Insecticides for Suppression of Nylanderia fulva
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ant Colonies
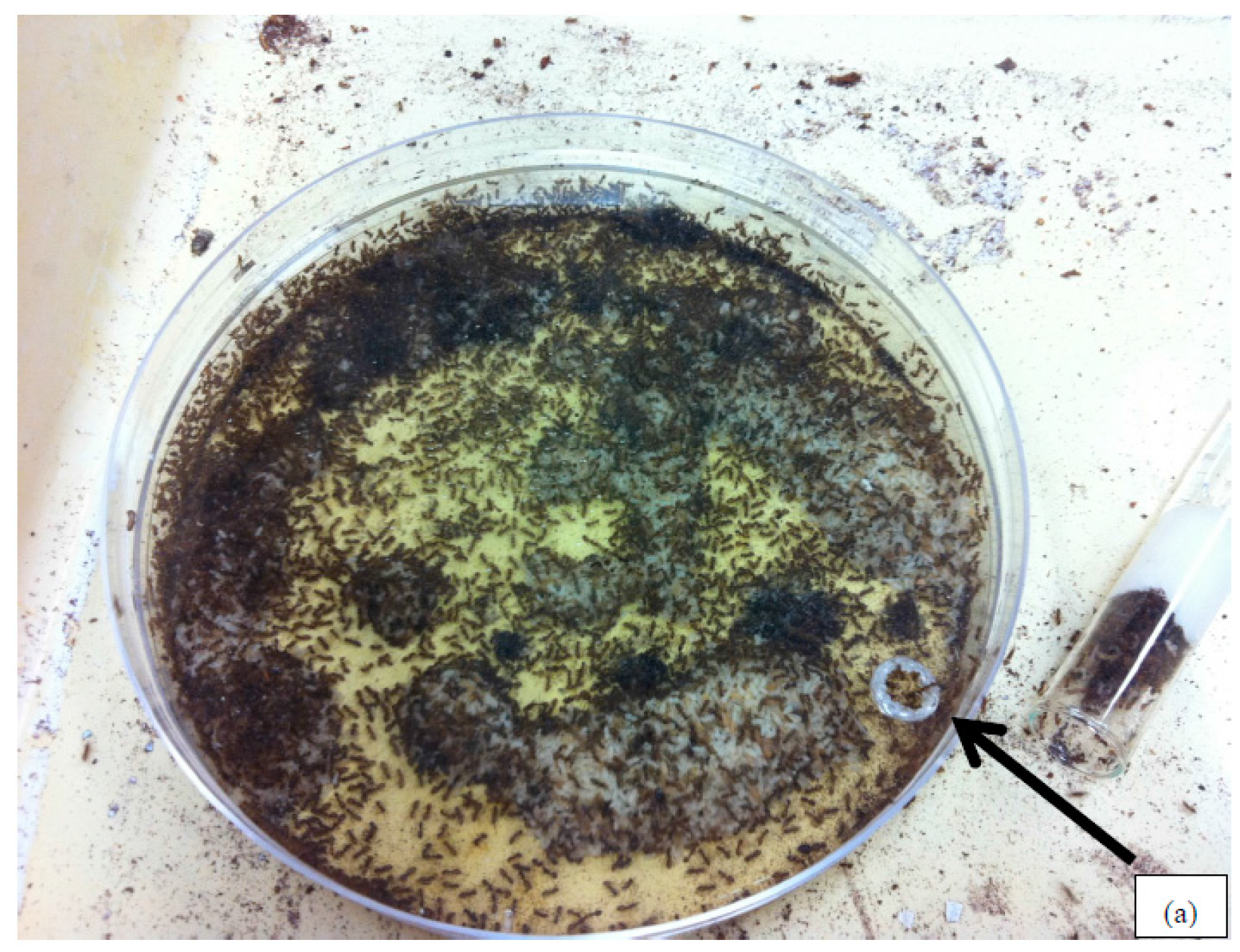
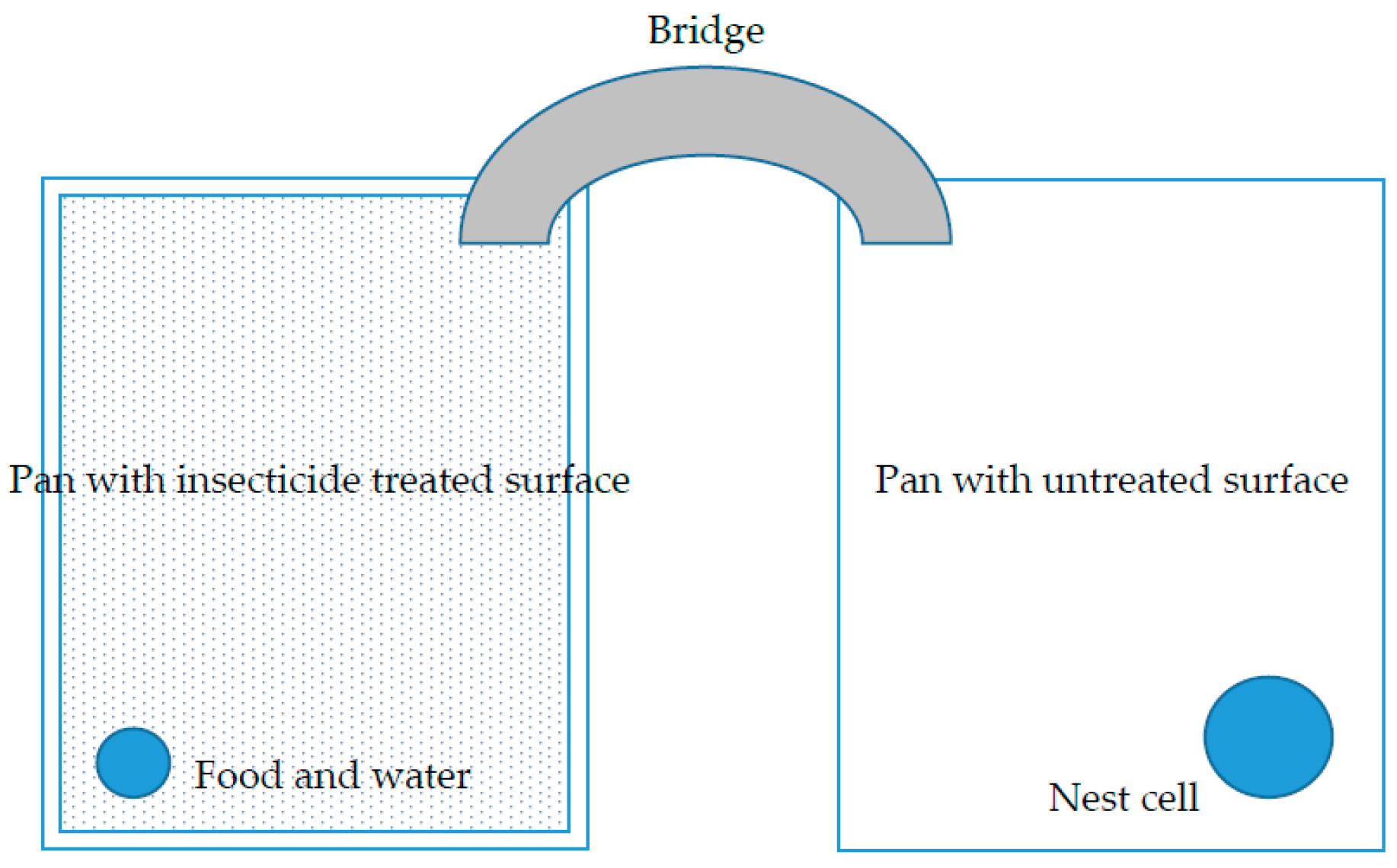
2.2. Liquid Insecticide Repellency and Efficacy Bioassays
2.3. Bait Acceptance and Efficacy Assays
3. Results
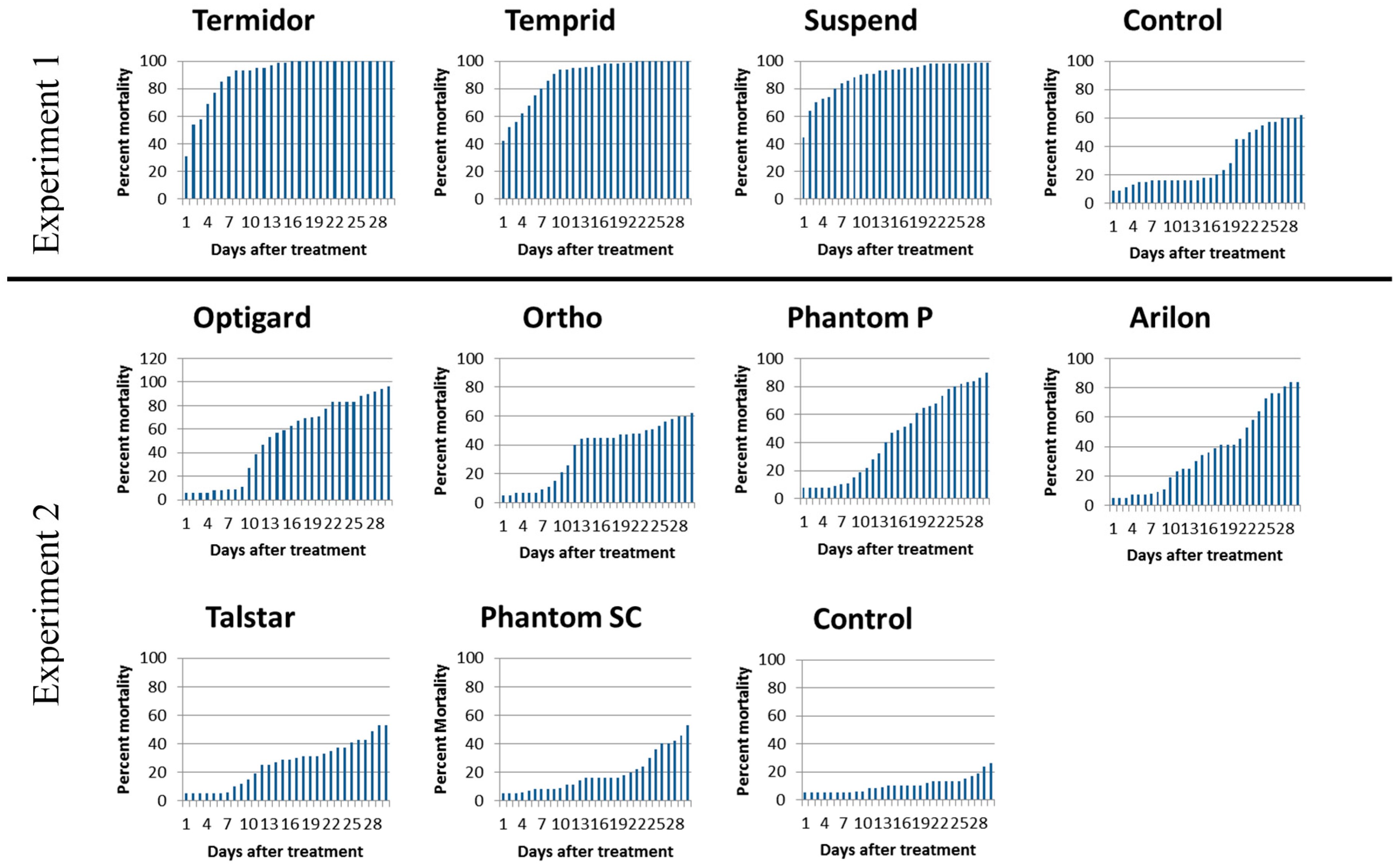
3.1. Contact Insecticide Repellency
3.2. Contact Insecticide Efficacy
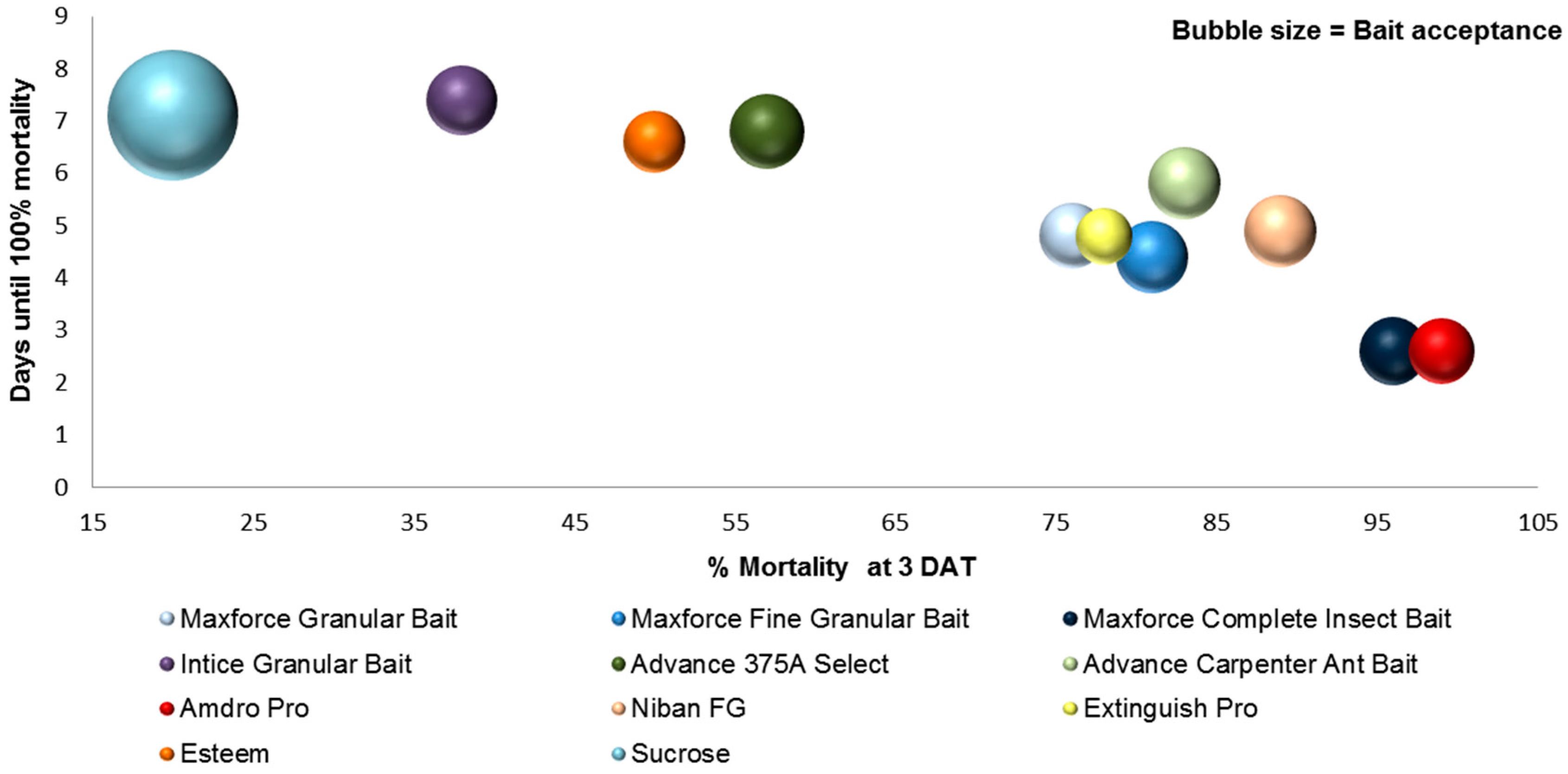
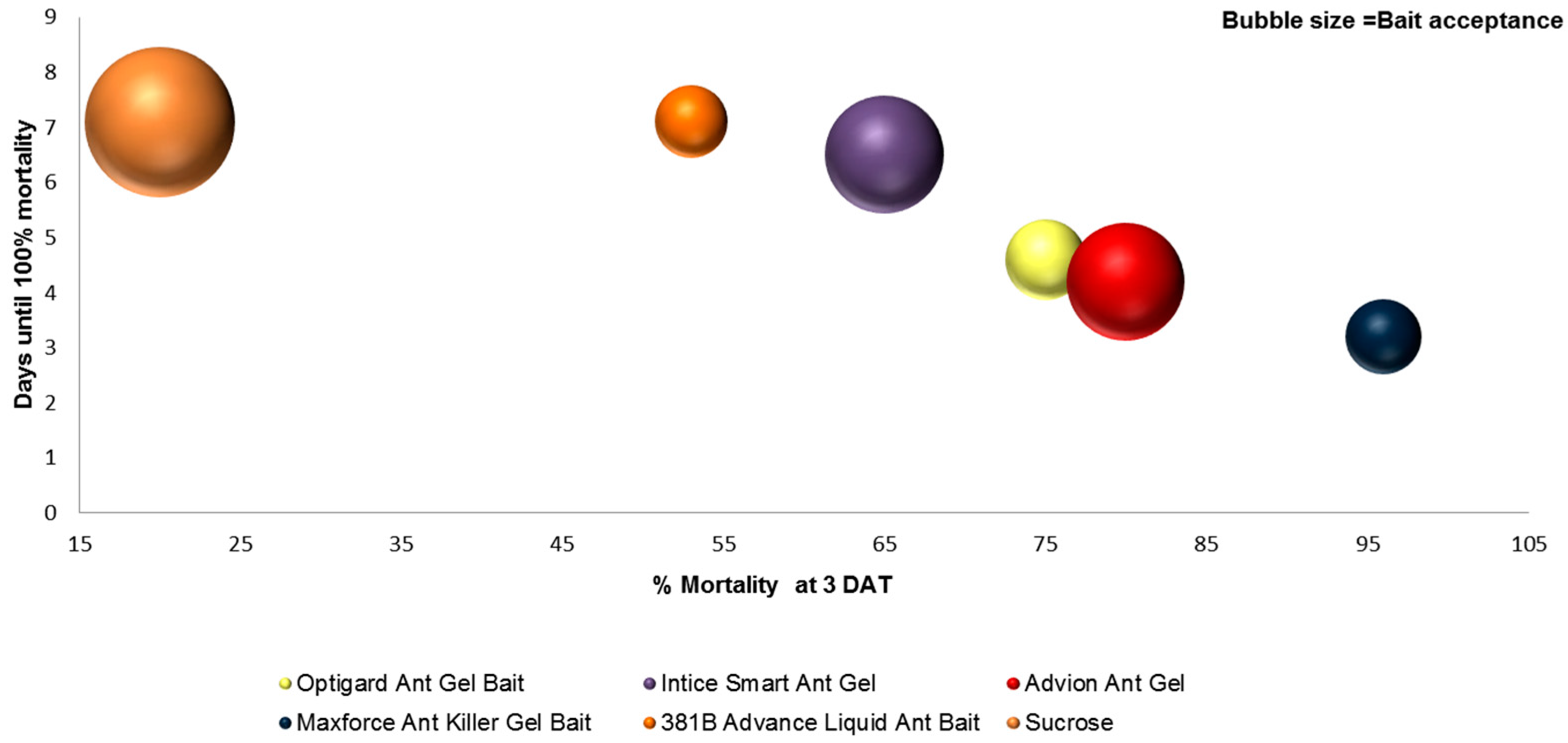
3.3. Bait Acceptance
3.4. Bait Efficacy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meyers, J.M. Identification, Distribution, and Control of an Invasive Pest Ant, Paratrechina sp. near pubens (Hymenoptera: Formicidae), in Texas. Ph.D. Dissertation, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zenner-Polania, I. Management of the “hormiga loca”, Paratrechina (Nylanderia) fulva (Mayr), in Colombia. In Applied Myrmecology: A World Perspective; Vander Meer, R.K., Jaffe, K., Cedeno, A., Eds.; Westview Press: Boulder, CO, USA, 1990; pp. 702–707. ISBN 0-8133-7785-4. [Google Scholar]
- LeBrun, E.G.; Abbot, J.; Gilbert, L.E. Imported crazy ant displaces imported fire ant, reduces and homogenizes ant and arthropod assemblages. Biol. Invasions 2013, 15, 2429–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetterer, J.K.; Davis, O.; Williamson, J.R. Boom and bust of the tawny crazy ant, Nylanderia fulva (Hymenoptera: Formicidae), on St. Crois, US Virgin Islands. Fla. Entomol. 2014, 97, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rust, M.K.; Haagsma, K.; Reierson, D.A. Barrier sprays to control Argentine ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 1996, 89, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharf, M.E.; Ratliff, C.A.; Bennett, G.W. Impacts of residual insecticide barriers on perimeter-invading ants, and particular reference to the odorous house ant, Tapinoma sessile. J. Econ. Entomol. 2004, 97, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverman, J.; Brightwell, R.J. The Argentine ant: Challenges in managing an invasive unicolonial pest. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 2008, 53, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calixto, A.A.; Harris, M.K.; Knutson, A.; Barr, C.L. Native ant responses to Solenopsis invicta Buren reduction using broadcast baits. Environ. Entomol. 2007, 36, 1112–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, S.J.; Rust, M.K. Determining the foraging range and origin of resurgence after treatment of Argentine ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in urban areas. J. Econ. Entomol. 2003, 96, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drees, B.M.; McDonald, D.; Calixto, A.; Nester, P.; Bowen, C.; Rasberry, T.; Gold, R. Evaluation of bait attractiveness for Rasberry crazy ant. In Integrated Pest Management Urban IPM Program 2010; AgriLife Extension: College Station, TX, USA, 2010; pp. 93–107. Available online: http://insects.tamu.edu/fireant/research/projects/pdf/2010IPM%20Handbook1.pdf (accessed on 24 July 2017).
- McDonald, D.L. Investigation of an Invasive Ant Species: Nylanderia fulva Colony Extraction, Management, Diet Preference, Fecundity, and Mechanical Vector Potential. Ph.D. Dissertation, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nester, P.R.; Rasberry, T. Response of Nylanderia sp. near pubens population to single broadcast application of Esteem 0.86% EC insect growth regulator. In Integrated Pest Management Urban IPM Program 2010; Agrilife Extension: College Station, TX, USA, 2010; pp. 108–113. Available online: http://insects.tamu.edu/fireant/research/projects/pdf/2010IPM%20Handbook1.pdf (accessed on 24 August 2017).
- Statistics Analysis System (SAS) Institute. Software Release 9.4; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Conover, W.J.; Iman, R.L. Rank transformations as a bridge between parametric and nonparametric statistics. Am. Stat. 1981, 35, 124–129. [Google Scholar]
- Rust, M.K.; Reierson, D.A.; Klotz, J.A. Delayed toxicity as a critical factor in the efficacy of aqueous baits for controlling Argentine ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2004, 97, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rust, M.K.; Saran, R.K. Toxicity, repellency, and transfer of chlorfenapyr against western subterranean termites (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2006, 99, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, H.A.; Henderson, G.; Fei, H. Toxicity, repellency, and horizontal transmission of fipronil in the Formosan subterranean termite (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2003, 96, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klotz, J.H.; Rust, M.K.; Soeprono, A. Why delay when you bait and spray? Pest Control 2004, 72, 33–34. [Google Scholar]
- Choe, D.H.; Rust, M.K. Horozontal transfer of insecticides in laboratory colonies of the Argentine ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2008, 101, 1397–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, R.E.; Strawn, A.J. Effectiveness of insecticides applied to concrete for Argentine ant control. Insectic. Acaric. Tests 1980, 5, 210–211. [Google Scholar]
- Buczkowski, G.; Scharf, M.E.; Ratliff, R.; Bennett, G.W. Efficacy of simulated barrier treatments against laboratory colonies of pharaoh ant. J. Econ. Entomol. 2005, 98, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oi, D.H.; Center for Medical, Agricultural and Veterinary Entomology, United States Department of Agriculture Agricultural Research Service (USDA ARS), Gainesville, FL, USA. Personal Communication, 2017.
- Klotz, J.H.; Greenberg, L.; Shorey, H.H.; Williams, D.F. Alternative control strategies for ants around homes. J. Agric. Entomol. 1997, 14, 249–257. [Google Scholar]
- Stanley, M.C. Review of the Efficacy of Baits Used for Ant Control and Eradication; Landcare Research Contract Report: LC0405/044; Landcare Research New Zealand Ltd.: Aukland, New Zealand, 2004; Available online: http://argentineants.landcareresearch.co.nz/documents/Stanley_2004_Bait_Efficacy_Report.pdf (accessed on 24 August 2017).
- Stanley, M.C.; Robinson, W.A. Relative attractiveness of baits to Paratrechina longicornis (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2007, 100, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oi, D.H. Effects of an insect growth regulating bait on the tawny crazy ant, Nylanderia fulva. In Proceedings of the Imported Fire Ant and Invasive Ant Conference, Palm Springs, CA, USA, 5–8 May 2014; Henke, J., Ed.; 2014; pp. 11–12. Available online: http://articles.extension.org/sites/default/files/IFA%20Conference%20Proceedings%202014.pdf (accessed on 24 August 2017).

| Trade Name | Active Ingredient | Concentration of Active Ingredient in Dilution | Marketed as Repellent or Non-Repellent | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arilon® | Indoxacarb | 0.10% | Non-repellent | Syngenta, Greensboro, NC, USA |
| Optigard® | Thiamethoxam | 0.10% | Non-repellent | Syngenta, Greensboro, NC, USA |
| Ortho® | Acephate | 0.07% | Repellent | Monsanto, San Ramon, CA, USA |
| Phantom® aerosol | Chlorfenapyr | 0.50% | Non-repellent | BASF, Research Triangle Park, NC, USA |
| Phantom® SC | Chlorfenapyr | 0.50% | Non-repellent | BASF, Research Triangle Park, NC, USA |
| Suspend® | Deltamethrin | 0.03% | Repellent | Bayer, Research Triangle Park, NC, USA |
| Talstar® | Bifenthrin | 0.062% | Repellent | FMC, Philadelphia, PA, USA |
| Temprid® | Imidacloprid + Beta cyfluthrin | 0.10% + 0.05% | Non-repellent and repellent active ingredients | Bayer, Research Triangle Park, NC, USA |
| Termidor® | Fipronil | 0.06% | Non-repellent | BASF, Research Triangle Park, NC, USA |
| Product | Active Ingredient | Formulation Type | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|
| InTice™ Granular Ant Bait | Orthoboric acid | Granular | Rockwell Labs, Ltd., North Kansas City, MO, USA |
| 381B Advance® Liquid Bait | Borax | Liquid | BASF, Research Triangle Park, NC, USA |
| Advance® 375A Select | Abamectin | Granular | BASF, Research Triangle Park, NC, USA |
| Advance® Carpenter Ant Bait | Abamectin | Granular | BASF, Research Triangle Park, NC, USA |
| Advion® Ant Gel | Indoxacarb | Gel | Dupont, Wilmington, DE, USA |
| Amdro® Pro | Hydramethylnon | Granular | BASF, Research Triangle Park, NC, USA |
| Esteem® Ant Bait | Pyriproxyfen | Granular | Valent USA Corporation, Walnut Creek, CA, USA |
| Extinguish® Professional | Methoprene | Granular | Wellmark International, Schaumberg, IL, USA |
| InTice™ Smart Ant Gel | Borax | Gel | Rockwell Labs, Ltd., North Kansas City, MO, USA |
| Maxforce® Ant Killer Bait Gel | Fipronil | Gel | Bayer Environmental Science, Research Triangle Park, NC, USA |
| Maxforce® Complete Bait | Hydramethylnon | Granular | Bayer Environmental Science, Research Triangle Park, NC, USA |
| Maxforce® Fine Granular Bait | Hydramethylnon | Granular | Bayer Environmental Science, Research Triangle Park, NC, USA |
| Maxforce® Granular Bait | Hydramethylnon | Granular | Bayer Environmental Science, Research Triangle Park, NC, USA |
| Niban® Fine Granular Bait | Orthoboric acid | Granular | Nisus Corporation, Rockford, TN, USA |
| Optigard® Ant Gel Bait | Thiamethoxam | Gel | Syngenta Crop Protection, Greensboro, NC, USA |
| Percent Mortality | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experiment | 10 DAT | 17 DAT | ||||
| Experiment 1 | Temprid | 94.0 | a 1 | Termidor | 100.0 | a |
| Termidor | 92.8 | a | Temprid | 97.6 | a | |
| Suspend | 90.0 | a | Suspend | 94.8 | a | |
| Control | 16.3 | b | Control | 20.0 | b | |
| 10 DAT | 28 DAT | |||||
| Experiment 2 | Optigard | 27.0 | Optigard | 92.0 | a | |
| Ortho | 21.0 | Phantom P | 84.0 | ab | ||
| Phantom P | 19.0 | Arilon | 80.6 | ab | ||
| Arilon | 19.0 | Ortho | 60.0 | ab | ||
| Talstar | 15.0 | Talstar | 49.0 | ab | ||
| Phantom SC | 9.0 | Phantom SC | 42.0 | ab | ||
| Control | 6.0 | Control | 19.0 | b | ||
| Mean Bait Acceptance Counts | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bait | Spring | Bait | Summer | Bait | Fall | |||
| Advion (g) 1 | 19.9 | a 2 | InTice (g) | 7.7 | a | InTice (g) | 24.8 | a |
| Control (l) | 9.1 | abc | Advion (g) | 5.7 | ab | InTice (gr) | 4.1 | abc |
| InTice (g) | 7.7 | bc | Advance Carpenter Ant (gr) | 3.9 | bc | Control (l) | 3.9 | b |
| Advance 375A Select (gr) | 4.1 | cd | Optigard (g) | 2.8 | cd | Advance 375A Select (gr) | 2.7 | bcd |
| Maxforce Fine Granular (gr) | 3.3 | cd | Maxforce Complete (gr) | 2.2 | cd | Niban FG (gr) | 1.9 | bcd |
| Maxforce Ant Killer (g) | 2.5 | de | InTice (gr) | 1.9 | cd | Maxforce Fine Granular (gr) | 2.8 | bd |
| Optigard (g) | 1.4 | de | Control (l) | 1.8 | cd | Advance Carpenter Ant (gr) | 2.3 | cd |
| Maxforce Granular Bait (gr) | 0.5 | de | Niban FG (gr) | 1.3 | cd | Optigard (g) | 2.2 | cde |
| 381B Advance (l) | 0.4 | de | Esteem (gr) | 0.7 | cd | Maxforce Granular Bait (gr) | 1.2 | cde |
| Advance Carpenter Ant (gr) | 0.4 | de | Amdro Pro (gr) | 0.5 | cd | Maxforce Complete (gr) | 1.1 | cde |
| InTice (gr) | 0.1 | e | Extinguish Pro (gr) | 0.4 | cd | 381B Advance (l) | 1.0 | cde |
| Maxforce Complete (gr) | 0.0 | e | Maxforce Fine Granular (gr) | 0.3 | cd | Amdro Pro (gr) | 0.6 | cde |
| Extinguish Pro (gr) | 0.0 | e | Advance 375A Select (gr) | 1.1 | d | Maxforce Ant Killer (g) | 0.5 | de |
| Esteem (gr) | 0.0 | e | Maxforce Ant Killer (g) | 0.9 | d | Esteem (gr) | 0.5 | de |
| Niban FG (gr) | NT | 381B Advance (l) | 0.3 | d | Extinguish Pro (gr) | 0.0 | e | |
| Amdro Pro (gr) | NT 3 | Maxforce Granular Bait (gr) | 0.3 | e | Advion (g) | NT | ||
| F = 16.82 | F = 11.46 | F = 26.50 | ||||||
| df = 13, 126 | df = 15, 144 | df = 14, 134 | ||||||
| P < 0.0001 | P < 0.0001 | P < 0.0001 | ||||||
| Mean Percent Mortality at 3 DAT Rank-Score 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bait 2 | Spring | Bait | Summer | Bait | Fall | |||
| Maxforce Fine Granular (g) | 4.9 | a 3 | Maxforce Complete (gr) | 5.0 | a | Maxforce Ant Killer (g) | 5.0 | a |
| Maxforce Ant Killer (g) | 4.9 | a | Amdro Pro (gr) | 5.0 | a | Maxforce Complete (gr) | 5.0 | a |
| Maxforce Granular (gr) | 4.9 | a | Niban FG (gr) | 4.8 | ab | Amdro Pro (gr) | 5.0 | a |
| Extinguish Pro (gr) | 4.8 | a | Maxforce Ant Killer (g) | 4.7 | abc | Maxforce Fine Granular (g) | 4.9 | a |
| Advion (g) | 4.6 | a | Maxforce Granular (gr) | 4.7 | abc | Niban FG (gr) | 4.7 | ab |
| Maxforce Complete (gr) | 4.5 | ab | Optigard (g) | 4.6 | abc | Advance Carpenter Ant (gr) | 4.3 | abc |
| Advance Carpenter Ant (gr) | 4.4 | ab | Advance Carpenter Ant (gr) | 4.6 | abc | Optigard (g) | 4.2 | abcd |
| InTice (g) | 4.0 | abc | Advance 375A Select (gr) | 4.5 | abcd | Extinguish Pro (gr) | 4.1 | abcde |
| Esteem (gr) | 3.8 | abc | InTice (g) | 3.9 | abcd | 381B Advance (l) | 3.9 | abcde |
| Optigard (g) | 3.3 | de | Advion (g) | 3.7 | abcde | InTice (g) | 3.1 | bcdef |
| Advance 375A Select (gr) | 1.4 | d | Extinguish Pro (gr) | 3.5 | abcde | Maxforce Granular(gr) | 2.7 | cdef |
| 381B Advance (l) | 1.2 | d | Maxforce Fine Granular (g) | 3.2 | bcde | Advance 375A Select (gr) | 2.6 | cdef |
| Control (l) | 1.1 | d | InTice (gr) | 3.1 | cde | InTice (gr) | 2.5 | def |
| InTice (gr) | 0.1 | e | Esteem (gr) | 2.9 | de | Control (l) | 2.4 | ef |
| Niban FG (gr) | NT 4 | 381B Advance (l) | 2.2 | ef | Esteem (gr) | 1.8 | F | |
| Amdro Pro (gr) | NT | Control (l) | 1.0 | f | Advion (g) | NT | ||
| F = 33.31 | F = 11.39 | F = 10.20 | ||||||
| df = 13, 126 | df = 15, 144 | df = 14, 135 | ||||||
| P < 0.0001 | P < 0.0001 | P < 0.0001 | ||||||
| Mean Number of Days Until 100% Mortality Rank-Score 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bait 2 | Spring | Bait | Summer | Bait | Fall | |||
| Maxforce Ant Killer (g) | 4.2 | a 3 | Maxforce Complete (gr) | 4.0 | a | Maxforce Complete (gr) | 4.2 | a |
| Advance 375A Select (gr) | 4.1 | a | Amdro Pro (gr) | 3.8 | ab | Maxforce Ant Killer (g) | 4.0 | ab |
| Extinguish Pro (gr) | 3.6 | ab | Optigard (g) | 3.6 | ab | Amdro Pro (gr) | 4.0 | ab |
| Maxforce (gr) | 3.5 | ab | Advion (g) | 3.3 | abc | Maxforce Fine Granular (g) | 3.3 | ab |
| Maxforce Complete (gr) | 3.3 | abc | Maxforce Ant Killer (g) | 3.0 | abcd | Niban FG (gr) | 3.0 | bcd |
| Advion (g) | 3.0 | bc | Maxforce Fine Granular (g) | 2.9 | abcd | Extinguish Pro (gr) | 2.6 | cde |
| Optigard (g) | 3.0 | bc | Extinguish Pro (gr) | 2.6 | abcde | Advance Carpenter Ant (gr) | 2.5 | cdef |
| Maxforce Fine Granular (g) | 2.9 | bc | Niban FG (gr) | 2.6 | abcde | Maxforce (gr) | 2.2 | def |
| InTice (g) | 2.6 | bc | Advance 375A Select (gr) | 2.4 | bcdef | Optigard (g) | 2.1 | def |
| Advance Carpenter Ant (gr) | 2.6 | bc | Advance Carpenter Ant (gr) | 1.9 | cdef | 381B Advance (l) | 2.1 | def |
| Esteem (gr) | 2.3 | cd | Esteem (gr) | 1.7 | def | InTice (g) | 2.0 | defg |
| Control (l) | 1.0 | d | InTice (g) | 1.4 | ef | InTice (gr) | 1.8 | efg |
| 381B Advance (l) | 1.0 | d | InTice (gr) | 1.2 | ef | Esteem (gr) | 1.5 | fg |
| InTice (gr) | 1.0 | d | Control (l) | 1.0 | f | Control (l) | 1.0 | g |
| Niban FG (gr) | NT 4 | Maxforce (gr) | 0.3 | e | Advance 375A Select (gr) | 1.0 | g | |
| Amdro Pro (gr) | NT | 381B Advance (l) | 0.3 | e | Advion (g) | NT | ||
| F = 18.37 | F = 10.75 | F = 22.47 | ||||||
| df = 12, 112 | df = 14, 135 | df = 14, 135 | ||||||
| P < 0.0001 | P < 0.0001 | P < 0.0001 | ||||||
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Calibeo, D.; Oi, F.; Oi, D.; Mannion, C. Insecticides for Suppression of Nylanderia fulva. Insects 2017, 8, 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects8030093
Calibeo D, Oi F, Oi D, Mannion C. Insecticides for Suppression of Nylanderia fulva. Insects. 2017; 8(3):93. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects8030093
Chicago/Turabian StyleCalibeo, Dawn, Faith Oi, David Oi, and Catharine Mannion. 2017. "Insecticides for Suppression of Nylanderia fulva" Insects 8, no. 3: 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects8030093
APA StyleCalibeo, D., Oi, F., Oi, D., & Mannion, C. (2017). Insecticides for Suppression of Nylanderia fulva. Insects, 8(3), 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects8030093






