Monitoring and Assessment of Salinity and Chemicals in Agricultural Lands by a Remote Sensing Technique and Soil Moisture with Chemical Index Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
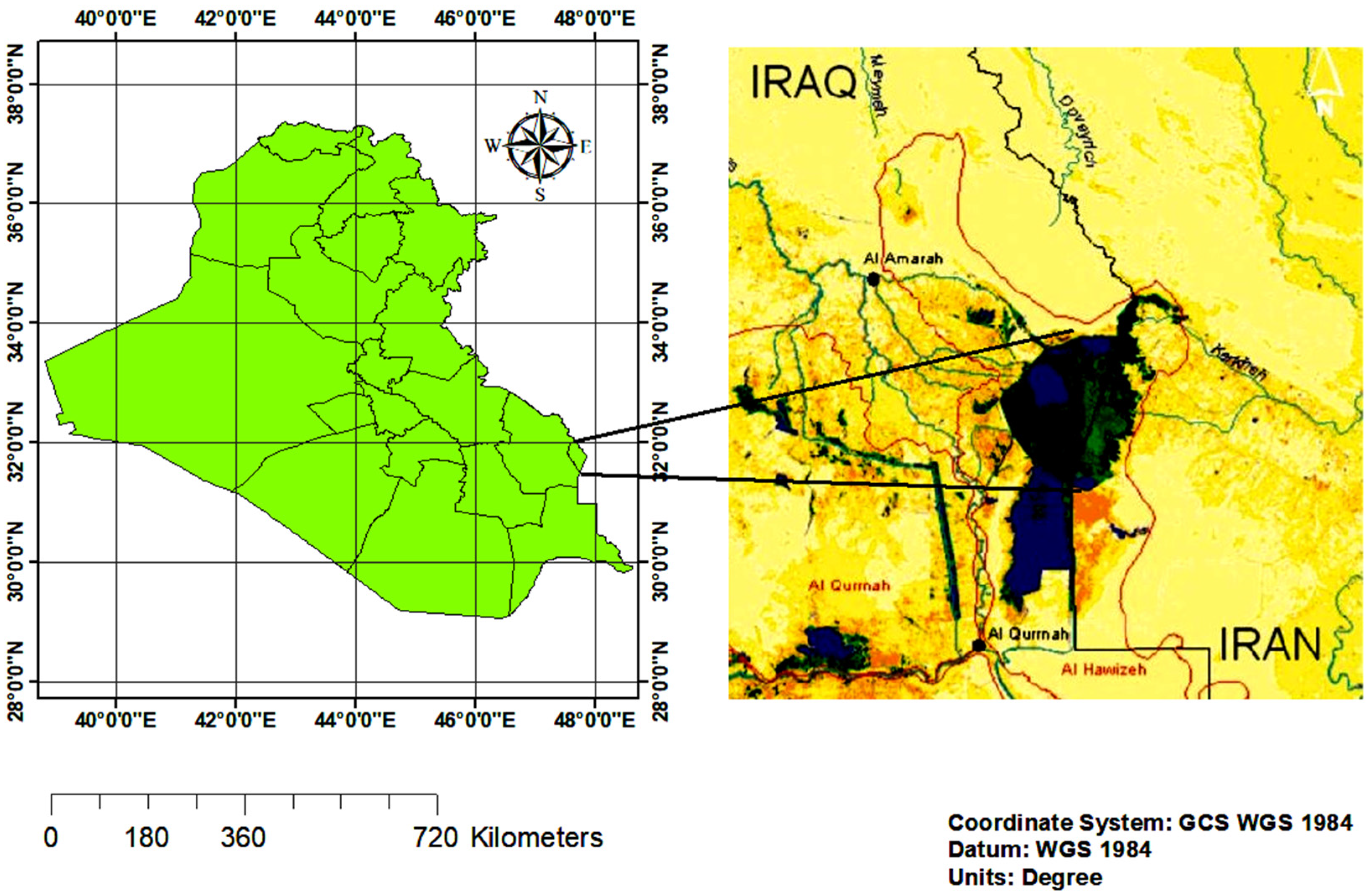
2. Study Area
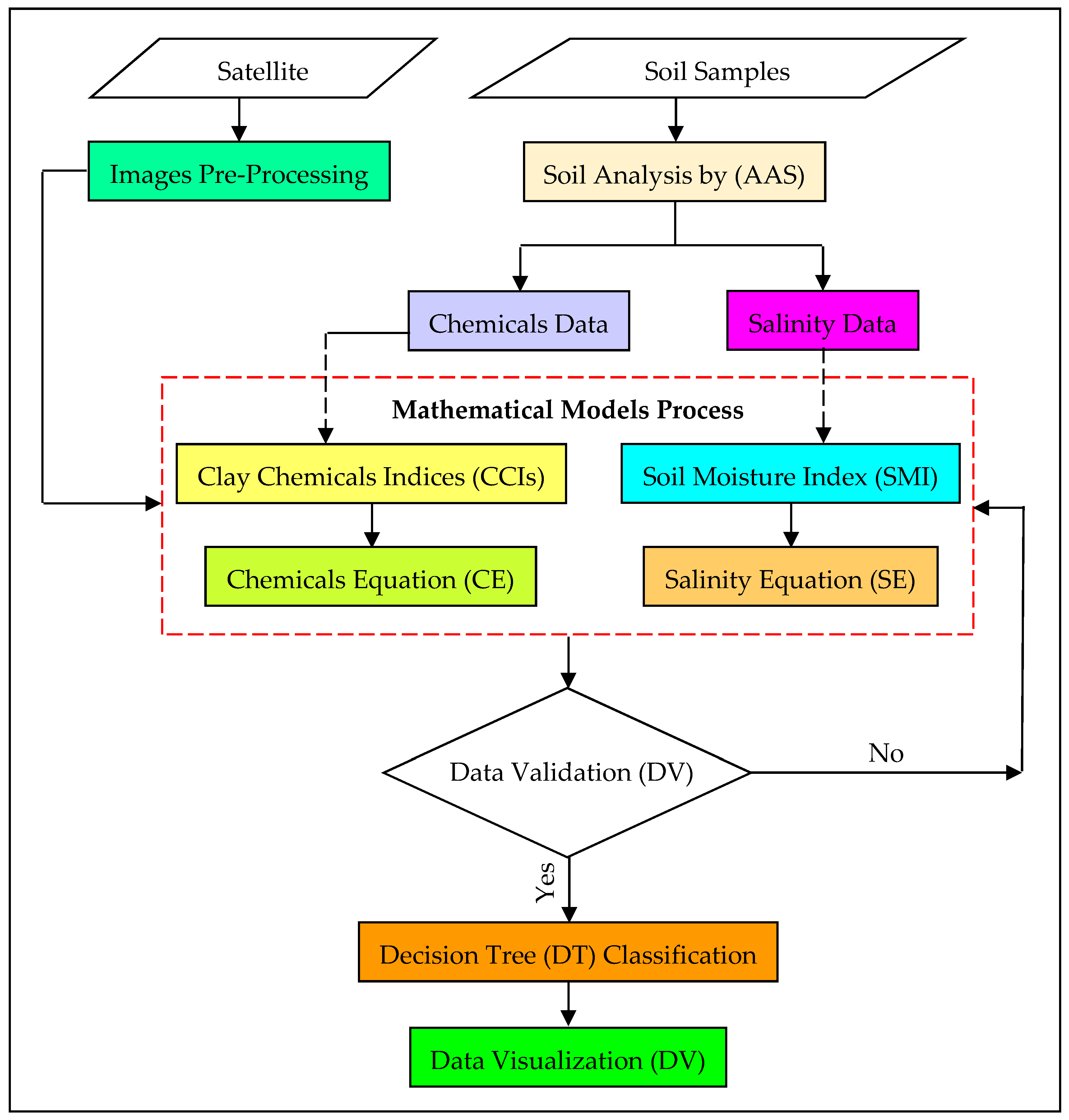
3. Methodology
3.1. Satellite Images and Pre-Processsing
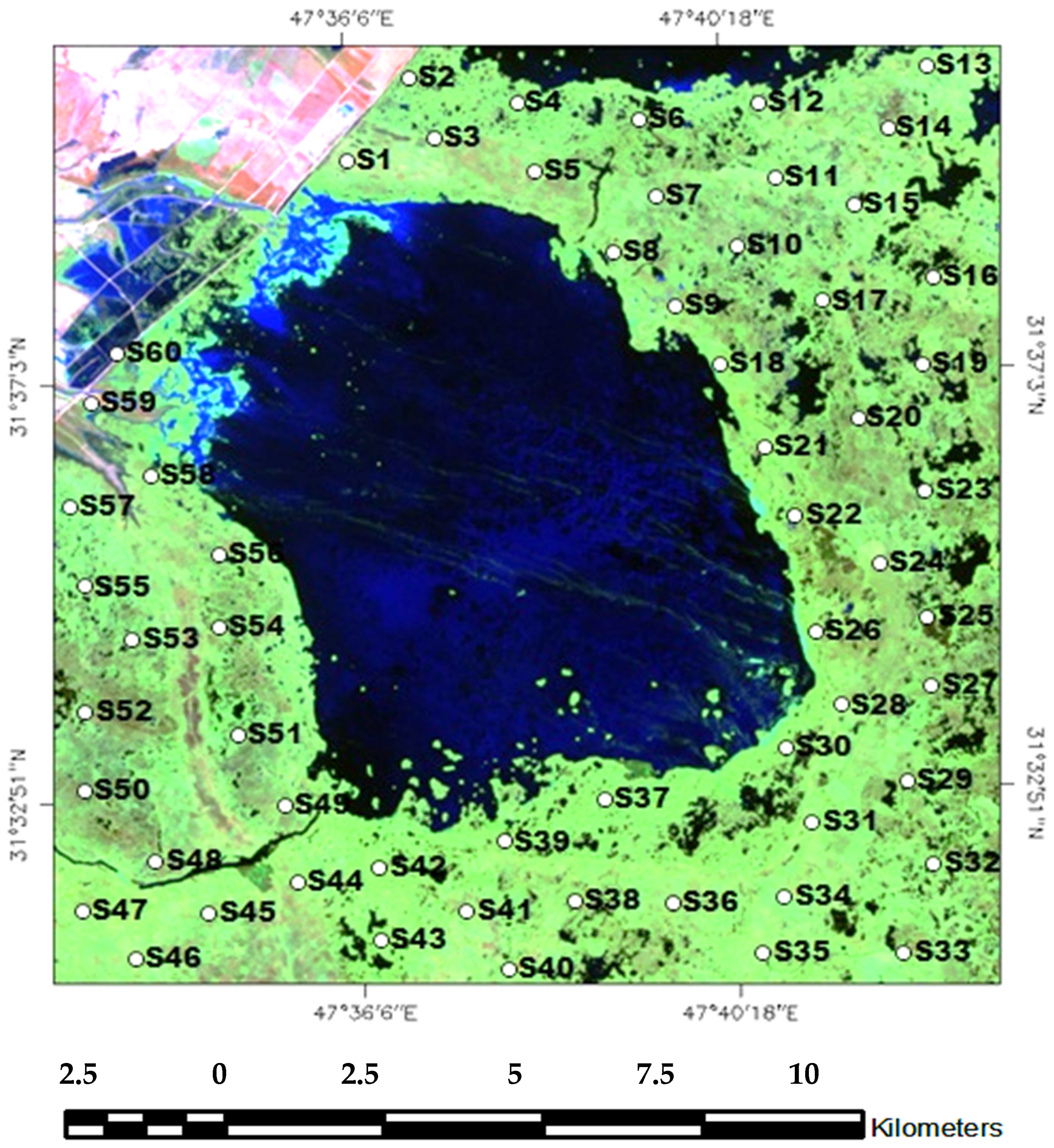
3.2. Soil Sample Collection
3.3. Analysis of Soil Samples
3.4. Mathematical Models
3.4.1. Soil Moisture Index (SMI)
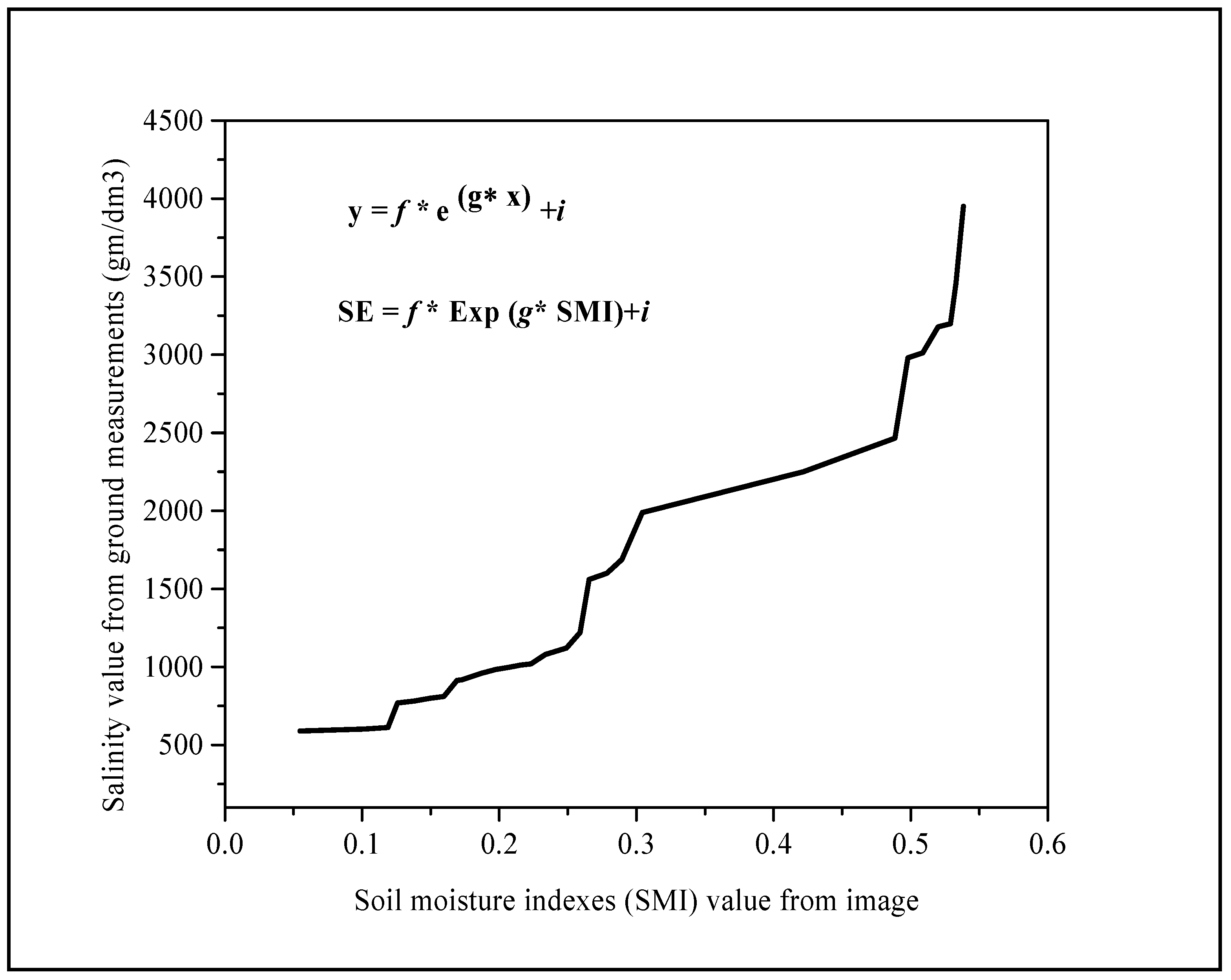
3.4.2. Salinity Equation (SE)
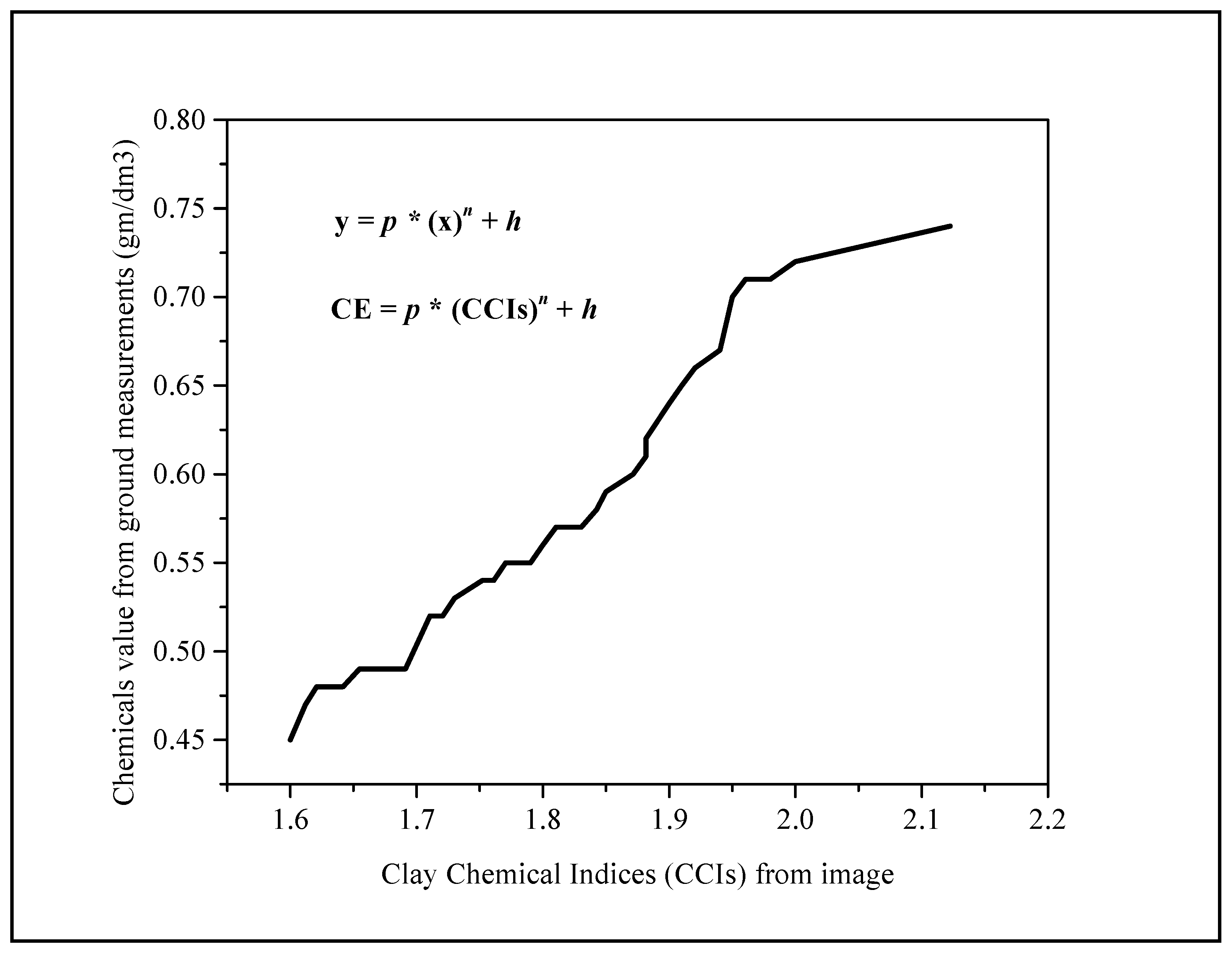
3.4.3. Clay Chemical Indices (CCIs)
3.4.4. Chemical Equation (CE)
3.5. Image Classification
3.6. Data Visualization
4. Results and Discussion
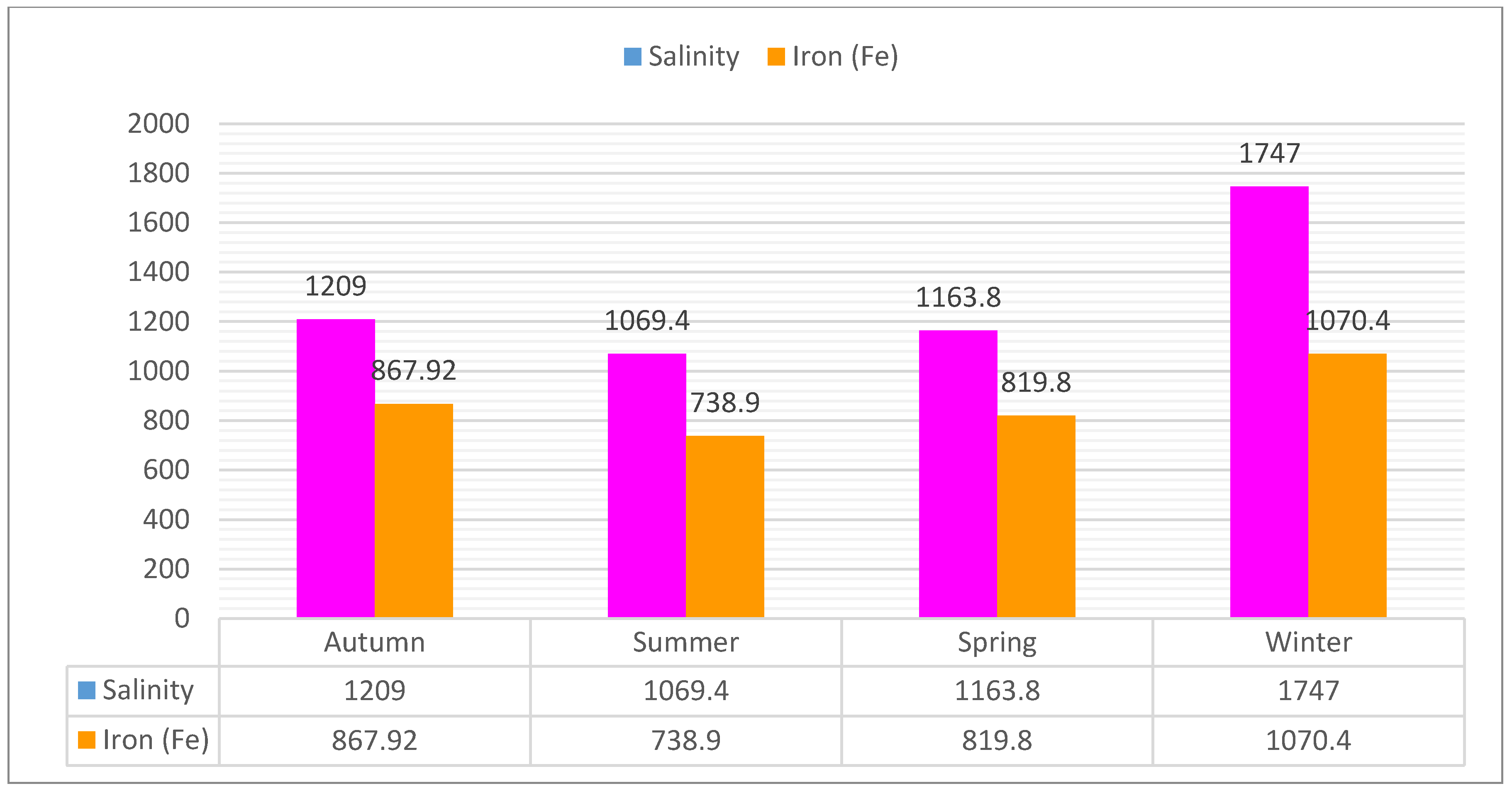
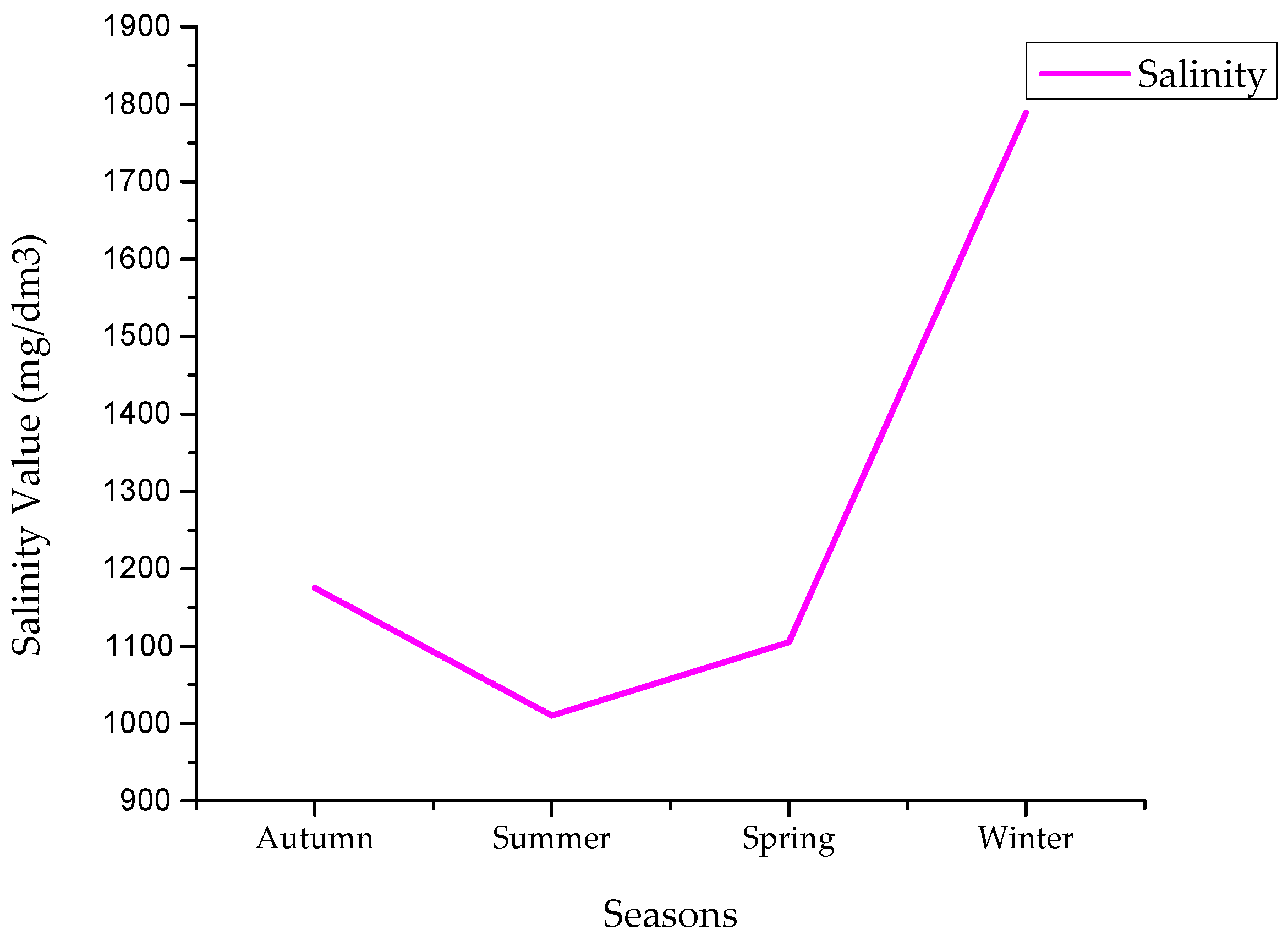
4.1. Salinity Values
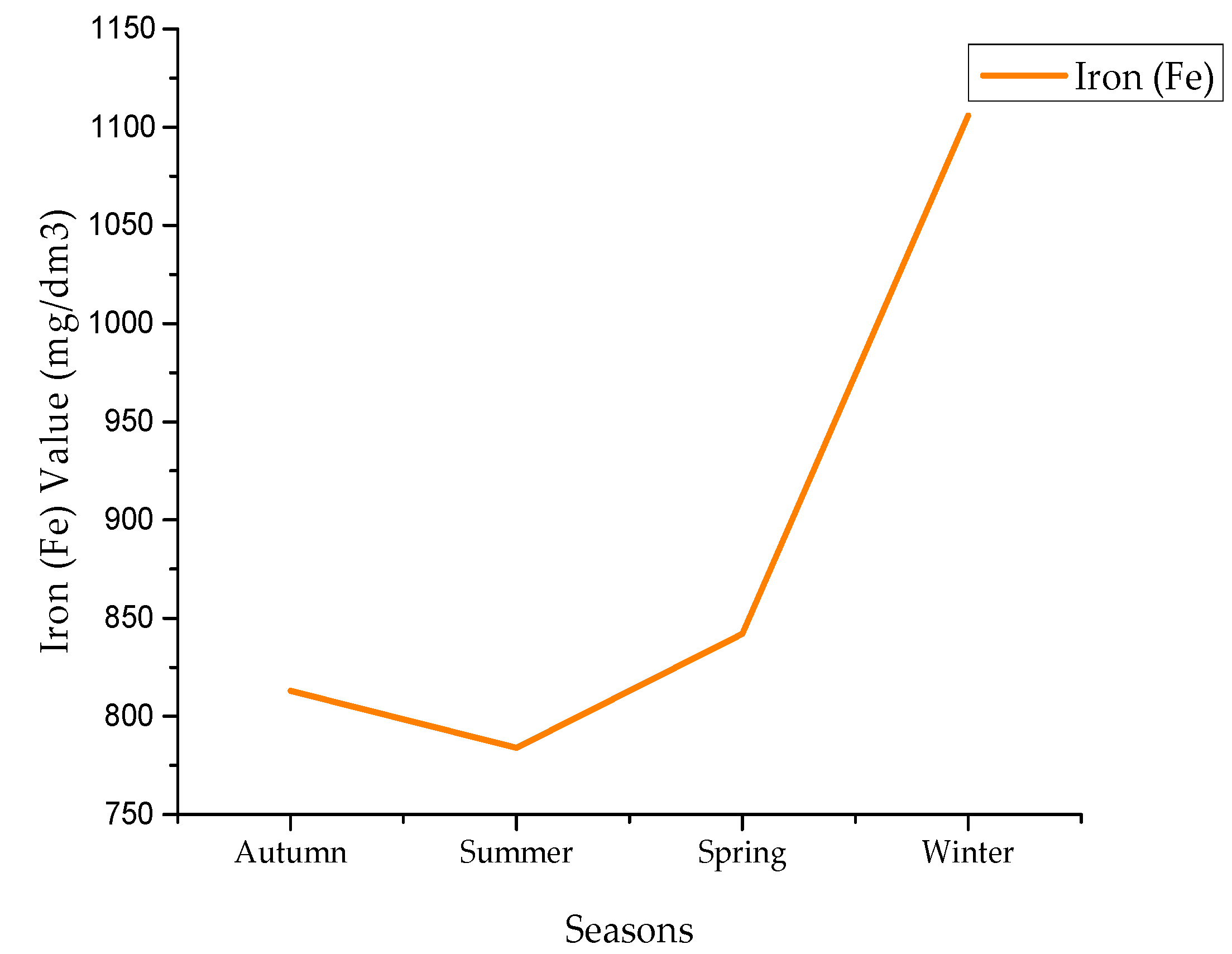
4.2. Iron Values
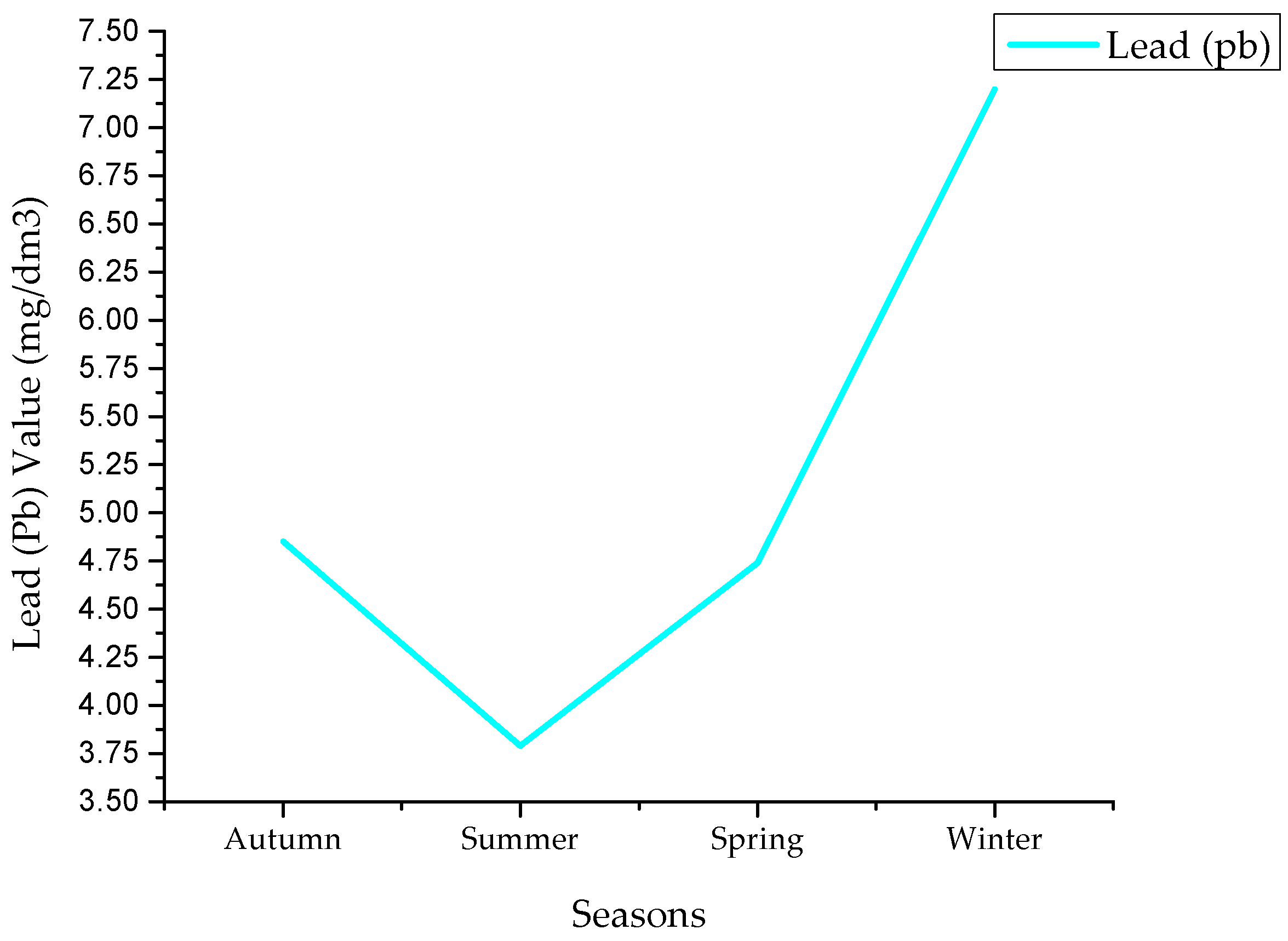
4.3. Lead Values
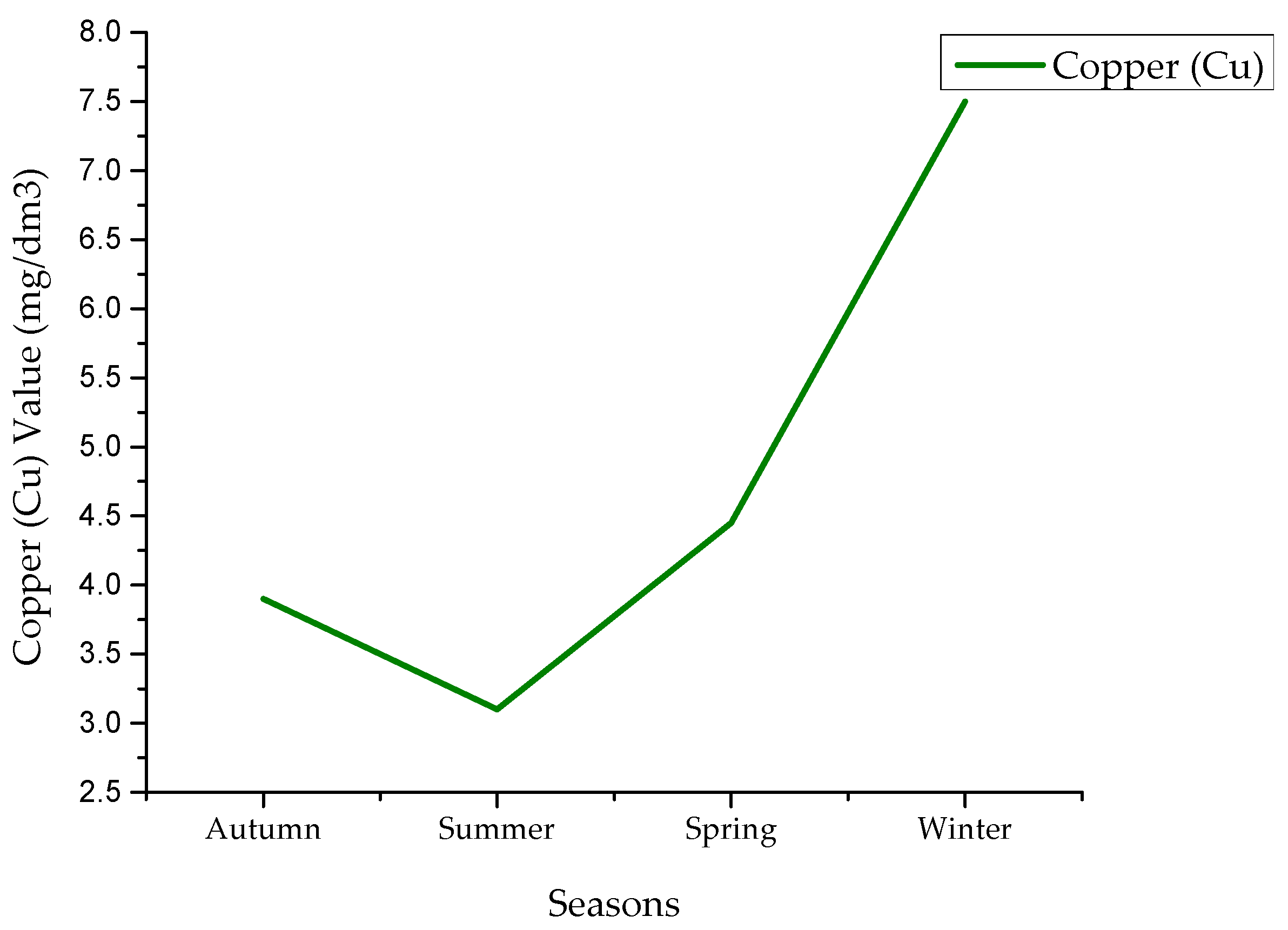
4.4. Copper Values
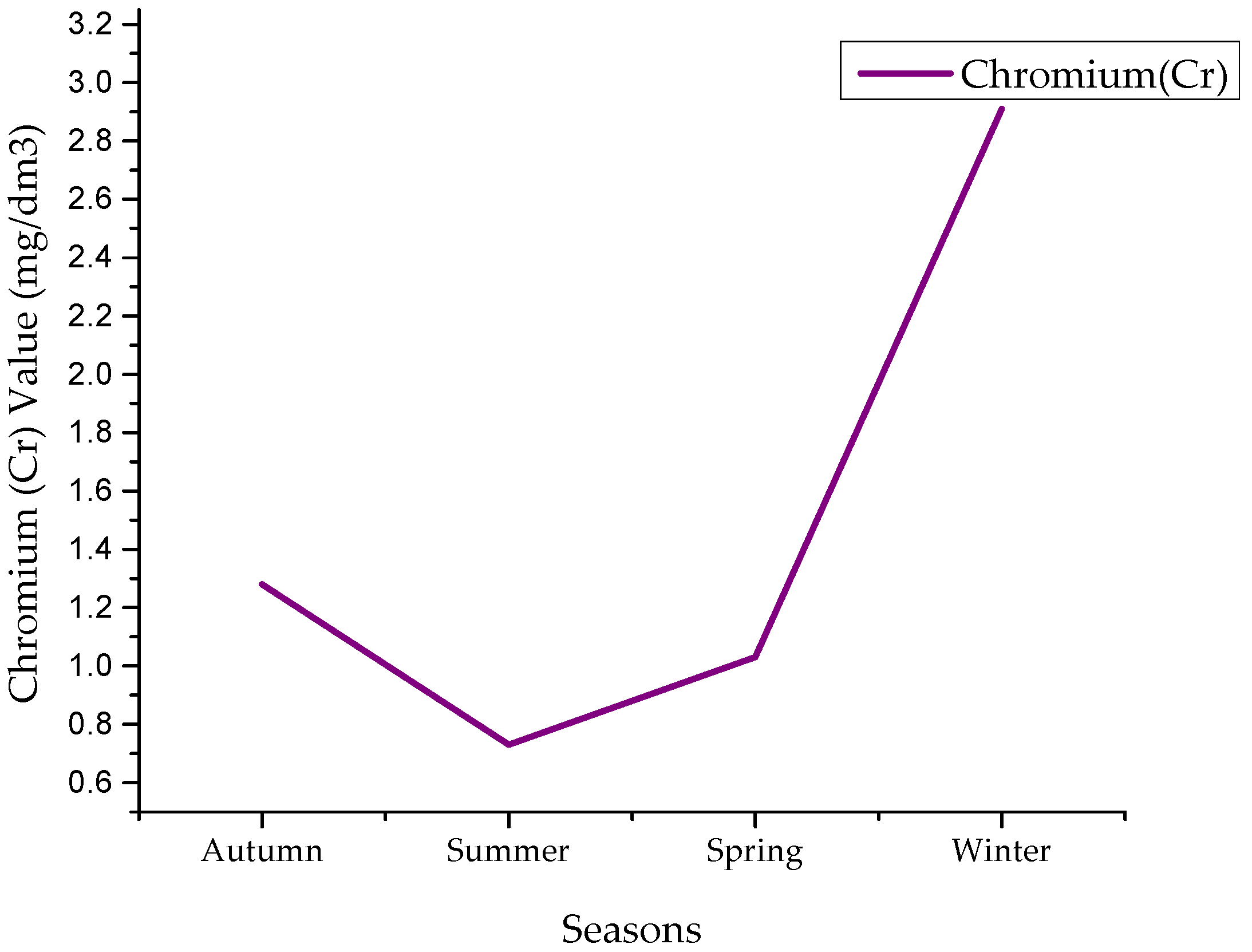
4.5. Chromium Values
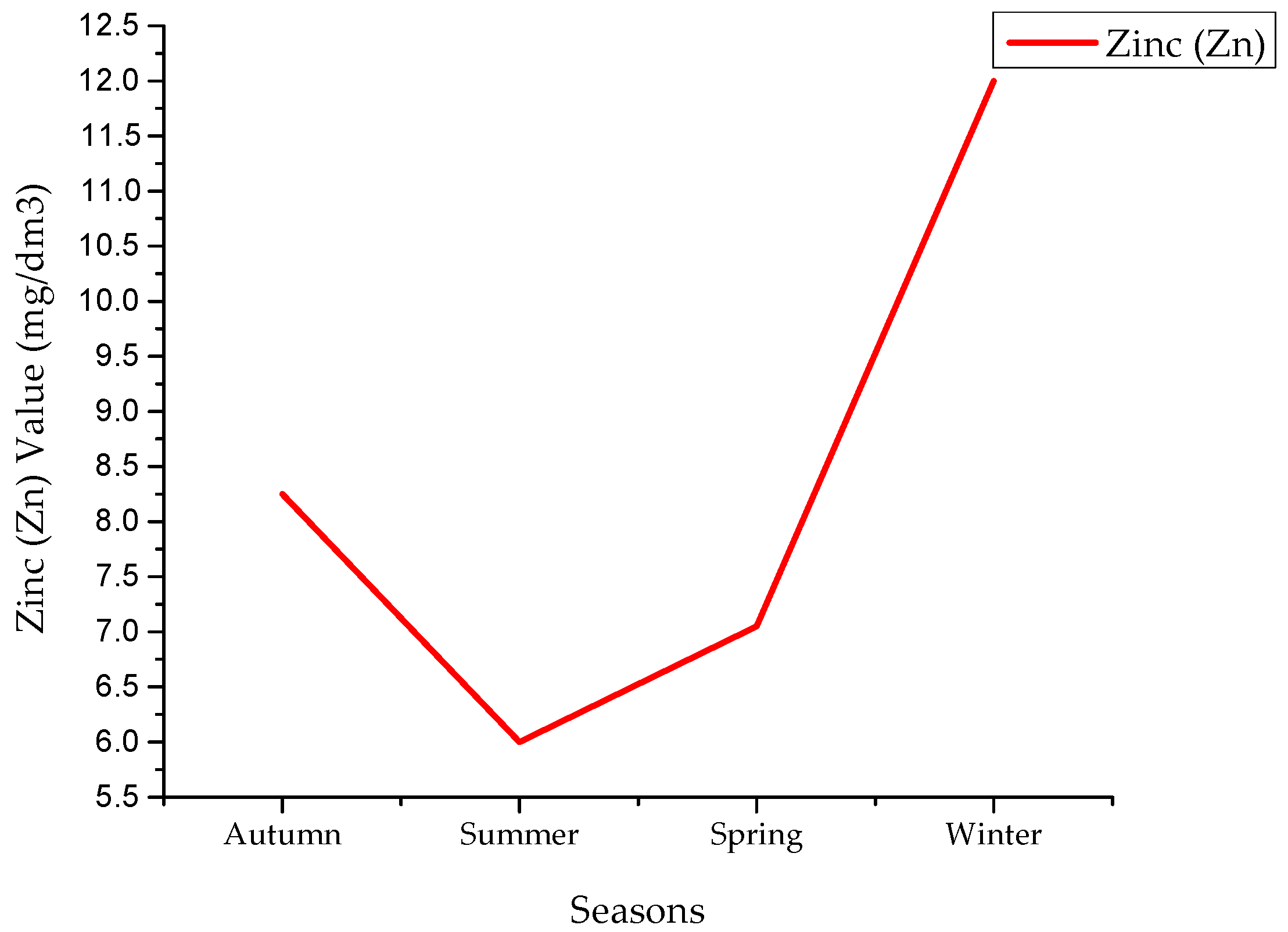
4.6. Zinc Values
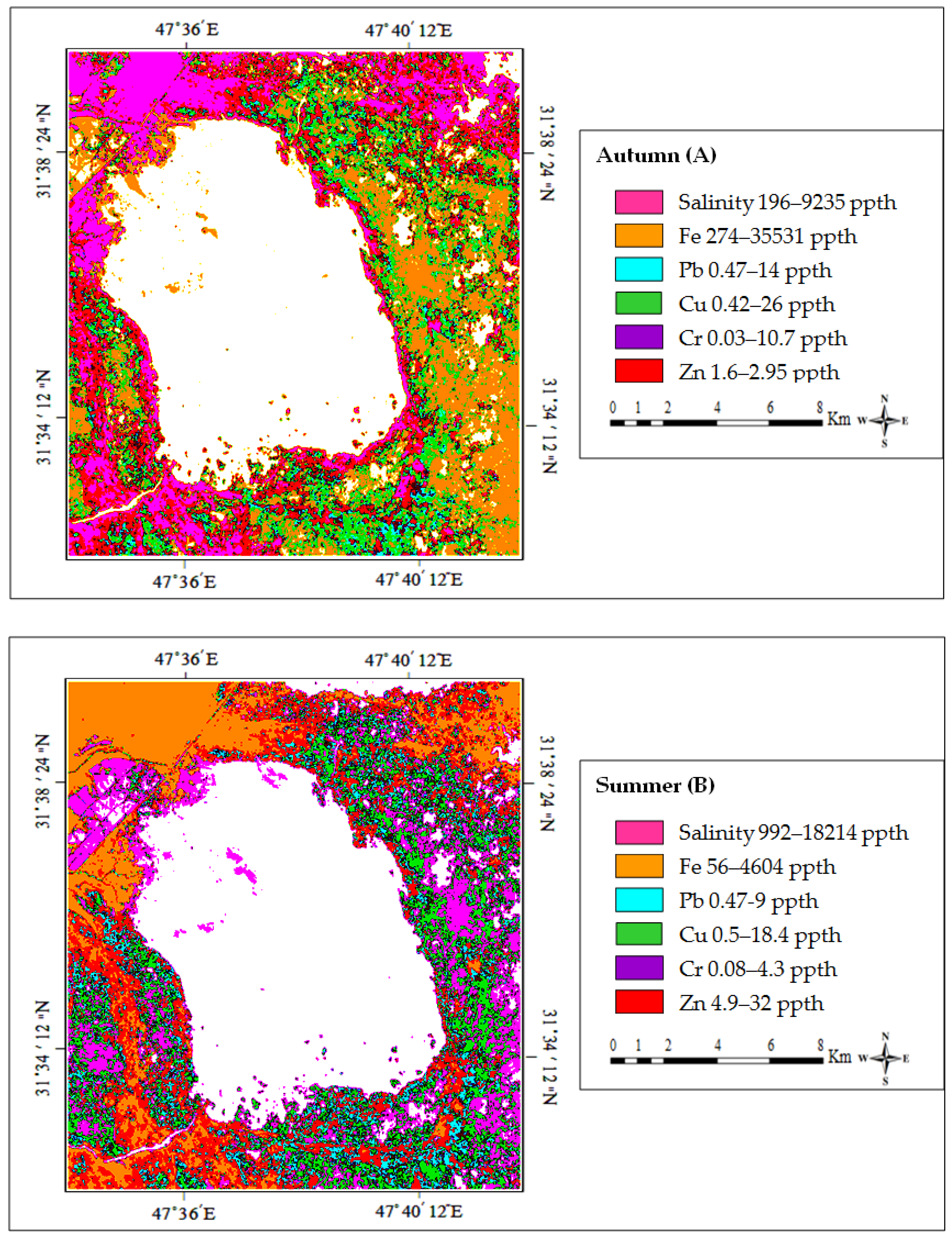
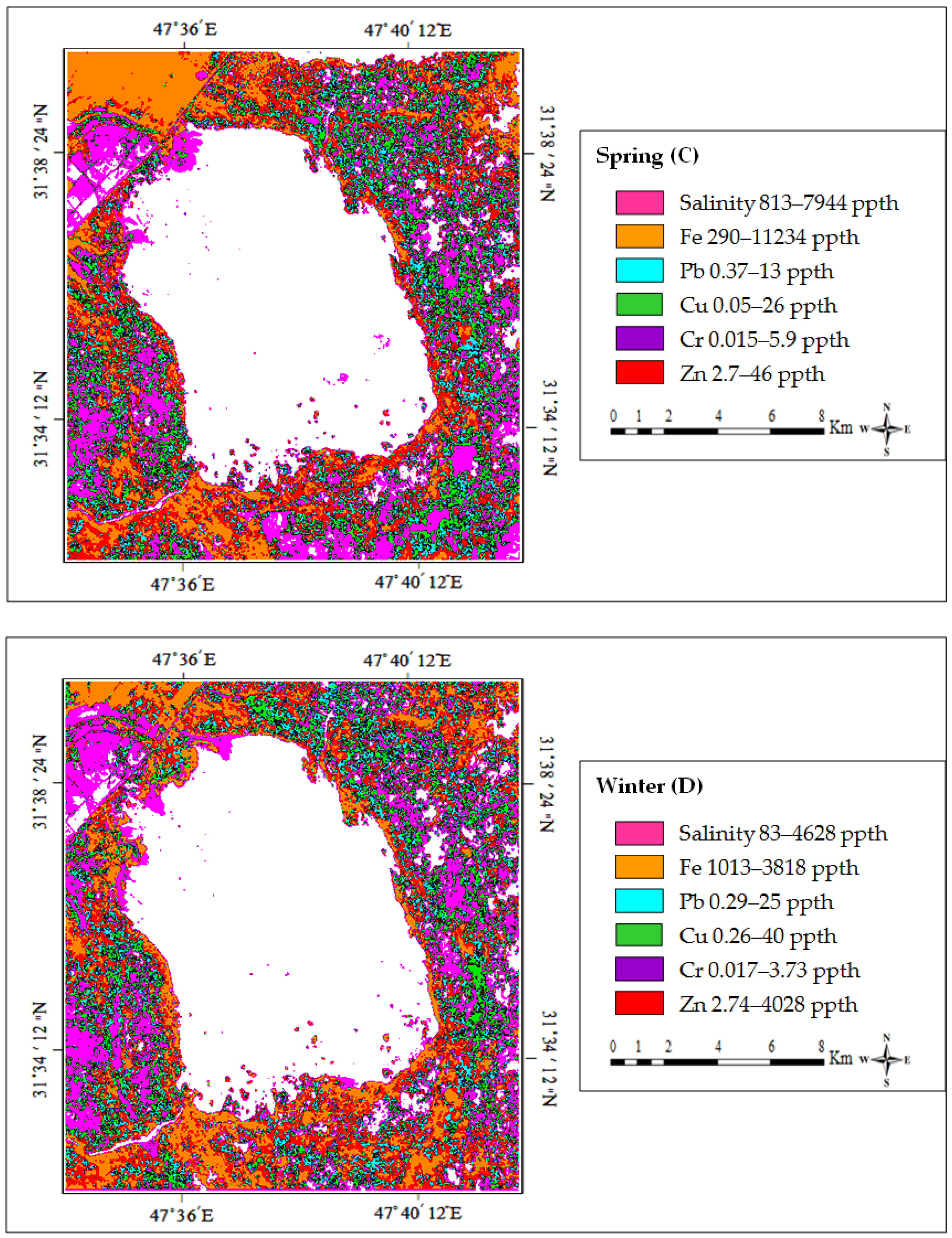
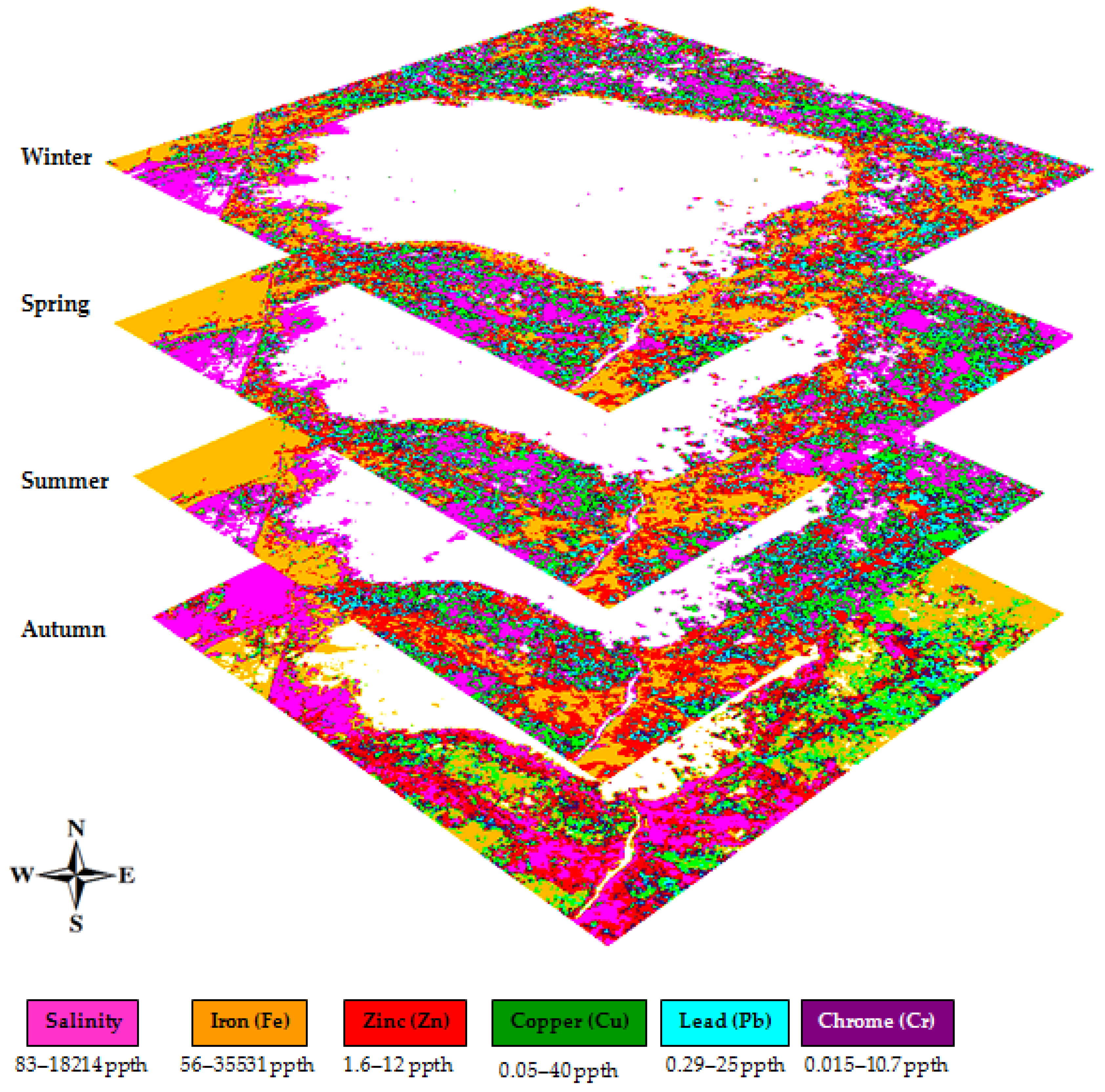
5. Image Classifications
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Handal, A.; Hu, C. MODIS observations of human-induced changes in the Mesopotamian Marshes in Iraq. Wetlands 2015, 35, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azab, A.M. Integrating GIS, remote sensing; mathematical modelling for surface water quality management in irrigated watersheds. Ihe Delft Inst. Water Educ. 2012, 24, 75. [Google Scholar]
- Kerekes, J.P.; Baum, J.E. Full-spectrum spectral imaging system analytical model, Geoscience; Remote Sensing. IEEE Trans. 2005, 43, 571–580. [Google Scholar]
- Mather, P.M.; Koch, M. Remote Sensing: Basic Principles: Computer Processing of Remotely-Sensed Images: An Introduction; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; p. 67. [Google Scholar]
- Ongley, E.D. Water quality management: Design, financing; sustainability considerations-II. In Proceedings of the 2000 Invited Presentation at the World Bank’s Water Week Conference: Towards a Strategy for Managing Water Quality Management, Washington, DC, USA, 2–4 April 2000; Volume 4, p. 34. [Google Scholar]
- Ustin, S. Manual of Remote Sensing: Remote Sensing for Natural Resource management; Environmental Monitoring; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; Volume 6, pp. 23–56. [Google Scholar]
- Zacharias, I.; Gianni, A. Hydrodynamic; Dispersion Modeling as a Tool for Restoration of Coastal Ecosystems, Application to a Re-Flooded Lagoon. Environ. Model. Softw. 2008, 23, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrawi, J.A. Evaluation of distinctive normalized difference vegetation indices in soil erosion estimation using remote sensing concepts in WadiYalamlam, Saudi Arabia. Indian J. Geo Mar. Sci. 2018, 47, 2087–2093. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, D.; Mausel, P.; Brondizio, E.; Moran, E. Change detection techniques. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azab, A. Integrating GIS, Remote Sensing; Mathematical moDelling for Surface Water Quality Management in Irrigated Watersheds; IHE Delft Institute for Water Education: Delft, The Netherlands, 2012; p. 21. [Google Scholar]
- Mujumdar, N. World development report, 2000/2001: Attacking poverty. Indian J. Agric. Econ. 2011, 56, 146. [Google Scholar]
- Green, E.A. Hydropolitics in the Middle East; US Policy; DTIC Document: Fort Belvoir, VA, USA, 1993; Volume 3, p. 87. [Google Scholar]
- Lowi, M.R. Rivers of conflict, rivers of peace. J. Int. Aff. 1995, 49, 123–144. [Google Scholar]
- Maltby, E. An Environmental & Ecological Study of the Marshlands of Mesopotamia, Draft Consultative Bulletin: AMAR appeal Trust; University of Exeter, Wetland Ecosystems Research Group: London, UK, 1994; Volume 3, pp. 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, E.; Clark, P. Iraqi Marshlands: Politico’s Pub; AMAR International Charitable Foundation: London, UK, 2003; Volume 2, p. 45. [Google Scholar]
- Partow, H. The Mesopotamian Marshlands: Demise of an Ecosystem. Nairobi (Kenya): Division of Early Warning; Assessment, United Nations Environment Programme; UNEP publication UNEP/DEWA: Nairobi, Kenya, 2001; Volume 4, pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Hayder, D.; Shattri, M.; Noordin, A.; Biswajeet, P. Band-to-band registration model for near-equatorial Earth observation satellite images with the use of automatic control point extraction. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 2184–2200. [Google Scholar]
- Hasab, H.A.; Jawad, H.A.; Dibs, H.; Hussain, H.M.; Al-Ansari, N. Evaluation of Water Quality Parameters in Marshes Zone Southern of Iraq Based on Remote Sensing; GIS Techniques. Water, AirSoil Pollut. 2020, 231, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarte, C. Environmental Protection in islamic Law: An Overview on Potential Influences for Legal Developments in Iraq. Local Environ. 2003, 8, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, A.; Marghany, M. Developing a hydrological model for water quality in Iraq marshes zone using Landsat-TM. J. IopscienceEarth; Environ. Sci. 2016, 37, 012073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammenberg, P.; Flink, P.; Lindell, T.; Pierson, D.; Strombeck, N. Bio-optical modelling combined with remote sensing to assess water quality. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 1621–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodchild, M.F.; Steyaert, L.T.; Parks, B.O. GIS; Environmental Modeling: Progress; Research Issues; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996; Volume 25, p. 183. [Google Scholar]
- Dellapenna, J.W.; Nicholason, E.; Clark, P. The Iraqi Marshlands; A Human Environmental Study; AMAR International Charitable Foundation: London, UK, 2001; Volume 7, p. 123. [Google Scholar]
- Mather, P.M.; Koch, M. Computer Processing of Remotely-Sensed Images: An Introduction; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; p. 95. [Google Scholar]
- El-Din, M.S.; Gaber, A.; Koch, M.; Ahmed, R.S.; Bahgat, I. Remote Sensing Application for Water Quality Assessment in Lake T imsah, Suez Canal, Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Technol. 2013, 1, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, D.V.C.; NO, U.G.A. The Anacostia River: Ecological Studies of Water Pollution Biology; DC Water Resources Research Center: Washington, DC, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zheng, L.; Yin, S. Multi-perspective analysis of vegetation cover changes; driving factors of long time series based on climate; terrain data in Hanjiang River Basin, China. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Feng, Y.; Wang, J. Remote sensing monitoring the spatio-temporal changes of aridification in the Mongolian Plateau based on the general Ts-NDVI space, 1981–2012. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 126, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.R. Introduction to Digital Image Processing: A Remote Sensing Perspective, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 239–247. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo, L.; Han, D.; Dai, Q. Exploration of empirical relationship between surface soil temperature; surface soil moisture over two catchments of contrasting climates; land covers. Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Keesari, T.; Sinha, U.K.; Sabarathinam, C. Delineating groundwater prospect zones in a region with extreme climatic conditions using GIS; remote sensing techniques: A case study from central India. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 128, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehmordi, L.M.; Savari, A.; Dostshenas, A.; Asgari, H.M.; Abasi, A. Remote chlorophyll-a, SST; kd490 retrieval in Northwest Persian gulf using landsat 8 satellite data. Indian J. Geo Mar. Sci. 2018, 47, 148–169. [Google Scholar]
- Jacintha, T.; Rajasree, S.R.; Kumar, J.D.; Sriganesh, J. Assessment of wetland change dynamics of Chennai coast, Tamil Nadu, India, using satellite remote sensing. Indian J. Geo Mar. Sci. 2019, 48, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar]
- Giri, S.; Singh, A.K.; Mahato, M.K. Metal contamination of agricultural soils in the copper mining areas of Singhbhum shear zone in India. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 126, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennaji, W.; Barakat, A.; El Baghdadi, M.; Oumenskou, H.; Aadraoui, M.; Karroum, L.A.; Hilali, A. GIS-based multi-criteria land suitability analysis for sustainable agriculture in the northeast area of Tadla plain (Morocco). J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 127, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platonov, A.; Noble, A.; Kuziev, R. Soil salinity mapping using multi-temporal satellite images in agricultural fields of syrdarya province of Uzbekistan Developments in Soil Salinity Assessment; Reclamation. Springer 2013, 112, 87–98. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.; Liu, Y.; Tao, J.; Weng, Y. Soil salinity retrieval from advanced multi-spectral sensor with partial least square regression. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 488–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allbed, A.; Kumar, L. Soil salinity mapping; monitoring in arid; semi-arid regions using remote sensing technology: A review. Adv. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haith, D.A.; Tubbs, L.J. Watershed loading functions for nonpoint sources. J. Environ. Eng. Div. 1981, 107, 121–137. [Google Scholar]
- Abuelaish, B.; Olmedo, M.T.C. Scenario of land use; land cover change in the Gaza Strip using remote sensing; GIS models. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasirian, H.; Irvine, K.; Sadeghi, S.M.T.; Mahvi, A.H.; Nazmara, S. Assessment of bed sediment metal contamination in the Shadegan; Hawr Al Azim wetlands, Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS. Landsat 8 Operational Land Imager (OLI); Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS); Frequently Asked Questions about the Landsat Missions; USGS. Science for a Changing World: Reston, VA, USA, 2016; pp. 1–6.
- USGS. Using the USGS Landsat-8 Product. USGS. Science for a Changing World; Geological Survey in Vandenberg Air Force Base, California on an Atlas-V rocket in USA; U.S. Department of the Interior: Washington, DC, USA, 2013.
- Muhaimeed, A.S. Status of Soil Information in Iraq, University of Baghdad College of Agriculture. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2014, 4, 434–443. [Google Scholar]
- Omer, Tara Mohamed Anwar. Country Pasture/Forage Resource Profile.University of Sulaimaniyah. Available online: http://www.fao.org/ag/agp/AGPC/doc/Counprof/Iraq/Iraq.html (accessed on 13 December 2019).
- Panagos, P.; Jones, A.; Bosco, C.; Senthil Kumar, P.S. European digital archive on soil maps (EuDASM): Preserving important soil data for public free access. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2011, 4, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaradjou, S.-K.L.; Montanarella, O.; Spaargaren, D. Dent.European Digital Archive of Soil Maps (EuDASM)—Soil Maps of Asia DVD-ROM version. EUR 21823 EN. Off. Off. Publ. Eur. CommunitiesLuxemb. 2005, 7, 134–143. [Google Scholar]
- Maurya, A.; Kesharwani, L.; Mishra, M.K. Analysis of Heavy Metal in Soil through Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy for Forensic Consideration. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2018, 6, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addis, W.; Abebaw, A. Determination of heavy metal concentration in soils used for cultivation of Allium sativum L.(garlic) in East Gojjam Zone, Amhara Region, Ethiopia. Cogent Chem. 2017, 1, 1419422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, M.F.; Merkel, B.J. Application of Landsat 5; Landsat 7 images data for water quality mapping in Mosul Dam Lake, Northern Iraq. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 3557–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, A.B.; Hashim, M. Hydrothermal alteration mapping from Landsat-8 data, SarCheshmeh copper mining district, south-eastern Islamic Republic of Iran. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2015, 9, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guide, E.U.S. ENVI on-line software user’s manual. ITT Visual Information Solutions 2008. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 154–167. [Google Scholar]
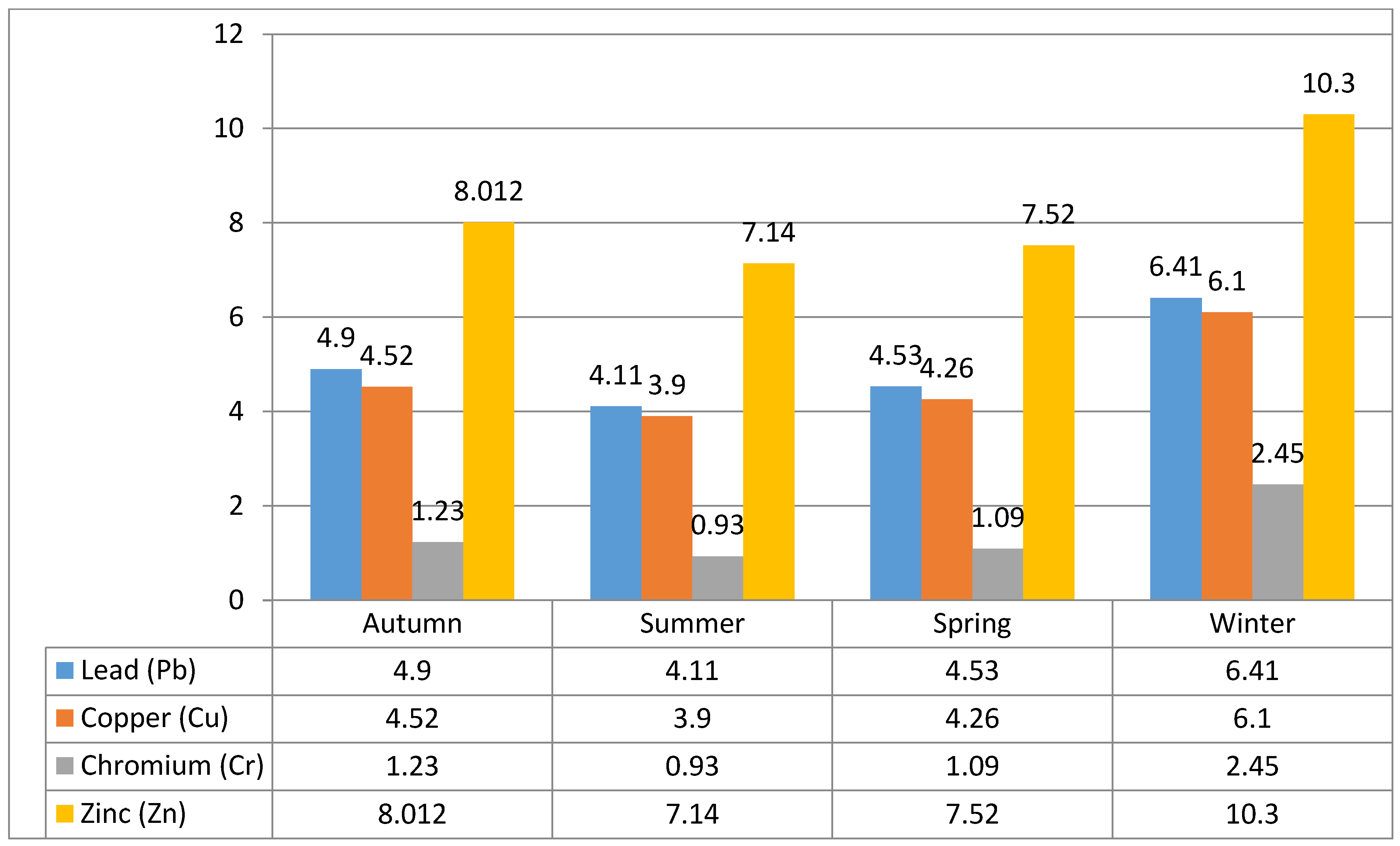
| Band | Wavelength | Useful for Mapping |
|---|---|---|
| Band 6—Short-wave Infrared (SWIR) 1 | 1.57–1.65 | Discriminates moisture content of soil and vegetation; penetrates thin clouds |
| Band 7—Short-wave Infrared (SWIR) 2 | 2.11–2.29 | Improved moisture content of soil and vegetation and thin cloud penetration |
| Band 11—TIRS 2 | 11.5–12.51 | 100 m resolution. Improved thermal mapping and estimated soil moisture |
| Minerals (mg/dm3) | Autumn | Summer | Spring | Winter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salinity | Min | 230 | 1012 | 913 | 98 |
| Max | 8975 | 17,321 | 7438 | 4109 | |
| Avg | 1209 | 1069.4 | 1163.8 | 1747 | |
| Iron | Min | 282 | 62 | 310 | 1101 |
| Max | 35,011 | 4123 | 10,951 | 2978 | |
| Avg | 867.92 | 738.9 | 819.8 | 1070.4 | |
| Lead | Min | 0.65 | 0.53 | 0.32 | 0.38 |
| Max | 12.3 | 8.14 | 11.87 | 21.45 | |
| Avg | 4.9 | 4.11 | 4.53 | 6.41 | |
| Copper | Min | 0.45 | 0.57 | 0.08 | 0.29 |
| Max | 24.65 | 16.94 | 24.62 | 38.21 | |
| Avg | 4.52 | 3.9 | 4.26 | 6.1 | |
| Chromium | Min | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.022 | 0.023 |
| Max | 8.27 | 3.53 | 5.2 | 3.13 | |
| Avg | 1.23 | 0.93 | 1.09 | 2.45 | |
| Zinc | Min | 1.8 | 5.2 | 2.8 | 2.87 |
| Max | 2.13 | 28.65 | 41.5 | 3980 | |
| Avg | 8.012 | 7.14 | 7.52 | 10.3 | |
| Minerals (mg/dm3) | Autumn | Summer | Spring | Winter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salinity | Min | 196 | 992 | 813 | 83 |
| Max | 9235 | 18,214 | 7944 | 4628 | |
| Avg | 1175 | 1010 | 1105 | 1789 | |
| Iron | Min | 274 | 56 | 290 | 1013 |
| Max | 35,531 | 4604 | 11,234 | 3818 | |
| Avg | 813 | 784 | 842 | 1106 | |
| Lead | Min | 0.47 | 0.47 | 0.37 | 0.29 |
| Max | 14 | 9 | 13 | 25 | |
| Avg | 4.85 | 3.79 | 4.74 | 7.2 | |
| Copper | Min | 0.42 | 0.5 | 0.05 | 0.26 |
| Max | 26 | 18.4 | 26 | 40 | |
| Avg | 3.9 | 3.1 | 4.45 | 7.5 | |
| Chromium | Min | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.015 | 0.017 |
| Max | 10.7 | 4.3 | 5.9 | 3.73 | |
| Avg | 1.28 | 0.73 | 1.03 | 2.91 | |
| Zinc | Min | 1.6 | 4.9 | 2.7 | 2.74 |
| Max | 2.95 | 32 | 46 | 4028 | |
| Avg | 8.25 | 6 | 7.05 | 12 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hasab, H.A.; Dibs, H.; Dawood, A.S.; Hadi, W.H.; Hussain, H.M.; Al-Ansari, N. Monitoring and Assessment of Salinity and Chemicals in Agricultural Lands by a Remote Sensing Technique and Soil Moisture with Chemical Index Models. Geosciences 2020, 10, 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10060207
Hasab HA, Dibs H, Dawood AS, Hadi WH, Hussain HM, Al-Ansari N. Monitoring and Assessment of Salinity and Chemicals in Agricultural Lands by a Remote Sensing Technique and Soil Moisture with Chemical Index Models. Geosciences. 2020; 10(6):207. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10060207
Chicago/Turabian StyleHasab, Hashim Ali, Hayder Dibs, Abdulameer Sulaiman Dawood, Wurood Hasan Hadi, Hussain M. Hussain, and Nadhir Al-Ansari. 2020. "Monitoring and Assessment of Salinity and Chemicals in Agricultural Lands by a Remote Sensing Technique and Soil Moisture with Chemical Index Models" Geosciences 10, no. 6: 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10060207
APA StyleHasab, H. A., Dibs, H., Dawood, A. S., Hadi, W. H., Hussain, H. M., & Al-Ansari, N. (2020). Monitoring and Assessment of Salinity and Chemicals in Agricultural Lands by a Remote Sensing Technique and Soil Moisture with Chemical Index Models. Geosciences, 10(6), 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10060207







