Abstract
Climate change has led to an increase in extreme weather events and desertification of vast areas of southern Argentina. Water shortages are a major concern, and this problem is expected to be exacerbated in the future. An exploration program was undertaken to investigate the groundwater occurrence in areas of the Chubut River basin in order to provide new supply options for pastoral farming. The investigation involved the drilling of exploration holes and construction of bores for long-term monitoring. Water quality and hydraulic test data were also collected. Findings from the study indicate that alluvial sediments extend to a maximum of 45 m below the surface, and are underlain by a sequence of clays and subordinated sands that exceed 100 m in thickness. The bulk of groundwater lies within the shallow sediments, which act as an unconfined aquifer. Hydraulic conductivities up to 10 m/day were estimated from pumping tests, although granulometric analyses indicate that higher values may occur. Chemical characterization indicates that waters are typically fresh, low in sodium, and largely suitable for stock-grazing or horticulture. Anomalous salinities at one of the sites are likely due to the effects of a nearby waste dump. Even though further work is required, the study contributes to a better understanding of the dynamics of the hydrogeological system in the basin under a warming climate, and provides useful information for the expansion of economic activities in remote communities of Argentina.
1. Introduction
The past few decades have seen mounting pressure on groundwater resources due to a drier climate and increased utilization of surface water. Chronically drought-prone areas have increased significantly across the globe, from about 17% of the global landmass in the first half of the 21st century to over 41% in 1950–2008 [1]. Similarly, weather events are becoming more extreme and unpredictable, with impacts not only on natural resources but also on economic activities, especially agriculture and pastoral farming. The Chubut River is the most important watercourse in the Chubut Province of southern Argentina, flowing for approximately 800 km from its headwaters in the Andes Mountains toward the Atlantic Ocean in the east. With a streamflow that is highly dependent on the precipitation regime, the river has been a source of water for irrigation and human consumption since 1865, when the first Welsh settlers arrived in Patagonia [2]. The center of the province receives a reduced average rainfall of about 200 mm/year and the land comprises semi-arid steppes covered with grass or shrubs [3]. The middle course of the river is typically formed by a largely ephemeral channel that receives minor flows from intermittent tributaries. Animal production based on extensive grazing of native rangelands has historically been the main economic activity in Patagonia [4]. Pastoral farming of sheep livestock is critical to sustain family-owned businesses and small communities in the region. The demand for water has been typically dependent on the type and number of animals, along with the duration of grazing and time of the year. Looking ahead, water resources and the wellbeing of rural communities in central Chubut are significantly threatened. An estimated 80% of the world’s population faces a high-level water security risk that threatens the availability of water of sufficient quantity and quality to support livelihoods [5]. Furthermore, Chubut is one of the most impacted provinces in Argentina by the process of desertification. Almost every glacier in the Patagonian Andes has been retreating over the last few decades, and these changes are predicted to reduce about 20% of the riverflow in the Chubut River, with a consequent impact on the basin’s land-use [6]. Future environmental changes highlight the need to urgently examine the prospect of developing aquifer resources and provide a reliable supply of water for pastoralists. Identifying new underground reserves will alleviate the water problem in the middle section of the Chubut River basin, and will increase the carrying capacity of the rangelands. In addition, the emergence of alternative water sources is expected to mitigate gradual land degradation and the unfavorable conditions faced by small producers, whose farming operations are considered to be at subsistence level because their land is inadequate for the development of productive practices [7]. Any future abstraction must be within sustainable limits, maintaining an adequate balance between water availability and demand. Population projections make it possible to estimate future water demand, although accounting for the sensitivity of the aquifers to pumping is more challenging. This is exacerbated by the lack of information about the hydrogeology of central Chubut. The first investigations date to [8], who provided an overview of the geology and paleontology of the region. Later, the stratigraphy of the middle Chubut River was described by [9], although the work focused mainly on the Eocene volcanic complex that is interpreted as part of a caldera evolution. More recently, [10] analyzed the dynamics of the fluvial regime in the mid- and upper-Chubut River in relation to seasonal runoff. According to local residents, mineral prospecting and a few environmental studies were undertaken by private companies in sections of the middle basin, but that information remains largely unpublished.
Therefore, it was decided that a groundwater exploration program was needed in a rural area of the Paso de Indios district, Chubut Province, to assess the potential of shallow aquifers as a water source for pastoral agriculture. Drilling of exploration boreholes, water quality measurements, and hydraulic tests were performed to gain an insight into the region’s scarce water resources. This paper presents an overview of the hydrogeological characteristics and potential groundwater availability in one of the driest parts of Argentina. Results of the study are preliminary and awaiting further work but they provide innovative approaches to local communities about stock watering and contribute to a better understanding of the options available in times of surface water deficiency. The investigation is especially relevant in light of predicted negative impacts from future climate variability.
2. Study Area
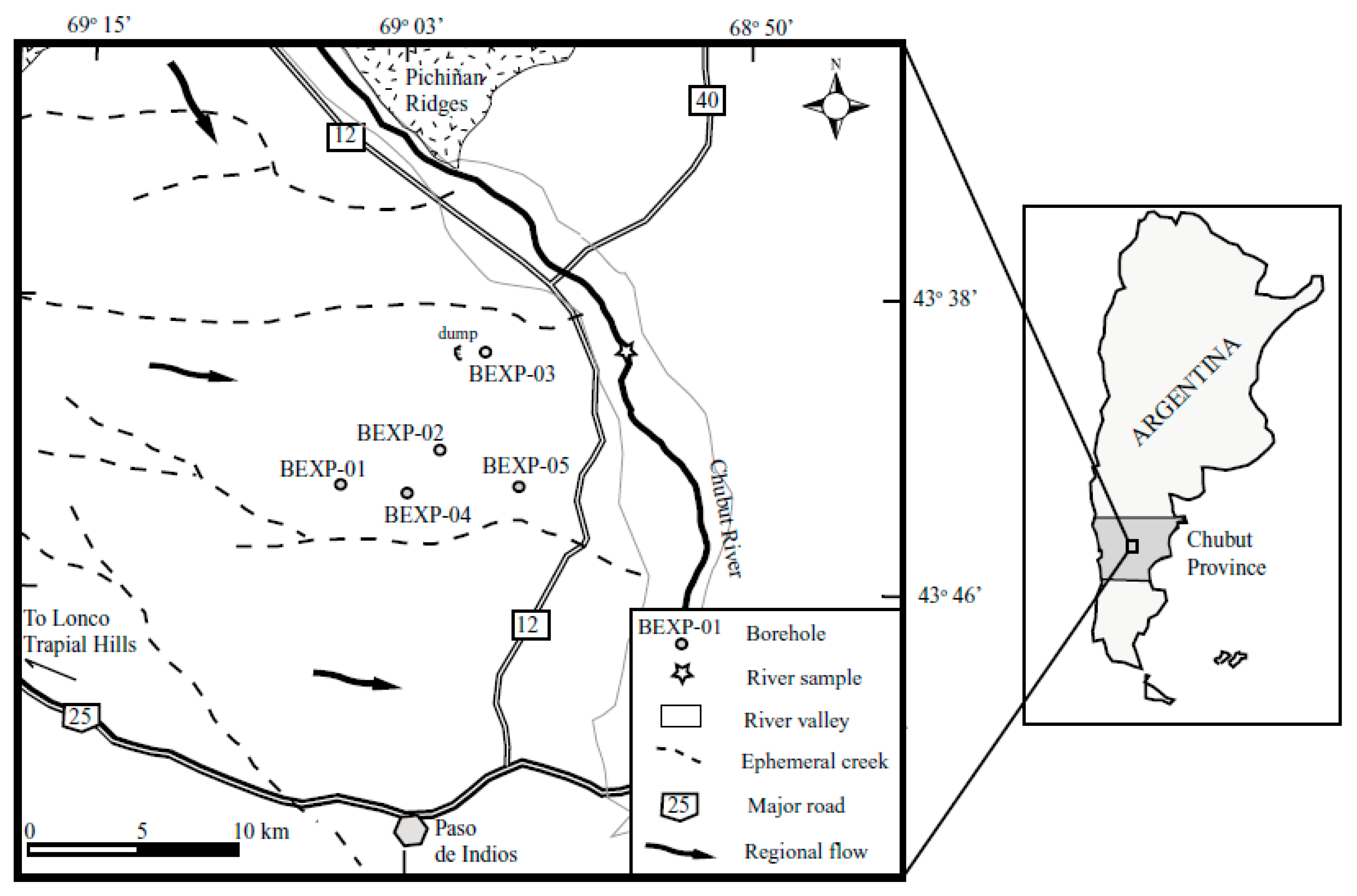
The study area is located in the middle section of the Rio Chubut catchment, approximately 25 km north of the town of Paso de Indios, in the center of the Chubut Province of Argentina (Figure 1). The site covers approximately 80 km2, and has a maximum elevation of about 750 m above sea level (ASL). The setting includes fluvial terraces of Cenozoic origin and recent alluvial fans that are up to about 20 km from the source of the Chubut River. According to [10], the river has a mixed hydrological regime, mainly controlled by cycles of rainfall and ice melting in the Andes. In this regard, the streamflow in the middle section of the basin oscillate between 80 m3/s at the peak of the snowmelt in spring to approximately 10 m3/s by the end of summer. Several ravines and ephemeral creeks drain to the river across the gently undulating plateau that characterizes the region. In addition, minor ridges and hills are present in the landscape, where intrusive rocks from the Jurassic outcrop. In general, the river terraces are covered by a mantle of gravels in calcareous cement (rodados patagonicos) that constitutes one of the most distinctive features of the Patagonian landscape. These sediments stretch homogeneously across an extensive area as a result of successive Pleistocene glacial transgressions [11]. The high hydraulic conductivity of the detritals forms a series of aquifers that alternate with silt and clay aquitards in a multilayer system. According to [12], groundwater in central Chubut is largely brackish to saline, although total dissolved solids (TDS) contents of 22 to 197 mg/L and 845 mg/L have been identified in the localities of Martires and Paso de Indios, respectively. This suggests the presence of freshwater lenses closer to the surface connected to brackish waters in the lower part of the saturated zone.
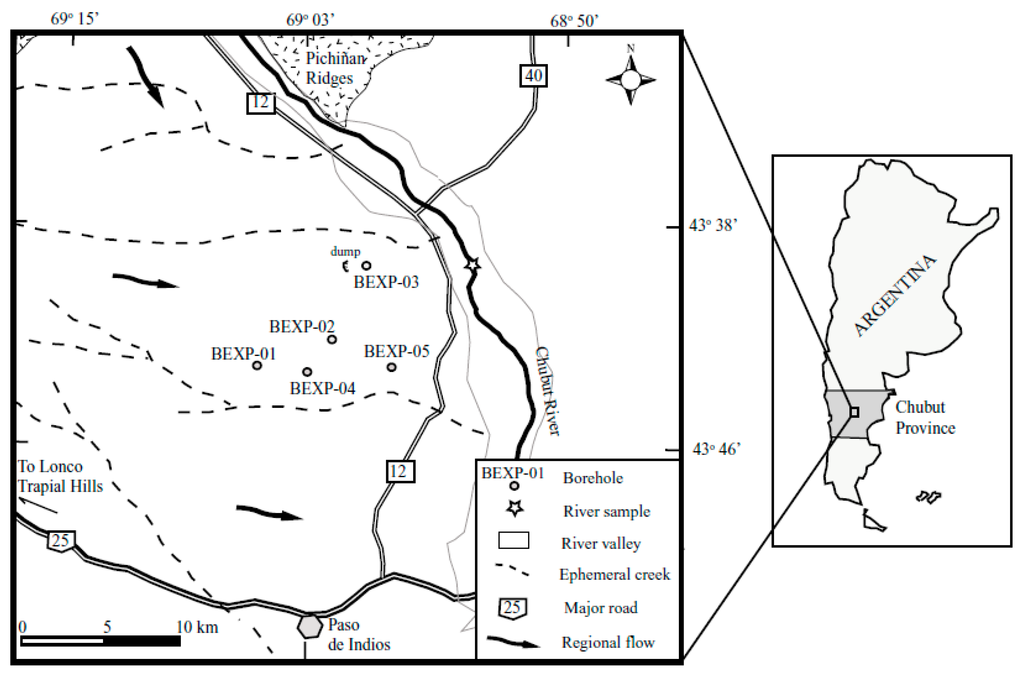
Figure 1.
Location of the study area.
The climate of the area is cold and arid, with low and irregular rainfall (~200 mm/year), and average temperatures range from 3 °C in winter to about 19 °C in January and February. In general, precipitation falls as snow in winter, with minimum temperatures frequently below −10 °C between June and July [13]. Recharge to the aquifers mostly occurs through rainfall and by direct infiltration from snowmelt in spring. Early estimates from [14] showed that the potential evaporation of the region exceeds 700 mm/year, which results in an annual water deficit of approximately 500 mm. This is consistent with the formation of soils that are extensively devoid of organic matter and are commonly enriched in argillites and carbonates. Thus, the regional soils can be classified as aridisoils covered by scrub vegetation and to a minor extent as entisols, which develop in eolian depressions, drainage lines, and the floodplains of the Chubut River [15]. Poor soils and harsh climatic conditions mean that agricultural activities in the area are mostly restricted to stock-grazing, particularly sheep herding. In general, pastoral activities are conducted by small producers, who reside in the region and usually have less than 300 animals [16].
3. Material and Methods
A drilling campaign was carried out at five sites using air reverse circulation to provide a continuous return of formation and water samples from a maximum depth of 108 m below ground level (BGL). The method involved air being blown down through the annulus of rods, with samples being returned to the surface through an inner tube in a drill string. This drilling method was chosen, as the cuttings and water are not contaminated with drilling additives or mixed with the formation materials and the sample is more representative. A drill hammer was used to achieve greater penetration through hard pebbles and cobblestones. Test holes of approximately 140 mm in diameter were drilled to selected depths, and logged for lithology at 3 m intervals. The boreholes were drilled without casing, although a precollar of about 12 m was typically required to prevent washing and scouring of superficial materials. Simultaneously, water quality parameters were measured along the vertical profile. Groundwater standard parameters (conductivity, pH, temperature) were measured with the use of an YSI ProDSS hand-held probe, and a Hatch test kit was used to estimate nitrate and alkalinity values in the field. Downhole geophysics was run immediately after the completion of the test hole. However, caving and collapse of the walls often compromised the tool’s deployment, especially in shallow horizons, where gravels and sands were interbedded in thin layers. Therefore, only a natural gamma log was run inside the drill string to better define the abundance of clay minerals in the surrounding sediments. The gamma log was run at a speed of about 3 m/min both on the way down and up. Two of the most promising boreholes were reamed to a suitable diameter in order to stabilize the formation, and a 150 mm PVC casing installed to selected depths. Over 50% of the saturated zone was intercepted using PVC screens 18 m in length, with a slot aperture of 1 mm. Siliceous gravel and drill cuttings were used to fill the annulus and construct a suitable test bore. The newly constructed bores were then developed by surging and pumping air to lift water and drilling fluids toward the surface. The discharged water was directed into a mud pit, and flow rates were estimated.
Groundwater from the exploration holes was collected through the rig cyclone. For constructed bores, samples were taken at the beginning and end of the hydraulic tests in order to evaluate any potential effects of pumping on water quality. Additionally, a deionized water blank and a duplicate were taken for quality control. Filtration was carried out in the field by the use of a 0.45 µm membrane, and samples stored at 4 °C in appropriate containers. They were then sent to a private nationally accredited laboratory in Buenos Aires, Argentina to be analyzed by ion chromatography and ICP-AES.
Furthermore, single-bore aquifer tests were performed on two of the constructed bores to estimate their performance and to calculate the transmissivity of prospective units. A 7.5 HP Franklin electric pump was employed to conduct a step-drawdown test that enabled the estimation of long-term pumping rates and friction losses within the aquifer and bore. A constant rate test was then undertaken at the maximum sustainable pumping rate, followed by a recovery test until water levels stabilized. Changes in water levels were measured using a hand-held groundwater dipper and datalogger, and the recorded readings were subsequently analyzed by the use of the AQTESOLV package [17]. Finally, six aquifer samples were analyzed through conventional sieves to determine the particle-size distribution. Samples contained less than 10% silts, therefore, mechanical sieving alone was considered sufficient to describe the particle distribution. A grain-size distribution test was performed on selected soil samples to quantify particle characteristics and to estimate the hydraulic conductivity of the sediments. The analysis was carried out mechanically for particle sizes between 63 µm and 6.35 mm in diameter, and results were expressed in terms of the percentage of the total weight of soil that passed through different sieves.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Geology
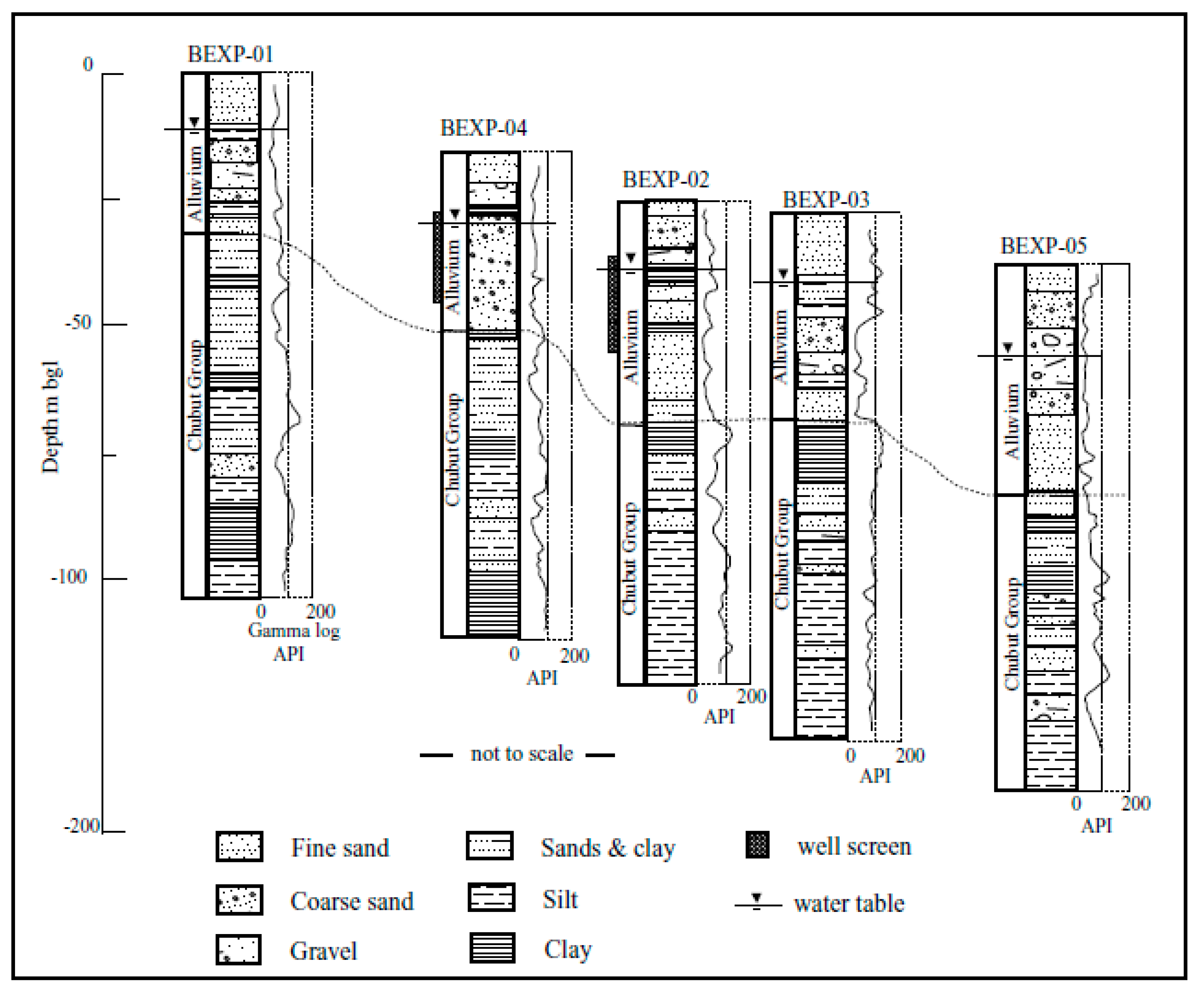
Drilling observations indicate that the stratigraphy in the area of study is characterized by two major units: an intercalation of clays and fine sand lenses at the bottom, unconformably overlain by alluvial sediments, with a predominantly gravel and sandy composition at the top (Figure 2). In general, the basal succession is dominated by grey silts and clays with limited foliation and a variable degree of consolidation. The unit was typically intercepted at 40 to 45 m BGL and extended to depths exceeding 100 m BGL. Traces of kaolinite and carbonates appear within the sediments. Furthermore, ochreous sandstones and fine tuffs occur as subordinated discrete layers within the sequence. These sediments are poorly consolidated and largely formed by subangular quartz of moderate sorting, polymodal, with iron oxides (i.e., limonite; goethite) disseminated within the matrix. These sandy lenses range from a few cm up to about 5 m in thickness. Findings from [18] suggest that sediments in the district correspond to the Chubut Group from the Cretaceous. The Chubut Group is one of the most extensive units in Patagonia, comprising a thick sequence of sedimentary rocks interpreted to be part of a fluvial and lacustrine environment in its lower section, grading into pyroclastic deposits at the top [19]. As previously mentioned, these formations are overlain by a succession of unconsolidated sands and gravels interpreted as accretion bars and superimposed channel bedforms associated with the lateral migration of the river during the Pleistocene. The interfingering of thin sheets of fine sands and gravels becomes more evident in the vicinities of BEXP-05, possibly in conjunction with the final stages of sedimentation from a fluvial cycle into an overbank regime. The deposits have been largely reworked by the successive events that shaped the current floodplain of the Chubut River and, therefore, exhibit irregular geometry, heterogeneous lithology, and considerable anisotropy. Thus, the typical mineralogy includes subrounded to subangular quartz, jaspillite, and minor feldspars commonly altered to clays. Fragments of chert and lithics with a maximum diameter of about 30 mm have been occasionally observed within the sediment’s fabric.
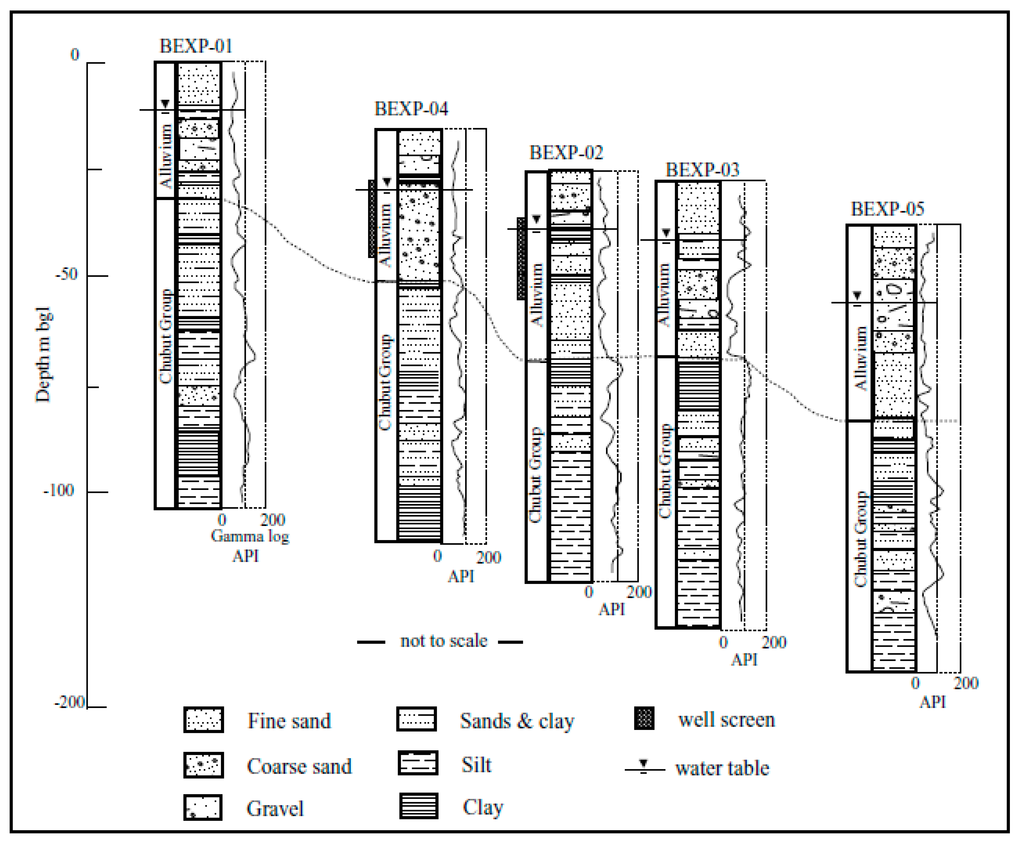
Figure 2.
Exploration boreholes and geological interpretation of intercepted units.
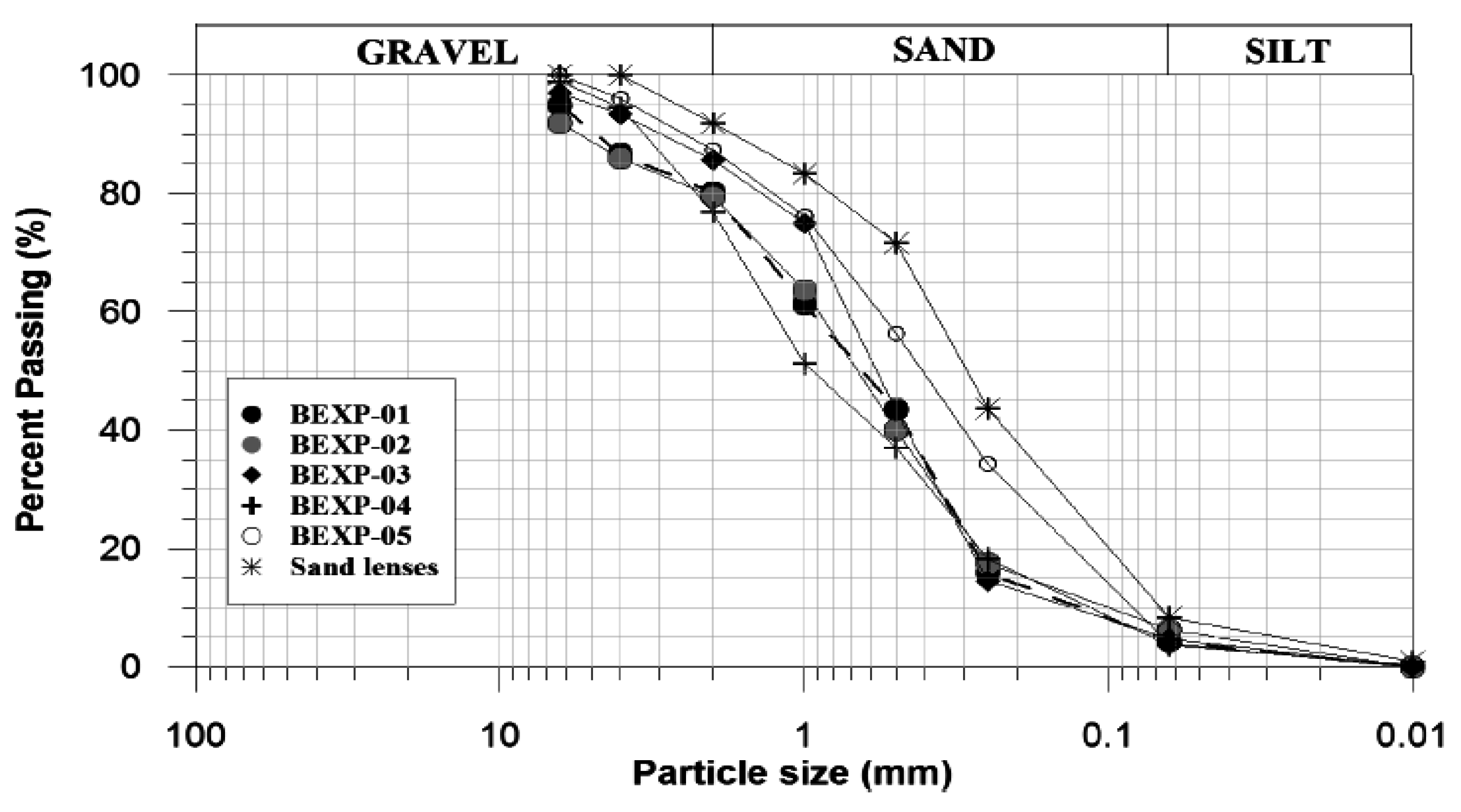
The aquifer sediments are somewhat heterogeneous, with a particle distribution ranging from silts to fine gravels (Figure 3).
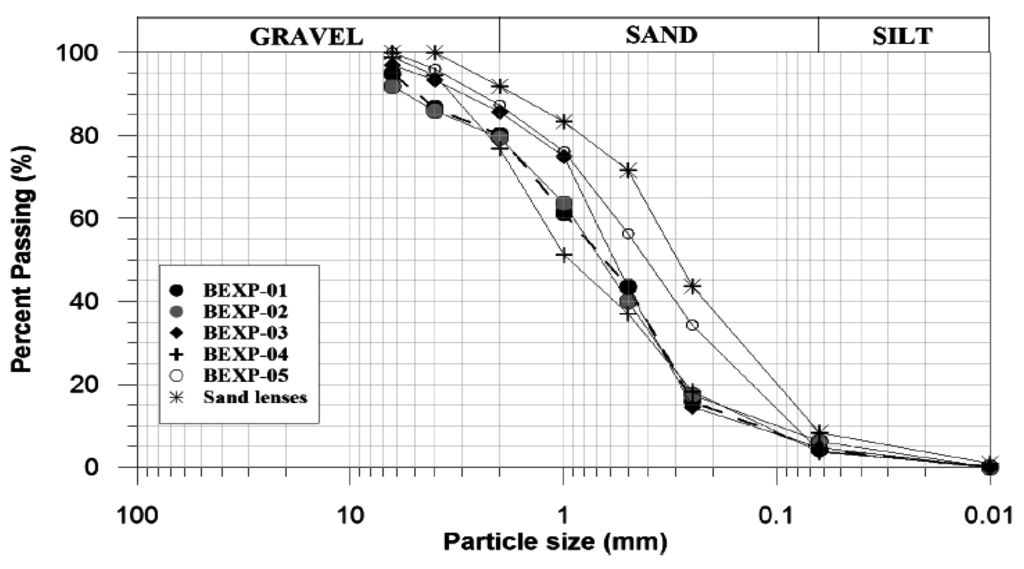
Figure 3.
Grain-size distribution curves for aquifers in the study area.
Previous theoretical and empirical investigations of the relation between particle size and intergranular permeability have resulted in the well-known formula for intrinsic permeability (K):
where d is the particle diameter, and c is a dimensionless constant [20]. Various approaches exist that relate the conductivity component to grain-size data, although one of the most widely used methods is the Hazen formula [21]. In this case, the particle diameter is the 10% finer grain size (d10) and c is a coefficient that ranges from 1 to 1000 depending on the material type. The method is not devoid of limitations, particularly due to the difficulty in selecting an appropriate coefficient value and the narrow range of grain sizes (very fine to coarse sands) for which it was developed. Nevertheless, it still constitutes a rapid and practical approach to obtain an estimate of the hydraulic conductivity of the materials for minimal cost. An empirical coefficient of 700 (when K is in m/day) was selected in view of the poor sorting and predominance of sands in the materials [22]. In this context, the hydraulic conductivity of the shallow aquifers was estimated to be between 4 and around 16 m/day. These values are within the range typically encountered in unconsolidated sands and gravels of Quaternary age [23] in this region. The results also show a significant spatial variability in hydraulic conductivity. The Hazen estimates are in good agreement with pumping test results at BEXP-04, although they are twice as high as conductivity values estimated from bore BEXP-02 (Table 1). This is perhaps due to the fact that the degree of compactness is not considered in Hazen’s formula [24]. The Hazen coefficient at BEXP-02 could still be empirically fitted to improve the results’ match, although it is argued that results from pumping and granulometric tests may not necessarily agree, as the aquifer is stratified and a fine intercalation of sands and gravels was observed.
K = cd2

Table 1.
Sediment parameters and hydraulic conductivity estimations.
4.2. Hydrogeology
The abundance of fine-grain materials makes the bedrock formation a poor prospective target for groundwater abstraction. In general, these units can be viewed as an undifferentiated aquitard, although internal lithological variations and individual sand interbeds create discreet aquifers across the area. The irregular thickness and discontinuity of the more permeable sandy layers indicate a complex history of erosion and filling during the development of the bedrock. Fine-sand lenses up to about 5 m were occasionally found at variable depths, with maximum recorded yields in the order of 1.5 L/s. These flows could provide a local groundwater source for stock and domestic uses. However, the limited areal extent of the permeable layers means that they are unlikely to sustain any major abstraction. Structural features and the consequent appearance of secondary permeability might also exert an important influence on the flow dynamics of the region [25]. As such, it is possible that some water could be mobilized through cracks and fractures in the host rocks. Nonetheless, aquifers that rely on secondary permeability generally have a much lower capacity to transmit water, especially because fracture zones are often not consistent throughout the rock [22]. Typically, water production during short-term testing is greater than the actual amount that can be supported by the surrounding rocks, and, as a result, the incidence of “well failure” is much higher in fractured units than in other settings [26].
In this context, the bulk of groundwater flow is considered to occur within alluvial deposits near the surface. The water-bearing materials consist primarily of unconsolidated sands and gravels that act as an unconfined aquifer. With a phreatic level between 12 and 17 m BGL, the superficial aquifer has a maximum saturated thickness of approximately 32 m. In general, the configuration of the water table is consistent with surface elevation, indicating that groundwater moves in an east-southeast direction from the uplands at the catchment margins. This is in line with [25], who postulated that groundwater would typically be recharged in vicinity of the Pichiñán Ridges in the north, following an easterly regional path toward the Chubut River. The hydraulic tests showed rapid inflows from the aquifer to the wells at the end of the abstraction period, suggesting that the alluvials are highly sensitive to rainfall infiltration. To the west, the boundaries of the catchment are mostly defined by the Lonco Trapial Hills approximately 30 km from the study area, while the Chubut River and its tributaries bound the aquifer on the other sides.
Due to budget constraints, only two single-well pumping tests could be conducted to confirm the hydraulic properties of the superficial aquifer. A step test was initially conducted at increasing abstraction rates to a maximum of 5.5 L/s, the maximum operational flow achieved by the pump. In this regard, drawdown in the bore can be explained as a result of both laminar and turbulent flow [27]:
where S is the drawdown in the bore; Q is the pumping rate; B is the linear aquifer loss coefficient; and C equals non-linear well losses due to turbulent flow. Values B and C were estimated using the Hantush-Bierschenk method, and the efficiency of the bores under the selected pumping rates was then evaluated. The test indicates that the bores can sustainably produce up to 4 L/s, with no significant drawdown over the long-term. At higher rates, the bore efficiency drops substantially, and the aquifer saturated thickness is predicted to be insufficient for long-term abstraction (Table 2).
S = BQ + CQ2

Table 2.
Results of step drawdown tests at selected bores.
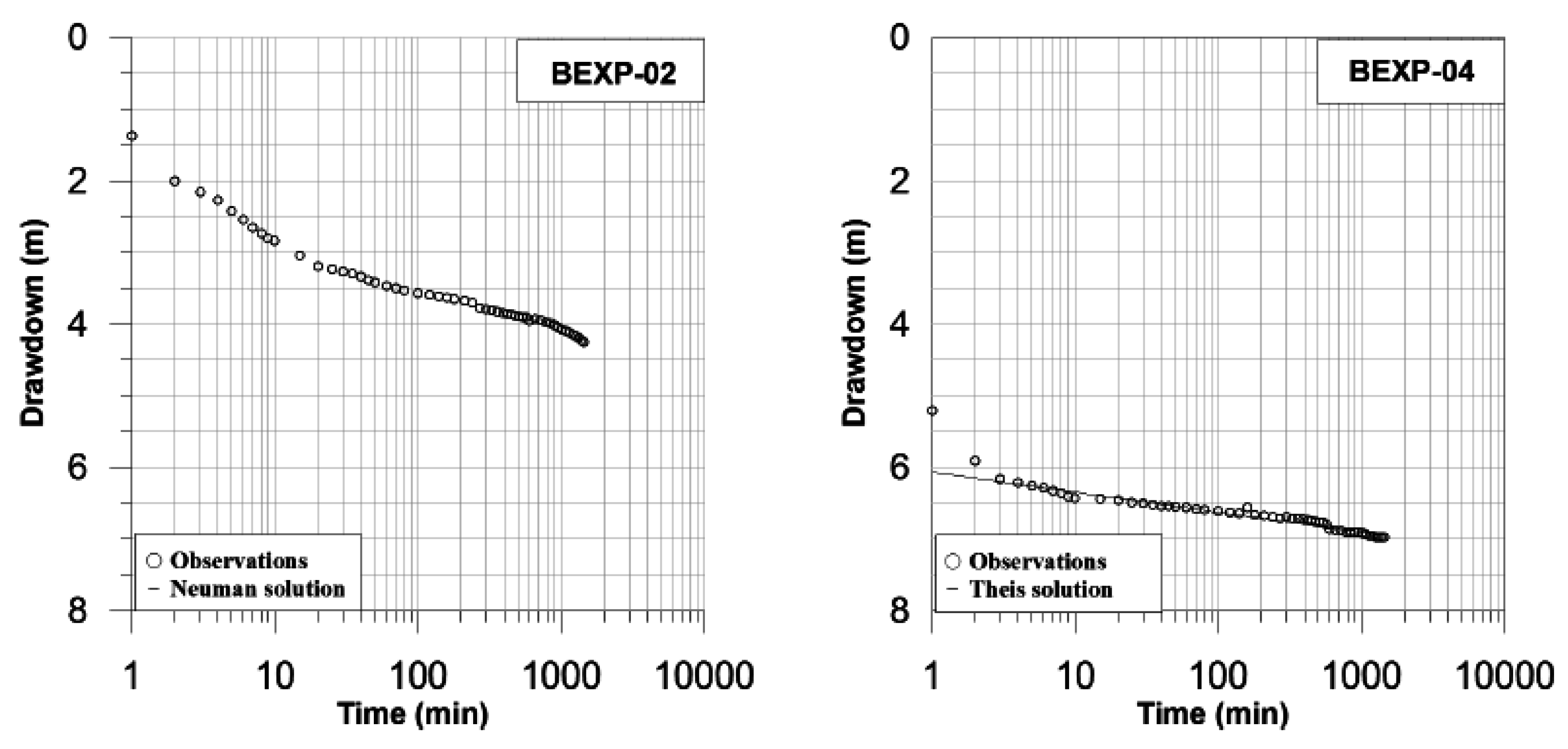
Constant rate tests were then conducted for 24 h at a rate of 4 L/s followed by recovery. Discharge rates showed minor oscillations due to fluctuations in the pump system, but the impact on the test was considered negligible. Data collected at bore BEXP-02 shows that the time-drawdown curve can be divided into three distinctive segments that correlate to the delayed water-table response of an unconfined aquifer [28].
The initial drawdown is ascribed to water released from well storage and extended for about 15 min after pumping commenced (Figure 4).
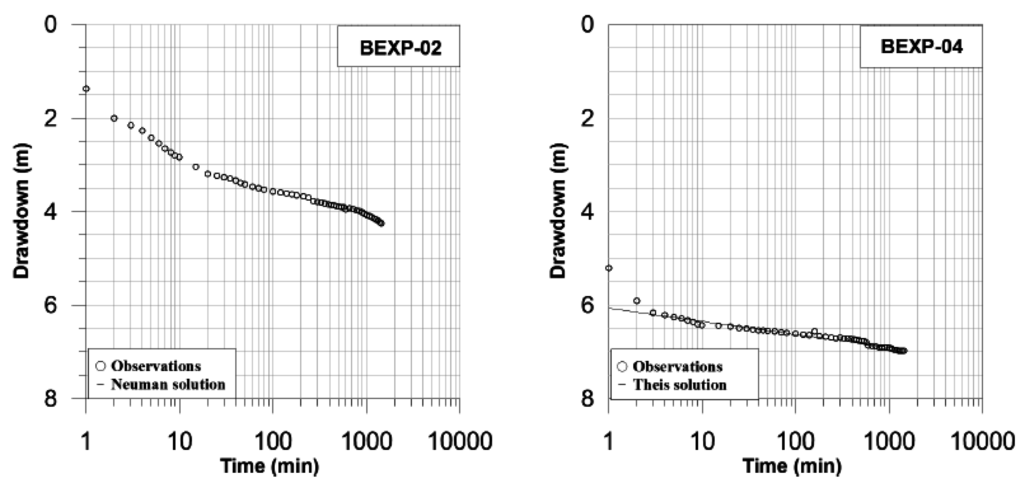
Figure 4.
Observed drawdown against time and interpretation of constant rate pumping tests.
Early-time conditions were followed by a moderate, but steady decline in water levels, which is interpreted as the effects of the aquifer dewatering under a falling water table. This segment tended to stabilize after approximately 10 h of pumping, although true steady state conditions were not reached. Further falls in water levels were later recorded as the cone of depression expanded. The steeper late-time segment reflects the situation where flow in the aquifer is essentially horizontal and, as such, the time-drawdown curve once again tends to conform to the Theis curve [29]. Under these conditions, the Neuman solution [30] indicates that transmissivity in the aquifer is in the order of 97 m2/day (K: 3 m/day). Thus, the aquifer could provide enough water for pastoral farming and withstand heavy pumping over short periods. In contrast, drawdown at the second testing site (BEXP-04) followed a more gradual decline that can be adequately evaluated by a straight-line solution, such as Theis [31]. In effect, if a pumped unconfined aquifer does not show a delayed water-table response, the time-drawdown only follows the late-time segment of the S-shape curve, which is identical to that of a confined aquifer [29]. The drawdown curve after the initial period resulted in an average transmissivity of 226 m2/day (K: 10.3 m/day), consistent with typical values for unconsolidated sands. Longer tests are required to corroborate the absence of impermeable boundaries farther away from the bores. Nevertheless, groundwater recovered to the initial static level within the first hour following the cessation of pumping, providing additional evidence to support the sustainability of long-term pumping at the tested rates.
4.3. Geochemistry
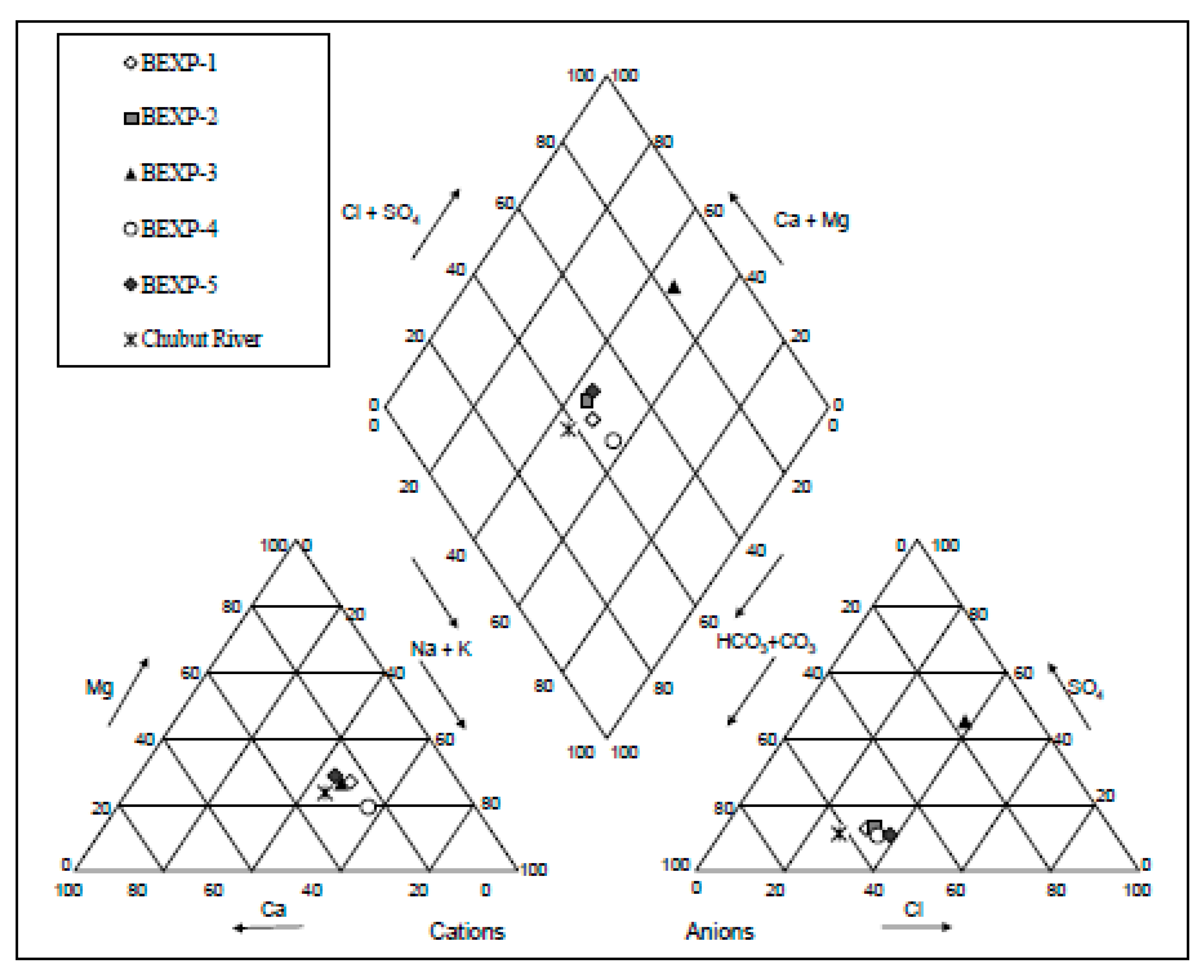
Groundwater in the alluvium is typically fresh and low in ions, with pH values between 7.1 and 7.6, and TDS usually below 800 mg/L (Table 3). Overall, the groundwater has an intermediate character, similar to the composition observed in the Chubut River (Figure 5). This suggests some hydraulic connection and possible water exchange between the alluvial aquifer and the riverbed, particularly in proximity to the streambanks. In general, the molar cation concentrations follow a trend where Na+ > Ca2+ > Mg2+ > K+, while molar anions exhibit a relationship of HCO32− > Cl− > SO42− > NO32−. The Na+/Cl− ratio in groundwater ranges between 1.25 and 1.70, suggesting some additional Na+ inputs other than from dissolution of disseminated halite. The Na+ enrichment might be attributed to the water-rock interaction, possibly associated with the exchange of Ca2+ or Mg2+ in groundwater with Na+ in the alluvium. In contrast, the contribution of K+ to groundwater appears to be limited. Low levels of K+ in groundwater would likely be a consequence of its tendency to be fixed by clay minerals and to participate in the formation of secondary minerals [32].

Table 3.
Major ion concentrations in the basin.
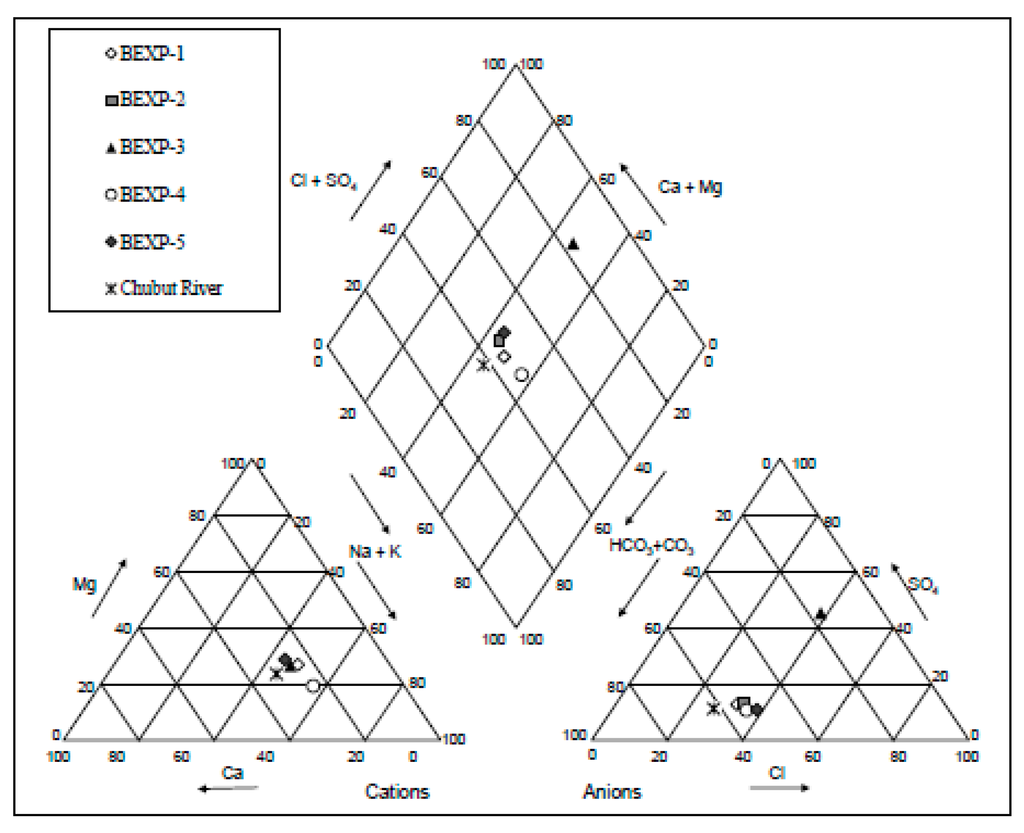
Figure 5.
Piper diagrams for cation and anions in groundwater and surface waters.
Low salinity and a relatively neutral pH mean that most waters can be considered potable [33]. Nevertheless, a bacteriological analysis is necessary to confirm whether groundwater is safe for human consumption. This is especially relevant in the vicinities of bore EXP-03, where TDS contents close to 2400 mg/L were recorded. The increase in concentrations is mostly associated with elevated SO42− and NO3− explained as leachate from a local dump site approximately 300 m west of the borehole. In addition, the local decrease in pH at the site could be attributed to the release of CO2 and methane during the decomposition of waste materials, which ultimately percolate through the sediments into the saturated zone. Waste observed at the time of the research largely comprised solids left on an unlined pond, although locals mentioned that dead animals and excreta were occasionally found.
Hardness is another important parameter to be taken into account for the use of groundwater. Groundwater hardness in the area ranges from about 80 to 110 mg/L, which can be considered moderately hard according to the classification of McGowan [34]. Hardness is mainly due to the presence of polyvalent metallic ions, predominantly Ca2+ and Mg2+, typically derived from sedimentary rocks [35]. In particular, the origin of the hardness at the site is attributed to carbonates within the matrix of the alluvial sediments and the enrichment of salts caused by dissolution from the clayey formations underneath. High concentrations of Ca2+ may cause P deficiency by interfering with its absorption in the gastrointestinal tract of cattle, although animals should tolerate concentrations up to 1000 mg/L if P levels are adequate [36].
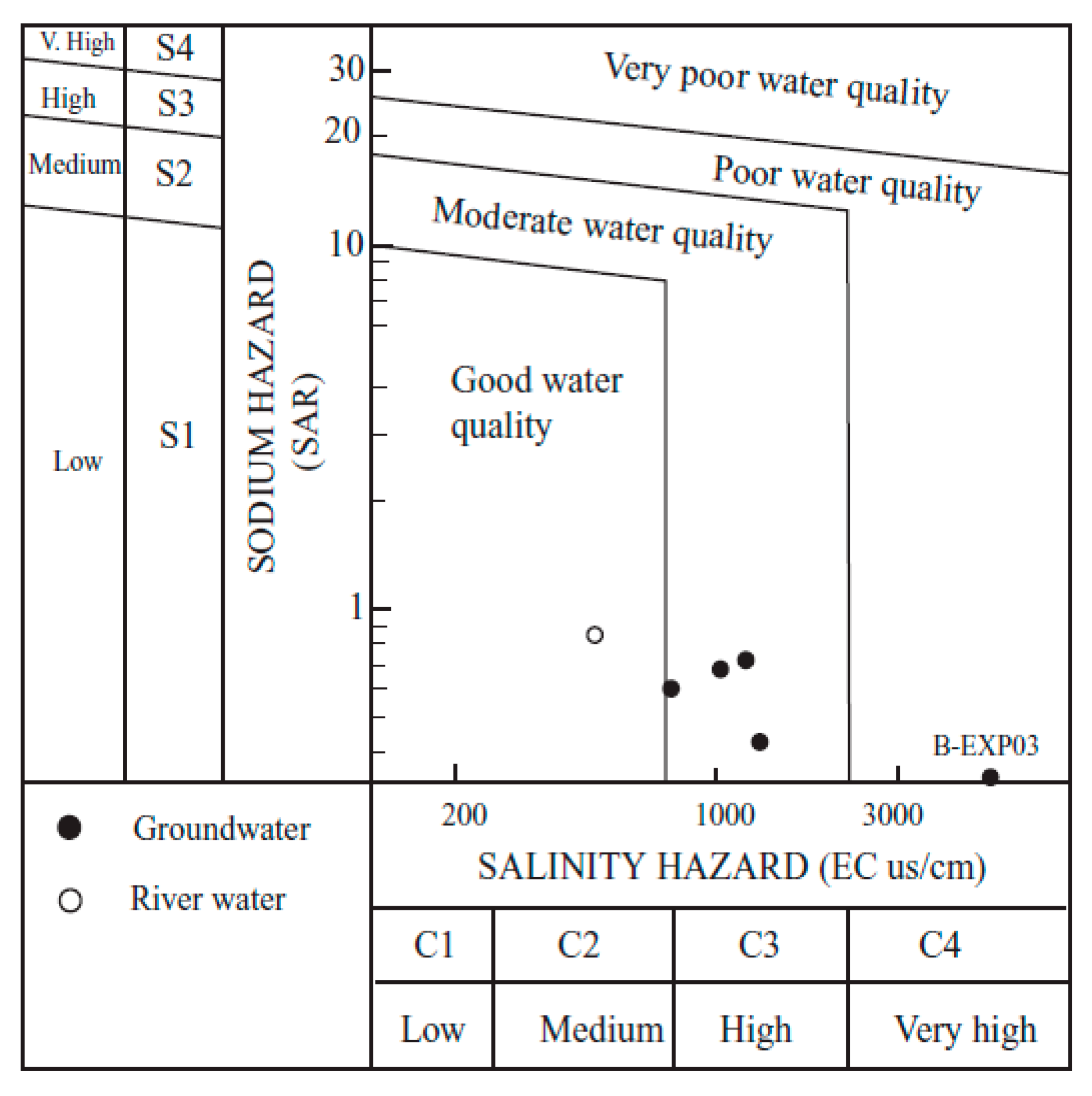
The suitability of water quality for horticulture irrigation was also explored (Table 4). The quality of irrigation water was determined on the basis of (a) total salinity; (b) sodicity; and (c) anion composition and concentration of toxic elements [37]. A high salt concentration in water leads to the formation of saline soils, while, high sodium leads to development of alkali soils [38]. Electrical conductivity values indicate that in most cases the waters would have medium (C2: 250 < EC < 750 µS/cm) to high salinity (C3: 750 < EC < 2250 µS/cm), with localized higher values (C4: EC > 2250 µS/cm) attributed to anthropogenic contamination. Waters in the western margins of the area (BEXP-01) would be acceptable for crops with a moderate salt tolerance, although, in general, plants having good tolerance for salt require special management practices. The sodicity hazard provides another indication of the impact of irrigation on agriculture. A common measure parameter to estimate this hazard is the sodium adsorption ratio (SAR), defined by the formula:
where the ions concentration are in mEq/L. Groundwater in the area is typically low in sodium (S1: SAR < 10) and, therefore, it would be suitable for irrigation in most soils (Figure 6). However, it is worth noting that an increase in evaporation rates during summer could promote the precipitation of carbonates and reduce the proportion of Ca2+ in groundwater. This might consequently create an excess of Na+ and raise the SAR values in soils from November to March. Calcite precipitation and an increase in SAR are also plausible in waters enriched in HCO3−. Therefore, it would likely be necessary to neutralize the HCO3− in the waters in order to use them for long-term irrigation if concentrations exceed 305 mg/L [39].

Table 4.
Content of major elements that determine the suitability of waters for irrigation.
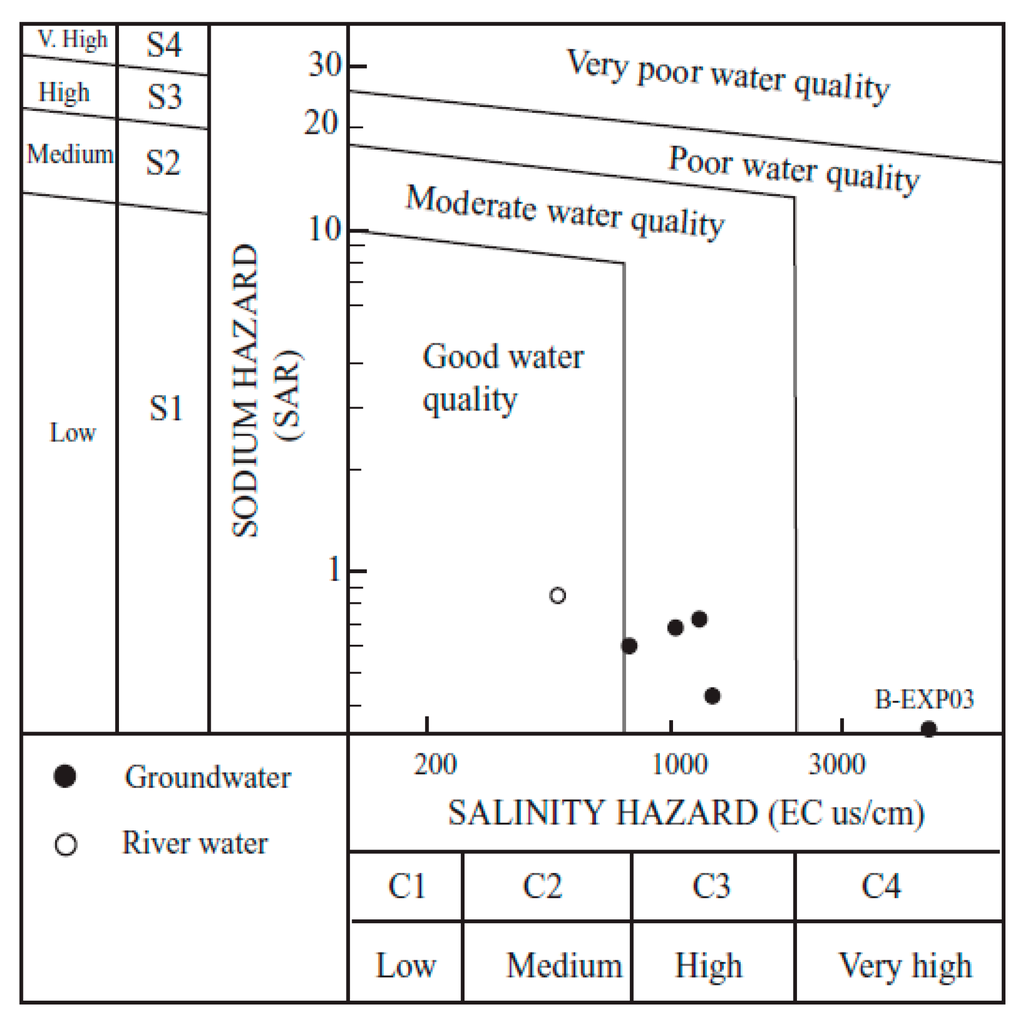
Figure 6.
Classification of water quality for irrigation purposes in the study area (after [40]).
Excess amounts of certain elements, notably B− and Cl−, are toxic to crops, and should also be examined. Boron present in water is low (<0.12 mg/L), and is not considered to be harmful to crops at concentrations below 0.33 mg/L [41]. As a conservative element, Cl− moves readily into the roots zone, where it is transported to crop stems and leaves. With an average content of 57 mg/L, Cl− in groundwater is deemed to be low. However, some foliar injury could still occur in highly sensitive crops, such as almonds, citrus, plums, or grapes [42]. Other constituents that may affect water quality from wells are NO3− and SO42−. With the exception of waters around the dump site, NO3− concentrations were negligible, while SO42− concentrations remain well below the maximum limit (250 mg/L) recommended by current guidelines in Argentina [43].
5. Study Limitations
The study has several limitations that are expected to be overcome by future work. This is an ongoing project, and, as such, only part of the data was available during manuscript preparation. Further sampling and monitoring is currently underway. Although additional domestic wells were also identified in the area, the absence of records of depth or construction details restricted their use in this study. Furthermore, the lack of information about casing integrity (if any) prevented their use as observation wells during the hydraulic tests. Single-bore tests provided meaningful information about the superficial aquifer, but many parameters can only be quantified with reasonable accuracy using multiple observation wells [44]. In addition, the unconfined aquifer is affected by the heterogeneity and vertical anisotropy of the sediments, which is highlighted by discrepancies between granulometric and hydraulic tests. The study represents a snapshot in time, as flow rates and the chemical composition of the waters are likely to vary on a seasonal basis. Long-term sampling and monitoring is, thus, required to better assess any temporal changes in groundwater and its possible interaction with the Chubut River. Finally, the success of a groundwater exploration program relies upon the accountable person, whether a geologist, hydrogeologist, or other professional, to make the right choice between the cost-effectiveness of various investigation techniques against the risk of drilling an unsuccessful borehole [45]. Budget constraints limited the density of the exploration targets and the amount of work that could be done in this survey. Clearly, many other factors, such as aquifers recharge, tectonic controls, and groundwater circulation, must be addressed in the future to refine the exploration approach and improve current interpretations.
6. Concluding Remarks
The environmental consequences of climate change create new challenges for water resource accessibility. Thus, a hydrogeological investigation was undertaken in an arid region of southern Argentina to better understand groundwater availability and the aquifer’s potential to sustain pastoral farming and minor agricultural activities. Results from the study indicate that the area is characterized by up to 45 m of Quaternary alluvial sediments, underlain by a sequence of silts and sands from the Cretaceous. The bulk of groundwater is encountered in superficial units, which act as an unconfined aquifer in the area. Several sand and gravel layers were found within the basal unit. However, their thickness and areal extent is limited for the purpose of water abstraction. Properties of the sediments were investigated by field and laboratory techniques. Estimates from pumping tests indicate that conductivity values in the alluvium vary between 3.5 and 10 m/day, while determinations by the Hazen solution resulted in maximum hydraulic conductivities close to 16 m/day. Some discrepancies in the results could be due to the fact that Hazen values are particularly affected by the fine-scale banding of sands and gravels, unlike aquifer tests that tend to average out the sediments’ variability. Although, no absolute hydraulic conductivity could be obtained, the analysis returned a range of values adequate to characterize the targeted aquifers.
Geochemical data show that shallow groundwater is typically fresh and mostly suitable for crops with moderate to good salt tolerance. Low sodium and negligible contents of toxic elements further suggest that waters are largely satisfactory for irrigation. An exception occurs in the northern margins of the site, where high salinity and anomalous nitrate concentrations were identified. This is explained as leachate from a nearby waste disposal site, and such groundwater pollution is expected to increase toward the source.
Field tests indicated that the alluvial aquifer could sustain abstraction rates up to about 4 L/s at any given time. Thus, the shallow units appear suitable to supply domestic or farm wells. Higher production would be attained by increasing the number and size of the bores. Nevertheless, the heterogeneity of sediments, limited recharge, and hydraulic connection between the aquifers and the Chubut River system are likely to have serious implications for the development of a water-supply scheme in the district.
The study is preliminary and not devoid of uncertainties and limitations. Further work is required to refine the understanding of the aquifer system and its connection with surface waters. Recharge rates, residence times, water-level fluctuations, and induced leakage of streamflow are only a few examples of additional information to be collected for further assessment.
Acknowledgments
The author acknowledges landowners and dwellers of the area for their assistance during fieldwork, and for providing valuable information that helped the interpretation of results. Many thanks to Chris O’Boy, Department of Water of Western Australia and James Bellin, BHP Billiton Pty Ltd. for their review comments and contribution to improve the manuscript. Special thanks to AHS Consulting for the financial support provided to the project and permission to utilize their data for publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, Q.; Wu, J.; Lei, T.; He, B.; Wu, Z.; Liu, M.; Mo, X.; Geng, G.; Li, X.; Zhou, H.; et al. Temporal-spatial characteristics of severe drought events and their impact on agriculture on a global scale. Quat. Int. 2014, 349, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen Jones, R. The Welsh language in Patagonia. In Language and Community in the Nineteenth Century; Jenkins, G.H., Ed.; University of Wales Press: Cardiff, UK, 1998; pp. 289–290. [Google Scholar]
- Rimoldi, P. Producción ovina en Chubut. IDIA XXI 2004, 4, 10–15. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Ares, J.; Beeskow, A.M.; Bertiller, M.; Rostagno, M.; Irrisarri, M.; Anchorena, J.; Defosse, G.; Merino, C. Structural and dynamic characteristics of overgrazed lands of Northern Patagonia, Argentina. In Managed Grasslands: Regional Studies; Bremeyer, A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990; pp. 149–175. [Google Scholar]
- Bakker, K. Water security: Research challenges and opportunities. Science 2012, 337, 914–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torcuato Di Tella Fundación. Comunicación nacional de cambio climático: Vulnerabilidad de la Patagonia y sur de las provincias de Buenos Aires y La Pampa. Informe Final; Fundación Torcuato Di Tella e Instituto Torcuato Di Tella: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2006; p. 368. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Méndez, P.M. The hidden face of the Patagonia Argentina. PASOS. Rev. Tur. Patrim. Cult. 2010, 8, 627–631. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, C.S. Estudios Geológicos en la Región del rio Chubut Medio; Secretaría de Industria y Comercio, Dirección General de Minas y Geología: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 1946; p. 202. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Aragón, E.; Mazzoni, M.M. Geología y estratigrafía del complejo volcánico piroclastico del rio Chubut medio (Eoceno), Chubut, Argentina. Rev. Asoc. Geol. Argent. 1997, 52, 243–256. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Moyano, C.H.; Moyano, M.C. Estudio hidrológico del rio Chubut. Cuenca superior y media. Contrib. Cient. GAEA 2013, 25, 149–164. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Auge, M.; Wetten, C.; Baudino, G.; Bonorino, G.; Gianni, R.; González, N.; Griznik, M.; Hernández, M.; Rodríguez, J.; Tineo, A.; et al. Hidrogeología de Argentina. Bol. Geol. Min. 2006, 117, 7–23. [Google Scholar]
- Scarpini, M.C.; Orfila, J.D. Características de las aguas subterráneas de la provincia del Chubut. Direccion de Proteccion Ambiental, Provincia de Chubut, Argentina, 2005. Available online: http://www.infogranjas.com.ar (accessed on 5 February 2016).
- Sánchez, R.M.; Dunel Guerra, L.; Scherger, M. Evaluación de las áreas bajo Riego Afectadas por Salinidad y/o Sodicidad en Argentina; Programa Nacional del Agua; INTA Publications: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2015; p. 65. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Beltramonte, C.; Del Valle, H.F. Reconocimiento de los recursos naturales y el medio ambiente de la región Noreste del Chubut Republica Argentina. In Centro Nacional Patagónico, Contribución No. 47; CONICET Publications: Chubut, Argentina, 1981; p. 33. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- INTA, Instituto Nacional de Tecnología Agropecuaria. Atlas de Suelos de la Republica Argentina. Escala 1:500,000/1:1,000,000; INTA Publications: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 1995. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Acebal, M. Proyecto de reforzamiento de la producción caprina de mohair en el Norte de la Patagonia Argentina. Programa Mohair 2007. Unpublished. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- HydroSolve, Inc. AQTESOLV pumping test software. Available online: http://www.aqtesolv.com (accessed on 5 May 2016).
- Cabaleri, N.; Volkheimer, W.; Armella, C.; Gallego, O.; Silva Nieto, D.; Páez, M.; Cagnoni, M.; Ramos, A.; Panarello, H.; Kouharsky, M. Estratigrafía, análisis de facies y paleambientes de la formación Cañadón Asfalto, en el depocentro Jurasico Cerro Cóndor, Provincia del Chubut. Rev. Asoc. Geol. Argent. 2010, 66, 349–367. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Marveggio, N.; Llorens, M. Nueva edad de la base del Grupo Chubut en la mena uranífera Cerro Solo, Provincia del Chubut. Rev. Asoc. Geol. Argent. 2013, 70, 318–326. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Shepperd, R.G. Correlations of permeability and grain size. Ground Water 1989, 27, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazen, A. Discussion: Dams on sand foundations. Trans. Am. Soc. Civil Eng. 1911, 73, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brassington, R. Field Hydrogeology, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2007; p. 264. [Google Scholar]
- Younger, P.L. Groundwater in the Environment: An Introduction; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2007; p. 336. [Google Scholar]
- Uma, K.O.; Egboka, B.C.E.; Onuoha, K.M. New statistical grain-size method for evaluating the hydraulic conductivity of sandy aquifers. J. Hydrol. 1989, 108, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nievas, H.O.; Caruso, M.; Pizzio, F.; Ferri, F.O.; Pérez, S. Monitoreo ambiental de aguas superficiales y subterráneas, consideración de áreas sensibles, distrito uranífero Pichiñan este, departamento Paso de Indios, provincia del Chubut. Rev. Asoc. Geol. Argent. 2013, 70, 327–334. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Krautkramer, F.M. Hydrogeology of the Pacific Northwest. A Summary Discussion. In NGWA Pacific NW Expo; Robinson Noble Inc.: Portland, OR, USA, 2012; p. 78. [Google Scholar]
- Jacob, C.E. Drawdown test to determine effective radius of artesian well. Trans. Am. Soc. Civil Eng. 1947, 112, 1047–1070. [Google Scholar]
- Boulton, N.S. Analysis of data from non-equilibrium pumping tests allowing for delayed yield from storage. Proc. Inst. Civil Eng. 1963, 26, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruseman, G.P.; de Ridder, N.A. Analysis and Evaluation of Pumping Test Data; Pudoc: Wagening, The Netherlands, 1990; p. 377. [Google Scholar]
- Neuman, S.P. Effect of partial penetration on flow in unconfined aquifers considering delayed gravity response. Water Resour. Res. 1974, 10, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theis, C.V. The relation between the lowering of the piezometric surface and the rate and duration of discharge of a well using groundwater storage. Am. Geophys. Union Trans. 1935, 16, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.F.; Su, Y.H.; Feng, Q. The hydrogeochemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater and surface water in the Heihe River Basin, northwest China. Hydrogeol. J. 2008, 16, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO (World Health Organization). Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality. Available online: http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/publications/2011/dwq_chapters/en/ (accessed on 5 February 2016).
- McGowan, W. Water Processing: Residential, Commercial, Light-Industrial, 3rd ed.; Water Quality Association: Lisle, IL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Evens, E.; Yanick, S.; Osnick, J. Characterization of hardness in the groundwater of Port-Au-Prince. An overview of the health significance of magnesium in the drinking water. Aqua LAC 2013, 5, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- ANZECC. Australian and New Zealand Guidelines for Fresh and Marine Water Quality. The Guidelines; Australian Water Association: New South Wales, Australia, 2000; Volume 1, p. 314. [Google Scholar]
- Gowariker, V.; Krishnamurthy, V.N.; Gowariker, S.; Dhanorkar, M.; Paranjape, K. The Fertilizer Encyclopedia; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; p. 860. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A. Water Pollution; A.P.H Publishing Corp.: New Delhi, India, 2004; p. 349. [Google Scholar]
- Shahabi, A.; Malakouti, M.J.; Fallahi, E. Effects of bicarbonate content of irrigation water on nutritional disorders of some apple varieties. J. Plant Nutr. 2005, 28, 1663–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, L.A. Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkaline Soils. In United States Salinity Laboratory Staff. Agricultural Handbook No. 60; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1954; pp. 1–160. [Google Scholar]
- Jarsun, O.; Bustos, V.; Carnero, M. Manual de uso e Interpretación de Aguas. Provincia de Córdoba; Report prepared by the Secretary of Environment of Cordoba: Cordoba, Argentina, 2008; p. 50. [Google Scholar]
- Maas, E.V. Crop salt tolerance. In Agricultural Salinity Assessment and Management, ASCE Manuals and Reports on Engineering Practice 71; Tanjii, K.K., Ed.; ASCE: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 262–304. [Google Scholar]
- Código Alimentario Argentino. Normas Oficiales Para la Calidad del Agua Argentina. Disposiciones de la ley 18.284. Available online: http://www.cdaguas.com.ar/pdf/aguas/24_Normas_oficiales.pdf (accessed on 5 February 2016).
- Hanson, R.T.; Nishikawa, T. Combined use of flowmeter and time-drawdown data to estimate hydraulic conductivities in layered aquifer systems. Ground Water 1996, 34, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, P. Lineaments in groundwater exploration: A review of applications and limitations. Hydrogeol. J. 2007, 15, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the author; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).