Stiffness Control of Variable Serial Elastic Actuators: Energy Efficiency through Exploitation of Natural Dynamics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
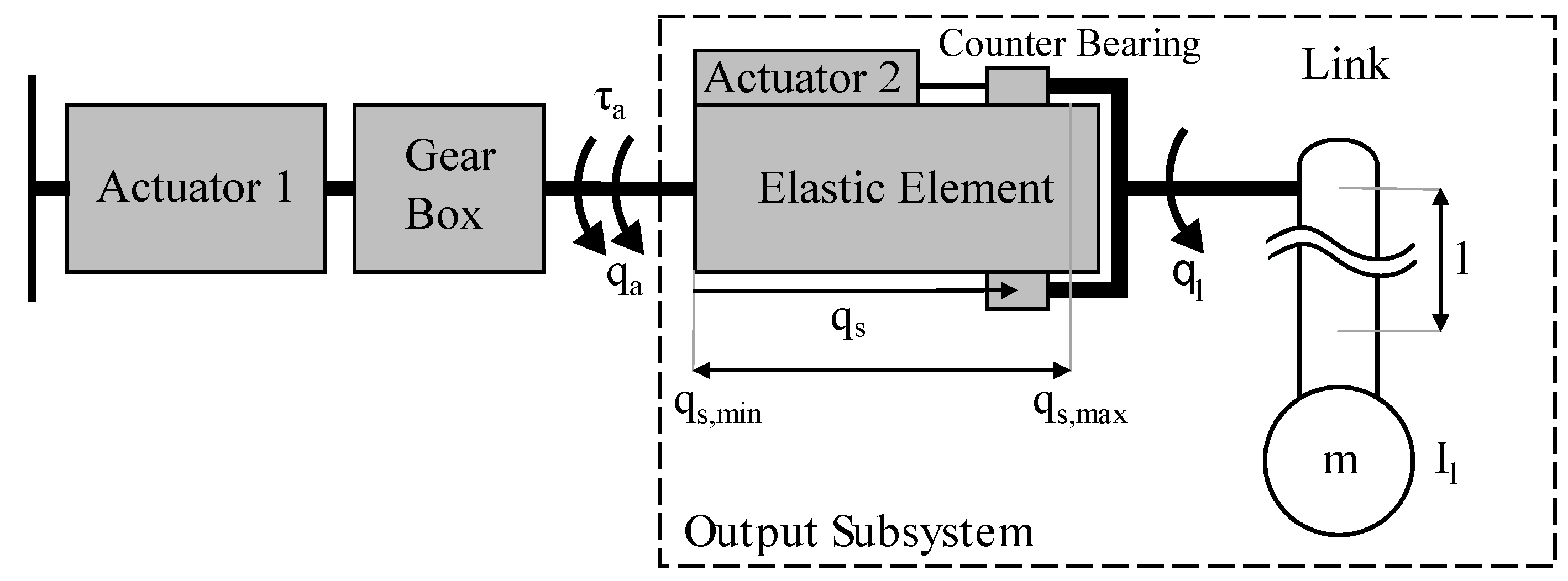
2. Actuator Modeling
2.1. Dynamics Equations
2.2. Natural Dynamics
3. Energy Consumption Analysis
3.1. Energy Calculation
3.2. Electrical Model Extensions
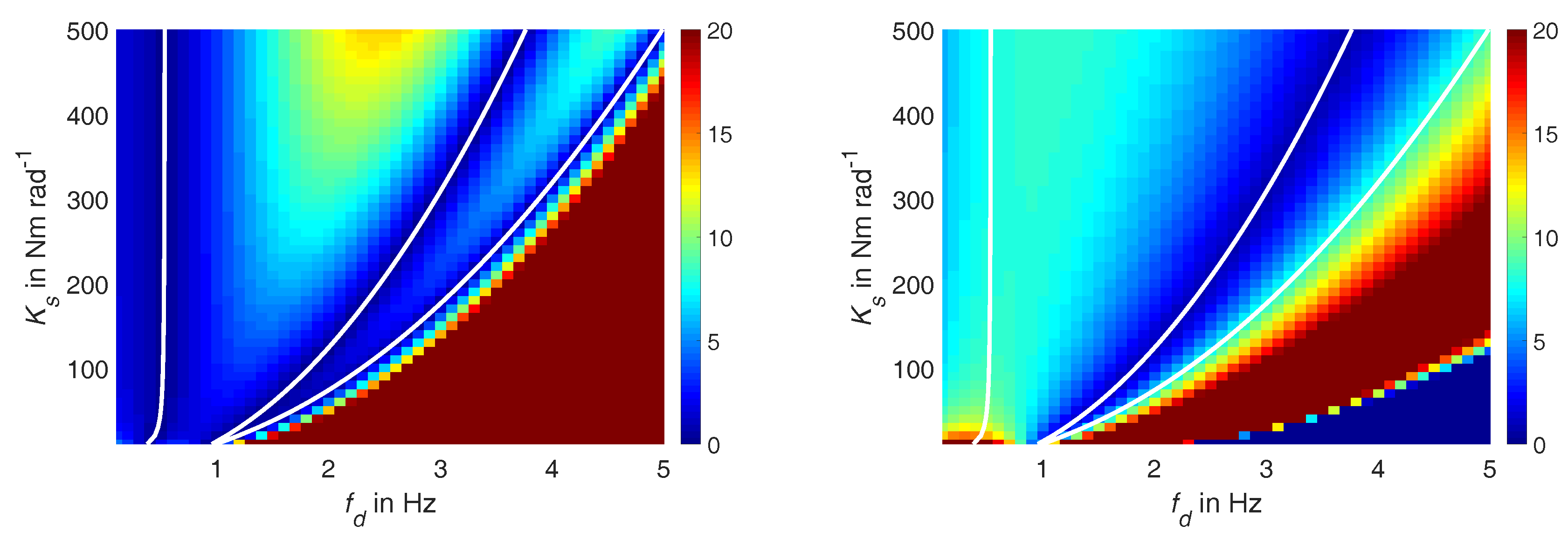
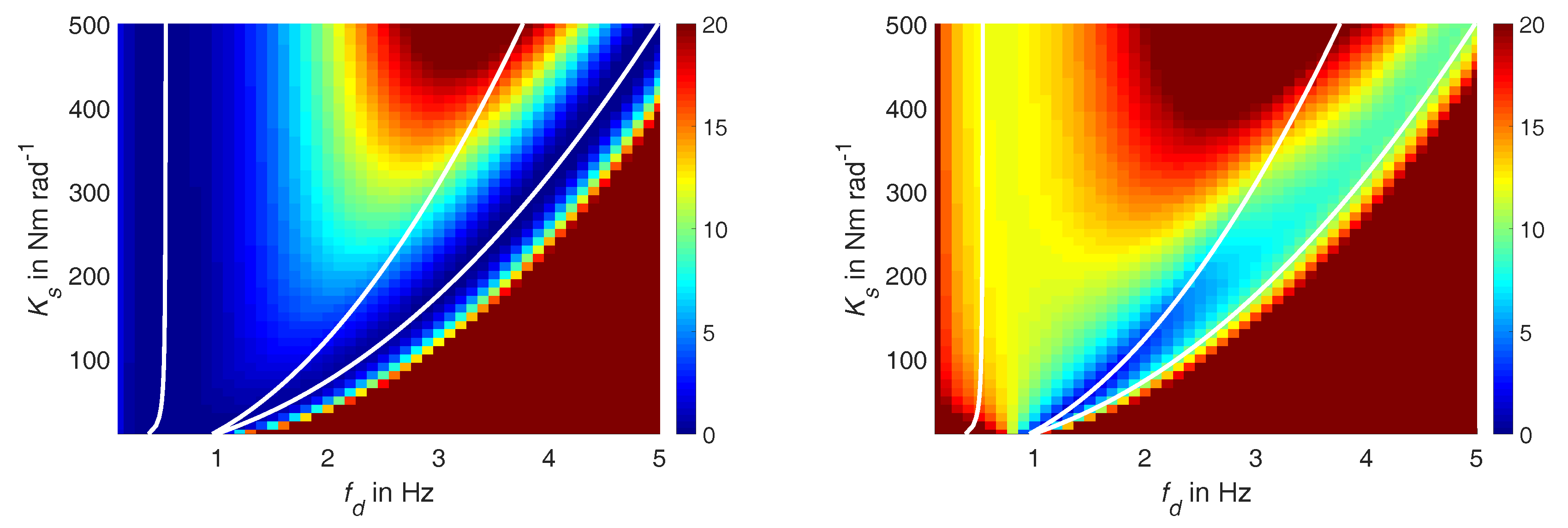
3.3. Results
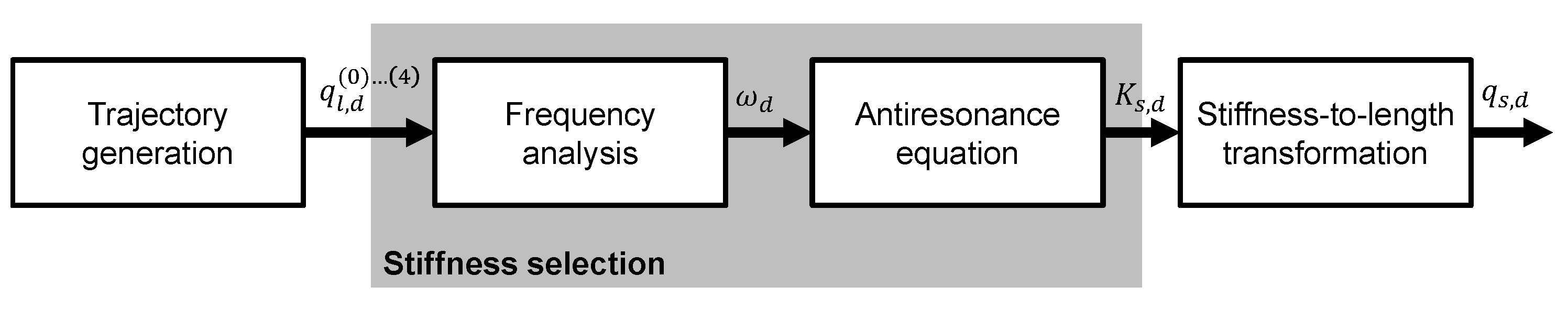
4. Stiffness Control
5. Experimental Evaluation
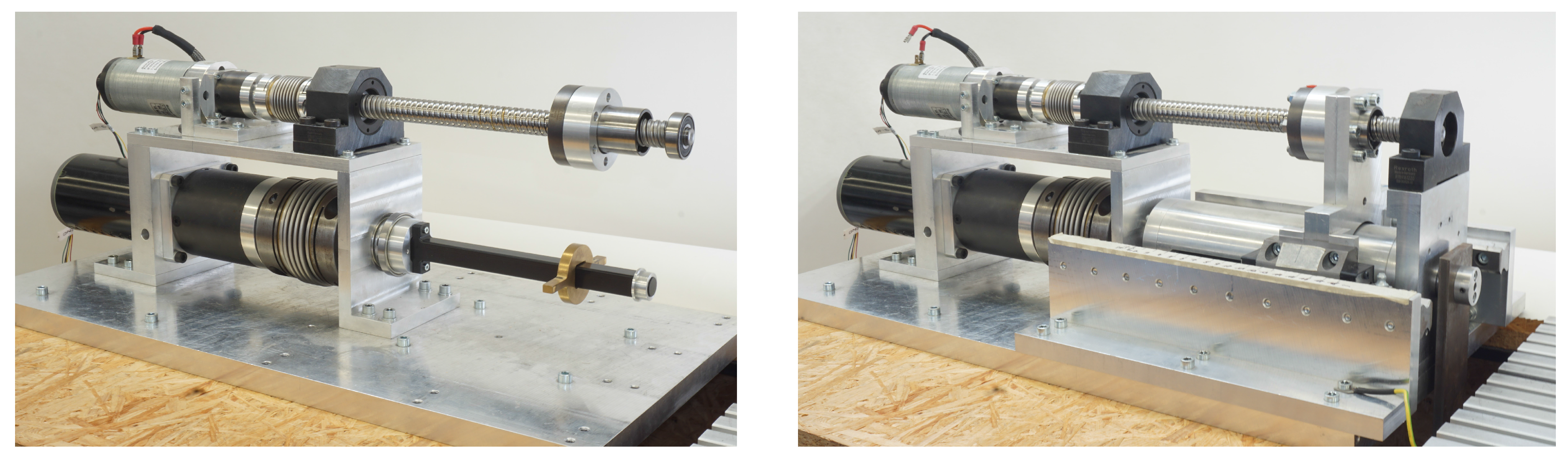
5.1. Experimental Setup
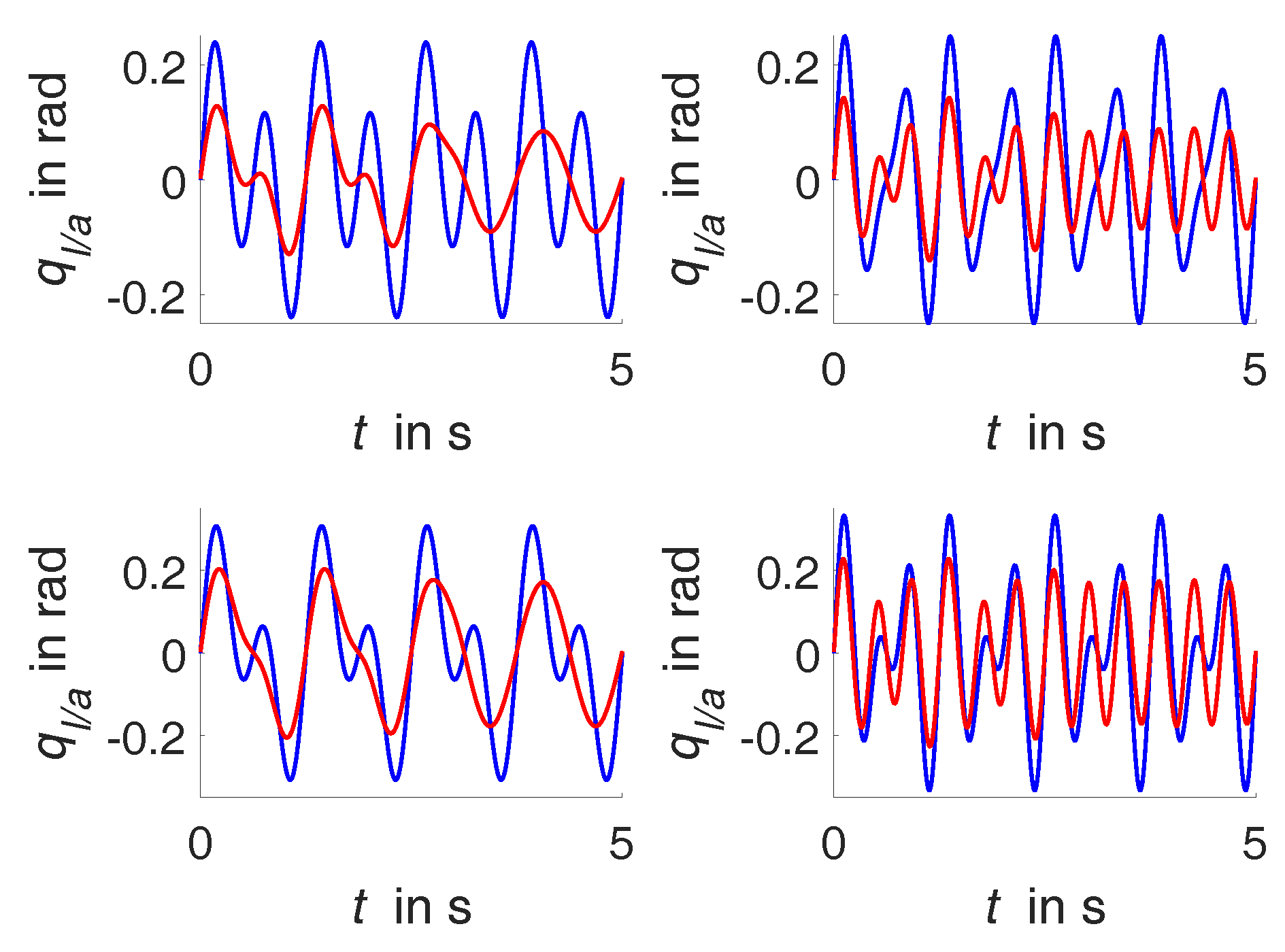
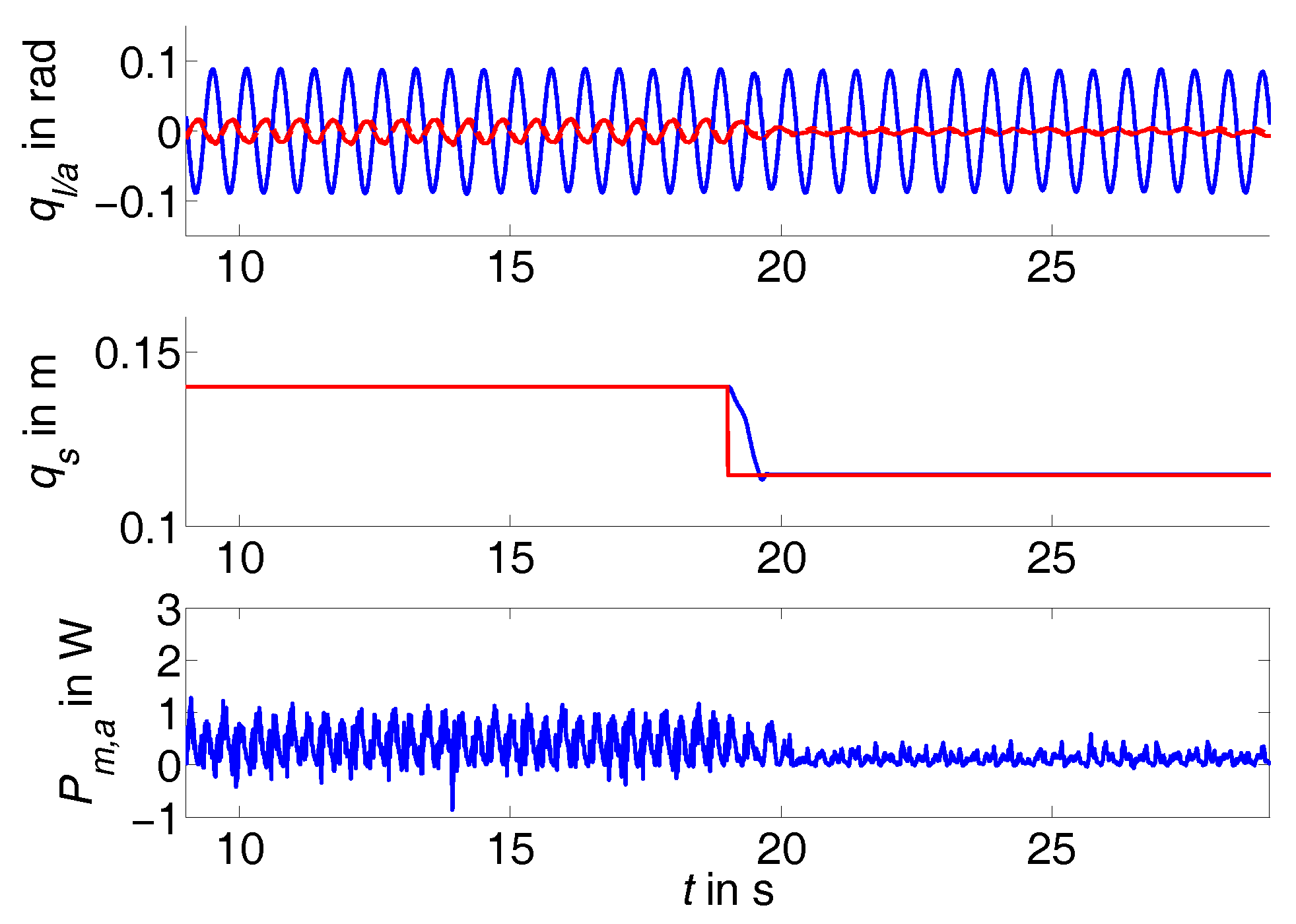
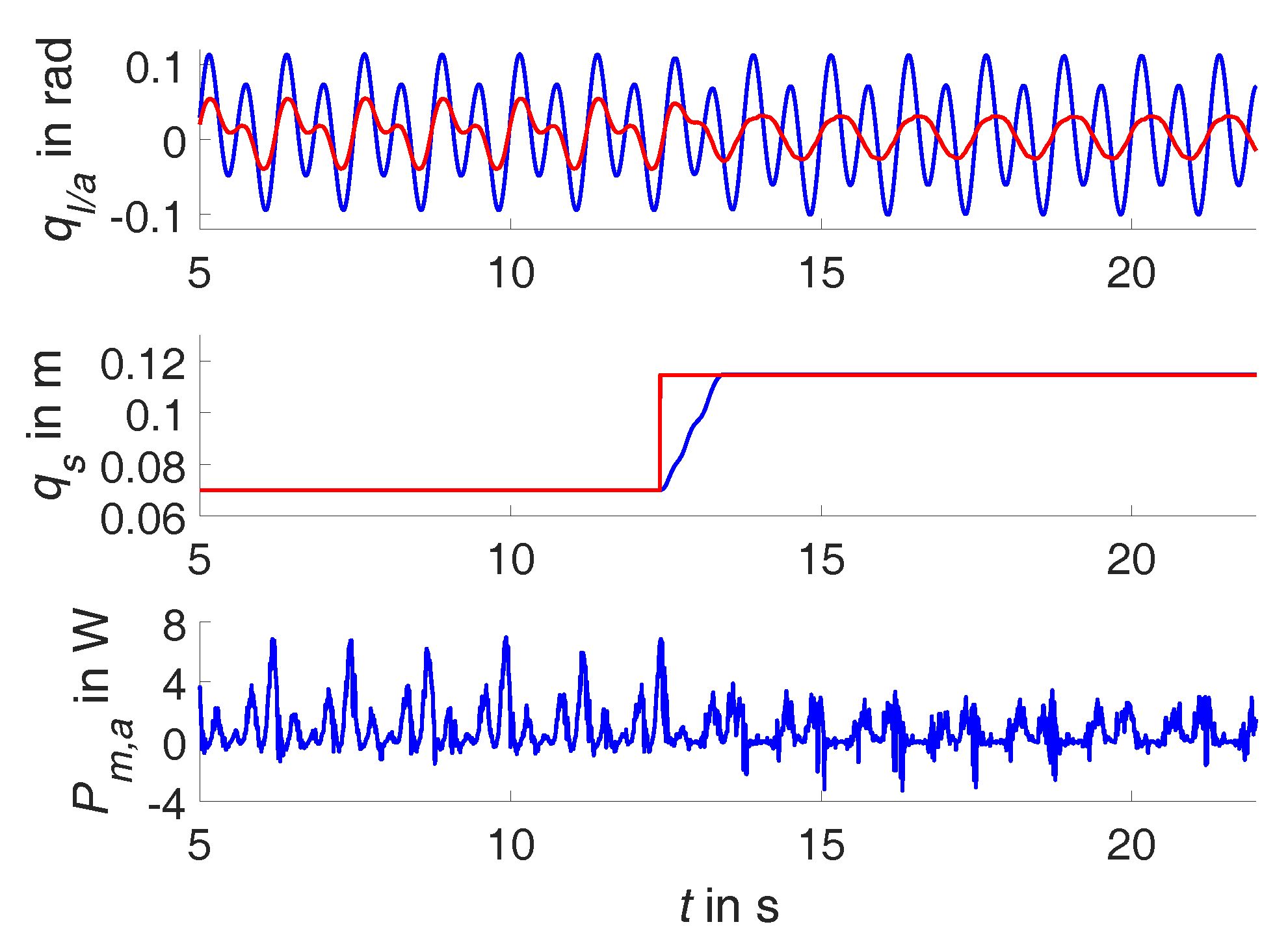
5.2. Sinusoidal Trajectory Experiments
6. Discussion and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albu-Schäffer, A.; Eiberger, O.; Grebenstein, M.; Haddadin, S.; Ott, C.; Wimbock, T.; Wolf, S.; Hirzinger, G. Soft Robotics. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2008, 15, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderborght, B.; Albu-Schaeffer, A.; Bicchi, A.; Burdet, E.; Caldwell, D.G.; Carloni, R.; Catalano, M.; Eiberger, O.; Friedl, W.; Ganesh, G.; et al. Variable Impedance Actuators: A review. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2013, 61, 1601–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddadin, S.; Albu-Schaeffer, A.; De Luca, A.; Hirzinger, G. Collision Detection and Reaction: A Contribution to Safe Physical Human–Robot Interaction. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Nice, France, 22–26 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lens, T.; von Stryk, O. Investigation of Safety in Human–Robot-Interaction for a Series Elastic, Tendon-Driven Robot Driven Robot Arm. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vilamoura, Portugal, 7–12 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Windrich, M.; Grimmer, M.; Christ, O.; Rinderknecht, S.; Beckerle, P. Active Lower Limb Prosthetics: A Systematic Review of Design Issues and Solutions. BioMed. Eng. OnLine 2016, 15, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veneman, J.; Burdet, E.; van der Kooij, H.; Lefeber, D. Emerging Directions in Lower Limb Externally Wearable Robots For Gait Rehabilitation and Augmentation—A Review. In Advances in Cooperative Robotics; World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd.: Singapore, 2017; pp. 840–850. [Google Scholar]
- Vanderborght, B.; Van Ham, R.; Lefeber, D.; Sugar, T.G.; Hollander, K.W. Comparison of Mechanical Design and Energy Consumption of Adaptable, Passive-Compliant Actuators. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2009, 28, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraten, T.; Beckerle, P.; Furnémont, R.; Mathijssen, G.; Vanderborght, B.; Lefeber, D. Series and Parallel Elastic Actuation: Impact of Natural Dynamics on Power and Energy Consumption. Mech. Mach. Theory 2016, 102, 232–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckerle, P.; Verstraten, T.; Mathijssen, G.; Furnémont, R.; Vanderborght, B.; Lefeber, D. Series and Parallel Elastic Actuation: Influence of Operating Positions on Design and Control. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2017, 22, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, G.A.; Williamson, M.M. Series Elastic Actuators. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 5–9 August 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Van Ham, R.; Sugar, T.G.; Vanderborght, B.; Hollander, K.W.; Lefeber, D. Compliant Actuator Designs Review of Actuators with Passive Adjustable Compliance/Controllable Stiffness for Robotic Applications. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2009, 16, 81–94. [Google Scholar]
- Vanderborght, B.; Verrelst, B.; Van Ham, R.; Van Damme, M.; Beyl, P.; Lefeber, D. Development of a Compliance Controller to Reduce Energy Consumption for Bipedal Robots. Auton. Robot. 2008, 24, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckerle, P.; Wojtusch, J.; Schuy, J.; Strah, B.; Rinderknecht, S.; Stryk, O.V. Power-Optimized Stiffness and Nonlinear Position Control of an Actuator with Variable Torsion Stiffness. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, Wollongong, NSW, Australia, 9–12 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Palli, G.; Melchiorri, C. On the Control of Redundant Robots with Variable Stiffness Actuation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vilamoura, Portugal, 7–12 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tonietti, G.; Schiavi, R.; Bicchi, A. Design and Control of a Variable Stiffness Actuator for Safe and Fast Physical Human/Robot Interaction. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Barcelona, Spain, 18–22 April 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Huh, S.; Tonietti, G.; Bicchi, A. Neural Network Based Robust Adaptive Control for a Variable Stiffness Actuator. In Proceedings of the Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation, Ajaccio, France, 25–27 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Albu-Schäffer, A.; Wolf, S.; Eiberger, O.; Haddadin, S.; Petit, F.; Chalon, M. Dynamic Modelling and Control of Variable Stiffness Actuators. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Anchorage, AK, USA, 3–8 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sardellitti, I.; Medrano-Cerda, G.A.; Tsagarakis, N.; Jafari, A.; Caldwell, D.G. Gain Scheduling Control for a Class of Variable Stiffness Actuators Based on Lever Mechanisms. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2013, 29, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, S.H.; Bien, Z. Robust Sliding Mode Control of a Robot Manipulator based on Variable Structure-Model Reference Adaptive Control Approach. IET Control Theory Appl. 2007, 1, 1355–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, A.; Flacco, F.; Bicchi, A.; Schiavi, R. Nonlinear Decoupled Motion-Stiffness Control and Collision Detection/Reaction for the VSA-II Variable Stiffness Device. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, St. Louis, MO, USA, 10–15 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Beckerle, P.; Rinderknecht, S. A Variable Stiffness Control Strategy Using System Dynamics and Spectral Trajectory Analysis. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Human–Machine Systems, Cyborgs and Enhancing Devices, Manchester, UK, 13 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Beckerle, P. Human–Machine-Centered Design and Actuation of Lower Limb Prosthetic Systems; Shaker Verlag: Herzogenrath, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Albu-Schäffer, A. Regelung von Robotern mit Elastischen Gelenken am Beispiel der DLR-Leichtbauarme. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität München, München, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lendermann, M.; Stuhlenmiller, F.; Erler, P.; Beckerle, P.; Rinderknecht, S. A Systematic Approach to Experimental Modeling of Elastic Actuators by Component-Wise Parameter Identification. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Erler, P.; Beckerle, P.; Strah, B.; Rinderknecht, S. Experimental Comparison of Nonlinear Motion Control Methods for a Variable Stiffness Actuator. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, Sao Paulo, Brazil, 12–15 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Schuy, J.; Beckerle, P.; Wojtusch, J.; Rinderknecht, S.; von Stryk, O. Conception and Evaluation of a Novel Variable Torsion Stiffness for Biomechanical Applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, Rome, Italy, 24–27 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Schuy, J.; Beckerle, P.; Faber, J.; Wojtusch, J.; Rinderknecht, S.; von Stryk, O. Dimensioning and Evaluation of the Elastic Element in a Variable Torsion Stiffness Actuator. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, Wollongong, NSW, Australia, 9–12 July 2013. [Google Scholar]


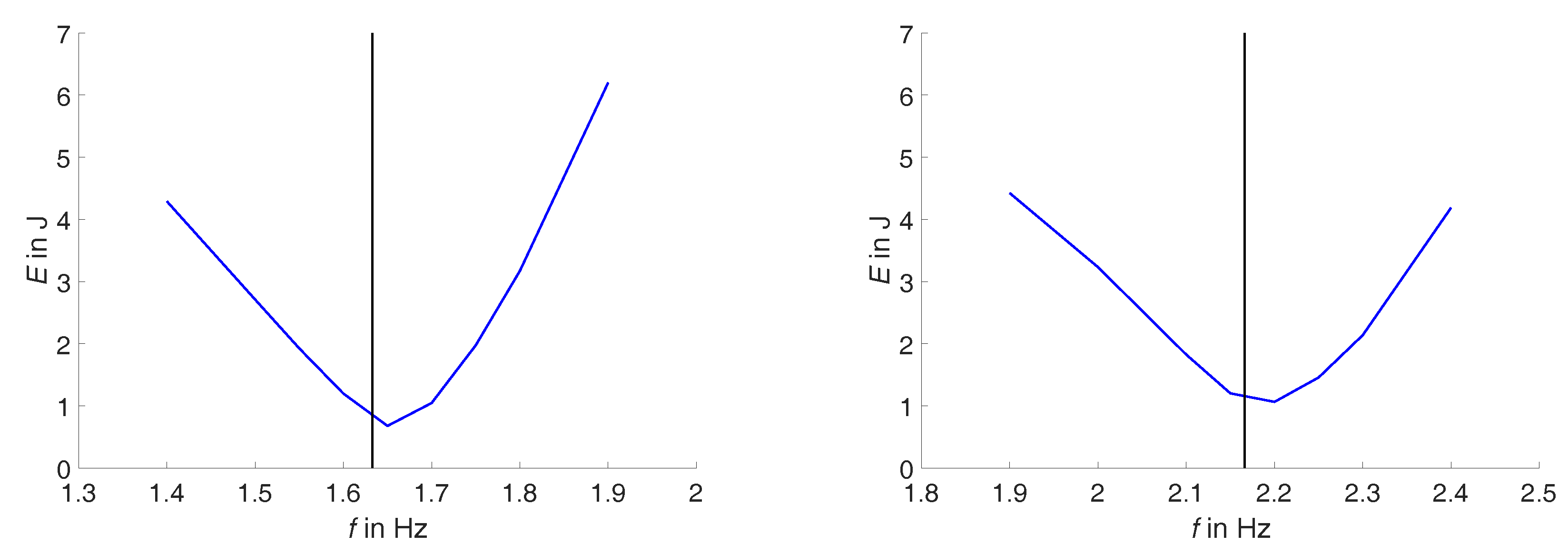
| Mechanical Properties | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Inertia link | 0.94 | Inertia actuator | 1.15 |
| Mass link | 6.81 | Length link | 0.362 |
| Coulomb fric. coeff. link | 3.3 × 10−2 | Coulomb fric. coeff. actuator | 2.4 |
| Viscous fric. coeff. | −0.8 | Stribeck fric. amplitude | 376.1 |
| Stribeck form factor | −0.13 | Stribeck friction velocity | 3.6 × 104 |
| Gear ratio | 80 | ||
| Electrical Properties | |||
| Terminal resistance R | 0.4 Ω | Torque constant | 55 −1 |
| Terminal inductance L | 0.8 | Speed constant | 173.6 −1 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beckerle, P.; Stuhlenmiller, F.; Rinderknecht, S. Stiffness Control of Variable Serial Elastic Actuators: Energy Efficiency through Exploitation of Natural Dynamics. Actuators 2017, 6, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/act6040028
Beckerle P, Stuhlenmiller F, Rinderknecht S. Stiffness Control of Variable Serial Elastic Actuators: Energy Efficiency through Exploitation of Natural Dynamics. Actuators. 2017; 6(4):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/act6040028
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeckerle, Philipp, Florian Stuhlenmiller, and Stephan Rinderknecht. 2017. "Stiffness Control of Variable Serial Elastic Actuators: Energy Efficiency through Exploitation of Natural Dynamics" Actuators 6, no. 4: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/act6040028
APA StyleBeckerle, P., Stuhlenmiller, F., & Rinderknecht, S. (2017). Stiffness Control of Variable Serial Elastic Actuators: Energy Efficiency through Exploitation of Natural Dynamics. Actuators, 6(4), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/act6040028