Transient Complete Resolution of Tourette Syndrome Symptoms Following Personalized Depth Electrode Placement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case Presentation
2.2. Deep Brain Stimulation
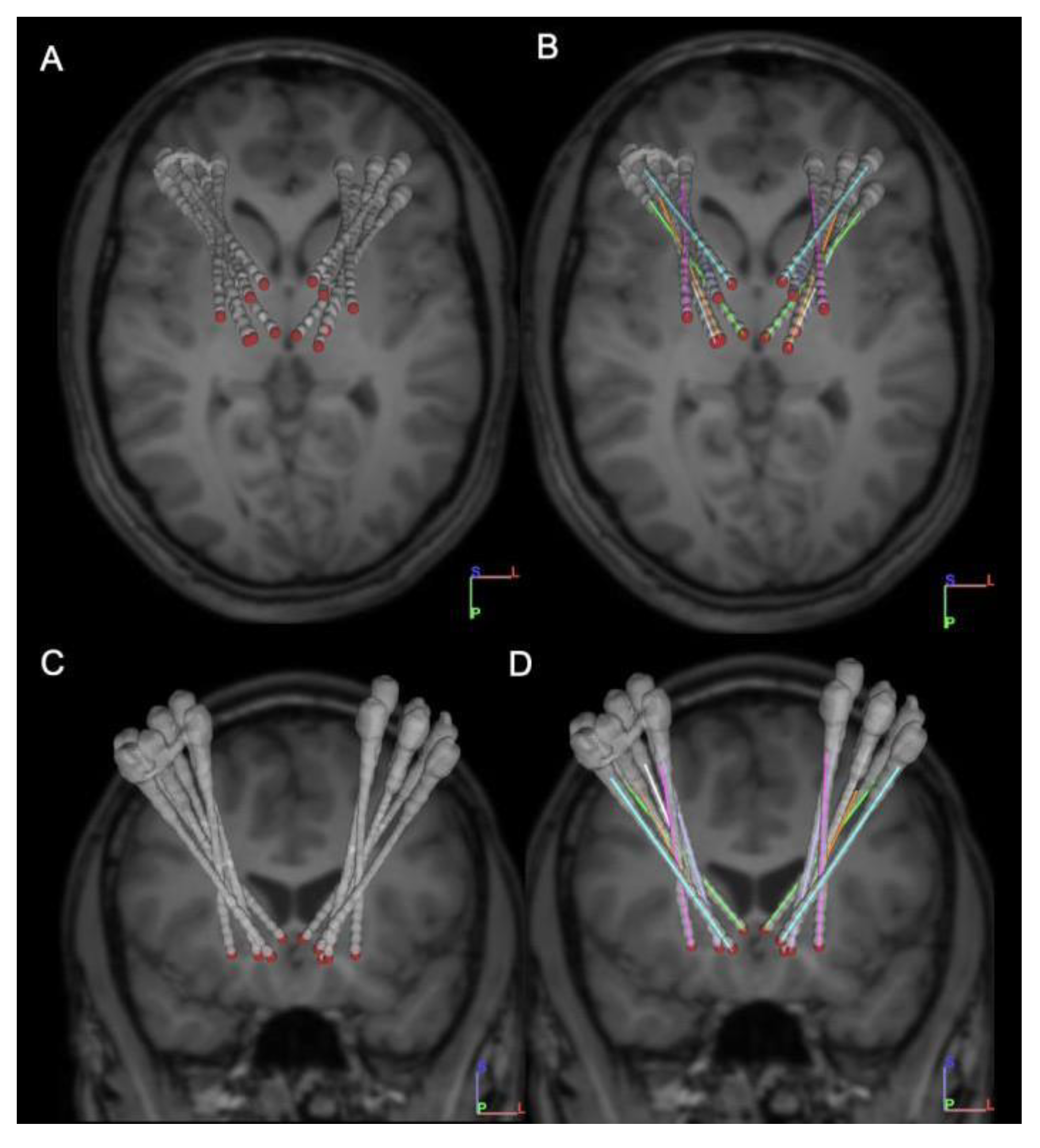
2.2.1. Implantation
2.2.2. Test Stimulation
2.2.3. Perioperative Medication
3. Results
Outcome Measures
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martinez-Ramirez, D.; Jimenez-Shahed, J.; Leckman, J.F.; Porta, M.; Servello, D.; Meng, F.-G.; Kuhn, J.; Huys, D.; Baldermann, J.C.; Foltynie, T.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Deep Brain Stimulation in Tourette Syndrome: The International Tourette Syndrome Deep Brain Stimulation Public Database and Registry. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schrock, L.E.; Mink, J.W.; Woods, D.W.; Porta, M.; Servello, D.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Silburn, P.A.; Foltynie, T.; Walker, H.C.; Shahed-Jimenez, J.; et al. Tourette Syndrome deep brain stimulation: A review and updated recommendations. Mov. Disord. 2014, 30, 448–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, A.; Jimenez-Shahed, J.; Carvallo, J.F.B.; Jankovic, J. Deep brain stimulation for Tourette Syndrome: Target selection. Ster. Funct. Neurosurg. 2012, 90, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeb, W.; Rossi, P.J.; Porta, M.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Servello, D.; Silburn, P.; Coyne, T.; Leckman, J.F.; Foltynie, T.; Hariz, M.; et al. The International Deep Brain Stimulation Registry and Database for Gilles de la Tourette Syndrome: How Does It Work? Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Savica, R.; Stead, M.; Mack, K.J.; Lee, K.H.; Klassen, B.T. Deep brain stimulation in tourette syndrome: A description of 3 patients with excellent outcome. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2012, 87, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perestelo-Pérez, L.; Rivero-Santana, A.; Pérez-Ramos, J.; Serrano-Pérez, P.; Panetta, J.; Hilarion, P. Deep brain stimulation in parkin- 375 son’s disease: Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Neurol. 2014, 261, 2051–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidailhet, M.; Vercueil, L.; Houeto, J.-L.; Krystkowiak, P.; Benabid, A.-L.; Cornu, P.; Lagrange, C.; du Montcel, S.T.; Dormont, D.; Grand, S.; et al. Bilateral deep-brain stimulation of the globus pallidus in primary generalized dystonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Denys, D.; Mantione, M.; Figee, M.; Munckhof, P.V.D.; Koerselman, F.; Westenberg, H.; Bosch, A.; Schuurman, R. Deep Brain Stimulation of the Nucleus Accumbens for Treatment-Refractory Obsessive Compulsive Disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knights, S.D.N.; Kawamura, A.; Switzer, L.; Fehlings, D. Further evaluation of the scoring, reliability, and validity of the Hypertonia Assessment Tool (HAT). J. Child Neurol. 2014, 29, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jethwa, A.M.J.; Macarthur, C.; Knights, S.; Fehlings, T.; Fehlings, D. Development of the hypertonia assessment tool (HAT): A discriminative tool for hypertonia in children. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2010, 52, e83–e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanger, T.D.; Robison, A.; Arguelles, E.; Ferman, D.; Liker, M. Case report: Targeting for deep brain stimulation surgery using chronic recording and stimulation in an inpatient neuromodulation monitoring unit, with implantation of electrodes in GPI and VIM in a 7-year-old child with progressive generalized dystonia. J. Child Neurol. 2018, 33, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanger, T.D.; Liker, M.; Arguelles, E.; Deshpande, R.; Maskooki, A.; Ferman, D.; Tongol, A.; Robison, A. Pediatric Deep Brain Stimulation Using Awake Recording and Stimulation for Target Selection in an Inpatient Neuromodulation Monitoring Unit. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bancaud, J.; Talairach, J. Methodology of stereo EEG exploration and surgical intervention in epilepsy. Rev. d’oto-Neuro-Ophtalmol. 1973, 45, 45. [Google Scholar]
- Larson, P.S.; Starr, P.A.; Martin, A.J. Deep brain stimulation: Interventional and intraoperative MRI approaches. Prog. Neurol. Surg. 2018, 33, 187–197. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano, A.M.; Lipsman, N.; Bergman, H.; Brown, P.; Chabardes, S.; Chang, J.W.; Matthews, K.; McIntyre, C.C.; Schlaepfer, T.E.; Schulder, M.; et al. Deep brain stimulation: Current challenges and future directions. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.; Walkup, J.T.; Woods, D.W.; Peterson, A.; Piacentini, J.; Wilhelm, S.; Katsovich, L.; McGuire, J.F.; Dziura, J.; Scahill, L. Detecting a clinically meaningful change in tic severity in Tourette syndrome: A comparison of three methods. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2013, 36, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.-G.; Ge, Y.; Stead, M.; Zhang, K.; Yan, S.-S.; Hu, W.; Meng, F.-G. Long-term outcome of globus pallidus internus deep brain stimulation in patients with Tourette syndrome. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2014, 89, 1506–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rungratsameetaweemana, N. Understanding motor abnormalities in psychiatric disorders as altered sensorimotor processing. Biol. Psychiatry Glob. Open Sci. 2021, 1, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleimaker, A.; Kleimaker, M.; Bäumer, T.; Beste, C.; Münchau, A. Gilles de la Tourette syndrome—A disorder of action-perception integration. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 597898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, J.B. A Developmental Perspective of Dopaminergic Dysfunction in Tourette Syndrome. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 84, e33–e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, H.S.; Szymanski, S.; Giuliano, J.; Yokoi, F.; Dogan, A.S.; Brašić, J.R.; Zhou, Y.; Grace, A.A.; Wong, D.F. Elevated intrasynaptic dopamine release in Tourette’s syndrome measured by PET. Am. J. Psychiatry 2002, 159, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarian-Tefaghi, L.; Zrinzo, L.; Foltynie, T. The use of deep brain stimulation in Tourette syndrome. Brain Sci. 2016, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maciunas, R.J.; Maddux, B.N.; Riley, D.E.; Whitney, C.M.; Schoenberg, M.; Ogrocki, P.J.; Albert, J.; Gould, D.J. Prospective randomized double-blind trial of bilateral thalamic deep brain stimulation in adults with Tourette syndrome. J. Neurosurg. 2007, 107, 1004–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casagrande, S.C.; Cury, R.G.; Alho, E.J.; Fonoff, E.T. Deep brain stimulation in Tourette’s syndrome: Evidence to date. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2019, 15, 1061–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Florence, G.; Sameshima, K.; Fonoff, E.T.; Hamani, C. Deep Brain Stimulation: More Complex than the Inhibition of Cells and Excitation of Fibers. Neuroscientist 2016, 22, 332–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| AC-PC Coordinates | ||
|---|---|---|
| Target | Left | Right |
| Vo STN | Lat: −13.5 | Lat: 13.5 |
| AP: −2.0 | AP: −2.0 | |
| Vert: 1.0 | Vert: 1.0 | |
| GPi Posterior | Lat: −21.5 | Lat: 21.5 |
| AP: 4.0 | AP: 4.0 | |
| Vert: −3.0 | Vert: −3.0 | |
| Gpi Anterior | Lat: −12.0 | Lat: 12.0 |
| AP: 9.0 | AP: 9.0 | |
| Vert: −3.0 | Vert: −3.0 | |
| CM Parafasciular nucleus | Lat: −5.0 | Lat: 5.0 |
| AP: −4.0 | AP: −4.0 | |
| Vert: 0.0 | Vert: 0.0 | |
| VIM Thalamus | Lat: −14.0 | Lat: 14.0 |
| AP: −5.0 | AP: −5.0 | |
| Vert: 0.0 | Vert: 0.0 | |
| NA | Lat: −9.3 | Lat: 9.0 |
| AP: 13.93 | AP: 14.68 | |
| Vert: −0.87 | Vert: −1.44 | |
| AC-PC Coordinates | ||
|---|---|---|
| Target | Left | Right |
| NA | Lat: −8.68 | Lat: 9.71 |
| A-P: 13.62 | AP: 13.18 | |
| Vert: −3.37 | Ver: −4.58 | |
| Gpi Posterior | Lat: −20.65 | Lat: 22.9 |
| A-P:4.92 | AP: 2.64 | |
| Vert: −5.58 | Vert: −6.58 | |
| Number of Leads in Place | Stimulation YGTSS Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial presentation | None | N/A | 100 |
| Temporary electrode implantation | 12 | none | 0 |
| 3 months after permanent lead implantation | 4 | + 1 | 75 |
| 15 months after permanent lead implantation | 4 | + 2 | 43 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
MacLean, J.A.; Ferman, D.; Chu, J.K.; Liker, M.A.; Sanger, T.D. Transient Complete Resolution of Tourette Syndrome Symptoms Following Personalized Depth Electrode Placement. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1559. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11121559
MacLean JA, Ferman D, Chu JK, Liker MA, Sanger TD. Transient Complete Resolution of Tourette Syndrome Symptoms Following Personalized Depth Electrode Placement. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(12):1559. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11121559
Chicago/Turabian StyleMacLean, Jennifer A., Diana Ferman, Jason K. Chu, Mark A. Liker, and Terence D. Sanger. 2021. "Transient Complete Resolution of Tourette Syndrome Symptoms Following Personalized Depth Electrode Placement" Brain Sciences 11, no. 12: 1559. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11121559
APA StyleMacLean, J. A., Ferman, D., Chu, J. K., Liker, M. A., & Sanger, T. D. (2021). Transient Complete Resolution of Tourette Syndrome Symptoms Following Personalized Depth Electrode Placement. Brain Sciences, 11(12), 1559. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11121559






