Neurosensory Rehabilitation and Olfactory Network Recovery in Covid-19-related Olfactory Dysfunction
Abstract
1. Introduction
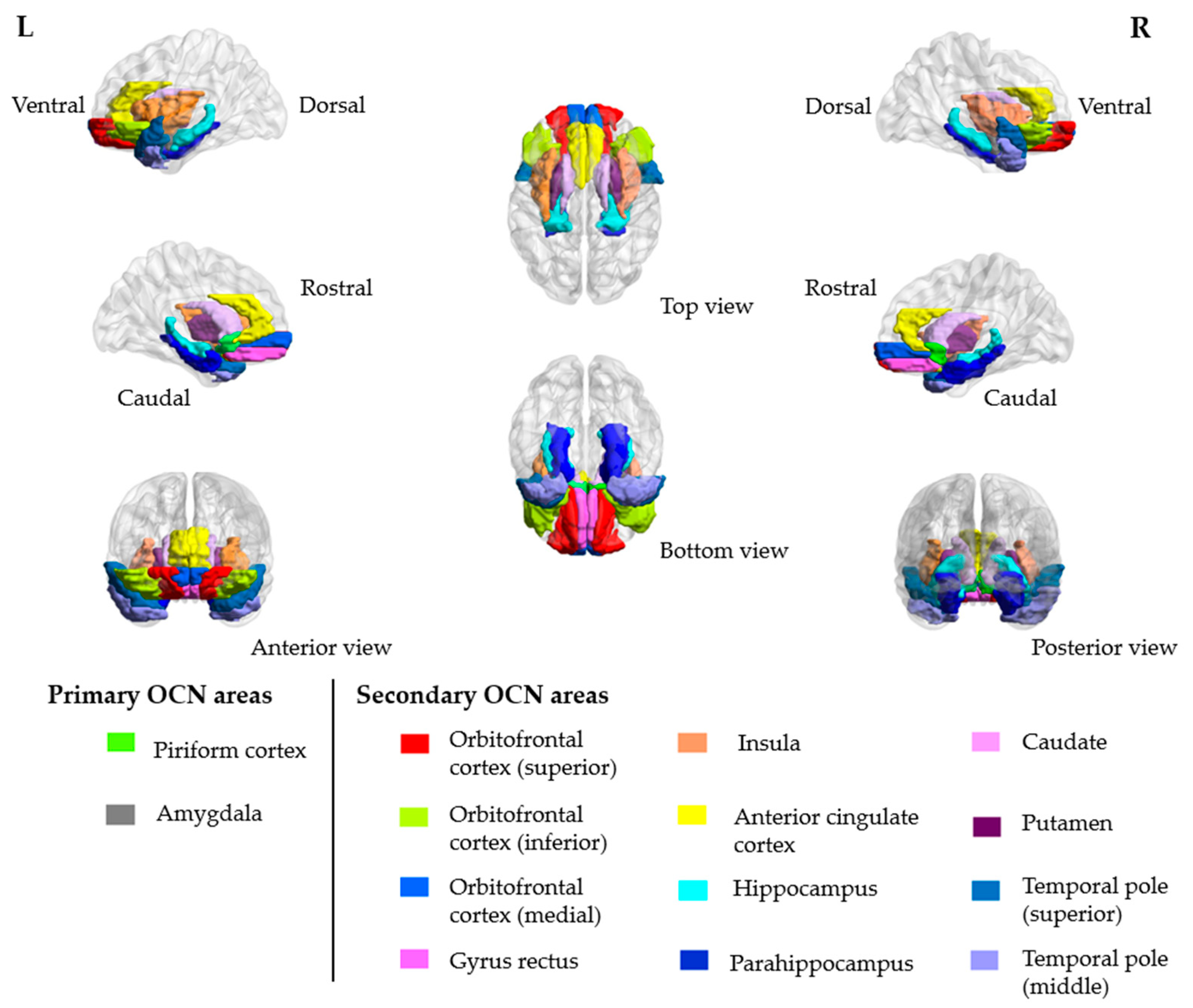
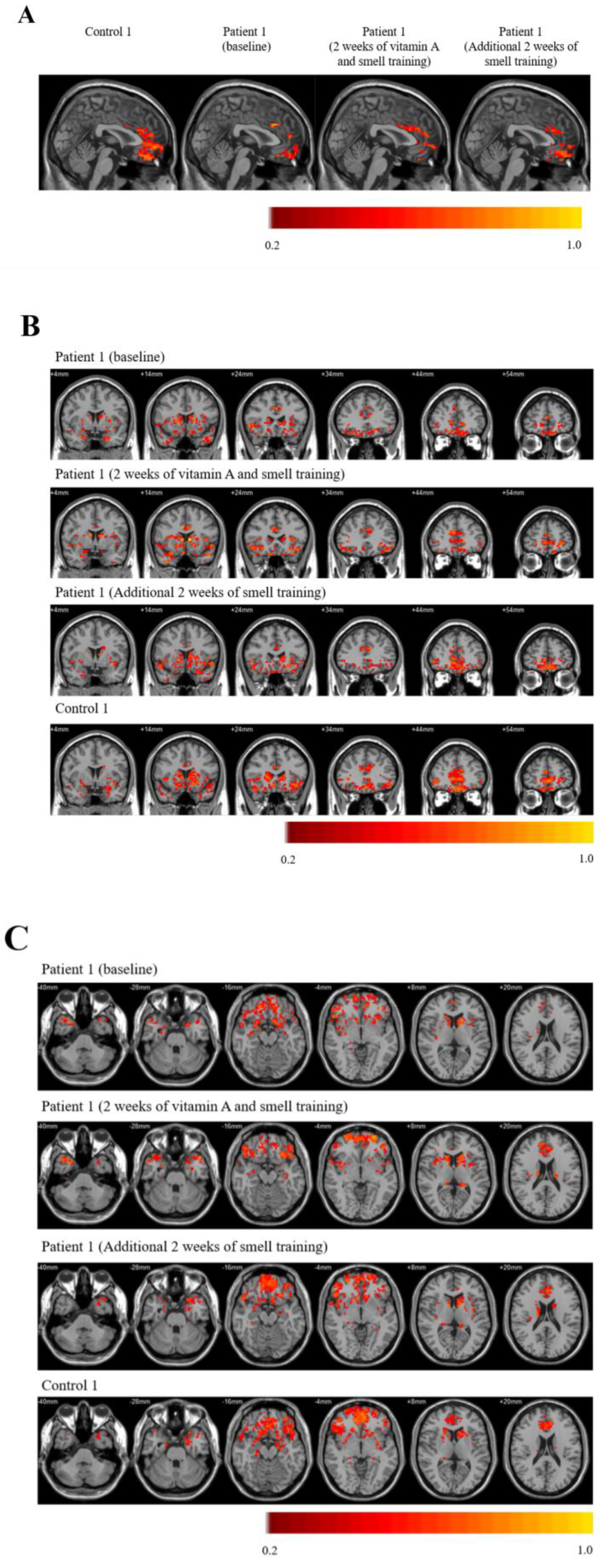
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chung, T.W.; Sridhar, S.; Zhang, A.J.; Chan, K.H.; Li, H.L.; Wong, F.K.; Ng, M.Y.; Tsang, R.K.; Lee, A.C.; Fan, Z.; et al. Olfactory Dysfunction in Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients: Observational Cohort Study and Systematic Review. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, ofaa199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Deng, Y.; Dai, Z.; Meng, Z. COVID-19 and anosmia: A review based on up-to-date knowledge. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2020, 41, 102581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paderno, A.; Mattavelli, D.; Rampinelli, V.; Grammatica, A.; Raffetti, E.; Tomasoni, M.; Gualtieri, T.; Taboni, S.; Zorzi, S.; Del Bon, F.; et al. Olfactory and Gustatory Outcomes in COVID-19: A Prospective Evaluation in Nonhospitalized Subjects. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020, 163, 1144–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinhardt, J.; Radke, J.; Dittmayer, C.; Franz, J.; Thomas, C.; Mothes, R.; Laue, M.; Schneider, J.; Brünink, S.; Greuel, S.; et al. Olfactory transmucosal SARS-CoV-2 invasion as a port of central nervous system entry in individuals with COVID-19. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, I.H.; Normandin, E.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Mukerji, S.S.; Keller, K.; Ali, A.S.; Adams, G.; Hornick, J.L.; Padera, R.F.; Sabeti, P. Neuropathological Features of Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 989–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puelles, V.G.; Lütgehetmann, M.; Lindenmeyer, M.T.; Sperhake, J.P.; Wong, M.N.; Allweiss, L.; Chilla, S.; Heinemann, A.; Wanner, N.; Liu, S.; et al. Multiorgan and Renal Tropism of SARS-CoV-2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 590–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Chan, J.F.; Yuen, T.T.; Shuai, H.; Yuan, S.; Wang, Y.; Hu, B.; Yip, C.C.; Tsang, J.O.; Huang, X.; et al. Comparative tropism, replication kinetics, and cell damage profiling of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV with implications for clinical manifestations, transmissibility, and laboratory studies of COVID-19: An observational study. Lancet Microbe 2020, 1, e14–e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.Z.; Chu, H.; Han, S.; Shuai, H.; Deng, J.; Hu, Y.F.; Gong, H.R.; Lee, A.C.; Zou, Z.; Yau, T.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infects human neural progenitor cells and brain organoids. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 928–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.J.; Lee, A.C.; Chu, H.; Chan, J.F.; Fan, Z.; Li, C.; Liu, F.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, S.; Poon, V.K.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infects and damages the mature and immature olfactory sensory neurons of hamsters. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, R.B.; Das, D.; Gadye, L.; Street, K.N.; Baudhuin, A.; Wagner, A.; Cole, M.B.; Flores, Q.; Choi, Y.G.; Yosef, N.; et al. Deconstructing Olfactory Stem Cell Trajectories at Single-Cell Resolution. Cell Stem Cell 2017, 20, 817–830.e818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, C.T.; Coulombe, P.A.; Reed, R.R. Contribution of olfactory neural stem cells to tissue maintenance and regeneration. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reden, J.; Lill, K.; Zahnert, T.; Haehner, A.; Hummel, T. Olfactory function in patients with postinfectious and posttraumatic smell disorders before and after treatment with vitamin A: A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 1906–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, T.; Whitcroft, K.L.; Rueter, G.; Haehner, A. Intranasal vitamin A is beneficial in post-infectious olfactory loss. Eur Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 274, 2819–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addison, A.B.; Wong, B.; Ahmed, T.; Macchi, A.; Konstantinidis, I.; Huart, C.; Frasnelli, J.; Fjaeldstad, A.W.; Ramakrishnan, V.R.; Rombaux, P.; et al. Clinical Olfactory Working Group consensus statement on the treatment of postinfectious olfactory dysfunction. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 1704–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, C.; Alanin, M.; Philpott, C.; Harries, P.; Whitcroft, K.; Qureishi, A.; Anari, S.; Ramakrishnan, Y.; Sama, A.; Davies, E.; et al. Management of new onset loss of sense of smell during the COVID-19 pandemic—BRS Consensus Guidelines. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2021, 46, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logothetis, N.K.; Pauls, J.; Augath, M.; Trinath, T.; Oeltermann, A. Neurophysiological investigation of the basis of the fMRI signal. Nature 2001, 412, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attwell, D.; Buchan, A.M.; Charpak, S.; Lauritzen, M.; Macvicar, B.A.; Newman, E.A. Glial and neuronal control of brain blood flow. Nature 2010, 468, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Esposito, M.; Deouell, L.Y.; Gazzaley, A. Alterations in the BOLD fMRI signal with ageing and disease: A challenge for neuroimaging. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollndorfer, K.; Fischmeister, F.P.; Kowalczyk, K.; Hoche, E.; Mueller, C.A.; Trattnig, S.; Schöpf, V. Olfactory training induces changes in regional functional connectivity in patients with long-term smell loss. Neuroimage Clin. 2015, 9, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollndorfer, K.; Kowalczyk, K.; Hoche, E.; Mueller, C.A.; Pollak, M.; Trattnig, S.; Schöpf, V. Recovery of olfactory function induces neuroplasticity effects in patients with smell loss. Neural Plast. 2014, 2014, 140419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oz, G.; Alger, J.R.; Barker, P.B.; Bartha, R.; Bizzi, A.; Boesch, C.; Bolan, P.J.; Brindle, K.M.; Cudalbu, C.; Dinçer, A.; et al. Clinical proton MR spectroscopy in central nervous system disorders. Radiology 2014, 270, 658–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, R.Q.; Li, W.T.V.; Shum, W.Z.; Chu, S.C.; Li, H.L.; Shea, Y.F.; Chung, T.W. A systematic review and meta-analysis protocol examining the clinical characteristics and epidemiological features of olfactory dysfunction (OD) in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnittke, N.; Herrick, D.B.; Lin, B.; Peterson, J.; Coleman, J.H.; Packard, A.I.; Jang, W.; Schwob, J.E. Transcription factor p63 controls the reserve status but not the stemness of horizontal basal cells in the olfactory epithelium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E5068–E5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrick, D.B.; Lin, B.; Peterson, J.; Schnittke, N.; Schwob, J.E. Notch1 maintains dormancy of olfactory horizontal basal cells, a reserve neural stem cell. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E5589–E5598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, B.; Coleman, J.H.; Peterson, J.N.; Zunitch, M.J.; Jang, W.; Herrick, D.B.; Schwob, J.E. Injury Induces Endogenous Reprogramming and Dedifferentiation of Neuronal Progenitors to Multipotency. Cell Stem Cell 2017, 21, 761–774.e765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, J.; Lin, B.; Barrios-Camacho, C.M.; Herrick, D.B.; Holbrook, E.H.; Jang, W.; Coleman, J.H.; Schwob, J.E. Activating a Reserve Neural Stem Cell Population In Vitro Enables Engraftment and Multipotency after Transplantation. Stem Cell Rep. 2019, 12, 680–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peluso, C.E.; Jang, W.; Dräger, U.C.; Schwob, J.E. Differential expression of components of the retinoic acid signaling pathway in the adult mouse olfactory epithelium. J. Comp. Neurol. 2012, 520, 3707–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paschaki, M.; Cammas, L.; Muta, Y.; Matsuoka, Y.; Mak, S.S.; Rataj-Baniowska, M.; Fraulob, V.; Dollé, P.; Ladher, R.K. Retinoic acid regulates olfactory progenitor cell fate and differentiation. Neural Dev. 2013, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragoso, Y.D.; Shearer, K.D.; Sementilli, A.; de Carvalho, L.V.; McCaffery, P.J. High expression of retinoic acid receptors and synthetic enzymes in the human hippocampus. Brain Struct. Funct. 2012, 217, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rioux, L.; Arnold, S.E. The expression of retinoic acid receptor alpha is increased in the granule cells of the dentate gyrus in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2005, 133, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoney, P.N.; Fragoso, Y.D.; Saeed, R.B.; Ashton, A.; Goodman, T.; Simons, C.; Gomaa, M.S.; Sementilli, A.; Sementilli, L.; Ross, A.W.; et al. Expression of the retinoic acid catabolic enzyme CYP26B1 in the human brain to maintain signaling homeostasis. Brain Struct. Funct. 2016, 221, 3315–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.W.; Zhang, H.; Parent, J.M. Retinoic acid regulates postnatal neurogenesis in the murine subventricular zone-olfactory bulb pathway. Development 2005, 132, 2721–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, S.; Lie, D.C.; DeCicco, K.L.; Shi, Y.; DeLuca, L.M.; Gage, F.H.; Evans, R.M. Retinoic acid is required early during adult neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3902–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damm, M.; Pikart, L.K.; Reimann, H.; Burkert, S.; Göktas, Ö.; Haxel, B.; Frey, S.; Charalampakis, I.; Beule, A.; Renner, B.; et al. Olfactory training is helpful in postinfectious olfactory loss: A randomized, controlled, multicenter study. Laryngoscope 2014, 124, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Aïn, S.; Poupon, D.; Hétu, S.; Mercier, N.; Steffener, J.; Frasnelli, J. Smell training improves olfactory function and alters brain structure. Neuroimage 2019, 189, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mainland, J.D.; Bremner, E.A.; Young, N.; Johnson, B.N.; Khan, R.M.; Bensafi, M.; Sobel, N. Olfactory plasticity: One nostril knows what the other learns. Nature 2002, 419, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, D.J.; Feinstein, P.; Rivers, A.L.; Mathews, G.A.; Kim, A.; Greer, C.A.; Mombaerts, P.; Firestein, S. Postnatal refinement of peripheral olfactory projections. Science 2004, 304, 1976–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chung, T.W.-H.; Zhang, H.; Wong, F.K.-C.; Sridhar, S.; Chan, K.-H.; Cheng, V.C.-C.; Yuen, K.-Y.; Hung, I.F.-N.; Mak, H.K.-F. Neurosensory Rehabilitation and Olfactory Network Recovery in Covid-19-related Olfactory Dysfunction. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11060686
Chung TW-H, Zhang H, Wong FK-C, Sridhar S, Chan K-H, Cheng VC-C, Yuen K-Y, Hung IF-N, Mak HK-F. Neurosensory Rehabilitation and Olfactory Network Recovery in Covid-19-related Olfactory Dysfunction. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(6):686. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11060686
Chicago/Turabian StyleChung, Tom Wai-Hin, Hui Zhang, Fergus Kai-Chuen Wong, Siddharth Sridhar, Kwok-Hung Chan, Vincent Chi-Chung Cheng, Kwok-Yung Yuen, Ivan Fan-Ngai Hung, and Henry Ka-Fung Mak. 2021. "Neurosensory Rehabilitation and Olfactory Network Recovery in Covid-19-related Olfactory Dysfunction" Brain Sciences 11, no. 6: 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11060686
APA StyleChung, T. W.-H., Zhang, H., Wong, F. K.-C., Sridhar, S., Chan, K.-H., Cheng, V. C.-C., Yuen, K.-Y., Hung, I. F.-N., & Mak, H. K.-F. (2021). Neurosensory Rehabilitation and Olfactory Network Recovery in Covid-19-related Olfactory Dysfunction. Brain Sciences, 11(6), 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11060686








