A Preemptive Scan Speed Control Strategy Based on Topographic Data for Optimized Atomic Force Microscopy Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
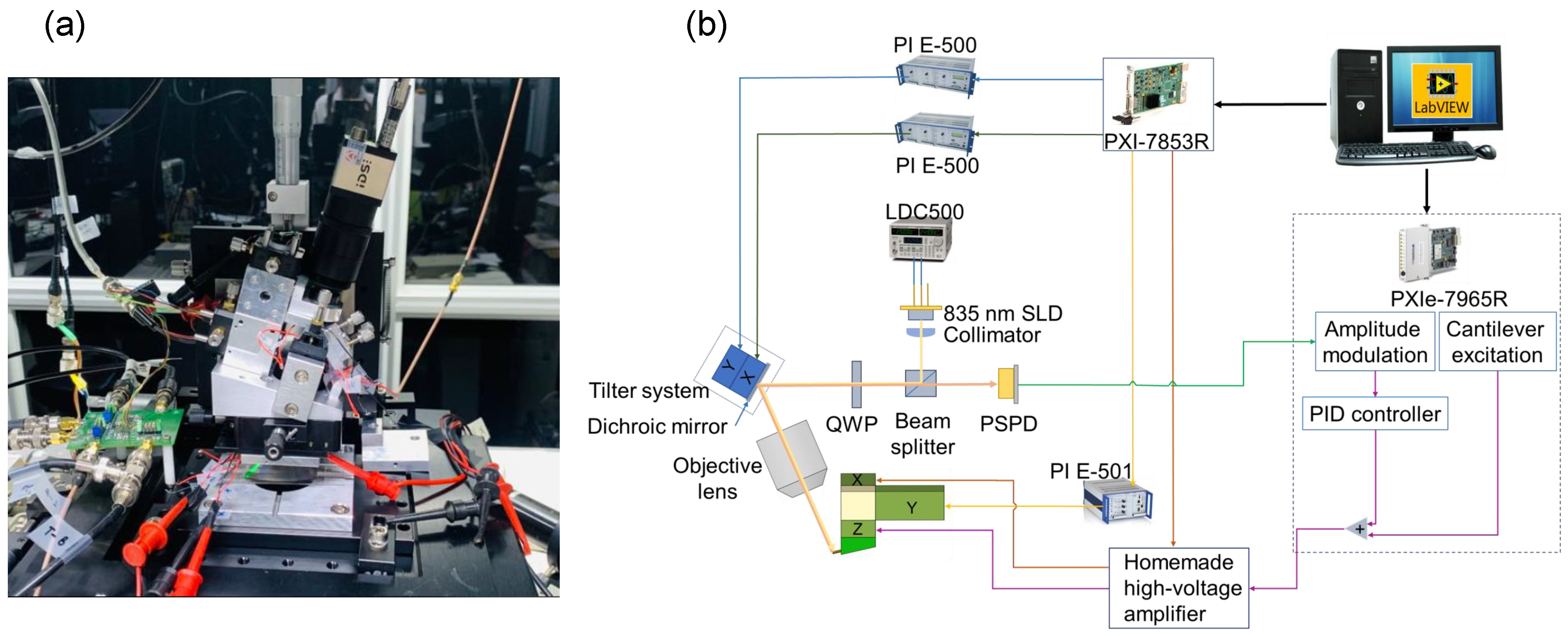
2.1. Experimental Setup
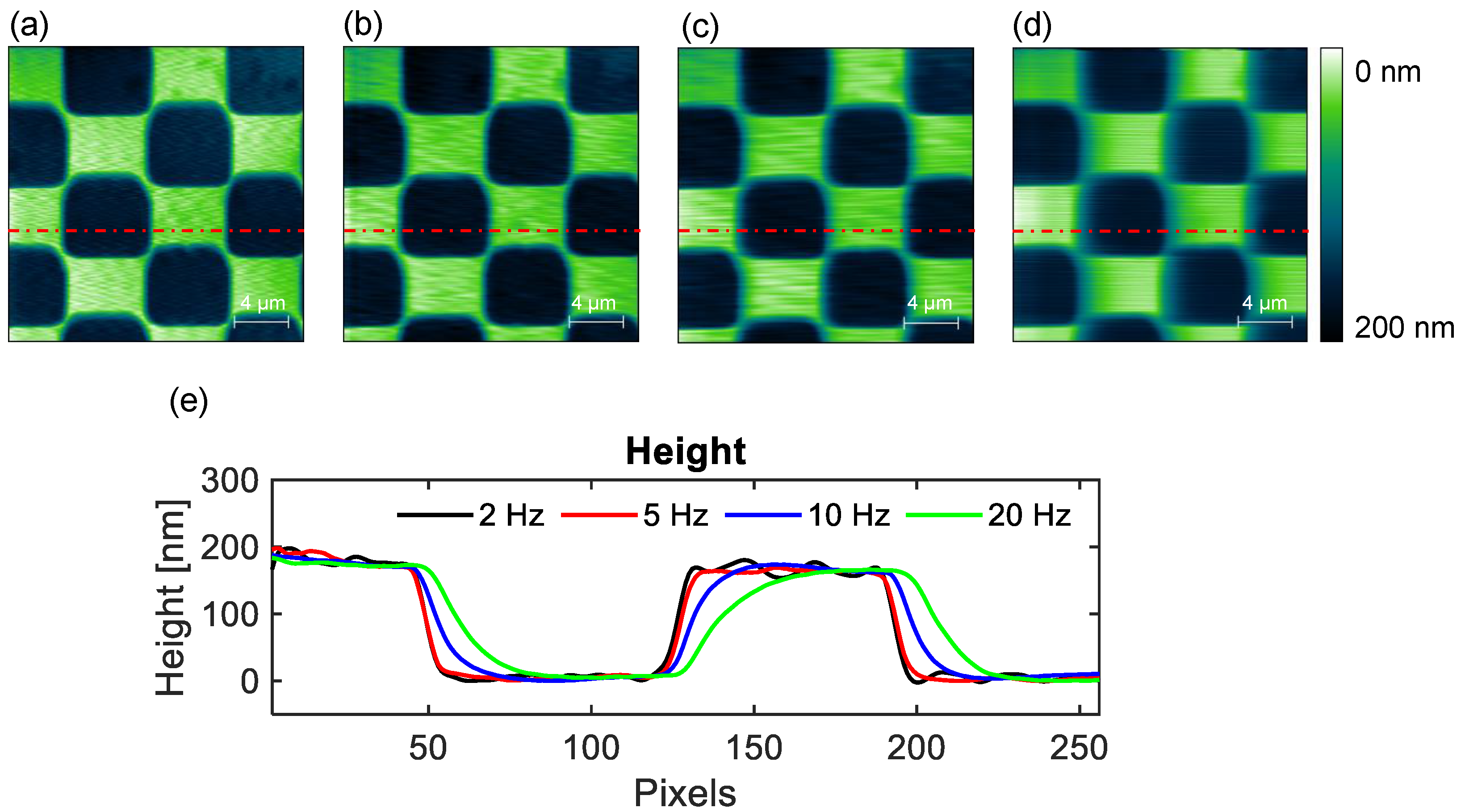
2.2. The Relationship Between Scan Speed and Image Quality
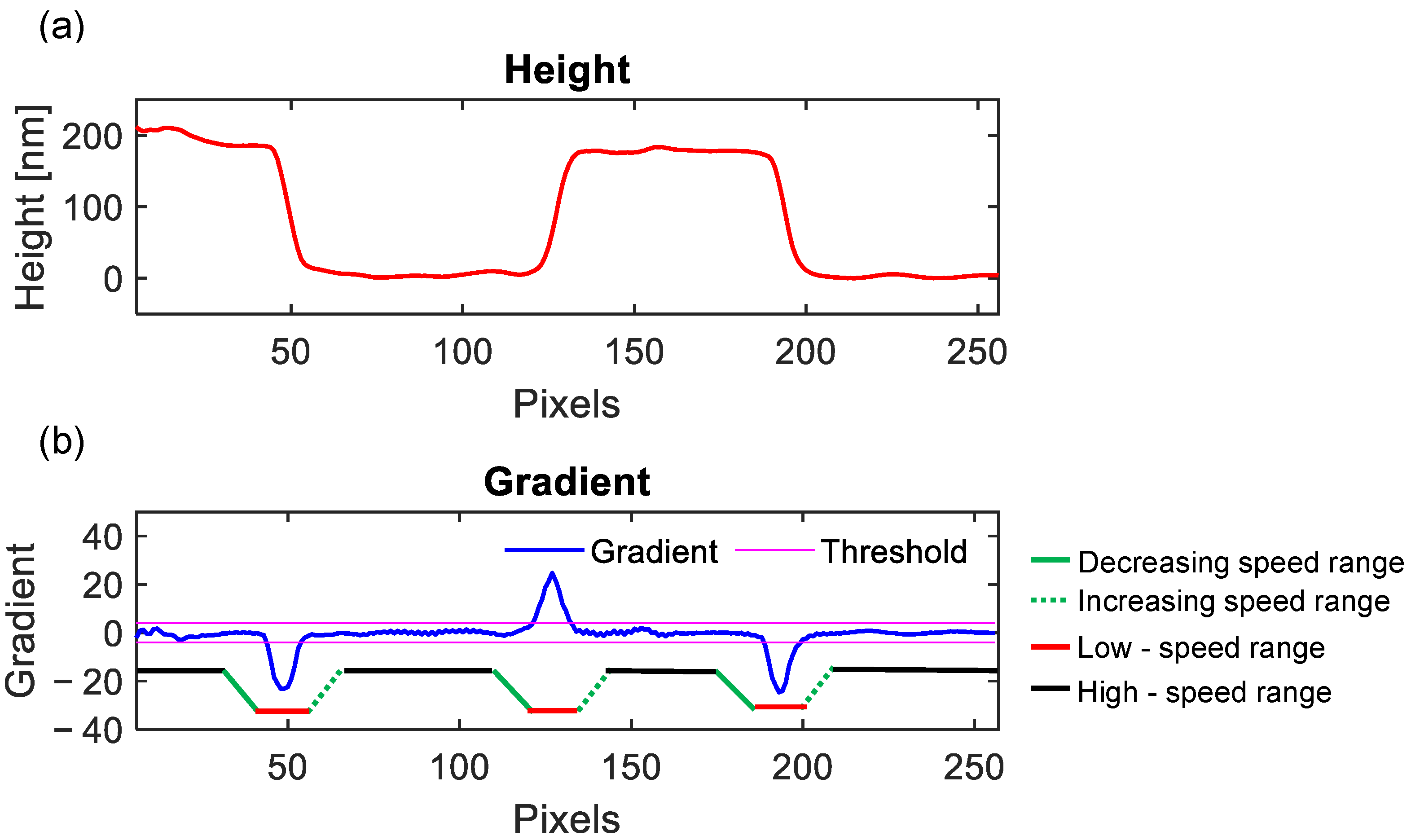
2.3. Real-Time Rate Adaptive Control Algorithm Design
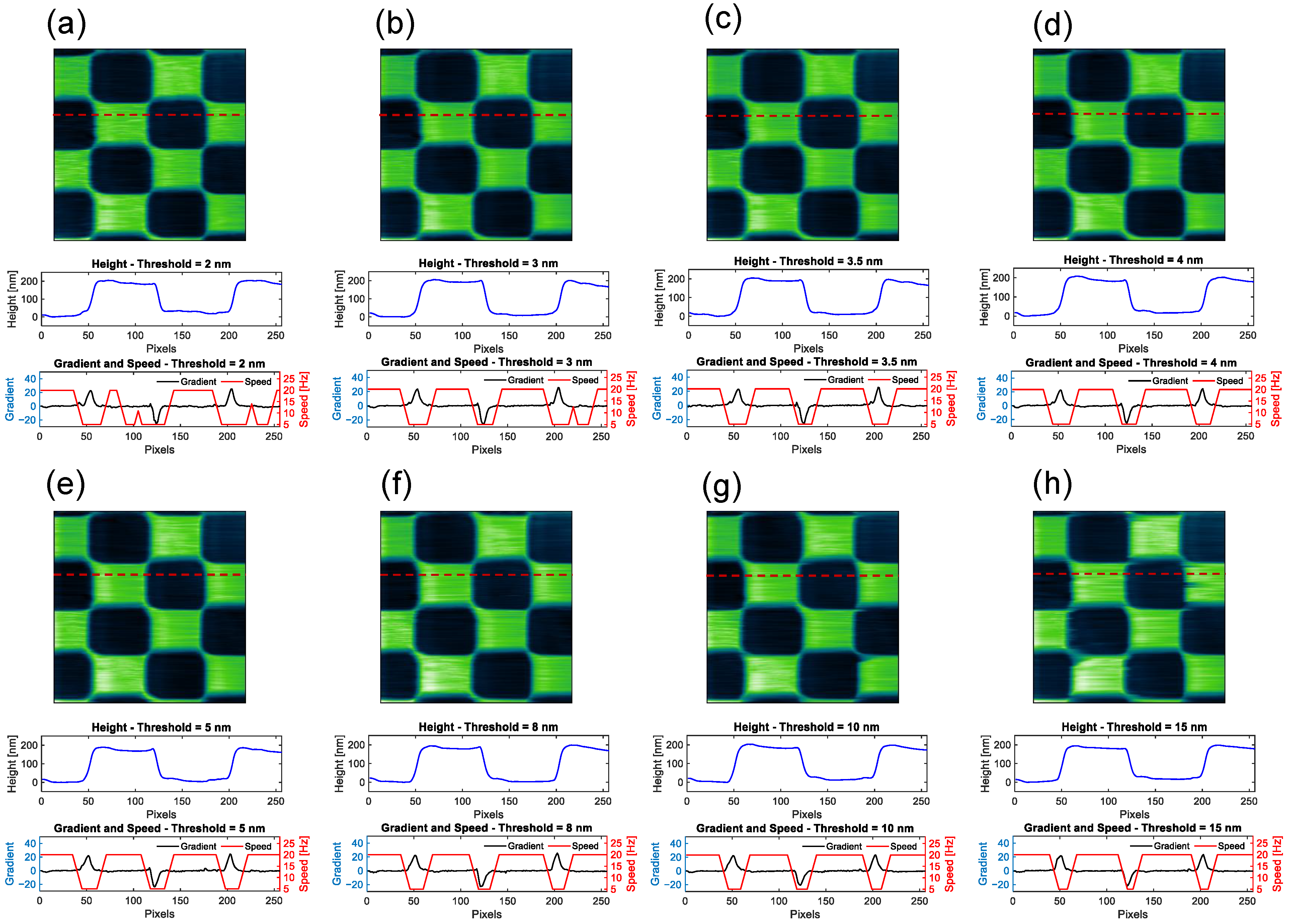
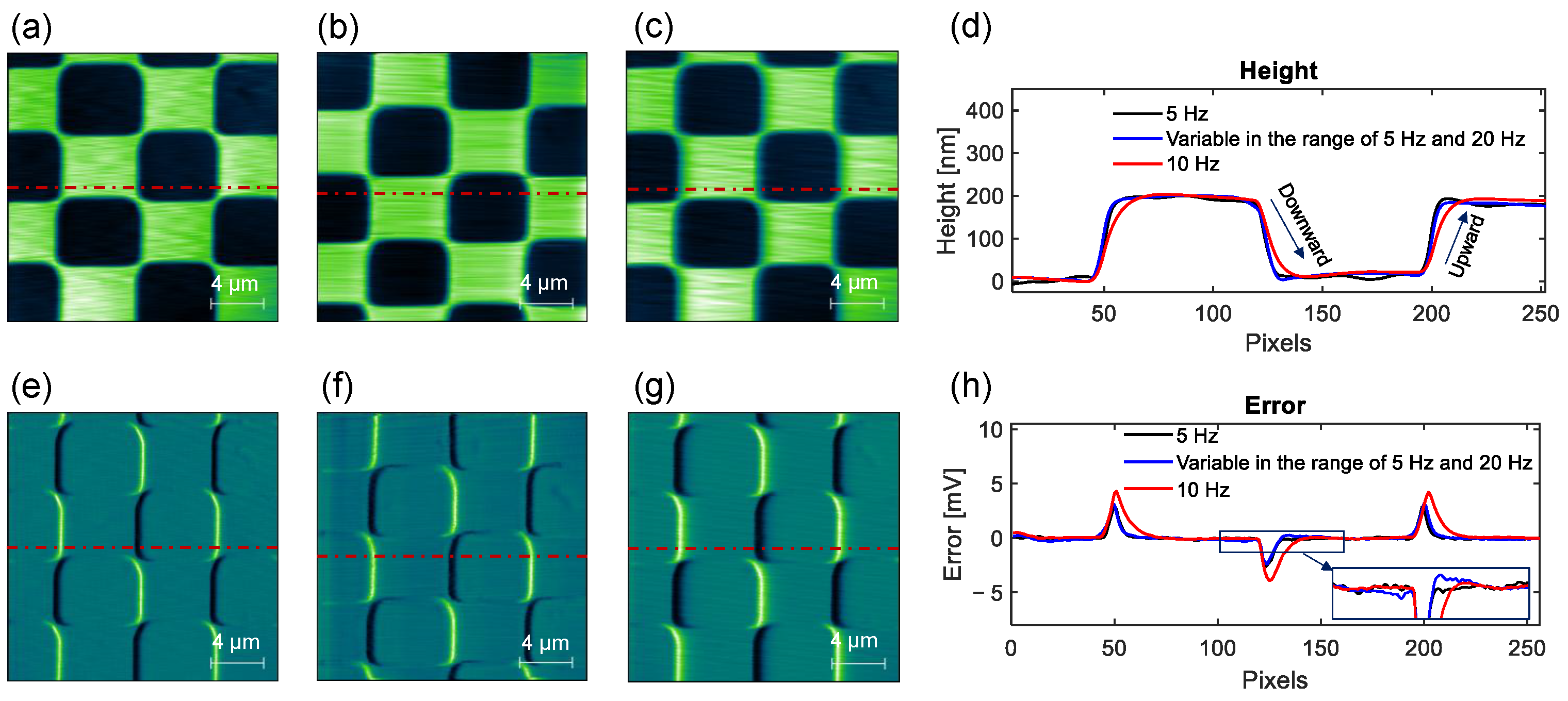
3. Results and Discussion
Effectiveness of the Proposed Variable Scan Speed Control Method
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Binnig, G.; Quate, C.F.; Gerber, C. Atomic force microscope. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1986, 56, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Sakai, N.; Yoshida, A.; Uekusa, Y.; Yagi, A.; Imaoka, Y.; Takeyasu, K. High-speed atomic force microscopy combined with inverted optical microscopy for studying cellular events. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Kong, M.; Wu, S.; Xu, X.; Wang, D. Error Analysis of the Combined-Scan High-Speed Atomic Force Microscopy. Sensors 2021, 21, 6139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viani, M.B.; Schäffer, T.E.; Chand, A.; Rief, M.; Gaub, H.E.; Hansma, P.K. Small cantilevers for force spectroscopy of single molecules. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 86, 2258–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantner, G.E.; Schitter, G.; Kindt, J.H.; Ivanov, T.; Ivanova, K.; Patel, R.; Hansma, P.K. Components for high speed atomic force microscopy. Ultramicroscopy 2006, 106, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, S.; Uchihashi, T.; Iino, R.; Okazaki, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Igarashi, K.; Ando, T. High-speed atomic force microscope combined with single-molecule fluorescence microscope. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2013, 84, 073706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umakoshi, T.; Fukuda, S.; Iino, R.; Uchihashi, T.; Ando, T. High-speed near-field fluorescence microscopy combined with high-speed atomic force microscopy for biological studies. BBA-Gen. Subj. 2020, 1864, 129325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Sajidah, E.S.; Kondo, S.; Narimatsu, S.; Sandira, M.I.; Higashiguchi, Y.; Wong, R.W. An Efficient Method for Isolating and Purifying Nuclei from Mice Brain for Single-Molecule Imaging Using High-Speed Atomic Force Microscopy. Cells 2024, 13, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Uchihashi, T. Development of Wide-area Tip-scanning High-speed Atomic Force Microscopy. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE the International Conference on Manipulation, Manufacturing and Measurement on the Nanoscale (3M-NANO), Zhenjiang, China, 4–8 August 2019; pp. 281–285. [Google Scholar]
- Uchihashi, T.; Watanabe, H.; Fukuda, S.; Shibata, M.; Ando, T. Functional extension of high-speed AFM for wider biological applications. Ultramicroscopy 2016, 160, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadikhaye, S.P.; Yong, Y.K.; Reza Moheimani, S.O. A serial-kinematic nanopositioner for high-speed atomic force microscopy. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2014, 85, 105104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schitter, G.; Thurner, P.J.; Hansma, P.K. Design and input-shaping control of a novel scanner for high-speed atomic force microscopy. Mechatronics 2008, 18, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphris, A.D.L.; Miles, M.J.; Hobbs, J.K. A mechanical microscope: High-speed atomic force microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 034106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuma, T.; Okazaki, Y.; Kodera, N.; Uchihashi, T.; Ando, T. High resonance frequency force microscope scanner using inertia balance support. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 243119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, T.; Uchihashi, T.; Fukuma, T. High-speed atomic force microscopy for nano-visualization of dynamic biomolecular processes. Prog. Surf. Sci. 2008, 83, 337–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, T.; Kodera, N.; Takai, E.; Maruyama, D.; Saito, K.; Toda, A. A high-speed atomic force microscope for studying biological macromolecules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 12468–12472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, K.; Usho, S.; Yamada, S.; Furuya, S.; Yoshida, K.; Asakawa, H.; Fukuma, T. Separate-type scanner and wideband high-voltage amplifier for atomic-resolution and high-speed atomic force microscopy. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2013, 84, 043705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenton, B.J.; Leang, K.K. Design and control of a three-axis serial-kinematic high-bandwidth nanopositioner. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2011, 17, 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Y.K.; Bhikkaji, B.; Moheimani, S.R.R. Design, modeling, and FPAA-based control of a high-speed atomic force microscope nanopositioner. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2012, 18, 1060–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schitter, G.; Menold, P.; Knapp, H.F.; Allgöwer, F.; Stemmer, A. High performance feedback for fast scanning atomic force microscopes. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2001, 72, 3320–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhikkaji, B.; Moheimani, S.R. Integral resonant control of a piezoelectric tube actuator for fast nanoscale positioning. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2008, 13, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadikhaye, S.P.; Yong, Y.K.; Bhikkaji, B.; Moheimani, S.R. Control of a piezoelectrically actuated high-speed serial-kinematic AFM nanopositioner. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 025030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantner, G.E.; Hegarty, P.; Kindt, J.H.; Schitter, G.; Cidade, G.A.; Hansma, P.K. Data acquisition system for high speed atomic force microscopy. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2005, 76, 026118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Shan, G.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qian, J. Real-time scan speed control of the atomic force microscopy for reducing imaging time based on sample topography. Micron 2018, 106, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Chen, Y.; Wu, T.; Li, H.; Luo, J. Adaptive AFM imaging based on object detection using compressive sensing. Micron 2022, 154, 103197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wan, J.; Hu, X.; Xu, L.; Wu, S.; Hu, X. A rate adaptive control method for improving the imaging speed of atomic force microscopy. Ultramicroscopy 2015, 155, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Schuh, A.; Rangelow, I.W. Adaptive AFM scan speed control for high aspect ratio fast structure tracking. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2014, 85, 103706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| The scanning point is in a rough range or is about to enter a rough range. | − | − | |
| The scanning point is in a smooth range. | + | + |
| Fixed Scan Speed (5 Hz) | Variable Scan Speed (Equivalent to 11.4 Hz) | Fixed Scan Speed (10 Hz) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time [s] | 52 | 22.5 | 26 | |
| Slope of downward edge | −15.79 | −13.63 | −6.98 | |
| Slope of upward edge | 17.16 | 17.05 | 8.19 | |
| MSE [mV] | 13.56 | 14.49 | 42.82 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, T.T.; Juma, O.M.; Otieno, L.O.; Nguyen, T.N.; Lee, Y.J. A Preemptive Scan Speed Control Strategy Based on Topographic Data for Optimized Atomic Force Microscopy Imaging. Actuators 2025, 14, 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14060262
Nguyen TT, Juma OM, Otieno LO, Nguyen TN, Lee YJ. A Preemptive Scan Speed Control Strategy Based on Topographic Data for Optimized Atomic Force Microscopy Imaging. Actuators. 2025; 14(6):262. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14060262
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Thi Thu, Oyoo Michael Juma, Luke Oduor Otieno, Thi Ngoc Nguyen, and Yong Joong Lee. 2025. "A Preemptive Scan Speed Control Strategy Based on Topographic Data for Optimized Atomic Force Microscopy Imaging" Actuators 14, no. 6: 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14060262
APA StyleNguyen, T. T., Juma, O. M., Otieno, L. O., Nguyen, T. N., & Lee, Y. J. (2025). A Preemptive Scan Speed Control Strategy Based on Topographic Data for Optimized Atomic Force Microscopy Imaging. Actuators, 14(6), 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14060262






