Abstract
Increasing dependence on groundwater requires a detailed determination of the different outputs and inputs of a basin for better water management. Determination of spatial and temporal actual evapotranspiration (ETa), in this regard, is of vital importance as there is significant water loss from drainage basins. This research paper uses the Surface Energy Balance Algorithm for Land (SEBAL), as well as the water balance, to estimate the spatial and temporal ETa in the Al-Khazir Gomal Basin, Northern Iraq. To compensate for the shortage in rainfall, and to irrigate summer crops, farmers in this basin have been depending, to a large extent, on groundwater extracted from the underlying unconfined aquifer, which is considered the major source for both domestic and agricultural uses in this basin. Rainfed farming of wheat and barley is one of the most important activities in the basin in the winter season, while in the summer season, agricultural activity is limited to small rice fields and narrow strips of vegetable cultivation along the Al-Khazir River. The Landsat Thematic Mapper images (TM5) acquired on 21 November 2006, 9 March 2007, 5 May 2007, 21 July 2007, and 23 September 2007 were used, along with a digital elevation model (DEM) and ground-based meteorological data, measured within the area of interest. Estimation of seasonal ETa from periods between satellite overpasses was computed using the evaporative fraction (Ʌ). The water balance approach was utilized, using meteorological data and river hydrograph analysis, to estimate the ETa as the only missing input in the predefined water balance equation. The results of the two applied methods were comparable. SEBAL results were compared with the land use land cover (LULC) map. The river showed the highest ETa, as evaporation from the free-water surface. Rice fields, irrigated in the summer season, have a high ETa in the images, as these fields are immersed in water during June, July and August. Vegetated corridors along the riverside showed different ETa values, as they contain a mosaic of different crops in different stages of growth. Conglomerate and bare sandstone outcrops showed no ETa, with some exceptions in the mountainous area, where these outcrops are affected by perennial springs. The results indicate the applicability of SEBAL in the study area, and they could be used in further studies to estimate the water budget of the basin.
1. Introduction
Water demand is on the rise everywhere in the world, especially in arid and semi-arid countries where agriculture depends, to a large extent, on irrigation using water extracted from groundwater. Iraq, although not an exception, is considered wealthy in terms of water resources in comparison to other countries in the Middle East. These resources, however, are becoming more and more strained under the constraint of population growth, development programs, and decreasing water inflow from neighboring countries (such as Turkey, Iran and Syria). Therefore, Iraq may face water resource shortages, similar to those of other Middle East countries unless rational management for sustainable use of limited water resources is planned and implemented.
A special case in Iraq is the Al-Khazir Gomal Basin. Groundwater, in addition to the Al-Khazir River, represents the main source of fresh water in the central sector of the plain. More than 30% of the plain is cultivated for rainfed barley and wheat, while vegetable and row crops are cultivated along the Al-Khazir River. Domestic use of groundwater is the main use in the plain. However, over the last decade, due to the scarcity of rainfall and agricultural development, the tendency has been to use the groundwater for sprinkler irrigation to compensate for the shortage in rainwater. Therefore, more than 250 government wells, as well as an unknown number of private wells, have been drilled in the region over the last 10 years, and groundwater has been used as an additional source for irrigation to compensate for the shortage in rainfall and to keep pace with agricultural development. If groundwater exploitation continues rising at the same rate, this might, as already expected, lead to irreversible negative qualitative and quantitative effects on the groundwater in the coming decades. Therefore, water management is a vital issue in this basin.
Successful water resources management depends on an accurate knowledge of water input and output in the area of interest. Evapotranspiration, a combination of evaporation and transpiration processes, represents the greater part of the output, and is a key indicator for water management and irrigation performance. Thus, increasing the accuracy of actual evapotranspiration (ETa) determination will reduce, to a large extent, the uncertainty in water balance calculations, thereby increasing the accuracy of the estimated recharge, which is the most important component in groundwater management [1].
In reference to evapotranspiration, spatial and temporal information about ETa distribution would help in the understanding of evaporative depletion and in establishing links between land use, water allocation and water use [2]. Therefore, many improvements have been made to acquire insight into local-scale evaporation processes through accurate point measurements with eddy covariance, a sap flow meter, Bowen ratio and a lysimeter. Although these methods, where available, can deliver reliable evapotranspiration measurements up to field scale, extrapolating the estimations to larger scales might lead to biased estimations [3,4,5,6,7].
Iraq in general and the Al-Khazir Gomal Basin, the study area in this research, in particular lack ETa point measurements. Therefore, many researchers [8,9,10] have used the traditional water balance equation, which depends on hydrometeorological data, to estimate ETa. In this regard, potential evapotranspiration (ETp) has frequently been calculated using Thornthwaite’s method [11], Kharrufa’s method [12] and Penman’s method [13]. Thereafter, ETa was equal to potential evapotranspiration (ETp) for water surplus periods and equal to rainfall during water deficit periods. In the case of availability of direct measurements of runoff and recharge in the scale of the watershed, the ETa can be estimated as a residual component. However, the water balance approach does not give a comprehensive idea about water resource management, and inaccurate determination of ETa might exaggerate errors in other elements of the hydrological cycle. In addition, one cannot estimate the evapotranspiration from an irrigated area through water balance without quantifying the amount of water used by irrigation. Therefore, quantifying the ETa on a regional scale is important for allocation of water resources, establishment of hydrologic water balances, water rights management and water regulation [14].
Remote sensing-based ETa models have been used for a long time as feasible means to depict the spatial and temporal distribution of regional ETa (e.g., [15,16]). In the last two decades, numerous complex models have been proposed for estimating ETa by using remotely sensed data, e.g., the Two Sources Energy Balance model (TSEB) [17], Surface Energy Balance Algorithm for Land (SEBAL) [18], the Simplified Surface Energy Balance Index (S-SEBI) [19], the Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) [20], the Simplified Two Sources Energy Balance (STSEB) [21], the Global Land-surface Evaporation: the Amsterdam Methodology (GLEAM) [22] and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer model for terrestrial evapotranspiration (MODIS-ET) [23]. Long and Singh [24] developed a Two-source Trapezoid Model for Evapotranspiration (TTME) from satellite imagery by interpreting the remotely sensed fractional vegetation cover (fc) and radiative surface temperature (Trad) space, and the concept of soil surface moisture availability isopleths superimposed on the space. More recently, the Hybrid Dual-Source Scheme and Trapezoid Framework Based Evapotranspiration Model (HTEM) were developed by Yang and Shang [25]. The last two models enable evaporation from the soil and transpiration from the canopy to be estimated separately, and differ in the way they parameterize aerodynamic resistance over the studied domain.
SEBAL, above all, uses satellite imagery and local meteorological data for estimating the instantaneous ETa as a residual component with a strong physical and empirical basis and has fewer requirements for concurrent ground-level observations [18], which is the case in the study area. Moreover, SEBAL uses an internal calibration procedure to compensate for errors in temperature and albedo without any need for complex atmospheric correction [9]. Bastiaanssen et al. [2] tested the accuracy and performance of SEBAL under several climatic conditions, and with several soil types and plant communities in more than 30 countries on both a field and regional scale. They stated that the average accuracy of SEBAL was 85% on a field scale for a single day and 95% for a seasonal scale, and the accuracy increased to 96% in larger watersheds. That underlines the applicability of the SEBAL model for estimating ETa, especially in large watersheds with few ground observation points. Moreover, the error reduces when evapotranspiration is aggregated over longer time steps, as the errors cancel out, which is demonstrated in different studies [26,27,28].
In this study, the SEBAL model was used to map spatial and temporal variation of ETa in the Al-Khazir Gomal Basin for the period 2006–2007. Five Landsat Thematic Mapper images (TM5) were used for this purpose, as well as meteorological ground data. The land use land cover (LULC) map was prepared using supervised classification in Earth Resources Data Analysis System (ERDAS) (Leica Geosystems, Atlanta, GA, USA) and used in visual comparison with spatial patterns of ETa in the region. Moreover, water balance was also used to validate the results of the SEBAL model. The SEBAL results also helped in understanding the interannual and seasonal variability of ETa in the study area.
2. Study Area
The Al-Khazir Gomal Basin is located in the northern part of Iraq, and covers an area of 3185 km2 with a geographic location of 43°44'25"–43°14'00"E longitude and 36°52'33"–36°22'00"N latitude (Figure 1). Al-Sam and Hanna [29] divided this basin into three regions in terms of structural and geological aspects: the first, the second and the third. The Aqre Mountains to the north of the basin (first region) is covered mainly by bare carbonate rocks belonging to the Cretaceous and Eocene age and recent slop sediments, while the second region—representing a vast plain—extends between the Aqre Mountains in the north and the Bardarash Mountains to the south. In this plain the predominant sediment is residual soil, which consists of silty clay and a sandy loam texture, in addition to slope sediments, and Pliocene alluvial sediments such as conglomerate and sandstone. The third region, to the south of the Bardarash Mountains, is covered mainly by Pliocene sediments. The maximum elevation within the area is 2165 meter above sea level (m.a.s.l.) in far north of the basin and the minimum elevation is 216 m.a.s.l. close to the basin outlet in the south.
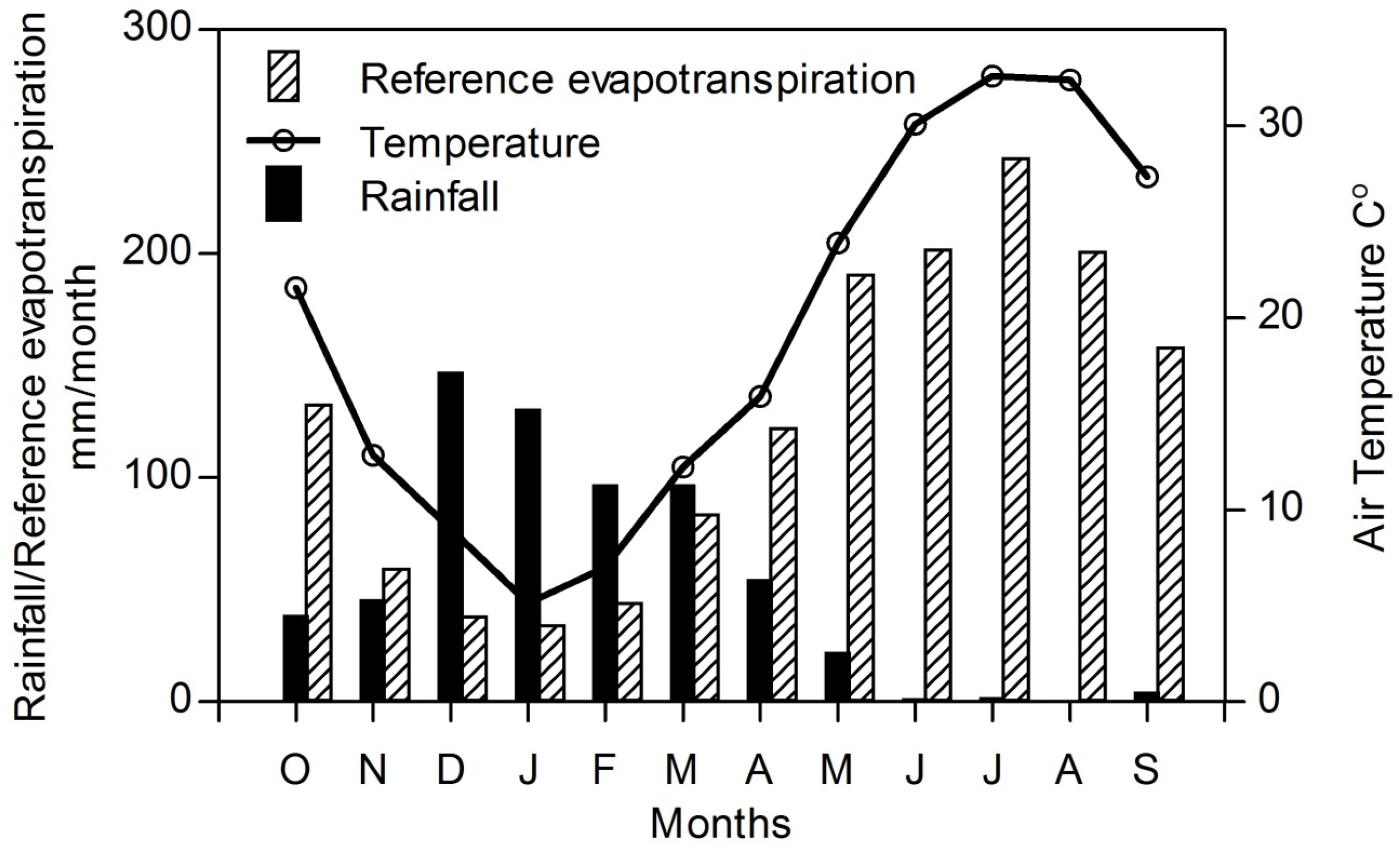
As shown in Figure 2, the area is characterized by a continental climate, being cold and rainy in winter and hot and dry in summer with an average annual temperature, precipitation and reference evapotranspiration (ETr) calculated using CROPWAT 8.0 (Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), Water Resources, Development and Management Service, Rome, Italy) of 20 °C, 650 mm and 1500 mm, respectively [30]. The annual average relative humidity is around 46% and the predominant wind direction is from the northwest with an average speed of 1.54 m/s. According to the aridity index, the study area is classified as a semi-arid to dry subhumid region [30]. The agricultural activity is concentrated in the second region, where the rainfed agriculture of wheat and barley in winter, and rice, maize and sunflowers in summer, is considered the most important activity in addition to vegetable cultivation along the Al-Khazir River. Olive, fig, grape and nut orchards irrigated by springs in the mountainous area cover the valley bottoms in this area.
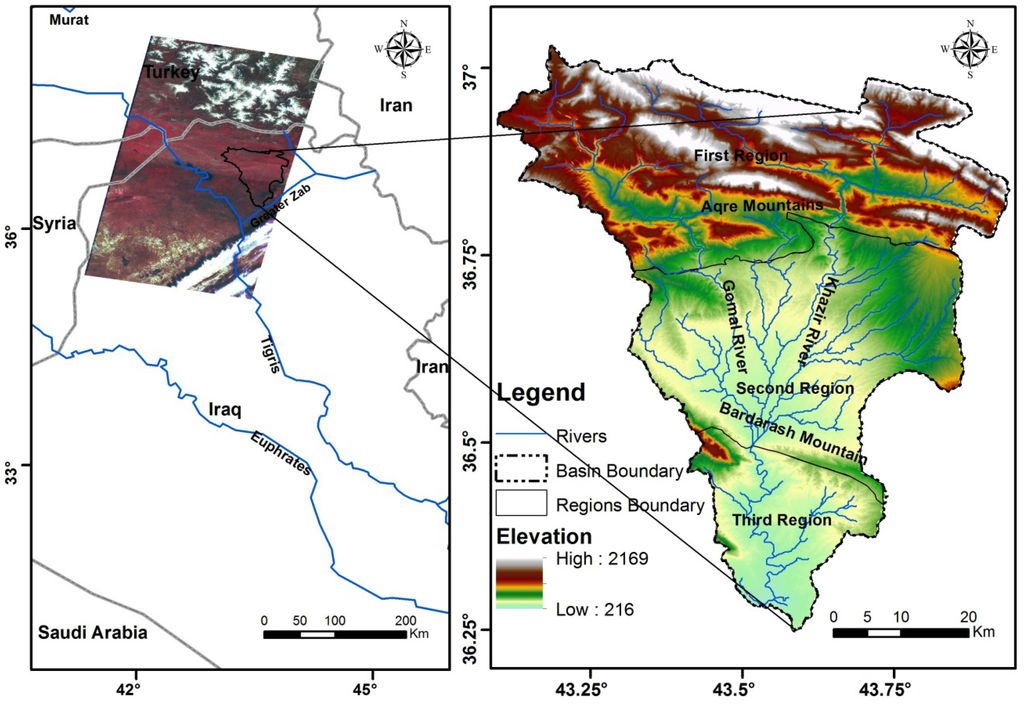
Figure 1.
Location map of the study area. The Landsat Thematic Mapper images (TM5) scenes covering the whole study area on the left, and the watershed map with elevation range (meter above sea level (m.a.s.l.)) on the right. The two satellite images that cover the study area (Landsat, path 170, row 34 and 35) are a false color composite (composite of bands 4, 3, and 2 of the multiband satellite image TM5) with 30 m resolution.
Figure 1.
Location map of the study area. The Landsat Thematic Mapper images (TM5) scenes covering the whole study area on the left, and the watershed map with elevation range (meter above sea level (m.a.s.l.)) on the right. The two satellite images that cover the study area (Landsat, path 170, row 34 and 35) are a false color composite (composite of bands 4, 3, and 2 of the multiband satellite image TM5) with 30 m resolution.
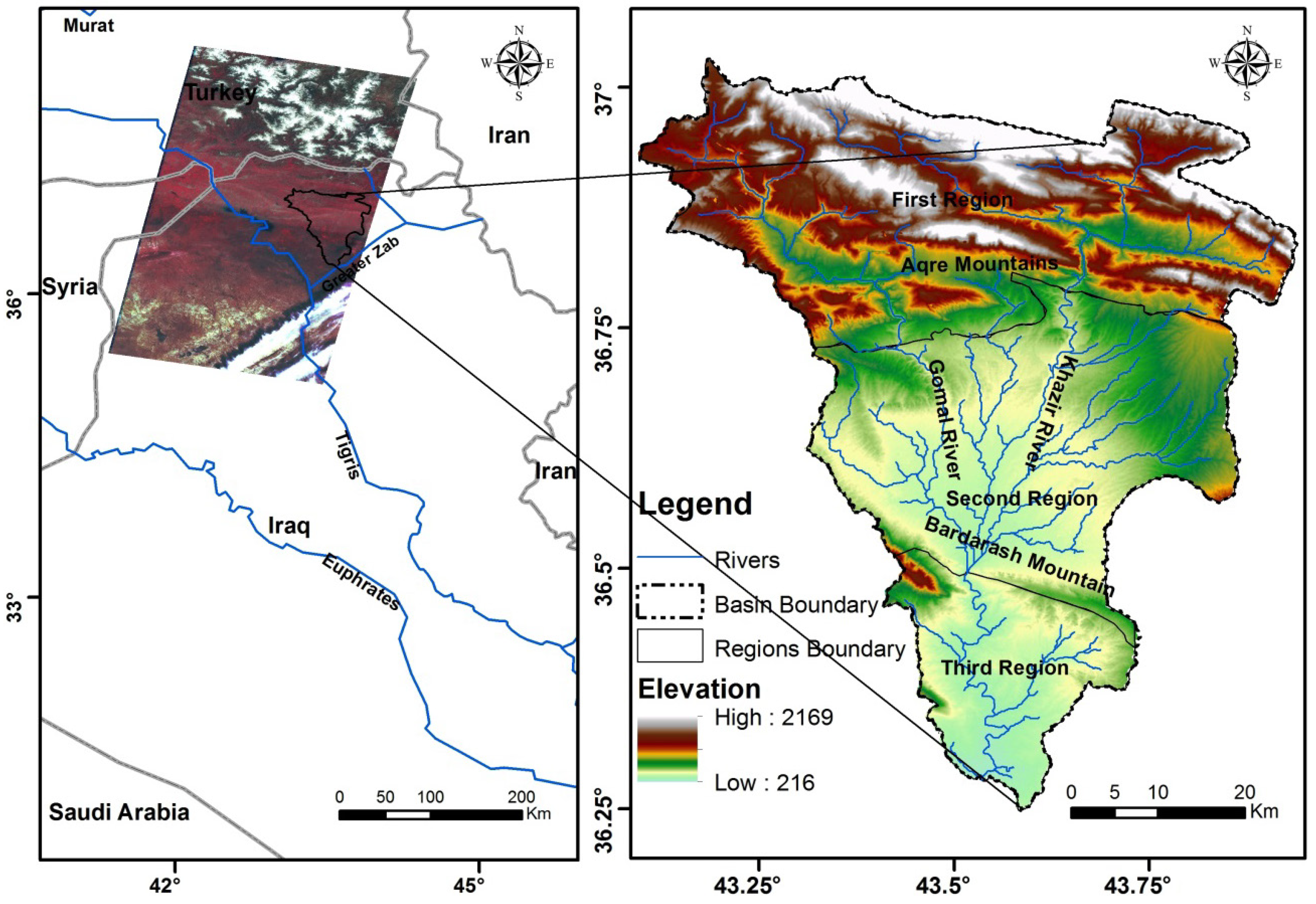
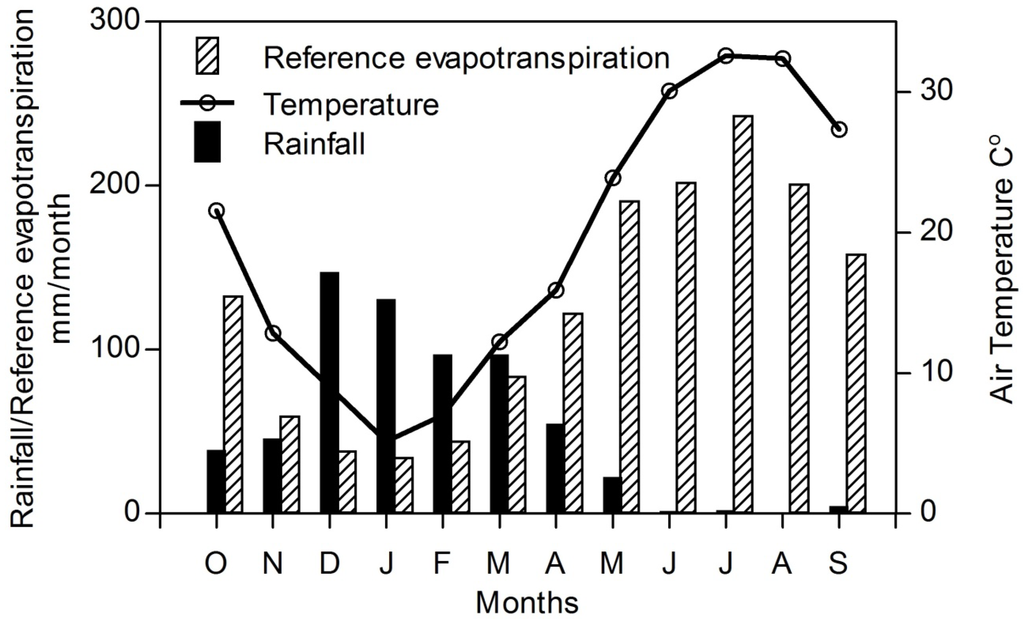
Figure 2.
General climate condition (temperature, rainfall, and reference evapotranspiration (ETr)) for the period 2001–2011 at Aqre meteorological station.
Figure 2.
General climate condition (temperature, rainfall, and reference evapotranspiration (ETr)) for the period 2001–2011 at Aqre meteorological station.
3. Land Use Land Cover
The LULC map supports users of the SEBAL model with a good working knowledge of the area being studied, so they can better recognize and evaluate the reliability of the SEBAL results [31]. In addition, LULC maps are fundamental tools for natural resource management and planning [32]. Using supervised classification (Maximum Likelihood method) for TM5 satellite image in March 2006 (spring season), the study area is classified into five main classes: vegetated land, fallow, conglomerate and sandstone, carbonate rocks, and urban and built-up land. The LULC map of the area (Figure 3) is based on the classification of each pixel of the TM5 image to be assigned to one of the five main LULC classes. Some classes were modified and interpolated after supervised classification using GIS software depending on information gathered from field observations and geological maps. This modification was applied to address the interference between these classes in some places on the map, or as a result of the occurrence of scattered pixels for any of these classes with other classes. The random sampling method was used for field checking, and the accuracy assessment, which was generated from the supervised classification technique, showed that the overall classification accuracy is 93.73% and that the overall kappa statistic is 0.9214.
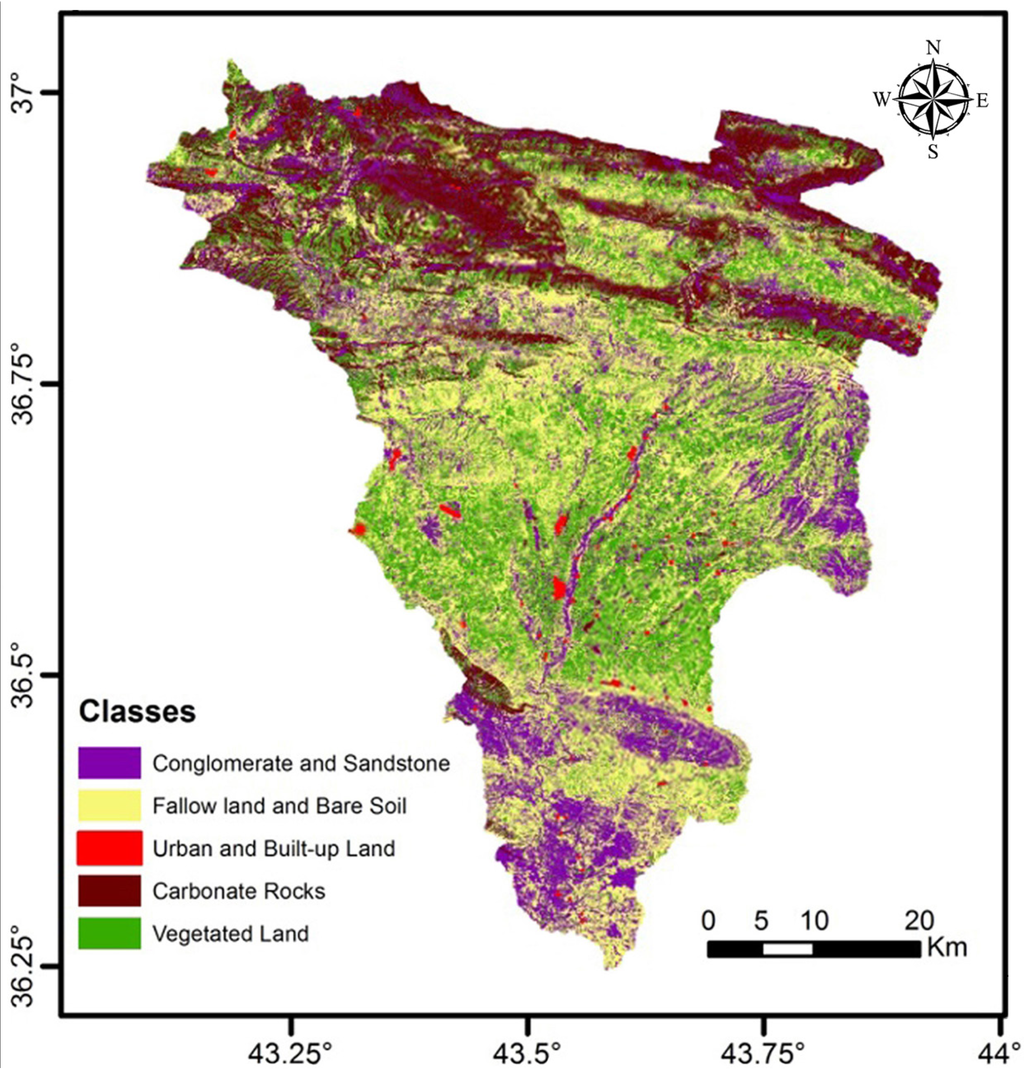
Figure 3.
Land use land cover (LULC) map illustrating the main classes in the study area on 9 March.
Figure 3.
Land use land cover (LULC) map illustrating the main classes in the study area on 9 March.
The vegetated land class during the growing season represents 31.7% of the basin area. This class includes all vegetation cover that grows naturally or as a result of human activities, such as forests, shrubs, grass, cropland, pastures and orchards, and other types of vegetated agricultural land. The vegetation cover in the study area is dominated by rainfed fields of wheat and barley, which are distributed in the flat-terrain and low-relief land areas of the Aqre plain (second region). The mountainous area in the north (first region) is dominated by olive, grape, fig and nut orchards, in addition to a patchwork of forests and scrublands. The orchards and forests cover the valley bottoms are watered by the springs. The fallow lands class covers 32% of the basin, including all types of agricultural land without vegetation cover on the date the satellite imagery was acquired, such as idle cropland, and cultivated and harvested land cover.
The conglomerate and sandstone class, which represents the outcrops of the highly permeable Pliocene sediments (recharge windows), as well as Quaternary slope sediments cover 20.2% of the basin. The carbonate rocks class covers 15.4% and is mainly exposed in the Aqre Mountains. These carbonate rocks constitute, along with the conglomerate and sandstone class, the bare areas in the basin. Urban land covers only 0.8% of the basin, comprising areas of intensive use, such as cities, towns and villages. It is difficult to represent all of the small villages and scattered buildings due to the spatial and spectral resolution of the Landsat images, but in general one can consider the basin to be pristine because of the low population and absence of big infrastructure.
4. Methodology
4.1. Surface Energy Balance Algorithm for Land (SEBAL)
The satellite digital image data of the TM5 and Advanced Space borne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) are considered the main input data for the SEBAL model. For estimating the ETa using the water balance approach, the daily meteorological data (2001–2011) from Aqre station and the daily Al-Khazir River discharge (1969–1981) at the outlet of the basin were collected. Landsat TM5 images (Path 170, Rows 34 and 35), covering the Al-Khazir Gomal Basin, were acquired on 21 November, 9 March, 5 May, 21 July and 23 September for the period 2006–2007 from the URL of the United State Geological Survey (USGS) Global Visualization Viewer (GLOVIS).
The slope and aspect for each pixel were derived from a Digital Elevation Model (DEM) by ArcGIS Desktop 10 (Environmental Systems Research Institute (ESRI), Redlands, CA, USA). Then, the elevation, aspect and slope were used in the SEBAL mountain model [27] to avoid overestimating ETa caused by the high elevation and south-sloping land. This model was applied only to the Aqre mountainous area (first region), while the second and third regions are considered flat areas because there is no significant relief in these two regions.
The Penman-Monteith formulation (P-M) is regarded as a suitable estimator for ETr in a wide range of climatic conditions [32]. The ETr was estimated using the CROPWAT 8.0 software from the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). ETr is used in SEBAL to estimate the instantaneous ETa at the “cold” pixels. The SEBAL model was described in detail by Bastiaanssen et al. [18], Bastiaanssen et al. [2], Bastiaanssen [33] and Tasumi [34]. In brief, SEBAL computes the instantaneous surface energy balance at the moment of satellite overpass on a pixel-by-pixel basis through a series of computations that generate: net surface radiation (Rn), soil heat flux (Go) and sensible heat flux to the air (H). By subtracting the soil heat flux and sensible heat flux from the net radiation at the surface, the “residual energy” will be the latent heat flux (LE) that is used for evapotranspiration:
The net surface radiation (Rn) represents the actual radiant energy available at the surface. It is computed by subtracting all outgoing radiant fluxes from all incoming radiant fluxes. This is given in the surface radiation balance equation:
where RS↓ is the incoming shortwave radiation (W/m2), α is the surface albedo (dimensionless), RL↓ is the incoming longwave radiation (W/m2), RL↑ is the outgoing longwave radiation (W/m2) and εo is the surface thermal emissivity (dimensionless). The total surface albedo (αtoa) is calculated from visible/near infrared and shortwave bands of the satellite image:
where ρλ is the band reflectivity, and ωλ is a weighting coefficient for each band. Surface albedo (α) is computed by correcting the αtoa for atmospheric transmissivity.
Incoming shortwave radiation, which represents the direct and diffuse solar radiation flux that actually reaches the earth’s surface (W/m2), is calculated, assuming clear sky conditions, as a constant for the image time using:
where Gsc is the solar constant (1367 W/m2), cosθ is the cosine of the solar incidence angle, dr is the inverse squared relative earth-sun distance, and τsw is the atmospheric transmissivity. Atmospheric emissivity and surface emissivity are used to calculate incoming and outgoing longwave radiation, respectively, from surface temperature using the Stefan-Boltzmann equation:
where εa is the atmospheric emissivity and εο surface emissivity (dimensionless), σ is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant (5.67 × 10−8 W/m2/K4), Ta is the near surface air temperature (K) and Ts is the surface temperature (K). Ta is measured at a ground station and Ts is calculated from the thermal band of the satellite image (the radiance of band 6 in TM5):
After calculating the net radiation using Equation (2), the empirical equation developed by Bastiaanssen [33] is applied to calculate the soil heat flux (Go):
where Ts is the surface temperature in (°C), α is the surface albedo and NDVI is the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index. The NDVI is calculated using the reflectivity of both the near-infrared band (ρ4) and the red band (ρ3) of the satellite image as follows:
where ρ4 and ρ3 are reflectivities of satellite image bands 4 and 3, respectively.
The sensible heat flux is estimated using the bulk aerodynamic resistance model and a procedure that assumes a linear relationship between Ts calculated at “hot” and “cold” pixels (extreme pixels) and air temperature difference (dT). The cold and hot pixels are selected from a well-irrigated crop surface and bare agricultural field, respectively, and the procedure for this selection is described in detail by [27]. Sensible heat flux is assumed to be zero for the cold pixels and equal to “Rn − Go” for hot pixels. Then, H for each pixel is calculated from:
where ρa is the air density (kg/m3), Cp is the air-specific heat (1004 J/kg/K), dT (K) is the temperature difference, and rah is the aerodynamic resistance to heat transport (s/m).
Regional ETa estimation in flat areas assumes a constant solar azimuth and solar elevation angles over the area of interest at the satellite overpass time. In mountainous areas, however, they are different for each pixel depending on the aspect and slope. In addition, the effect of mountain shadow causes further variation in the incoming solar radiation. Thus, an accurate estimation of ETa using satellite images in mountainous areas requires that some modifications, particularly terrain correction, be made to each pixel. Mountain terrain corrections are performed in the “SEBAL Mountainous Model” using topographic features (slope, aspect and elevation) extracted from the ASTER elevation model. These features are then implemented in calculating incoming shortwave radiation (), atmospheric transmissivity (τsw) and surface temperature (Ts) for terrain correction. The cosine of the Solar Incidence Angle (cosθ) is the first step in the mountainous model; it is calculated using the sine and cosine of the slope/aspect, the declination, the latitude and the hour angle. Afterwards, reflectivity, transmissivity, surface albedo, incoming shortwave radiation, surface temperature and incoming longwave radiation are calculated for each pixel. For instance, atmospheric transmissivity (τsw) varies here for each pixel as a function of the elevation. The following equation [27] is used for correcting the transmissivity:
where ZDEM is the elevation of each pixel above sea level (m). Surface temperature (Ts) decreases with increasing elevation and the rate of decrease is assumed to be 0.65 °C/100 m, which is the same as that for a typical air profile [27]. The terrain correction for Ts is computed as:
where
is the difference between the reference elevation of the micrometeorological station and the DEM elevation. Moreover, selecting wet and dry pixels is the same as for flat terrain; the only difference here is the use of the corrected surface temperature raster.
The internal calibration inherent in the sensible heat flux computation procedures eliminates the need for atmospheric correction of Ts or using transfer models for reflectance measurements [35]. There are different methods for converting the output of SEBAL instantaneous ETa to more practical daily ETa. The most widely used methods in this regard are the evaporative fraction method [36,37] and the alfalfa ETr fraction method [38]. The evaporative fraction method works better on a regional scale with heterogeneous vegetation cover conditions under moisture stress, while the alfalfa ETr is more suitable in the case of homogeneous and well-irrigated vegetation conditions [39,40]. In this study the evaporative fraction (Ʌ) was selected to estimate the daily evapotranspiration.
The instantaneous (Ʌ) is considered to be constant during daytime hours [33,37,41]. For timescales of 1 day or longer, Bastiaanssen et al. [42] ignored Go and reduced the net available energy (Rn − Go) to net radiation (Rn),
where ET24 is the 24 h actual evaporation, Rn24 is the 24 h average net radiation, ʎ is the latent heat of vaporization (J·kg−1), ρw is the water density (kg·m−3).
Because of the temporal satellite resolution (visit time) and image gap acquisition due to temporal cloud cover, the interpolation of the daily to seasonal and annual ETa is not an easy task. Bastiaanssen et al. [18,43] estimated the annual ETa in the Indus Basin using the SEBAL model and reported that the annual ETa on a field scale varies from 0% to 10% and 5% on a regional scale compared to the Soil Water Atmosphere Plant model (SWAP).
Therefore, for upscaling the daily ETa to monthly or seasonal ETa, the Bastiaanssen equation is used:
where ETint is the average daily evapotranspiration in the time period corresponding to one satellite image, and Rn24t is the average Rn24 value for the time interval (dt) measured in days (W·m−2).
4.2. Water Balance
Groundwater balancing is a well-known technique that has often been utilized to quantitatively estimate water resources and the impact of the different activities of man on the hydrologic cycle. The essence of this method is to define the supply and use of water within the geographic region under consideration for a defined period. According to the law of conservation of mass, the main concept of water balance is [44]:
Input to the system − output from the system = change in storage in the system
Solving this equation requires the following:
- (1)
- Determination of significant and insignificant components.
- (2)
- Quantification of individual components.
- (3)
- Presentation in the final form of a water balance equation.
One form of groundwater balance equation for an unconfined aquifer within a time span Δt is given as:
where R is rainfall, Rf is irrigation return flow, Ro is runoff, Iin and Iout are groundwater flow into and off the basin, ETa is the sum of evapotranspiration and evaporation from the water table, Pg is the abstraction of groundwater by pumping, and ΔS is change in the water storage (water stored in the unsaturated and saturated zone) (mm).
Iin and Iout are neglected because the study area is a complete watershed that has its boundaries as water divide. Hence, no groundwater flows across these boundaries. Moreover, no field or statistical estimations have been done yet regarding the abstraction of groundwater for irrigation and domestic uses (Pg) and irrigation return flow (Rf). Therefore, Pg and Rf are neglected in this study. This assumption is satisfied if one takes into account the population (~40,000), which is very small in comparison to the area of the studied watershed (3185 km2), and the fact that rainfed agriculture is the main agricultural activity in the watershed. The water stored in the unsaturated zone as part of ΔS is normally referred to as soil moisture; unfortunately, no measured soil moisture data is available in the study area, and satellite data might deliver information about soil moisture from the few uppermost centimeters of the unsaturated zone [45], so that the change in stored water is taken as almost the change in groundwater storage (Ri). The monthly water balance for the study area becomes:
where R is rainfall, Ro is runoff, ETa is the actual evapotranspiration, and Ri is the change in groundwater storage.
Uncertainty Analysis in the Water Balance
Uncertainty is inherent in the calculated ETa using different methods; this uncertainty is due to the inaccuracy in the parameters used in the estimation, which in turn has an associated impact on the calculated parameter. For instance, groundwater recharge was previously calculated using different approaches, and each of those approaches takes into account different simplifications and different algorithms. Therefore, this uncertainty has to be taken into consideration when used in calculating the ETa as a residual in the water balance equation.
The easiest way to account for this uncertainty in groundwater balance is to consider the error of the model input data using a simple statistical approach. The following formula is used in estimating the uncertainty:
where X is the calculated parameter, Xbest is the best estimation, which is taken as the average of the calculated parameters using different methods, and ΔX is the error, which here is the standard error. The previous equation is written in another form as:
where SD is the standard deviation, and n is the number of measurements. The ratio of the standard deviation to the square root of the n is referred to as the standard error of the mean.
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. SEBAL
Because only five satellite images covering the study area were available at no cost, five evapotranspiration maps were prepared, encompassing the entire studied Al-Khazir Gomal watershed. Fortunately, these available images cover the different seasons in the area, which could help ultimately to extrapolate the results of each processed image to the whole related season using the aforementioned (Ʌ) and Equation (5). Each map consists of 3.5 million pixels, each of which is 30 m × 30 m.
Calculations of the net incoming radiation, the soil heat flux and the sensible heat flux were carried out according to the energy balance equations in SEBAL. Estimation of the air density was required for calculating the first temperature difference between air and soil for both “cold” and “hot” pixels (i.e., where the LE is maximum and minimum, respectively). This was done by generalizing the meteorological data at the time of satellite overpass. Iterations of sensible heat flux were conducted three times until the result was stabilized. The daily ETa was calculated from the instantaneous Λ, and the 24 h average net radiation, Rn24. Five maps of the instantaneous LE were made, followed by five daily integrated evapotranspiration maps. The results for all of the aforementioned months corresponding to the images’ acquisition dates, plus the annual evapotranspiration map, are shown in Figure 4.
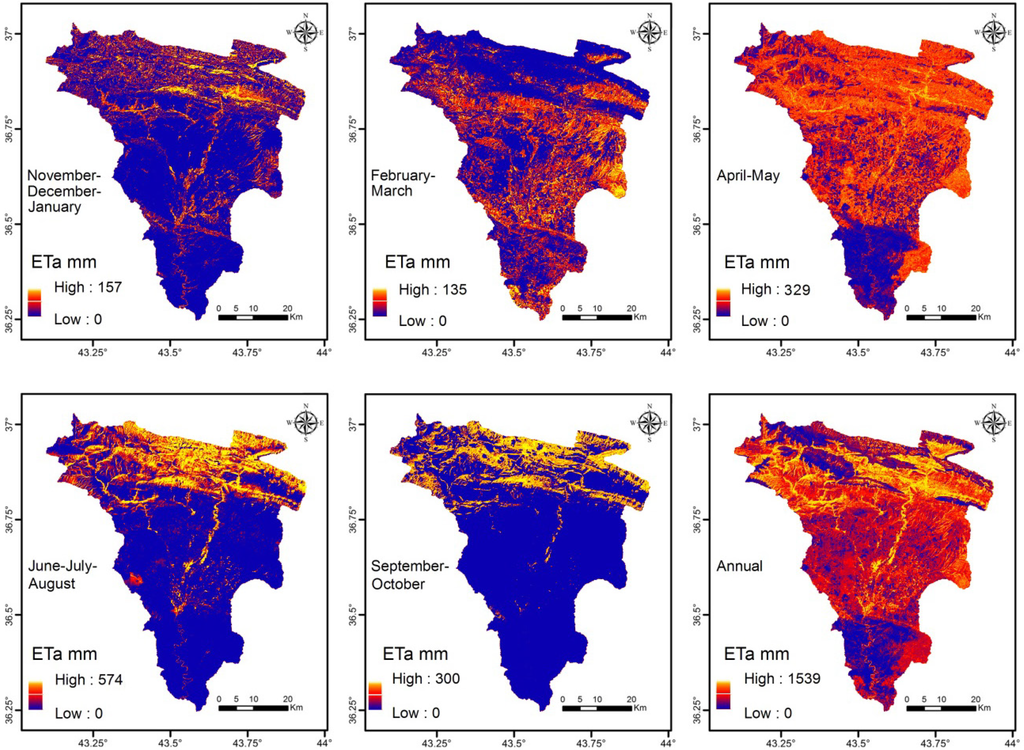
Figure 4.
Actual evapotranspiration (ETa) in Al-Khazir Gomal watershed calculated with Surface Energy Balance Algorithm for Land (SEBAL) within the corresponding months referred to on each map, and the actual annual total.
Figure 4.
Actual evapotranspiration (ETa) in Al-Khazir Gomal watershed calculated with Surface Energy Balance Algorithm for Land (SEBAL) within the corresponding months referred to on each map, and the actual annual total.
The ETa map (Figure 4) clearly indicates spatial and temporal patterns of ETa for various land use classes that include agricultural crops, native vegetation, dry/barren land, and water bodies (river). It is clear from the evapotranspiration maps that the ETa increases from January to April and May, and then decreases until December. The highest evapotranspiration values in April and May could be explained by the simultaneous stronger extraterrestrial solar radiation and intensive rainfall during this time span (Figure 5) and the high value of NDVI (data is not mentioned here) during May when the vegetation cover is well developed, which maintains the high evapotranspiration from the high value of soil moisture retained in the soil from the intensive rainfall during the preceding month. The high ETa in May is due to soil moisture available for root absorption, which is sufficient to maintain the evapotranspiration at an even greater rate than in rainy April. This suggests that transpiration in May is the main source for the regional ETa. This is caused by fields of wheat and barley and their growth peaks in this period.
In the period from June to October, which covers the period from the beginning of the harvesting month to the beginning of the new vegetation season, the vegetation cover is minimal and, therefore, evapotranspiration is limited to rice fields in the second region (on the left bank of the Al-Khazir River) and vegetable fields along the river, in addition to the forests and orchards in the mountainous area. The main use of the groundwater in the dry season is irrigating the rice fields (274 km2), whereby these fields are immersed in water during June, July and August. The net groundwater used to irrigate rice fields estimated by SEBAL is about 4.3 × 106 m3/year. From the statistical investigation of the different periods (Table 1), it is clear that the minimum ETa is zero, which is explained by the fact that only a little evapotranspiration will take place in sloped rock outcrops (carbonate and conglomerate rocks) or that high permeable sediments with no vegetation cover will develop even during the spring months. Moreover, the range of standard deviations in the different seasons shows that the variability of ETa in these seasons is large and consistent with the meteorological data.
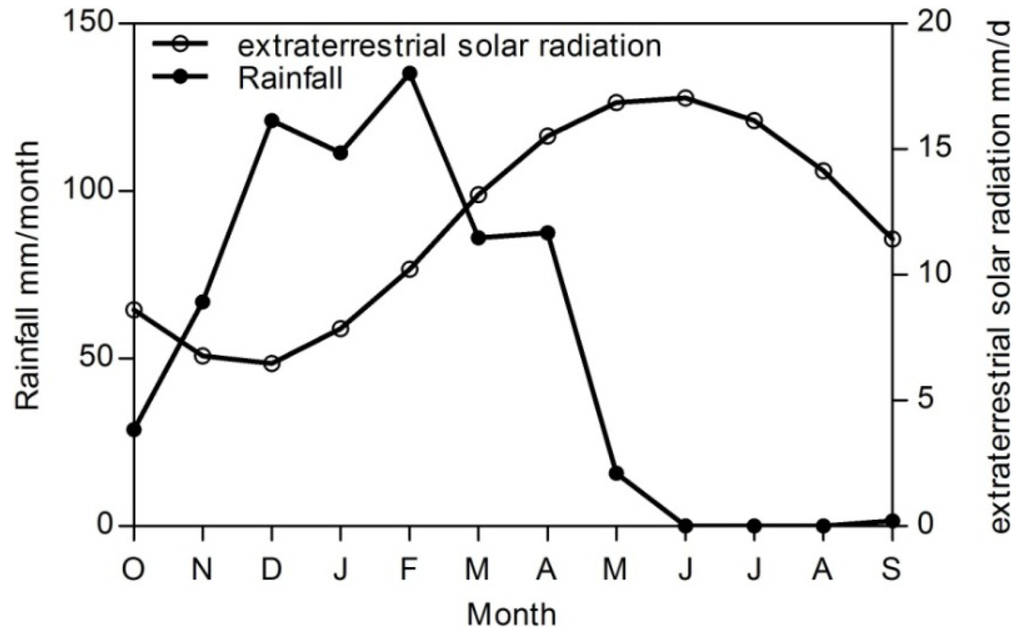
Figure 5.
Rainfall and extraterrestrial solar radiation for Al-Khazir Gomal watershed.
Figure 5.
Rainfall and extraterrestrial solar radiation for Al-Khazir Gomal watershed.
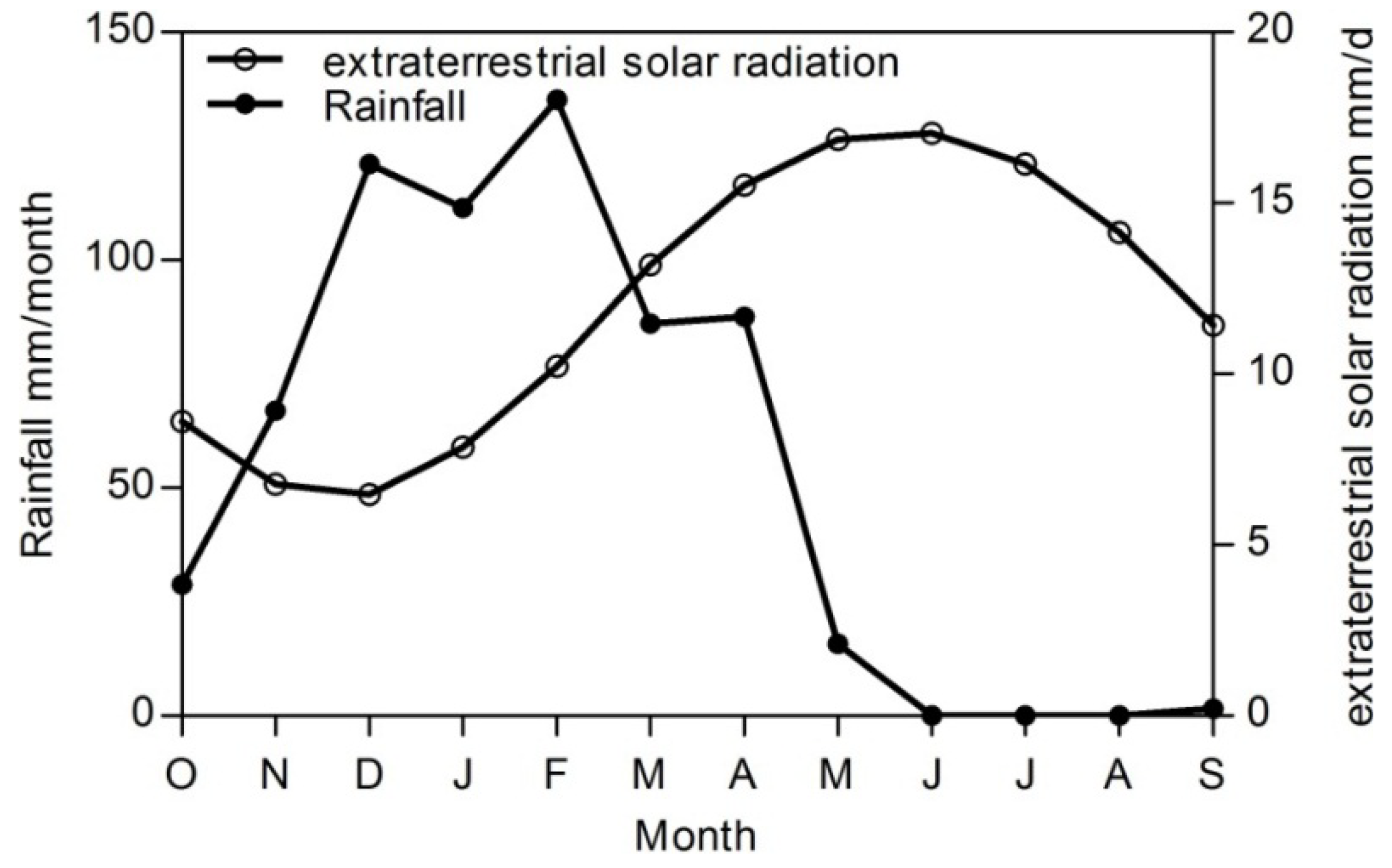

Table 1.
Statistical results of the upscaled results of the actual evapotranspiration (ETa) (mm) from November 2006 to October 2007.
| Statistical Parameter | November–January | February–March | April–May | June–August | September–October |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum (mm) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Maximum (mm) | 157 | 135 | 329 | 574 | 300 |
| Mean (mm) | 80 | 87 | 152 | 61 | 35 |
| SD (mm) | 31 | 34 | 94 | 118 | 69 |
| Skewness | 2 | 1 | 0.4 | 1.7 | 2 |
| Kurtosis | 6 | 2.8 | 1.5 | 4.7 | 5.8 |
| Sum (mm) | 257,373,721 | 277,286,162 | 491,000,135 | 196,540 | 112,452,822 |
The Λ is likely to increase during the rainy months (December, January, February, March) when plant canopies and soils are wet; however, satellite images are limited due to cloud cover. The range of evapotranspiration occurring in summer (June–August) is wider than that in the spring months (April–May) due to the fact that evapotranspiration is restricted to the vegetation strip along the river, forest and orchards in the mountainous area, as well as the sparse rice cultivation in the second region.
Comparison between ETr and well-irrigated fields can give an impression of the consistency of SEBAL in the study area. Therefore, some well-irrigated areas were selected based on NDVI maps. Normally, areas that have high NDVI values should resemble the required well-irrigated fields. The ETr values were also calculated for these areas and the results for the five satellite images are reported in Table 2. It is clear that there is good consistency between the ETr calculated by the Penman-Monteith equation and the daily ETa estimated by the SEBAL model. This agreement reflects the good performance and reliability of the SEBAL model.

Table 2.
Comparison between reference evapotranspiration (ETr) and ETa for different well-irrigated areas from the five satellite images.
| Acquisition Date | Minimum ETa (SEBAL) mm/day | Maximum ETa (SEBAL) mm/day | Mean ETa (SEBAL) mm/day | SD | Coeff. of Variation | ETr mm/day |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 March 2007 | 1.9 | 3.3 | 2.2 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 2.72 |
| 5 May 2007 | 3.8 | 6.8 | 5.35 | 0.95 | 0.18 | 6.14 |
| 21 July 2007 | 5.2 | 7.4 | 6.5 | 0.9 | 0.14 | 7.82 |
| 23 September 2007 | 3.8 | 5.6 | 4.8 | 0.4 | 0.083 | 5.27 |
| 21 November 2006 | 1.2 | 2.3 | 1.45 | 0.45 | 0.31 | 1.98 |
Visual Comparison
ETa calculated by SEBAL consumes about 63% of the total precipitation. Figure 6 shows the reasonable relationship between LULC and spatial distribution of ETa in the spring season (April and May). During the rainy season, it is plausible that ETa is minimal in conglomerate and sandstone outcrops (A), carbonate outcrops (C) and in urban areas. This is due to the high permeability of the conglomerate and fractured carbonate rocks, and scarcity or lack of vegetation cover, in addition to the fact that conglomerate and carbonate rocks crop out in a sloped area, which means a minimum retention time. The field of wheat and barley in the second region (B), the vegetable fields along the Al-Khazir River, and the forests and orchards in the mountainous area showed high ETa value.
The ETa in the mountainous area (northern part) is relatively high because of the evergreen forests and orchards, which are watered by the perennial springs all year round. However, there is some discrepancy in some parts of the mountainous area covered by conglomerate, sandstone and carbonate rocks (e.g., along the uppermost edge); these areas, which are expected to result in low ETa, show relatively high ETa in some parts. This discrepancy could be explained by the fact that such areas, due to the perennial springs, have considerable moisture content (referred to as cold pixels). These areas were not classified on the LULC map as wet or dry conglomerate or sandstone. Moreover, the effect of low temperature should not be neglected in some spots in the mountainous areas on the border of the basin.
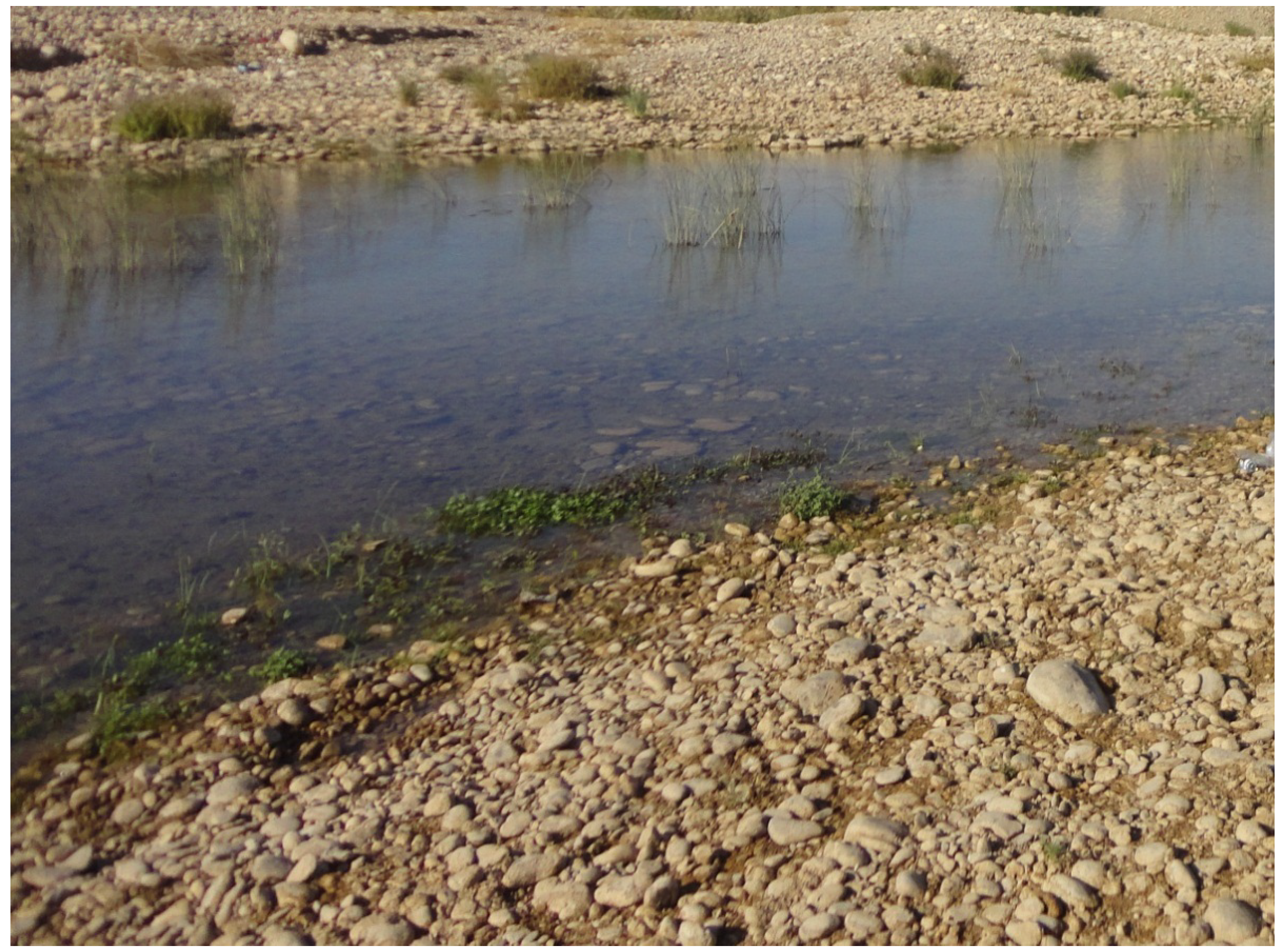
The conglomerate riverbed of the Al-Khazir and Gomal rivers is classified clearly on the LULC map. The course of the river, flowing from the north to the south, shows high evapotranspiration, which is logical as it represents evaporation from a free-water surface. However, the course of the river disappears in the middle of the basin (on the ETa map), which is due to the fact that the river narrows (Figure 7) to less than the image resolution.
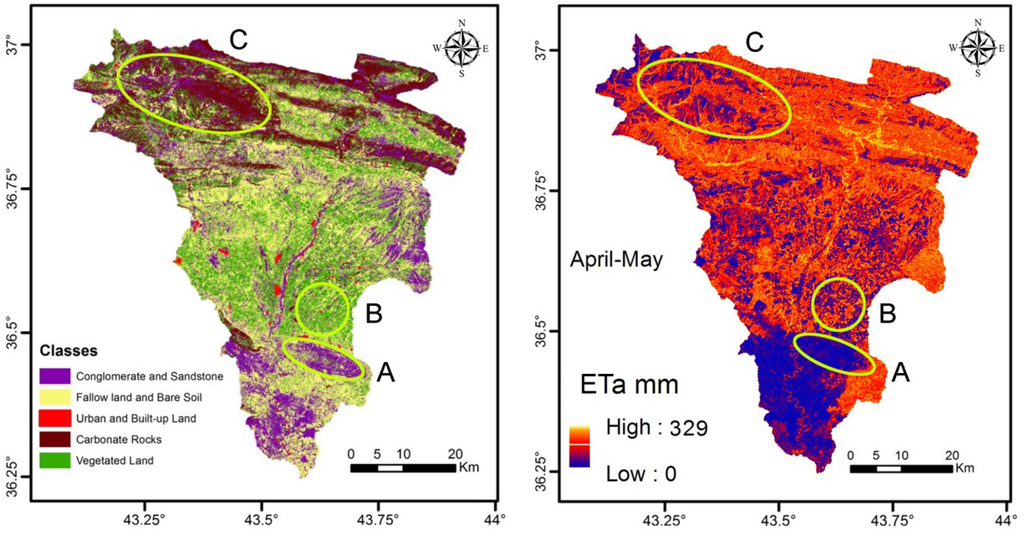
Figure 6.
Visual comparison between the LULC map and seasonal ETa in the spring season (April–May) for the Al-Khazir Gomal watershed.
Figure 6.
Visual comparison between the LULC map and seasonal ETa in the spring season (April–May) for the Al-Khazir Gomal watershed.
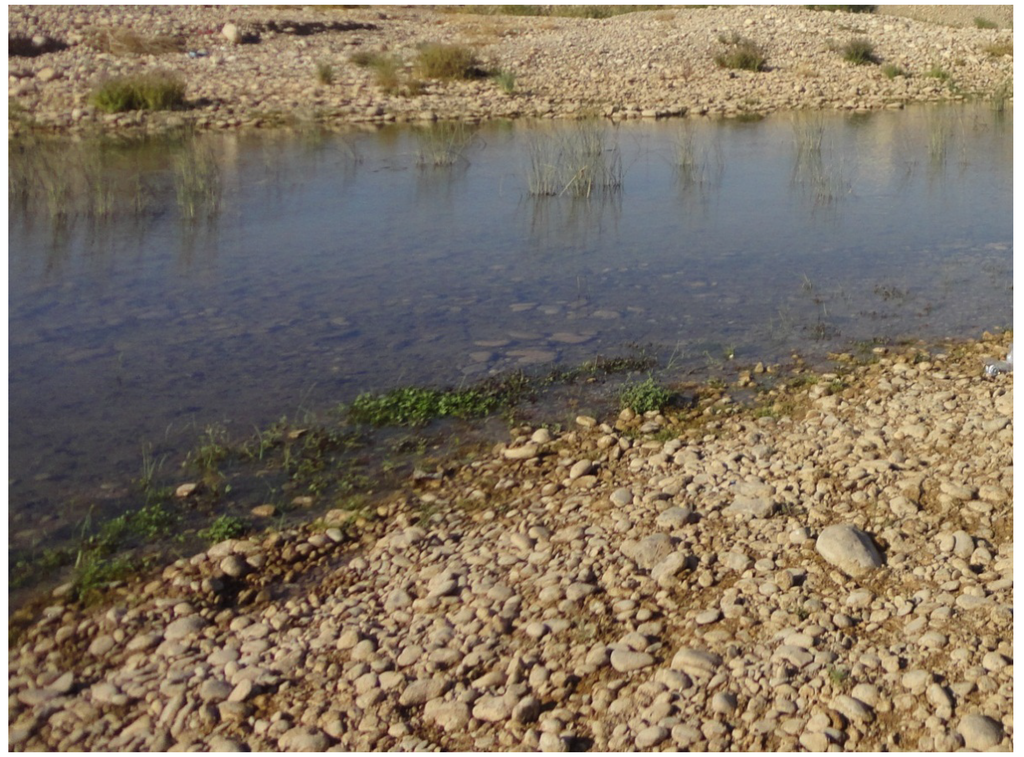
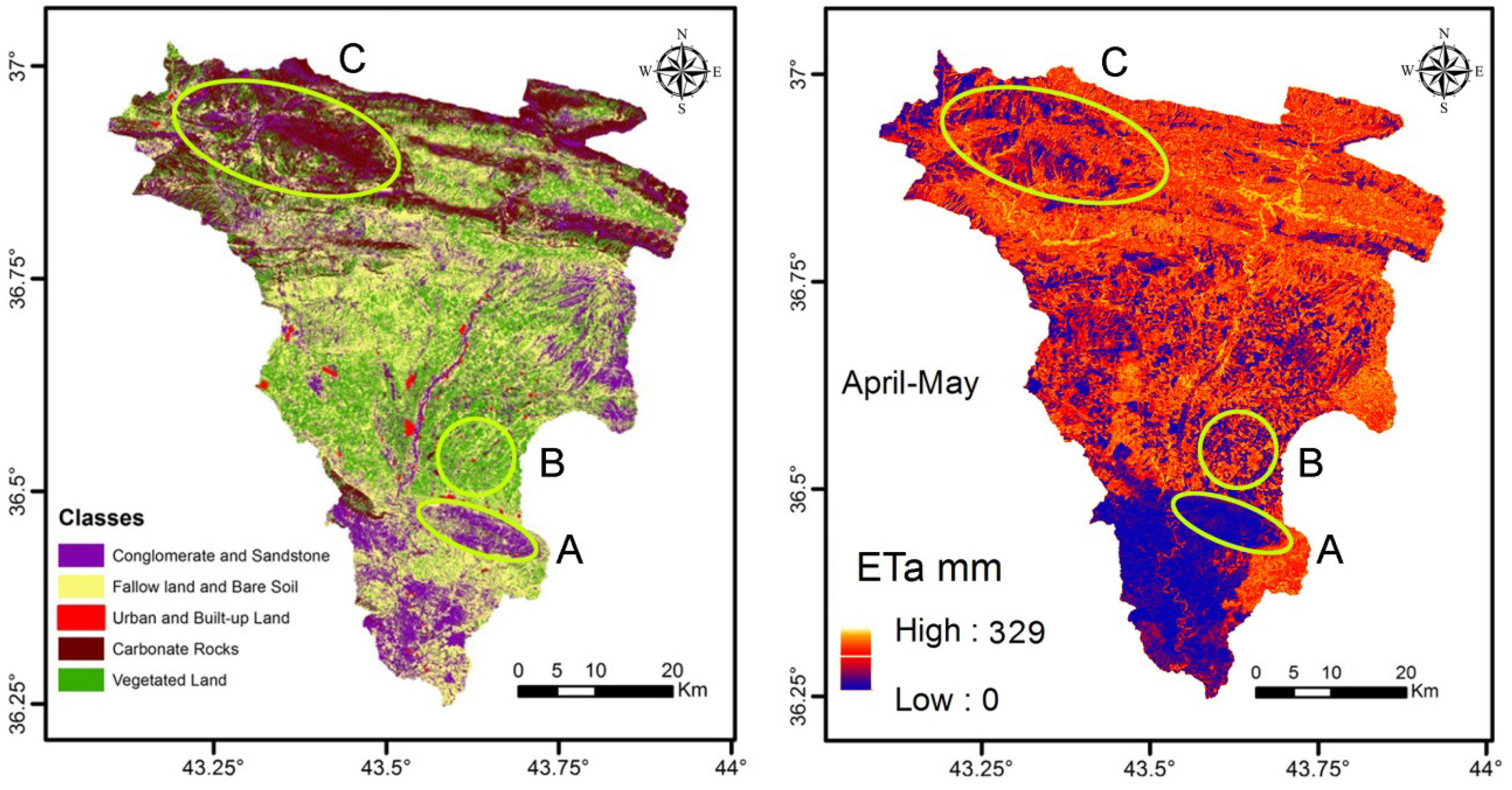

Figure 7.
Large-scale photo (fieldwork 2011) of the Al-Khazir River where its course narrows to around 10 m.
Figure 7.
Large-scale photo (fieldwork 2011) of the Al-Khazir River where its course narrows to around 10 m.

5.2. Water Balance
Normally, validation of ETa calculations from satellite data is carried out using eddy covariance (EC) data. Unfortunately, such techniques and data are not available in most developing countries, including Iraq. Thus, the water balance equation was used to assess the suitability of SEBAL in the area of interest.
The water balance equation was applied using runoff, groundwater recharge and rainfall data. Rainfall data for the period 2001–2011 was collected from the Aqre weather station, which is located at the eastern boundary of the watershed. The daily stream flow of the Al-Khazir River at the watershed outlet for the period 1969–1981 was used to separate runoff and base flow by four separation methods, namely graphical separation, the Ekhardt method, the Local Minimum method and the Single Parameter method [30]. From these methods, the mean annual base flow and runoff were calculated to be 119.6 and 74.9 mm/year, respectively. Moreover, groundwater recharge was estimated using the water table fluctuation method (WTF). According to the previously mentioned boundary condition (closed system), one can suppose that the base flow represents the minimum integrated groundwater recharge. Thus, the only missing parameter in Equation (17) is the ETa, which was determined by substitution to be 448.5 mm/year. Applying the aforementioned water balance to estimate the ETa required determination of the uncertainty in the calculations. The uncertainty was calculated as mentioned beforehand. The average ETa is 448.5 mm and the standard error is 6.48 mm, so the ETa is written in the form ETa = 448.5 ± 6.48. In comparison to this, SEBAL estimated the annual ETa to be 415 mm/year. Trezza [38] stated that such lower values could be a result of advective effects, especially in agricultural areas that are surrounded by bare land or a low-vegetation area. The difference between these two methods (~9%) could pertain to the uncertainty in measuring the runoff and the assumption inherent in the calculated groundwater recharge. In addition, the calculated recharge was used as the output of the base flow estimation methods and it is known that base flow is the minimum boundary of groundwater recharge.
6. Conclusions
SEBAL is an approach that requires a minimal amount of ancillary data. It was applied to the TM5 images (Path 170, Rows 34 and 35) covering the Al-Khazir Gomal watershed, which were acquired on 21 November, 9 March, 5 May, 21 July and 23 September for the period 2006–2007 from the GLOVIS. It is apparent that there is a distinct water deficit from the end of March to the beginning of November, because ETp exceeds precipitation and, consequently, the utilization of soil moisture. From the beginning of December to the end of March, precipitation exceeds ETp, resulting in returning soil moisture to its capacity, and the additional or excess water may become groundwater recharge and surface runoff. Given the minimal amount of ancillary data required for applying SEBAL and the excellent performance in predicting instantaneous ETa on irrigated fields, SEBAL is a promising tool for mapping ETa in semi-arid areas. However, verifying the validity of the results is difficult due to the absence of local-scale evapotranspiration measurements, and the dependency was only on meteorological data available in the area of interest. SEBAL proved to be effective in distinguishing spatially the variability of evapotranspiration and sensible heat flux.
The results of this study show that, if applied to temporal and spatial data, the technique can be used as an essential tool in the monitoring of irrigation water needs. This will lead to an improvement in irrigation water management, which can be achieved when crop water use is accurately quantified in time and space. Moreover, an important part of water management is calculating the water budget developed by hydrological modeling, which requires, in turn, evapotranspiration as one of its main input parameters.
One main drawback of SEBAL is that it relies on the presence of extreme surface temperature Ts (hot and cold or dry and wet) pixels in the imagery. In general, without the presence of high water use crops in the imagery, these methods may underscale the ETa if it is not adjusted to the true potential surface temperature range, thus leading to errors in spatial ETa estimation.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the German Academic Exchange Service (DAAD), the Geological Survey of Iraq (GEOSURV) and the Iraqi Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research.
Author Contributions
The idea for this study, the literature research, calculations, figures, maps and preparation of the first draft of the article were the work of Hussein Jassas and Wael Kanoua under the supervision of Broder Merkel, who contributed by proofreading the text and discussing the results.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Oki, T.; Kanae, S. Global Hydrological Cycles and World Water Resources. Science 2006, 313, 1068–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastiaanssen, W.; Noordman, E.; Pelgrum, H.; Davids, G.; Thoreson, B.; Allen, R. SEBAL Model with Remotely Sensed Data to Improve Water-Resources Management under Actual Field Conditions. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2005, 131, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalma, J.D.; McVicar, T.R.; McCabe, F.M. Estimating Land Surface Evaporation: A Review of Methods Using Remotely Sensed Surface Temperature Data. Surv. Geophys. 2008, 29, 421–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, P.; Chavez, J.; Colaizzi, P.; Evett, S.; Howell, T.; Tolk, J. ET mapping for agricultural water management: Present status and challenges. Irrig. Sci. 2008, 26, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.A.C.; Bezerra, B.G.; Silva, B.B.; Rao, T.V.R. Assessment of daily actual evapotranspiration with SEBAL and S-SEBI algorithms in cotton crop. Rev. Bras. Meteorol. 2010, 25, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shang, S.; Jiang, L. Remote sensing temporal and spatial patterns of evapotranspiration and the responses to water management in a large irrigation district of North China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2012, 164, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-G.; Wang, W.; Huang, D.; Yong, B.; Chen, X. Modifying SEBAL Model Based on the Trapezoidal Relationship between Land Surface Temperature and Vegetation Index for Actual Evapotranspiration Estimation. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 5909–5937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqrawi, Z.A.A. Hydrological and Hydrogeological Study of the Etot-Aloka Basin, Dohuk Governorate, Iraqi Kurdistan Region. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Salahadin, Erbil, Iraq, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Manmi, D.A. Water Resources Management in Rania Area, Sulaimaniyah NE-Iraq. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Baghdad, Baghdad, Iraq, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Shwani, S.O. Hydrogeology and Hydrochemistry of Bashtapa Sub-Basin in Erbil Governorate Kurdistan Region-Iraq. Master’s Thesis, University of Salahadin, Erbil, Iraq, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Thornthwaite, C.W.; Wilm, H.G. Report of the Committee on Transpiration and Evaporation. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union. 1944, 25, 686–693. [Google Scholar]
- Kharrufa, N.S. Simplified equation for evapotranspiration in arid regions. Hydrol. Sonderh. 1985, 5, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Penman, H.L. Natural evaporation from open water, bare soil, and grass. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1948, 193, 120–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.; Irmak, A.; Trezza, R.; Hendrickx, J.M.H.; Bastiaanssen, W.; Kjaersgaard, J. Satellite-based ET estimation in agriculture using SEBAL and METRIC. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 4011–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, A.B.; Colwell, R.N.; Meyers, V.F. Resource Survey by Satellite; Science Fiction Coming True. Yearb. Agric. 1968, 1968, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, R.D. Remote sensing of vegetation characteristics for farm management. Proc. SPIE 1984, 475, 81–96. [Google Scholar]
- Norman, J.; Kustas, W.; Humes, K. A two-source approach for estimating soil and vegetation energy fluxes from observations of directional radiometric surface temperature. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1995, 77, 263–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Menenti, M.; Feddes, R.A.; Holtslag, A.A.M. A remote sensing surface energy balance algorithm for land (SEBAL). Part1. Formulation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212–213, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roerink, G.J.; Su, Z.; Menenti, M. S-SEBI: A simple remote sensing algorithm to estimate the surface energy balance. Phys. Chem. Earth Part B Hydrol. Ocean Atmos. 2000, 25, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z. The Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) for estimation of turbulent heat fluxes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2002, 6, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.M.; Kustas, W.P.; Caselles, V.; Anderson, M.C. Modelling surface energy fluxes over maize using a two-source patch model and radiometric soil and canopy temperature observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1130–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralles, D.G.; Holmes, T.R.H.; de Jeu, R.A.M.; Gash, J.H.; Meesters, A.G.; Dolman, C.A. Global land-surface evaporation estimated from satellite-based observations. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 453–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Improvements to a MODIS Global Terrestrial Evapotranspiration Algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1781–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Singh, V.P. A Two-source Trapezoid Model for Evapotranspiration (TTME) from satellite imagery. Remote Sens Environ. 2012, 121, 370–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shang, S. A hybrid dual-source scheme and trapezoid framework–based evapotranspiration model (HTEM) using satellite images: Algorithm and model test. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 2284–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, H.O. Estimation of Regional Evaporation under Different Weather Conditions from Satellite and Meteorological Data: A Case Study in the Naivasha Basin Kenya; Wageningen University: Wageningen, The Netherland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Surface Energy Balance Algorithms for Land (SEBAL). Available online: ftp://ftp.funceme.br/Cospar_Funceme_2010/CLASS_DAY_04.11.2010/LAB/quixere/quixere/Final%20Sebal%20Manual.pdf (accessed on 13 April 2015).
- Hemakumara, H.M.; Chandrapala, L.; Moene, A.F. Evapotranspiration fluxes over mixed vegetation areas measured from large aperture scintillometer. Agric Water Manag. 2003, 58, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sam, S.; Hanna, F. Evaluation of Groundwater Resources in Al-Khazir Gomal Basin. Report No. 1270. Unpublished Report. GEOSURV: Baghdad, Iraq, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Jassas, H.; Merkel, B. Estimating Groundwater Recharge in the Semiarid Al-Khazir Gomal Basin, North Iraq. Water 2014, 6, 2467–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.R.; Hardy, E.E.; Roach, J.T.; Witmer, R.E. A Land Use and Land Cover Classification System for Use with Remote Sensor Data; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1976.
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.A.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration: Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO): Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M. SEBAL-based sensible and latent heat fluxes in the irrigated Gediz Basin, Turkey. J. Hydrol. 2000, 229, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasumi, M. Progress in Operational Estimation of Regional Evapotranspiration Using Satellite Imagery. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Idaho, Moscow, ID, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, B.R.G.; Morse, A.; Tasumi, M.; Trezza, R.; Bastiaanssen, W.; Wright, J.L. Evapotranspiration from a Satellite-Based Surface Energy Balance for the Snake Plain Aquifer in Idaho. Calif. Water Plan Update 2005, 4, 162–175. [Google Scholar]
- Shuttleworth, W.J.; Gurney, R.J.; Hsu, A.Y.; Ormsby, J.P. FIFE: The Variation in Energy Partitioning at Surface Flux Sites; IAHS Publication: Wallingford, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Brutsaert, W.; Sugita, M. Application of self preservation in the diurnal evolution of the surface budget to determine daily evaporation. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 377–382. [Google Scholar]
- Trezza, R. Evapotranspiration Using a Satellite-Based Surface Energy Balance with Standardized Ground Control. Ph.D. Thesis, Utah State University, Logan, UT, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chavez, J.; Neale, C.; Prueger, J.; Kustas, W. Daily evapotranspiration estimates from extrapolating instantaneous airborne remote sensing ET values. Irrig. Sci. 2008, 27, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Liu, S.; Tieszen, L.L.; Suyker, A.E.; Verma, S.B. Estimating seasonal evapotranspiration from temporal satellite images. Irrig. Sci. 2012, 30, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crago, R.D. Conservation and variability of the evaporative fraction during the daytime. J. Hydrol. 1996, 180, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Ahmad, M.D.; Chemin, Y. Satellite surveillance of evaporative depletion across the Indus Basin. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 1273. [Google Scholar]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Pelgrum, H.; Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Moreno, J.F.; Roerink, G.J. A remote sensing surface energy balance algorithm for land (SEBAL): Part 2: Validation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212–213, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushton, K.R.; Ward, C. The estimation of groundwater recharge. J. Hydrol. 1979, 41, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, Y. Soil moisture from space: Where are we? Hydrogeol. J. 2007, 15, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
