Influence of Climatic Trends and Cycles on Varve Deposition in Crawford Lake, Ontario, Canada
Abstract
1. Introduction
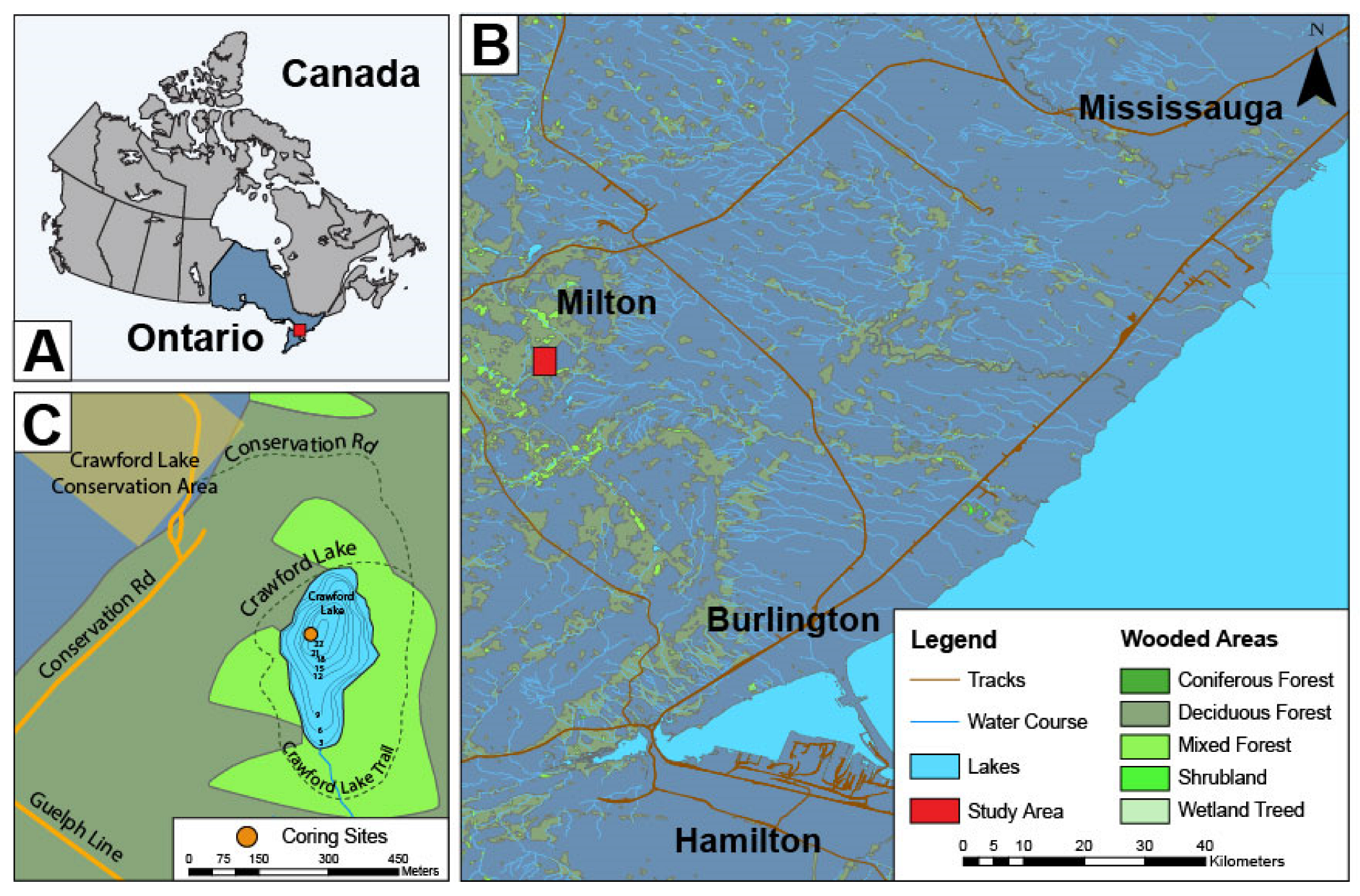
1.1. Varved Sedimentation in Crawford Lake
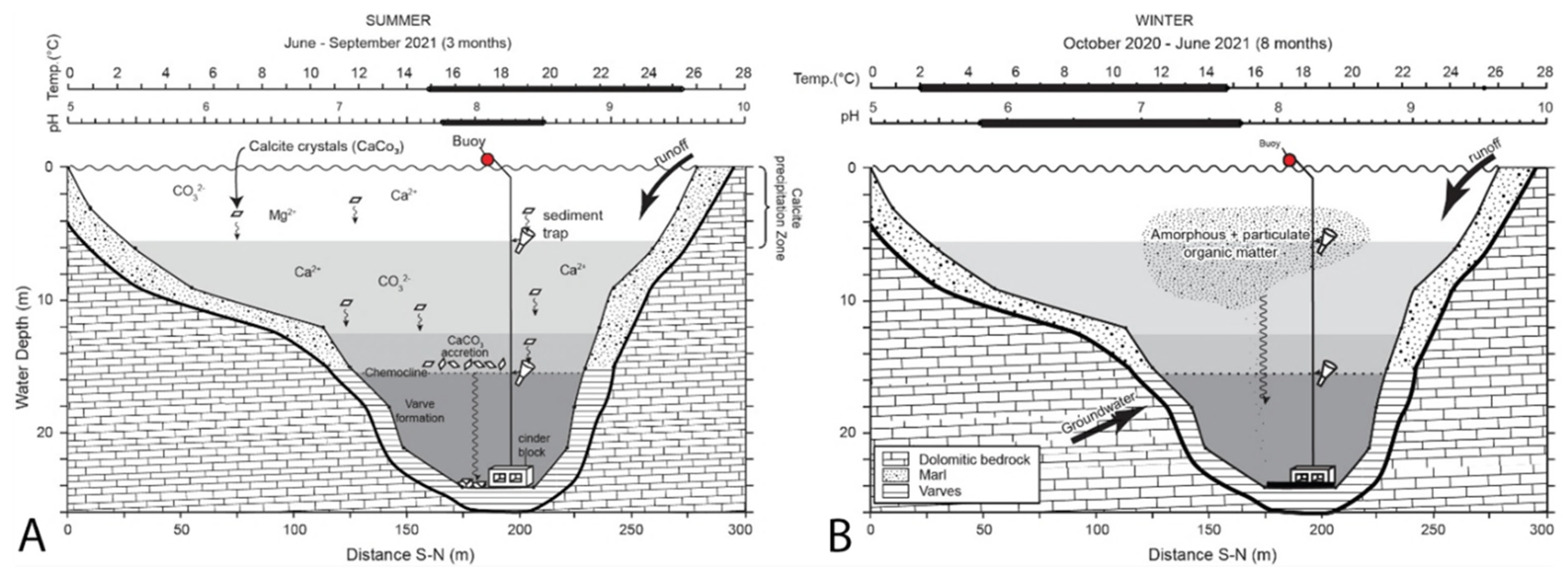
1.2. Lake Physiography, Limnology, and Varve Formation
1.3. Climatic Cycles and Prominent Trends
2. Materials and Methods
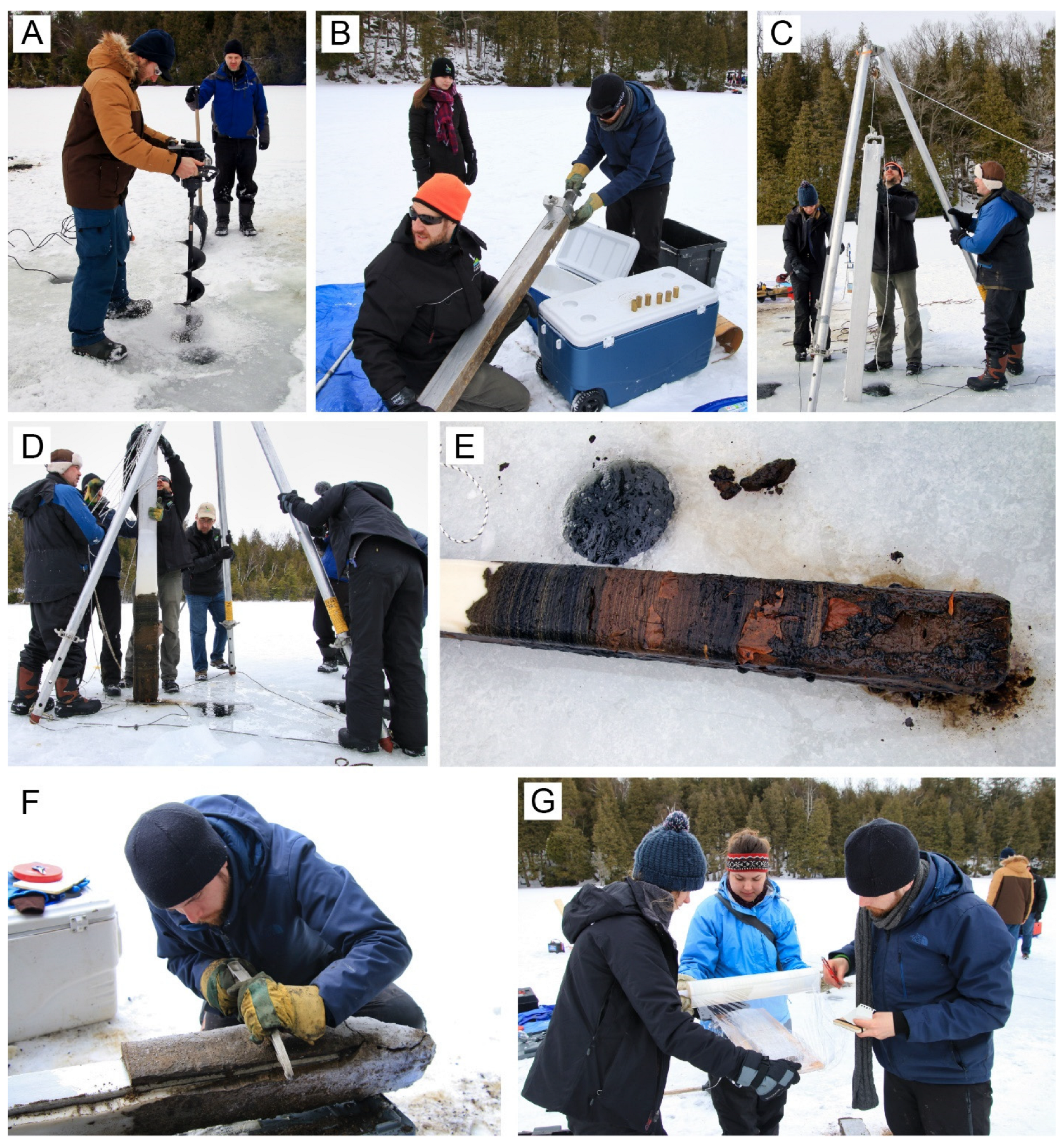
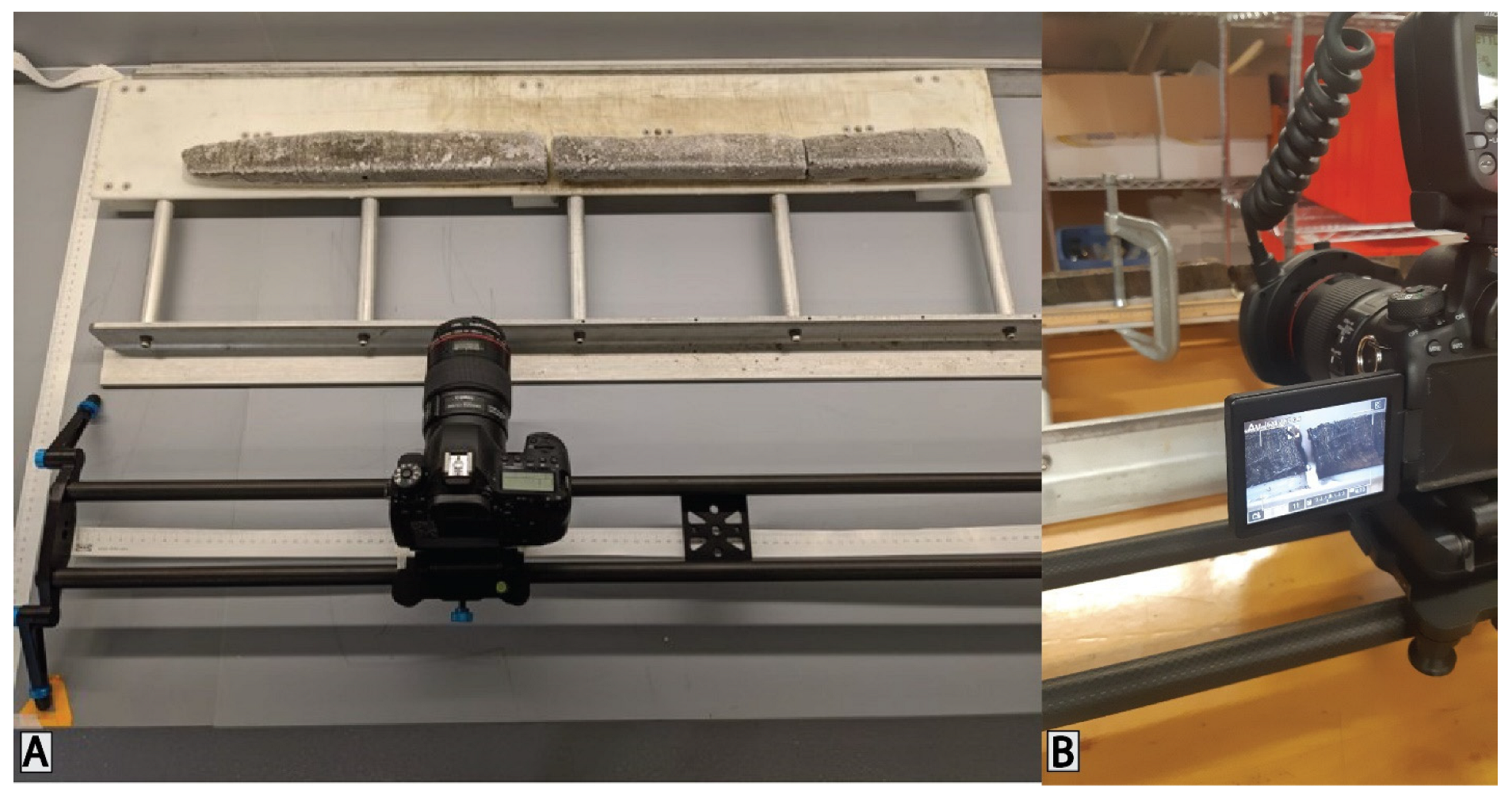
2.1. Freeze Core Collection and Preparation
2.2. Core Photography
2.3. Image Processing
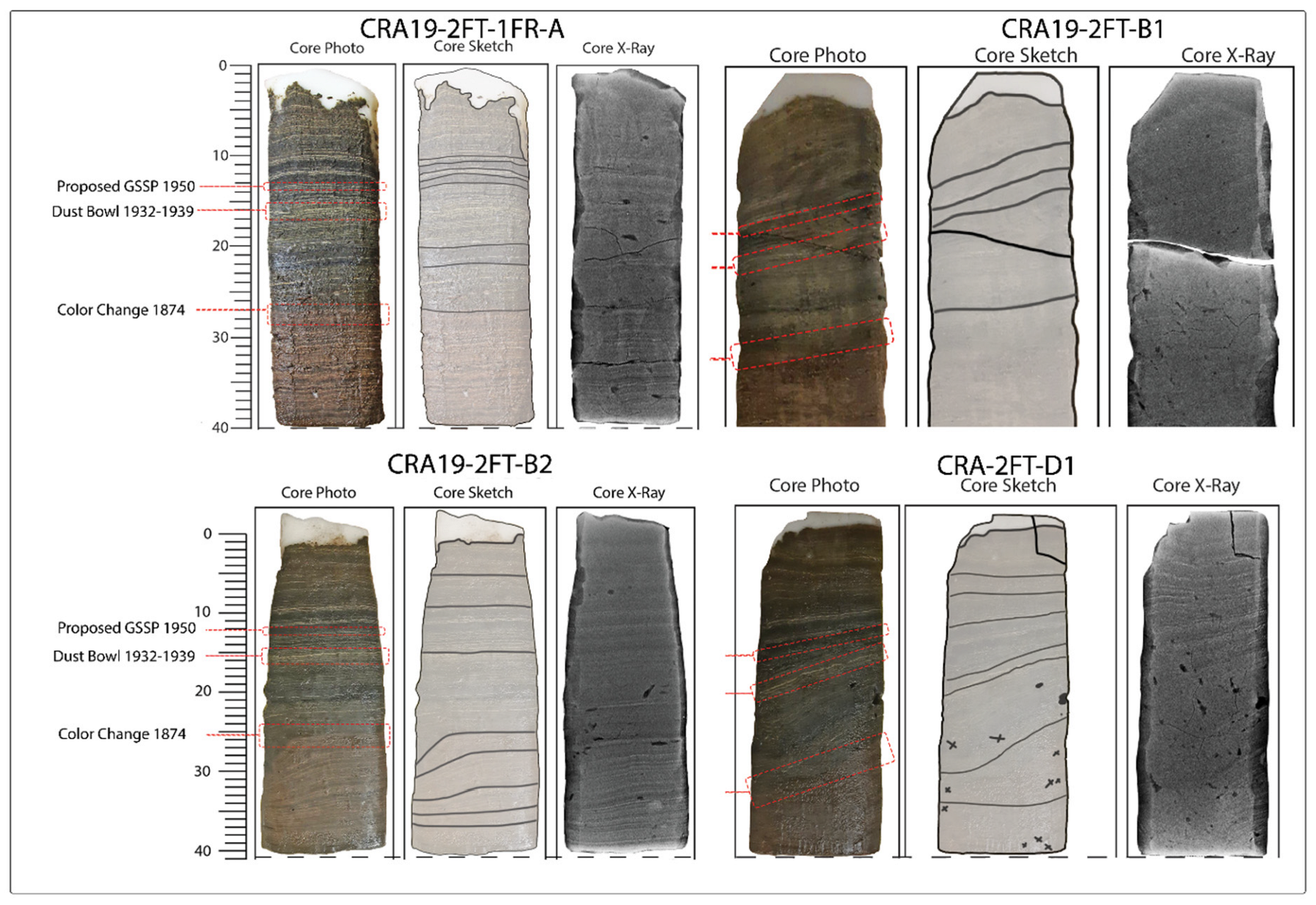
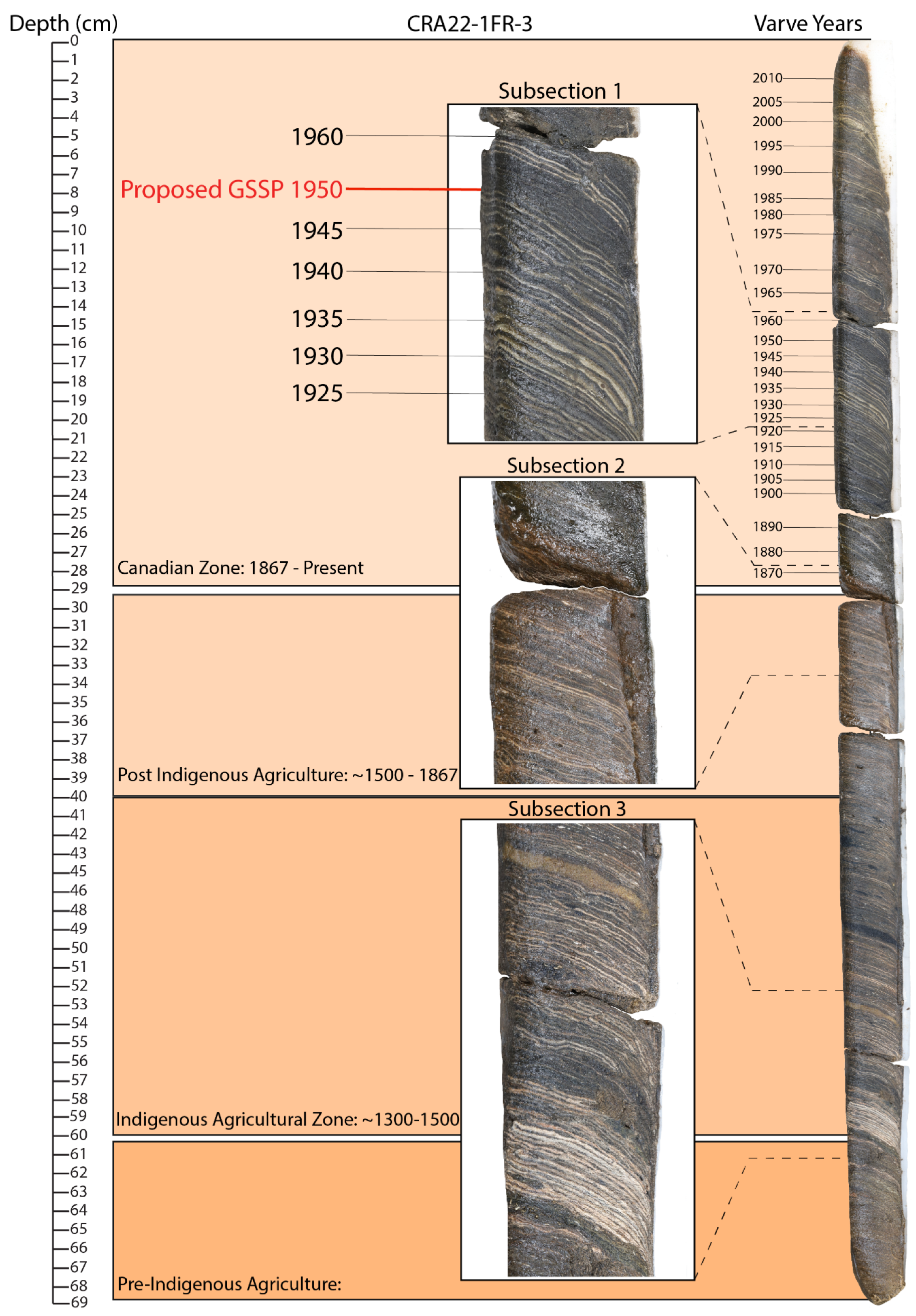
2.4. Varve Dating
2.5. Measuring Varve Thickness and Time Series Analysis
3. Results
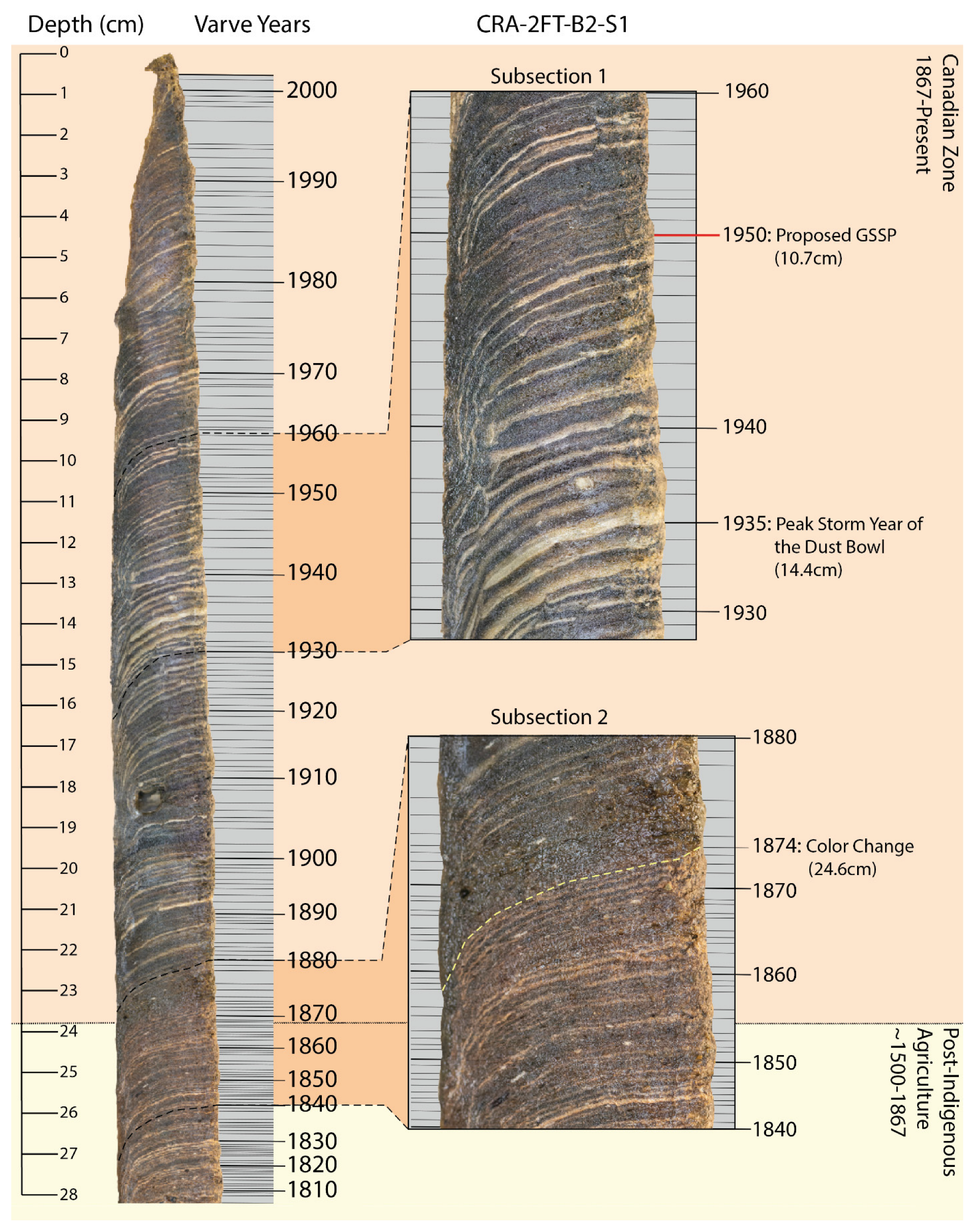
3.1. Varve Thickness and Chronology
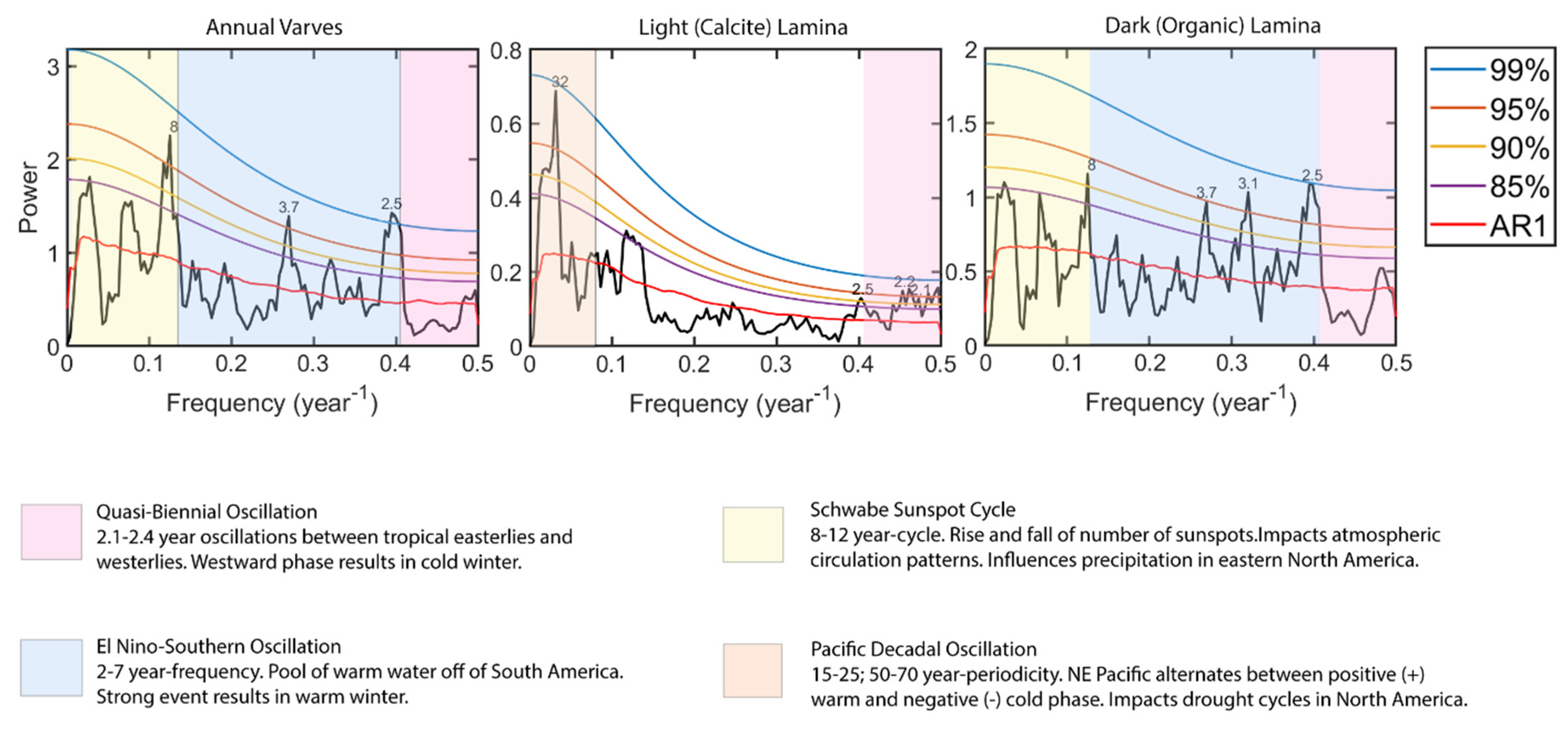
3.2. Spectral Analysis
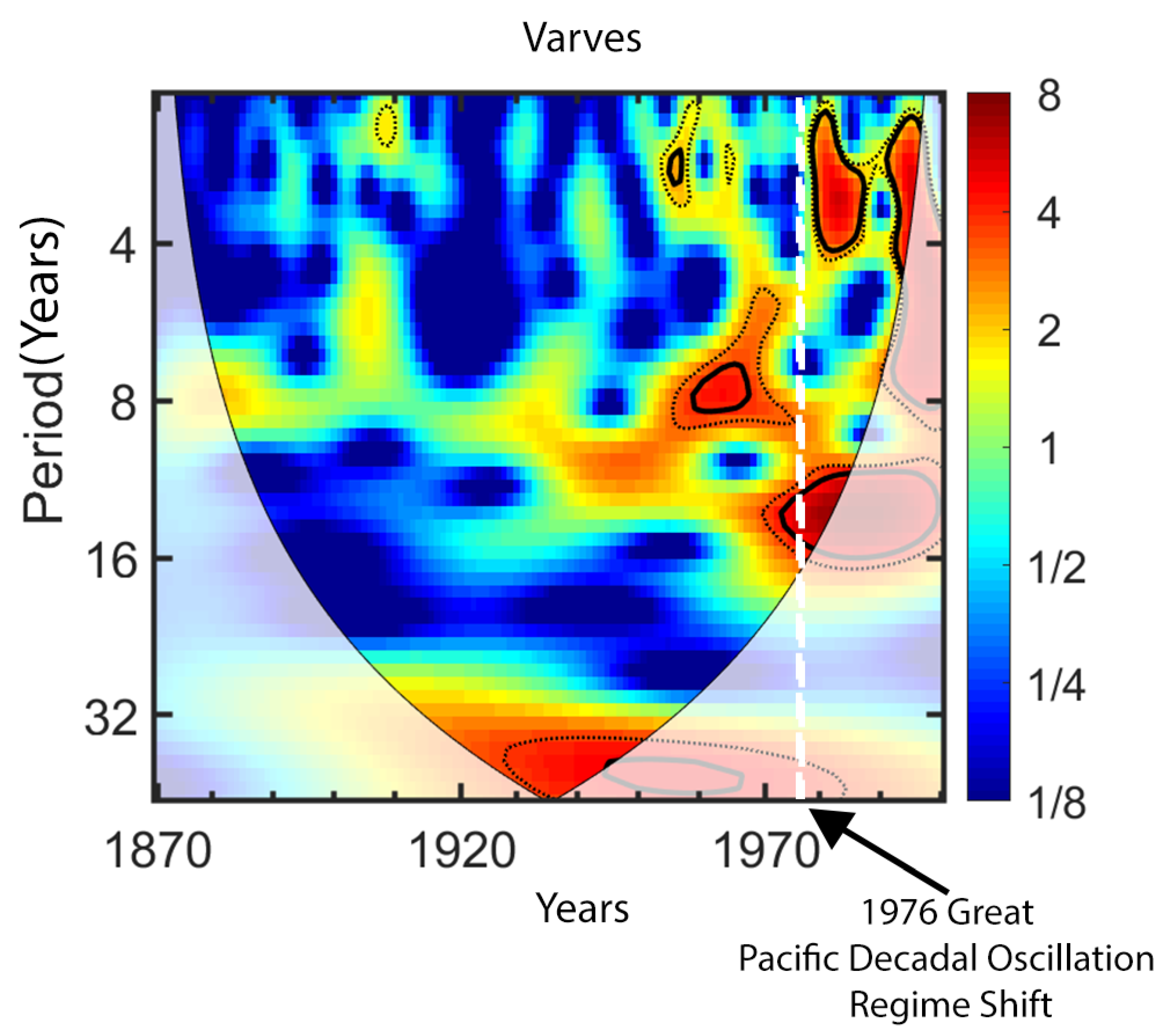
3.3. Continuous Wavelet Transform (CWT) Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Sedimentary Record
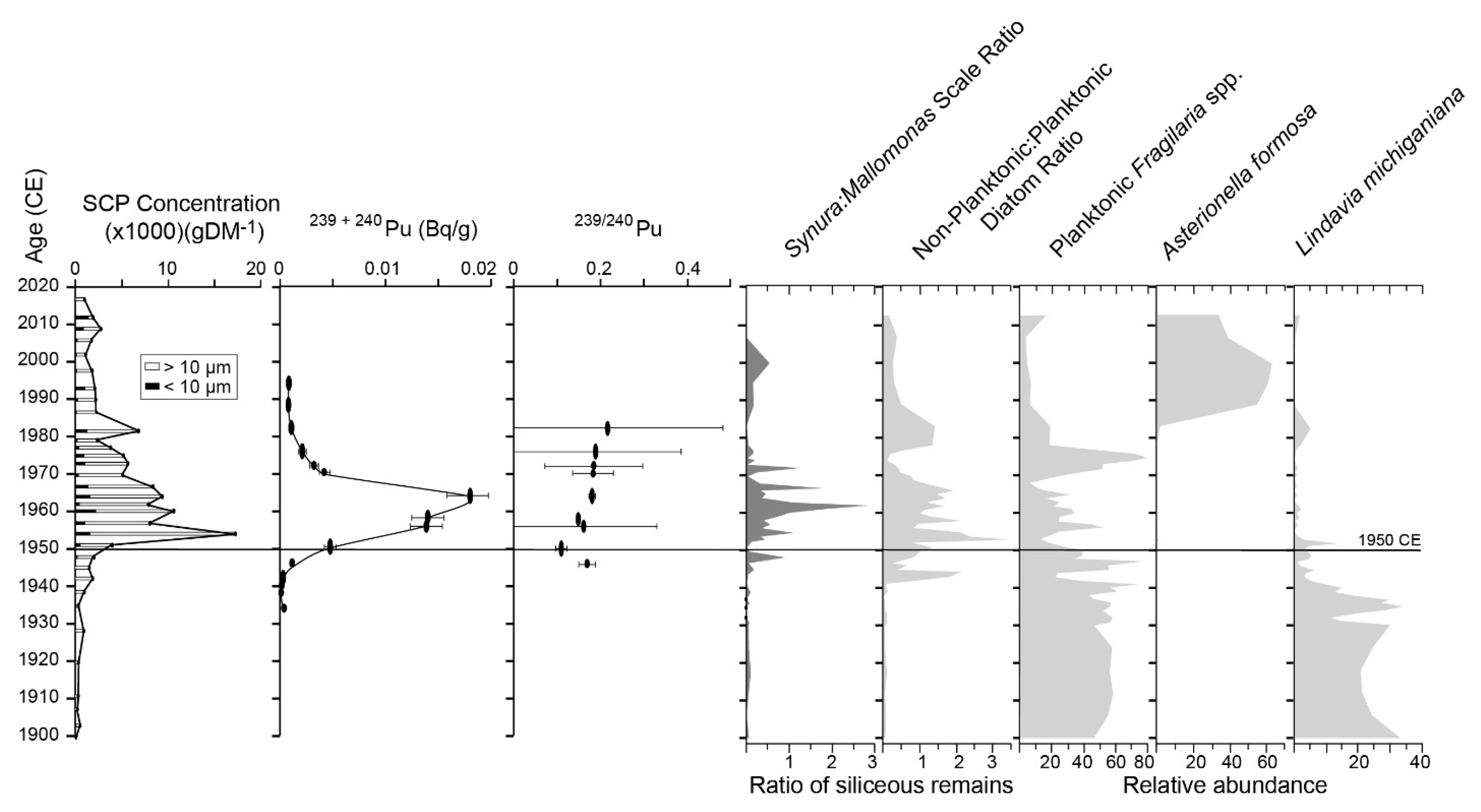
4.2. Varve Deposition Mechanism and the Anthropocene GSSP
4.3. Climate Cycles Influence in Crawford Lake
4.3.1. Quasi-Biennial Oscillation (QBO)
4.3.2. El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO)
4.3.3. Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO)
4.3.4. Schwabe Sunspot Cycle (SSC)
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smol, J.P. Paleolimnology, an important tool for effective ecosystem management. J. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health 1992, 1, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.S. Paleolimnology, The History and Evolution of Lake Systems; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2004; ISBN 9780195133530. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, R.Y.; Dean, W.E. Lacustrine varve formation through time. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1988, 62, 215–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauer, A.; Endres, C.; Günter, C.; Litt, T.; Stebich, M.; Negendank, J.F. High resolution sediment and vegetation responses to Younger Dryas climate change in varved lake sediments from Meerfelder Maar, Germany. Quat. Sci. Rev. 1999, 18, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauer, A. Annually laminated lake sediments and their palaeoclimatic relevance. In The Climate in Historical Times; GKSS School of Environmental Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, G.; Sun, Q.; Rioual, P.; Boltovskoy, A.; Liu, Q.; Sun, P.; Han, J.; Liu, J. Dinocyst microlaminations and freshwater" red tides" recorded in Lake Xiaolongwan, northeastern China. J. Paleolimnol. 2008, 39, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolitschka, B.; Francus, P.; Ojala, A.E.K.; Schimmelmann, A. Varves in lakes sediments—A review. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2015, 117, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renberg, I. Concentration and annual accumulation values of heavy metals in lake sediments, their significance in studies of the history of heavy metal pollution. In Paleolimnology IV; Developments in Hydrobiology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1987; Volume 37, pp. 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leemann, A.; Niessen, F. Varve formation and the climatic record in an Alpine proglacial lake, calibrating annually-laminated sediments against hydrological and meteorological data. Holocene 1994, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outridge, P.M.; Stern, G.A.; Hamilton, P.B.; Percival, J.B.; McNeely, R.; Lockhart, W.L. Trace metal profiles in the varved sediment of an Arctic lake. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 4881–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaminder, J.; Appleby, P.; Crook, P.; Renberg, I. Post-deposition diffusion of 137Cs in lake sediment, Implications for radiocaesium dating. Sedimentology 2012, 59, 2259–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, J.W.; Arvidson, R.S.; Lüttge, A. Calcium carbonate formation and dissolution. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 342–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boere, A.C.; Damsté, J.S.S.; Rijpstra, W.I.C.; Volkman, J.K.; Coolen, M.J. Source-specific variability in post-depositional DNA preservation with potential implications for DNA based paleoecological records. Org. Geochem. 2011, 42, 1216–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parducci, L.; Nota, K.; Wood, J. Reconstructing past vegetation communities using ancient DNA from lake sediments. In Paleogenomics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 163–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokoph, A.; Patterson, R.T. Application of wavelet and regression analysis in assessing temporal and geographic climate variability, Eastern Ontario, Canada as a case study. Atmos. Ocean. 2004, 42, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ólafsdóttir, K.B.; Geirsdóttir, Á.; Miller, G.H.; Larsen, D.J. Evolution of NAO and AMO strength and cyclicity derived from a 3-ka varve-thickness record from Iceland. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2013, 69, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, C.R.; Patterson, R.T. Regional impact of large-scale climate oscillations on ice out variability in New Brunswick and Maine. PeerJ. 2022, 10, e13741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak, M.; Rybak, I.; Dickman, M. Fossil chrysophycean cyst flora in a small meromictic lake in southern Ontario, and its paleoecological interpretation. Can. J. Bot. 1987, 65, 2425–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak, M.; Dickman, M. Paleoecological reconstruction of changes in the productivity of a small, meromictic lake in southern Ontario, Canada. Hydrobiologia 1988, 169, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekdahl, E.J.; Teranes, J.L.; Guilderson, T.P.; Turton, C.L.; McAndrews, J.H.; Wittkokp, C.A.; Stoermer, E.F. Prehistorical record of cultural eutrophication from Crawford Lake, Canada. Geology 2004, 32, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekdahl, E.J.; Teranes, J.L.; Wittkop, C.A.; Stoermer, E.F.; Reavie, E.D.; Smol, J.P. Diatom assemblage response to Iroquoian and Euro-Canadian eutrophication of Crawford Lake, Ontario, Canada. J. Paleolimnol. 2007, 37, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAndrews, J.H.; Turton, C.L. Canada Geese Dispersed Cultigen Pollen Grains from Prehistoric Iroquoian Fields to Crawford Lake, Ontario, Canada. Palynology 2007, 31, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAndrews, J.H.; Boyko-Diakonow, M. Pollen analysis of varved sediment at Crawford Lake, Ontario, evidence of Indian and European farming. Quat. Geol. Can. Greenl. 1989, 1, 528–530. [Google Scholar]
- Krueger, A.; McCarthy, F. Great Canadian lagerstätten 5. Crawford lake–A Canadian holocene lacustrine konservat-lagerstätte with two-century-old viable dinoflagellate cysts. Geosci. Can. J. Geol. Assoc. Can. 2016, 43, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, F.M.; Riddick, N.L.; Volik, O.; Danesh, D.C.; Krueger, A.M. Algal palynomorphs as proxies of human impact on freshwater resources in the Great Lakes region. Anthropocene 2018, 21, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeill, J.R.; Engelke, P. The Great Acceleration, an Environmental History of the Anthropocene Since 1945; The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Steffen, W.; Broadgate, W.; Deutsch, L.; Gaffney, O.; Ludwig, C. The trajectory of the Anthropocene, the great acceleration. Anthr. Rev. 2015, 2, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gushulak, C.; Marshall, M.; Cumming, B.; Llew-Williams, B.; Patterson, R.T.; McCarthy, F.M.G. Siliceous algae response to the ‘Great Acceleration’ of the mid-twentieth century in Crawford Lake (Ontario, Canada), a candidate for the Anthropocene GSSP. Anthr. Rev. 2022, 9, 571–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Head, M.J.; Steffen, W.; Fagerlind, D.; Waters, C.N.; Poirier, C.; Syvitski, J.; Zalasiewicz, J.A.; Barnosky, A.D.; Cearreta, A.; Jeandel, C.; et al. The Great Acceleration is real and provides a quantitative basis for the proposed Anthropocene series/Epoch. Episodes 2022, 45, 359–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, F.M.G.; Patterson, R.T.; Head, M.J.; Riddick, N.L.; Cumming, B.F.; Hamilton, P.B.; Pisaric, M.F.J.; Gushulak, A.C.; Leavitt, P.R.; Lafond, K.M.; et al. The varved succession of Crawford Lake, Milton, Ontario, Canada as a candidate Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point for the Anthropocene Series/Epoch. Anthr. Rev. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, M.; Hamilton, P.B.; Lafond, K.M.; Nasser, N.A.; McCarthy, F.M.G.; Patterson, R.T. Annual-scale assessment of mid-20th century anthropogenic impacts on the algal ecology of Crawford Lake, Ontario, Canada. Peer J. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, C.N.; Zalasiewicz, J.; Summerhayes, C.; Fairchild, I.J.; Rose, N.L.; Loader, J.; Shotyk, W.; Caerreta, A.; Head, M.J.; Williams, M.; et al. Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP) for the Anthropocene Series, Where and how to look for potential candidates. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 178, 379–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, C.N.; Turner, S.D.; Zalasiewicz, J.; Head, M.J. Candidate sites and other reference sections for the Global boundary Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP) of the Anthropocene Series. Anthr. Rev. 2023; in submission. [Google Scholar]
- Dickman, M.D. A possible varving mechanism for meromictic lakes. Quat. Res. 1979, 11, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickman, M.D. Seasonal succession and microlamina formation in a meromictic lake displaying varved sediments. Sedimentology 1985, 32, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llew-Williams, B. The Hydrological and Limnological Characterization of Two Canadian Water Catchments Sensitive to Anthropogenic Influences, Crawford Lake, Ontario and Old Crow Flats, Yukon. Master’s Thesis, Brock University, St. Catharines, ON, Canada, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Llew-Williams, B.M.; McCarthy, F.M.; Krueger, A.M.; Riddick, N.L.; MacKinnon, M.; Lafond, K.M.; Patterson, R.T.; Nasser, N.A.; Head, M.J.; Pisaric, M.; et al. Varve formation in meromictic Crawford Lake, Ontario, Canada, important process for characterizing the Anthropocene epoch. 2023; in review. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; McAndrews, J.H.; Eicher, U. Middle Holocene dry climate caused by change in atmospheric circulation patterns, Evidence from lake levels and stable isotopes. Geology 1997, 25, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyko, M. European Impact on the Vegetation around Crawford Lake in Southern Ontario. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Boyko-Diakonow, M. The laminated sediments of Crawford Lake, southern Ontario, Canada. Moraines Varves. AA Balkema Rotterdam 1979, 303–307. [Google Scholar]
- Zadereev, E.S.; Boehrer, B.; Gulati, R.D. Chapter 1. Introduction, Meromictic Lakes, Their Terminology and Geographic Distribution. In Ecology of Meromictic Lakes; Springer International Publishing: New Yor, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyde, A. Crawford Lake Consumers, Water Column and Palynological Studies. Master’s Thesis, Brock University, St. Catherines, ON, Canada, 2021. Available online: https://dr.library.brocku.ca/handle/10464/15161 (accessed on 8 August 2021).
- Francis, A. Microbial mobilization and immobilization of plutonium. J. Alloy. Compd. 2007, 444, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geckeis, H.; Salbu, B.; Chaefer, T.; Zavarin, M. Environmental Chemistry of Plutonium, Plutonium Handbook; Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory: Livermore, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zalasiewicz, J.; Waters, C.N.; Head, M.J.; Poirier, C.; Summerhayes, C.P.; Leinfelder, R.; Grinevald, J.; Steffen, W.; Syvitski, J.; Haff, P.; et al. A formal Anthropocene is compatible with but distinct from its diachronous anthropogenic counterparts, A response to W.F. Ruddiman’s ‘three flaws in defining a formal Anthropocene’. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2019, 43, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonk, A.; Tylmann, W.; Amann, B.; Enters, D.; Grosjean, M. Modern limnology and varve-formation processes in Lake Żabińskie, northeastern Poland, comprehensive process studies as a key to understand the sediment record. J. Limnol. 2015, 74, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeser, P.; Dräger, N.; Brykała, D.; Ott, F.; Pinkerneil, S.; Gierszewski, P.; Lindemann, C.; Plessen, B.; Brademann, B.; Kaszubski, M.; et al. Differences in calcite varve formation discerned by a dual lake monitoring approach in the southern Baltic lowlands. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference, Online, 4–8 May 2020; Available online: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/link_gateway/2020EGUGA..2212343R/ (accessed on 8 August 2021). [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, M.P.; Gray, L.J.; Dunkerton, T.J.; Hamilton, K.; Haynes, P.H.; Randel, W.J.; Holton, J.R.; Alexander, M.J.; Hirota, I.; Horinouchi, T.; et al. The quasi-biennial oscillation. Rev. Geophys. 2001, 39, 179–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, R.T.; Swindles, G.T. Influence of ocean-atmospheric oscillations on lake ice phenology in Eastern North America. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 45, 2293–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, C.R.; Patterson, R.T. Precipitation and temperature trends and cycles derived from historical 1890–2019 weather data for the City of Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. Environments 2022, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.M.; Sheu, P. Annual cycle, Quasi-Biennial Oscillation, and Southern Oscillation in global precipitation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1988, 93, 10975–10988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brázdil, R.; Zolotokrylin, A. The QBO signal in monthly precipitation fields over Europe. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 1995, 51, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Yamakawa, S. Relationships between Stratospheric Quasi-Biennial Oscillation (QBO). J. Geogr. 2010, 119, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Choi, W.; Youn, D.; Park, D.-S.R.; Kim, J.Y. Relationship between the stratospheric Quasi-Biennial Oscillation and the spring rainfall in the western North Pacific. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 5949–5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastos, P.T.; Zerefos, C.S. On extreme daily precipitation totals at Athens, Greece. Adv. Geosci. 2007, 10, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, S.; Hartmann, H.; Coulibaly, M.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, T. Quasi periodicities of extreme precipitation events in the Yangtze River basin, China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2008, 94, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Li, S.; Hao, X.; Guo, X. A statistical prediction model for summer extreme precipitation days over the northern central China. Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 40, 4189–4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henke, L.M.; Lambert, F.H.; Charman, D.J. Was the little ice age more or less El Niño-like than the mediaeval climate anomaly? Evidence from hydrological and temperature proxy data. Clim. Past Discuss. 2015, 11, 5549–5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalley, D.; Adamowski, J.; Khalil, B.; Ozga-Zielinski, B. Trend detection in surface air temperature in Ontario and Quebec, Canada during 1967–2006 using the discrete wavelet transform. Atmos. Res. 2013, 132, 375–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, N.; Cornuelle, B.D. The Forcing of the Pacific Decadal Oscillation. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 4355–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, R.T.; Chang, A.S.; Prokoph, A.; Roe, H.M.; Swindles, G.T. Influence on the Pacific Decadal Oscillation, El Niño-Southern Oscillation and solar forcing on climate and primary productivity changes in the northeast Pacific. Quat. Int. 2013, 310, 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, A.S.; Patterson, R.T.; Roe, H.M.; Macumber, A.L.; Swindles, G.T.; Galloway, J.M.; Falck, H. Late Holocene climatic variability in Subarctic Canada, Insights from a high-resolution lake record from the central Northwest Territories. PLoS ONE. 2018, 13, e0199872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, R.T.; Kumar, A. A review of current testate rhizopod (thecamoebian) research in Canada. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2002, 180, 225–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, J.M.; Macumber, A.; Patterson, R.T.; Falck, H.; Hadlari, T.; Madsen, E. Paleoclimatological Assessment of the Southern Northwest Territories and Implications for the Long-Term Viability of the Tibbitt to Contwoyto Winter Road, Part I, Core Collection; Northwest Territories Geoscience Office: Yellowknife, NT, Canada, 2010; NWT Open Report 2010-002; 23p. [CrossRef]
- McAndrews, J.H. Fossil history of man’s impact on the Canadian flora, An example from southern Ontario. Can. Bot. Assoc. Bull. 1976, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Crusius, J.; Anderson, R.F. Core compression and surficial sediment loss of lake sediments of high porosity caused by gravity coring. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1991, 36, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, B.I.; Miller, R.L.; Seager, R. Dust and sea surface temperature forcing of the 1930s “Dust Bowl” drought. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seager, R.; Kushnir, Y.; Ting, M.; Cane, M.; Naik, N.; Miller, J. Would advance knowledge of 1930s SSTs have allowed prediction of the Dust Bowl drought? J. Clim. 2008, 21, 3261–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donat, M.G.; King, A.D.; Overpeck, J.T.; Alexander, L.V.; Durre, I.; Karoly, D.J. Extraordinary heat during the 1930s US Dust Bowl and associated large-scale conditions. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 46, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, J.M.S.; Cumming, B.F.; Smol, J.P. A 900-year pollen-inferred temperature and effective moisture record from varved Lake Mina, west-central Minnesota, USA. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2008, 27, 781–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, K.R.; Das, B.; Kingsbury, M.; Moos, M.T.; Pla-Rabes, S.; Ahad, J.M.; Wiltse, B.; Cumming, B.F. Paleolimnological assessment of limnological change in 10 lakes from northwest Saskatchewan downwind of the Athabasca oils sands based on analysis of siliceous algae and trace metals in sediment cores. Hydrobiologia 2013, 720, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokoph, A.; Fowler, A.D.; Patterson, R.T. Evidence for periodicity and nonlinearity in a high-resolution fossil record of long-term evolution. Geology 2000, 28, 867–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MathWorks. MATLAB Version 9.6.0.10 (Time Series); The MathWorks Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, D.J. Spectrum estimation and harmonic analysis. Proc. IEEE 1982, 70, 1055–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husson, D.; Thibault, N.; Galbrun, B.; Gardin, S.; Minoletti, F.; Sageman, B.; Huret, E. Lower Maastrichtian cyclostratigraphy of the Bidart section (Basque Country, SW France), A remarkable record of precessional forcing. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2014, 395, 176–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorothée. Red Noise Confidence Levels. MATLAB Central File Exchange. Retrieved 26 August 2020. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/45539-rednoise_confidencelevels (accessed on 26 August 2020).
- Torrence, C.; Compo, G.P. A practical guide to wavelet analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syvitski, J.; Waters, C.N.; Day, J.; Milliman, J.D.; Summerhayes, C.; Steffen, W.; Zalasiewicz, J.; Cearreta, A.; Galuszka, A.; Hajdas, I.; et al. Extraordinary human energy consumption and resultant geological impacts beginning around 1950 CE initiated the proposed Anthropocene Epoch. Commun. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation. UNSCEAR 2000 Report Vol I. In Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation. Annex D, Medical Radiation Exposures; UNSCEAR; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bush, I.C.; Cwynar, L.C. Crawford Lake research and development project. In Halton Regional Conservation Authority; Halton Region Conservation Authority: Halton, ON, Canada, 1972; p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- Brunskill, G.J.; Ludlam, S.D. Fayetteville Green Lake, New York. I. Physical and chemical limnology 1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1969, 14, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dustin, N.M.; Wilkinson, B.H.; Owen, R.M. Littlefield Lake, Michigan, Carbonate budget of Holocene sedimentation in a temperate-region lacustrine system 1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1986, 31, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAndrews, J.H.; Turton, C.L. Fungal spores record Iroquoian and Canadian agriculture in 2nd millennium a.d. sediment of Crawford Lake, Ontario, Canada. Veg. Hist. Archaeobotany 2010, 19, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Steinschneider, S. A diagnostic-predictive assessment of winter precipitation over the Laurentian Great Lakes, Effects of ENSO and other teleconnections. J. Hydrometeorol. 2019, 20, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, N.; Murtugudde, R. All flavours of El Niño have similar early subsurface origins. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, L.J.; Beer, J.; Geller, M.; Haigh, J.D.; Lockwood, M.; Matthes, K.; Cubasch, U.; Fleitmann, D.; Harrison, D.; Hood, L.; et al. Solar influences on climate. Rev. Geophys. 2010, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Puertas, C.; Matthes, K.; Brauer, A.; Muscheler, R.; Hansen, F.; Petrick, C.; Aldahan, A.; Possnert, G.; Van Geel, B. Regional atmospheric circulation shifts induced by a grand solar minimum. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usoskin, I.G.; Mursula, K.; Arlt, R.; Kovaltsov, G.A. A solar cycle lost in 1793–1800, early sunspot observations resolve the old mystery. Astrophys. J. 2009, 700, L154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deser, C.; Alexander, M.A.; Xie, S.P.; Phillips, A.S. Sea surface temperature variability, Patterns and mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2010, 2, 115–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, C.R.; Patterson, R.T. Attribution of Observed Periodicity in Extreme Weather Events in Eastern North America. Earth Space Sci. 2022, 9, e2022EA002359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.; Royall, P. Transformation of a northern hardwood forest by aboriginal (Iroquois) fire, Charcoal evidence from Crawford Lake, Ontario, Canada. Holocene 1994, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrich, G.B. Multidecadal climate variability and drought in the United States. Geogr. Compass 2007, 1, 713–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabbar, A.; Bonsal, B. Associations between low frequency variability modes and winter temperature extremes in Canada. Atmos. -Ocean. 2004, 42, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appenzeller, C.; Stocker, T.F.; Anklin, M. North Atlantic Oscillation dynamics recorded in Greenland ice cores. Science 1998, 282, 446–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubeny, J.B.; King, J.W.; Cantwell, M. Anthropogenic influences on estuarine sedimentation and ecology, examples from the varved sediments of the Pettaquamscutt River Estuary, Rhode Island. J. Paleolimnol. 2009, 41, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabbar, A.; Khandekar, M. The impact of El Nino-Southern oscillation on the temperature field over Canada, Research note. Atmos. -Ocean. 1996, 34, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabbar, A.; Bonsal, B.; Khandekar, M. Canadian precipitation patterns associated with the Southern Oscillation. J. Clim. 1997, 10, 3016–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobena, A.K.; Gan, T.Y. Low-frequency variability in Southwestern Canadian stream flow, links with large-scale climate anomalies. Int. J. Climatol. 2006, 26, 1843–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horel, J.D.; Wallace, J.M. Planetary-scale atmospheric phenomena associated with the Southern Oscillation. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1981, 109, 813–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulard, N.; Lin, H.; Yu, B. The changing relationship between ENSO and its extratropical response patterns. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, J.J.; Hughen, K.A.; Miller, G.H.; Overpeck, J.T. Little Ice Age recorded in summer temperature reconstruction from vared sediments of Donard Lake, Baffin Island, Canada. J. Paleolimnol. 2001, 25, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, S.G.; Cobb, K.M.; Emile-Geay, J.; Ault, T.R.; Edwards, R.L.; Cheng, H.; Charles, C.D. No consistent ENSO response to volcanic forcing over the last millennium. Science 2020, 367, 1477–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckman, B.H. The little ice age in the Canadian Rockies. Geomorphology 2000, 32, 357–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapointe, F.; Bradley, R.S.; Francus, P.; Balascio, N.L.; Abbott, M.B.; Stoner, J.S.; St-Onge, G.; De Coninck, A.; Labarre, T. Annually resolved Atlantic sea surface temperature variability over the past 2,900 y. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 27171–27178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantua, N.J.; Hare, S.R.; Zhang, Y.; Wallace, J.M.; Francis, R.C. A Pacific interdecadal climate oscillation with impacts on salmon production. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 78, 1069–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantua, N.J.; Hare, S.R. The Pacific decadal oscillation. J. Oceanogr. 2002, 58, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, B.; Wendler, G. The significance of the 1976 Pacific climate shift in the climatology of Alaska. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 4824–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.; Ren, R.; Xia, X.; Shi, C.; Guo, D. Combined impact of El Niño–Southern Oscillation and Pacific Decadal Oscillation on the northern winter stratosphere. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labitzke, K. The global signal of the 11-year sunspot cycle in the atmosphere, When do we need the QBO? Meteorol. Zeitschrift. 2001, 12, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meehl, G.A.; Arblaster, J.M.; Matthes, K.; Sassi, F.; Van Loon, H. Amplifying the Pacific climate system response to a small 11-year solar cycle forcing. Science 2009, 325, 1114–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurenz, L.; Lüdecke, H.J.; Lüning, S. Influence of solar activity changes on European rainfall. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2019, 185, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthakrishnan, R.; Parthasarathy, B. Indian rainfall in relation to the sunspot cycle, 1871–1978. J. Climatol. 1984, 4, 149–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, R.G.; O’Brien, D.P. Periodic 18.6-year and cyclic 10 to 11 year signals in northeastern United States precipitation data. J. Climatol. 1988, 8, 255–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, R.G. Luni-solar 18.6-and solar cycle 10--11-year signals in USA air temperature records. Int. J. Climatol. 1993, 13, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, B.; Lara, A.; Maravilla, D.; Ja´uregui, E. Temperature variability in central Mexico and its possible association to solar activity. J. Atmos. Sol. -Terr. Phys. 2001, 63, 1891–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, B.; Velasco, V.; J´auregui, E. A study of historical droughts in southeastern Mexico. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 2916–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokoph, A.; Adamowski, J.; Adamowski, K. Influence of the 11-year solar cycle on annual streamflow maxima in Southern Canada. J. Hydrol. 2012, 442, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, H.H. Climate, History and the Modern World; Routledge: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


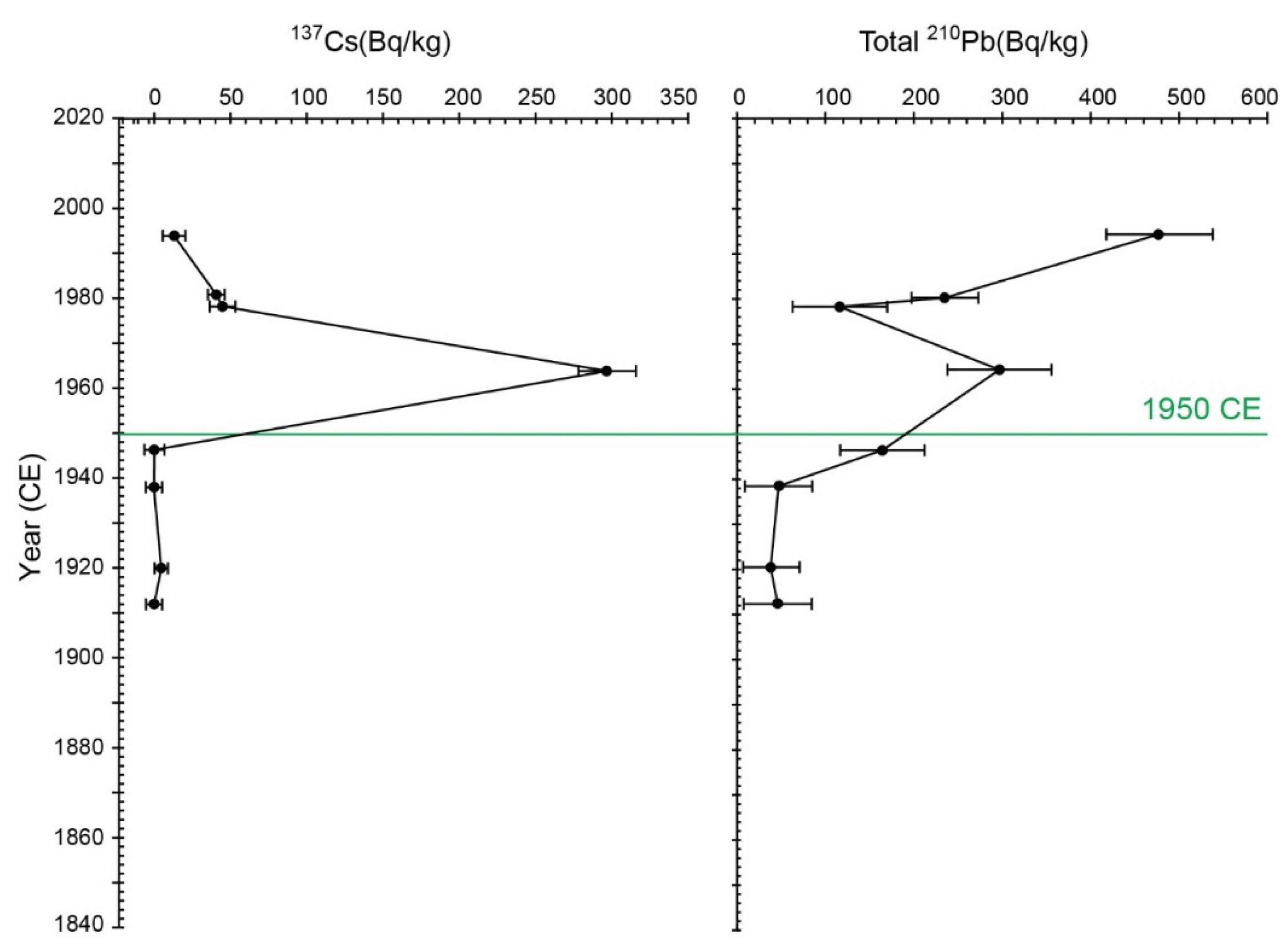

| Lab ID | Varve Age | 137Cs (Bq/kg) | Error 137Cs (Bq/kg) | 210Pb (Bq/kg) | Error 210Pb (Bq/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Queens-1 | 1994–1995 | 9.02 | 7.44 | 477.21 | 61.99 |
| Queens-2 | 1980–1981 | 41 | 5.92 | 235.19 | 38.32 |
| Queens-3 | 1978–1979 | 44.16 | 8.24 | 116.53 | 54.25 |
| Queens-4 | 1964–1965 | 298.04 | 18.9 | 295.71 | 59.2 |
| Queens-5 | 1946–1947 | 0 | 6.59 | 165.2 | 48.85 |
| Queens-6 | 1938–1939 | 0 | 5.26 | 47.7 | 38.23 |
| Queens-7 | 1920–1921 | 3.13 | 4.61 | 38.97 | 32.3 |
| Queens-8 | 1912–1913 | 0 | 5.26 | 46.1 | 39.01 |
| Lamina | Min (mm) | Max (mm) | Average (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcite | 0.0396 | 1.5295 | 0.3711 |
| Organic | 0.1055 | 3.4413 | 0.8901 |
| Total Annual | 0.2110 | 3.7578 | 1.2612 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lafond, K.M.; Walsh, C.R.; Patterson, R.T.; McCarthy, F.M.G.; Llew-Williams, B.M.; Hamilton, P.B.; Nasser, N.A.; Cumming, B. Influence of Climatic Trends and Cycles on Varve Deposition in Crawford Lake, Ontario, Canada. Geosciences 2023, 13, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences13030087
Lafond KM, Walsh CR, Patterson RT, McCarthy FMG, Llew-Williams BM, Hamilton PB, Nasser NA, Cumming B. Influence of Climatic Trends and Cycles on Varve Deposition in Crawford Lake, Ontario, Canada. Geosciences. 2023; 13(3):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences13030087
Chicago/Turabian StyleLafond, Krysten M., Carling R. Walsh, R. Timothy Patterson, Francine M. G. McCarthy, Brendan M. Llew-Williams, Paul B. Hamilton, Nawaf A. Nasser, and Brian Cumming. 2023. "Influence of Climatic Trends and Cycles on Varve Deposition in Crawford Lake, Ontario, Canada" Geosciences 13, no. 3: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences13030087
APA StyleLafond, K. M., Walsh, C. R., Patterson, R. T., McCarthy, F. M. G., Llew-Williams, B. M., Hamilton, P. B., Nasser, N. A., & Cumming, B. (2023). Influence of Climatic Trends and Cycles on Varve Deposition in Crawford Lake, Ontario, Canada. Geosciences, 13(3), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences13030087






