Dietary Supplementation of Honey Bee Larvae with Arginine and Abscisic Acid Enhances Nitric Oxide and Granulocyte Immune Responses after Trauma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- NO participates in granulocyte spreading [18].
- (2)
- Wounding induces NO production in granulocytes and augmented the total number of granulocytes in larvae hemolymph [19].
- (3)
- ABA supplementation in the syrup of honey bee colonies enhanced granulocyte spreading [15].
- (4)
- ABA supplementation enhanced the number of granulocytes (which are the NO-producing hemocyte type described in A. mellifera) in larvae hemolymph after wound challenge [15].
- (5)
- ABA supplementation enhanced wound healing in larvae, reversing the anticoagulant effects of Varroa destructor (V. destructor) parasitism [15].
- (6)
- ABA supplementation enhanced phenoloxidase activity in adult bees [15].
- (7)
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. In Vitro Rearing of Bees
2.2. Lipopolysaccharide Challenge of in Vitro-Reared A. mellifera Larvae
2.3. Hemolymph Collection
2.4. Nitric Oxide Detection and Quantification
2.5. Hemocyte Spreading Evaluation
2.6. Microscopy
2.7. Statistical Analysis
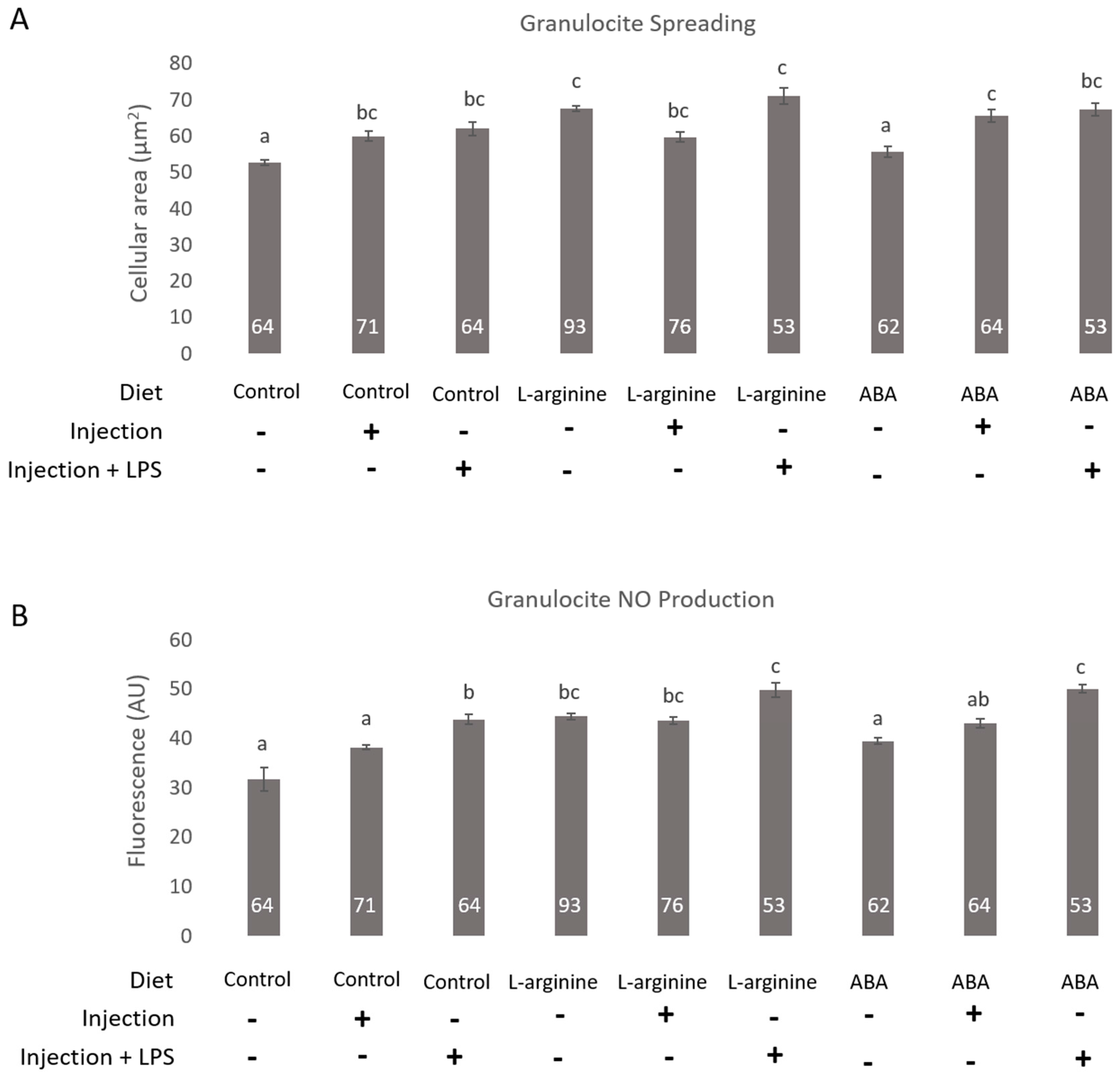
3. Results
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Potts, S.G.; Biesmeijer, J.C.; Kremen, C.; Neumann, P.; Schweiger, O.; Kunin, W.E. Global pollinator declines: Trends, impacts and drivers. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meixner, M.D.; Le Conte, Y. A current perspective on honey bee health. Apidologie 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dainat, B.; Evans, J.D.; Chen, Y.P.; Gauthier, L.; Neumann, P. Predictive Markers of Honey Bee Colony Collapse. PLoS ONE 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negri, P.; Maggi, M.; Ramirez, L.; Szwarski, N.; De Feudis, L.; Lamattina, L.; Eguaras, M. Cellular immunity in Apis mellifera: Studying hemocytes brings light about bees skills to confront threats. Apidologie 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.D.; Aronstein, K.; Chen, Y.P.; Hetru, C.; Imler, J.L.; Jiang, H.; Kanost, M.; Thompson, G.J.; Zou, Z.; Hultmark, D. Immune pathways and defence mechanisms in honey bee Apis mellifera. Insect Mol. Biol. 2006, 15, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeGrandi-Hoffman, G.; Chen, Y. Nutrition, immunity and viral infections in honey bees. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2015, 10, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson-Rich, N.; Dres, D.; Starks, P. The ontogeny of immunity: Development of innate immune strength in the honey bee. J. Insect Physiol. 2008, 54, 1392–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negri, P.; Maggi, M.; Szawarski, N.; Lamattina, L.; Eguaras, M. Apis mellifera hemocytes in vitro: What type of cells are they? Functional analysis before and after the pupae metamorphosis black box. J. Apic. Res. 2014, 53, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdan, C.; Röllinghoff, M.; Diefenbach, A. The role of nitric oxide in innate immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2000, 173, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero, A. Nitric oxide: An antiparasitic molecule of invertebrates. Trends Parasitol. 2006, 22, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adie, B.A.T.; Pérez-Pérez, J.; Pérez-Pérez, M.M.; Godoy, M.; Sánchez-Serrano, J.; Schmelz, E.A.; Solanoa, R. ABA is an essential signal for plant resistance to pathogens affecting JA biosynthesis and the activation of defences in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 1665–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipp, J. Nachweis und herkunft von abscisinsäure und prolin in honig. Apidologie 1990, 21, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuberoso, C.I.; Bifulco, E.; Caboni, P.; Cottiglia, F.; Cabras, P.; Floris, I. Floral markers of strawberry tree (Arbutus unedo L.) honey. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreres, F.; Andrade, P.; Tomás-Barberán, F. Natural occurrence of abscisic acid in heather honey and floral nectar. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 2053–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, P.; Maggi, M.; Ramirez, L.; De Feudis, L.; Szawarski, N.; Quintana, S.; Eguaras, M.; Lamattina, L. Abscisic acid enhances the immune response in Apis mellifera and contributes to the colony fitness. Apidologie 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, L.; Negri, P.; Sturla, L.; Guida, L.; Vigliarolo, T.; Maggi, M.; Eguaras, M.; Zocchi, E.; Lamattina, L. Abscisic acid enhances cold tolerance in honeybee larvae. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruzzone, S.; Moreschi, I.; Usai, C.; Guida, L.; Damonte, G.; Salis, A.; Scarfì, S.; Millo, E.; De Flora, A.; Zocchi, E. Abscisic acid is an endogenous cytokine in human granulocytes with cyclic ADP-ribose as second messenger. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 5759–5764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negri, P.; Maggi, M.; Correa-Aragunde, N.; Brasesco, C.; Eguaras, M.; Lamattina, L. Nitric oxide participates at the first steps of A. mellifera cellular immune activation in response to non-self recognition. Apidologie 2013, 44, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, P.; Quintana, S.; Maggi, M.; Szawarski, N.; Lamattina, L.; Eguaras, M. Apis mellifera hemocytes generate increased amounts of NO in response to wounding/encapsulation. Apidologie 2014, 45, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aupinel, P.; Fortini, D.; Dufour, H.; Tasei, J.N.; Michaud, B.; Odoux, J.F.; Pham-Delègue, M. Improvement of artificial feeding in a standard in vitro method for rearing Apis mellifera larvae. Bull. Insectol. 2005, 58, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Crailsheim, K.; Brodschneider, R.; Aupinel, P.; Behrens, D.; Genersch, E.; Vollmann, J.; Riessberger-Gallé, U. Standard Methods for Artificial Rearing of Apis Mellifera Larvae. J. Apic. Res. 2013, 52, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittwer, D.; Weise, C.; Götz, P.; Wiesner, A. LPS (lipopolysaccharide)-activated immune responses in a hemocyte cell line from Estigmene acraea (Lepidoptera). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 1997, 21, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiske, J.; Wiesner, A. Stimulation of NO synthase activity in the immune-competent lepidopteran Estigmene acraea hemocyte line. Nitric Oxide 1999, 3, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeidler, D.; Zähringer, U.; Gerber, I.; Dubery, I.; Hartung, T.; Bors, W.; Hutzler, P.; Durner, J. Innate immunity in Arabidopsis thaliana: Lipopolysaccharides activate nitric oxide synthase (NOS) and induce defense genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15811–15816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraaijeveld, A.R.; Elrayes, N.P.; Schuppe, H.; Newland, P.L. l-Arginine enhances immunity to parasitoids in Drosophila melanogaster and increases NO production in lamellocytes. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arefin, B.; Kucerova, L.; Krautz, R.; Kranenburg, H.; Parvin, F.; Theopold, U. Apoptosis in Hemocytes Induces a Shift in Effector Mechanisms in the Drosophila Immune System and Leads to a Pro-Inflammatory State. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tossi, V.; Cassia, R.; Bruzzone, S.; Zochi, E.; Lamattina, L. ABA says NO to UV-B: A universal response? Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janashia, I.; Alaux, C. Specific Immune Stimulation by Endogenous Bacteria in Honey Bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Negri, P.; Ramirez, L.; Quintana, S.; Szawarski, N.; Maggi, M.; Le Conte, Y.; Lamattina, L.; Eguaras, M. Dietary Supplementation of Honey Bee Larvae with Arginine and Abscisic Acid Enhances Nitric Oxide and Granulocyte Immune Responses after Trauma. Insects 2017, 8, 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects8030085
Negri P, Ramirez L, Quintana S, Szawarski N, Maggi M, Le Conte Y, Lamattina L, Eguaras M. Dietary Supplementation of Honey Bee Larvae with Arginine and Abscisic Acid Enhances Nitric Oxide and Granulocyte Immune Responses after Trauma. Insects. 2017; 8(3):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects8030085
Chicago/Turabian StyleNegri, Pedro, Leonor Ramirez, Silvina Quintana, Nicolás Szawarski, Matías Maggi, Yves Le Conte, Lorenzo Lamattina, and Martin Eguaras. 2017. "Dietary Supplementation of Honey Bee Larvae with Arginine and Abscisic Acid Enhances Nitric Oxide and Granulocyte Immune Responses after Trauma" Insects 8, no. 3: 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects8030085
APA StyleNegri, P., Ramirez, L., Quintana, S., Szawarski, N., Maggi, M., Le Conte, Y., Lamattina, L., & Eguaras, M. (2017). Dietary Supplementation of Honey Bee Larvae with Arginine and Abscisic Acid Enhances Nitric Oxide and Granulocyte Immune Responses after Trauma. Insects, 8(3), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects8030085




