The Critical Role of the Boundary Layer Thickness for the Initiation of Aeolian Sediment Transport
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Conceptual Framework of Aeolian Sediment Transport Initiation
2.1. Torque Balance Criterion Associated with a Turbulent Fluctuation Event
2.2. Energy Criterion Associated with a Turbulent Fluctuation Event
2.3. Torque Balance Criterion Associated with the Mean Turbulent Flow
2.4. The Intermediate Regime between Mean Flow Entrainment and Fluctuation-Induced Entrainment
2.5. The Time Scale Ratio
2.6. The Maximal Relative Amplitude of Turbulent Velocity Fluctuations
2.7. The Rolling-Saltation Transition
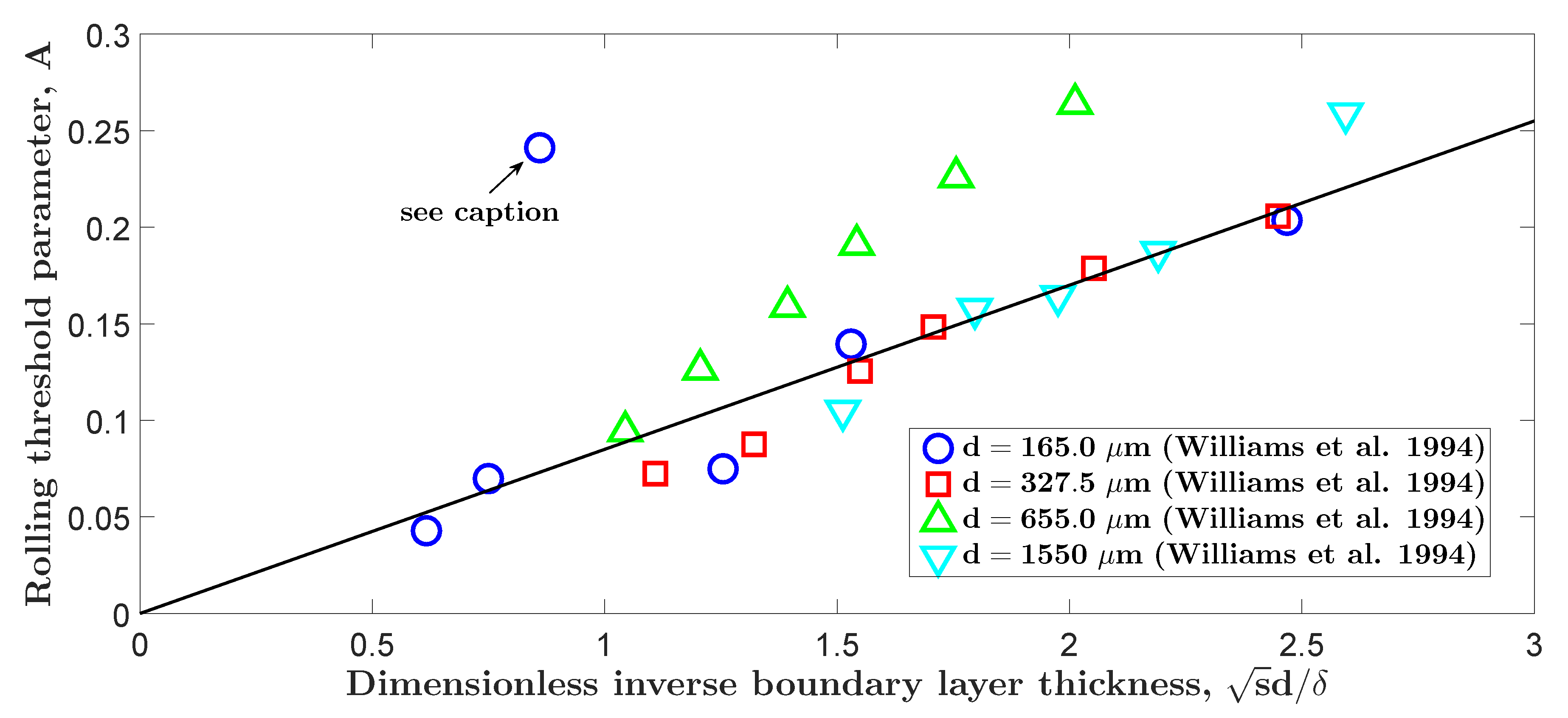
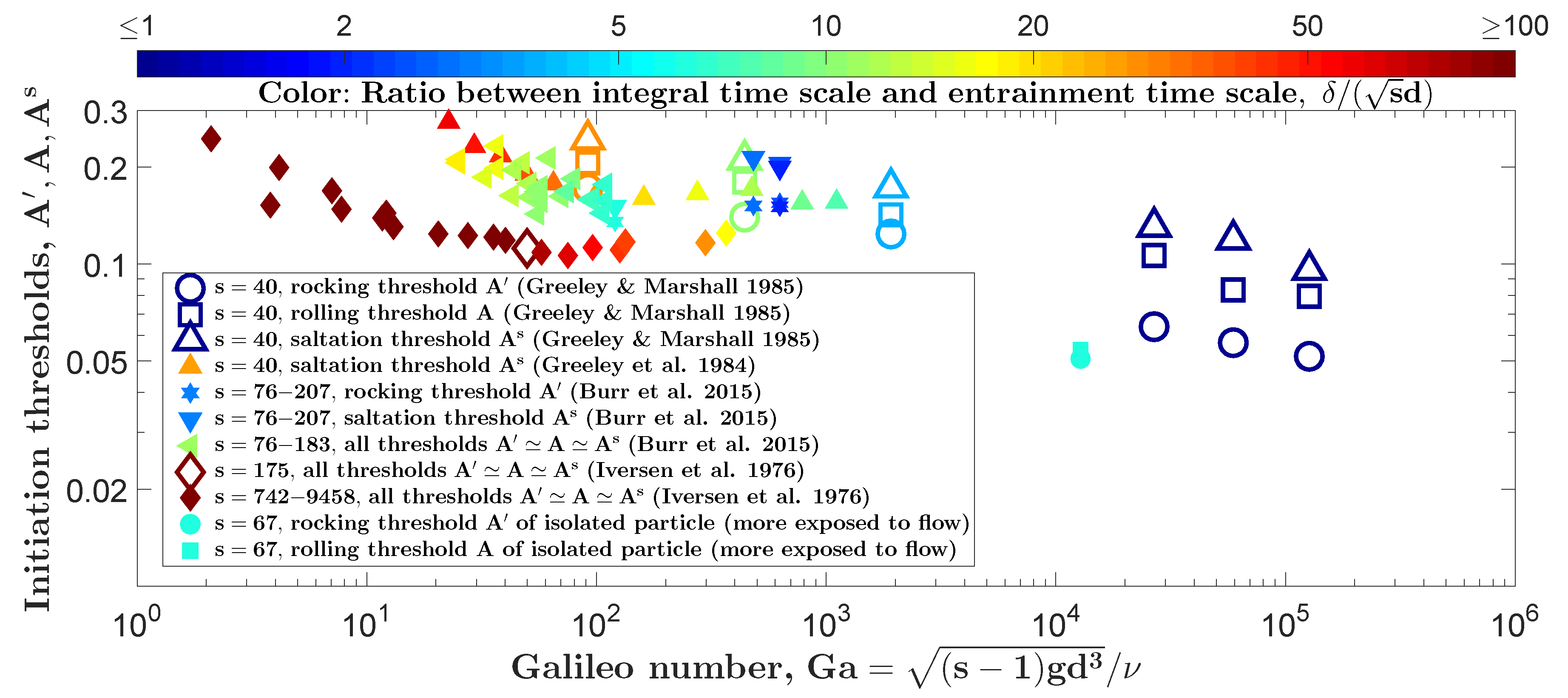
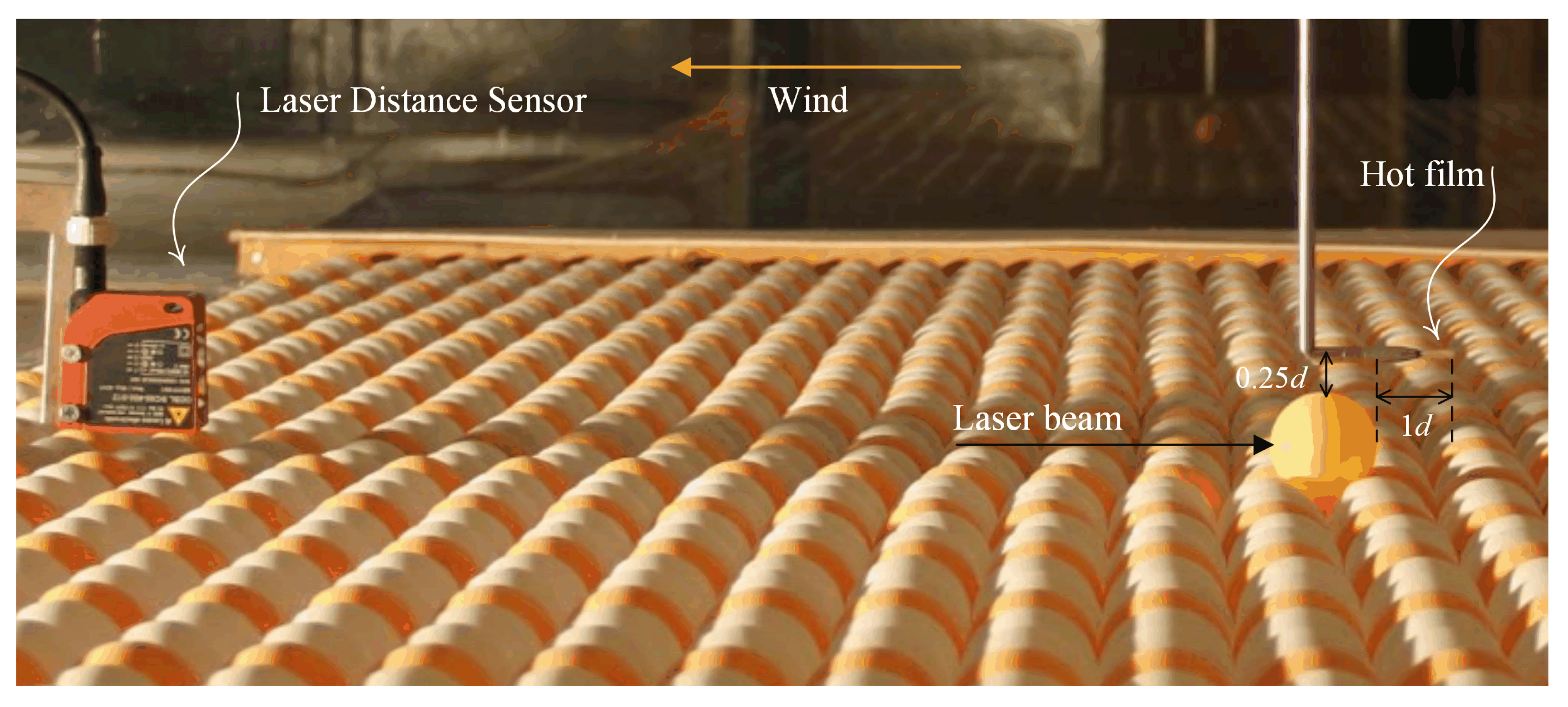
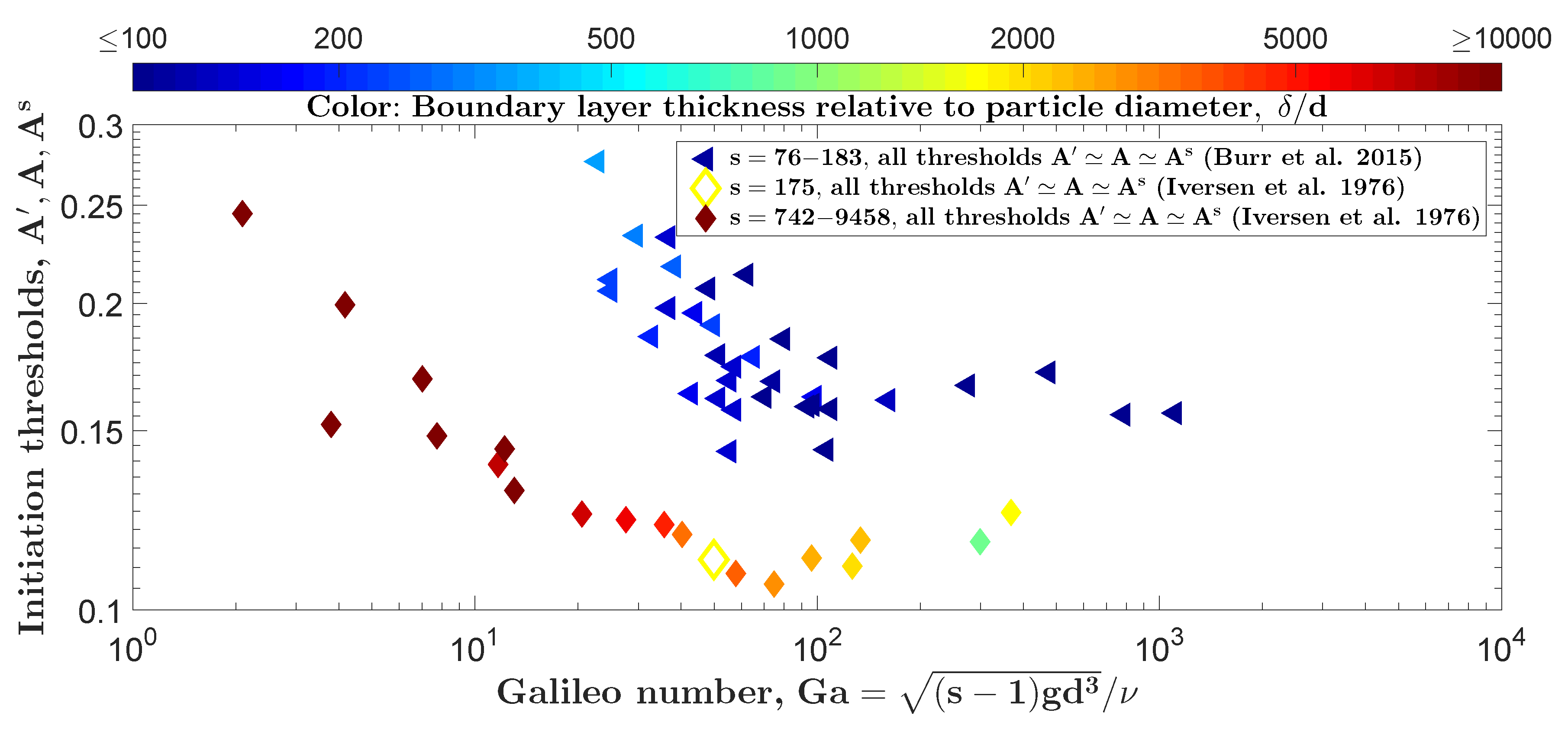
3. Test of Entrainment Framework with Existing and New Experimental Data
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kok, J.F.; Mahowald, N.M.; Fratini, G.; Gillies, J.A.; Ishizuka, M.; Leys, J.F.; Mikami, M.; Park, M.S.; Park, S.U.; Pelt, R.S.V.; et al. An improved dust emission model—Part 1: Model description and comparison against measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 13023–13041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, J.F.; Albani, S.; Mahowald, N.M.; Ward, D.S. An improved dust emission model—Part 2: Evaluation in the Community Earth System Model, with implications for the use of dust source functions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 13043–13061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haustein, K.; Washington, R.; King, J.; Wiggs, G.; Thomas, D.S.G.; Eckardt, F.D.; Bryant, R.G.; Menut, L. Testing the performance of state-of-the-art dust emission schemes using DO4Models field data. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 341–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, J.F.; Ward, D.S.; Mahowald, N.M.; Evan, A.T. Global and regional importance of the direct dust-climate feedback. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourke, M.C.; Lancaster, N.; Fenton, L.K.; Parteli, E.J.R.; Zimbelman, J.R.; Radebaugh, J. Extraterrestrial dunes: An introduction to the special issue on planetary dune systems. Geomorphology 2010, 121, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, R.D. Physics of saltation and sand transport on Titan: A brief review. Icarus 2014, 230, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, K.R.; Valance, A.; Merrison, J. Laboratory studies of Aeolian sediment transport processes on planetary surfaces. Geomorphology 2015, 244, 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, N.T.; Ayoub, F.; Avouac, J.P.; Leprince, S.; Lucas, A.; Mattson, S. Earth-like sand fluxes on Mars. Nature 2012, 485, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayoub, F.; Avouac, J.P.; Newman, C.E.; Richardson, M.I.; Lucas, A.; Leprince, S.; Bridges, N. Threshold for sand mobility on Mars calibrated from seasonal variations of sand flux. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindhorst, S.; Betzler, C. The climate-archive dune: Sedimentary record of annual wind intensity. Geology 2016, 44, 711–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.J.; Butterfield, G.R.; Clark, D.G. Aerodynamic entrainment threshold: Effects of boundary layer flow conditions. Sedimentology 1994, 41, 309–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnold, R.A. The Physics of Blown Sand and Desert Dunes; Methuen: New York, NY, USA, 1941. [Google Scholar]
- De Vet, S.J.; Merrison, J.P.; Mittelmeijer-Hazeleger, M.C.; van Loon, E.E.; Cammeraat, L.H. Effects of rolling on wind-induced detachment thresholds of volcanic glass on Mars. Planet. Space Sci. 2014, 103, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, J.; Greeley, R.; Marshall, J.R.; Pollack, J.B. Aeolian saltation threshold: The effect of density ratio. Sedimentology 1987, 34, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burr, D.M.; Bridges, N.T.; Marshall, J.R.; Smith, J.K.; White, B.R.; Emery, J.P. Higher-than-predicted saltation threshold wind speeds on Titan. Nature 2015, 517, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffaele, L.; Bruno, L.; Pellerey, F.; Preziosi, L. Windblown sand saltation: A statistical approach to fluid threshold shear velocity. Aeolian Res. 2016, 23, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, R.D.; Claudin, P.; Andreotti, B.; Radebaugh, J.; Tokanod, T. A 3 km atmospheric boundary layer on Titan indicated by dune spacing and Huygens data. Icarus 2010, 205, 719–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrosyan, A.; Galperin, B.; Larsen, S.E.; Lewis, S.R.; Määttänen, A.; Read, P.L.; Renno, N.; Rogberg, L.P.H.T.; Savijärvi, H.; Siili, T.; et al. The Martian Atmospheric Boundary Layer. Rev. Geophys. 2011, 49, RG3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, J.F.; Parteli, E.J.R.; Michaels, T.I.; Karam, D.B. The physics of wind-blown sand and dust. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2012, 75, 106901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebonnois, S.; Schubert, G.; Forgeta, F.; Spiga, A. Planetary Boundary Layer and Slope Winds on Venus. Icarus 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, S.L.; Spagnuolo, M.G.; Bridges, N.T.; Zimbelman, J.R. Gravel-mantled megaripples of the Argentinean Puna: A model for their origin and growth with implications for Mars. GSA Bull. 2013, 125, 1912–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, R.; Kok, J.F. Aeolian saltation on Mars at low wind speeds. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2017, 122, 2111–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, N.T.; Bourke, M.C.; Geissler, P.E.; Banks, M.E.; Colon, C.; Diniega, S.; Golombek, M.P.; Hansen, C.J.; Mattson, S.; McEwen, A.S.; et al. Planet-wide sand motion on Mars. Geology 2012, 40, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestro, S.; Vaz, D.A.; Ewing, R.C.; Rossi, A.P.; Fenton, L.K.; Michaels, T.I.; Flahaut, J.; Geissler, P.E. Pervasive Aeolian activity along rover Curiosity’s traverse in Gale Crater, Mars. Geology 2013, 41, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chojnacki, M.; Johnson, J.R.; Moersch, J.E.; Fenton, L.K.; Michaels, T.I.; Bell, J.F., III. Persistent Aeolian activity at Endeavour crater, Meridiani Planum, Mars; new observations from orbit and the surface. Icarus 2015, 251, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.M.; Newman, C.E.; Lapotre, M.G.A.; Sullivan, R.; Bridges, N.T.; Lewis, K.W. Coarse Sediment Transport in the Modern Martian Environment. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2018, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greeley, R.; Iversen, J.D. Wind as a Geological Process on Earth, Mars, Venus, and Titan; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Y.; Lu, H. A simple expression for wind erosion threshold friction velocity. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 22437–22443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrison, J.P.; Gunnlaugsson, H.P.; Nørnberg, P.; Jensen, A.E.; Rasmussen, K. Determination of the wind induced detachment threshold for granular material on Mars using wind tunnel simulations. Icarus 2007, 191, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrison, J.P. Sand transport, erosion and granular electrification. Aeolian Res. 2012, 4, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diplas, P.; Dancey, C.L.; Celik, A.O.; Valyrakis, M.; Greer, K.; Akar, T. The Role of Impulse on the Initiation of Particle Movement Under Turbulent Flow Conditions. Science 2008, 322, 717–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valyrakis, M.; Diplas, P.; Dancey, C.L.; Greer, K.; Celik, A.O. Role of instantaneous force magnitude and duration on particle entrainment. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, F02006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valyrakis, M.; Diplas, P.; Dancey, C.L. Entrainment of coarse particles in turbulent flows: An energy approach. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Raupach, M.R.; Richards, K.S. Modeling entrainment of sedimentary particles by wind and water: A generalized approach. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D24114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Ali, S.Z. Review Article: Advances in modeling of bed particle entrainment sheared by turbulent flow. Phys. Fluids 2018, 30, 061301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claudin, P.; Andreotti, B. A scaling law for Aeolian dunes on Mars, Venus, Earth, and for subaqueous ripples. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2006, 252, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, J.F. An improved parametrization of wind blown sand flux on Mars that includes the effect of hysteresis. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L12202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pähtz, T.; Kok, J.F.; Herrmann, H.J. The apparent roughness of a sand surface blown by wind from an analytical model of saltation. New J. Phys. 2012, 14, 043035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzi, D.; Valance, A.; Jenkins, J.T. The threshold for continuing saltation on Earth and other Solar System bodies. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2017, 122, 1374–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pähtz, T.; Durán, O. The Cessation Threshold of Nonsuspended Sediment Transport Across Aeolian and Fluvial Environments. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2018, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greeley, R.; Marshall, J.R. Transport of venusian rolling ‘stones’ by wind? Nature 1985, 313, 771–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziskind, G.; Fichman, M.; Gutfinger, C. Resuspension of particulates from surfaces to turbulent flows-Review and analysis. J. Aerosol Sci. 1995, 26, 613–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeks, M.W.; Hall, D. Kinetic models for particle resuspension in turbulent flows: Theory and measurement. Aerosol Sci. 2001, 32, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, K.; Poddar, K. Experiments on integral length scale control in atmospheric boundary layer wind tunnel. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2011, 106, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhamdi, S.F.H.; Bailey, S.C.C. Universality of local dissipation scales in turbulent boundary layer flows with and without free-stream turbulence. Phys. Fluids 2017, 29, 115103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, O.; Claudin, P.; Andreotti, B. On Aeolian transport: Grain-scale interactions, dynamical mechanisms and scaling laws. Aeolian Res. 2011, 3, 243–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, A.J.; McKeon, B.J.; Marusic, I. High–Reynolds Number Wall Turbulence. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2011, 43, 353–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marusic, I.; Kunkel, G.J. Streamwise turbulence intensity formulation for flat-plate boundary layers. Phys. Fluids 2003, 15, 2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chepil, W.S. Dynamics of wind erosion: II. Initiation of soil movement. Soil Sci. 1945, 60, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.L.; Kok, J.F. Distinct Thresholds for the Initiation and Cessation of Aeolian Saltation From Field Measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2018, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.P.; Parteli, E.J.R.; Andrade, J.S.; Herrmann, H.J. Giant saltation on Mars. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6222–6226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kok, J.F. Difference in the wind speeds required for initiation versus continuation of sand transport on Mars: Implications for dunes and dust storms. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 074502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iversen, J.D.; Pollack, J.B.; Greeley, R.; White, B.R. Saltation threshold on Mars—Effect of interparticle force, surface-roughness, and low atmospheric density. Icarus 1976, 29, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, J.D.; White, B.R. Saltation threshold on Earth, Mars and Venus. Sedimentology 1982, 29, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greeley, R.; Iversen, J.; Leach, R.; Marshall, J.; White, B.; Williams, S. Windblown sand on Venus—Preliminary results of laboratory simulations. Icarus 1984, 57, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, J.D.; Abbott, J.E. Initial movement of grains on a stream bed: The effect of relative protrusion. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1977, 352, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pähtz, T.; Valyrakis, M.; Zhao, X.-H.; Li, Z.-S. The Critical Role of the Boundary Layer Thickness for the Initiation of Aeolian Sediment Transport. Geosciences 2018, 8, 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8090314
Pähtz T, Valyrakis M, Zhao X-H, Li Z-S. The Critical Role of the Boundary Layer Thickness for the Initiation of Aeolian Sediment Transport. Geosciences. 2018; 8(9):314. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8090314
Chicago/Turabian StylePähtz, Thomas, Manousos Valyrakis, Xiao-Hu Zhao, and Zhen-Shan Li. 2018. "The Critical Role of the Boundary Layer Thickness for the Initiation of Aeolian Sediment Transport" Geosciences 8, no. 9: 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8090314
APA StylePähtz, T., Valyrakis, M., Zhao, X.-H., & Li, Z.-S. (2018). The Critical Role of the Boundary Layer Thickness for the Initiation of Aeolian Sediment Transport. Geosciences, 8(9), 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8090314





