Prism Adaptation and Optokinetic Stimulation Comparison in the Rehabilitation of Unilateral Spatial Neglect
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Neuropsychological Tests
2.2.1. Letter Cancellation
2.2.2. Star Cancellation
2.2.3. Copy Drawing
2.2.4. Sentence Reading
2.2.5. Comb and Razor
2.2.6. Line Bisection
2.2.7. Clock Drawing
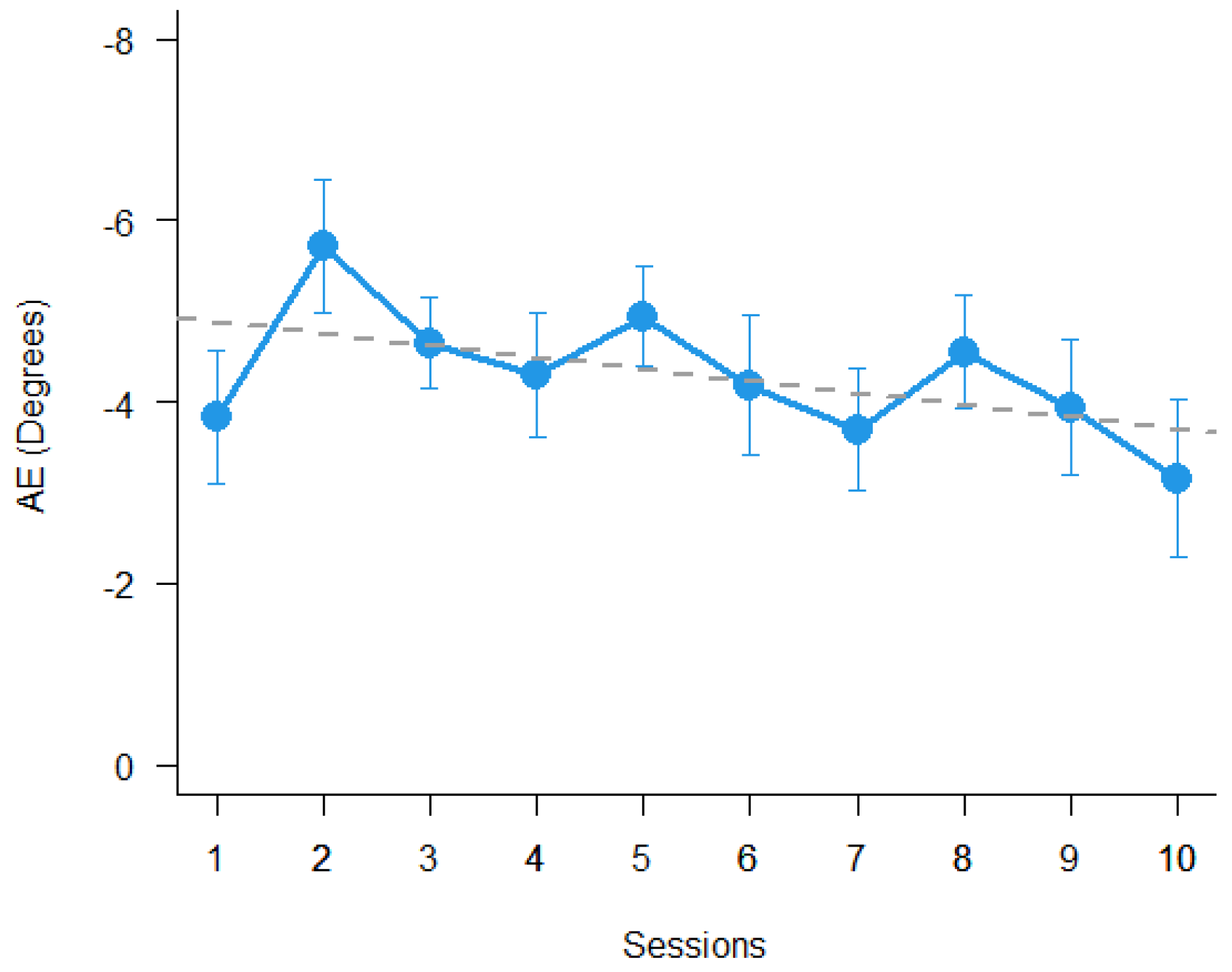
2.3. Prism Adaptation
- (1)
- OLP pre-adaptation. The participant was asked to perform six pointing movements toward the central target from the sternum up to the transparent panel, without prism glasses;
- (2)
- Adaptation. The participant performed the pointing movements with prism glasses, viewing his or her index finger emerging from the examiner’s side of the box for a total of 90 trials;
- (3)
- OLP post-adaptation. Same as point (1) above.
2.4. Optokinetic Stimulation
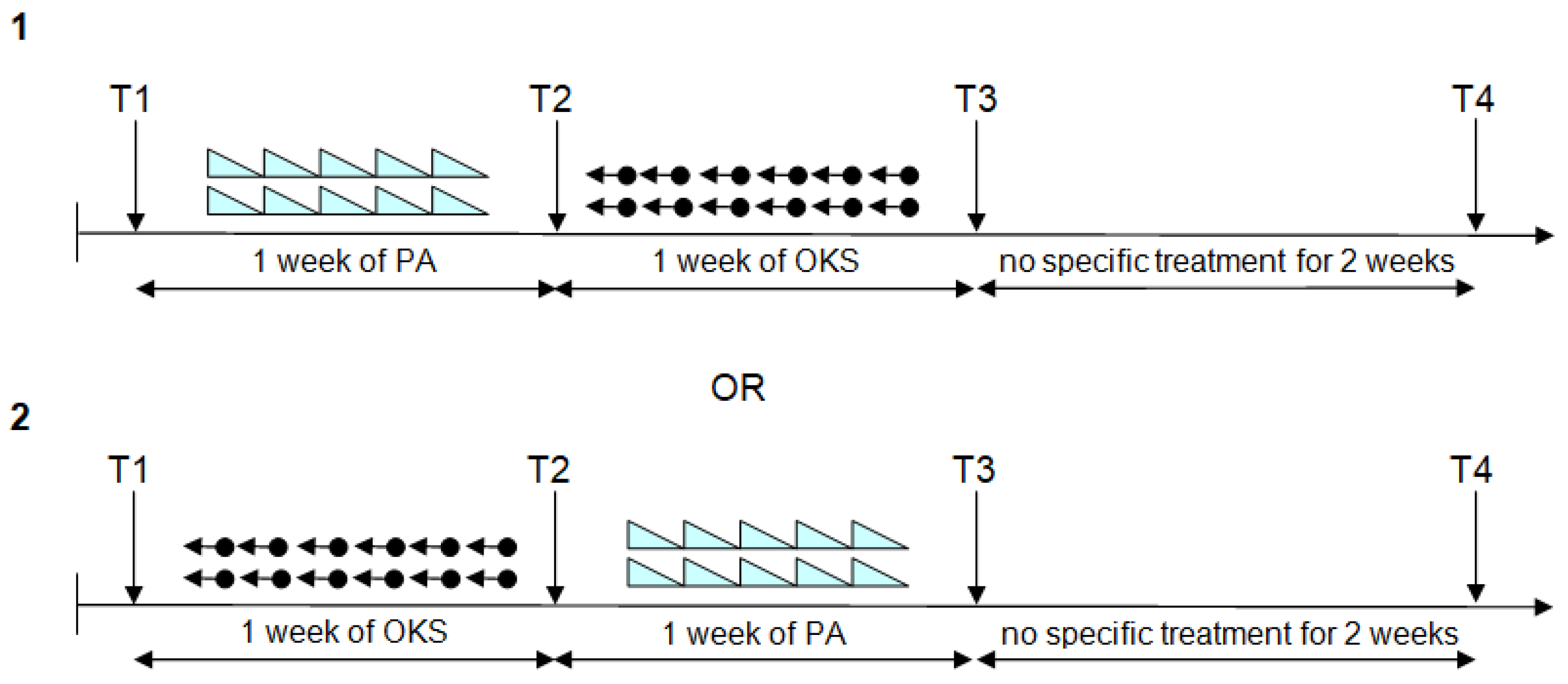
2.5. Procedure
2.6. Statistical Methods
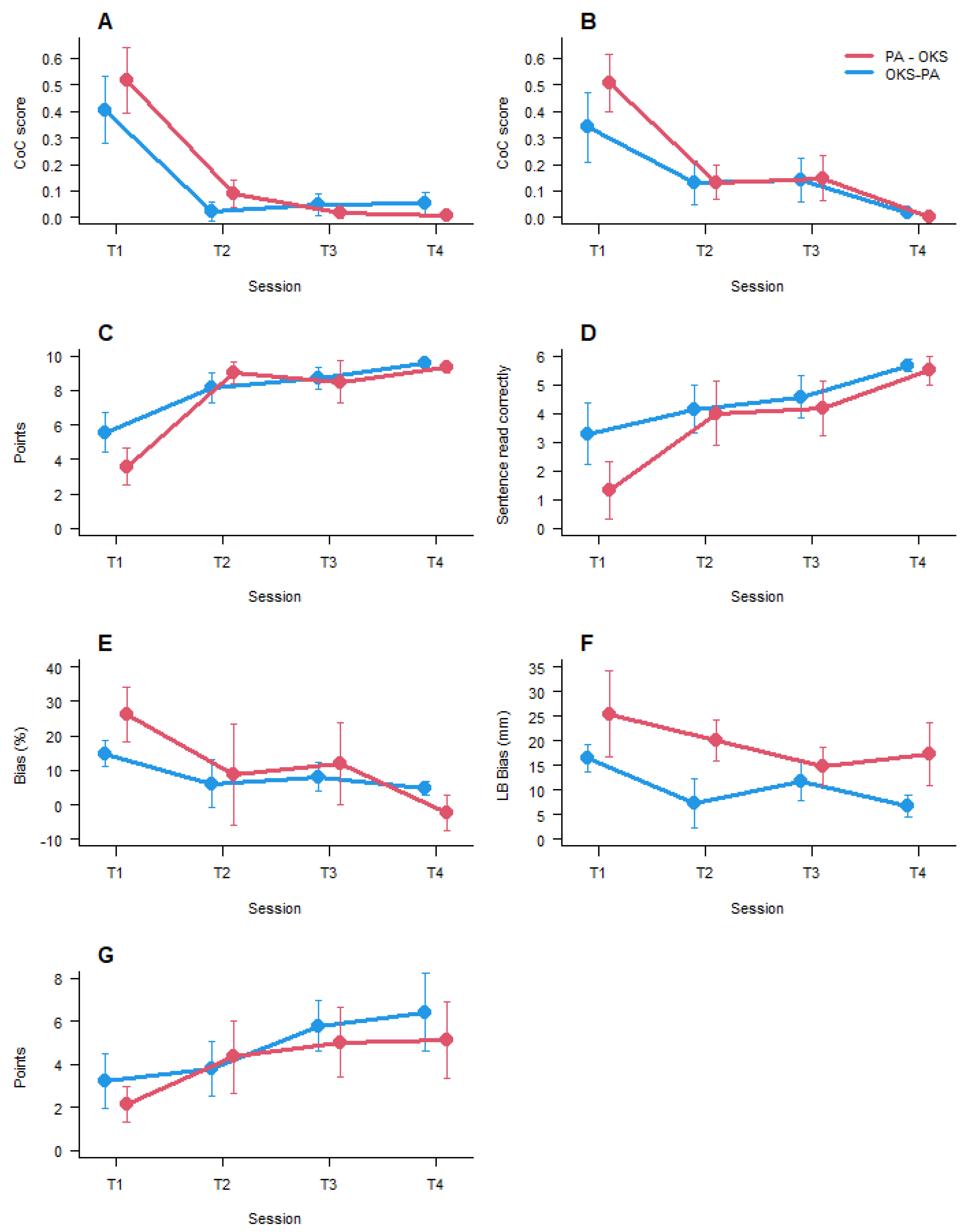
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cubelli, R. Definition: Spatial neglect. Cortex 2017, 92, 320–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, M.S.; Kilbride, C.; Reynolds, F.A. What are the functional outcomes of right hemisphere stroke patients with or without hemi-inattention complications? A critical narrative review and suggestions for further research. Disabil. Rehabil. 2015, 38, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bosma, M.; Nijboer, T.C.; Caljouw, M.A.; Achterberg, W.P. Impact of visuospatial neglect post-stroke on daily activities, participation and informal caregiver burden: A systematic review. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 63, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luauté, J.; Halligan, P.; Rode, G.; Rossetti, Y.; Boisson, D. Visuo-spatial neglect: A systematic review of current interventions and their effectiveness. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2006, 30, 961–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccolotti, P.; Cantagallo, A.; De Luca, M.; Guariglia, C.; Serino, A.; Trojano, L. Selective and integrated rehabilitation programs for disturbances of visual/spatial attention and executive function after brain damage: A neuropsychological evidence-based review. Eur J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2011, 47, 123–147. [Google Scholar]
- Azouvi, P.; Jacquin-Courtois, S.; Luauté, J. Rehabilitation of unilateral neglect: Evidence-based medicine. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 60, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evald, L.; Wilms, I.L.; Nordfang, M. Treatment of spatial neglect in clinical practice: A nationwide survey. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2020, 141, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meidian, A.C.; Wahyuddin; Amimoto, K. Rehabilitation interventions of unilateral spatial neglect based on the functional outcome measure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuropsychol. Rehabil. 2020, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeonwuka, C.; Roos, R.; Ntsiea, V. Current trends in the treatment of patients with post-stroke unilateral spatial neglect: A scoping review. Disabil. Rehabil. 2020, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.P.; Hanly, J.; Fahey, P.; Fong, S.S.; Bye, R. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Rehabilitative Interventions for Unilateral Spatial Neglect and Hemianopia Poststroke from 2006 through 2016. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 100, 956–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavaszi, I.; Nagy, A.S.; Szabo, G.; Fazekas, G. Neglect syndrome in post-stroke conditions: Assessment and treatment (scoping review). Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 2020, 44, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luauté, J.; Villeneuve, L.; Roux, A.; Nash, S.; Bar, J.-Y.; Chabanat, E.; Cotton, F.; Ciancia, S.; Sancho, P.-O.; Hovantruc, P.; et al. Adding methylphenidate to prism-adaptation improves outcome in neglect patients. A randomized clinical trial. Cortex 2018, 106, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgut, N.; Miranda, M.; Kastrup, A.; Eling, P.; Hildebrandt, H. tDCS combined with optokinetic drift reduces egocentric neglect in severely impaired post-acute patients. Neuropsychol. Rehabil. 2016, 28, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerkhoff, G. Rehabilitation of Visuospatial Cognition and Visual Exploration in Neglect: A Cross-over Study. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 1998, 12, 27–40. [Google Scholar]
- Schröder, A.; Wist, E.R.; Hömberg, V. TENS and optokinetic stimulation in neglect therapy after cerebrovascular accident: A randomized controlled study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2008, 15, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champod, A.S.; Frank, R.C.; Taylor, K.; Eskes, G.A. The effects of prism adaptation on daily life activities in patients with visuospatial neglect: A systematic review. Neuropsychol. Rehabil. 2018, 28, 491–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, V.; Meneghello, F.; Mattioli, F.; Ladavas, E. Mechanisms Underlying Visuo-Spatial Amelioration of Neglect After Prism Adaptation. Cortex 2004, 40, 155–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferber, S.; Danckert, J.; Joanisse, M.; Goltz, H.C.; Goodale, M.A. Eye movements tell only half the story. Neurology 2003, 60, 1826–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saevarsson, S.; Kristjánsson, Á. A note on Striemer and Danckert’s theory of prism adaptation in unilateral neglect. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serino, A.; Angeli, V.; Frassinetti, F.; Làdavas, E. Mechanisms underlying neglect recovery after prism adaptation. Neuropsychologia 2006, 44, 1068–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraishi, H.; Yamakawa, Y.; Itou, A.; Muraki, T.; Asada, T. Long-term effects of prism adaptation on chronic neglect after stroke. NeuroRehabil. 2008, 23, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priftis, K.; Passarini, L.; Pilosio, C.; Meneghello, F.; Pitteri, M. Visual scanning training, limb activation treatment, and prism adaptation for rehabilitating left neglect: Who is the winner? Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dijkerman, H.; Webeling, M.; ter Wal, J.; Groet, E.; van Zandvoort, M. A long-lasting improvement of somatosensory function after prism adaptation, a case study. Neuropsychologia 2004, 42, 1697–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maravita, A.; McNeil, J.; Malhotra, P.; Greenwood, R.; Husain, M.; Driver, J. Prism adaptation can improve contralesional tactile perception in neglect. Neurology 2003, 60, 1829–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchin, A.; Sartori, E.; Luisetti, C.; De Galeazzi, A.; Beschin, N. Effect of prism adaptation on neglect hemianesthesia. Cortex 2019, 113, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnè, A.; Rossetti, Y.; Toniolo, S.; Làdavas, E. Ameliorating neglect with prism adaptation: Visuo-manual and visuo-verbal measures. Neuropsychologia 2002, 40, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquin-Courtois, S.; Rode, G.; Pisella, L.; Boisson, D.; Rossetti, Y. Wheel-chair driving improvement following visuo-manual prism adaptation. Cortex 2008, 44, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Amimoto, K. Generalization of Prism Adaptation for Wheelchair Driving Task in Patients with Unilateral Spatial Neglect. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2010, 91, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh-Park, M.; Hung, C.; Chen, P.; Barrett, A. Severity of Spatial Neglect during Acute Inpatient Rehabilitation Predicts Community Mobility after Stroke. PM&R 2014, 6, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frassinetti, F.; Angeli, V.; Meneghello, F.; Avanzi, S.; Ladavas, E. Long-lasting amelioration of visuospatial neglect by prism adaptation. Brain 2002, 125, 608–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goedert, K.M.; Chen, P.; Boston, R.C.; Foundas, A.L.; Barrett, A. Presence of Motor-Intentional Aiming Deficit Predicts Functional Improvement of Spatial Neglect with Prism Adaptation. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2014, 28, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brink, A.T.; Visser-Meily, J.M.A.; Schut, M.J.; Kouwenhoven, M.; Eijsackers, A.L.H.; Nijboer, T.C.W. Prism Adaptation in Rehabilitation? No Additional Effects of Prism Adaptation on Neglect Recovery in the Subacute Phase Poststroke: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2017, 31, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turton, A.J.; O’Leary, K.; Gabb, J.; Woodward, R.; Gilchrist, I.D. A single blinded randomised controlled pilot trial of prism adaptation for improving self-care in stroke patients with neglect. Neuropsychol. Rehabil. 2010, 20, 180–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rode, G.; Lacour, S.; Jacquin-Courtois, S.; Pisella, L.; Michel, C.; Revol, P.; Alahyane, N.; Luauté, J.; Gallagher, S.; Halligan, P.; et al. Long-term sensorimotor and therapeutical effects of a mild regime of prism adaptation in spatial neglect. A double-blind RCT essay. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2015, 58, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijboer, T.; Kitazawa, S.; Rossetti, Y. Prism adaptation: Reflections and future shifts for circular translational research? Cortex 2020, 126, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Wang, J.; Yi, W.; Yin, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, J. Effects of Prism Adaptation on Unilateral Neglect After Stroke: An Updated Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 100, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Chen, S. Effects of Prism Adaptation for Unilateral Spatial Neglect After Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 100, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkhoff, G.; Keller, I.; Ritter, V.; Marquardt, C. Repetitive optokinetic stimulation induces lasting recovery from visual neglect. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2006, 24, 357–369. [Google Scholar]
- Kerkhoff, G.; Keller, I.; Artinger, F.; Hildebrandt, H.; Marquardt, C.; Reinhart, S.; Ziegler, W. Recovery from auditory and visual neglect after optokinetic stimulation with pursuit eye movements—Transient modulation and enduring treatment effects. Neuropsychologia 2012, 50, 1164–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkhoff, G.; Schenk, T. Rehabilitation of neglect: An update. Neuropsychologia 2012, 50, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daini, R.; Albonico, A.; Malaspina, M.; Martelli, M.; Primativo, S.; Arduino, L.S. Dissociation in Optokinetic Stimulation Sensitivity between Omission and Substitution Reading Errors in Neglect Dyslexia. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Machner, B.; Könemund, I.; Sprenger, A.; Von Der Gablentz, J.; Helmchen, C. Randomized Controlled Trial on Hemifield Eye Patching and Optokinetic Stimulation in Acute Spatial Neglect. Stroke 2014, 45, 2465–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Redding, G.M.; Wallace, B. Prism adaptation and unilateral neglect: Review and analysis. Neuropsychologia 2006, 44, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchin, A.; Vallar, G.; Daini, R. The Brentano Illusion Test (BRIT): An implicit task of perceptual processing for the assessment of visual field defects in neglect patients. Neuropsychol. Rehabil. 2021, 31, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rorden, C.; Karnath, H.-O.; Bonilha, L. Improving Lesion-Symptom Mapping. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2007, 19, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rorden, C.; Bonilha, L.; Fridriksson, J.; Bender, B.; Karnath, H.-O. Age-specific CT and MRI templates for spatial normalization. NeuroImage 2012, 61, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazoyera, N.; Landeau, B.; Papathanassiou, D.; Crivello, F.; Etard, O.; Delcroix, N.; Tzourio-Mazoyer, N.; Joliot, M. Automated Anatomical Labeling of Activations in SPM Using a Macroscopic Anatomical Parcellation of the MNI MRI Single-Subject Brain. NeuroImage 2002, 15, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facchin, A.; Bultitude, J.H.; Mornati, G.; Peverelli, M.; Daini, R. A comparison of prism adaptation with terminal versus concurrent exposure on sensorimotor changes and spatial neglect. Neuropsychol. Rehabil. 2020, 30, 613–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folstein, M.F.; Folstein, S.E.; McHugh, P.R. “Mini-mental state”: A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1975, 12, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Measso, G.; Cavarzeran, F.; Zappalà, G.; Lebowitz, B.D.; Crook, T.H.; Pirozzolo, F.J.; Amaducci, L.A.; Massari, D.C.; Grigoletto, F. The mini-mental state examination: Normative study of an Italian random sample. Dev. Neuropsychol. 1993, 9, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisiach, E.; Vallar, G.; Perani, D.; Papagno, C.; Berti, A. Unawareness of disease following lesions of the right hemisphere: Anosognosia for hemiplegia and anosognosia for hemianopia. Neuropsychologia 1986, 24, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rode, G.; Fourtassi, M.; Pagliari, C.; Pisella, L.; Rossetti, Y. Complexity vs. unity in unilateral spatial neglect. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 173, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diller, L.; Weinberg, J. Hemi-Inattention in Rehabilitation: The Evolution of a Rational Remediation Program; Raven Press: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Vallar, G.; Rusconi, M.L.; Fontana, S.; Musicco, M. Tre test di esplorazione visuo-spaziale: Taratura su 212 soggetti normali. Arch. Psicol. Neurol. Psichiatr. 1994, 4, 827–841. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, B.; Cockburn, J.; Halligan, P. Behavioural Inattention Test; Thames Valley Test Company: London, UK, 1987; ISBN 0951432222. [Google Scholar]
- Spinazzola, L.; Pagliari, C.; Beschin, N. BIT—Behavioural Inattention Test; Italian adaptation manual; Giunti O.S.: Firenze, Italy, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rorden, C.; Karnath, H.-O. A simple measure of neglect severity. Neuropsychologia 2010, 48, 2758–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gainotti, G.; Messerli, P.; Tissot, R. Drawing disabilities and left and right unilateral retrorolandic hemispheric lesions. Encephale 1972, 61, 245–264. [Google Scholar]
- Mancini, F.; Bricolo, E.; Mattioli, F.C.; Vallar, G. Visuo-Haptic Interactions in Unilateral Spatial Neglect: The Cross Modal Judd Illusion. Front. Psychol. 2011, 2, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pizzamiglio, L.; Antonucci, G.; Judica, A.; Montenero, P.; Razzano, C.; Zoccolotti, P. Cognitive rehabilitation of the hemineglect disorder in chronic patients with unilateral right brain damage. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 1992, 14, 901–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caramazza, A.; Hillis, A.E. Where do semantic errors come from? Cortex 1990, 26, 95–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, R.D.; Brodie, E.E.; Beschin, N.; Robertson, I.H. Improving the Clinical Diagnosis of Personal Neglect: A Reformulated Comb and Razor Test. Cortex 2000, 36, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halligan, P.W.; Marshall, J.C. How Long is a Piece of String? A Study of Line Bisection in a Case of Visual Neglect. Cortex 1988, 24, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondini, S.; Mapelli, D.; Vestri, A.; Bisiacchi, P.S. Esame Neuropsicologico Breve; Raffaello Cortina Ed.: Milano, Italy, 2003; p. 160. [Google Scholar]
- Goedert, K.M.; Boston, R.C.; Barrett, A.M. Advancing the Science of Spatial Neglect Rehabilitation: An Improved Statistical Approach with Mixed Linear Modeling. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goedert, K.M.; Chen, P.; Foundas, A.L.; Barrett, A.M. Frontal lesions predict response to prism adaptation treatment in spatial neglect: A randomised controlled study. Neuropsychol. Rehabil. 2020, 30, 32–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, Vienna, R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Available online: http://www.R-project.org (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- von der Gablentz, J.; Könemund, I.; Sprenger, A.; Heide, W.; Heldmann, M.; Helmchen, C.; Machner, B. Brain activations during optokinetic stimulation in acute right-hemisphere stroke patients and hemispatial neglect: An fMRI study. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2019, 33, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thimm, M.; Fink, G.R.; Küst, J.; Karbe, H.; Willmes, K.; Sturm, W. Recovery from hemineglect: Differential neurobiological effects of optokinetic stimulation and alertness training. Cortex 2009, 45, 850–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerkhoff, G.; Bucher, L.; Brasse, M.; Leonhart, E.; Holzgraefe, M.; Völzke, V.; Keller, I.; Reinhart, S. Smooth pursuit “bedside” training reduces disability and unawareness during the activities of daily living in neglect: A randomized controlled trial. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2014, 28, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konen, C.S.; Kleiser, R.; Seitz, R.J.; Bremmer, F. An fMRI study of optokinetic nystagmus and smooth-pursuit eye movements in humans. Exp. Brain Res. 2005, 165, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crottaz-Herbette, S.; Fornari, E.; Notter, M.P.; Bindschaedler, C.; Manzoni, L.; Clarke, S. Reshaping the brain after stroke: The effect of prismatic adaptation in patients with right brain damage. Neuropsychologia 2017, 104, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, S.; Crottaz-Herbette, S. Modulation of visual attention by prismatic adaptation. Neuropsychologia 2016, 92, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saj, A.; Cojan, Y.; Vocat, R.; Luauté, J.; Vuilleumier, P. Prism adaptation enhances activity of intact fronto-parietal areas in both hemispheres in neglect patients. Cortex 2013, 49, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luauté, J.; Schwartz, S.; Rossetti, Y.; Spiridon, M.; Rode, G.; Boisson, D.; Vuilleumier, P. Dynamic Changes in Brain Activity during Prism Adaptation. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bisiach, E.; Geminiani, G.; Berti, A.; Rusconi, M.L. Perceptual and premotor factors of unilateral neglect. Neurology 1990, 40, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saevarsson, S. Prism adaptation theory in unilateral neglect: Motor and perceptual components. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saevarsson, S.; Eger, S.; Gutierrez-Herrera, M. Neglected premotor neglect. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Striemer, C.; Danckert, J. Dissociating perceptual and motor effects of prism adaptation in neglect. Neuroreport 2010, 21, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gossmann, A.; Kastrup, A.; Kerkhoff, G.; López-Herrero, C.; Hildebrandt, H. Prism Adaptation Improves Ego-Centered but Not Allocentric Neglect in Early Rehabilitation Patients. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2013, 27, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, G.W.; Watelet, A.; Riddoch, M.J. Long-term effects of prism adaptation in chronic visual neglect: A single case study. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 2006, 23, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijboer, T.C.; Nys, G.M.; van der Smagt, M.J.; van der Stigchel, S.; Dijkerman, H.C. Repetitive long-term prism adaptation permanently improves the detection of contralesional visual stimuli in a patient with chronic neglect. Cortex 2011, 47, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Shea, J.; Revol, P.; Cousijn, H.; Near, J.; Petitet, P.; Jacquin-Courtois, S.; Johansen-Berg, H.; Rode, G.; Rossetti, Y. Induced sensorimotor cortex plasticity remediates chronic treatment-resistant visual neglect. eLife 2017, 6, e26602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luauté, J.; Halligan, P.; Rode, G.; Jacquin-Courtois, S.; Boisson, D. Prism adaptation first among equals in alleviating left neglect: A review. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2006, 24, 409–418. [Google Scholar]
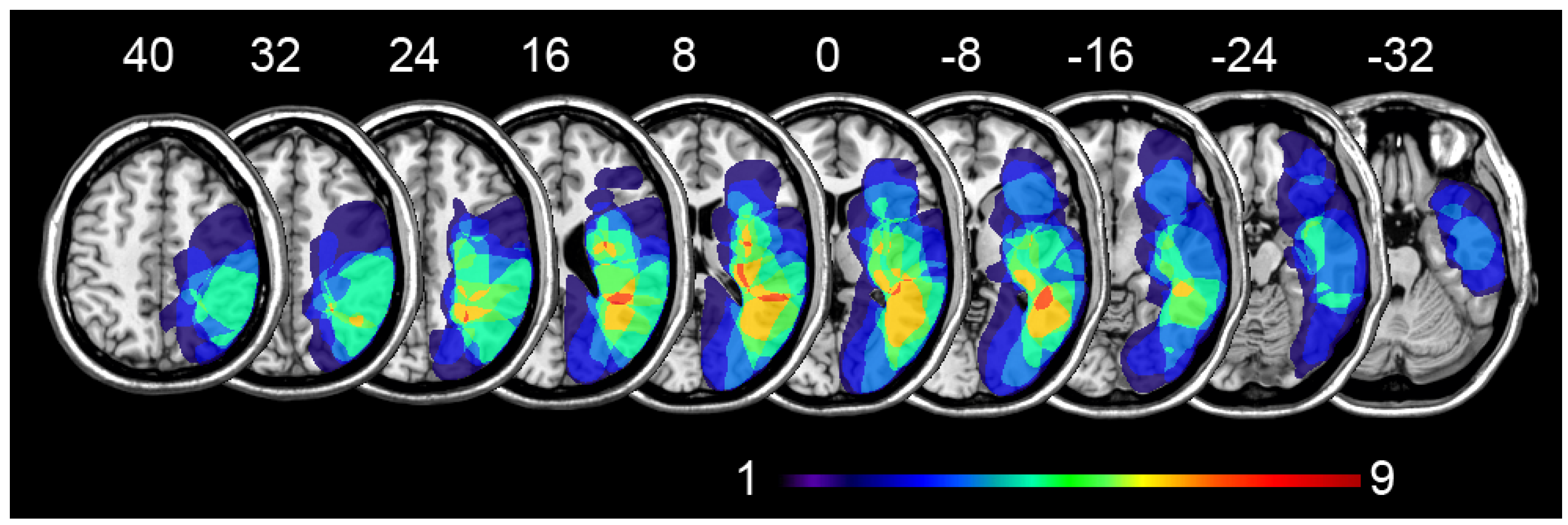
| Pt. Id | Age | Edu | Sex | Stroke Dist. | Lesion | MMSE | Motor Deficits | Somat. Deficits | VFD | BHT SIE80 | BHT SIE160 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt. 1 | 82 | 5 | F | 55 | I | 22 | + | + | + | 25.6 * | 58.8 *,# |
| Pt. 2 | 74 | 8 | M | 23 | I | 20.2 | + | − | − | 13 * | 27 *,# |
| Pt. 3 | 85 | 8 | M | 18 | I | 19.2 | + | + | + | 19 * | 66.6 *,# |
| Pt. 4 | 78 | 5 | F | 18 | H | 26.0 | + | + | − | 27.2 * | 42 *,# |
| Pt. 5 | 73 | 10 | M | 21 | H | 27.9 | − | − | + | 26 * | 21.4 *,# |
| Pt. 6 | 67 | 5 | F | 24 | I | 24.5 | + | + | − | −7.8 * | −6 |
| Pt. 7 | 75 | 8 | M | 18 | I | 24.2 | − | + | + | −4.8 | −1.2 |
| Pt. 8 | 60 | 11 | M | 12 | I | 25.5 | + | + | + | 32.2 * | 30.8 *,# |
| Pt. 9 | 71 | 13 | M | 20 | I | 19.7 | + | + | + | 4.8 | 0.6 |
| Pt. 10 | 71 | 11 | M | 29 | I | 19.4 | + | + | + | 2.8 | 2 |
| Pt. 11 | 77 | 5 | F | 22 | H | 18.7 | + | + | + | 6.4 | 24.2 * |
| Pt. 12 | 68 | 8 | M | 26 | I | 23 | + | − | + | 1.6 | −3.6 |
| Pt. 13 | 58 | 8 | M | 34 | I | 23 | − | + | − | 15.6 * | 27.4 *,# |
| PT. Id | Letter Cancellation | Star Cancellation | Copy Drawing | Sentence Reading | Comb and Razor | Line Bisection | Clock Drawing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt. 1 | 12 * | 5 * | 1.5 * | 0 * | 8 | 12.8 * | 2 * |
| Pt. 2 | 48 * | 24 * | 6.5 * | 0 * | 14.3 * | 21.4 * | 0 * |
| Pt. 3 | 36 * | −2 | 9.5 | 5 * | 15 * | 13.1 * | 1 * |
| Pt. 4 | 26 * | 16 * | 4.5 * | 2 * | 13.1 * | 11.6 * | 2 * |
| Pt. 5 | 11 * | 10 * | 5 * | 6 | 5.3 | 23.1 * | 7.5 |
| Pt. 6 | 11 * | 2 | 8.5 * | 5 * | 17.7 * | 9.9 * | 1 * |
| Pt. 7 | 28 * | 23 * | 1 * | 6 | 60 * | 14 * | 1 * |
| Pt. 8 | 30 * | 13 * | 8 * | 0 * | 12.9 * | 15.4 * | 8.5 |
| Pt. 9 | 25 * | 1 | 2 * | 6 | 33.3 * | 6.3 * | 0 * |
| Pt. 10 | 10 * | 14 * | 1.5 * | 0 * | 23.8 * | 67.3 * | 2 * |
| Pt. 11 | 23 * | 17 * | 2 * | 0 * | 3.9 * | 19.3 * | 1.5 * |
| Pt. 12 | 30 * | 20 * | 6.5 * | 0 * | 37.9 * | 25.5 * | 6 |
| Pt. 13 | 12 * | 18 * | 4 * | 1 * | 16 * | 28 * | 3 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Facchin, A.; Figliano, G.; Daini, R. Prism Adaptation and Optokinetic Stimulation Comparison in the Rehabilitation of Unilateral Spatial Neglect. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111488
Facchin A, Figliano G, Daini R. Prism Adaptation and Optokinetic Stimulation Comparison in the Rehabilitation of Unilateral Spatial Neglect. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(11):1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111488
Chicago/Turabian StyleFacchin, Alessio, Giusi Figliano, and Roberta Daini. 2021. "Prism Adaptation and Optokinetic Stimulation Comparison in the Rehabilitation of Unilateral Spatial Neglect" Brain Sciences 11, no. 11: 1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111488
APA StyleFacchin, A., Figliano, G., & Daini, R. (2021). Prism Adaptation and Optokinetic Stimulation Comparison in the Rehabilitation of Unilateral Spatial Neglect. Brain Sciences, 11(11), 1488. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111488







