An Extended Model for Ripple Analysis of 2–4 Phase Resonant Electrostatic Induction Motors
Abstract
1. Introduction
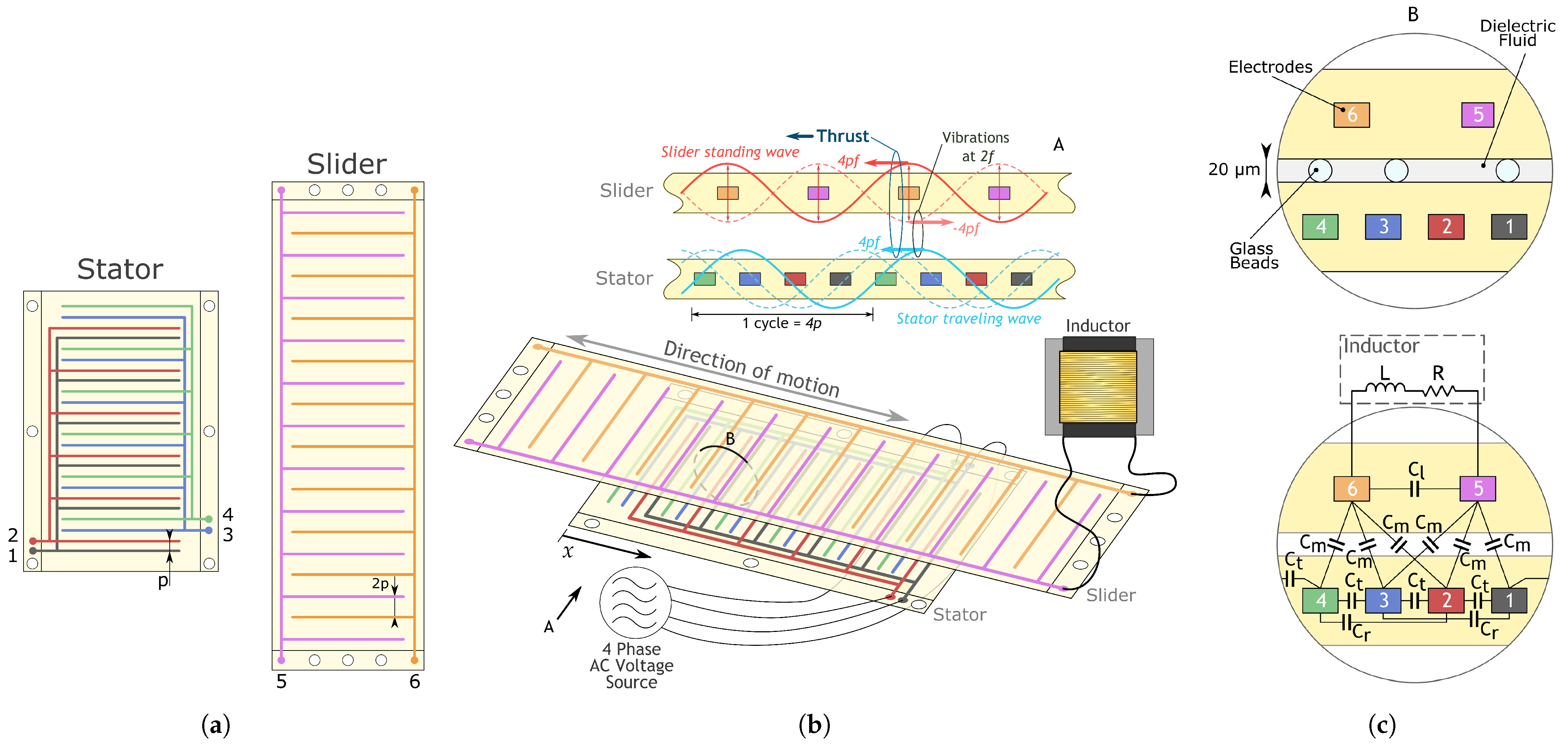
2. Electrostatic Induction Motor with 2–4 Phase Electrodes
2.1. Structure and Operation
2.2. Capacitance Matrix Model
2.3. Simplified Capacitance Identification
3. Analysis of Motor Characteristics
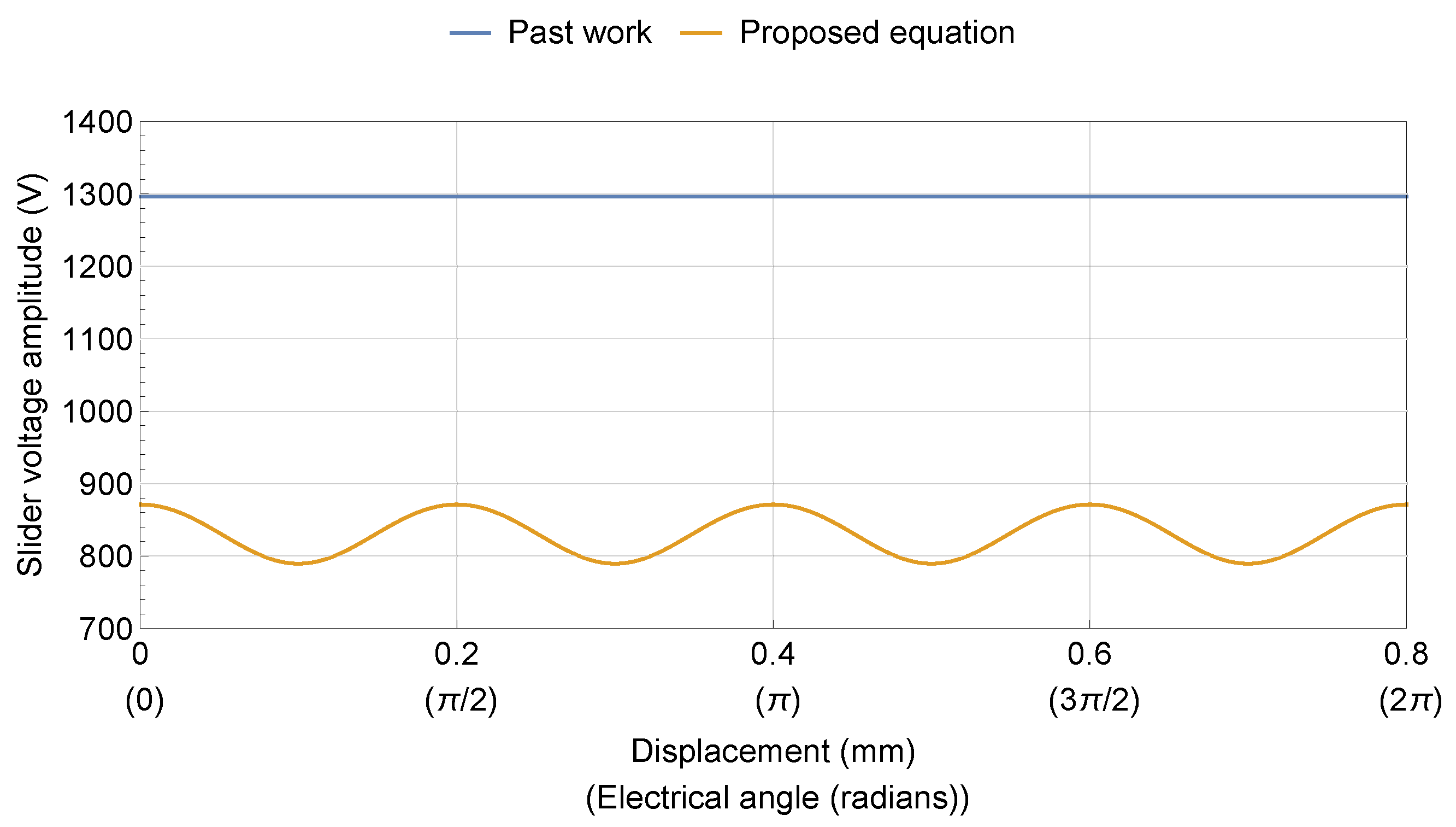
3.1. Slider Voltage
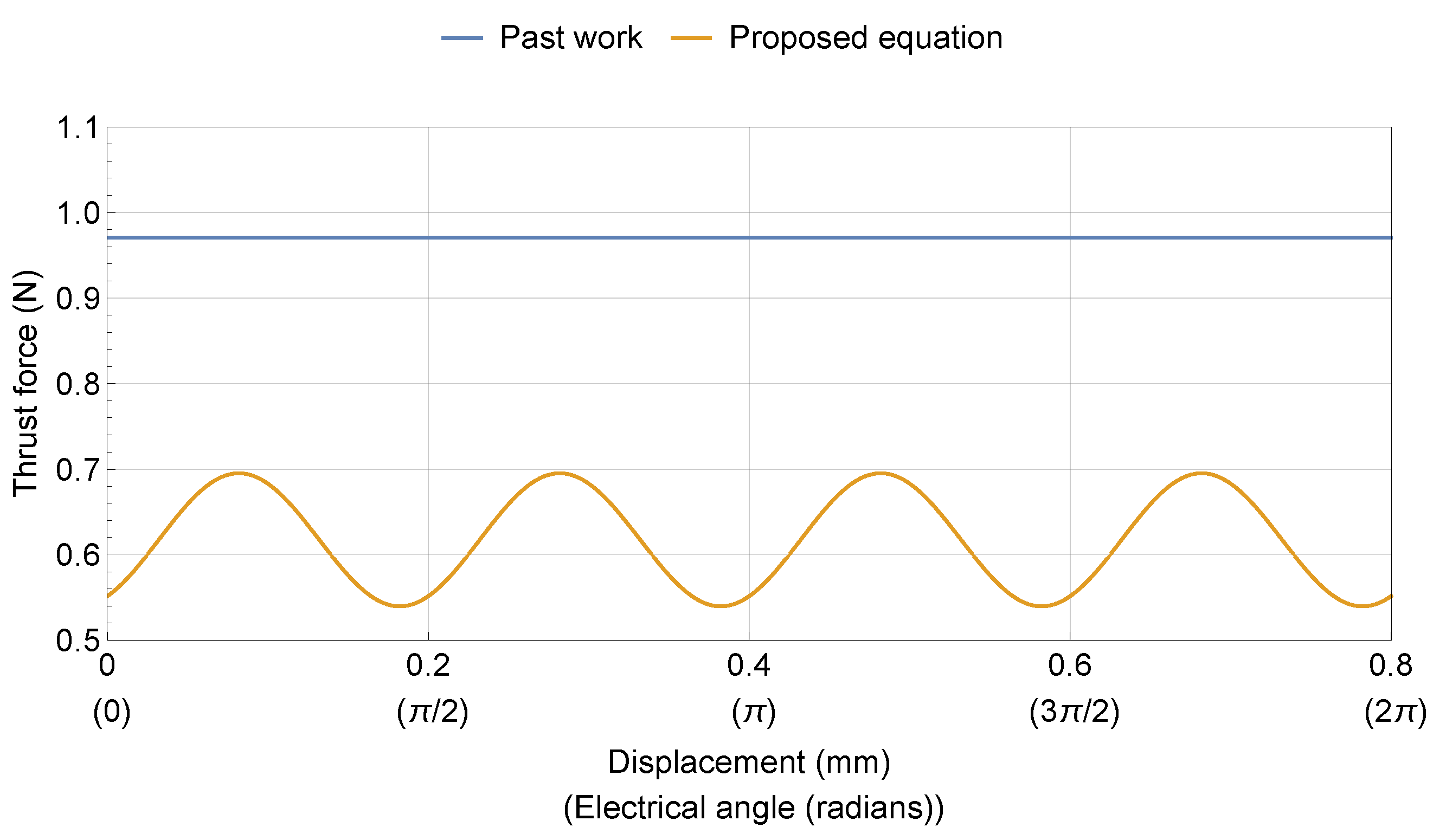
3.2. Thrust Force
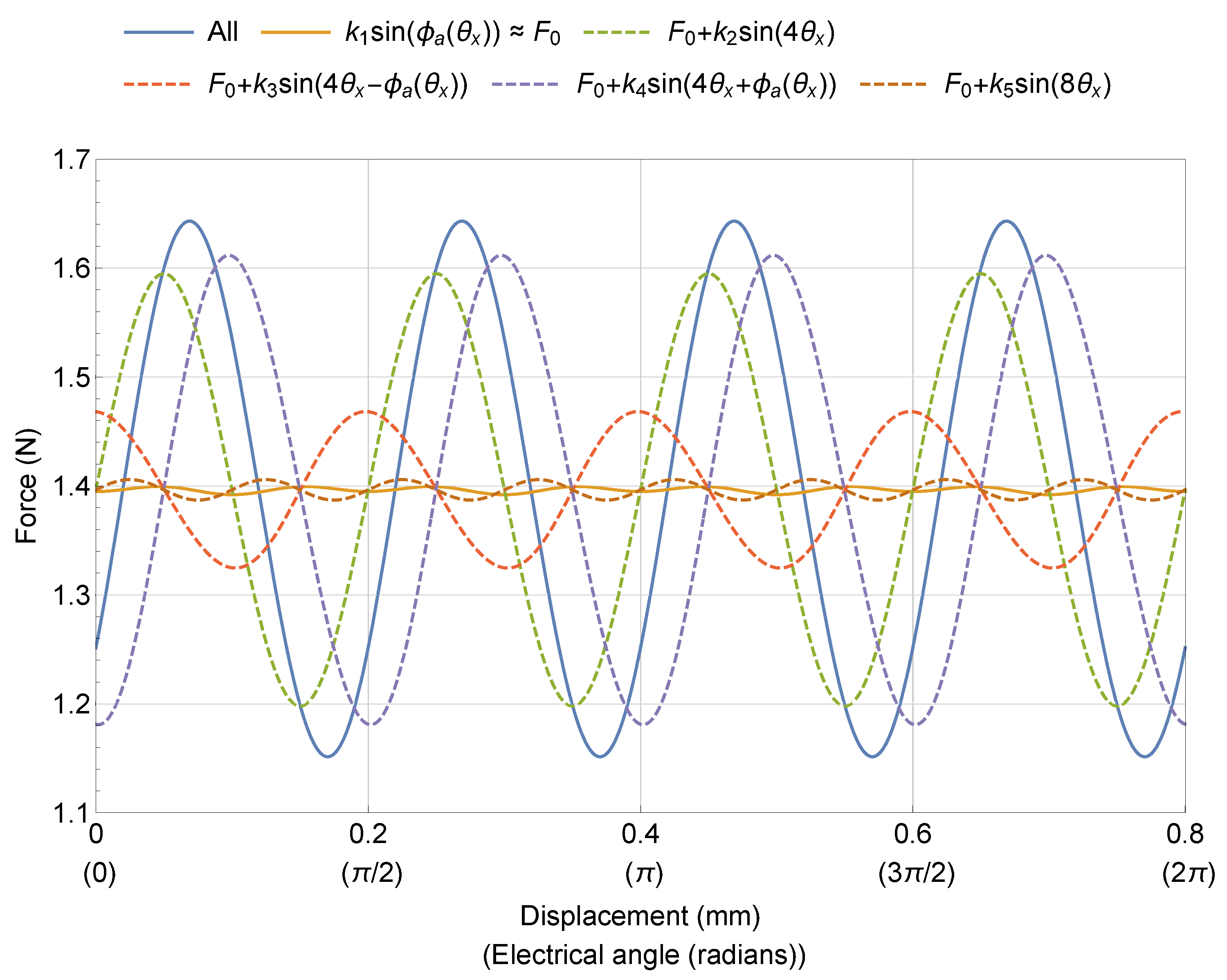
3.3. Force Ripple Analysis
4. Experimental Validation
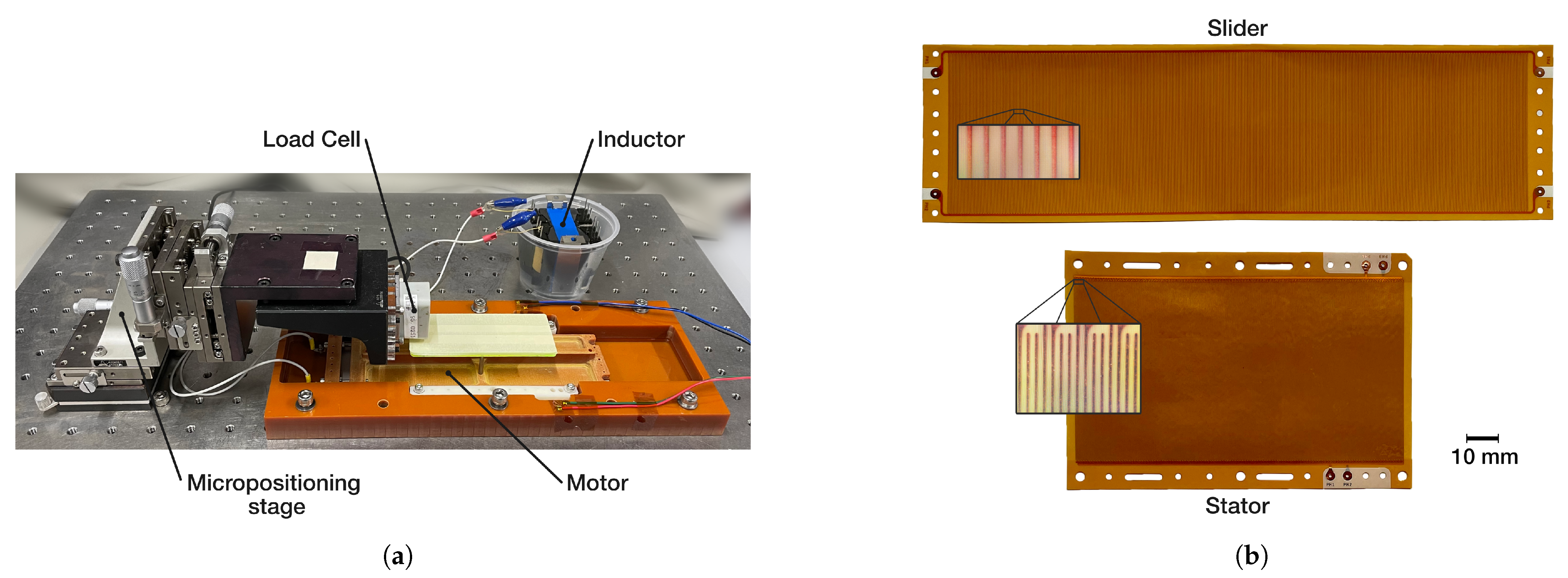
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.2. Experimental Procedure
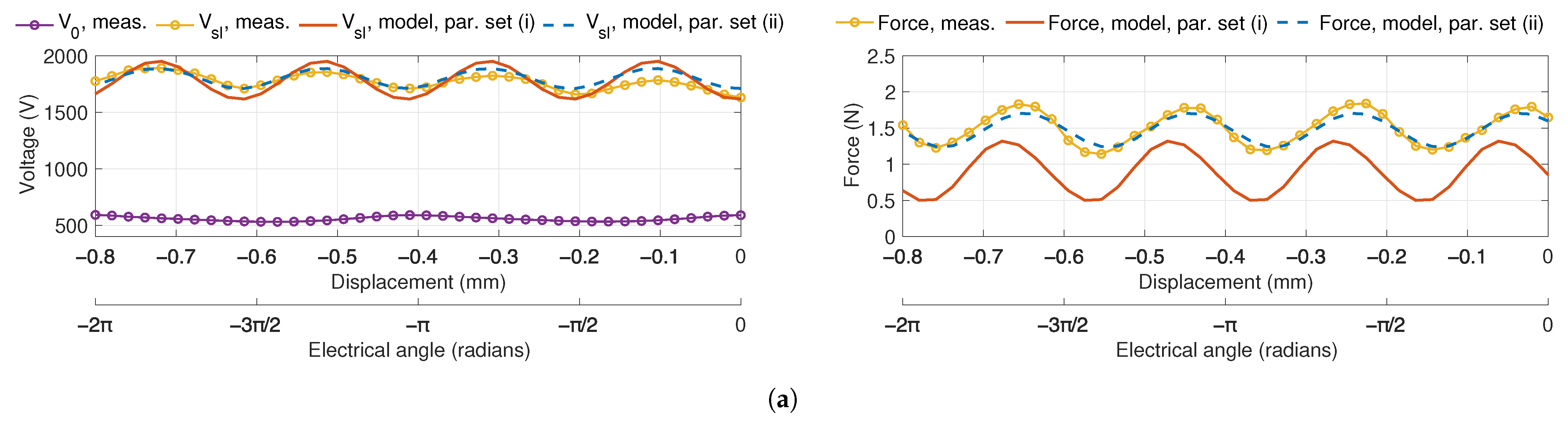
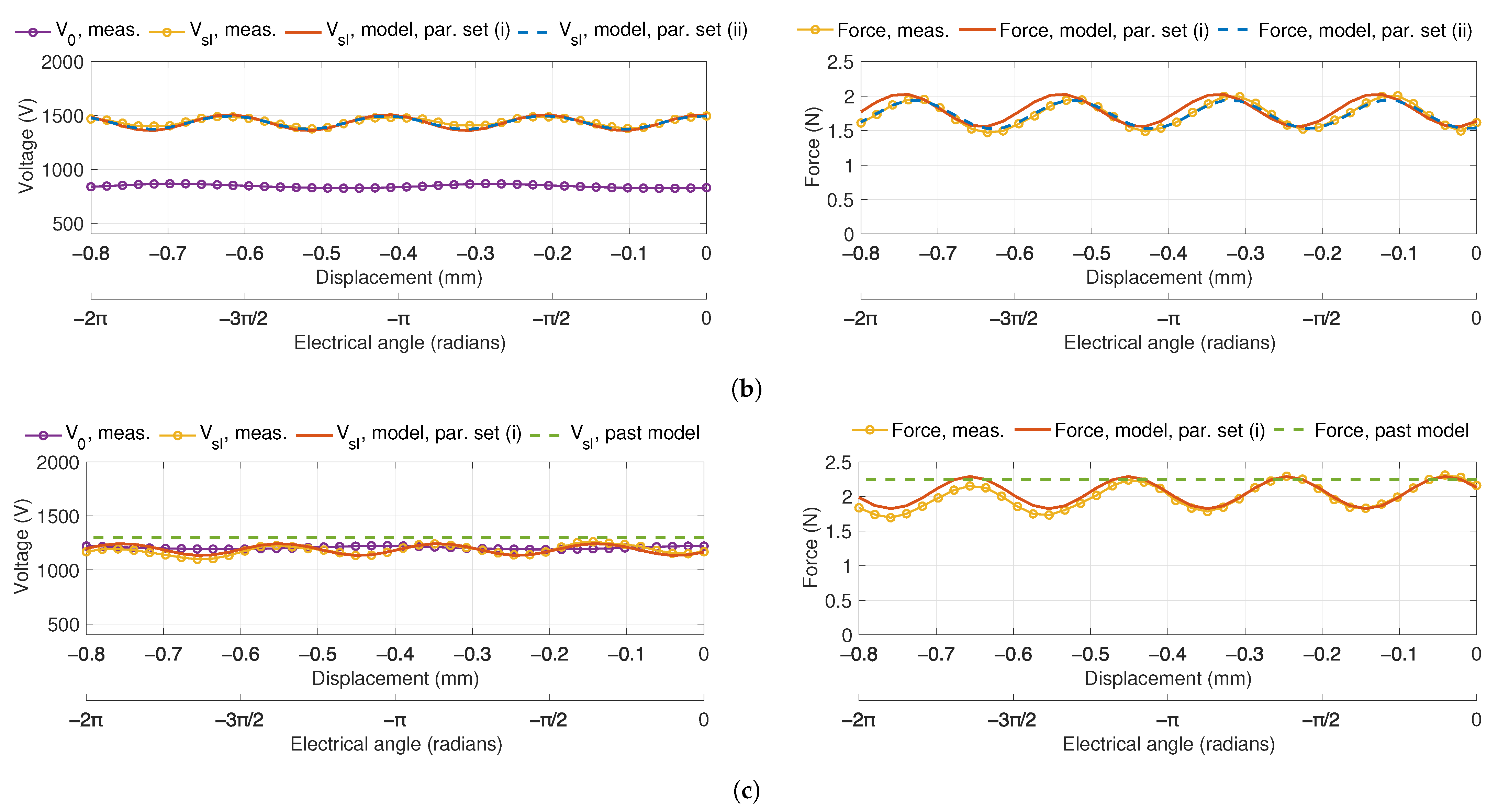
4.3. Experimental Results
5. Discussion
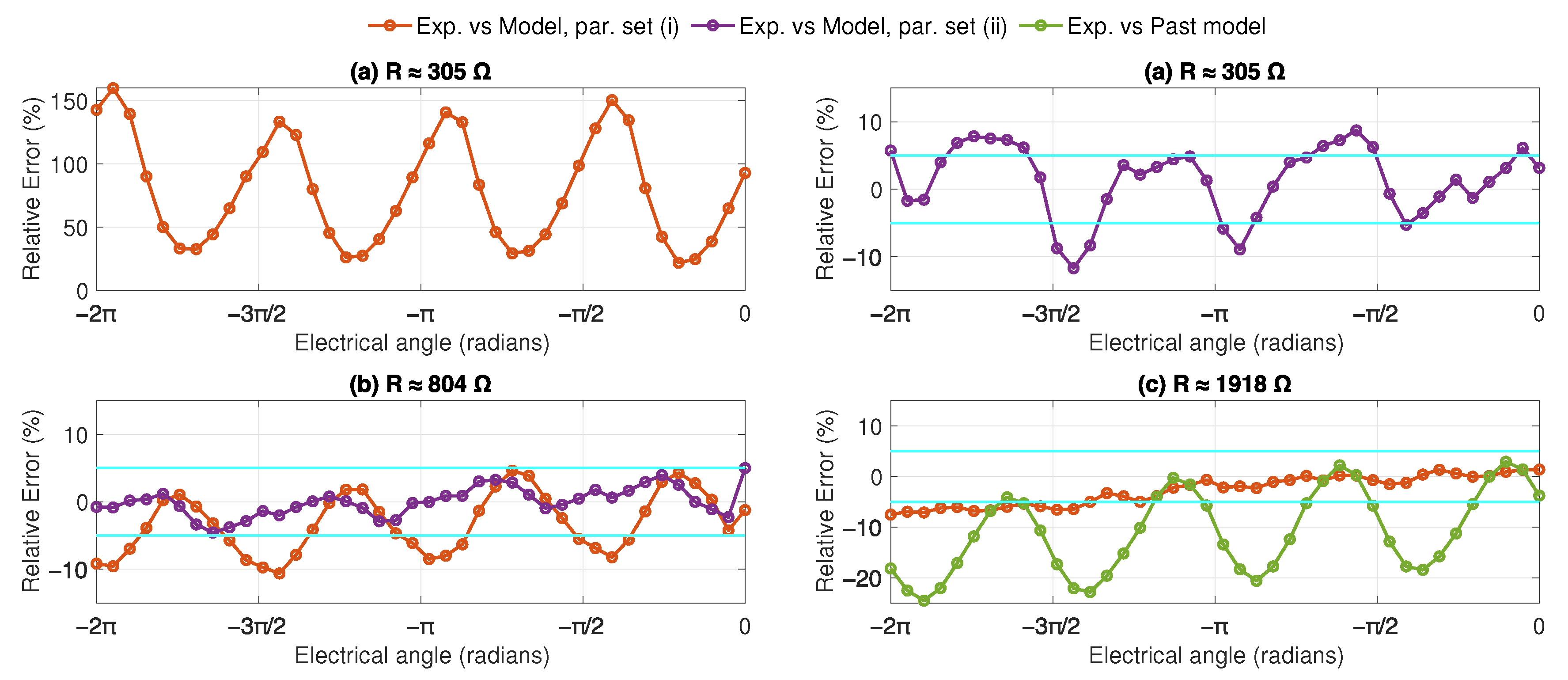
5.1. General Model Evaluation
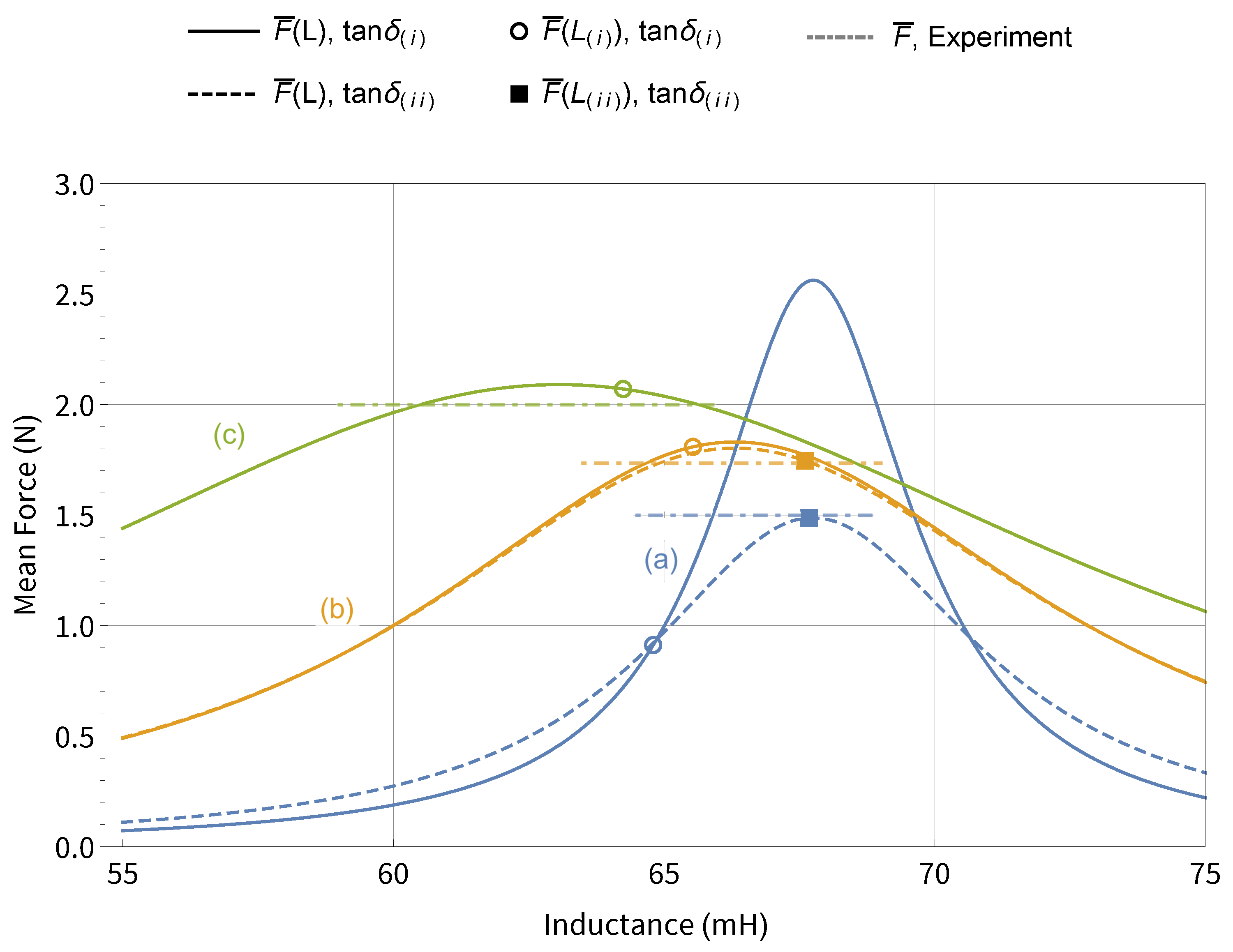
5.2. Mean Force Changes with Inductance
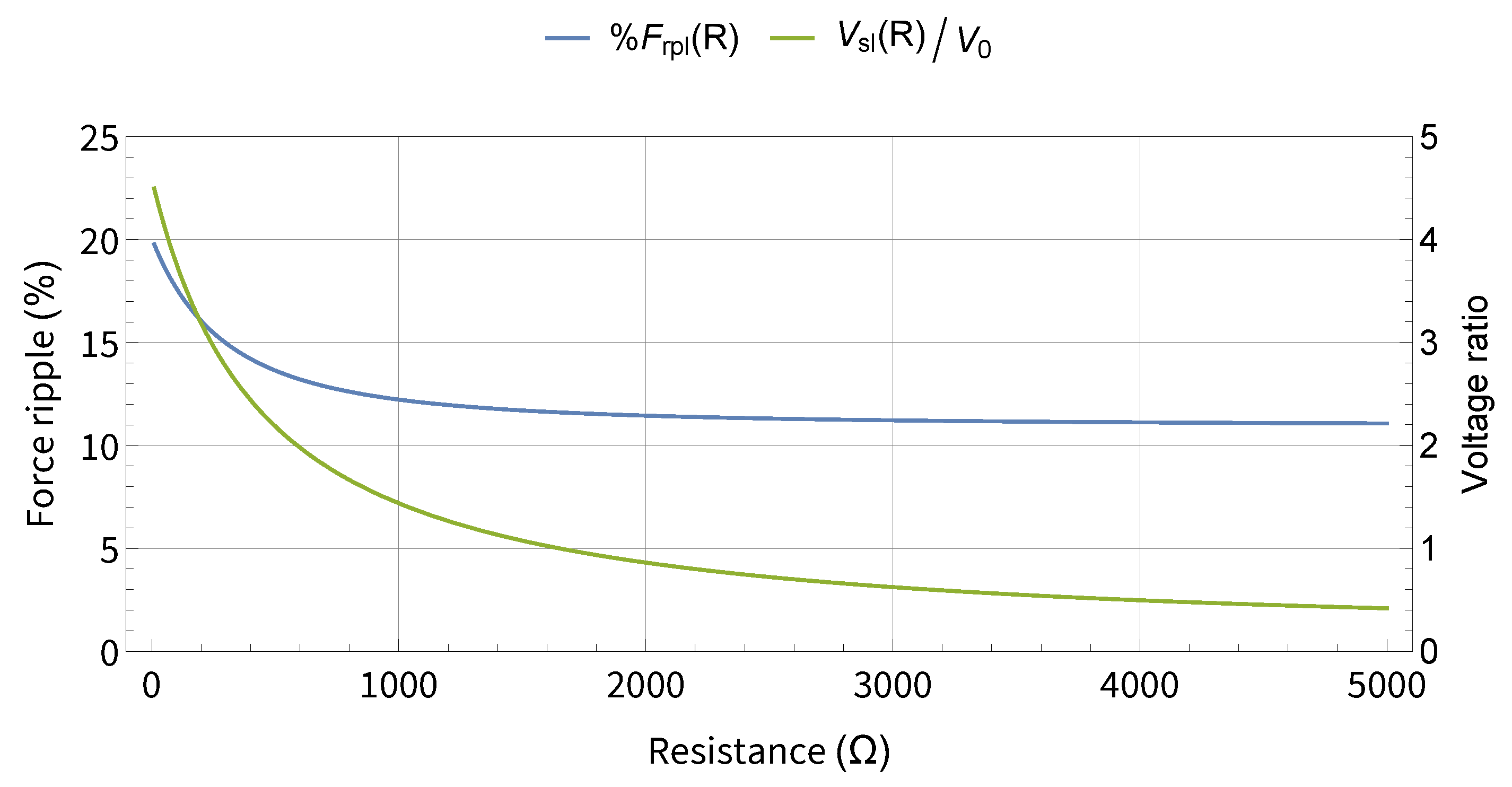
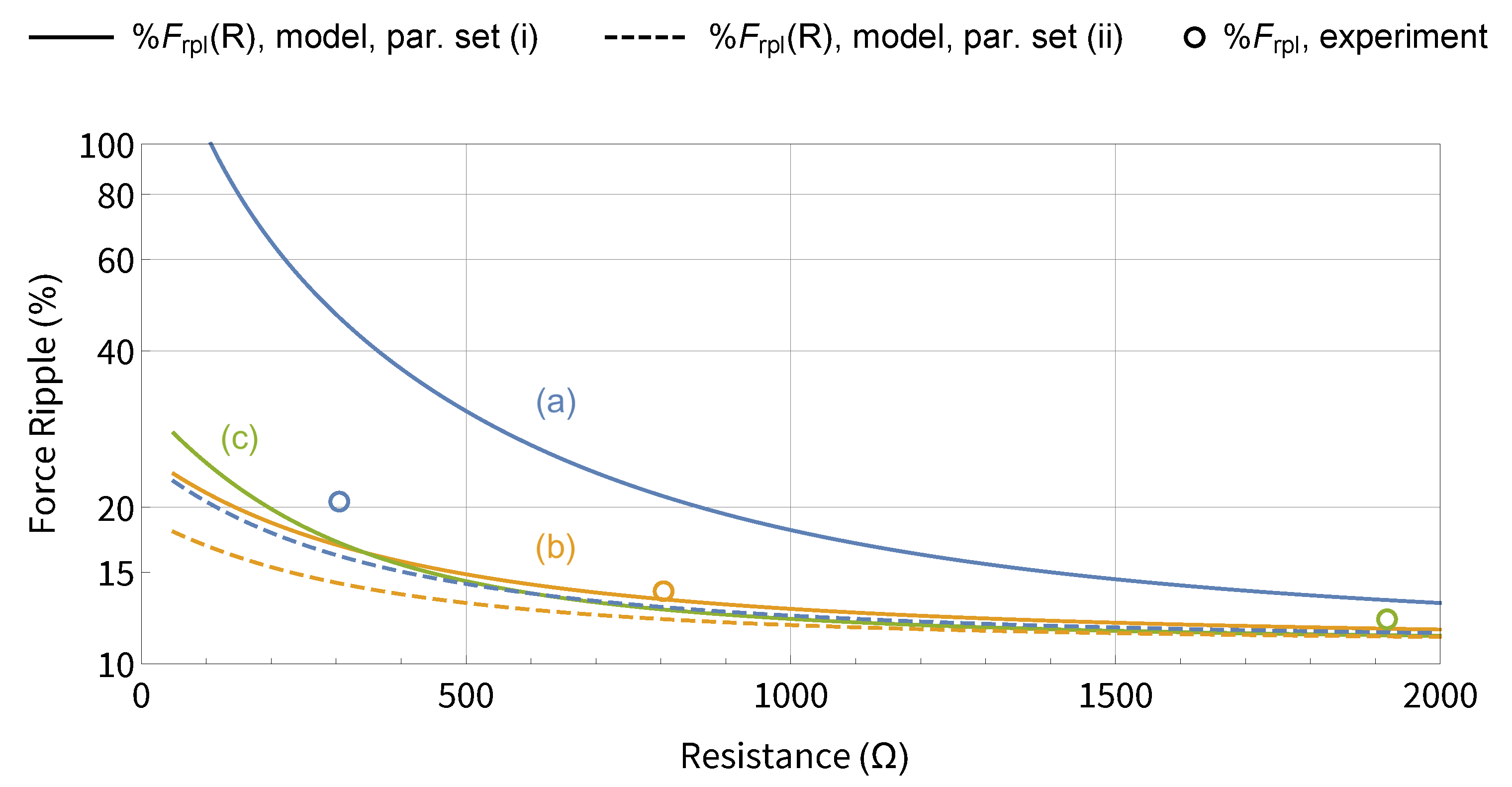
5.3. Force Ripple
5.4. General Comment
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, Z.; Shi, Q.; Fukuda, T.; Li, C.; Huang, Q. An overview of biomimetic robots with animal behaviors. Neurocomputing 2019, 332, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, G.; Liang, Y.; Cheng, T.; Dai, J.; Yang, X.; Liu, B.; Zeng, Z.; Huang, Z.; Luo, Y.; et al. Fast-moving soft electronic fish. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1602045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, C.; Gorb, S.N. Body-catapult mechanism of the sandhopper jump and its biomimetic implications. Acta Biomater. 2021, 124, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yim, J.K.; Liang, J.; Shao, Z.; Qi, M.; Zhong, J.; Luo, Z.; Yan, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; et al. Insect-scale fast moving and ultrarobust soft robot. Sci. Robot. 2019, 4, eaax1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, G.; Zou, J.; Zhao, R.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, X. Soft wall-climbing robots. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3, eaat2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Qin, L.; Liu, J.; Ren, Q.; Foo, C.C.; Wang, H.; Lee, H.P.; Zhu, J. Untethered soft robot capable of stable locomotion using soft electrostatic actuators. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2018, 21, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafferis, N.T.; Helbling, E.F.; Karpelson, M.; Wood, R.J. Untethered flight of an insect-sized flapping-wing microscale aerial vehicle. Nature 2019, 570, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Laschi, C.; Trimmer, B. Soft robotics: A bioinspired evolution in robotics. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robla-Gomez, S.; Becerra, V.M.; Llata, J.R.; Gonzalez-Sarabia, E.; Torre-Ferrero, C.; Perez-Oria, J. Working Together: A Review on Safe Human-Robot Collaboration in Industrial Environments. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 26754–26773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coltelli, M.A.; Catterlin, J.; Scherer, A.; Kartalov, E.P. Simulations of 3D-Printable biomimetic artificial muscles based on microfluidic microcapacitors for exoskeletal actuation and stealthy underwater propulsion. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 325, 112700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Shu, J.; Jin, H.; Tao, Z.; Xie, J.; Tang, S.Y.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Dickey, M.D.; Zhang, S. Liquid metal motor. iScience 2021, 24, 101911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Byun, J.; Kim, J.K.; Choi, W.Y.; Jakobsen, K.; Jakobsen, J.; Lee, D.Y.; Cho, K.J. Bioinspired dual-morphing stretchable origami. Sci. Robot. 2019, 4, eaay3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Zuo, J.; Zhu, C.; Xie, S.Q. Design and control of soft rehabilitation robots actuated by pneumatic muscles: State of the art. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 113, 620–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villoslada, A.; Flores, A.; Copaci, D.; Blanco, D.; Moreno, L. High-displacement flexible Shape Memory Alloy actuator for soft wearable robots. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2015, 73, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, J.S.; Cho, K.J. Omegabot: Biomimetic inchworm robot using SMA coil actuator and smart composite microstructures (SCM). In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Guilin, China, 19–23 December 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.B.; Zhang, W.M.; Gao, Q.H.; Guo, Q.W.; Wu, S.; Zou, H.X.; Yan, H.; Peng, Z.K.; Meng, G. Electrostatic field induced coupling actuation mechanism for dielectric elastomer actuators. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2020, 35, 100638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, M.; Moroka, H.; Kawamoto, H.; Wakabayashi, S.; Hoshino, T. Particle-size sorting system of lunar regolith using electrostatic traveling wave. J. Electrost. 2017, 89, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duduta, M.; Wood, R.J.; Clarke, D.R. Multilayer Dielectric Elastomers for Fast, Programmable Actuation without Prestretch. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 8058–8063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Huang, D.; Qi, M.; Yan, X. Design and analysis of a corona motor with a novel multi-stage structure. J. Electrost. 2021, 109, 103538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; Ludois, D.C. Dielectric liquids for enhanced field force in macro scale direct drive electrostatic actuators and rotating machinery. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2016, 23, 1924–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaler, E.W.; Zohdi, T.I.; Fearing, R.S. Thin-film repulsive-force electrostatic actuators. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 270, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niino, T.; Egawa, S.; Higuchi, T. High-power and high-efficiency electrostatic actuator. In Proceedings of the IEEE Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 10 February 1993; pp. 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egawa, S.; Higuchi, T. Multi-layered electrostatic film actuator. In Proceedings of the IEEE Proceedings on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, An Investigation of Micro Structures, Sensors, Actuators, Machines and Robots, Napa Valley, CA, USA, 11–14 February 1990; pp. 166–171. [Google Scholar]
- Niino, T.; Higuchi, T.; Egawa, S. Dual excitation multiphase electrostatic drive. In Proceedings of the IAS’95. Conference Record of the 1995 IEEE Industry Applications Conference Thirtieth IAS Annual Meeting, Orlando, FL, USA, 8–12 October 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, A.; Nishijima, T.; Higuchi, T.; Inaba, A. Robotic arm using flexible electrostatic film actuators. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (Cat. No.03TH8692), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 9–11 June 2003; Volume 2, pp. 940–945. [Google Scholar]
- Hosobata, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Higuchi, T. An electrostatic induction motor utilizing electrical resonance for torque enhancement. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2012, 173, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosobata, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Higuchi, T. Modeling and Analysis of a Linear Resonant Electrostatic Induction Motor Considering Capacitance Imbalance. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 3439–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, K.; Yamamoto, A. Modeling of voltage induction of a resonant electrostatic induction motor using 2-phase slider and a single coil. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII), Sapporo, Japan, 13–15 December 2016; pp. 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, F.; Osada, M.; Zhang, G.; Yoshimoto, S.; Yamamoto, A. Achieving Resonance with Piezoelectric Transducers on 2–4 Phase Resonant Electrostatic Induction Motors. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics (ICM), Kashiwa, Japan, 7–9 March 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, F.; Osada, M.; Zhang, G.; Yoshimoto, S.; Yamamoto, A. Increasing Thrust Force on 2–4 Phase Resonant Electrostatic Induction Motors through Stacking. In Proceedings of the IECON 2020 The 46th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Singapore, 18–21 October 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YAmashita, N.; Yamamoto, A.; Higuchi, T. Effects of Electrode Configuration for Performances of Voltage-Induction-Type Electrostatic Motors. J. Adv. Mech. Des. Syst. Manuf. 2013, 7, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yamamoto, A.; Niino, T.; Higuchi, T. Modeling and identification of an electrostatic motor. Precis. Eng. 2006, 30, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
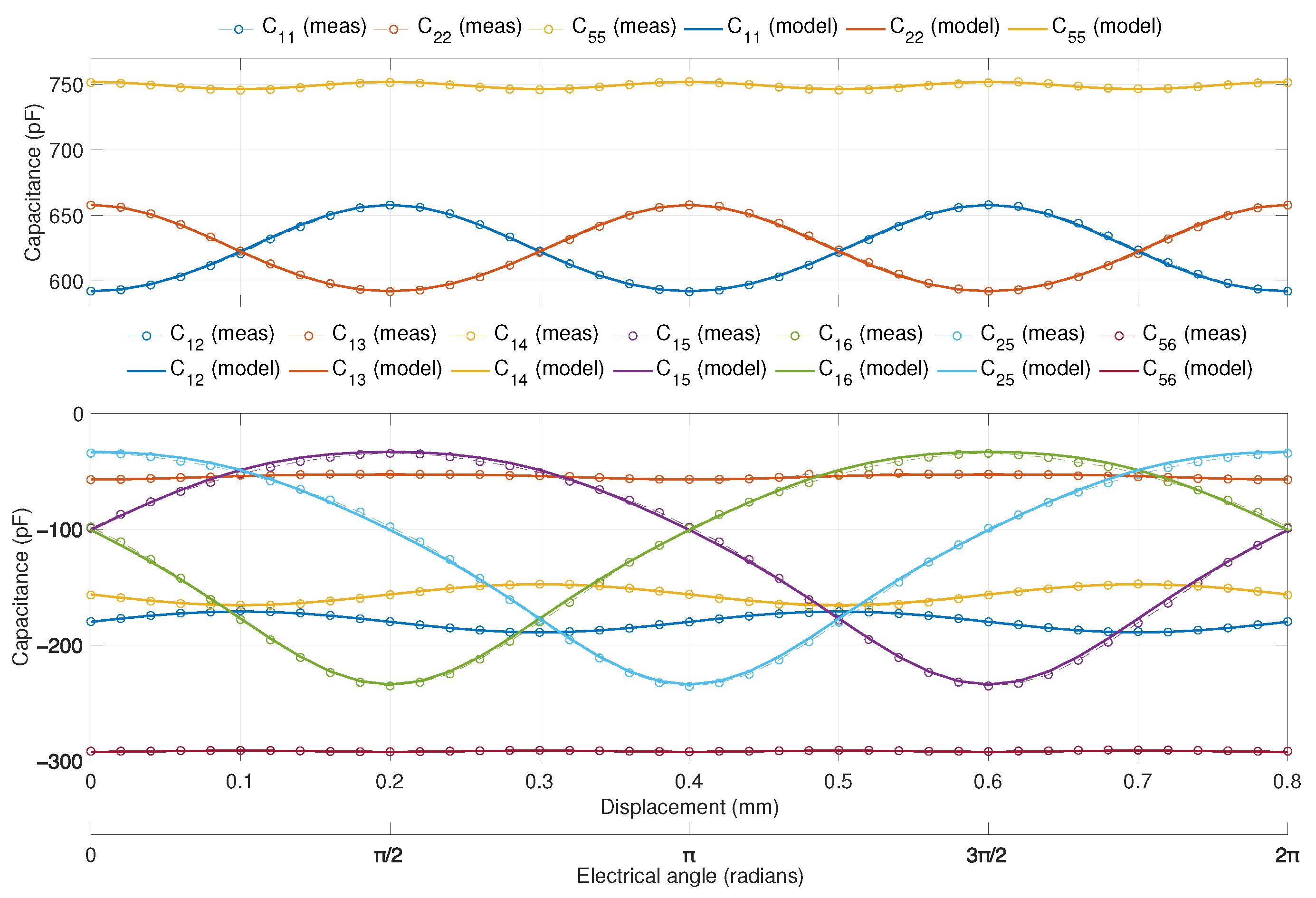
| Measured Capacitance † | Offset | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1,1), (2,2), (3,3), (4,4) | – | – | |||
| (5,5), (6,6) | – | – | – | ||
| (1,2), (1,4), (2,3), (3,4) | – | – | |||
| (1,3), (2,4) | – | – | |||
| – | – | ||||
| (5,6) | – | – | – |
| (V) | p (mm) | L (mH) | R (Ω) | tan δ | f (kHz) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | 0.2 | 66.6 | 800 | 0.04 | 27 | |||
| 115.1 | 95.6 | 4.88 | 291.8 | 0.506 | 749.1 | 2.82 | 0.401 | 1.32 |
| Exp. | Parameter Set | Experimentally Measured | Inferred | Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R (Ω) | L (mH) | (V) | (kHz) | L (mH) | tan δ | (kHz) | ||
| (a) | (i) | 304.8 (7.3–650.2) | 64.80 (63.87–65.31) | 550 | 26.80 | – | 0.00585 | 27.38 |
| (ii) | 67.68 | 0.02935 | 26.80 | |||||
| (b) | (i) | 804.2 (420.9–1207) | 65.53 (65.16–65.93) | 840 | 27.10 | – | 0.035 | 27.31 |
| (ii) | 67.60 | 0.03665 | 26.88 | |||||
| (c) | (i) | 1918 (1548–2297) | 64.244 (63.55–64.94) | 1205 | 27.80 | – | 0.0172 | 27.75 |
| (ii) | – | – | – | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carneiro, F.; Zhang, G.; Osada, M.; Yoshimoto, S.; Yamamoto, A. An Extended Model for Ripple Analysis of 2–4 Phase Resonant Electrostatic Induction Motors. Actuators 2021, 10, 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/act10110291
Carneiro F, Zhang G, Osada M, Yoshimoto S, Yamamoto A. An Extended Model for Ripple Analysis of 2–4 Phase Resonant Electrostatic Induction Motors. Actuators. 2021; 10(11):291. https://doi.org/10.3390/act10110291
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarneiro, Fernando, Guangwei Zhang, Masahiko Osada, Shunsuke Yoshimoto, and Akio Yamamoto. 2021. "An Extended Model for Ripple Analysis of 2–4 Phase Resonant Electrostatic Induction Motors" Actuators 10, no. 11: 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/act10110291
APA StyleCarneiro, F., Zhang, G., Osada, M., Yoshimoto, S., & Yamamoto, A. (2021). An Extended Model for Ripple Analysis of 2–4 Phase Resonant Electrostatic Induction Motors. Actuators, 10(11), 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/act10110291







