RETRACTED: Differential Regulation of the EGFR/PI3K/AKT/PTEN Pathway between Low- and High-Grade Gliomas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Specimens
2.2. DNA, ARN, and Protein Isolation
2.3. Mutations Analysis
2.4. Analysis of Gene Amplification of EGFR, PI3K, and AKT
2.5. Expression Level of AKT, PI3K, Bcl-2, and Bax
2.6. Immunoblotting for AKT and PTEN Phosphorylation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Samples
3.2. Mutation Analysis of PI3KCA and PTEN Genes
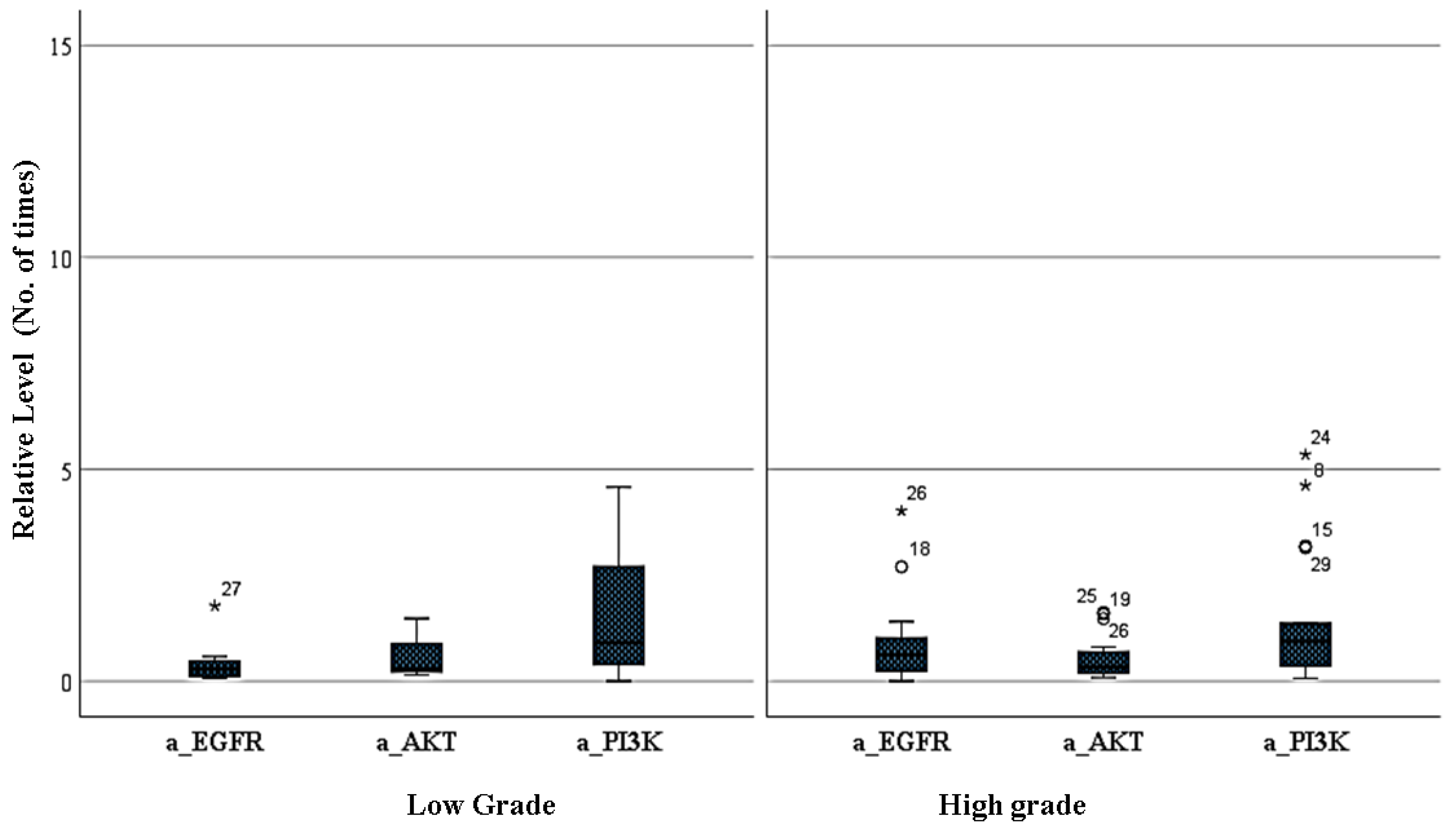
3.3. Amplification Level of EGFR, PI3K, and AKT Genes between Low- and High-Grade Gliomas
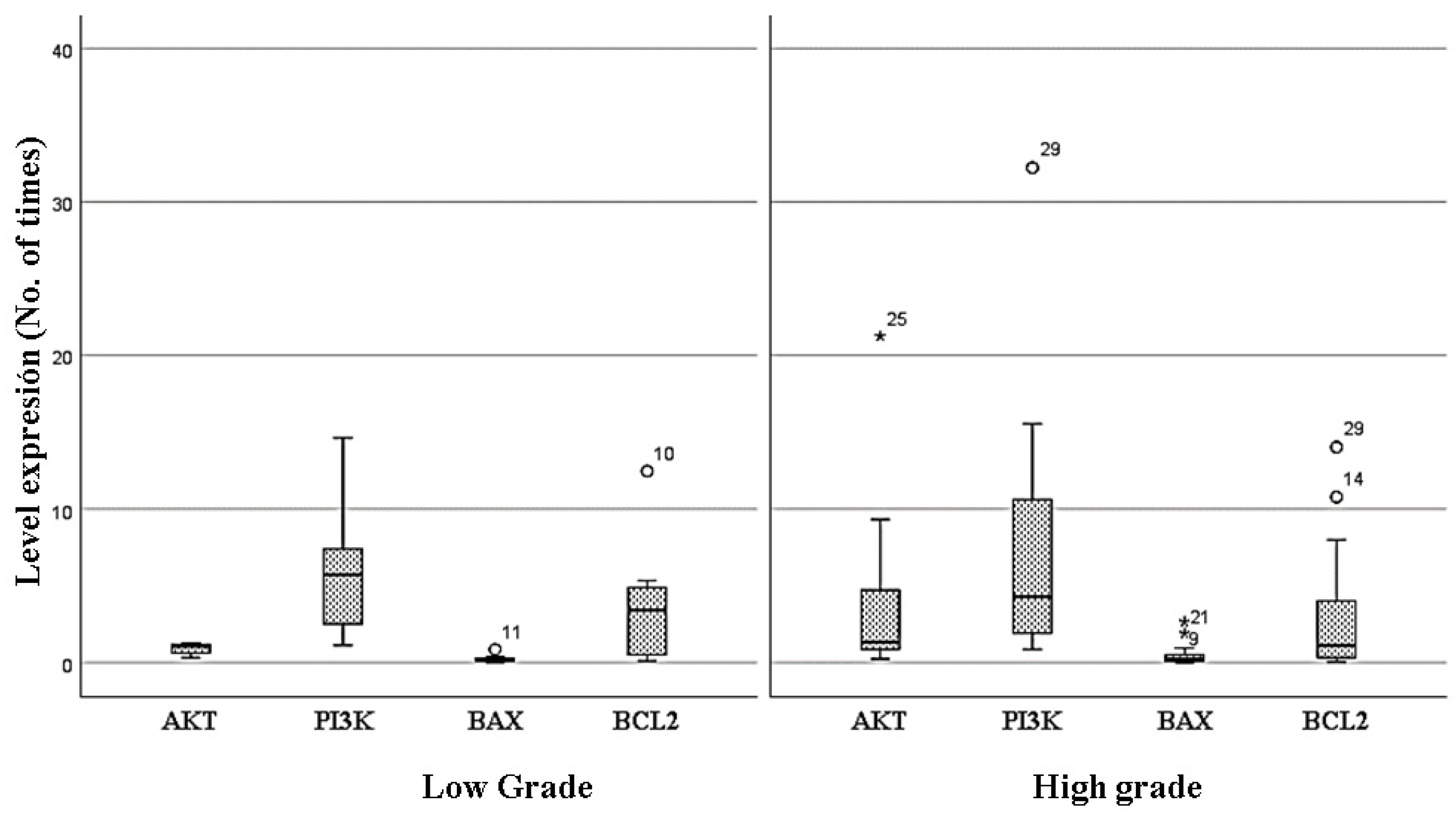
3.4. Changes in the Expression Levels of AKT, PI3K, BAX, and BCL2 between Low- and High-Grade Gliomas
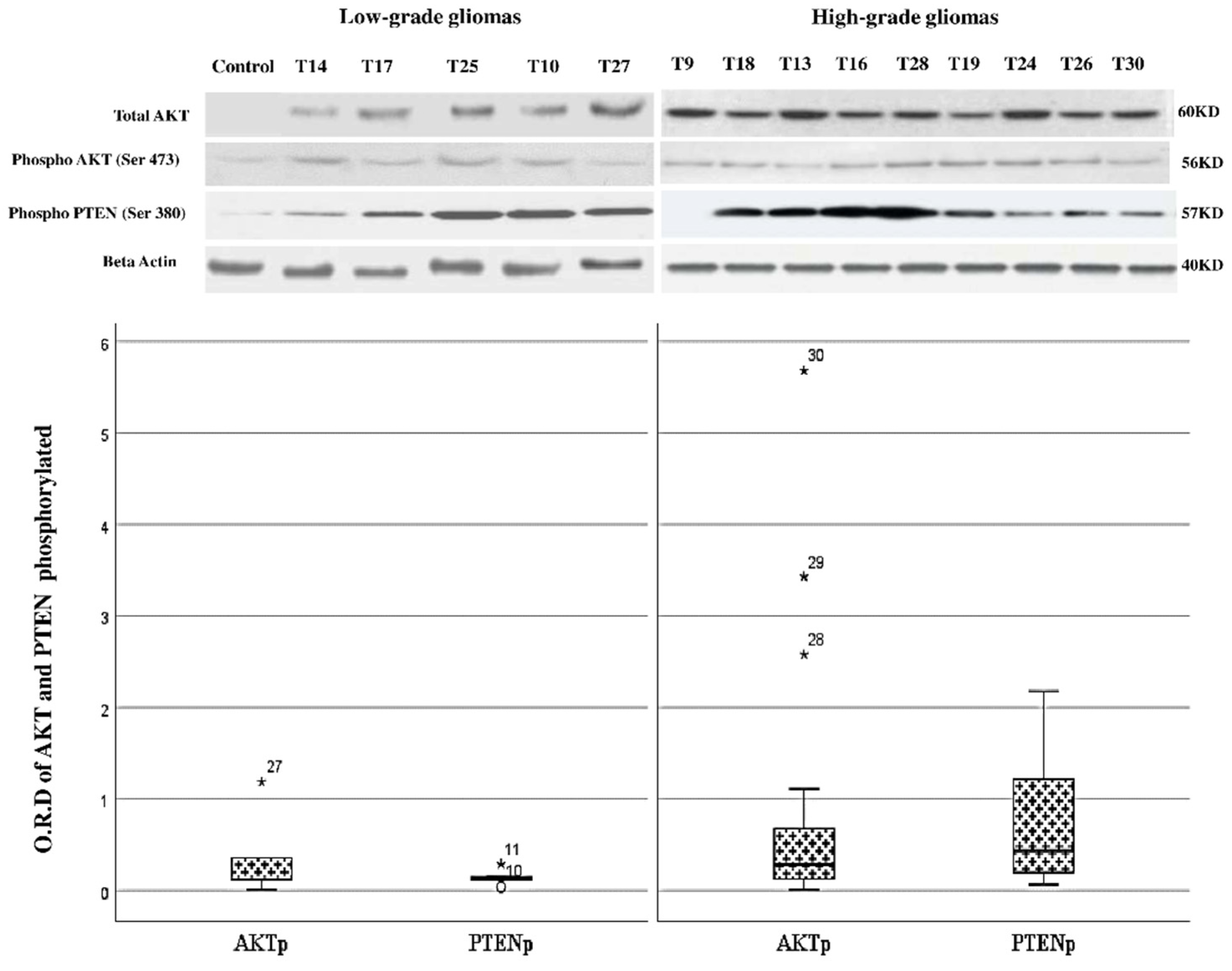
3.5. Changes in the Level of Phosphorylation of AKT and PTEN between Low- and High-Grade Gliomas
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- D’Amico, A.; Maugeri, G.; Vanella, L.; Pittalà, V.; Reglodi, D.; D’Agata, V. Multimodal Role of PACAP in Glioblastoma. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaley, T.; Touat, M.; Subbiah, V.; Hollebecque, A.; Rodon, J.; Lockhart, A.C.; Keedy, V.; Bielle, F.; Hofheinz, R.-D.; Joly, F.; et al. BRAF Inhibition in BRAFV600-Mutant Gliomas: Results from the VE-BASKET Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 3477–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teo, W.-Y.; Sekar, K.; Seshachalam, P.; Shen, J.; Chow, W.-Y.; Lau, C.C.; Yang, H.; Park, J.; Kang, S.-G.; Li, X.; et al. Relevance of a TCGA-derived Glioblastoma Subtype Gene-Classifier among Patient Populations. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñeros, M.; Sierra, M.S.; Izarzugaza, M.I.; Forman, D. Descriptive epidemiology of brain and central nervous system cancers in Central and South America. Cancer Epidemiol. 2016, 44 (Suppl. 1), S141–S149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldape, K.; Zadeh, G.; Mansouri, S.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A. Glioblastoma: Pathology, molecular mechanisms and markers. Acta Neuropathol. 2015, 129, 829–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virtuoso, A.; Giovannoni, R.; De Luca, C.; Gargano, F.; Cerasuolo, M.; Maggio, N.; Lavitrano, M.; Papa, M. The Glioblastoma Microenvironment: Morphology, Metabolism, and Molecular Signature of Glial Dynamics to Discover Metabolic Rewiring Sequence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maugeri, G.; D’Amico, A.; Saccone, S.; Federico, C.; Rasà, D.; Caltabiano, R.; Broggi, G.; Giunta, S.; Musumeci, G.; D’Agata, V. Effect of PACAP on Hypoxia-Induced Angiogenesis and Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Glioblastoma. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, S.; Phillips, J.; Onar-Thomas, A.; Romero, E.; Zheng, S.; Wiencke, J.K.; McBride, S.M.; Cowdrey, C.; Prados, M.D.; Weiss, W.A.; et al. PTEN promoter methylation and activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in pediatric gliomas and influence on clinical outcome. Neuro-Oncology 2012, 14, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, S.M.; Perez, D.A.; Polley, M.-Y.; Vandenberg, S.R.; Smith, J.S.; Zheng, S.; Lamborn, K.R.; Wiencke, J.K.; Chang, S.M.; Prados, M.D.; et al. Activation of the PI3K/mTOR pathway occurs in most adult low-grade gliomas and predicts patient survival. J. Neuro-Oncology 2010, 97, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Chowdhry, S.; Wu, S.; Zhang, W.; Masui, K.; Mischel, P.S. Altered cellular metabolism in gliomas—An emerging landscape of actionable co-dependency targets. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Lim, S.K.; Liang, Q.; Iyer, S.V.; Wang, H.-Y.; Wang, Z.; Xie, X.; Sun, D.; Chen, Y.-J.; Tabar, V.; et al. Gboxin is an oxidative phosphorylation inhibitor that targets glioblastoma. Nature 2019, 567, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafeh, R.; Samuels, Y. PIK3CA in cancer: The past 30 years. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 59, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, G.V.; Tawil, Y.; Wise, H.M.; Leslie, N.R. Mechanisms of PTEN loss in cancer: It’s all about diversity. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 59, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivas, S.; Gómez, O.C.; Antón, I.M.; Wandosell, F. Role of Akt Isoforms Controlling Cancer Stem Cell Survival, Phenotype and Self-Renewal. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.C.; Jiang, C. Recent Advances in Targeted Therapy for Glioma. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 1365–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.F.; Wang, J.; Shao, W.; Wu, C.P.; Chen, Z.P.; To, S.T.; Li, W.P. Recent advances in the use of PI3K inhibitors for glioblastoma multiforme: Current preclinical and clinical development. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gousias, K.; Markou, M.; Voulgaris, S.; Goussia, A.; Voulgari, P.; Bai, M.; Polyzoidis, K.; Kyritsis, A.; Alamanos, Y. Descriptive Epidemiology of Cerebral Gliomas in Northwest Greece and Study of Potential Predisposing Factors, 2005–2007. Neuroepidemiology 2009, 33, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohgaki, H.; Kleihues, P. Population-Based Studies on Incidence, Survival Rates, and Genetic Alterations in Astrocytic and Oligodendroglial Gliomas. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 64, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, I.; Cockburn, M.; Cozen, W.; Wang, Y.P.; Preston, M.S. A population-based description of glioblastoma multiforme in Los Angeles County, 1974–1999. Cancer 2005, 104, 2798–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Vogt, P.K. Class I PI3K in oncogenic cellular transformation. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5486–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, D.K.; Di, C.; Parrett, T.J.; Samuels, Y.R.; Cummins, J.M.; McLendon, R.E.; Fults, D.W.; Velculescu, V.; Bigner, D.D.; Yan, H. Mutations of PIK3CA in Anaplastic Oligodendrogliomas, High-Grade Astrocytomas, and Medulloblastomas. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 5048–5050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuels, Y.; Wang, Z.; Bardelli, A.; Silliman, N.; Ptak, J.; Szabo, S.; Yan, H.; Gazdar, A.; Powell, S.M.; Riggins, G.J.; et al. High Frequency of Mutations of the PIK3CA Gene in Human Cancers. Science 2004, 304, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, C.; Bartels, G.; Gehlhaar, C.; Holtkamp, N.; von Deimling, A. PIK3CA mutations in glioblastoma multiforme. Acta Neuropathol. 2005, 109, 639–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benito, R.; Gil-Benso, R.; Quilis, V.; Pérez, M.; Gregori-Romero, M.; Roldan, P.; Gonzalez-Darder, J.; Cerda-Nicolas, M.; Lopez-Gines, C. Primary glioblastomas with and without EGFR amplification: Relationship to genetic alterations and clinicopathological features. Neuropathology 2010, 30, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuncel, G.; Kalkan, R. Receptor tyrosine kinase-Ras-PI 3 kinase-Akt signaling network in glioblastoma multiforme. Med. Oncol. 2018, 35, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Wang, M.; Zhang, G.; Bao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, W.; Cui, H. E2F7−EZH2 axis regulates PTEN/AKT/mTOR signalling and glioblastoma progression. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 123, 1445–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brlek, P.; Kafka, A.; Bukovac, A.; Pećina, S.N. Integrative cBioPortal Analysis Revealed Molecular Mechanisms That Regulate EGFR-PI3K-AKT-mTOR Pathway in Diffuse Gliomas of the Brain. Cancers 2021, 13, 3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Wang, P.-F.; Cai, H.-Q.; Wan, J.-H.; Li, S.-W.; Lin, Z.-H.; Yu, C.-J.; Yan, C.-X. Alterations in the RTK/Ras/PI3K/AKT pathway serve as potential biomarkers for immunotherapy outcome of diffuse gliomas. Aging 2021, 13, 15444–15458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reifenberger, G.; Wirsching, H.G.; Knobbe, T.C.; Weller, M. Advances in the molecular genetics of gliomas—implications for classification and therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 434–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colorado, M.; Segatto, M.; Di Bartolomeo, S. argeting RTK-PI3K-mTOR Axis in Gliomas: An Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, R.S.; Fedrigo, C.A.; Brands, E.; Dik, R.; Stalpers, L.J.; Baumert, B.G.; Slotman, B.J.; Westerman, B.A.; Peters, G.J.; Sminia, P. The allosteric AKT inhibitor MK2206 shows a synergistic interaction with chemotherapy and radiotherapy in glioblastoma spheroid cultures. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Yu, Q.; Peng, Z.; Huang, Y.; Diao, S.; Cheng, J.; Wang, W.; Hong, M. miR-200b inhibits CD133+ glioma cells by targeting the AKT pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 4701–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahmad, H.F.; Mouhieddine, T.H.; Chalhoub, R.M.; Assi, S.; Araji, T.; Chamaa, F.; Itani, M.M.; Nokkari, A.; Kobeissy, F.; Daoud, G.; et al. The Akt/mTOR pathway in cancer stem/progenitor cells is a potential therapeutic target for glioblastoma and neuroblastoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 33549–33561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, P.A.; Bhattacharya, S.; Elmayan, A.; Darjatmoko, S.R.; Thuro, B.A.; Yan, M.B.; Van Ginkel, P.R.; Polans, A.S.; Kuo, J.S. Resveratrol targeting of AKT and p53 in glioblastoma and glioblastoma stem-like cells to suppress growth and infiltration. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 126, 1448–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, J.M.; Cory, S. The BCL-2 arbiters of apoptosis and their growing role as cancer targets. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Zhou, K.; Tang, X.; Duan, J.; Zhao, L. MicroRNA-34a inhibits cell proliferation and induces cell apoptosis of glioma cells via targeting of Bcl-2. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, X. Targeting Bcl-2 for cancer therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2021, 1876, 188569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouri, F.M.; Jensen, S.A.; Stegh, A.H. The role of Bcl-2 family proteins in therapy responses of malignant astrocytic gliomas: Bcl2L12 and beyond. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 838916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doucette, T.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Fuller, G.N.; Suki, D.; Fults, D.W.; Rao, G. Bcl-2 promotes malignant progression in a PDGF-B-dependent murine model of oligodendroglioma. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 2093–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.Y.; Jiang, C.X.; Wu, M.Y.; Mei, R.Y.; Yang, A.F.; Tao, H.P.; Chen, X.J.; Zhang, J.; Huang, L.; Zhao, X.F. Theabrownin Induces Cell Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest of Oligodendroglioma and Astrocytoma in Different Pathways. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirapelli, D.P.; Lustosa, I.L.; Menezes, S.B.; Franco, I.M.; Rodrigues, A.R.; Peria, F.M.; Marinho, A.M.D.N.; Neder Serafini, L.; Carlotti, C.G., Jr. High expression of XIAP and Bcl-2 may inhibit programmed cell death in glioblastomas. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatria 2017, 75, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Primer Exon 9 PI3KCA | Forward 5′ CCA CAA ATA TCA ATT TAC AAC CAT TG 3’ Reverse 5′ GAT TGG TTC TTT CCT GTC TCT G 3′ |
| Primer Exon 20A PI3KCA | Forward 5′ CCA CAA ATA TCA ATT TAC AAC CAT TG 3′ Reverse 5′ GAT TGG TTC TTT CCT GTC TCT G 3′ |
| Primer Exon 20B PI3KCA | Forward 5′ GGG GAT TTT TGT TTT GTT TTG 3′ Reverse 5′ TTG CAT ACA TTC GAA AGA CC 3′ |
| Primer Exon 5 PTEN | Forward 5′ AAA AAG GAA AGG AGA AGG ACC 3′ Reverse 5′ CCT GAA TAA AAT GGG GGA AA 3′ |
| Primer Exon 6 PTEN | Forward 5′ TGT TCC AAT ACA TGG AAG GAT 3′ Reverse 5′ ACG ACC CAG TTA CCA TAG CA 3′ |
| n (%) | Female (%) | Male (%) | Age (Range) | Type | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOW GRADE | GRADE I | 2 (6.6%) | 1 (50%) | 1 (50%) | 5–40 | 1 GG | 1 AP | ||
| GRADE II | 6 (20%) | 3 (50%) | 3 (50%) | 20–56 | 2 EPM | 2 ODG | 2 OA | ||
| HIGH GRADE | GRADE III | 9 (30%) | 2 (22.2%) | 7 (77.7%) | 30–56 | 3 AA | 3 OAA | 1 ODA | 2 EPMA |
| GRADE IV | 13 (43.3%) | 3 (23%) | 10 (76.92%) | 20–58 | 13 GM | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Erira, A.; Velandia, F.; Penagos, J.; Zubieta, C.; Arboleda, G. RETRACTED: Differential Regulation of the EGFR/PI3K/AKT/PTEN Pathway between Low- and High-Grade Gliomas. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11121655
Erira A, Velandia F, Penagos J, Zubieta C, Arboleda G. RETRACTED: Differential Regulation of the EGFR/PI3K/AKT/PTEN Pathway between Low- and High-Grade Gliomas. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(12):1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11121655
Chicago/Turabian StyleErira, Alveiro, Fernando Velandia, José Penagos, Camilo Zubieta, and Gonzalo Arboleda. 2021. "RETRACTED: Differential Regulation of the EGFR/PI3K/AKT/PTEN Pathway between Low- and High-Grade Gliomas" Brain Sciences 11, no. 12: 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11121655
APA StyleErira, A., Velandia, F., Penagos, J., Zubieta, C., & Arboleda, G. (2021). RETRACTED: Differential Regulation of the EGFR/PI3K/AKT/PTEN Pathway between Low- and High-Grade Gliomas. Brain Sciences, 11(12), 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11121655






