1. Introduction
Subterranean termites search for food by constructing a ramified tunnel and gallery system underneath and above the soil. Usually primary tunnels radiate from the nest and as they go farther away these main tunnels split into secondary and tertiary tunnels [
1,
2]. The efficiency of food finding by subterranean termites therefore depends on the organization of the tunnel systems [
3]. Studies have shown that environmental factors such as soil texture, soil moisture, ambient temperature and the presence or absence of food sources influence the search tunnel formation by subterranean termites [
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11].
The presence and amount of food have been reported to influence the branching and total length of tunnel system constructed by subterranean termites such as
C. formosanus [
1] and
Reticulitermes santonensis De Feytaud [
12]. On the other hand, there are studies [
13,
14] which suggest that food search by
C. formosanus is systematic and not affected by food in the foraging arena. Nevertheless, these studies agree that the main and branched tunnels are organized in a way that they avoid searching the area that was already explored.
Although there is no debate on the requirement of substrate moisture in the foraging arena, there are still contradictory reports on the influence of a particular level of moisture in different substrates for search tunnel formation by subterranean termites. An early tunneling activity by
C. formosanus was found to be greater in high moisture sand than in low moisture sand when provided with a moisture gradient [
8]. Likewise, the tunneling rate by
C. frenchi Hill was reported to be greater in wet sand than in dry sand [
7] and
C. gestroi (Wasmann) was found to construct more secondary tunnels at 15% moisture sand than in 5% moisture sand [
2]. In contrast, Potter
et al. demonstrated from their field study that there was no difference in damage ratings between Sentricon
® stations placed in wet soil or dry soil [
15]. One confounding factor here is the use of ‘dry soil’ in the experiment. It is difficult to determine (the authors have not mentioned) whether the dry soil in these studies was completely dry or had low moisture levels, because the survival of subterranean termites is a major issue in a completely dry soil. When a wet food matrix is provided or when the dry soil is adjoining wet soil then termites can relocate water to make the dry soil moist [
16,
17]. Like moisture, ambient temperature also influences the tunneling behavior of subterranean termites. For example,
C. gestroi and
Heterotermes tenuis (Hagen) constructed more secondary tunnels at 20 °C and 25 °C than at 15 °C in sand [
2].
Soil texture impacts subterranean termite foraging both by its particle size and its water holding properties. As the soil particles become coarser the water holding capacity of the soil decreases [
18]; as a result, relatively more water is directly available to the termites. In sand, the moisture content as low as 4% by wt. provides sufficient moisture for
C. formosanus to tunnel and aggregate normally [
11]. A faster rate of tunneling by
C. formosanus was reported in sand than in top soil and clay [
10]. In moist conditions, however,
C. formosanus preferred to aggregate in soil with finer particles than in soils with coarser particles and the opposite was found in dry condition [
10].
C. gestroi excavated significantly more secondary tunnels in soil with uniform particle size of 2.0 mm than in soil with heterogeneous particle size (0.002–4.00 mm) while
H. tenuis could not even penetrate the arenas filled with the latter soil type [
2].
C. formosanus and
Reticulitermes hesperus Banks constructed different tunneling patterns based on the soil particle size [
5]. In this study, first we aimed to test the substrate preference between sand and sandy loam at two different moisture levels and second to compare the rate and pattern of tunneling among sand, sandy loam and silt loam at two ambient temperatures.
2. Results and Discussion
Termite mortality was insignificant in both the experiments as ≥96% termites were recovered active and live at the end of the bioassays (survival data for the preference test is given in
Figure 1 but the survival data for tunneling test is not provided). In the preference tests, a significantly greater total length of tunnels was excavated in sand compared to sandy loam (
F = 35.26; df = 1, 16;
p < 0.0001) in the 24 h period. However, tunnel length was not significantly different between the two moisture levels (
F = 1.19; df = 1, 16;
p = 0.29) and there was no interaction effect of the substrates and the moisture levels (
F = 0.48; df = 1, 16;
p = 0.50) (
Figure 2)
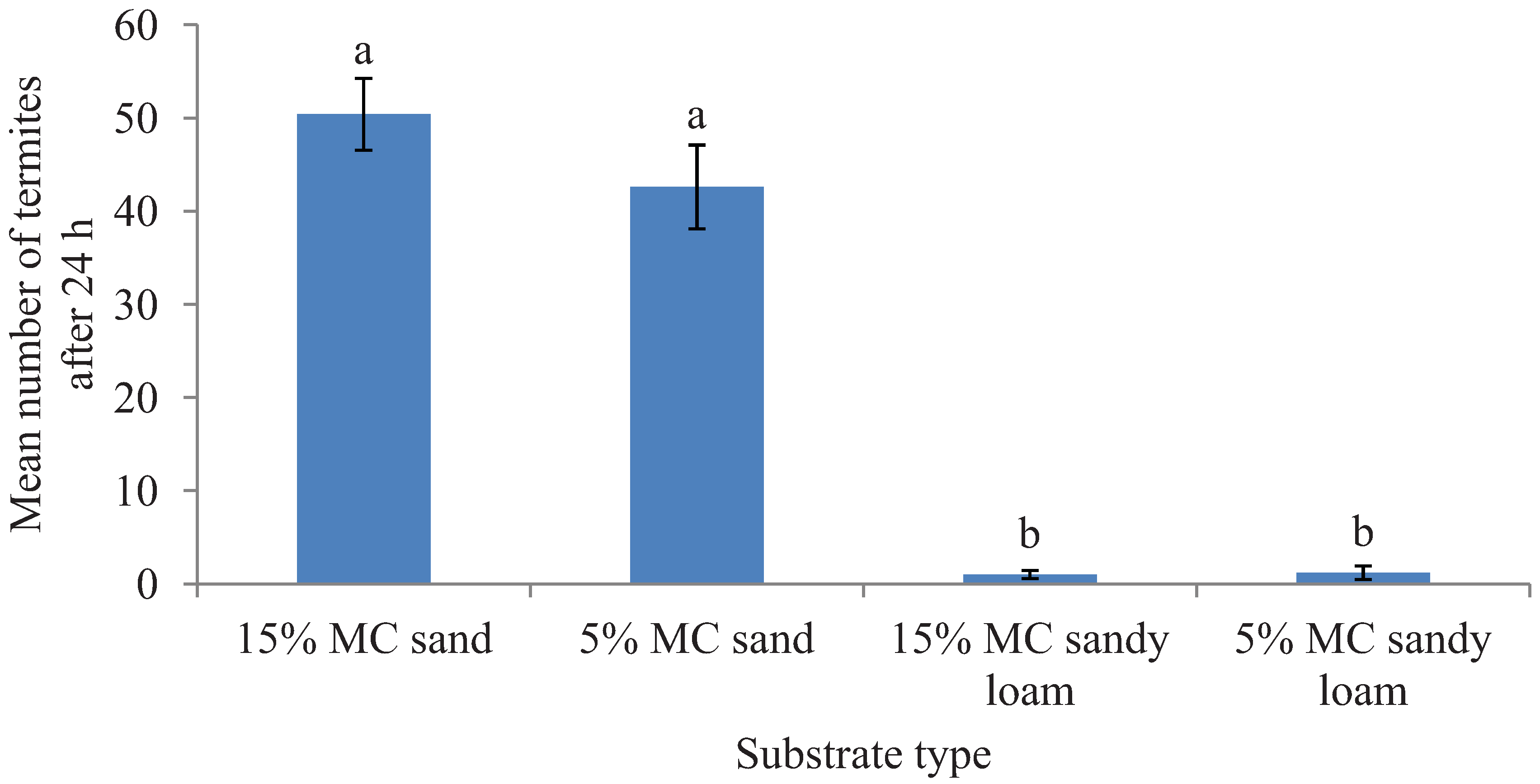
. Likewise, after 24 h, a significantly greater proportion of released termites were recovered in sand than in the sandy loam (
F = 325.37; df = 1, 16;
p < 0.0001) but the tested moisture levels had no significant impact on the number of termites found on a given substrate type (
F = 0.69; df = 1, 16;
p = 0.43) and had no interaction effect of the substrate and moisture levels (
F = 0.88; df = 1, 16;
p = 0.36) (
Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Mean number (±SEM) of termites recovered in two different substrates each with two moisture levels (MC) in the preference tests after 24 h period. Bars with different letters are significantly different (α < 0.05, Tukey’s test) from each other.
Figure 1.
Mean number (±SEM) of termites recovered in two different substrates each with two moisture levels (MC) in the preference tests after 24 h period. Bars with different letters are significantly different (α < 0.05, Tukey’s test) from each other.
In the tunneling tests, substrate type had a significant impact on the length of tunnels at both time periods (14 h post-release:
F = 6.57; df = 2, 12;
p = 0.0118 and 24 h post-release:
F = 7.71; df = 2, 12;
p = 0.0070). The length of tunnels was not significantly different between 22 °C and 28 °C (14 h post-release:
F = 0.03; df = 1, 12;
p = 0.8745 and 24 h post-release:
F = 0.01; df = 1, 12;
p = 0.9260), however, there was a substrate type and temperature interaction effect at 24 h post-release (14 h post-release:
F = 3.77; df = 2, 12;
p = 0.0538 and 24 h post-release:
F = 5.28; df = 2, 12;
p = 0.0227). Means comparison showed that there was significant difference in the lengths of tunnels among the substrates at 22 °C but not at 28 °C. At 14 h post-release, the length of tunnels was significantly greater in sand than in sandy loam and after 24 h post-release it was significantly greater in both the sand and the silt loam compared to sandy loam (
Table 1).
Figure 2.
Mean length (±SEM) of tunnels excavated in two different substrates each with two moisture levels (MC) in the preference tests in 24 h period. Bars with different letters are significantly different (α < 0.05, Tukey’s test) from each other.
Figure 2.
Mean length (±SEM) of tunnels excavated in two different substrates each with two moisture levels (MC) in the preference tests in 24 h period. Bars with different letters are significantly different (α < 0.05, Tukey’s test) from each other.
Table 1.
Mean length (±SEM) of tunnels excavated in 14 h and 24 h periods in three different substrates at two temperature conditions.
Table 1.
Mean length (±SEM) of tunnels excavated in 14 h and 24 h periods in three different substrates at two temperature conditions.
| Substrate | Mean length of tunnels in 14 h (cm) | Mean lengths of tunnels in 24 h (cm) |
|---|
| 28 °C | 22 °C | 28 °C | 22 °C |
|---|
| sand | 80.00 ± 16.64 a | 99.36 ± 7.62 a | 104.83 ± 13.49 a | 123.16 ± 9.09 a |
| sandy loam | 66.83 ± 13.63 a | 28.53 ± 10.25 b | 86.73 ± 14.30 a | 39.90 ±13.73 b |
| silt loam | 58.00 ± 2.51 a | 72.33 ± 13.41 ab | 72.33 ± 2.42 a | 103.83 ± 18.33 a |
Substrate type had a significant effect on the number of primary tunnels after 24 h of release (
F = 7.75; df = 2, 12;
p = 0.0069), however, there was no temperature effect (
F = 1.33; df = 1, 12;
p = 0.2707) and also no interaction effect (
F = 0.58; df = 1, 12;
p = 0.5731). Similarly, substrate type effected the number of branched tunnels (
F = 10.07; df = 2, 12;
p = 0.0027) but not the temperature (
F = 4.17; df = 1, 12;
p = 0.638) or the interaction of substrate and temperature (
F = 3.31; df = 2, 12;
p = 0.0717). The number of branched tunnels was greater in sand or silt loam than in the sandy loam at 22 °C and the number of primary tunnels was greater in sand compared to sandy loam but not the silt loam at 24 h post-release (
Table 2).
Table 2.
Mean number (±SEM) of primary and branched tunnels excavated in 24 h period in three different substrates at two temperature conditions.
Table 2.
Mean number (±SEM) of primary and branched tunnels excavated in 24 h period in three different substrates at two temperature conditions.
| Substrate | Mean number of primary tunnels in 24 h | Mean number of branched tunnels in 24 h |
|---|
| 28 °C | 22°C | 28 °C | 22 °C |
|---|
| sand | 2.33 ± 0.33 a | 3.33 ± 0.88 a | 9.33 ± 3.33 a | 18.00 ± 3.60 a |
| sandy loam | 1.00 ± 0.00 a | 1.00 ± 0.00 b | 4.66 ± 1.20 a | 1.66 ± 0.66 b |
| silt loam | 2.00 ± 0.57 a | 2.33 ± 0.33 ab | 7.33 ± 0.33 a | 13.66 ± 2.90 a |
It is generally agreed that substrate moisture is one of the critical factors that favor foraging activity of subterranean termites. However, there are wide-ranging suggestions when it comes to concluding what is the preferred level of moisture for optimum tunneling activity [
2,
7,
8,
10,
11]. The rate of tunneling by
C. formosanus was found to be faster in higher moisture sand than in lower moisture sand only during the middle 3–4 days of the 10 days test period [
8]. Similarly, the tunneling rate by
C. frenchi was reported to be faster in wet sand than in dry sand [
7], however, the exact moisture content of the wet sand was not determined. The present data shows that the total tunnel length excavated by
C. formosanus did not differ between 5% and 15% moisture sand. Our earlier study on sand moisture preference also showed that
C. formosanus did not preferentially select a particular moisture level among a range of moisture levels from 4 to 24% [
11]. This suggests that
C. formosanus readily gets moisture required for its normal tunneling activity from sand that has as low as 4% moisture. In sandy loam,
C. formosanus constructed very short tunnels initially but later stopped and very few termites were recovered at the end of the test period. Since both of the substrates had equal amount of moisture by wt., it is conceivable that sandy loam had lower moisture availability compared to sand. However, only moisture availability may not have determined the preference as evident from the fact that 15% moisture sand has more moisture availability than the 5% moisture sand but the termites did not prefer one over the other. Therefore, we suggest that both the texture type and the lower moisture availability could have contributed to make the sandy loam less preferable over sand.
The present results showed that the rate of tunneling and the spatial dispersion of tunnel webs were influenced by the substrate type and ambient temperature. The greater total length of tunnel network in sand than in sandy loam at 12 h or 24 h post-release could primarily be due to the uniformly coarser particle size present in the sand. Termites construct tunnels by picking up soil particles and depositing them elsewhere to clear the way for tunnels [
19,
20]. Tunnel construction by
C. formosanus was reported to be faster in uniformly coarse sand (particle size: 0.59–0.84 mm) than in the sand with varied particle size (0.30–2.0 mm) [
21]. Although coarse particles would usually be faster to excavate, very coarse particles also could be impenetrable for termites. Studies have shown that sand particle sizes that ranged from 1.2–1.7 mm and 1.7–2.4 mm diameter were impenetrable to
R. hesperus [
22] and
C. formosanus [
23], respectively. As termites pick up individual particles while excavating tunnels, they would have to travel back and forth more often to displace the same volume of substrate with finer particles thus requiring more effort and time to do the same job. Li and Su suggested that the four mouth parts form buccal cavity and load 3–4 sand particles (0.300–0.355 mm) at a time depending upon the size [
19]. However, this may not necessarily mean that termites always collect as many fine particles from silt or clay to make the equivalent bulk as a few particles of coarse sand or a single particle of maximum size they can load. In addition, some of the finer particles may drop on the way requiring another trip thus delaying the excavation work. Our observation where longer tunnels were recorded in sand than in the sandy loam or silt loam demonstrates that
C. formosanus excavates faster in uniform coarse particles than the substrate having finer particle size.
An efficient search tunnel system would be the one that minimizes the energy expenditure in tunnel excavation and be achieved by minimizing the total length of tunnels from origin to the first food source. Construction of relatively straight and narrow tunnels helps to optimize the time and speed of excavation [
24]. The branching frequency and the branch tunnel length play an important role in termite foraging efficiency [
25]. Primary tunnels mainly determine how far the foraging area is covered from the origin and the organization of branching system determines how efficient the food search system foraging groups of subterranean termites employ [
1]. Construction of a larger number of branched tunnels (secondary, tertiary and quaternary tunnels) helps to exploit the maximum area of the foraging site. In the present experiment,
C. formosanus built more extensive tunnel webs in sand than in sandy loam as evident from higher number of primary as well as secondary tunnels in both the temperature conditions. We did not determine, however, whether the width and the straightness of the tunnels were some of the possible reasons of greater tunnel length in sand as suggested by Sim and Lee [
24].
C. gestroi and
H. tenuis were reported to construct more secondary tunnels at 20 °C and 25 °C than at 15 °C in sand (2). Probably 15 °C is very low temperature for normal activities for the termites. It would be interesting to see how
C. formosanus tunneling would be impacted at 15 °C. Surprisingly, silt loam, which has a lower proportion of sand than the sandy loam, had greater number of branched tunnels and greater total length of tunnels. We do not think moisture was a limiting factor in sandy loam or silt loam because the moisture content of these substrates was 30% whereas that of the sand was only 15%. We assume that, in addition to particle size and soil moisture, there are some other factors that influence the speed of excavation. Organic matter content was exceptionally high in the sandy loam and pH was slightly higher, however, it is unknown whether these factors have a role to lessen the tunneling activity. An increase in tunneling activity by
C. formosanus has direct biological relevance as it will increase the likelihood of finding a monitor or bait placed in the nearby areas of infested structures.