1. Introduction
Glacier–permafrost relationships were initially studied on polar and subpolar glaciers more than 50 years ago. Mathews and Mackay [
1] investigated the deformation of proglacial unconsolidated sediments in periglacial environments. In the context of thrust moraine evolution at polar and subpolar glaciers, Kälin [
2] provided evidence on glacier–permafrost interaction for the first time. Further important studies in this context dealt with the deformation of frozen sediments [
3] or the interaction between frozen proglacial sediments and the subglacial hydraulic system [
4,
5]. Hambrey and Huddart [
6] and Bennett [
7] presented multi-processual models of moraine genesis through glacier–permafrost interaction. In these studies, the properties of the glacial stress field, glacial flow patterns, the sub- and proglacial hydrological system as well as the properties of the proglacial sediments were also considered.
Thrust moraines, also known as push moraines, are geomorphological features, which are result of the interaction between advancing cold or polythermal glaciers and proglacial and subglacial permafrost. Permafrost in ice-marginal sediments leads to a transmission of glacial stress, which can result in a glaciotectonic deformation of proglacial sediments. Glaciotectonic shear processes enable a (large-scale) thrusting of the proglacial area and lead to the formation of multi-ridge thrust moraine complexes. A review of glacier–permafrost interactions also highlighting the important and dominant factors on thrust moraine formation was given by Waller et al. [
8].
The investigation of glacier–permafrost interactions in alpine environments started much later than in polar regions. For the first time, Haeberli [
9] expressed the assumption of the occurrence of polythermal glaciers in the European Alps and questioned the previous opinion that only temperate alpine glaciers were present. Although initial geophysical studies were subsequently carried out to investigate interactions and relationships between glaciers and permafrost [
10], alpine permafrost research was focused more on the study of rock glaciers at that time [
11,
12,
13]. The investigation of the distribution and development of permafrost in recently deglaciated glacier forefields in the European Alps started from the end of the last millennium [
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19]. For most of the studies mentioned above, geophysical measurements were performed. The use of geophysical methods to investigate the actual state of ground conditions is common in the field of permafrost research because of the contrasts between frozen and unfrozen sediments in several geophysical parameters. In particular, the use of one-dimensional geoelectrical methods in high alpine permafrost environments was established to investigate permafrost distribution in the European Alps more than 20 years ago [
20]. Since the turn of the millennium, the two-dimensional approach—electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) or electrical resistivity imaging (ERI)—has been predominantly performed. This innovation enabled a faster and more detailed investigation of larger areas, which was important progress in the often heterogeneous alpine periglacial environments. In recent years, three-dimensional measurements have also been performed within the field of mountain permafrost research [
21,
22,
23], but they are currently not very common because of the large effort required in comparison to the small spatial coverage. Nevertheless, the gain in knowledge using three-dimensional measurements is significant.
The use of ground-penetrating radar (GPR) in permafrost research also has a long tradition. The first tests of the applicability of GPR in the periglacial environments of high mountain regions were done by King et al. [
24], but the method established itself solidly much later [
25,
26,
27]. Due to its advantages in the detection of sedimentological interfaces, the method finally prevailed and is now mainly used in periglacial environments to study internal structures of moraines and rock glaciers [
28,
29,
30].
The investigation of permafrost and its development in the glacier forefield Muragl has a tradition of more than 20 years. In 1999, Kneisel [
15] had already detected the coexistence of different types of ground ice and inferred different phases of permafrost evolution within the glacier forefield. These assumptions were based on geophysical differences and different thermal regimes and were supported by geomorphological evidence of a former polythermal regime of the Muragl glacier. These studies also suggested the presence of a massive ice core within the moraine complex. Based on the electrical resistivity value, it must be assumed that this massive ice core consists of sedimentary ice, according to the definition of Shumskii [
31]. Whether this massive ice core could be indicative of a glacier–permafrost interaction could not be proven beyond reasonable doubt, because sedimentological boundaries or internal shear planes were not detectable by resistivity surveys alone [
15,
16]. Hence, the objective of this study was to investigate the internal structures of the moraine complex with special emphasis on ice content and origin as well as sedimentological boundaries and internal shear planes in order to deduce process dynamics during moraine formation. In contrast to glacier forefields of large polar or subpolar glaciers, the sediments in small alpine glacier forefields, such as the glacier forefield Muragl, are dominated by coarse-grained materials like stones and boulders because of the short transport routes in alpine cirques. The processes during moraine formation in such coarse-grained material may differ from that in fine-grained sediments of larger forefields. Therefore, new findings from further geophysical investigations are presented. In addition to the ERT data already published in the past, further ERT profiles as well as GPR profiles were performed in the area of the thrust moraine complex. The use of GPR should enable a more detailed investigation of sedimentological boundaries and internal shear planes [
28,
32]. These findings offered better knowledge of the thrust moraine formation, which allowed us to generate a conceptual model of the moraine genesis in the glacier forefield Muragl.
2. Study Site
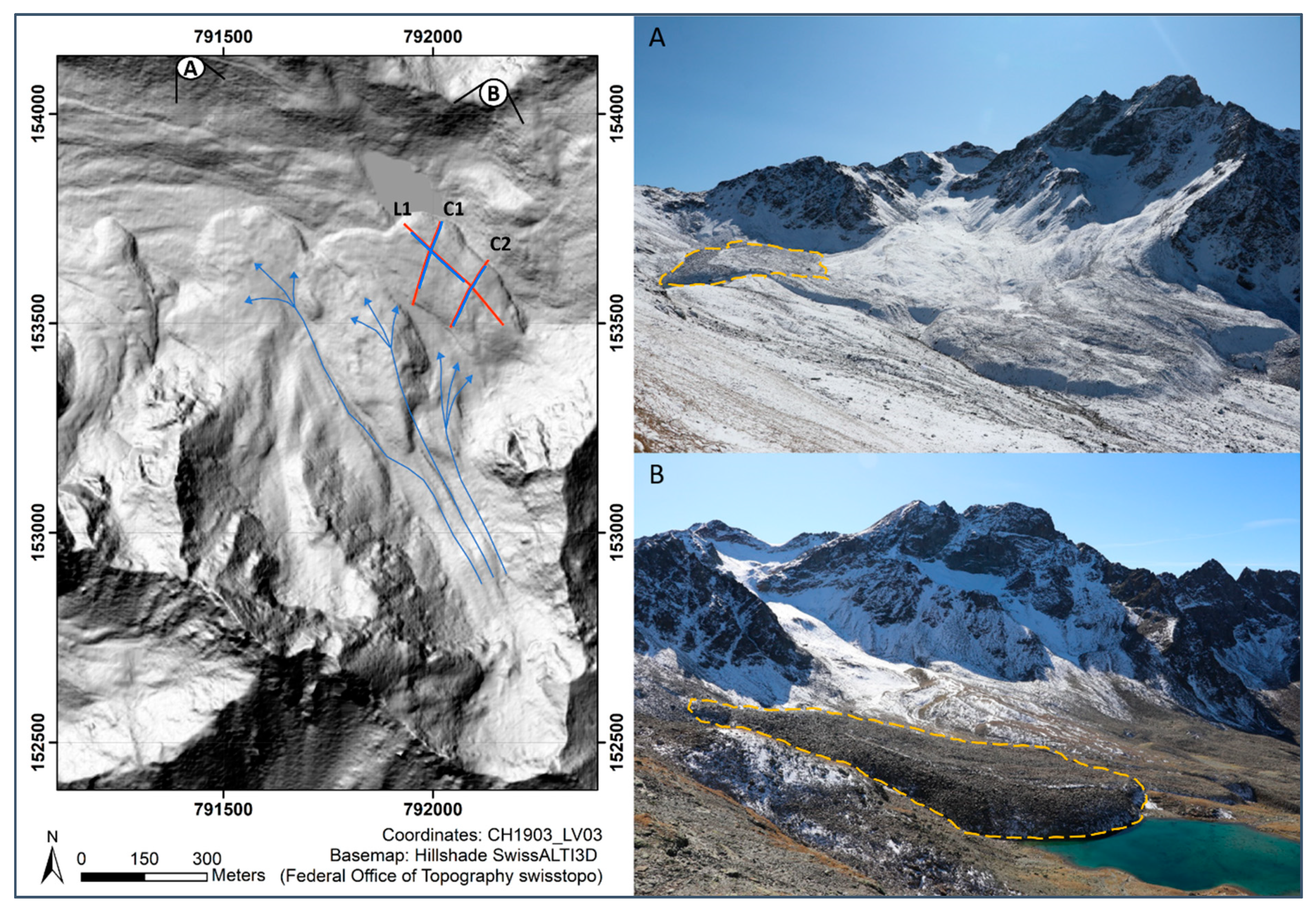
The glacier forefield Muragl (46°30′15″ N, 9°56′20″ E) (
Figure 1) is located between 2650 m and 2980 m a.s.l. in the north slope of Piz Muragl (Upper Engadine, Swiss Alps). The remnant of the former Muragl glacier extends currently between 2980 m and 3080 m a.s.l. and covers an area of only approximately 0.038 km
2 with a maximum ice thickness of 16 m as deduced by GPR soundings [
33].
The climate at this site is characterized by mean annual air temperatures between −2 and −4 °C and low precipitation (1000–1200 mm/y), which can be inferred from two nearby climate stations (Piz Corvatsch, 3302 m a.s.l., −5.4 °C, 1295 mm and Samedan 1709 m a.s.l., 2.0 °C, 713 mm) [
34,
35].
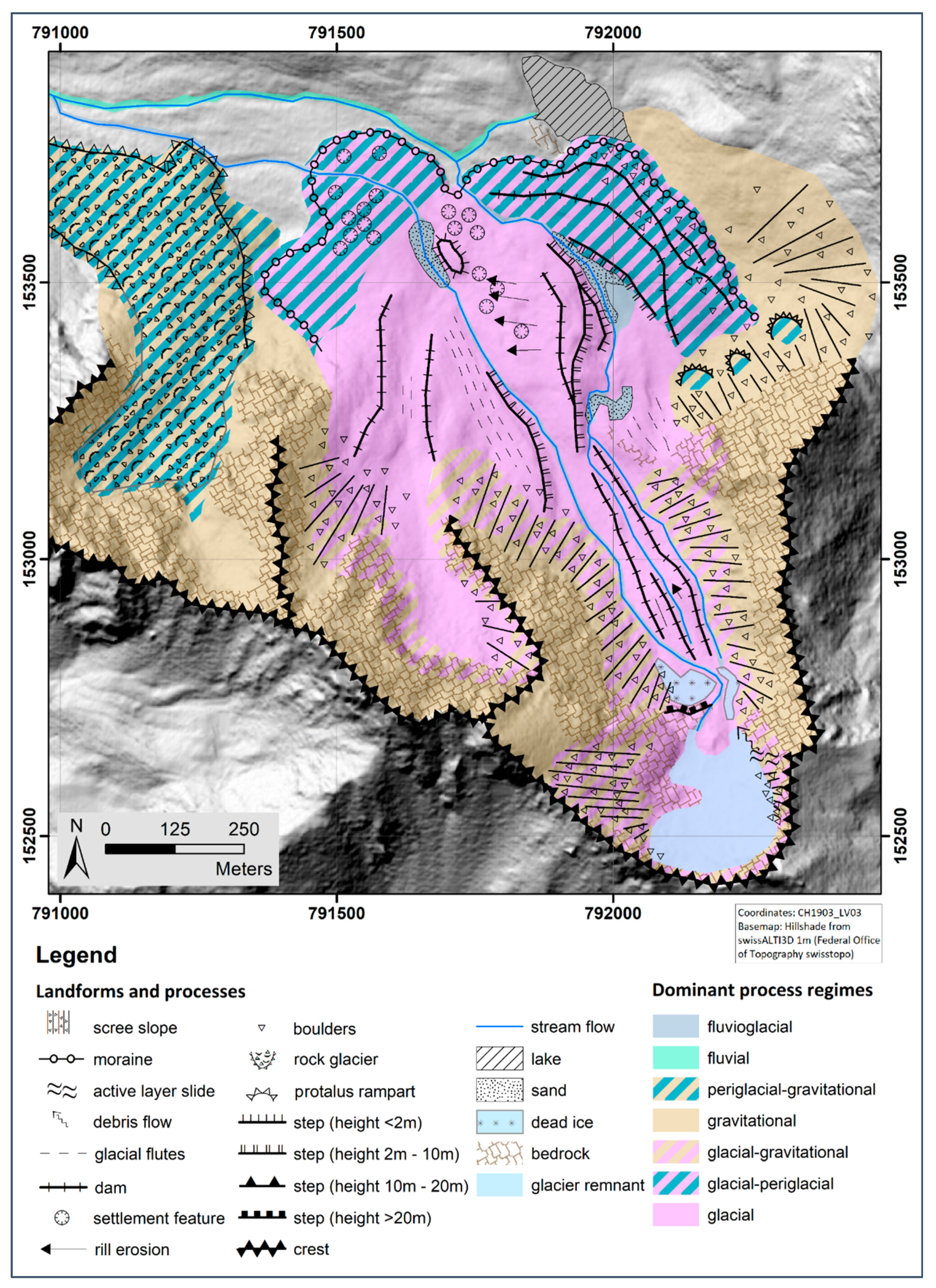
The geomorphology of the glacier forefield (
Figure 2) is dominated by the raised sediment bed (thickness of several meters to decameters) of the former Muragl glacier in the central and northwestern part and the well-developed thrust moraine complex in the northeastern part (highlighted in
Figure 1).
The elevated sediment bed and the thrust moraine complex roughly mark the outer limits of the Muragl glacier at the Little Ice Age (LIA) maximum, whereby it must be noted that the moraine and the sediment bed are subject to a permafrost-induced creep process after deglaciation, which continued to current times in some parts of the glacier forefield [
36]. In contrast to the thrust moraine in the northeastern part, which signals a glacier–permafrost interaction, glacial flutes in the central part of the forefield suggest a warm-based glacier and thus a polythermal regime of the former Muragl glacier. While several settlement features in the northwestern part suggest a melt out of buried ice or permafrost-related ground ice, the postglacial evolution of three protalus ramparts in the northwest exposed scree slopes adjacent to the thrust moraine complex implies a permafrost aggradation or at least stable permafrost conditions. Also prominent is a dome-like or ridge-like structure in the central part of the glacier forefield, which has a steep flank, especially in the direction of the thrust moraine.
4. Results and Interpretation
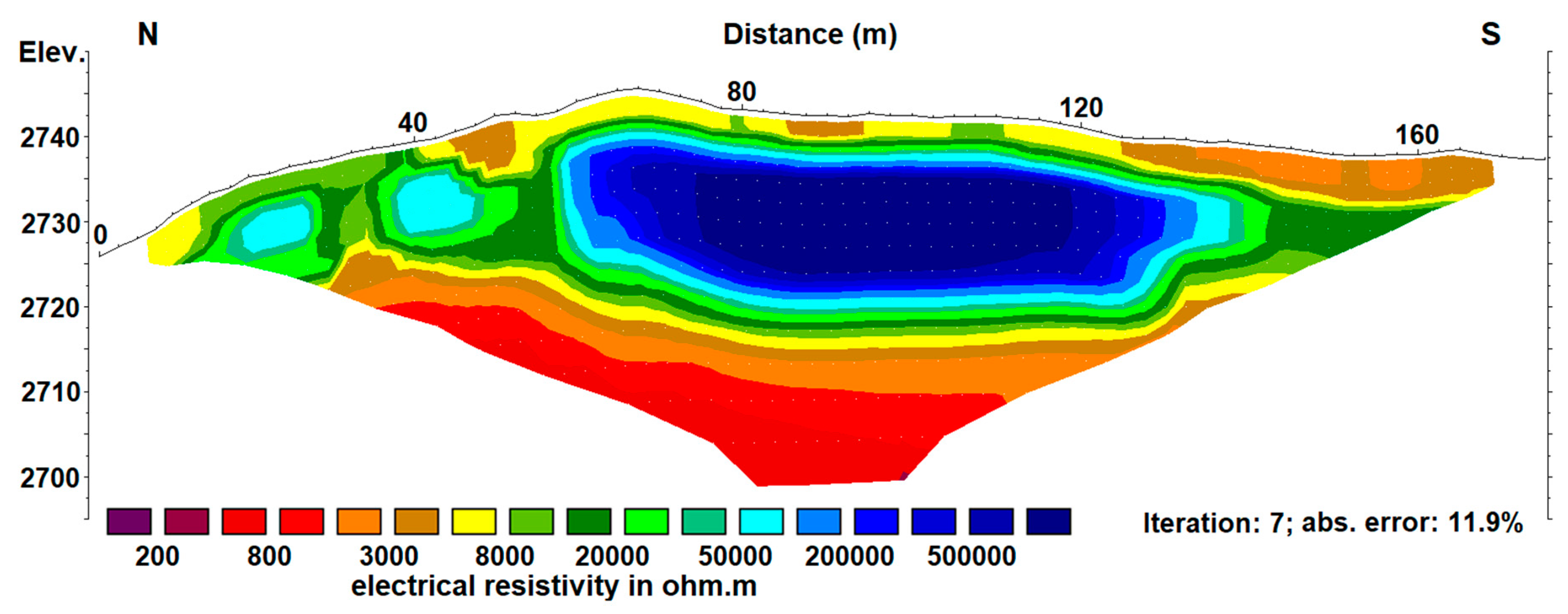
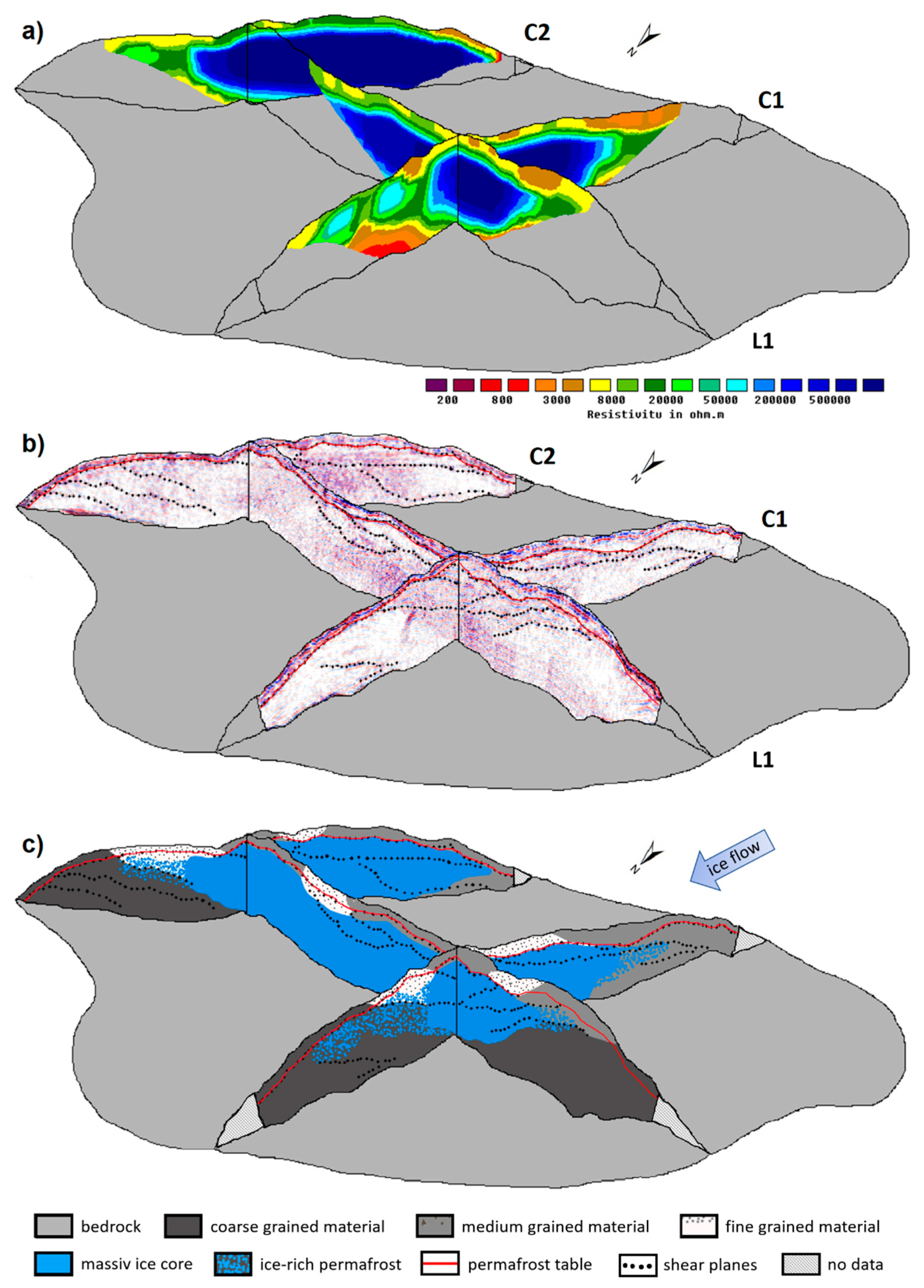
The ERT cross profile C1 (
Figure 3) shows a three-layered structure typical for thin permafrost occurrences. At the top of the profile, there is a 2 to 6 m thick layer with resistivity values between 2 and 15 kΩm. In the distal part of the moraine (north slope), the layer is slightly thinner and the resistivity values are between 5 and 15 kΩm, whereas the proximal area is characterized by a thicker uppermost layer and lower resistivity values (<5 kΩm). Based on the geomorphological situation and the resistivity values as well as the GPR data (cf.
Figure 4 and interpretations further below), this layer is interpreted as the active layer. Below the active layer, a large high resistivity anomaly exists in the central and proximal part of the moraine complex. It begins approximately 3 to 6 m below the surface and extends to a maximum depth of approximately 18 m. The lateral extent in the profile direction is about 70 m. The high resistivity area (values > 1.5 MΩm), which was previously detected by Kneisel [
15,
16], seems to be homogeneous and relatively sharp bounded and is interpreted as a massive ice core. In the distal moraine slope, two additional and slightly thinner (up to 10 m thick) high resistivity anomalies were detected. In contrast to the large anomaly in the central and proximal part, it is very prominent that the resistivity values (50–100 kΩm) are high, but are lower by an order of magnitude compared to the central part. Based on this finding, they were interpreted as ice-rich permafrost within the outermost, coarse blocky moraine ridge (blue speckles in
Figure 5c). Below the three anomalies, a sharp boundary to an underlying low resistivity layer (<3 kΩm) was detected. This layer was interpreted as unfrozen material. A massive ice core of the central part was also detected in the longitudinal profile (L1), which crosses C1 in the area of this structure. At the cross point of the profiles, the coincidence in terms of absolute resistivity values, depth, and thickness of the anomaly is striking. Furthermore, it also seems to extend from the longitudinal profile in an easterly direction, since a similar area of high resistivity can also be seen in the cross profile C2 further east. In this profile, it extends from the center of the moraine to the edge of the profile on the proximal moraine flank and is significantly thicker. Because of the very high resistivity values, similar to those in previous studies [
36], this anomaly is interpreted as a massive ice core of sedimentary or polygenetic origin. Its extent is also marked in the schematic model of the moraine complex (
Figure 5c).
In profile C1 and in L1, unfrozen material beneath the massive ice core was detected. In the second cross profile (C2), this layer was not detected. The massive ice core in this part of the moraine was too thick to penetrate it with the applied array length. Additionally, a smaller high resistivity anomaly in the outermost moraine ridge was detected in the second cross profile further east. At the top of the profiles C2 and L1, the active layer was characterized by resistivity values between 2 and 30 kΩm. In the distal flank of the moraine, it was 2 to 3 m thick, whereas it is 3–6 m thick in the proximal zone of the complex. Since the measurements were carried out in early September, the active layer had reached its maximum thickness and its base was comparable to the permafrost table. Variations of resistivity in the topmost layer matched the boundaries of different substrates in the moraine complex, which is probably due to different grain sizes and corresponding different moisture contents.
Results of the GPR surveying confirm these results and present new insights into the internal sedimentological structure of the moraine complex. In the central part of the moraine complex, CMP measurements (not shown) confirmed the assumption of a massive ice core because of high signal propagation velocities. These high values of around 0.16 m/ns are indicative of massive sedimentary ice and exceed the normal range of permafrost, determined as being between 0.11 and 0.15 m/ns in the common literature [
37,
38,
39,
40].
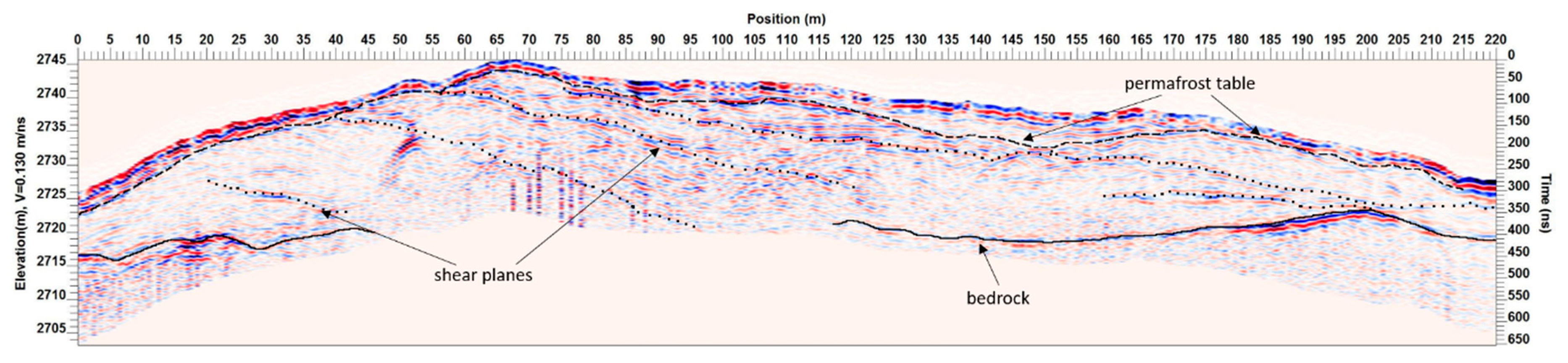
In the upper few meters of profile C1 (
Figure 4), but also in the other profiles, a more or less continuous, nearly surface-parallel reflector is visible, which is interpreted as the permafrost table. Its location matches the findings of the ERT measurements that the active layer in the proximal slope is deeper than in the distal slope. It can be observed that the area above the permafrost table is characterized by much stronger reflections than the area underneath. This is probably due to the alternating layers of blocks and cavities, which in combination with moisty surfaces of blocks and boulders within the active layer leads to a strong signal scattering.
Furthermore, the GPR measurements enabled a detection of the bedrock underneath broad parts of the moraine complex. There are strong linear continuous reflectors dipping into the central part of the moraine complex, which are different in reflection behavior in comparison with all other reflections. Specifically, the high signal intensity at this depth beneath the ground surface suggests a sharp boundary and strong contrasts in the geophysical properties. Looking at the depth of these reflectors, it fits well with the moraine height above the bedrock at the margins of the moraine complex.
In the two cross profiles, many linear dipping reflectors towards the proximal flank were detected, in addition to the nearly surface-parallel reflector of the permafrost table and the lowermost reflections of the bedrock. The reflectors start on the surface and dip at a relatively uniform angle into the proximal moraine flank. The start positions of the strongest of these dipping reflectors are equivalent to the positions of substrate boundaries between zones of coarse blocky material, blocky material, and stony material at the surface. These substrate boundaries were mapped along the profiles and were also visible in phase changes of the surface waves in the GPR profiles. The location at the substrate boundaries as well as the shape and the structure of these reflectors lead to the assumption that these reflectors mark sedimentological structures that originated during moraine formation. The dotted lines in
Figure 4 and
Figure 5b mark the main reflectors of this type. The areas between these reflectors are characterized by chaotic reflections, which indicate a missing sorting or layering of the moraine material. The shape and the orientation of these reflectors indicate that these structures could represent shear planes, which resulted from glaciotectonic processes during the formation of the moraine complex. This would also explain why these linear reflectors run through the assumed massive ice core and do not end at its boundaries. The glacial thrusting leads to an inclusion and transportation of subglacial till into the ice and thus to a concentration of fine-grained sediments along these shear planes. In turn, this sediment concentration leads to a stronger geophysical contrast within the ice body, so that it is visible as a continuous or discontinuous linear reflector amidst the chaotic reflections of the surrounding ice–debris mixture.
When comparing the depth of the lowermost reflector and the results of the ERT measurements, a coincidence between the two data sets occurs. The location of the bedrock reflector and the boundary between the high resistivity anomaly and the underlying low resistivity layer in the central part of the moraine complex correspond to each other. Accordingly, it can be assumed that the low resistivity layer at the bottom of the profiles C1 and L1 is to be equated with unfrozen bedrock beneath the frozen moraine material. Another comparison of the results from ERT and GPR shows that the reflection intensity and density in the GPR data are noticeably higher in the areas of the high resistivity anomalies of the ERT data. This is surprising at first, assuming that the center of the moraine is characterized by a massive ice core. The strong reflections do not deny this; however, they indicate a high degree of impurity of the ice or a high proportion of debris in the ice. Assuming that this is basal thrusted glacier ice of the basal and frontal parts of the glacier, such a concentration of debris would not be unusual but is even to be expected. The assumptions of the internal structures of the moraine complex were summarized in a conceptual model, which is shown in
Figure 5c. It presents a schematic model of the internal moraine structures including the massive ice core, the ice-rich permafrost lenses in the outermost moraine ridges as well as linear structures like the permafrost table and the detected shear planes. Additionally, the different dominating clast size of each moraine ridge or thrust block is presented.
5. Discussion
Evidence of a former polythermal regime of the Muragl glacier is given by the strongly differentiated morphology within the forefield. One clear evidence is the coexistence of a thrust moraine complex and glacial flutes within the glacier forefield. While the thrust moraine is a clear evidence of permafrost in the marginal positions, the flutes signal temperate conditions in the central part of the glacier forefield. The cause of this could be the relief of the former glacier bed, which led to a canalization of the ice into two narrowed streams through a dome-like structure in the central apron (see
Figure 1 and
Figure 2). The channeling led to convergent flow in the central apron and consequently to an increase in pressure and internal friction, which could contribute to a tempering of the glacier. Following the veined canal, especially in the orographic right part of the apron, it was possible to spread strongly (divergent flow) (see
Figure 1), resulting in lower ice thicknesses and lower pressures. Thus, the pressure melting point possibly could not be reached and the glacier froze to the bed. These differences in the subglacial thermal regime have had a major impact on permafrost distribution in the glacier forefield even after deglaciation [
14,
15]. As is also similar in other glacier forefields, a direct link between sub- or englacial conditions and the distribution of permafrost in the glacier forefield was also detected in ice-marginal positions [
41].
A differentiation of frozen and unfrozen materials based on geophysical properties, especially electrical resistivity, is quite common in the field of permafrost research. In this case study, values for the unfrozen active layer varied between 1.5 and 30 kΩm and showed a significant dependence on the substrate classes. While the resistivity values of the active layer ranged between 1.5 and 8 kΩm in areas with fine-grained materials, they increased up to 30 kΩm in areas of coarse blocky moraine material. These values match the observations from other studies [
15,
22,
36], but the strong spatial variations complicate the interpretation and delineation of the active layer thickness. A clear differentiation between frozen and unfrozen sediments using a single threshold is not possible because of the changing substrate conditions at the surface. Nevertheless, because of the mapped substrate classes along the profile and the particular threshold of each substrate class, a delineation of the active layer is still possible.
The determination of different ice types is more complex. In the context of this study, two different types classified by Shumskii [
31], namely sedimentary ice and congelation ice, are particularly important. The fact that determination is possible with geoelectrical methods has already been shown in some studies; the boundary value of the electrical resistivity values between the two ice types was determined at a few MΩm (for glacier ice in the European Alps). According to King [
42] or Vonder Mühll [
20], the resistivity values of congelation ice are between 10 kΩm and a few MΩm, whereas the values of sedimentary ice are more than 10 MΩm. The resistivity values of the anomaly in the central part of the moraine complex were higher than 1.5 MΩm, which is therefore lower than the assumed threshold value. Nevertheless, former ERT measurements on the Muragl glacier proved that the resistivity values of the glacier ice were around 2 MΩm in some areas [
15], and are therefore similar to the values detected within the moraine complex.
Since profile C2 is located at a similar position as the profile that was shown by Kneisel and Kääb [
36] (profile was measured in reverse direction and a few meters further north), a comparison of the structures and the resistivity values is possible. The internal structures of the moraine complex did not change significantly, but the unprocessed raw data showed slightly lower resistivity values for the data presented herein compared to those measured in 2002. This could be due to the slightly differing profile position, but it could also be due to an alteration in the physical properties of the massive ice core, induced by percolating melt water and increasing temperatures. Such a slightly decreasing effect of electrical resistivity values was observed by Mollaret et al. [
43] at several permafrost sites within the European Alps.
The GPR data could also not absolutely clarify the origin of the ice core. Its margins are not visible as a single sharp boundary, but the reflection behavior changes significantly, which stands out if comparing the data from ERT and GPR. The reflections in the high resistivity area of the moraine complex are much stronger than in the other parts. According to theory, the area should be transparent for electromagnetic waves if it contains a pure massive ice core. The intense reflections would therefore tend to disprove a pure massive ice core, but considering the position in the glacial system, we would not expect pure ice. The ice in the cold-based frontal part of a polythermal glacier is particularly subject to strong glaciotectonic shearing that leads to the incorporation of debris [
44,
45,
46,
47,
48]. Consequently, the sedimentary ice has a high content of debris and is not transparent for electromagnetic signals. A sedimentary origin of the ice would also explain the high signal velocities of 0.16 m/ns that were determined in the center of the moraine during the CMP measurements. This value is greater than the expected value for permafrost and fits well with the expected values for buried glacier ice, which are between 0.15 and 0.17 m/ns [
49,
50].
The detected linear structures within the moraine complex could also be a result of the thrusting in front of the advancing glacier. Their alignment and the accordance with the substrate boundaries lead to the assumption that these must be shear planes, which result from the glaciotectonic processes occurring during the moraine genesis. The alignment of the different linear structures fits well with observations from other studies, which investigated the internal structures of thrust moraines [
44,
45,
50,
51]. The linear shape of these reflectors and the absence of larger faults are a direct hint to brittle deformation of the moraine material during genesis and therefore evidence of frozen ground conditions at that time. Specifically, the fact that the spaces in between the linear reflectors are characterized by chaotic reflections and therefore by a missing layering strengthens the theory of the shear planes. If the different layers were formed by slow glacial accumulation, such as the process of dumping, then the material would have an adjustment [
52] that would be indicated by ordered reflections [
29,
51]. Since these are not present, this gives evidence of a shift in the blocks of frozen materials. As a strong cohesion of the individual blocks must prevail for this type of displacement, the question arises as to how it could come to the process of thrusting in such a coarse material at all. This could be explained only by very high contents of interstitial ice within the coarse-grained loose material, which ensure a corresponding cohesion of the material. On the other hand, low temperatures and/or low water contents within the ice leads to hard-frozen ground and prevents a plastic deformability, so that a brittle deformation is the only way to respond to the strain [
8]. Regardless of this, however, it is clear that the moraine complex in the center is characterized by very high ice contents, which will also be of great importance for the future development of the moraine complex and its morphology. In particular, the increasing degradation of permafrost in the course of global warming can lead to distinct changes in surface topography through melt out of the massive ice core as it was shown in other studies [
53,
54,
55].
6. Conclusions
The combination of electrical resistivity tomography and ground-penetrating radar enabled a more detailed investigation of the internal structures of the moraine complex in the glacier forefield Muragl. In addition to the already roughly known distribution of resistivity values within the moraine complex, GPR allowed the determination of internal sedimentological structures of the complex. The detected structures resemble those of large thrust moraine complexes only on a smaller scale and give evidence of a glaciotectonic origin of the moraine complex. That, in turn, confirms the assumption of a glacier–permafrost interaction during moraine formation and reinforces the theory of a polygenetic origin of the detected massive ice core in the central part of the moraine complex. At the same time, however, the question arises as to how it could undergo the process of thrusting in such coarse-grained material, since the process has so far only been verified in much finer sediments, such as sands or gravels. One answer may be the high ice contents in the coarse blocky material, which prevented a plastic deformation of the moraine material. The internal structures and the occurrence of the different units and layers of the moraine contributed to a better understanding of the moraine genesis and enabled the creation of a conceptual model of thrust moraine formation in the glacier forefield Muragl. While the study of moraine formation initially represents pure fundamental research, the study of current internal structures in such cases also shows a need for applied research in this field of research. In the context of climate change and global warming, this type of moraines in particular, which are characterized by very high ice contents, may undergo intense morphological changes as well as reactivation of moraine material.