotol. 2013, 34, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhabib, S.F.; Saliba, I. Video head impulse test: A review of the literature. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 274, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDougall, H.G.; McGarvie, L.A.; Halmagyi, G.M.; Curthoys, I.S.; Weber, K.P. Application of the video head impulse test to detect vertical semicircular canal dysfunction. Otol. Neurotol. 2013, 34, 974–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.-S.; Hsieh, L.-C.; Lin, H.-C. Aging of vestibular function evaluated using correlational vestibular autorotation test. Clin. Interv. Aging 2014, 9, 1463–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blatt, P.J.; Schubert, M.C.; Roach, K.E.; Tusa, R.J. The reliability of the Vestibular Autorotation Test (VAT) in patients with dizziness. J. Neurol. Phys. Ther. 2008, 32, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, D.P.; Davis, L.L. Vestibular autorotation testing of Menière’s disease. Otolaryngol.—Head Neck Surg. Off. J. Am. Acad. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1990, 103, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thungavelu, Y.; Wang, W.; Lin, P.; Chen, T.; Xu, K. The clinical utility of vestibular autorotation test in patients with vestibular migraine. Acta Otolaryngol. 2017, 137, 1046–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corvera, J.; Corvera-Behar, G.; Lapilover, V.; Ysunza, A. Objective evaluation of the effect of flunarizine on vestibular neuritis. Otol. Neurotol. 2002, 23, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, N.; Martin, E.; Perez-Fernandez, N.; Martin-Sanz, E. Results of vestibular autorotation testing at the end of intratympanic gentamicin treatment for Ménière’s disease. Acta Otolaryngol. 2003, 123, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyykkö, I.; Manchaiah, V.; Färkkilä, M.; Kentala, E.; Zou, J. Association between Ménière’s disease and vestibular migraine. Auris Nasus Larynx 2019, 46, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teggi, R.; Familiari, M.; Gatti, O.; Bussi, M. Vertigo without cochlear symptoms: Vestibular migraine or Menière disease? Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 5071–5076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Guo, Z.; Wang, J.; Tian, E.; Chen, J.; Zhou, L.; Kong, W.; Zhang, S. Development and Validation of the Predictive Model for the Differentiation between Vestibular Migraine and Menière’s Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, M.S.; Egilmez, O.K.; Kara, A.; Guven, M.; Demir, D.; Elden, S.G. Comparison of the results of caloric and video head impulse tests in patients with Menière’s disease and vestibular migraine. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 278, 1829–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannigan, I.P.; Welgampola, M.S.; Watson, S.R.D. Dissociation of caloric and head impulse tests: A marker of Menière’s disease. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Fernández, N.; Dominguez, P.; Manrique-Huarte, R.; Calavia, D.; Arbizu, L.; Garcia-Eulate, R.; Alvarez-Gomez, L.; Guajardo, C.; Zubieta, J.L. Endolymphatic hydrops severity in magnetic resonance imaging evidences disparate vestibular test results. Auris Nasus Larynx 2019, 46, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, P.; Manrique-Huarte, R.; Suárez-Vega, V.; López-Laguna, N.; Guajardo, C.; Pérez-Fernández, N. Endolymphatic Hydrops in Fluctuating Hearing Loss and Recurrent Vertigo. Front. Surg. 2021, 8, 673847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakada, T.; Yoshida, T.; Suga, K.; Kato, M.; Otake, H.; Kato, K.; Teranishi, M.; Sone, M.; Sugiura, S.; Kuno, K.; et al. Endolymphatic space size in patients with vestibular migraine and Ménière’s disease. J. Neurol. 2014, 261, 2079–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Guo, P.; Ren, T.; Wang, W. Magnetic resonance imaging of intratympanic gadolinium helps differentiate vestibular migraine from Ménière disease. Laryngoscope 2017, 127, 2382–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliezer, M.; Toupet, M.; Housset, J.; Houdart, E.; Hautefort, C. Recurrent vestibulopathy: Are cVEMP, oVEMP and inner ear MRI useful to distinguish patients with Menière’s disease and vestibular migraine? Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 279, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, L.-C.; Lin, T.-M.; Chang, Y.-M.; Kuo, T.B.; Lee, G.-S. Clinical applications of correlational vestibular autorotation test. Acta Otolaryngol. 2015, 135, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helm, M.R. Vestibulo-ocular reflex abnormalities in patients with migraine. Headache 2005, 45, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, A.G.; Zhang, L. Eye and head movements and vestibulo-ocular reflex in the context of indirect, referent control of motor actions. J. Neurophysiol. 2020, 124, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clément, G.; Wood, S.J.; Paloski, W.H.; Reschke, M.F. Changes in gain of horizontal vestibulo-ocular reflex during spaceflight. J. Vestib. Res. 2019, 29, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-Y.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, J.-S. Chasing dizzy chimera: Diagnosis of combined peripheral and central vestibulopathy. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 371, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisdorff, A.R.; Staab, J.; Newman-Toker, D.E. Overview of the International Classification of Vestibular Disorders. Neurol. Clin. 2015, 33, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokgoz, M.C.; Satar, B.; Hıdır, Y.; Ceyhan, A.; Coban, V.K.; Throat, P.E.H.C.O.E.N. Recognizing Decompensated Menière’s Disease Using High Frequency Rotational Test. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2020, 16, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, S.L.; Alghwiri, A.; Alghadir, A. Physical therapy for persons with vestibular disorders. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2015, 28, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arriaga, M.A.; Chen, D.A.; Hillman, T.A.; Kunschner, L.; Arriaga, R.Y. Visually enhanced vestibulo-ocular reflex: A diagnostic tool for migraine vestibulopathy. Laryngoscope 2006, 116, 1577–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, W.S.; Lee, S.H.; Yang, C.J.; Ahn, J.H.; Chung, J.W.; Park, H.J. Vestibular Function Tests for Vestibular Migraine: Clinical Implication of Video Head Impulse and Caloric Tests. Front. Neurol. 2016, 7, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Disease | p-Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | MD (n = 69) | VM (n = 79) | MD with Migraine (n = 72) | MD vs. VM | MD vs. MD with Migraine | VM vs. MD with Migraine |
| Age (range), year | 50.22 ± 12.90 | 47.51 ± 14.15 | 42.44 ± 10.99 | 0.032 * | <0.001 *** | 0.017 * |
| Gender (female) | 27 (39.1%) | 49 (62.0%) | 52 (72.2%) | 0.009 ** | <0.001 *** | 0.247 |
| Illness duration | 12 months | 5 months | 11 months | <0.001 *** | 0.248 | <0.001 *** |
| Vertigo/dizzy | 67 (97.1%) | 73 (92.4%) | 67 (93.1%) | 0.370 | 0.473 | 1.000 |
| Visual motion | 40 (58%) | 50 (63.3%) | 44 (61.1%) | 0.622 | 0.835 | 0.914 |
| Nausea and vomiting | 55 (79.8%) | 46 (58.2%) | 48 (66.7%) | 0.009 ** | 0.120 | 0.368 |
| Hearing impairment | 58 (84.1%) | 30 (38.0%) | 40 (55.6%) | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | 0.045* |
| Tinnitus | 62 (89.9%) | 51 (64.6%) | 56 (77.8%) | <0.001 *** | 0.087 | 0.108 |
| Aural fullness | 50 (72.5%) | 42 (53.2%) | 45 (62.5%) | 0.025 * | 0.279 | 0.320 |
| Light-photophobia | 15 (21.7%) | 62 (78.5%) | 45 (62.5%) | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | 0.048* |
| Sound-phonophobia | 14 (20.3%) | 59 (74.7%) | 47 (65.3%) | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | 0.278 |
| Parameter | Horizontal Gain | Horizontal Phase | Vertical Gain | Vertical Phase | Asymmetry | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classification | Decrease | Normal | Increase | Decrease | Normal | Increase | Decrease | Normal | Increase | Decrease | Normal | Increase | Normal | Abnormal |
| OR | 1.00 | 0.32 | 0.02 | 1.00 | 0.54 | 0.34 | 1.00 | 0.55 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.55 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.39 |
| 95%CI | - | 0.10~0.92 | 0.00~0.08 | - | 0.12~2.35 | 0.08~1.47 | - | 0.14~2.03 | 0.11~8.94 | - | 0.14~2.03 | 0.11~8.94 | - | 0.64~2.99 |
| p | <0.001 *** | 0.03 * | <0.001 *** | 0.21 | 0.41 | 0.15 | 0.56 | 0.37 | 1.00 | 0.56 | 0.37 | 1.00 | 0.23 | 0.40 |
| Frequency (Hz) | MD (n = 60) (%) | VM (n = 79) (%) | MD with Migraine (n = 72) (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decrease | Increase | Decrease | Increase | Decrease | Increase | |
| 2 | 9.1 | 81.8 | 7.7 | 89.7 | 6.3 | 93.8 |
| 2.3 | 36.4 | 63.6 | 20.5 | 76.9 | 12.5 | 75.0 |
| 2.7 | 63.6 | 36.4 | 23.1 | 66.7 | 31.3 | 68.8 |
| 3.1 | 90.9 | 9.1 | 30.8 | 61.5 | 37.5 | 62.5 |
| 3.5 | 90.9 | 9.1 | 35.9 | 61.5 | 43.8 | 56.3 |
| 3.9 | 81.8 | 18.2 | 35.9 | 59.0 | 37.5 | 62.5 |
| 4.3 | 72.7 | 27.3 | 41.0 | 59.0 | 31.3 | 62.5 |
| 4.7 | 72.7 | 27.3 | 38.5 | 59.0 | 37.5 | 62.5 |
| 5.1 | 72.7 | 27.3 | 48.7 | 51.3 | 56.3 | 43.8 |
| 5.5 | 72.7 | 27.3 | 46.2 | 53.8 | 56.3 | 43.8 |
| 5.9 | 63.6 | 36.4 | 48.7 | 51.3 | 62.5 | 37.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Tian, E.; Guo, Z.-q.; Chen, J.-y.; Kong, W.-j.; Zhang, S.-l. Diagnostic Value of the Vestibular Autorotation Test in Menière’s Disease, Vestibular Migraine and Menière’s Disease with Migraine. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12111432
Liu D, Wang J, Tian E, Guo Z-q, Chen J-y, Kong W-j, Zhang S-l. Diagnostic Value of the Vestibular Autorotation Test in Menière’s Disease, Vestibular Migraine and Menière’s Disease with Migraine. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(11):1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12111432
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Dan, Jun Wang, E Tian, Zhao-qi Guo, Jing-yu Chen, Wei-jia Kong, and Su-lin Zhang. 2022. "Diagnostic Value of the Vestibular Autorotation Test in Menière’s Disease, Vestibular Migraine and Menière’s Disease with Migraine" Brain Sciences 12, no. 11: 1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12111432
APA StyleLiu, D., Wang, J., Tian, E., Guo, Z.-q., Chen, J.-y., Kong, W.-j., & Zhang, S.-l. (2022). Diagnostic Value of the Vestibular Autorotation Test in Menière’s Disease, Vestibular Migraine and Menière’s Disease with Migraine. Brain Sciences, 12(11), 1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12111432









