Utility of the Intelligibility in Context Scale for Predicting Speech Intelligibility of Children with Cerebral Palsy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.1.1. Children with Cerebral Palsy
2.1.2. Adult Listeners
2.2. Measures
2.2.1. Transcription Intelligibility Scores
2.2.2. Intelligibility in Context Scale Ratings
2.3. Statistical Procedures
3. Results
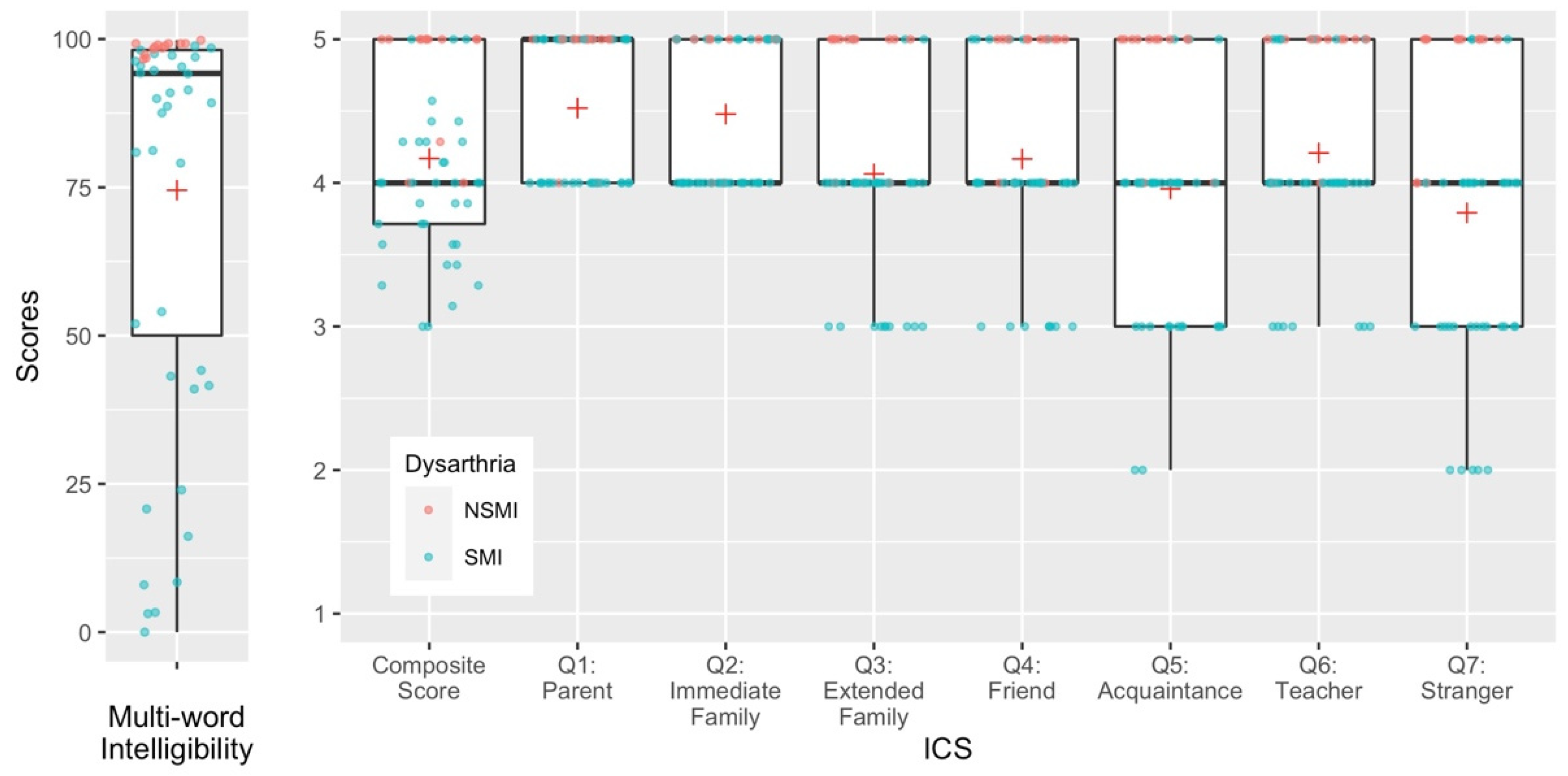
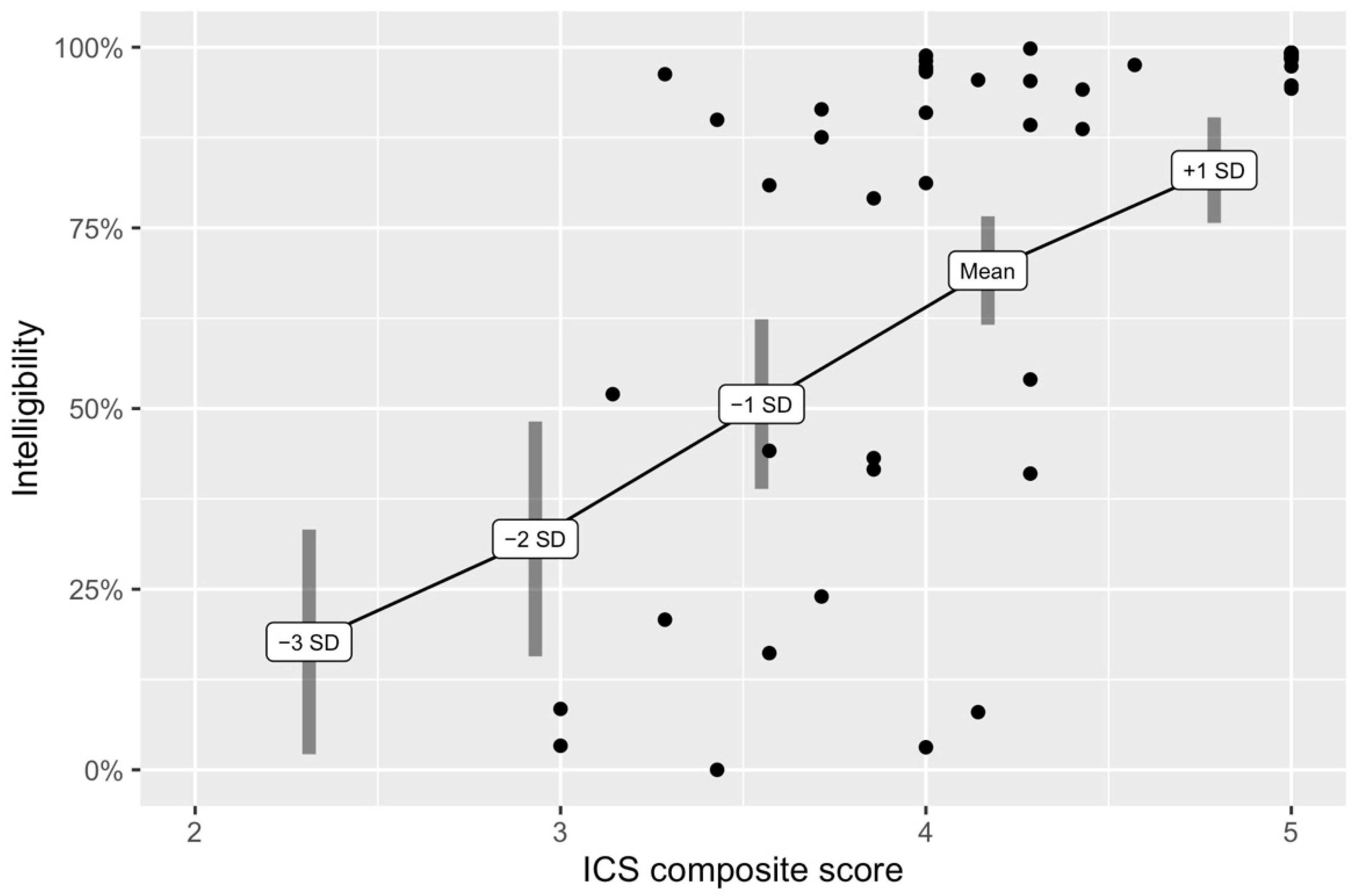
3.1. Research Question 1: How Well Do ICS Composite Scores Predict Transcription Intelligibility Scores?
3.2. Research Question 2: Do Individual Questions from the ICS Differentially Predict Transcription Intelligibility Scores?
3.3. Research Question 3: How Well Do ICS Composite Scores Differentiate between Children with and without Speech Motor Impairment?
4. Discussion
4.1. ICS Composite Scores Predicted Transcription Intelligibility Scores with a Moderate Effect Size
4.2. Individual ICS Items Differentially Predicted Transcription Intelligibility Scores
4.3. ICS Composite Scores below 4 Indicated Higher Likelihood of Having Dysarthria
5. Limitations and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nordberg, A.; Miniscalco, C.; Lohmander, A.; Himmelmann, K. Speech Problems Affect More than One in Two Children with Cerebral Palsy: Swedish Population-Based Study. Acta Paediatr. 2012, 102, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, K.M.; Hustad, K.C. Data-Driven Classification of Dysarthria Profiles in Children with Cerebral Palsy. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. JSLHR 2018, 61, 2837–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, C.; Reilly, S.; Bickerton, M.; Mensah, F.; Turner, S.; Kumaranayagam, D.; Pennington, L.; Reddihough, D.; Morgan, A.T. Speech in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2020, 62, 1374–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braza, M.D.; Sakash, A.; Natzke, P.; Hustad, K.C. Longitudinal Change in Speech Rate and Intelligibility between 5 and 7 Years in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Am. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2019, 28, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hustad, K.C.; Sakash, A.; Broman, A.T.; Rathouz, P.J. Differentiating Typical from Atypical Speech Production in 5-Year-Old Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Comparative Analysis. Am. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2019, 28, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natzke, P.; Sakash, A.; Mahr, T.; Hustad, K.C. Measuring Speech Production Development in Children with Cerebral Palsy between 6 and 8 Years of Age: Relationships among Measures. Lang. Speech Hear. Serv. Sch. 2020, 51, 882–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansel, B.M.; Kent, R.D. Acoustic-Phonetic Contrasts and Intelligibility in the Dysarthria Associated with Mixed Cerebral Palsy. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 1992, 35, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schölderle, T.; Haas, E.; Baumeister, S.; Ziegler, W. Intelligibility, Articulation Rate, Fluency, and Communicative Efficiency in Typically Developing Children. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2021, 64, 2575–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hustad, K.C.; Mahr, T.J.; Natzke, P.; Rathouz, P.J. Speech Development Between 30 and 119 Months in Typical Children I: Intelligibility Growth Curves for Single-Word and Multiword Productions. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hustad, K.C.; Mahr, T.; Natzke, P.E.M.; Rathouz, P.J. Development of Speech Intelligibility between 30 and 47 Months in Typically Developing Children: A Cross-Sectional Study of Growth. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2020, 63, 1675–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hustad, K.C.; Mahr, T.J.; Broman, A.T.; Rathouz, P.J. Longitudinal Growth in Single-Word Intelligibility among Children with Cerebral Palsy from 24 to 96 Months of Age: Effects of Speech-Language Profile Group Membership on Outcomes. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. JSLHR 2020, 63, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hustad, K.C.; Sakash, A.; Natzke, P.E.M.; Broman, A.T.; Rathouz, P.J. Longitudinal Growth in Single Word Intelligibility among Children with Cerebral Palsy from 24 to 96 Months of Age: Predicting Later Outcomes from Early Speech Production. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. JSLHR 2019, 62, 1599–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahr, T.; Rathouz, P.J.; Hustad, K.C. Longitudinal Growth in Intelligibility of Connected Speech from 2 to 8 Years in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Novel Bayesian Approach. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2020, 63, 2880–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tikofsky, R.S.; Tikofsky, R.P. Intelligibility Measures of Dysarthric Speech. J. Speech Hear. Res. 1964, 7, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorkston, K.M.; Beukelman, D.R. A Comparison of Techniques for Measuring Intelligibility of Dysarthric Speech. J. Commun. Disord. 1978, 11, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjaden, K.K.; Liss, J.M. The Role of Listener Familiarity in the Perception of Dysarthric Speech. Clin. Linguist. Phon. 1995, 9, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansford, K.L.; Liss, J.M. Vowel Acoustics in Dysarthria: Mapping to Perception. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2014, 57, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykstra, A.D.; Hakel, M.E.; Adams, S.G. Application of the ICF in Reduced Speech Intelligibility in Dysarthria. Semin. Speech Lang. 2007, 28, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakash, A.; Mahr, T.; Hustad, K.C. Validity of Parent Ratings of Speech Intelligibility for Children with Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Neurorehabilit. 2021, 24, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLeod, S. Intelligibility in Context Scale: Cross-Linguistic Use, Validity, and Reliability. Speech Lang. Hear. 2020, 23, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McLeod, S.; Crowe, K.; Shahaeian, A. Intelligibility in Context Scale: Normative and Validation Data for English-Speaking Preschoolers. Lang. Speech Hear. Serv. Sch. 2015, 46, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miller, N. Measuring up to Speech Intelligibility: Measuring up to Speech Intelligibility. Int. J. Lang. Commun. Disord. 2013, 48, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veenhuis, S.J.G.; Os, N.J.H.; Gerven, M.H.J.C.; Haaften, L.; Mulder, E.H.; Weemaes, C.M.R.; Willemsen, M.A.A.P. Dysarthria in Children and Adults with Ataxia Telangiectasia. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2021, 63, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, K.Y.M.; To, C.K.S.; Mcleod, S. Validation of the Intelligibility in Context Scale as a Screening Tool for Preschoolers in Hong Kong. Clin. Linguist. Phon. 2014, 28, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopf, S.C.; McLeod, S.; McDonagh, S.H. Validation of the Intelligibility in Context Scale for School Students in Fiji. Clin. Linguist. Phon. 2017, 31, 487–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, S.; Rietz, C.; Stenneken, P. The German Intelligibility in Context Scale (ICS-G): Reliability and Validity Evidence: German ICS-G: Reliability and Validity Evidence. Int. J. Lang. Commun. Disord. 2017, 52, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzalunga, S.; Salerni, N.; Limarzi, S.; Fassina, S.; Schindler, A. Can You Understand Your Child? Reliability and Validity of a Parent Questionnaire: The Intelligibility in Context Scale: Italian. Folia Phoniatr. Logop. 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y. Validation of the Intelligibility in Context Scale for Korean-Speaking Pre-School Children. Int. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2019, 21, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, S. Intelligibility in Context Scale: A Parent-Report Screening Tool Translated into 60 Languages. J. Clin. Pract. Speech-Lang. Pathol. 2015, 17, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Lagerberg, T.B.; Anrep-Nordin, E.; Emanuelsson, H.; Strömbergsson, S. Parent Rating of Intelligibility: A Discussion of the Construct Validity of the Intelligibility in Context Scale (ICS) and Normative Data of the Swedish Version of the ICS. Int. J. Lang. Commun. Disord. 2021, 56, 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinabad, H.H.; Washington, K.N.; Boyce, S.E.; Silbert, N.; Kummer, A.W. Assessment of Intelligibility in Children with Velopharyngeal Insufficiency: The Relationship between Intelligibility in Context Scale and Experimental Measures. Folia Phoniatr. Logop. 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodge, M.; Gotzke, C.L. Criterion-Related Validity of the Test of Children’s Speech Sentence Intelligibility Measure for Children with Cerebral Palsy and Dysarthria. Int. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2014, 16, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hustad, K.C.; Gorton, K.; Lee, J. Classification of Speech and Language Profiles in 4-Year Old Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Prospective Preliminary Study. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2010, 53, 1496–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamer, M.; Lemon, J.; Fellows, I.; Singh, P. Irr: Various Coefficients of Interrater Reliability and Agreement; 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cribari-Neto, F.; Zeileis, A. Beta Regression in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021.
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R; RStudio, PBC.: Boston, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lenth, R.V. Emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, Aka Least-Squares Means; 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zeileis, A.; Hothorn, T. Diagnostic Checking in Regression Relationships. R News 2002, 2, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Harrell, F.E. Rms: Regression Modeling Strategies; 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Cohen, P.; Chen, S. How Big Is a Big Odds Ratio? Interpreting the Magnitudes of Odds Ratios in Epidemiological Studies. Commun. Stat.-Simul. Comput. 2010, 39, 860–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, E.C.E.; To, C.K.S. Revisiting the Cutoff Criteria of Intelligibility in Context Scale–Traditional Chinese. Lang. Speech Hear. Serv. Sch. 2019, 50, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, K.M.; Hustad, K.C. Acoustic Predictors of Pediatric Dysarthria in Cerebral Palsy. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2018, 61, 462–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yorkston, K.M.; Beukelman, D.R.; Strand, E.A.; Bell, K.R. Management of Motor Speech Disorders in Children and Adults, 2nd ed.; Pro-Ed: Austin, TX, USA, 1999; ISBN 978-0-89079-784-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hodge, M.; Gotzke, C.L. Preliminary Results of an Intelligibility Measure for English-Speaking Children with Cleft Palate. Cleft Palate. Craniofac. J. 2007, 44, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| NSMI (n = 13) | SMI (n = 35) | Total (n = 48) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male:female ratio | 9:4 | 19:16 | 28:20 |
| Age in years: Mean (SD) | 13.01 (1.92) | 12.74 (1.97) | 12.82 (1.94) |
| Cerebral palsy type | |||
| Spastic | 13 | 26 | 39 |
| Diplegia | 4 | 6 | 10 |
| Hemiplegia (left) | 6 | 5 | 11 |
| Hemiplegia (right) | 3 | 9 | 12 |
| Triplegia | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Quadriplegia | 0 | 4 | 4 |
| Not reported | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Ataxic | 0 | 4 | 4 |
| Hypotonic | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Mixed | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Unknown | 0 | 3 | 3 |
| Dyskinetic | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| GMFCS | |||
| I | 12 | 12 | 24 |
| II | 1 | 15 | 16 |
| III | 0 | 4 | 4 |
| IV | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| V | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| MACS | |||
| I | 6 | 10 | 16 |
| II | 7 | 16 | 23 |
| III | 0 | 8 | 8 |
| IV | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| V | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 95% Confidence Interval | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICS Score | Intelligibility Score | Standard Error | Lower Boundary | Upper Boundary | |
| −3 SD | 2.31 | 17.71% | 0.08 | 2.16% | 33.26% |
| −2 SD | 2.93 | 31.96% | 0.08 | 15.70% | 48.21% |
| −1 SD | 3.55 | 50.61% | 0.06 | 38.87% | 62.35% |
| Mean | 4.17 | 69.10% | 0.04 | 61.59% | 76.61% |
| +1 SD | 4.79 | 82.99% | 0.04 | 75.69% | 90.30% |
| ICS Items | AIC | |
|---|---|---|
| Q7: Stranger | −84.04 | 0.53 |
| Q5: Acquaintance | −75.72 | 0.43 |
| Q4: Friend | −74.63 | 0.41 |
| Q3: Extended Family | −74.36 | 0.41 |
| Q6: Teacher | −61.90 | 0.16 |
| Q2: Immediate Family | −60.78 | 0.13 |
| Q1: Parent | −59.34 | 0.09 |
| ICS Items | Chi Square | p-Value | AIC Difference | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q7 (Stranger) + Q6 (Teacher) | 2.72 | 0.10 | 0.72 | 0.02 |
| Q7 (Stranger) + Q1 (Parent) | 1.07 | 0.30 | −0.93 | 0.01 |
| Q7 (Stranger) + Q2 (Immediate Family) | 0.94 | 0.33 | −1.06 | 0.01 |
| Q7 (Stranger) + Q4 (Extended Family | 0.64 | 0.43 | −1.36 | 0.01 |
| Q7 (Stranger) + Q5 (Friend) | 0.09 | 0.77 | −1.91 | 0.00 |
| Q7 (Stranger) + Q3 (Extended Family) | 0.00 | 0.95 | −2.00 | 0.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soriano, J.U.; Olivieri, A.; Hustad, K.C. Utility of the Intelligibility in Context Scale for Predicting Speech Intelligibility of Children with Cerebral Palsy. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1540. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111540
Soriano JU, Olivieri A, Hustad KC. Utility of the Intelligibility in Context Scale for Predicting Speech Intelligibility of Children with Cerebral Palsy. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(11):1540. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111540
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoriano, Jennifer U., Abby Olivieri, and Katherine C. Hustad. 2021. "Utility of the Intelligibility in Context Scale for Predicting Speech Intelligibility of Children with Cerebral Palsy" Brain Sciences 11, no. 11: 1540. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111540
APA StyleSoriano, J. U., Olivieri, A., & Hustad, K. C. (2021). Utility of the Intelligibility in Context Scale for Predicting Speech Intelligibility of Children with Cerebral Palsy. Brain Sciences, 11(11), 1540. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111540







