Abstract
Serifos island is characterized by rich geodiversity, industrial and cultural heritage. The present paper focuses on the geological and mining heritage of Serifos, with the aim of integrating the island in the international environment of Geoparks, in the near future. In this geopark, Serifos can highlight the rich geological heritage of the island combined with the rich industrial heritage as expressed by mining activities since prehistoric times and the mining facilities of iron and copper mines. During the present study, six geotrails have been developed to link these cultural and ecological sites with the geological heritage. Along the routes, the geodiversity is explained, including its relationship with the surrounding biodiversity, and the historical and cultural aspects of the region. In the proposed geocultural routes (geotrails), the dialectic relationship between Humans and Nature is determined by historical conditions and by the record of the process that transforms space into a landscape. The geological-mining heritage of Serifos will attract people from all over the world with different kind of interests and will make it known to alternative tourists. The results of this paper are intended to constitute a valuable tool for enhancing and raising awareness of the geological heritage of the island of Serifos.
1. Introduction
Geoheritage comprises those elements of the Earth’s geodiversity (rocks, minerals, fossils, landforms, sediments, water and soils) that are considered to have significant scientific, educational, cultural or aesthetic value [1,2]. Traditionally, the valorization and the use of geological valuable areas as touristic resources has been linked to areas characterized by the beauty of the landscape, the spectacular rock formations or relevant features (mountains, glacier formations, rivers, canyons, caves, etc.) interesting for people loving geology or, at least, nature [1,2,3,4]. As stated by Carcavilla et al. [4] “Geological-geomorphological heritage is the collection of geotopes, deposits, forms, and processes that comprise the geological history of each region, and the concept of preserving geological-geomorphological heritage is a cultural concept”. Geoheritage aims to highlight the diversity of our planet to illustrate the importance of the biotic and abiotic factors, which document the historical evolution of the Earth [5]. The value of geological heritage is further underlined in a report from UNESCO [6], according to which geological heritage is characterized as the whole of the most interesting geological sites (geotopes, geoparks, and geological natural monuments) that deserve to be preserved for scientific, didactic, historical, aesthetic, and cultural reasons.
In addition to geoheritage, the industrial and mining heritage means all the sources of the industrial past that contribute to the knowledge of the history of the productive activities of a country or a population. Considering a monument or an object of industrial use as an information carrier is important and necessary since it incorporates all the influences of culture and the environment.
Geotourism is connecting the geological heritage with the natural environment and the cultural monuments [7,8,9,10]. Geoheritage is the driving force of the geotourism itineraries and cultural heritage is also added to increase the value of the visited regions. The management of industrial and geological heritage has demonstrated a number of special applications, such as geoparks, technology parks, eco-museums or theme parks, cultural centers, recreation sites and industrial museums in order to emerge as tourist destinations.
At present, there are 169 UNESCO Global Geoparks in 44 countries, six among them in Greece [11] (Figure 1). Geoparks are wider areas that contain significant sites of geological monuments and geotopes as well as sites of ecological, archaeological, historical or cultural interest and are tools for environmental education [6,12,13]. The concept of geopark was attributed to areas with special geological appearances, which can contribute to sustainable local development. Thus, the establishment of a geopark not only opens up new opportunities and creates enthusiasm for geoconservation, but the park also becomes a new tourist attraction.
Serifos island, located in the South Aegean Sea, represents a multiple-mineralized district, including porphyry, skarn, carbonate-replacement and vein-type ores [14,15,16,17,18]. The Serifos mineralization is related with the emplacement of I-type granodiorite, considered to be synchronous with Miocene extensional detachment faulting, and intruded gneisses, amphibolites, schists and marbles causing an extensive contact metamorphic aureole [14,15,19,20,21,22,23].
Serifos is well known to collectors for its spectacular skarn-related mineralization with gem quality green quartz crystals with actinolite inclusions (prase or prasem) [24,25,26,27,28,29,30]. The Serifos minerals are among the most impressive collectable objects exhibited in museums and private collections worldwide. These minerals at Serifos can be founds either on the surface, but also underground in mining sites and include species of exceptional beauty and scientific value [28].
The Serifos island is also known for its numerous iron mines opened in: (i) numerous magnetite-rich skarns; (ii) hematite/limonite ± barite ore bodies hosted in marbles that were exploited until 1963 [15,31]. Already Ducoux et al. [15] emphasized the role of low-angle detachment fault systems to ore mineralization at the various mining sites, and described the geological and mineralogical characteristics of Serifos. From an archeological point of view, Serifos island is famous for the exploitation of copper ore during ancient times [32,33].
The aim of this article is to summarize the current state of knowledge on the geology, petrology, mineralization, and the primary mineralogy and mining characteristics of Serifos island, and to expand on previous work by highlighting its unique geological, petrological, mineralogical, mining, and educational features. We suggest various geosites and industrial sites on the island, present new geotrails that could be used for geotourism, cultural, education and research activities, and evaluate all data considering Serifos as a best candidate for integration in a potential new Unesco Global Geopark.
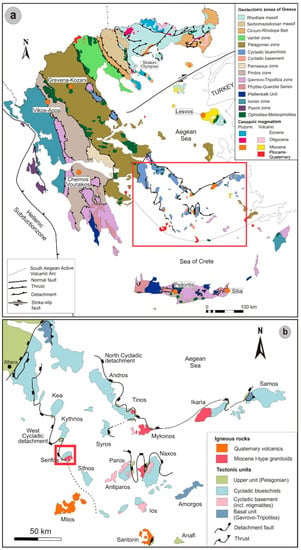
Figure 1.
Geological map of (a) Greece and (b) Attic-Cycladic Crystalline Belt, showing the major tectonic structures, as for example, the North Cycladic Detachment System (NCDS), the West Cycladic Detachment System (WCDS). The location of Lesvos, Psiloritis, Chelmos-Vouraikos, Vikos-Aoos, Sitia and Grevena-Kozani UNESCO Global Geoparks are shown, while the Serifos area is marked with a red square in Figure 1b and described in detail in Figure 2. Other mining sites with exemplary geological and mineralogical characteristics include Stratoni and Olympias at Chalkidiki, and Milos, Syros, and Naxos islands. Modified from Voudouris et al. [34] and references therein.
2. Geological Setting
Serifos island belongs to the Attic-Cycladic crystalline belt, which represents a polymetamorphic terrane of the Hellenides, in the back-arc region of the Hellenic subduction zone [35,36] (Figure 1). Since Oligocene, slab roll-back resulted in the southward migration of magmatic activity from north to south, in orogenic collapse, and the post-orogenic exhumation of the crust as metamorphic core complexes, associated with voluminous magmatism [36]. The Attic-Cycladic belt comprises four major units, the Cycladic basement, the so-called Basal unit, the Cycladic blueschist unit, and the Upper tectonic unit (e.g., [36,37,38], Figure 1b). The Cycladic basement includes Pre-Carboniferous schists and Carboniferous gneisses tectonically overlain by the Cycladic blueschist unit consisting of a volcano-sedimentary sequence of metasediments, marbles, calc-silicate schists, and meta-igneous rocks of Permo-Carboniferous to latest Cretaceous ages [35,36]. The Upper tectonic unit consists of various unmetamorphosed Upper Permian to Jurassic volcaniclastics, ophiolites, and carbonates, greenschist-facies rocks of Cretaceous to Tertiary age, and Late Cretaceous amphibolite-facies rocks and granitoids (e.g., [39,40]).
All tectonic units in the Cyclades are separated by crustal-scale detachment faults [21,35,41] (Figure 1b). Three stages of metamorphism during the Tertiary characterize the Cycladic area (e.g., [42,43]): blueschist-to-eclogite facies metamorphism during the Eocene (~52–40 Ma), followed by Eocene-Oligocene (ca. 40–30 Ma) upper greenschist-facies metamorphism, and then, by Oligo-Miocene (25–17 Ma) greenschist to upper amphibolite-facies metamorphism (locally with crustal anatexis at about 17 Ma). The Oligo-Miocene event was accompanied by exhumation of Attic-Cycladic metamorphic core complexes along several low-angle extensional detachment faults, such as the Northern and the Western Cycladic detachment systems, the latter also exposed at Serifos island [21,41] (Figure 1b). Intrusion of various granitoids throughout the Attic-Cycladic belt between 15 and 6 Ma was accommodated by movement of detachments [44,45].
Serifos Island is interpreted as a metamorphic core complex exhumed below the Western Cycladic detachment system [19,20]. The northern part of the island is dominated from base to top by (Figure 2): (1) metamorphic rocks of the Cycladic Continental Basements Unit (CCB) composed of gneiss and mylonitic schists, covered with calcite and dolomite mylonitic marbles; (2) the Cycladic Blueschist Unit (CBU) composed of amphibolites at the base overlain by greenschists with marble intercalations; (3) the Upper Cycladic Unit (UCU), composed of marbles, ankeritized cataclastic shales and schists exposed in the southwestern part, the Kyklopas area, and the northern part, at Platy Gialos [15,21]. These three units are separated by two detachments which both show top-to-the-SSW kinematics, which belong to the WCDS [15]: the Megalo Livadi detachment (MLD) separating the CCB from CBU, is well exposed at Megalo Livadi and Koundouros, and the Kavos Kiklopas detachment (KKD) separating the CBU from UCU which is exposed at Kavos Kiklopas and Platy Gialos [15].
On Serifos, blueschist facies metamorphism dated between 38 to 35 Ma based on 40Ar/39Ar in phengites [46], while all metamorphic rocks have been affected by retrograde LP/HT greenschist facies metamorphism during the Late Oligocene-Early Miocene [15,47,48]. During the Late Miocene the metamorphic pile is intruded by a I-type hornblende and biotite-bearing granodiorite with an age between 11.6 to 9.5 Ma, based on zircon U–Pb dating [22,44,47,48,49,50]. The pluton has two distinct facies [15,47,48]: an inner facies which is fine-grained equigranular unfoliated and a border coarse-grained facies with large biotite flakes and mafic enclaves. The pluton intrudes the MLD and the granodiorite roof is deformed by extensional shear zones in the south (Vagia Bay) and east (Agios Sostis) of Serifos [15].
The Serifos granodiorite was emplaced along the West Cycladic detachment fault in the CCB and the CBU units and caused contact metamorphism with the development of high-temperature Ca-Fe endo- and exoskarns and iron ores (Figure 2). Both the Megalo Livadi and Kavos Kyklopas detachment faults acted as pathways by the magmatic-hydrothermal fluids resulting to the development of medium-temperature Ca-Fe-Mg exoskarn zones in the southwestern part of the island (Figure 2) [15]. Skarns and iron ores demonstrate ductile and brittle structures as a consequence of the activity of the detachment fault [15]. Sulfide ore was formed during the retrograde stage and consists mainly of pyrite, chalcopyrite, galena, sphalerite and is extensively oxidized [14,15,16,18]. Calcite, barite, garnet, pyroxene, epidote, fluorite, talc, chlorite, adularia are the main gangue minerals [14,15,16,18].
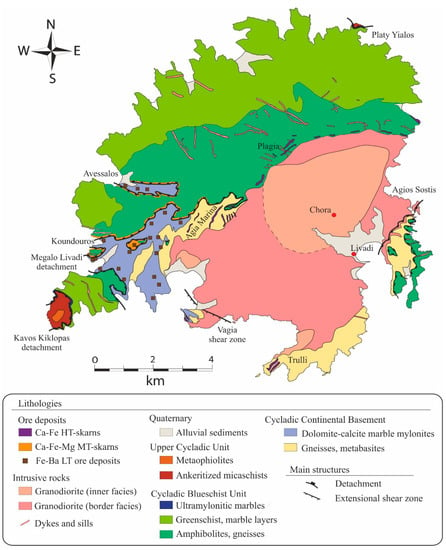
Figure 2.
Geological map (modified after Ducoux et al. [15]). HT/MT/LT for high, medium and low temperature, respectively.
3. Results
The data used in this study have derived from several field trips in Serifos island. During this fieldwork, all identified geosites were assessed and ranked. The geosites (and mining sites) considered in this paper are of great scientific interest, as they provide information about the conditions and timing of metamorphism, the subsequent exhumation paths of the metamorphic core complexes, and the magmatic and hydrothermal processes leading to magma emplacement, and subsequent ore deposition and exploitation, as well as of crystallization of rare minerals. The geosites (and industrial sites) have been classified based on their physical and scientific characteristics into various categories such as: (a) Geomorphosites, such as landforms resulting from differential erosion and weathering (tafoni), tectonics, drainage network, sea level changes and depositional processes of the geological formations and karstic geotopes, such as caves; (b) Geological, which are also distinguished in petrological or mineralogical geotopes; (c) Tectonics, including detachments, tectonic covers and contacts, faults and folds; (d) Hydrogeological, concerning the springs; (e) Mining heritage. Localities for the various geosites and mining sites at Serifos island are presented in Figure 3 and described in detail in the following paragraphs.
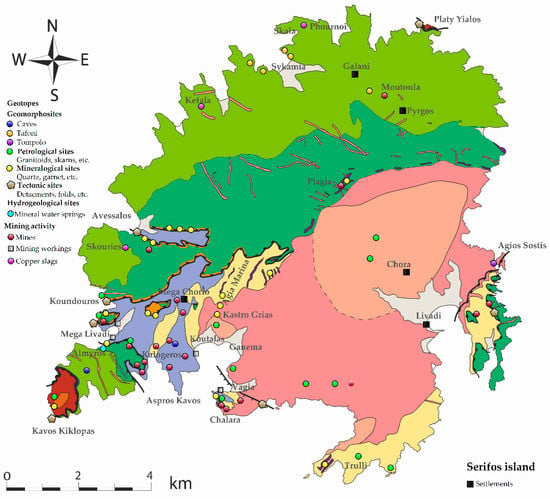
Figure 3.
Localities of various geosites and mining sites for the suggested Serifos geopark. Geological map modified after Ducoux et al. [15]).
3.1. Geological-Tectonic Geosites at Serifos
On Serifos Island, geological, tectonic, magmatic, and skarnization processes can be best demonstrated at hundreds of sites, thus making the island a natural geological observatory. Lithological and tectonic contacts can be observed around Megalo Livadi and Kavos Kiklopas, where both the Megalo Livadi and the Kavos Kiklopas detachments are exposed (Figure 4a–d). At these sites, marbles from the CCB, amphibolites from the CBU and schist and serpentinites from the UCU are well exposed. Mylonitic gneisses from the CCB can be observed in the Tsilipaki area and at Trulli (Figure 4e,f).

Figure 4.
Field photos showing typical lithologies and tectonic features at Serifos. (a) The Megalo Livadi detachment (MLD) separating marbles of the Cycladic Continental Basement (CCB, footwall) from amphibolite and gneisses of the Cycladic Blueschist Unit (CBU, hanging wall). Note the location of Fe-mines beneath and along the detachment fault; (b) the MLD separating marbles of the CCB from hedenbergitic skarn hosted in brecciated amphibolite of the CBU at Koundouros area; (c,d) the Kavos Kiklopas detachment (KKD) separating mylonitic marbles of the CBU (footwall) from metaophiolites and schists of the Upper Cycladic Unit (UCU); (e) panoramic view of the mylonitic orthogneiss of the CCB at Trulli area (view from W to E); (f) undeformed S-type (?) granitoid (leucogranite) at Trulli area intruding the mylonitic orthogneiss; (g) I-type granodiorite (border facies) at Vagia area; (h) dacitic dikes crosscutting Fe-oxides stained marbles of the CCB at Megalo Livadi area; (i,j) I-type granodiorite including high-T endoskarn garnet-pyroxene-magnetite bodies (dark areas) intruding white and grey marbles of the CCB at Chalara area; (k) medium-T hedenbergite skarn crosscutting epidotized amphibolite at Avessalos area; (l) modern galleries within oxidized ore hosted in schists and marbles of the CBU at Galani area (Moutoula, Pyrgos).
The I-type granodiorite pluton with its border facies is well exposed around Chora and Vagia (Figure 4g,i), and dacite dikes crosscut marbles of the CCB at Megalo Livadi (Figure 4h). Another igneous body, located in the southern part of the island, was mentioned by Voudouris et al. [51] as an undeformed leucogranite composed of K-feldspar, quartz, minor plagioclase and biotite and hosts molybdenite-pyrite mineralization (Figure 4f).
High-temperature endo- and exoskarns, medium-temperature distal exoskarns with prograde and retrograde assemblages including iron oxides and sulfides occur among others at Chalara (Figure 4i,j), Agia Marina, Megalo Livadi, Avessalos (Figure 4k) and Moutoulas (Figure 4l). Additional sites and photos with petrological and mineralogical characteristics are demonstrated in the following paragraphs.
3.2. Mineralogical and Petrological Geotopes at Serifos
Serifos is not only famous because of the mining activity in the past, it also shows unique mineralogical and petrological features: its very rare and worldwide known skarn minerals (e.g., garnets, quartz and its green variety called prase, ilvaite; Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9), attracted scientists and mineral collectors from all over the world. This has led to a dramatic reduction in the abundance of the mineral occurrences of the island, making their preservation necessary. The Serifos skarn is unique in the world containing the best varieties of prase (e.g., the green quartz variety) and ilvaite [24,25,26,27,28,29,30].

Figure 5.
Field and hand specimen photos showing typical petrological and mineralogical features of geotopes at Agia Marina (a to j), and Koutalas (k to o) areas. (a) Panoramic view of Agia Marina area from N to S with mylonitc orthogneiss outcrop; (b) mineralized geode within hedenbergitic skarn surrounding orthogneiss; (c) quartz crystals from the previous geode; (d,e) garnetite (andraditic skarn) hosted in orthogneiss at the contact to I-type granodiorite (view from N to S and E to W respectively); (f–h) garnetite with idiomorphic andradite and late quartz crystals; (i,j) geode within hedenbergite filled with quartz crystals, occasionally amethystine at their basis; (k) I-type granodiorite (inner facies) at the Kastro Grias area (view from S to N); (l) hydrothermal breccia composed of sericite-altered granodiorite fragments within a matrix of Fe-oxides and barite at the Kastro Grias locality; (m) Fe-Pb mines within marbles of the CCB; (n,o) barite crystals with galena and Fe-oxides at the Koutalas mines.

Figure 6.
Field and hand specimen photos showing typical petrological and mineralogical features of geotopes at Megalo Livadi area. (a–c) Panoramic view (from S to N) showing marbles of the CCB and hedenbergite skarn separated by the MLD fault. Note location of mine within marbles just beneath the detachment fault; (d,e) hand specimens with calcite rhombohedron coated by quartz associated with hedenbergite; (f) hand specimen with quartz crystals coated with Fe-oxides; (g) hand specimen with barite crystals covered with calcite; (h) panoramic view (from N to S) showing location of ilvaite in the hedenbergitic skarn on the road towards Megalo Livadi; (i) hedenbergite followed by ilvaite and then by quartz being part of breccia cement of the cockade megabreccia in the previous locality; (j) amethyst and prase as late open-space filling in geodes of the hedenbergite bearing megabreccia.
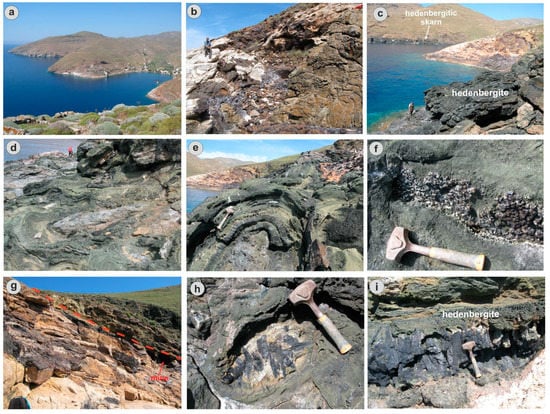

Figure 7.
Field photos showing typical petrological and mineralogical features of geotopes along (a) the Megalo Livadi-Koundouros geotrail; (b) magnetite replacing marbles of the CCB; (c) panoramic view (from SW to NE) of the Koundouros geosite, showing mineralized marbles of the CCB, and hedenbergitic skarn on both sides; (d,e) hedenbergitic skarn developed in several growth zones around fragments of amphibolite; (f) prase and hematite (iron roses) in cavities of hedenbergite; (g) the Megalo Livadi detachment (red dotted line) separating Fe-oxide mineralized marbles of the CCB from amphibolite-hosted hedenbergitic skarn of the CBU. Note the location of mine entrances just beneath the detachment fault; (h,i) ilvaite crystals developed in geodes within hedenbergitic skarn at the Koundouros geosite.

Figure 8.
Field and hand specimen photos showing typical petrological and mineralogical features of geotopes at north (a–f) and south (g–m) Avessalos area. (a) Panoramic view from W to E with location of dark green prase crystals and red-colored andradite within hedenbergite skarn. Marbles of the CCB can also be seen; (b) panoramic view from E to W with outcrops of mineralized geodes within hedenbergite skarn; (c,d) hedenbergite with geodes filled by red andradite; (e) hand specimen with red andradite on hedenbergite both covered by green quartz (prase) (photo courtesy of B. Ottens); (f) hand specimen of dark green variety of quartz with hematite roses at its base; (g) panoramic view from W to E with location of light green prase crystals and amethyst scepters within hedenbergite skarn at south Avessalos; (h–j) goesite with huge geodes within hedenberite filled with prase, at the previous locality; (k) hand specimen of prase crystals with orange-colored upper parts due to iron oxide inclusion; (l) hand specimen with amethyst scepter on prase; (m) hand specimen with intergrowth between prase and platy calcite.

Figure 9.
Field photos showing typical petrological, mineralogical and mining features of the geotope at Chalara area. (a) Panoramic view (from S to N) showing marbles of the CCB intruded by I-type granodiorite. Note location of garnet-pyroxene-magnetite endoskarn within the granodiorite; (b) granodiorite veins intruding marbles of the CCB; (c) garnet-bearing endoskarn of granodiorite sill intruding marbles of the CCB; (d) garnet-pyroxene exoskarn within layers of CCB marbles; (e) pyrite-magnetite mineralization associated with garnet-pyroxene endoskarn within granodiorite; (f) pyrite-magnetite mineralization within exoskarn.
Quartz is a very common mineral in the skarns of Serifos. Combinations of amethyst and prase forming scepter growths at Serifos are worldwide unique specimens. Garnet is a major constituent of skarn and represented by several varieties at Serifos. The Serifos andradites are famous due to their zonal growth with colors ranging from deep brown to orange. Ilvaite, up to 50 cm long in association with hedenbergite at Serifos, represent the best occurrence of this mineral worldwide. Calcite crystals up to 35 cm are intergrown with prase at Serifos. The carbonate-replacement deposits at Serifos contain large crystals of fluorite (up to 5 cm) and barite (up to 50 cm). Native bismuth in grains up to 5 cm occurs at Moutoulas, near Galani in the northern part of Serifos island. A list of all known collective minerals in Serifos, including primary, supergene as well as slag minerals are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
List of collective minerals from Serifos island (data from Ottens and Voudouris [28] and this study).
In addition, under the microscope, the minerals arsenopyrite, sphalerite, cobaltite, glaucodot, gersdorffite, marcasite, native Au and native Bi and sulfosalts of the bismuthinite-aikinite series were identified in southwestern Serifos mineralization by Korisidis et al. [18] and Bi- and Te-rich tetrahedrite-tennantite solid solutions, greenockite tellurides, tetradymite, hessite, and melonite are additionally mentioned by Fitros et al. [16]. Beyerite, bismutite, and bismite replaced native bismuth at Moutoulas, and together with covellite, cerussite, anglesite, chalcocite, goethite, are products of the supergene stage.
The SW part of Serifos island, including the Agia Marina-Koutalas, Megalo Livadi-Koundouro and Avessalos subareas, displays all the criteria necessary to be characterized as a mineralogical and petrological geotope [25,26,27,52,53].
The Agia Marina area is dominated by mylonitic gneisses of the CCB intruded by granodiorite veins and sills transformed to granatitic endoskarn bodies (Figure 5a–l; see also Ducoux et al. [15]). The geotope includes splendid occurrences of andraditic garnets (crystals up to 5 cm in size) formed during the prograde stage in association with quartz crystals crystallized during the retrograde skarn stage (Figure 5c–h). Quartz (often amethystine) is associated with hematite in quartz veins crosscutting garnetite or hedenbergitic skarn (Figure 5i,j). Towards the Kastro Grias locality, a brecciated granodiorite with iron oxide and barite in the breccia matrix is exposed (Figure 5k,l). At the adjacent Koutalas area, the Fe-Pb mines within marbles of the CCB contains large barite crystals (up to 30 cm), in associated with galena (Figure 5m–o).
The Megalo Livadi-Koundouro area is dominated by several Fe mines hosted within medium temperature hedenbergitic skarns and CCB marbles, following the trace of the Megalo Livadi detachment (Figure 6a–c). Magnetite was formed during the retrograde stage and followed by pyrite-arsenopyrite-chalcopyrite-Bi-Au mineralization [18]. Retrograde minerals also include calcite, quartz and barite (Figure 6d–g). At about 1 km NE of Megalo Livadi, a cockade megabreccia is composed of epidotized amphibolite fragments, rimmed by several bands of prograde hedenbergite in association with ilvaite, followed by quartz (also amethystine) and late calcite (Figure 6h–j). The Koundouros locality is characterized by hedenbergitic skarn including the best ilvaite crystals worldwide. Geodes within the skarn are filled by idiomorphic crystals of ilvaite, hematite (iron roses), quartz and calcite. The ilvaite crystals are associated with hedenbergite, forming radial aggregates reaching sizes of up to 50 cm (Figure 7).
The Avessalos area is the best site in the world in respect to the mineral green quartz (prase). Similarly to Megalo Livadi-Koundouro, at Avessalos, the mineralization occurs in geodes developed within a cockade megabreccia just below the Megalo Livadi detachment, formed around epidotized amphibolite, subsequently covered by hedenbergite and garnet during prograde skarnization and by quartz during the retrograde stage. The northern Avessalos geosite was discovered 20 years ago and represents the best locality of the mineral prase, the green variety of quartz [24]. The crystal forms, intergrowths and sizes (up to 40 cm) of green quartz specimens from this locality are unique. Similar crystals have never been observed elsewhere in the world. The very deep green-colored prase crystals are accompanied by iron roses. The northern Avessalos area is characterized by a granatitic and hedenbergitic exoskarn and by the development of huge geodes filled by prograde and retrograde skarn minerals (Figure 8a–f). Zoned andraditic garnets occur in this location, but the spectacular specimens of green quartz and amethyst are those which attracted the interest of mineral collectors in that geosite. In the double-colored crystals of prase-amethyst, the transition between these two crystals is abrupt within the same crystal, where prase occurs at the base and amethyst at the top of the crystal. The amethysts are transparent and of gemstone quality [30,54,55,56].
The second geosite is located at the southern part of the Avessalos area (Figure 8g,h). This geosite includes large geodes, containing unique quartz crystals, not only in respect to their quality but also for their crystal forms, which reflect very special growth conditions (Figure 8i–l).
Rare combinations of prase-amethyst scepter crystals contain phase alternations, including transitions from prase towards amethyst, and finally, to prase even within a single composite crystal [30,54,55,56]. Scepters include both normal and reverse forms. Calcite-prase intergrowths, abundant within the southern Avessalos geodes, were found for the first time in Serifos island: calcite crystals, either as rhombohedron, or in platy forms alternate with the prase suggesting contemporaneous deposition probably during boiling processes (Figure 8m). The Avessalos area underwent extensive mineral exploitation by local and foreign dealers, often destroying scientific information on the geological evolution and valuable elements of the geocultural heritage.
The Chalara locality best demonstrates outcrops of high-temperature endo- and exoskarn and of typical prograde and retrograde skarn sequences as described in the literature (e.g., [57,58]). Skarn formation is related to intrusion of granodiorite (Figure 9a–d), whereas at places granodiorite sills intruding marbles of the CCB are totally transformed to garnetites (Figure 9c,d). Pyroxene accompanies garnet during prograde skarn formation followed by magnetite and then by pyrite in the retrograde stage (Figure 9d–f).
3.3. Geomorphological–Hydrogeological Geosites at Serifos
The geotopes considered in this paper as geomorphosites include a variety of geomorphological landscapes. The lithology of Serifos consists of various lithological formations with different resistance in erosion and weathering, which in combination with the action of the hydrographic network and tectonics, has created the geomorphosites (tafoni) located in the NW part of Serifos’ coast (Figure 3 and Figure 10). The increased presence of halite indicates a salt-induced weathering (humidity and seawater spray) that plays an important role in their development.

Figure 10.
Field photos showing typical geomorphological features of geotopes at Serifos. (a) Tombolo at Agios Sostis; (b–d) landforms resulting from differential erosion and weathering (tafoni) at Skala, Moutoula and Sykamia, respectively; (e,f) the hot springs of Almyros area.
Additionally, karstic geotopes, such as caves are areas with unique characteristics and archaeological findings. The Koutalas cave is decorated with stalactites and columns, while the next chamber is covered almost along its entire length by a small lake.
In the coastal zone, the most characteristic geomorphosites are due to deposition processes with notable examples of coastal dunes, tombolo (Figure 10), as well as lagoon in the Tsilipaki area.
The hydrogeological geotopes include rivers, a number of springs (created by the discontinuities of the granite), fountains and wells and the presence of hot springs such as the Almyros springs near the old loading facility of Megalo Livadi (Figure 3 and Figure 10). During the mining period, the Mining Company had built stone baths for therapeutic purposes.
3.4. Mining Heritage of Serifos
Serifos was aptly named “the iron island” among the Cycladic islands, due to the flourishing of the iron industry. Iron ore mining activities have been witnessed in Serifos since antiquity. Minoans and Mycenaeans developed mining activities here, which continued during Roman times and Venetian domination from the 14th to 16th century. Prehistoric clay kilns have been identified in Avessalos in the Phournoi area and on the Kefala peninsula, a fact that testifies the extraction and processing of ore in the early stages [32,33]. Copper minerals are more frequent in the southern part of the island in association with the magnetite-hematite deposits [18]. Unique in Greece are the kilns that melted iron and copper in various places on the island [32,33]. By far the largest known copper slag heap in the Aegean area is that of Skouries at Avessalos with estimates of about 100,000 tons of slags present. Kefala and Phournoi with several hundred tons and a few tens of tons of slags, respectively, are minor compared to Skouries [32,33]. In addition to copper and iron ores, galena-rich ores are known in the northeastern part of Serifos at Moutoula (Figure 4l) and Pyrgos close to Galani. The Moutoula deposit was exploited in the 19th century for galena, while a possibly earlier undated gallery has also been noted [31].
Modern mining of the district started from 1861 and the iron ore mines finally ceased operations in 1965 [59,60]. From 1861, and systematically, from 1869, began the extraction of iron ores by the Hellenic Mining Company, which remained there until 1875. After 1880, the French company Serifos-Spiliazeza proceeded to intensive exploitation of the deposits of Serifos [59,60]. Andreas Sygros and Giovanni Baptista Serpieri were involved in its operation. In 1886, the German miner Emilios Groman took over the management of the company Serifos-Spiliazeza and essentially all the mines of Serifos [59,60,61,62,63]. The Gromans effectively controlled the island, while building extensive infrastructure for the extraction, transport and loading of ore on ships. From 1869 to 1940, a total export of 6.59 × 106 tons of iron ore (e.g., hematite, limonite and magnetite) from several mines mainly in the southwestern part of the island was made (Figure 11). When Grohmann undertook the operation of the mines, the headquarters of the company were transferred to Megalo Livadi, where a two-story neoclassical building with architectural elements of the “Ziller” style were created, ruins of which still stand at the end of the beach today (Figure 11d). Megalo Livadi was the main iron ore export harbor of Serifos, equipped with all the necessary sorting and shipment facilities (Figure 11a,b).

Figure 11.
Field and underground photos showing evidence of mining activity at Serifos. (a,b) Loading bridges at Megalo Livadi; (c) entrance of gallery at Megalo Livadi; (d) the headquarters of the iron ore mines at Megalo Livadi; (e) loading bridge at Koutalas; (f) mining wagon in a Koutalas mine.
The Ministry of Culture declared the following as historical monuments: the Headquarters of the mines, the loading bridge in Megalo Livadi, the ore loading bridge in Koutalas, the workers’ residencies, as well as any kind of equipment that remains to provoke memories of the flourishing of the island in another era (Figure 11). The activities of the mines in their three-thousand-year history have left behind monuments and residential complexes, which are an important part of the pre-industrial history of Greece [63]. They are an important testimony of the industrial activity that had been developed on the island and are of historical, architectural, and sociological interest.
Serifos is in itself an Open Air Museum of mining activity since its hinterland is engraved with mining galleries, its ports have been turned into loading stations of its minerals, and its social and economic history is timelessly tied to the mines [63]. All the facilities created from 1869 to 1964, including the loading ladder, the hydromechanical enrichment complex, the engine room with the equipment of the workers’ houses of the 19th century and a newer house complex from 1950 are preserved in the mining center of Koutalas. The ruins of a residential complex and a loading ladder are preserved along the coast in Chalara. West of Koutalas, in Aspros Kavos, dozens of galleries reach sea level. Dozens of galleries and transport routes are maintained throughout the area. In the bay of Avessalos, there are ruins of a loading ladder and mining facilities, and in the place Aerata, traces of ancient piles of slag and carved basins in the rocks for the cleaning of the ore can be found. The installations date from the 4th century BC. In the area of Mountaki, a large gallery was built, 1400 m long, which connected it with Kalogeros. The gallery served the transport of the ore from Kalogiros to the loading ladder in Mountaki.
4. Discussion
4.1. The Possibilities of Geotourism Development in Serifos—Geotourism Perspectives
Geoparks are wider areas that contain significant sites of geological monuments and geotopes as well as sites of ecological, archaeological, historical or cultural interest and are tools for environmental education [6,11,12,13,64]. Geoparks are of particular scientific interest since the purpose of their existence is to explore the relationships between geological, natural and cultural heritage. Serifos has been included in the Atlas of the Aegean geological monuments of the Ministry of the Aegean since 2002 with the Koutalas Cave, the Mineral occurrences and Iron Mines [65].
The inclusion of Serifos as a future UNESCO Global Geopark will highlight the concept of geotopes, the scientific–educational–touristic interest they raise, and the values they advocate (geo-conservation, geoprotection) contributing to the development of geotourism.
Green values of the cultural and natural heritage of the Serifos island, and therefore, the interest about it may be briefly highlighted as follows:
Geological and mineralogical value: Interesting geology with noticeable scientific and educational values. The area presents an impressive variety of minerals. In Serifos, they also found some rare and highly developed crystals for their kind of minerals, such as green quartz, amethyst, ilvaite, hedenbergite, garnet, calcite and barite.
Mining and metallurgical value: By far the largest known copper slag heap in the Aegean area is that of Avessalos on Serifos, with estimates of about 100,000 tons of slag present.
Environmental value: Interesting and important types of ecosystems and habitats as well as numerous and/or important flora and fauna species are also found. Areas of Serifos Island have joined the Natura 2000 network, such as GR4220009 South Serifos and GR4220029 coastal zone and the islands Serifopoula, Piperi and Vous.
Industrial value: The mines of Serifos are an example of an industrial monument and present a uniqueness, since the mineral areas of the island were mainly exploited in three different periods (prehistoric period, 14th century and from 1869 to 1963).
Historical value: Serifos is in itself an Open Air Museum of mining activity since its hinterland is engraved with mining galleries, its ports have been turned into loading stations of its minerals, and its social and economic history is timelessly tied to the mines.
Social value: With the influx of workers, Serifos became the center of the early Greek trade union movement contributing greatly to the shaping of the Greek trade union culture [61,62].
Archaeological and cultural value: In historical times, the presence of circular towers, such as Aspropyrgos in the bay of Koutalas, and other buildings may be associated with mining and metallurgical activity on the island. Prehistoric clay kilns have been identified at Moutoula, on the northern slope of Vigla hill, on Avessalos in the Phournoi area and on the Kefala peninsula, which testify to the extraction and processing of ore in the early stages.
Aesthetic value: The two-story neoclassical building, with architectural elements of the “Ziller” style in Megalo Livadi. Mineral species of extraordinary aesthetic and scientific value suitable for exhibition in museums and collections.
Nowadays, geotourism has proved to be a new and much promising trend for the whole district. The geotouristic development of mineralogical and petrological geotopes at Serifos ensures the preservation of the geological heritage of Serifos Island and also offers the opportunity for sustainable development.
The Serifos geotopes belong to the Greek mineralogical and geological heritage and can be considered as mineralogical treasures, some of them unique throughout world, as listed below (see also Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11):
- Serifos geomorphosites, such as lagoons, sand dunes, tompolo, landforms resulting from differential erosion and weathering (tafoni) (Figure 10).
- The Serifos granodiorite considered to be synchronous with Miocene extensional detachment faulting, intruded gneisses, schists and marbles causing an extensive contact metamorphic aureole.
- Tectonics geotopes, including Megalo Livadi and Kavos Kiklopas detachments.
- The Koutalas cave, between the bays of Megalo Livadi and Koutalas with stalactites and stalagmites, at Stavrakopoulos, discovered in 1893 during excavations. In one of the rooms formed by the cave, utensils and pottery were found, which prove that in ancient times, it was a place of worship. The first room of the cave is decorated with stalactites and columns, while the next chamber is covered almost along its entire length by a small lake. In the chamber that follows is an altar framed by various utensils, traces of fire and bones, covered with stalagmite material. A protection zone of 500 m has been defined around the cave (Government Gazette 29/B/26/1/63).
- The cave of the Cyclops. It is located near the monastery of Evangelistria and Kavos Kiklopas detachments.
- The hot springs at the bay of Almyros, near the sea (Figure 10). There, tabular translucent barite and rhombohedral calcite have been found in exceptional crystals.
- Agia Marina-Koutalas. The Agia Marina area is characterized by splendid occurrences of andraditic garnets in association with quartz crystals. The Koutalas area is characterized by the operations of mining activity, such as rail systems, ore transport, wagons and the workers’ residencies.
- Avessalos. The Avessalos area is the best site in the world in respect to the mineral green quartz (prase). The crystal forms, intergrowths and sizes (up to 40 cm) of green quartz specimens from this locality are spectacular.
- Chalara with iconic mining infrastructure and also best development of proximal high-T skarn.
- Miners pathway. Τhe hiking trail leading from “Giftika” area to Ano Chora was the road that the miners used to take in order to reach the western areas of the island and get to work. It was built in 1858, it is still well-preserved and it constitutes one of the most beautiful paths of the island.
- Prehistoric clay kilns have been identified on Avessalos in the Phournoi area and on the Kefala peninsula, which testify to the extraction and processing of ore in the early stages. The presence of circular towers, such as Aspropyrgos in the bay of Koutalas, and other buildings may be associated with mining and metallurgical activity on the island.
- Moutoula sulfide ore deposits (galena).
4.2. The Proposed Network of Geocultural Routes of Serifos (Geotrails of Serifos)
During the present study, six geotrails—georoutes of exceptional mineralogical and petrological interest—have been developed during field and laboratory work using GPS and geographical information systems (GIS) to link these geotopes with the cultural and ecological sites. Figure 12 and Table 2 demonstrate the proposed network of georoutes (total length: 30 km) and the geotouristic comparative advantage of the island. Along the routes, the geodiversity is interpreted, including its relationship with the surrounding historical and industrial activity of the region. These geotrails—georoutes include the Agia Marina-Koutalas, Megalo Livadi-Koundouros, Pyrgos-Galani and the Avessalos area—form part of the proposed Serifos geopark.
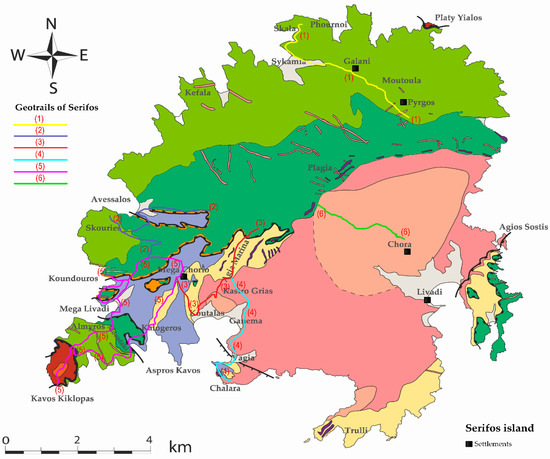
Figure 12.
The routes of geotrails suggested for the Serifos geopark. Geological map modified after Ducoux et al. [15].

Table 2.
Geotrails of Serifos.
The geotrails are involving stopping places which help us find out more about the variety of geology in the area and see a different side to the scenery. This includes site interpretation panels, training courses and other educational and interpretative activities that do not demand large financial and/or organizational investments, but could significantly benefit visitors’ activities in the park [66,67]. Good interpretation and educational activities could attract more visitors, especially non-experts or casual geotourists [67,68], who do not possess great knowledge of geology and other similar topics. Interpretation is a vital part of how people experience the places they visit, as it explains the natural and cultural heritage and brings them to life. Interpretative methods could be divided in two categories [68], depending on the location of their implementation:
- In situ interpretive form implemented at the geosites which provides direct and visual aspect (information signs, panels, geotrails, guided tours, etc.). These provide information about the attractions and the geoheritage and their significance [69]. The information signs will be placed in central points of the settlements and at the entry points of an important junction of paths, where they will inform the visitor of all the geotopes and the routes. Specifically, these signs will contain informative texts and photos and a thematic map that will inform the visitor about its location in the geopark and will lead him to the geotopes through a map that will be designed and will depict the existing roads and paths, the main place names, the settlements, and any useful information for the visitor [69,70].
- Ex situ interpretive form used in related facilities (visitor centers, museums, etc.), such as popular lectures, interactive and video presentations, museum artefacts, laboratories, etc. [70].
In this case study of the Serifos geopark, both of these methods could be used. Visitors should be able to see and hear many scientific facts not only about mining, but also about history and the time period in which they worked. Other educational activities could include different programs for visitors, such as the junior mineralogist program in which children take part in simulated excavations. The main idea behind these projects would be to enable learning through practice. The most effective tools for interpretation and visitor involvement could include guided tours to the mining sites, workshops (e.g., simulated mining, mineral identification, etc.), or multimedia performances. Besides interpretation and education, the park should also support the local people in producing and selling their local products and souvenirs [67,71].
Interpretation therefore needs to meet the requirements of a broad spectrum of audiences from the specific site-related geological and educational information for the dedicated geotourist and those actively seeking to learn about the geology of an area.
The suggested routes are the first geo-walking paths of the area, in which an Outdoor Geological Museum can operate, in the context of the proclamation of the wider part of the island as a geopark. Many of the entrances to the old network of underground mines remain open on the hillsides around. The terrain on the routes consists mainly of a variety of quiet roads and paths across fields. These paths were further examined in order to highlight the geological sites and to characterize both the individual sites as geotopes and the wider area as a geopark. The georoutes, where possible, followed the existing network of the island. The old Hiking Network of Serifos Island has a logo that connects the history and nature of the island, as in ancient times, the frog was the symbol of the island. In addition, the title “Iron and stone paths” reflects the geology of the island, but also its mythology, during which Perseus with the head of Medusa petrified the whole island [63].
4.3. Serifos: A Potential New Unesco Global Geopark
There are six UNESCO Global Geoparks in Greece: Lesvos island, Psiloritis and Sitia in Crete, Chelmos-Vouraikos at Peloponnese, and Vikos-Aoos in Epirus and Grevena-Kozani (e.g., [11,72,73,74,75]) (Figure 1). These geoparks combine extraordinary geological, paleontological, and natural features. The proposed Serifos geopark is an area enclosing features of special geological significance, rarity or beauty. However, the potential Serifos geopark combines spectacular mineralogical, petrological, geological, mining, cultural characteristics and can be described as a polythematic geopark.
Besides the above mentioned six geoparks, similar geological projects in Greece include: the Syros island, Cyclades complex, as a prime locality for the study of processes active in deep levels of orogeny and is world famous for its exceptionally well-preserved glaucophane schist-to eclogite-facies lithologies [76]; the Meteora and Mount Olympos in central Greece with legendary geological history and mythology [77,78]; the Kefalonia, Ithaki Lefkas and Meganisi islands, in the active geotectonic region of the Ionian Sea, Western Greece and in the convergent zone between the African and Eurasian plates [79]; the Naxos island in the Cyclades, characterized by intense mining and quarrying activities, since the antiquity and by distinctive geological and mineral wealth [80].
The suggested Serifos geopark is also comparable to the Lavrion geopark, which in addition to mineralogical, petrological, geological, mining and cultural features also displays worldwide unique archaeological characteristics [34].
Worldwide, a research on mineralogical, petrological and mining heritage, comparable to that of Serifos has been demonstrated: in post-mining areas of central Mexico [81], Poland (Gold Mine in Zloty Stok), Spain (La Tortilla Mine in Linares), UK (King Edward Mine, in Cornwall) [82], Italy (the Traversella Mining Site at Piemonte, Italy) [83]; in petrological and mineralogical geosites such as granite landforms of Seoraksan Mountains, Republic of Korea [84]; the Monviso Massif and the Cottian Alps in Piemonte, Italy, with some of the best preserved ophiolites in the Alps and associated Cu–Fe mineralizations, the first primary source of jade in the Alps, the world-famous minerals such as coesite and giant pyrope, as well as type localities for new minerals [85]; the eastern limb of the Bushveld Igneous Complex, South Africa, with layered ultramafic-mafic rocks, metamorphic aureole outcrops, orebodies of chromitites, PGE reefs, etc. [86].
The Serifos geopark is designated with a focus on three main components: the protection and the conservation of Serifos’ heritage, the tourism-related infrastructural development and the socio-economically sustainable development of the local community using a sustainable territorial development strategy. Heritage sites within a geopark can be related not only to geology but also to archaeology, ecology, history and culture. All these sites in the Serifos geopark constitute thematic parks and will be linked in a network with routes, trails and sections that should be protected and managed. The mineralogical “treasures” of Serifos Island, featuring in a worldwide unique hedenbergite-ilvaite-garnet-prase-bearing skarn, and the unique geological structure of the island, due to specific tectonic processes, makes it a special site with great archaeological, as well as aesthetical, cultural and scientific value. Some specific actions should be developed such as a management plan of the Serifos geopark and a clear presentation of the geotopes of Serifos and their quantitative assessment. The aim of a quantitative assessment is to decrease the subjectivity associated with any evaluation procedure. The result of this numerical assessment is a sorted list of sites, which is a powerful tool for the establishment of management priorities. Inventorying and quantitative assessment, statutory protection, conservation, promotion and interpretation and monitoring of sites are some specific methods used to promote geoconservation.
The suggested six geotrails–geocultural routes are of exceptional mineralogical and petrological interest, and have been developed in order to discover the natural, geological and cultural treasure of the island. Along the routes, the geodiversity is explained, including its relationship with the surrounding biodiversity, and the historical and cultural aspects of the region. The southwestern part of Serifos forms a wide network of habitats for the flora and the rich fauna of the region because of the combination of its geomorphological and hydrogeological features. Serifos and particularly its southwestern part is also included in the European network of protected areas NATURA 2000, which is the main national means for the purpose of Directive 92/43/EEC of the European Council “for the conservation of natural habitats and wild fauna and flora” which are significant at the European level [87]. The region, as the whole of the Cyclades islands, is a passage of sea turtles and migratory birds and there are seasonal hunting restrictions. Almost half of the island is covered by typical low Aegean phrygana. There are also sand dunes with characteristic vegetation. The hydrographic net of the site includes rivers with N–S direction and a total length of about 14 km. It also includes a number of springs, fountains and wells.
The combination of its rich morphological relief and the ancient and historical monuments—in the western part of the region, there are abandoned mines, which have been characterized as historical monuments—gives great value to the region, which requires special protection.
The suggested geotrails can be important management and interpretative tools for geotourism development. The selection of the content is not limited to natural and historical information but incorporates the geoenvironment with the cultural character of the landscape, as the design goal of this touristic product is the perception of timelessness of space. While designing a matrix of geotrails–geocultural routes the old path networks are revealed, activating at the same time the local community. In these routes, tourists through experiential activities turn into travelers, exploring the features of a place, creating experiences and, finally, emotional binding.
A necessary condition for the integration of the proposed network of georoutes with the aim of highlighting the geodiversity and the mining history of Serifos is the perfect organization of the marking and its annual maintenance by the municipality.
The municipality of Serifos will install new signs (information signs and direction signs). In addition, it will be instrumental the procurement and placement of interpretive panels for geoheritage and display of the relief of the island using 3D printing technique. Signage is an integral part of the construction and operation of a Hiking Trail Network. In order to hike the geotrails, a walking map is recommended that contains detailed maps and short descriptions of the waypoints on the route.
The inclusion of Serifos in the network of Global Unesco Geoparks is a basic goal of the municipality. In Megalo Livadi, there is a small museum of minerals and rocks of Serifos, while some samples of minerals are also exhibited among the other exhibits of the folklore museum of Chora. As a place for the creation of an open-air museum, Megalo Livadi is proposed, in which all the facilities that were built between 1869–1875 by the Mining Company are preserved. The facilities of the neoclassical building (command post), the workers’ residences, towers, explosives depot, rails, wagons, galleries, stairs will be restored and will be highlighted with modern museum teaching materials and will be the central core and the open part of the Museum [63]. Megalo Livadi is located in the center of an extensive area of special historical interest.
The works that will be required for the creation of the museum include restorations of buildings, landscaping, fixing and maintenance of metal structures (e.g., loading ladder, tipping pylons, etc.), reconstruction of railway networks, fixing and highlighting selected galleries, decoration uniting the basic cores of the museum, etc.
Nowadays, the historic building of the neoclassical building is being reconstructed and upgraded to a cultural/conference center and a museum of mineral wealth and mining history. A series of exhibits will be exhibited in the historic building, including collections of rocks and minerals, information and educational materials will be displayed and educational seminars and workshops will be organized. Exhibition sections will be developed at the headquarters regarding the geological and mining image of Serifos, its mineral wealth, the history of quarrying operations from antiquity to modern times, the productive process of exploitation of mineral wealth, social and economic context, as well as the workforce. With its operation, Serifos will be promoted and will be promoted worldwide through conferences, seminars and other special events, in order to attract visitors with special interests but also to inform the local community about its history and the identity of its place.
The touristic infrastructure of Serifos is well developed. It includes, besides the famous beaches, a lot of hotels and private accommodations, traditional restaurants, and water sport possibilities, as well as other leisure and sportive activities (diving).
Serifos island is a unique site for education and research in several disciplines, such as geological investigation, prospecting, mineralogy, geochemistry, mining, metallurgical processes, economic, political, and social sciences. Serifos provides an almost inexhaustible field of activity for scientists and the public, and also offers ideal opportunities for educational and geotourism. We conclude that Serifos Island meets all the scientific, educational, cultural, and touristic criteria that makes the area highly suitable for its development as a UNESCO Global Geopark.
5. Conclusions
Serifos is a geographical unity which represents the combined work of nature and humans depicting the evolution of the local society under the influence of the physical constraints of this island area. It is characterized by a worldwide unique geological, petrological and mineralogical diversity, combined with a very rich cultural heritage, biodiversity and folk tradition. The Serifos geotopes belong to the world mineralogical and geological heritage and should be protected from further commercial exploitation. The geotouristic development of the geological, mineralogical and petrological geotopes at Serifos, combined with the foundation of a mineralogy-petrology museum, ensures the preservation of the geological heritage of Serifos Island and also offers the opportunity for sustainable development.
The present paper focuses on exemplary mineralogical, geological and mining features of Serifos, and presents six geotrails which have been developed to link the geological heritage with cultural and ecological sites. The suggested Serifos geopark focuses on the promotion of the geological and mining heritage of the island, with the aim of integrating Serifos in the network of Global Unesco Geoparks, in the near future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.V. and P.V.; methodology, N.V.; investigation, N.V.; resources, N.V. and P.V.; writing—original draft preparation, N.V.; writing—review and editing, N.V. and P.V.; supervision, P.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully thank Maxime Ducoux for kindly providing his geological Serifos map. We also gratefully thank the journal editor and the two reviewers for their thorough consideration of this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Crofts, R. Putting Geoheritage Conservation on All Agendas. Geoheritage 2018, 10, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crofts, R.; Tormey, D.; Gordon, J. Introducing New Guidelines on Geoheritage Conservation in Protected and Conserved Areas. Geoheritage 2021, 13, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santangelo, N.; Valente, E. Geoheritage and Geotourism. Resources 2020, 9, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcavilla, L.; Durán Valsero, J.; García-Cortés, Á.; López-Martínez, J. Geological Heritage and Geoconservation in Spain: Past, Present, and Future. Geoheritage 2009, 1, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.E. Geoheritage, Geotourism and the Cultural Landscape: Enhancing the Visitor Experience and Promoting Geoconservation. Geosciences 2018, 8, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO Geoparks Program—A New Initiative to Promote a Global Network of Geoparks Safeguarding and Developing Selected Areas Having Significant Geological Features; Document 156 EX/11 Rev., Executive Board, 156th session; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1999; p. 4.
- Farsani, N.D.; Coelho, C.; Costa, C. Geotourism and Geoparks as novel strategies for socio-economic development in rural areas. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2011, 13, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, R.; Newsome, D. (Eds.) Geotourism; Elsevier/Heineman: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Dowling, R.K. Global geotourism—An emerging form of sustainable tourism. Czech J. Tour. 2013, 2, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hose, T.A. 3G’s for Modern. Geotourism. Geoheritage 2012, 4, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Available online: https://en.unesco.org/global-geoparks (accessed on 22 June 2021).
- UNESCO. Global Geoparks Network; Division of Ecological and Earth Sciences: Paris, France, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mc Keever, P.; Zouros, N. Geoparks: Celebrating earth heritage, sustaining local communities. Episodes 2005, 28, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salemink, J. Skarn and Ore Formation at Serifos, Greece as a Consequence of Granodiorite Intrusion. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Utrecht, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Ducoux, M.; Branquet, Y.; Jolivet, L.; Arbaret, L.; Grasemann, B.; Rabillard, A.; Gumiaux, C.; Drufin, S. Synkinematic skarns and fluid drainage along detachments: The West Cycladic Detachment System on Serifos Island (Cyclades, Greece) and its related mineralization. Tectonophysics 2017, 695, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitros, M.; Tombros, S.; Williams-Jones, A.E.; Tsikouras, B.; Koutsopoulou, E.; Hatzipanagiotou, K. Physicochemical controls on bismuth mineralization: An example from Moutoulas, Serifos island, Cyclades, Greece. Amer. Miner. 2017, 102, 1622–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voudouris, P.; Mavrogonatos, C.; Spry, P.G.; Baker, T.; Melfos, V.; Klemd, R.; Haase, K.; Repstock, A.; Djiba, A.; Bismayer, U.; et al. Porphyry and epithermal deposits in Greece: An overview, new discoveries, and mineralogical constraints on their genesis. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 107, 654–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korosidis, J.; Voudouris, P.; Kouzmanov, K. Distal Fe skarn deposits of Serifos Island: New mineralogical and geochemical constrains on the retrograde assemblage and associated ore mineralization. In The Critical Role of Minerals in the Carbon-Neutral Future, Proceedings of the 16th SGA Biennial Meeting, Rotorua, New Zealand, 28–31 March 2022; Society Geology Applied: Rotorua, New Zealand, 2022; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Grasemann, B.; Zamolyi, A.; Petrakakis, K.; Rambousek, C.; Igelseder, C. Ein neuer metamorphic core complex in den West- Kykladen (Serifos, Greichenland). Erlanger Geol. Abh. 2002, 3, 36–37. [Google Scholar]
- Grasemann, B.; Petrakakis, K. Evolution of the Serifos metamorphic core complex. J. Virtual Explor. 2007, 27, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasemann, B.; Schneider, D.A.; Stockli, D.F.; Iglseder, C. Miocene bivergent crustal extension in the Aegean: Evidence from the western Cyclades (Greece). Lithosphere 2012, 4, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglseder, C.; Grasemann, B.; Schneider, D.A.; Petrakakis, K.; Miller, C.; Klötzli, U.S.; Thöni, M.; Zámolyi, A.; Rambousek, C. I and S-type plutonism on Serifos (W-Cyclades, Greece). Tectonophysics 2009, 473, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabillard, A.; Arbaret, L.; Jolivet, L.; Le Breton, N.; Gumiaux, C.; Augier, R.; Grasemann, B. Interactions between plutonism and detachments during metamorphic core complex formation, Serifos Island (Cyclades, Greece). Tectonics 2015, 34, 1080–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, G.; Albandakis, N. Minerals from the Serifos skarn, Greece. Miner. Rec. 1991, 22, 303–308. [Google Scholar]
- Voudouris, P.; Katerinopoulos, A.; Christofalou, F.; Kassimi, G. Serifos island, Aegean Sea/Greece: A worldwide unique mineralogical and petrological geotope. ProGeo. News 2007, 1, 7–8. [Google Scholar]
- Voudouris, P.; Voulgaris, N.; Christophalou, F.; Kassimi, P. Development of Mineralogical-Petrological Geotopes on the Serifos Island, using Geographic Information Systems (GIS). In Proceedings of the 11th Conference of the Greek Geological Society, Special Session of the Geological and Geomorphological Heritage Conservation Committee, Athens, Greece, 24–26 May 2007; pp. 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Voudouris, P.; Katerinopoulos, A.; Magganas, A. Mineralogical geotopes in Greece: Preservation and promotion of museum specimens of minerals and gemstones. Sofia Initiative “Mineral diversity preservation”. In Proceedings of the IX International Symposium Mineral Diversity Research and Reservation, Sofia, Bulgaria, 16–18 October 2017; pp. 149–159. [Google Scholar]
- Ottens, B.; Voudouris, P. Griechenland: Mineralien-Fundorte-Lagerstätten; Christian Weise Verlag: Munich, Germany, 2018; p. 480. ISBN 978-3-921656-86-0. [Google Scholar]
- Klemme, S.; Berndt, J.; Mavrogonatos, C.; Flemetakis, S.; Baziotis, I.; Voudouris, P.; Xydous, S. On the Color and Genesis of Prase (Green Quartz) and Amethyst from the Island of Serifos, Cyclades, Greece. Minerals 2018, 8, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voudouris, P.; Mavrogonatos, C.; Graham, I.; Giuliani, G.; Tarantola, A.; Melfos, V.; Karampelas, S.; Katerinopoulos, A.; Magganas, A. Gemstones of Greece: Geology and Crystallizing Environments. Minerals 2019, 9, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinos, G. Geology and metallogeny of Serifos island. Geol. Geophys. Res. 1951, 1, 95–127. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Georgakopoulou, M.; Bassiakos, Y.; Philaniotou, O. Seriphos surfaces: A study of copper slag heaps and copper sources in the context of Early Bronze Age Aegean metal production. Archaeometry 2011, 53, 123–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philaniotou, O.; Bassiakos, Y.; Georgakopoulou, M. Early Bronze Age copper production on Seriphos (Cyclades, Greece). In Metallurgy: Understanding How, Learning Why. Studies in Honour of James D. Muhly; Betancourt, P.P., Ferrence, S.C., Eds.; Prehistory Monographs 29; INSTAP Academic Press: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011; pp. 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Voudouris, P.; Melfos, M.; Mavrogonatos, C.; Photiades, A.; Moraiti, E.; Rieck, B.; Kolitsch, U.; Tarantola, A.; Scheffer, C.; Morin, D.; et al. The Lavrion mines: A unique site of geological and mineralogical heritage. Minerals 2021, 11, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ring, U.; Glodny, J.; Will, T.; Thomson, S. The Hellenic subduction system: High-pressure metamorphism, exhumation, normal faulting, and large-scale extension. Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2010, 38, 45–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolivet, L.; Faccenna, C.; Huet, B.; Labrousse, L.; Le Pourhiet, L.; Lacombe, O.; Lecomte, E.; Burov, E.; Denèle, Y.; Brun, J.-P.; et al. Aegean tectonics: Strain localization, slab tearing and trench retreat. Tectonophysics 2013, 597, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wind, S.C.; Schneider, D.A.; Hannington, M.D.; McFarlane, C.R.M. Regional similarities in lead isotopes and trace elements in galena of the Cyclades Mineral District, Greece with implications for the underlying basement. Lithos 2020, 366, 105559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seman, S.; Stockli, D.F.; Soukis, K. The provenance and internal structure of the Cycladic Blueschist Unit revealed by detrital zircon geochronology, Western Cyclades, Greece. Tectonics 2017, 36, 1407–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinecke, T.; Altherr, R.; Hartung, B.; Hatzipanagiotou, K.; Kreuzer, H.; Harre, W.; Klein, H.; Keller, J.; Geenen, E.; Boeger, H. Remnants of a Late Cretaceous high temperature belt on the island of Anafi (Cyclades, Greece). N. Jahrbuch Miner. Abhandl. 1982, 145, 157–182. [Google Scholar]
- Stouraiti, C.; Pantziris, I.; Vasilatos, C.; Kanellopoulos, C.; Mitropoulos, P.; Pomonis, P.; Moritz, R.; Chiaradia, M. Ophiolitic Remnants from the Upper and Intermediate Structural Unit of the Attic-Cycladic Crystalline Belt (Aegean, Greece): Fingerprinting Geochemical Affinities of Magmatic Precursors. Geosciences 2017, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolivet, L.; Brun, J.P. Cenozoic geodynamic evolution of the Aegean region. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2010, 99, 109–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, M.J.; Schneider, D.A.; Grasemann, B.; Soukis, K.; Lozios, S.; Hollinetz, M.S. Lateral termination of a Cycladic-style detachment system (Hymittos, Greece). Tectonics 2020, 39, e2020TC006128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruckenberg, S.C.; Vanderhaeghe, O.; Ferré, E.C.; Teyssier, C.; Whitney, D.L. Flow of partially molten crust and the internal dynamics of a migmatite dome, Naxos, Greece. Tectonics 2011, 30, TC3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altherr, R.; Kreuzer, H.; Wendt, I.; Lenz, H.; Wagner, G.A.; Keller, J.; Harre, W.; Höndorf, A. A late Oligocene/early Miocene high temperature belt in the Attic-Cycladic crystalline complex (SE Pelagonian, Greece). Geol. Jahrb. 1982, 23, 97–164. [Google Scholar]
- Menant, A.; Jolivet, L.; Vrielynck, B. Kinematic reconstructions and magmatic evolution illuminating crustal and mantle dynamics of the eastern Mediterranean region since the late Cretaceous. Tectonophysics 2016, 675, 103–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, D.A.; Senkowski, C.; Vogel, H.; Grasemann, B.; Iglseder, C.; Schmitt, A.K. Eocene tectonometamorphism on Serifos (western Cyclades) deduced from zircon depth-profiling geochronology and mica thermochronology. Lithos 2011, 125, 151–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salemink, J. On the Geology and Petrology of Serifos island (Cyclades, Greece). Ann. Geol. Pays Hell. 1980, 30, 342–365. [Google Scholar]
- Stouraiti, C. Geochemistry and Petrogenesis of the Serifos Granite, in Relation to Other Aegean Granitoids, Greece. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Leicester, Leicester, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Stouraiti, C.; Mitropoulos, P.; Tarney, J.; Barreiro, B.; McGrath, A.M.; Baltatzis, E. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of late Miocene granitoids, Cyclades, southern Aegean: Nature of source components. Lithos 2010, 114, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stouraiti, C.; Baziotis, I.; Asimow, P.D.; Downes, H. Geochemistry of the Serifos calc-alkaline granodiorite pluton, Greece: Constraining the crust and mantle contributions to I-type granitoids. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2018, 107, 1657–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voudouris, P.; Melfos, V.; Moritz, R.; Spry, P.G.; Ortelli, M.; Kartal, T. Molybdenite Occurrences in Greece: Mineralogy, Geochemistry and Rhenium Content. In Scientific Annals of the School of Geology AUTH, Proceedings of the XIX Congress of the Carpathian-Balkan Geological Association, Thessaloniki, Greece, 23–26 September 2010; Charis Ltd.: Thessaloniki, Greece, 2010; pp. 369–378. [Google Scholar]
- Vlachopoulos, N.; Voudouris, P. Geological and mining history of Serifos island, Greece: Current state and perspectives for protection of mineralogical and petrological geotopes. In Proceedings of the 15th Congress of the Geological Society of Greece, Athens, Greece, 22–24 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Voudouris, P.; Photiades, A.; Tarantola, A.; Scheffer, C.; Vanderhaeghe, O.; Morin, D.; Vlachopoulos, N. The Lavrion and Serifos mining centers: Two worldwide unique mineralogical and geological monuments and perspectives for their protection. In The Value Framework for the Protection and Management of Sites and Monuments Extracted during the Antiquity: Current Uses and Future Synergies, Proceedings of the Greek ICOMOS Conference, Athens-Lavrion, Greece, 29–30 November 2019; ResearchGate: Berlin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voudouris, P.; Katerinopoulos, A. New occurences of mineral megacrysts in tertiary magmatic-hydrothermal and epithermal environments in Greece. Doc. Nat. 2004, 151, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Maneta, V.; Voudouris, P. Quartz megacrysts in Greece: Mineralogy and environment of formation. Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2010, 43, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voudouris, P.; Maneta, V. Quartz in Greece; CreateSpace Publ.: Seattle, WA, USA; Amazon.com, Inc.: Seattle, WA, USA, 2017. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Meinert, L.D. Variability of skarn deposits—Guides to exploration. In Revolution in the Earth Sciences; Boardman, S.J., Ed.; Kendall-Hunt Publishing: Dubuque, IA, USA, 1983; pp. 301–316. [Google Scholar]
- Meinert, L.; Dipple, G.; Nicolescu, S. World skarn deposits. In Economic Geology 100th Anniversary Volume; Hedenquist, J.W., Thompson, J.F.H., Goldfarb, R.J., Richards, J.P., Eds.; Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CO, USA, 2005; pp. 299–336. [Google Scholar]
- Mavrokordatou, D.; Balodimou, M.; Belavilas, N.; Papastefanaki, L.; Frangiskos, A.Z. Historical Mines in the Aegean, Laboratory of Urban Environment, School of Architecture, NTUA, Athens 2000–2006. Available online: https://www.elke.ntua.gr/en/research_project/historical-aegean-mines/ (accessed on 22 June 2021). (In Greek).
- Belavilas, N.; Papastefanaki, L. Historical Mines in the Aegean, 1st ed.; Melissa: Athens, Greece, 2009; Available online: http://courses.arch.ntua.gr/111992.html (accessed on 22 June 2021). (In Greek)
- Skonis, N. The Bloody Strike of the Miners of Serifos–21 August 1916, 1st ed.; Federation of Miners of Greece: Athens, Greece, 1990. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Speras, K. The Strike of Serifos, 3rd ed.; Bibliopelagos: Athens, Greece, 2001. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Katsilieri, M.; Louvi, A.; Mavrokordatou, D.; Belavilas, N.; Economou, M.; Trova, V.; Frangiskos, A.Z. Open Air Museum of Mining Activities and Mineral Wealth of Serifos, 1st ed.; Piraeus Group Cultural Foundation: Athens, Greece, 1998. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Zouros, N. The European Geoparks Network. Episodes 2004, 27, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velitzelos, E.; Mountrakis, D.; Zouros, N.; Soulakellis, N. Atlas of the Geological Monuments of the Aegean; Ministry of the Aegean: Athens, Greece, 2003; p. 352. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, B.C.; Wallace, A. Interpretive Panels for Geoheritage Sites: Guidelines for Design and Evaluation. Geoheritage 2019, 11, 1315–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hose, T.A. European ‘geotourism’—Geological interpretation and geoconservation promotion for tourists. In Geological Heritage: Its Conservation and Management; Barretino, D., Wimbledon, W.P., Gallego, E., Eds.; Instituto Tecnologico Geominero de Espana: Madrid, Spain, 2000; pp. 127–146. [Google Scholar]
- Hose, T.A. Geotourism and interpretation. In Geotourism; Dowling, R.K., Newsome, D., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 221–241. [Google Scholar]
- Hose, T.A.; Vasiljevic, D.A. Defining the nature and purpose of modern geotourism with particular reference to the United Kingdom and south-east Europe. Geoheritage 2012, 4, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomić, N.; Marković, S.B.; Korać, M.; Mrđić, N.; Hose, T.A.; Vasiljević, D.A.; Jovičić, M.; Gavrilov, M.B. Exposing mammoths: From loess research discovery to public palaeontological park. Quat. Int. 2015, 372, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antić, A.; Tomić, N.; Đorđević, T.; Marković, S.B. Promoting palaeontological heritage of mammoths in Serbia through a cross-country thematic route. Geoheritage 2021, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouros, N. Lesvos petrified forest geopark, Greece: Geoconservation, geotourism, and local development. In The George Wright Forum; George Wright Society: Hancock, MI, USA, 2010; pp. 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Fassoulas, C.; Zouros, N. Evaluating the influence of Greek geoparks to the local communities. Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2010, 43, 896–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassoulas, C.; Staridas, S.; Perakis, V.; Mavrokosta, C. Revealing the geoheritage of Eastern Crete, through the development of Sitia Geopark, Crete, Greece. Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2013, 47, 1004–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafeiropoulos, G.; Drinia, H.; Antonarakou, A.; Zouros, N. From Geoheritage to Geoeducation, Geoethics and Geotourism: A Critical Evaluation of the Greek Region. Geosciences 2021, 11, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drinia, H.; Tsipra, T.; Panagiaris, G.; Patsoules, M.; Papantoniou, C.; Magganas, A. Geological Heritage of Syros Island, Cyclades Complex, Greece: An Assessment and Geotourism Perspectives. Geosciences 2021, 11, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassios, A.E.; Ghikas, D.; Dilek, Y.; Vamvaka, A.; Batsi, A.; Koutsovitis, P. Meteora: A Billion Years of Geological History in Greece to Create a World Heritage Site. Geoheritage 2020, 12, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassios, A.E.; Krikeli, A.; Dilek, Y.; Ghikas, C.; Batsi, A.; Koutsovitis, P.; Hua, J. The Geoheritage of Mount Olympus: Ancient Mythology and Modern Geology. Geoheritage 2022, 14, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyrou, E.; Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Tsourou, T.; Vassilakis, E.; Asimakopoulos, C.; Konsolaki, A.; Markakis, D.; Marketou-Galari, D.; Skentos, A. Assessment of Geological Heritage Sites and Their Significance for Geotouristic Exploitation: The Case of Lefkas, Meganisi, Kefalonia and Ithaki Islands, Ionian Sea, Greece. Geosciences 2022, 12, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periferakis, A. The emery of Naxos: A multidisciplinary study of the effects of mining at a local and national context. J. NX-Multidiscip. Peer Rev. J. 2021, 7, 93–115. [Google Scholar]
- García-Sánchez, L.; Canet, C.; Cruz-Pérez, M.Á.; Morelos-Rodríguez, L.; Salgado-Martínez, E.; Corona-Chávez, P. A comparison between local sustainable development strategies based on the geoheritage of two post-mining areas of Central Mexico. Int. J. Geoheritage Parks 2021, 9, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaźmierczak, U.; Strzałkowski, P.; Lorenc, M.W.; Szumska, E.; Sánchez, A.A.P.; Baker, K.A. Post-mining Remnants and Revitalization. Geoheritage 2019, 11, 2025–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.; Dino, G.A.; Benna, P.; Rossetti, P. The Traversella Mining Site as Piemonte Geosite. Geoheritage 2019, 11, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migoń, P.; Kasprzak, M.; Woo, K.S. Granite Landform Diversity and Dynamics Underpin Geoheritage Values of Seoraksan Mountains, Republic of Korea. Geoheritage 2019, 11, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolfo, F.; Benna, P.; Cadoppi, P.; Castelli, D.; Favero-Longo, S.E.; Giardino, M.; Balestro, G.; Belluso, E.; Borghi, A.; Cámara, F.; et al. The Monviso Massif and the Cottian Alps as Symbols of the Alpine Chain and Geological Heritage in Piemonte, Italy. Geoheritage 2015, 7, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Scoon, R.N.; Viljoen, M.J. Geoheritage of the Eastern Limb of the Bushveld Igneous Complex, South Africa: A Uniquely Exposed Layered Igneous Intrusion. Geoheritage 2019, 11, 1723–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natura 2000. Available online: https://natura2000.eea.europa.eu/Natura2000/SDF.aspx?site=GR4220009 (accessed on 22 June 2021).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).