Preliminary Study on the Activity of the Rupture Zone in the Eastern Segment of the Ba Co Fault in Ngari Prefecture, Tibet
Abstract
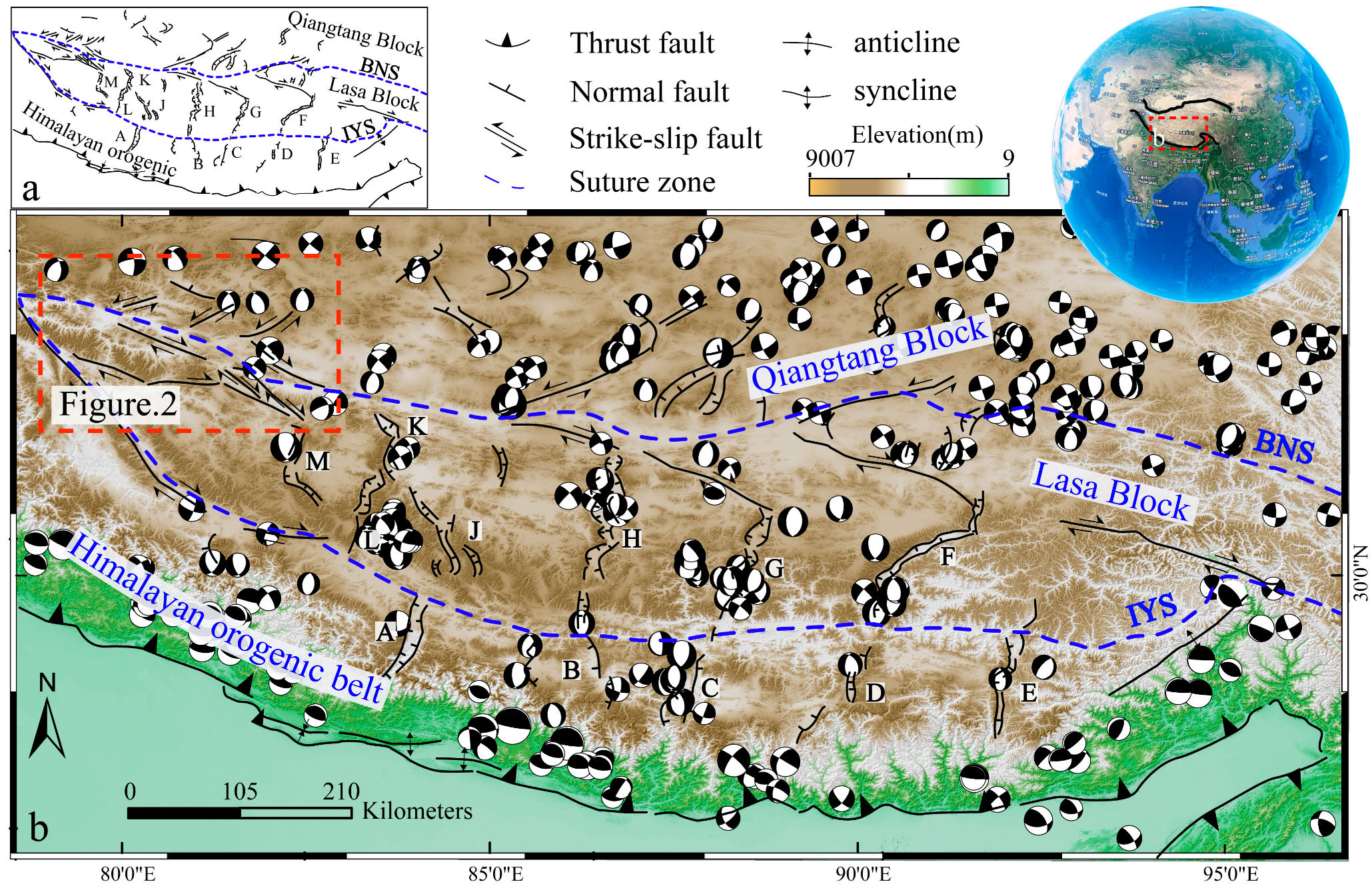
1. Introduction
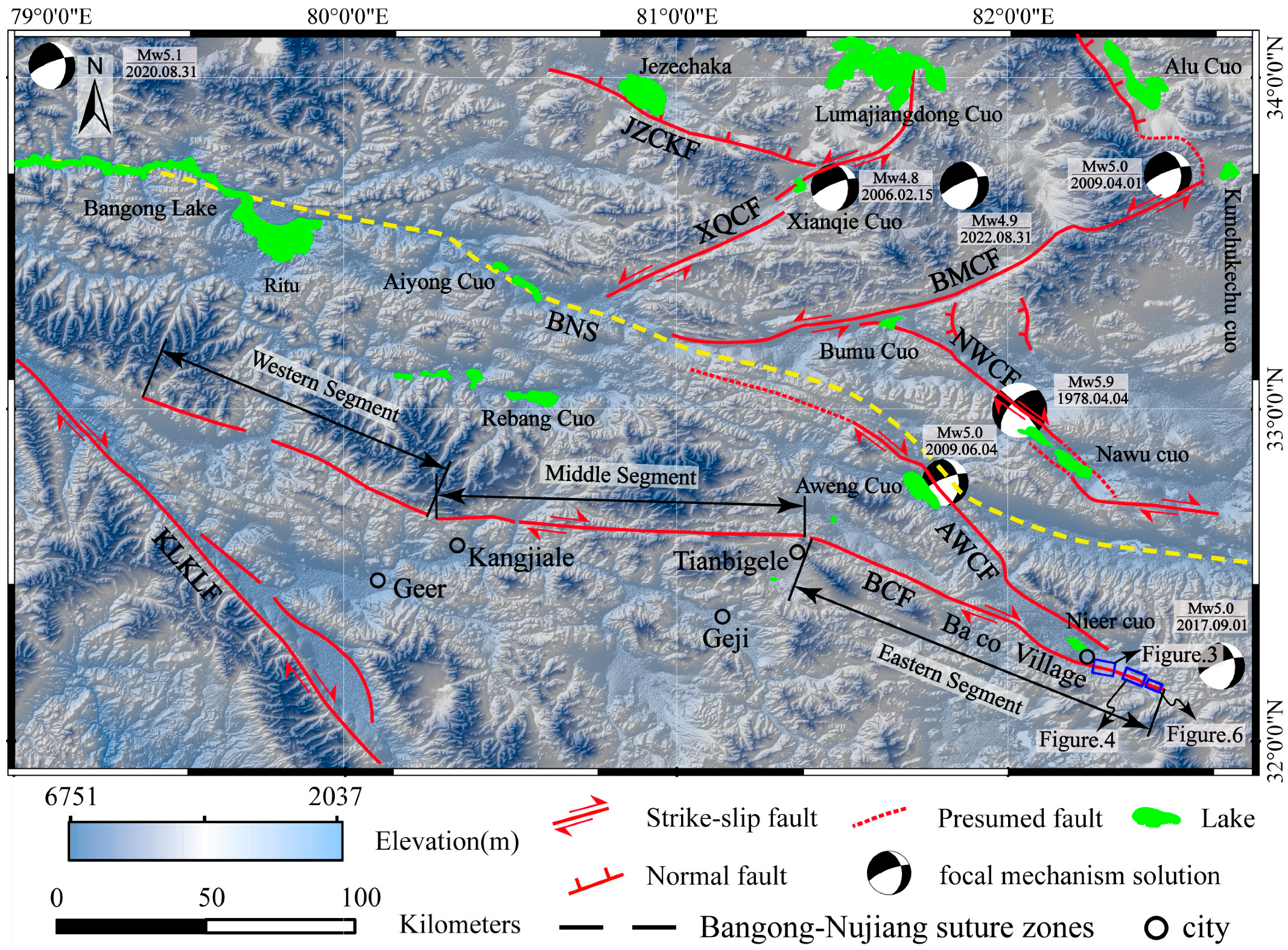
2. Background of the Study Area
3. Data and Methods
3.1. UAV Photogrammetry
3.2. Optically Stimulated Luminescence (OSL) Dating
4. Characteristics of the BCF Activity and Eastern Segment Rupture
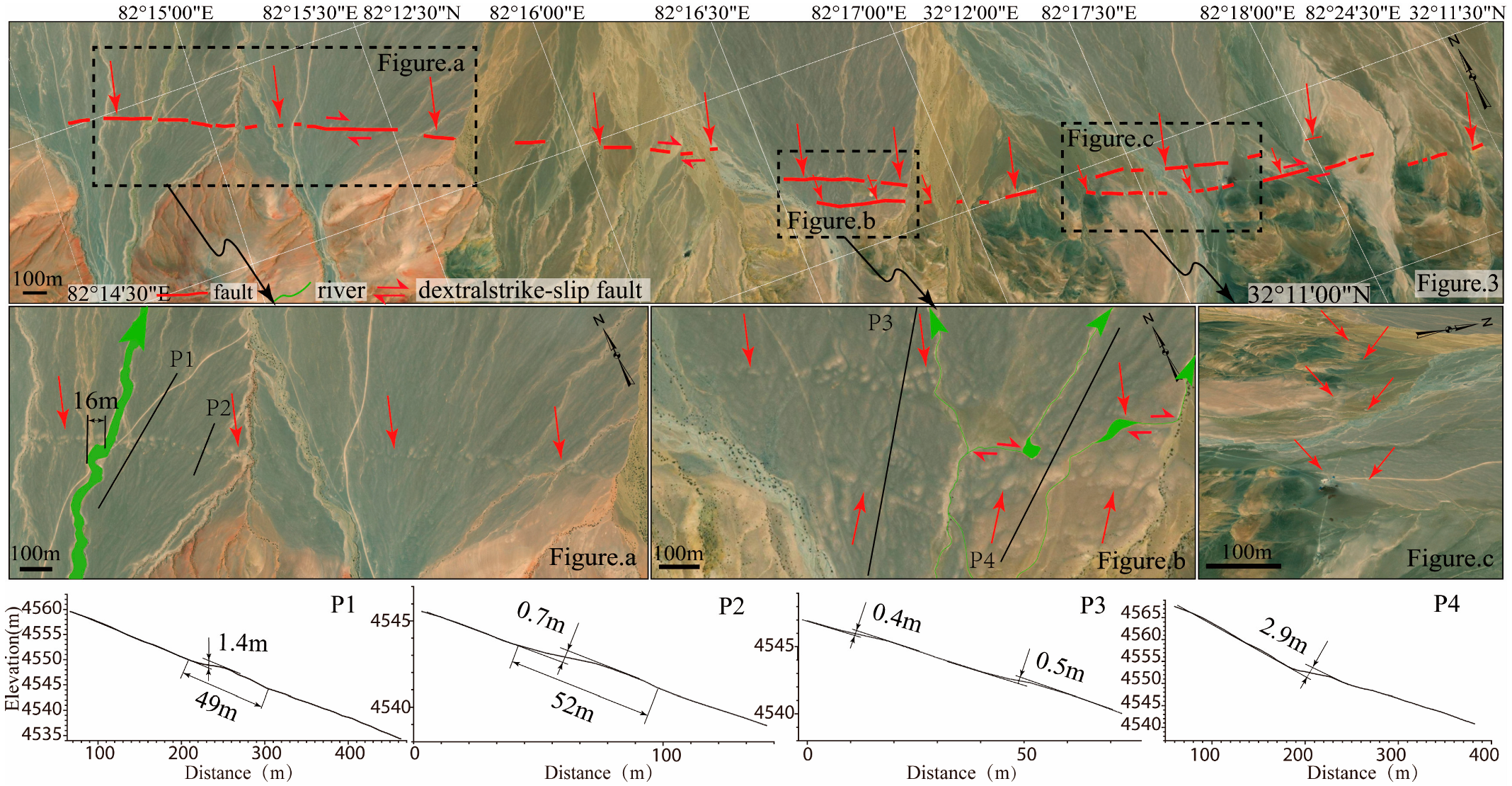
4.1. Geomorphic Features of the BCF
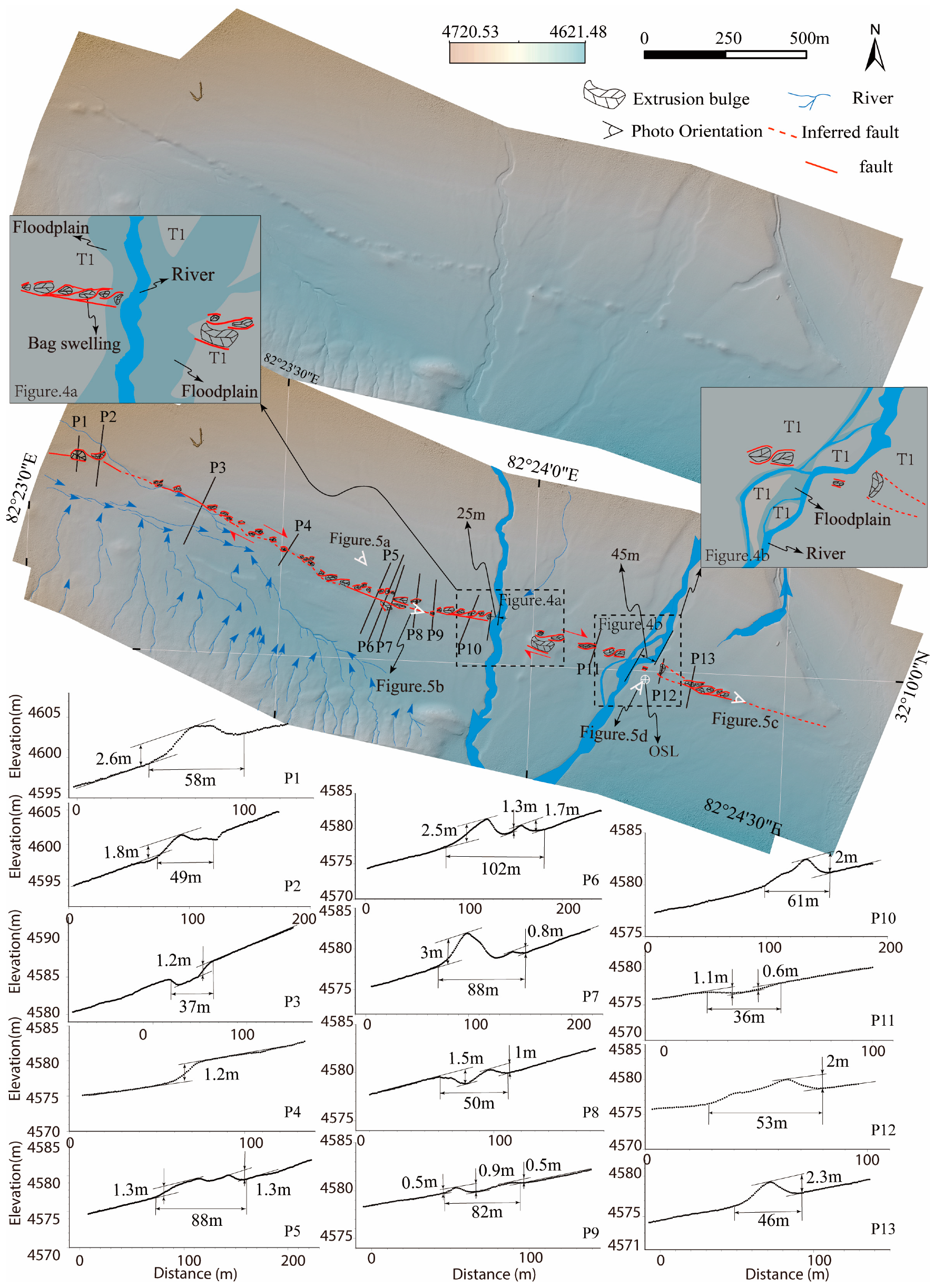
4.2. Geomorphic and Developmental Characteristics of the Eastern Segment Surface Rupture

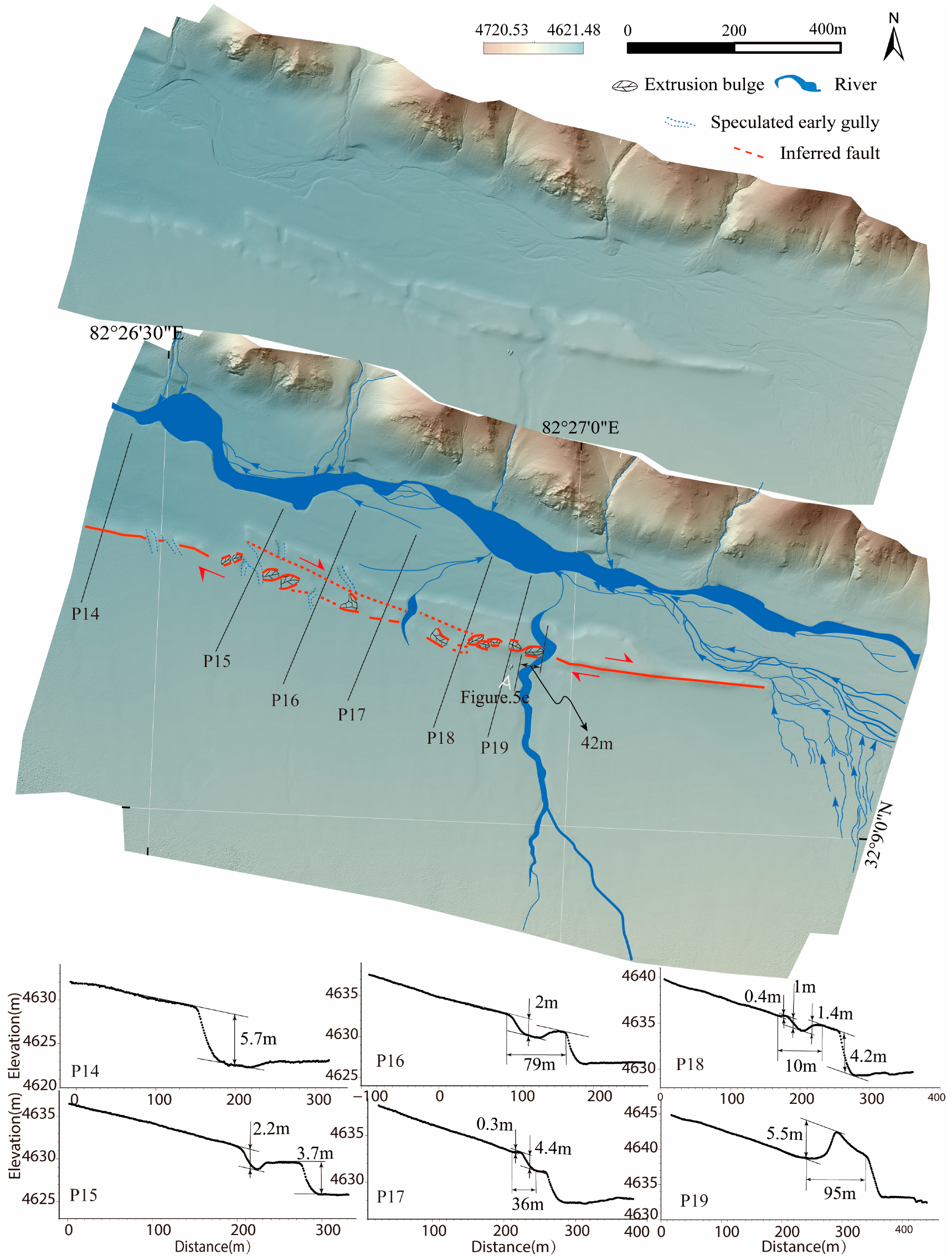
5. Chronological Constraints on Surface Rupture Zones
6. Discussion
6.1. Magnitude Estimation for the Co-Seismic Surface Rupture Along the Eastern Segment of the BCF
6.2. Regional Tectonic Implications of the Rupture Zone Along the Eastern BCF Segment
7. Conclusions
- (1)
- The eastern segment of the BCF is a Holocene-active right-lateral strike-slip fault. Geomorphically, it displaces Holocene alluvial–fluvial fans and partially offsets ridges along the mountain front. Associated landforms include pressure ridges, linear erosional trenches, counter-slope scarps, and shutter ridge ponds. Selected gullies exhibit dextral offsets ranging from 16 to 45 m.
- (2)
- A newly mapped ~21-km-long co-seismic surface rupture zone extends along Holocene alluvial–fluvial fans at the mountain front. This rupture displays a left-stepping en echelon pattern dominated by pressure ridges (0.30–5.5 m high) and trenches (0.60–15 m deep), within a total width of 30–102 m. OSL dating of samples from the T1 terrace constrains the formation of the surface rupture zone to post- 5.73 ± 0.17 ka.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Molnar, P.; Tapponnier, P. Cenozoic tectonics of Asia: Effects of a continental collision. Science 1975, 1989, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapponnier, P.; Peltzer, G.; Le Dain, A.Y.; Armijo, R.; Cobbold, P. Propagating extrusion tectonics in Asia: New insights from simple experiments with plasticine. Geology 1982, 10, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapponnier, P.; Zhiqin, X.; Roger, F.; Meyer, B.; Arnaud, N.; Wittlinger, G.; Jingsui, Y. Oblique stepwise rise and growth of the Tibet Plateau. Science 2001, 294, 1671–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnar, P.; England, P.; Martinod, J. Mantle dynamies, uplift of the Tibetan plateau, and the Indian monsoon. Rev. Geophys. 1993, 31, 357–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewey, J.; Shackelton, R.; Chang, C.; Sun, Y. The tectonic evolution of the Tibetan plateau. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1988, 327, 379–413. [Google Scholar]
- Molnar, P.; Lyon-Caen, H. Fault-plane solutions of earthquakes and active tectonies of the Tibetan plateau and its margins. Geophys. J. Int. 1989, 99, 123–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, H.; Yang, J. Orogenic Plateau: The Giant Orogenic Collage and Orogenic Types of the Tibetan Plateau. Earth Sci. Front. 2006, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Molnar, P.; Tapponnier, P. Active tectonics of Tibet. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1978, 83, 5361–5375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapponnier, P.; Molnar, P. Active faulting and tectonics in China. J. Geophys. Res. 1977, 82, 2905–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, A.; Harrison, T.M. Geologic evolution of the Hima-layan-Tibetan Orogen. Annu. Rev. Earth Plane-Tary Sci. 2000, 28, 211–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.; Yin, A.; Ryerson, F.J.; Kapp, P.; Ding, L. Conjugate strike-slip faulting along the Bangong-Nujiang suture zone accommodates coeval east-west extension and north-south shortening in the interior of the Tibetan Plateau. Tectonies 2003, 22, 1044–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Yue, Y.H.; Cai, F.L.; Xu, X.X.; Zhang, Q.H. High-Mg ultrapotassic volcanic rocks in the Lhasa Block, Tibet: Constraints on the timing and depth of N-S-trending rift formation. Acta Geol. Sin. 2006, 80, 1252–1261. [Google Scholar]
- Armijo, R.; Tapponnier, P.; Mereier, J.L.; Han, T.-L. Quatermary extension in souther Tibet: Field observations and tectonic implications. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earh 1986, 91, 13803–13872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegre, C.J.; Courtillot, V.; Tapponnier, P.; Hirn, A.; Mattauer, M.; Coulon, C.; Jaeger, J.J.; Achache, J.; Schärer, U.; Marcoux, J.; et al. Structure and Evolution of the Himalaya-Tibet Orogenic Belt. Nature 1984, 307, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, S.; Yu, Z.; Gong, J.; Yang, R.; Cheng, X.; Lin, X.; Chen, H. Spatiotemporal distribution and geodynamic mechanism ofthe nearly NS-trending rifts in the Tibetan plateau. J. Geomech. 2021, 27, 178–194. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Rothery, D.A.; Drury, S.A. The neotectonies of the Tibetan plateau. Tectonics 1984, 3, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratschbacher, L.; Krumrei, I.; Blumenwitz, M.; Staiger, M.; Gloaguen, R.; Miller, B.V.; Samson, S.D.; Edwards, M.A.; Appel, E. Rifting and strike-slip shear in central Tibet and the geometry, age and kinematics of upper crustal extension in Tibet. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2011, 353, 127–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, P.; Houseman, G. Role of lithospherie strength heterogeneities in the tectonies of Tibet and neighboringregions. Nature 1985, 315, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ren, J. The tension-shear of Gyaring Co Fault and the implication for dynamic model in south-central Tibet. Chin. Joumal Geophys. 2012, 55, 3285–3295. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.F.; Chen, N.S.; Coward, M.P.; Wanming, D.; Dewey, J.F.; Gansser, A.; Harris, N.B.W.; Chengwei, J.; Kidd, W.S.F.; Leeder, M.R.; et al. Preliminary Conclusions of the Royal Society and Academia Sinica 1985 Geotraverse of Tibet. Nature 1986, 323, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.B.; Jin, S.; Ye, G.F.; Deng, M.; Tan, Z.; Unsworth, M.; Jones, A.G.; Booker, J. Conductivity structure of crust and upper mantle beneath the northern Tibetan Plateau:Results of superwide band magnetotelluric sounding. Chin. J. Geophys. 2006, 49, 1215–1225. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kapp, P.; DeCelles, P.G.; Gehrels, G.E.; Heizler, M.; Ding, L. Geological Records of the Lhasa-Qiangtang and Indo-Asian Collisions in the Nima Area of Central Tibet. Geo-Log. Soc. Am. Bull. 2007, 119, 917–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yin, C.; Guilmette, C.; Ding, L.; Zhang, J. Birth and Demise of the Bangong-Nujiang Tethyan Ocean: A Review from the Gerze Area of Central Tibet. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 198, 102907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.G.; Wang, B.D.; Xi, L.; Mao, G.Z.; Liu, H.Y.; Liu, G.X. Suture zones in Tibet and the evolution of the Tethys. Earth Sci. 2020, 45, 2735–2763. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, M.; Yin, A. Active structures of the Himalayan-Tibetanorogen and their relationships to earthquake distribution, contemporary strain field, and Cenozoic volcanism. Geosphere 2009, 5, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Ding, L. East west extension of the Tibetan Plateau and its geological significance. Sci. Geol. Sin. 2003, 38, 179–189. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Tectonic Geomorphology of the Geji Fault Zone in Central Tibetan Plateau. Master’s Thesis, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Wang, D.; Shao, Q.; Xu, X. Holocene slip rate along the NE-rending Qixiang Co Fault in the eentral Tibetan plateau and its tectonic implications. Seismol. Geol. 2018, 40, 1204–1215. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.X.; Chen, Z.W.; Ren, J.W.; Zhang, J. Activity and Segments of Gyaring Co Fault Zone in Center Tibet Plateau. Acta Seismol. Sin. 2011, 33, 362–372. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.X. Late Quaternary activity and regional dynamics of the Geren Fault in central-southern Tibet. Recent Dev. World Seismol. 2015, 7, 44–46. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D. Late Quaternary activity of the Geren Fault. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D. Tectonic Geomorphology Along the Gyaring Co Fault in Central Tibet; China Earthquake Administration Institute o Geology: Beijing, China, 2018. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.H.; Zhang, X.D.; Han, S.; Shi, Y.R.; Gao, Y.; Ye, Q.; Nima, C.R. Quaternary active faults within the Qiangtang Block, northern Ngari, Tibet, and their deformation mechanisms. Acta Geol. Sin. 2022, 96, 3761–3777. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.D.; Han, S.; Shi, Y.R.; Gao, Y.; Ye, Q.; Nimaciren; Zhang, B.; Li, Z.B. The Quatemary normal faulting and recent co-seismic surface rupture and related seismological significance along the Aru Co graben system in northem Ngari, Tibet. J. Seismol. Geol. 2023, 45, 67–91. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.; Wu, Z.; Wang, S.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lu, S.; Zhang, M. Surface deformation and tectonic implication of the late Quaternary Bue Co strike-slip fault system, mid-western Oiangtang block. J. Geomech. 2024, 30, 298–313. [Google Scholar]
- Bemis, S.P.; Micklethwaite, S.; Turner, D.; James, M.R.; Akciz, S.; Thiele, S.T.; Bangash, H.A. Ground-based and UAV-based photogrammetry: A multi-scale, high-resolution mapping tool for structural geology and paleoseismology. J. Struct. Geol. 2014, 69, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.T.; Shao, Y.X.; Zhang, H.P.; Liu, H.; Wu, Z. Application of SUAV photogrammetry in active tectonic studies: A case study of the Pianmagogou segment of the Haiyuan Fault. Quat. Sci. 2016, 36, 433–442. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, M.; Bi, H.Y.; Zheng, W.J.; Yin, J.H.; Yuan, D.Y.; Ren, Z.K.; Cheng, G.; Liu, J.R. Extraction of quantitative parameters of active tectonics using UAV photogrammetry. Seismol. Geol. 2018, 40, 1277–1289. [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes, E.J. Optically Stimulated Luminescence Dating of Sediments over the Past 200,000Years. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2011, 39, 461–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.; Lian, O. llluminating the past. Nature 2015, 520, 438–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.; Arnold, L.J.; Buylaert, J.-P.; Guérin, G.; Qin, J.; Singhvi, A.K.; Smedley, R.; Thomsen, K.J. Optically stimulated luminescence dating using quartz. Nat. Rev. Methods Prim. 2021, 1, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahan, S.A.; Rittenour, T.M.; Nelson, M.S.; Ataee, N.; Brown, N.; DeWitt, R.; Durcan, J.; Evans, M.; Feathers, J.; Frouin, M.; et al. Guide for interpreting and reporting luminescence dating results. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2022, 135, 1480–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.P.; Ou, X.J. Basic procedures of optically stimulated luminescence dating. Prog. Geogr. 2013, 32, 683–693. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, A.; Wintle, A. The single aliquot regenerative dose protocol: Potential for improvements in reliability. Radiat. Meas. 2003, 37, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, D.L.; Coppersmith, K.J. New empirical relationships among magnitude, rupture length, rupture width. rupture area, and surface displacement. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1994, 84, 9741002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armijo, R.; Tapponnier, P.; Han, T. Late Cenozoic right-lateral strikeslip faulting in southern Tibet. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 2787–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.; Peltzer, G. Current slip rates on conjugate strike-slip faults in central Tibet using synthetic aperture radar inter ferometry. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, B12402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.X.; Wang, G.C.; Cao, K.; Liu, C.; Xiang, S.; Hong, H.; Kou, X.; Xu, Y.; Chen, F.; Meng, Y.; et al. Cenozoie sedimentaryrecords and geochronological constraints of differential upliftof the Qinghai Tibet plateau. Sci. China 2008, 51, 1658–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
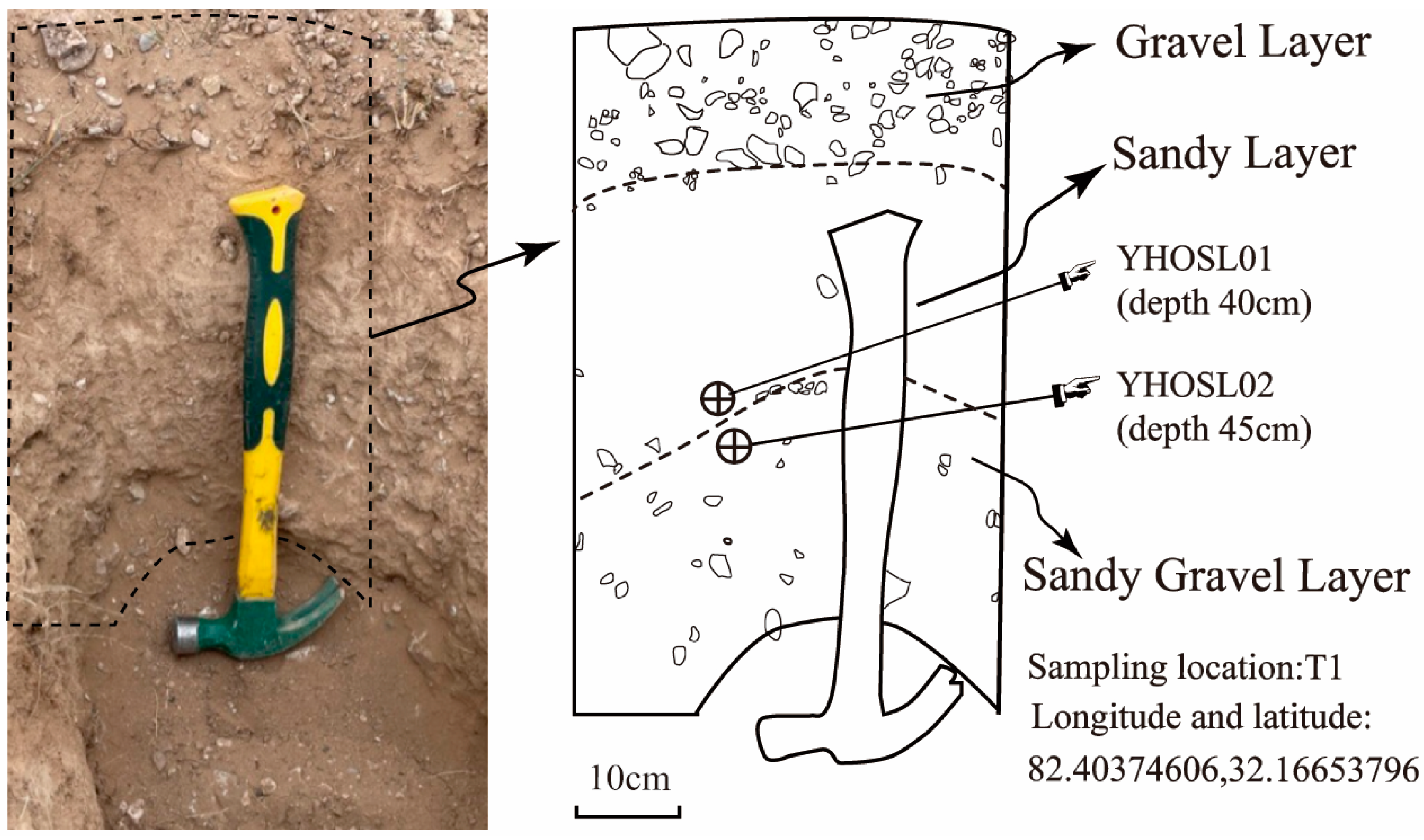
| Field No. | Depth (m) | Grain Size (μm) | Aliquots (n) | Equivalent Dose (Gy) | OD (%) | U (ppm) | Th (ppm) | K (%) | Rb (ppm) | Water Content (%) | Dose Rate (Gy/ka) | CAM Age (ka) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YH01 | 0.40 | 63–90 | 16/16 | 26.90 ± 0.67 | 8 ± 2 | 3.10 ± 0.03 | 18.74 ± 0.16 | 2.25 ± 0.02 | 125.06 ± 0.79 | 3.54 | 4.69 ± 0.08 | 5.73 ± 0.17 |
| YH02 | 0.45 | 63–90 | 16/16 | 26.86 ± 0.37 | 17 ± 3 | 3.08 ± 0.02 | 17.87 ± 0.07 | 2.16 ± 0.03 | 121.09 ± 1.69 | 4.45 | 4.49 ± 0.09 | 5.99 ± 0.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, Y.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, B. Preliminary Study on the Activity of the Rupture Zone in the Eastern Segment of the Ba Co Fault in Ngari Prefecture, Tibet. Geosciences 2025, 15, 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15100377
Yao Y, Shao Y, Zhang B. Preliminary Study on the Activity of the Rupture Zone in the Eastern Segment of the Ba Co Fault in Ngari Prefecture, Tibet. Geosciences. 2025; 15(10):377. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15100377
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Yunsheng, Yanxiu Shao, and Bo Zhang. 2025. "Preliminary Study on the Activity of the Rupture Zone in the Eastern Segment of the Ba Co Fault in Ngari Prefecture, Tibet" Geosciences 15, no. 10: 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15100377
APA StyleYao, Y., Shao, Y., & Zhang, B. (2025). Preliminary Study on the Activity of the Rupture Zone in the Eastern Segment of the Ba Co Fault in Ngari Prefecture, Tibet. Geosciences, 15(10), 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15100377






